Bioactive Triple-Helical Recombinant Collagen Gels for Improved Healing of Sunburned Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of THRC Gel
2.3. Stability Assessment of THRC Gel
2.4. Rheological Behavior of THRC Gel
2.5. Skin Irritation Test of THRC Gels on Rabbits
2.6. Animal Experiment of THRC Gels in Sunburn Skin Healing
2.7. Non-Invasive Evaluation by Combo to Assess the Skin Condition
2.8. Histological Analysis
2.9. Quantitative Analysis of Collagen Volume Fraction and Hydroxyproline
2.10. Effect of THRC Gels on MDA, SOD, and GSH Levels
2.11. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Stability Determination of THRC Gels
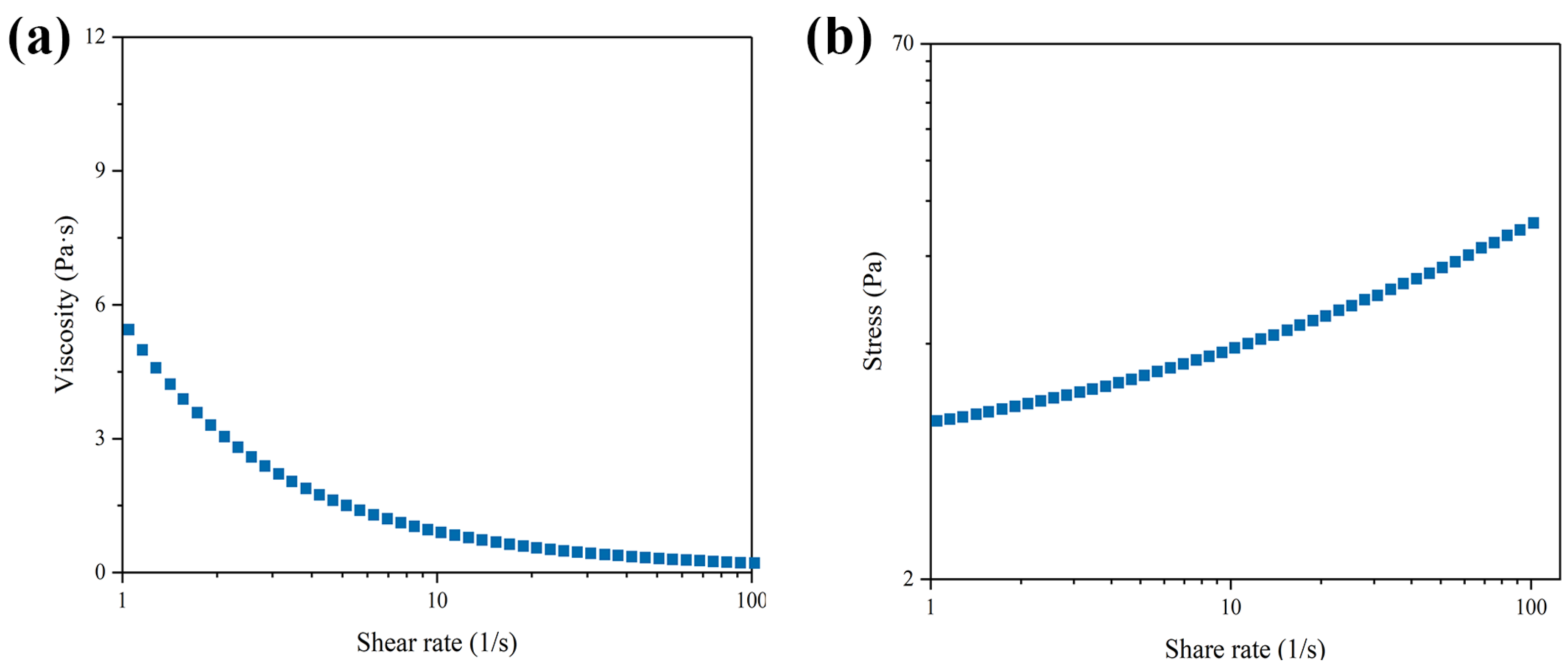
3.2. The Rheological Behavior of THRC Gels
3.3. Skin Irritation Evaluation of THRC Gels on Rabbits
3.4. DermaLab Combo Evaluation of the Performance of THRC Gels on the Repair of Sunburned Skin
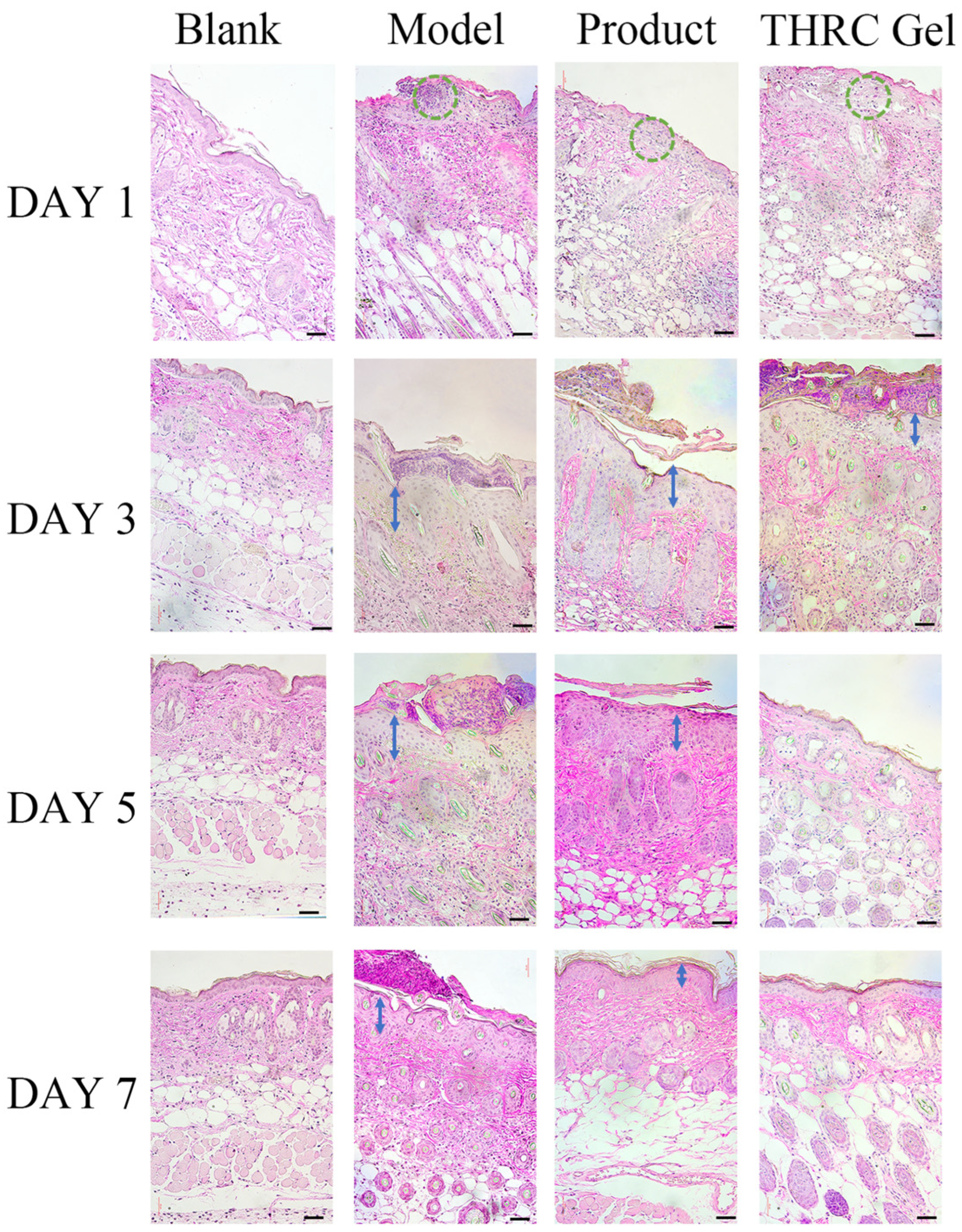
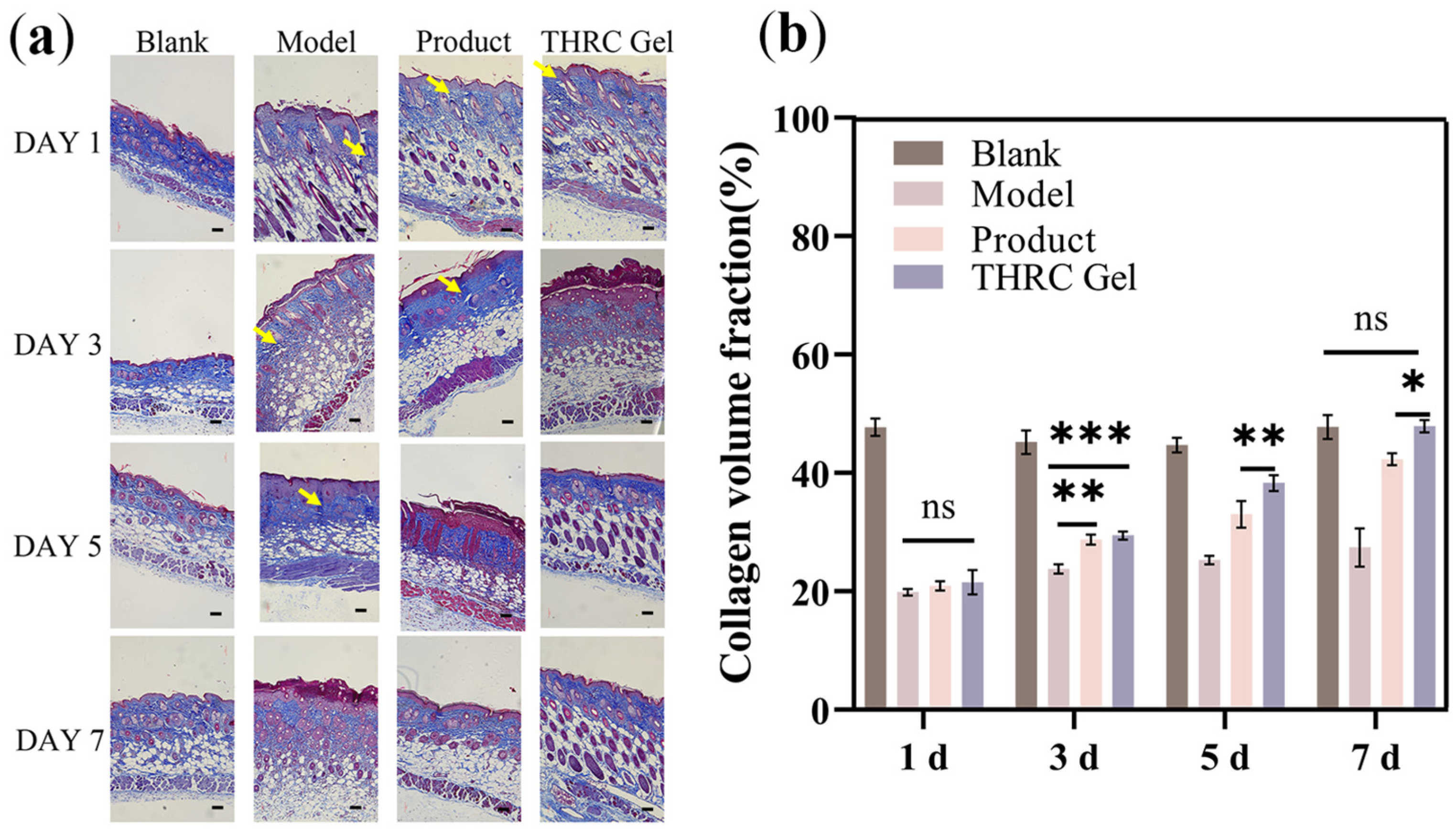
3.5. Histological Analysis to Investigate the Repair Ability of THRC Gels
3.6. Effect of THRC Gels on Hyp, MDA, SOD, and GSH Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choi, S.-I.; Jung, T.-D.; Cho, B.-Y.; Choi, S.-H.; Sim, W.-S.; Han, X.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, Y.-C.; Lee, O.-H. Anti-photoaging effect of fermented agricultural by-products on ultraviolet B-irradiated hairless mouse skin. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indirapriyadarshini, R.; Kanimozhi, G.; Natarajan, D.; Jeevakaruniyam, S.J. Andrographolide protects acute ultraviolet-B radiation-induced photodamages in the mouse skin. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2023, 315, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.; He, X.; Liu, N.; Deng, H. Role of reactive oxygen species in ultraviolet-induced photodamage of the skin. Cell Div. 2024, 19, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Feng, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, H.; Xie, C.; Fu, Y.; Tao, J.; et