Integrating Large Language Models into Medication Management in Remote Healthcare: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background on Remote Healthcare
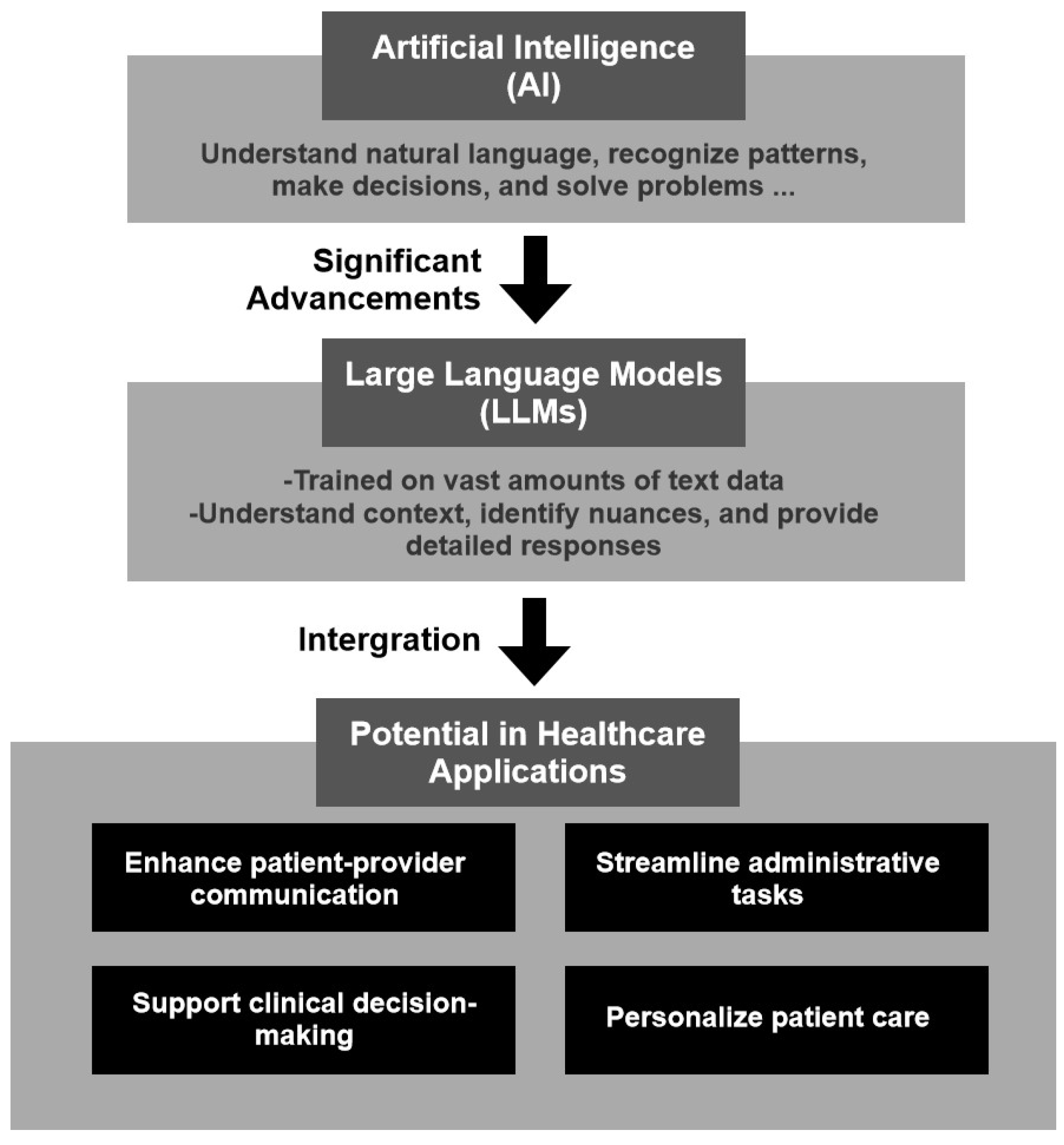
1.2. Introduction to AI and LLMs
1.3. Purpose and Scope of the Review
- Overview of medication management in remote healthcare: understanding the current state of remote medication management practices, including existing challenges and limitations.