al. A novel amphibian-derived peptide alleviated ultraviolet B-induced photodamage in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 136, 111258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Hu, Y.; Bai, W.; Zhao, J.; Huang, C.; Wen, C.; Deng, L.; Lu, D. Cyanidin-3-o-glucoside inhibits UVA-induced human dermal fibroblast injury by upregulating autophagy. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2019, 35, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daré, R.G.; Nakamura, C.V.; Ximenes, V.F.; Lautenschlager, S.O.S. Tannic acid, a promising anti-photoaging agent: Evidences of its antioxidant and anti-wrinkle potentials, and its ability to prevent photodamage and MMP-1 expression in L929 fibroblasts exposed to UVB. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 160, 342–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, K.; Cao, J.; Yao, M.; Qin, L.; Qu, C.; Miao, J. Protective Effects of ζ-Carotene-like Compounds against Acute UVB-Induced Skin Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilchrest, B.A. Photoaging. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2013, 133, E2–E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fillon, M. Melanoma threats from ultraviolet exposure vary by state. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.R.; Claveau, J.; Rossi, A.B. Ultraviolet radiation and the skin: Photobiology and sunscreen photoprotection. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 76 (Suppl. 1), S100–S109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Qiu, H.; Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Tan, P.; Zhao, R.; Liu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Bao, C.; et al. The biological effect of recombinant humanized collagen on damaged skin induced by UV-photoaging: An in vivo study. Bioact. Mater. 