- Case studies: reviewing medical LLM cases and where LLMs have been implemented to improve medication management in remote healthcare.
- The role of LLMs in medication management: analyzing the specific applications of LLMs in enhancing communication, monitoring adherence, and supporting clinical decision-making in remote settings.
- Challenges and ethical considerations: discussing the technical, ethical, and regulatory challenges associated with the integration of LLMs in remote medication management.
- Future directions and research opportunities: identifying potential areas for future research and innovation in the use of LLMs for remote medication management.
2. Overview of Medication Management in Remote Healthcare
2.1. Importance of Remote Medication Management
2.2. Current Technologies in Remote Medication Management
3. Overview of LLMs in Medication
- Publications in peer-reviewed journals, conferences, or high-quality preprints published between 2022 and 2024; this period reflects the boom in LLM popularity.
- Studies reporting benchmark evaluations on standard medical datasets. The datasets include the following standard examinations: USMLE (United States Medical Licensing Examination), MCQA, and PubMedQA.
- Evidence of real-world applications or clinical relevance.
3.1. Medical Large Language Models
3.2. Applications of LLMs in Remote Healthcare
4. The Role of LLMs in Remote Healthcare
4.1. Patient Communication and Support
4.2. Medication Adherence Monitoring
4.3. Personalized Medication Management
4.4. Overall Contribution to CDSSs
5. Comparative Analysis of LLM-Based and Traditional Approaches
6. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
6.1. Technical and Operational Challenges
6.2. Ethical Considerations
6.3. Regulatory and Compliance Issues
7. Future Directions and Research Opportunities
7.1. Advancements in LLM Technology
7.2. Research Gaps and Opportunities
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dorsey, E.R.; Topol, E.J. Telemedicine 2020 and the next decade. Lancet 2020, 395, 859–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kichloo, A.; Albosta, M.; Dettloff, K.; Wani, F.; El-Amir, Z.; Singh, J.; Aljadah, M.; Chakinala, R.C.; Kanugula, A.K.; Solanki, S.; et al. Telemedicine, the current COVID-19 pandemic and the future: A narrative review and perspectives moving forward in the USA. Fam. Med. Community Health 2020, 8, e000530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollander, J.E.; Carr, B.G. Virtually perfect? Telemedicine for COVID-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1679–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Car, J.; Koh, G.C.H.; Foong, P.S.; Wang, C.J. Video consultations in primary and specialist care during the covid-19 pandemic and beyond. BMJ 2020, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokolo, A., Jr. Application of telemedicine and eHealth technology for clinical services in response to COVID-19 pandemic. Health Technol. 2021, 11, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topol, E. Deep Medicine: How Artificial Intelligence Can Make Healthcare Human Again; Hachette UK: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, F.; Jiang, Y.; Zhi, H.; Dong, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Shen, H.; Wang, Y. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: Past, present and future. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2017, 2, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.; Kalakota, R. The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare. Future Healthc. J. 2019, 6, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. GPT-4: Technical Report. 2023. Available online: https://openai.com/research/gpt-4 (accessed on 24 August 2024).
- Wiggins, W.F.; Tejani, A.S. On the Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models for Natural Language Processing in Radiology. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, e220119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, J.; Rangaswamy, M.; Banerjee, B.; Prajapati, A.; Akhtar, Z.; Sakauye, K.; Joseph, A. 12—Applications of artificial intelligence to neurological disorders: Current technologies and open problems. In Augmenting Neurological Disorder Prediction and Rehabilitation Using Artificial Intelligence; Pillai, A.S., Menon, B., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 243–272. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.T.; Bussell, J.K. Medication adherence: WHO cares? Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardas, P. Prevalence of non-adherence to medication among patients treated for selected chronic conditions. Pol. Merkur. Lek. Organ Pol. Tow. Lek. 2011, 31, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Coombs, N.C.; Campbell, D.G.; Caringi, J. A qualitative study of rural healthcare providers’ views of social, cultural, and programmatic barriers to healthcare access. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2022, 15, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktar, S.F.; Rana, F.J.; Rezwan, S.; Iqbal, I.; Kabir, L.; Islam, R.; Ahamed, S.I. Reviewing Polypharmacy in Elderly Individuals of Rural Regions. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 45th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Madrid, Spain, 12–16 July 2021; pp. 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masnoon, N.; Shakib, S.; Kalisch-Ellett, L.; Caughey, G.E. What is polypharmacy? A systematic review of definitions. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Topol, E.J. State of telehealth. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, L.G.; Howie-Esquivel, J.; Dracup, K. Mobile phone interventions for the secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 56, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuwandy, M.L.; Zaidan, B.; Zaidan, A.; Albahri, A.; Alamoodi, A.; Albahri, O.; Alazab, M. mHealth Authentication Approach Based 3D Touchscreen and Microphone Sensors for Real-Time Remote Healthcare Monitoring System: Comprehensive Review, Open Issues and Methodological Aspects. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2020, 38, 100300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Asghar, Z.; Kumar, T.; Li, G.; Manzoor, A.; Mikhaylov, K.; Shah, S.A.; Höyhtyä, M.; Reponen, J.; Huusko, J.; et al. Emerging Technologies for Next Generation Remote Health Care and Assisted Living. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 56094–56132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, M.; Kinnear, M.; Bond, C.; McKinstry, B. A systematic review of electronic multi-compartment medication devices with reminder systems for improving adherence to self-administered medications. Int. J. Pharm. Pract. 2017, 25, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawski, K.; Ghazinouri, R.; Krumme, A.; Lauffenburger, J.C.; Lu, E.; Durfee, E.; Oley, L.; Lee, J.; Haff, N.; McDonough, K.E.; et al. Real-world adherence and persistence to oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation: A systematic review. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2018, 11, e005116. [Google Scholar]
- Tebra Inc. Telehealth: The Advantages of Telemedicine. 2024. Available online: https://sa1s3optim.patientpop.com/assets/images/provider/photos/2519949.jpg (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Lahoti, N. How Are mHealth Apps Changing the Face of the Healthcare Industry? 2020. Available online: https://mobisoftinfotech.com/resources/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/mhealth-apps-in-healthcare-industry.png (accessed on 20 November 2024).
- Wellness Pharmacy. Smart Dispenser. 2020. Available online: https://www.wellpharmacy.com/smart-dispenser/ (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372. [Google Scholar]
- Liévin, V.; Hother, C.E.; Motzfeldt, A.G.; Winther, O. Can large language models reason about medical questions? Patterns 2024, 5, 100943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, F.; Gu, B.; Zou, X.; Huang, J.; Wu, J.; Li, Y.; Chen, S.S.; Zhou, P.; Liu, J.; et al. A Survey of Large Language Models in Medicine: Progress, Application, and Challenge. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2311.05112. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, A.; Hou, M.; Xi, R.; Zeng, X.; Shah, S.A. Prompt-Eng: Healthcare Prompt Engineering: Revolutionizing Healthcare Applications with Precision Prompts. In Proceedings of the Companion Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2024, WWW ’24, Singapore, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvitz, E. The Power of Prompting. 2023. Available online: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/the-power-of-prompting/ (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Nori, H.; Usuyama, N.; King, N.; McKinney, S.M.; Fernandes, X.; Zhang, S.; Horvitz, E. From Medprompt to o1: Exploration of Run-Time Strategies for Medical Challenge Problems and Beyond. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2411.03590. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Cai, G.; Liu, B. A Liver Cancer Question-Answering System Based on Next-Generation Intelligence and the Large Model Med-PaLM 2. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inf. Technol. 2024, 2, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Google Research. Med-PaLM: A Large Language Model from Google Research, Designed for the Medical Domain. 2023. Available online: https://sites.research.google/med-palm/ (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Mumtaz, U.; Ahmed, A.; Mumtaz, S. LLMs-Healthcare: Current Applications and Challenges of Large Language Models in various Medical Specialties. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2311.12882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portilla, N.; Garcia-Font, M.; Nagendrababu, V.; Abbott, P.; Sanchez, J.; Abella, F. Accuracy and Consistency of Gemini Responses Regarding the Management of Traumatized Permanent Teeth. Dent. Traumatol. 2024, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, G.; Barral, J. Advancing Medical AI with Med-Gemini. 2024. Available online: https://research.google/blog/advancing-medical-ai-with-med-gemini/ (accessed on 24 November 2024).
- Saab, K.; Tu, T.; Weng, W.H.; Tanno, R.; Stutz, D.; Wulczyn, E.; Zhang, F.; Strother, T.; Park, C.; Vedadi, E.; et al. Capabilities of Gemini Models in Medicine. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.18416. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Xu, S.; Sellergren, A.; Kohlberger, T.; Zhou, Y.; Ktena, I.; Kiraly, A.; Ahmed, F.; Hormozdiari, F.; Jaroensri, T.; et al. Advancing Multimodal Medical Capabilities of Gemini. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.03162. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, K.H.; Healey, E.; Leong, T.Y.; Kohane, I.S.; Manrai, A.K. Medical Artificial Intelligence and Human Values. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 1895–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
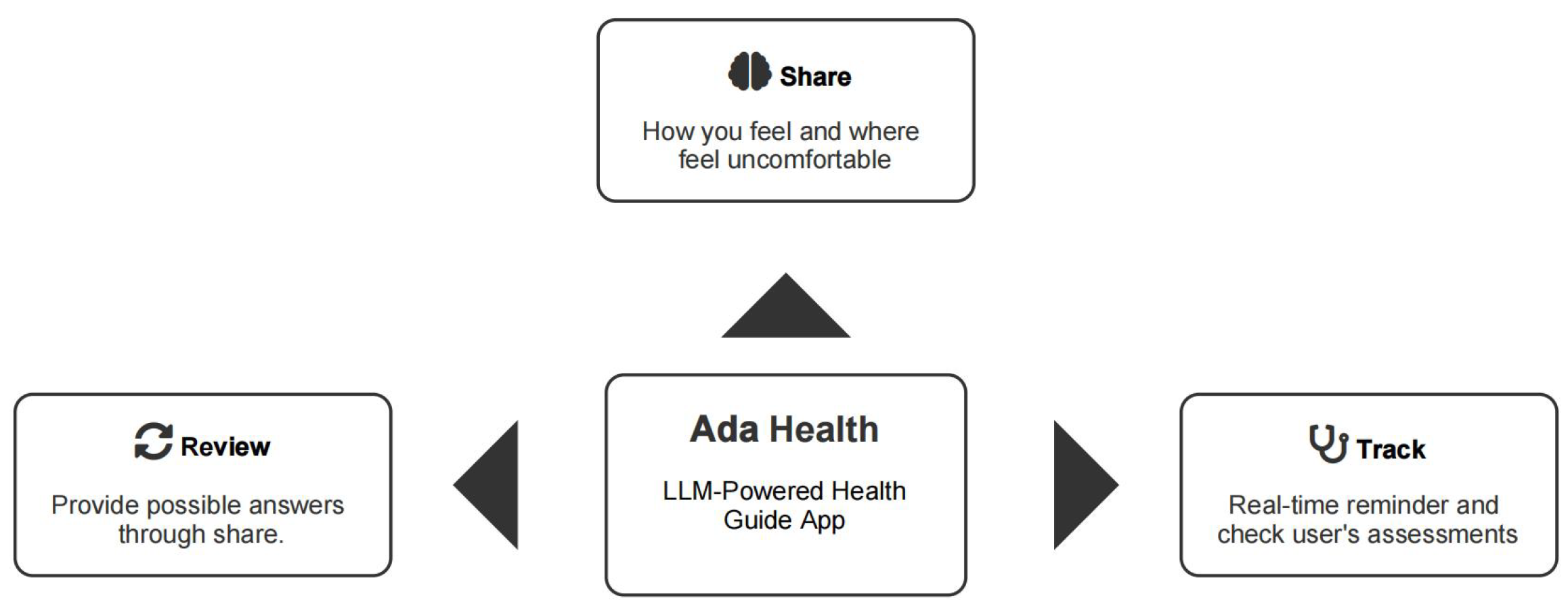
- Ada Health GmbH. Health. Powered by Ada. 2024. Available online: https://ada.com/ (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Buoy Health. Buoy Health: Check Symptoms & Find the Right Care. 2024. Available online: https://www.buoyhealth.com/ (accessed on 26 November 2024).
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, S.; Wang, F.; Hoetzlein, R.; Zhang, R. A review of reinforcement learning for natural language processing and applications in healthcare. J. Am. Med. Informatics Assoc. 2024, 31, 2379–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Muhic, J.; Robert, L.P.; Park, S.Y. Designing Chatbots with Black Americans with Chronic Conditions: Overcoming Challenges against COVID-19. In Proceedings of the 2022 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 29 April–5 May 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, T.; Schweizer, M. Successful Business Model Transformations in Disruptive Times: A Conceptual Framework for Established Corporations; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG: Boston, MA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Clochesy, J.M.; Dolansky, M.A.; Ronald, L.; Hickman, J.; Gittner, L.S. Enhancing Communication between Patients and Healthcare Providers: Sbar3. J. Health Hum. Serv. Adm. 2015, 38, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Mohebbi, M.; O’Callaghan, E.; Winsberg, M. Large Language Models Versus Expert Clinicians in Crisis Prediction Among Telemental Health Patients: Comparative Study. JMIR Ment. Health 2024, 11, e58129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, J.; Indulska, M.; Sadiq, S. Large language models and generative AI in telehealth: A responsible use lens. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2024, 31, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Wei, C.J.; Tseng, T.Y.; Chiu, M.C.; Chang, C.C. Applying Object Detection and Large Language Model to Establish a Smart Telemedicine Diagnosis System with Chatbot: A Case Study of Pressure Injuries Diagnosis System. Telemed. e-Health 2024, 30, e1705–e1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pais, C.; Liu, J.; Voigt, R.; Gupta, V.; Wade, E.; Bayati, M. Large language models for preventing medication direction errors in online pharmacies. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebreab, S.A.; Salah, K.; Jayaraman, R.; Habib ur Rehman, M.; Ellaham, S. LLM-Based Framework for Administrative Task Automation in Healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2024 12th International Symposium on Digital Forensics and Security (ISDFS), San Antonio, TX, USA, 29–30 April 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalamanchili, A.; Sengupta, B.; Song, J.; Lim, S.; Thomas, T.O.; Mittal, B.B.; Abazeed, M.E.; Teo, P.T. Quality of Large Language Model Responses to Radiation Oncology Patient Care Questions. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e244630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, S.; Berkhouse, H.; Schooler, M.; Pu, W.; Sun, A.; Gong, E.; Yan, L.L. Effectiveness of mHealth interventions in improving medication adherence among people with hypertension: A systematic review. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, D.; Teo, J.Y.C.; Wang, W.; Nguyen, H.D. LLM-Powered Multimodal AI Conversations for Diabetes Prevention. In Proceedings of the 1st ACM Workshop on AI-Powered Q&A Systems for Multimedia, Phuket, Thailand, 10–14 June 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Bae, S.; Kim, H.A.; Lee, S.W.; Hong, H.; Yang, C.; Kim, Y.H. MindfulDiary: Harnessing Large Language Model to Support Psychiatric Patients’ Journaling. In Proceedings of the 2024 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, O’ahu, HI, USA, 11–16 May 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Nurmatov, U.B.; Nwaru, B.I.; Mukherjee, M.; Grant, L.; Pagliari, C. Effectiveness of mHealth interventions for maternal, newborn and child health in low–and middle–income countries: Systematic review and meta–analysis. J. Glob. Health 2016, 6, 010401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brat, G.A.; Weber, G.M.; Gehlenborg, N.; Avillach, P.; Palmer, N.P.; Chiovato, L.; Cimino, J.; Waitman, L.R.; Omenn, G.S.; Malovini, A. International electronic health record-derived COVID-19 clinical course profiles: The 4CE consortium. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, A.T.; Ho, C.N.; Kerr, D.; Cichosz, S.L.; Mathioudakis, N.; Wang, M.; Najafi, B.; Moon, S.J.; Pandey, A.; Klonoff, D.C. Artificial Intelligence to Diagnose Complications of Diabetes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2025, 19, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazi, Z.A.; Peng, W. Large Language Models in Healthcare and Medical Domain: A Review. Informatics 2024, 11, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, J.L.; Longo, D.L. Precision medicine—Personalized, problematic, and promising. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2015, 70, 612–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afanasieva, T.V.; Platov, P.V.; Komolov, A.V.; Kuzlyakin, A.V. Leveraging ChatGPT and Long Short-Term Memory in Recommender Algorithm for Self-Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Mathematics 2024, 12, 2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Kendall, F.; Khozin, S.; Goosen, R.; Hu, J.; Laramie, J.; Ringel, M.; Schork, N. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in clinical development: A translational perspective. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridharan, K.; Sivaramakrishnan, G. Unlocking the potential of advanced large language models in medication review and reconciliation: A proof-of-concept investigation. Explor. Res. Clin. Soc. Pharm. 2024, 15, 100492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkomar, A.; Oren, E.; Chen, K.; Dai, A.M.; Hajaj, N.; Hardt, M.; Liu, P.J.; Liu, X.; Marcus, J.; Sun, M.; et al. Scalable and accurate deep learning with electronic health records. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajashekar, N.C.; Shin, Y.E.; Pu, Y.; Chung, S.; You, K.; Giuffre, M.; Chan, C.E.; Saarinen, T.; Hsiao, A.; Sekhon, J.; et al. Human-Algorithmic Interaction Using a Large Language Model-Augmented Artificial Intelligence Clinical Decision Support System. In Proceedings of the 2024 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, O’ahu, HI, USA, 11–16 May 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.T.; Pincock, D.; Baumgart, D.C.; Sadowski, D.C.; Fedorak, R.N.; Kroeker, K.I. An overview of clinical decision support systems: Benefits, risks, and strategies for success. NPJ Digit. Med. 2020, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximilian, K. Artificial intelligence in medicine and the disclosure of risks. AI Soc. 2021, 36, 705–713. [Google Scholar]
- Gates, T.J.; Boville, B.M.; Beal, S.G. Machine learning in medicine: A practical introduction. Am. J. Med. 2021, 134, 364–368. [Google Scholar]
- Eric, T. Transforming medicine via digital innovation. NPJ Digit. Med. 2010, 2, 16cm4. [Google Scholar]
- den Heuvel, J.V.; Hvidt, E.A.; Dahl-Larsen, R.; Thomsen, J.L.; Merrild, C.H. Patient-initiated video consultations: A qualitative study on reasons for patient-booking in Danish general practice. Digit. Health 2024, 10, 20552076241288637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, A.; Mostafa, J.; Kumar, M. Machine learning and medication adherence: Scoping review. JMIRx Med. 2021, 2, e26993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, L.P.; Maita, K.C.; Avila, F.R.; Torres-Guzman, R.A.; Garcia, J.P.; Eldaly, A.S.; Haider, C.R.; Felton, C.L.; Paulson, M.R.; Maniaci, M.J.; et al. Benefits and challenges of remote patient monitoring as perceived by health care practitioners: A systematic review. Perm. J. 2023, 27, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, H.; Wick, E.C.; Housman, M.; Freischlag, J.A.; Makary, M.A. Patient Satisfaction as a Possible Indicator of Quality Surgical Care. JAMA Surg. 2013, 148, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Liao, M.; Walther, J.B.; Sundar, S.S. When an AI Doctor Gets Personal: The Effects of Social and Medical Individuation in Encounters With Human and AI Doctors. Commun. Res. 2024, 51, 747–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A. A Survey on Security and Privacy of Multimodal LLMs - Connected Healthcare Perspective. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–8 December 2023; pp. 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, K.S.; Nenova, M.; Iliev, G. A study of cyber attacks: In the healthcare sector. In Proceedings of the 2021 Sixth Junior Conference on Lighting (Lighting), Gabrovo, Bulgaria, 23–25 September 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallam, M.; Al-Mahzoum, K.; Sallam, M. Generative Artificial Intelligence and Cybersecurity Risks: Implications for Healthcare Security Based on Real-life Incidents. Mesopotamian J. Artif. Intell. Healthc. 2024, 2024, 184–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nankya, M.; Mugisa, A.; Usman, Y.; Upadhyay, A.; Chataut, R. Security and Privacy in E-Health Systems: A Review of AI and Machine Learning Techniques. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 148796–148816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam Riad, A.K.; Barek, M.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Akter, M.S.; Islam, T.; Rahman, M.A.; Mia, M.R.; Shahriar, H.; Wu, F.; Ahamed, S.I. Enhancing HIPAA Compliance in AI-driven mHealth Devices Security and Privacy. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 48th Annual Computers, Software, and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Osaka, Japan, 2–4 July 2024; pp. 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, M.M.; Ganiga, R.; Pai, R.M.; Sinha, R.K. Standard electronic health record (EHR) framework for Indian healthcare system. Health Serv. Outcomes Res. Methodol. 2021, 21, 339–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagar, P.; Ravi, V.; Aalami, L.; Krusche, S.; Aalami, O.; Schmiedmayer, P. Dynamic Fog Computing for Enhanced LLM Execution in Medical Applications. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.04680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaqer, S.; Alajmi, S.; Ahmad, I.; Alfailakawi, M. The potential of llms in hardware design. J. Eng. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denecke, K.; May, R.; LLMHealthGroup; Rivera Romero, O. Potential of Large Language Models in Health Care: Delphi Study. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e52399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roselli, D.; Matthews, J.; Talagala, N. Managing Bias in AI. In Proceedings of the 2019 World Wide Web Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 May 2019; pp. 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, E. Fairness and Bias in Artificial Intelligence: A Brief Survey of Sources, Impacts, and Mitigation Strategies. Sci 2024, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, W.M.; Yax, N.; Palminteri, S. Large Language Models are Biased Reinforcement Learners. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2405.11422. [Google Scholar]
- Barman, K.G.; Wood, N.; Pawlowski, P. Beyond transparency and explainability: On the need for adequate and contextualized user guidelines for LLM use. Ethics Inf. Technol. 2024, 26, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhod, K.J. Integrating Large Language Models for Enhanced Clinical Decision Support Systems in Modern Healthcare. J. Mach. Learn. Healthc. Decis. Support 2023, 3, 18–62. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, I.S.; Link, K.E.; Daneshjou, R.; Cortés-Penfield, N. Black Box Warning: Large Language Models and the Future of Infectious Diseases Consultation. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 78, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.; Dave, D.; Naik, H.; Singhal, S.; Omer, R.; Patel, P.; Qian, B.; Wen, Z.; Shah, T.; Morgan, G.; et al. Explainable AI (XAI): Core Ideas, Techniques, and Solutions. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaddad, A.; Peng, J.; Xu, J.; Bouridane, A. Survey of explainable AI techniques in healthcare. Sensors 2023, 23, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owusu, F.W.; Yeboah, G.N.; Aboagye, R.A.; Amengor, C.D.K.; Entsie, P. The role of the patient information leaflet in patients’ medication therapy: A case study within the Kumasi metropolis of Ghana. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 2489137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, M.S.; Curtis, L.M.; Waite, K.; Bailey, S.C.; Hedlund, L.A.; Davis, T.C.; Shrank, W.H.; Parker, R.M.; Wood, A.J. Helping patients simplify and safely use complex prescription regimens. Arch. Intern. Med. 2011, 171, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoopendaal, A.; van de Bovenkamp, H. The mutual shaping of governance and regulation of quality and safety in Dutch healthcare. Health Serv. Manag. Res. 2015, 28, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palaniappan, K.; Lin, E.Y.T.; Vogel, S. Global Regulatory Frameworks for the Use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Healthcare Services Sector. Healthcare 2024, 12, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murikah, W.; Nthenge, J.K.; Musyoka, F.M. Bias and Ethics of AI Systems Applied in Auditing-A Systematic Review. Sci. Afr. 2024, 25, e02281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Fei, H.; Qu, L.; Ji, W.; Chua, T.S. NExT-GPT: Any-to-Any Multimodal LLM. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2309.05519. [Google Scholar]
- AlSaad, R.; Abd-Alrazaq, A.; Boughorbel, S.; Ahmed, A.; Renault, M.A.; Damseh, R.; Sheikh, J. Multimodal large language models in health care: Applications, challenges, and future outlook. J. Med. Internet Res. 2024, 26, e59505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, W.; Biswas, A. Improving Large Language Model (LLM) fidelity through context-aware grounding: A systematic approach to reliability and veracity. World J. Adv. Eng. Technol. Sci. 2023, 10, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, H.C.; Upperman, J.S.; Robinson, J.R. A systematic review of large language models and their implications in medical education. Med. Educ. 2024, 58, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambience Healthcare. Specialty-Specific Ambient AI Scribe with Compliant CDI for Healthcare. 2024. Available online: https://www.ambiencehealthcare.com/ (accessed on 26 February 2025).
- Whitfield, J.; LePoire, E.; Stanczyk, B.; Ratzliff, A.; Cerimele, J.M. Remote collaborative care with off-site behavioral health care managers: A systematic review of clinical trials. J. Acad.-Consult.-Liaison Psychiatry 2022, 63, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, D.S.W.; Tan, G.S.W. Telemedicine for diabetic retinopathy screening. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017, 135, 722–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, R.; Gupta, S.; Singh, S.N. A Comprehensive Survey of Bias in LLMs: Current Landscape and Future Directions. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.16430. [Google Scholar]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kwan, H.Y.; Shell, J.; Fahy, C.; Yang, S.; Xing, Y. Integrating Large Language Models into Medication Management in Remote Healthcare: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Systems 2025, 13, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13040281
Kwan HY, Shell J, Fahy C, Yang S, Xing Y. Integrating Large Language Models into Medication Management in Remote Healthcare: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Systems. 2025; 13(4):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13040281
Chicago/Turabian StyleKwan, Ho Yan, Jethro Shell, Conor Fahy, Shengxiang Yang, and Yongkang Xing. 2025. "Integrating Large Language Models into Medication Management in Remote Healthcare: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects" Systems 13, no. 4: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13040281
APA StyleKwan, H. Y., Shell, J., Fahy, C., Yang, S., & Xing, Y. (2025). Integrating Large Language Models into Medication Management in Remote Healthcare: Current Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Systems, 13(4), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13040281