2022, 11, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.N.A.; Roswandi, N.L.; Waqas, M.; Habib, H.; Hussain, F.; Khan, S.; Sohail, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: A review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120 Pt B, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Duan, X.; Zhong, D.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Hu, Z.; Han, F. Pharmaceutical applications of chitosan in skin regeneration: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 261 Pt 1, 129064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, S.; Reis, C.A.; Reis, R.L.; Pires, R.A. Extracellular Matrix Mimics Using Hyaluronan-Based Biomaterials. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assunção, M.; Yiu, C.H.K.; Wan, H.-Y.; Wang, D.; Ker, D.F.E.; Tuan, R.S.; Blocki, A. Hyaluronic acid drives mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular matrix assembly by promoting fibronectin fibrillogenesis. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 7205–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.-W. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 deficiency exacerbates dermis damage by ultraviolet-B via ΔNp63 downregulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Shi, S.; Tian, J.; Gu, H.; Yao, L.; Xiao, J. Non-denatured yak type I collagen accelerates sunburned skin healing by stimulating and replenishing dermal collagen. Biotechnol. Rep. 2023, 37, e00778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.; Shi, S.; Wei, N.; Fan, Y.; Gu, H.; Liu, P.; Xiao, J. Biocompatible Triple-Helical Recombinant Collagen Dressings for Accelerated Wound Healing in Microneedle-Injured and Photodamaged Skin. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilamaran, M.; Janeena, A.; Valappil, S.; Ramudu, K.N.; Shanmugam, G.; Niraikulam, A. A self-assembly and higher order structure forming triple helical protein as a novel biomaterial for cell proliferation. Biomater. Sci. 2019, 7, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljghami, M.E.; Saboor, S.; Amini-Nik, S. Emerging Innovative Wound Dressings. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2019, 47, 659–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghomi, E.R.; Khalili, S.; Khorasani, S.N.; Neisiany, R.E.; Ramakrishna, S. Wound dressings: Current advances and future directions. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, D.; Garg, Y.; Mahmood, S.; Chopra, S.; Bhatia, A. Marine-derived polysaccharides and their therapeutic potential in wound healing application—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253 Pt 6, 127331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shao, Y.; Wang, J. Selection of Appropriate Wound Dressing for Various Wounds. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, T.D.A.; Heimfarth, L.; Santos, D.M.D.; Santos, M.R.V.D.; Albuquerque-Júnior, R.L.C.D.; Santos-Neto, A.G.D.; Araujo, G.R.S.D.; Lira, A.A.M.; Matos, S.S.; Frank, L.A.; et al. Hesperetin-Based Hydrogels Protect the Skin against UV Radiation-Induced Damage. AAPS PharmSciTech 2022, 23, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huixia, H.; Fan, Y.; Shanshan, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zaiman, L.; Linghui, Y.; Jianxi, X. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 loaded triple helix recombinant collagen-based hydrogels for enhancing bone defect healing. Biomed. Mater. 2024, 19, 035029. [Google Scholar]
- Panyachariwat, N.; Jimtaisong, A.; Saewan, N. Antioxidative Potentials of Eleutherine bulbosa Bulb and Its Utilization in Topical Cosmetic Emulsion. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QB/T 2872-2017; Light Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Mask. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of PRC: Beijing, China, 2017. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/QBT2872-2017 (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- GB/T 13531.1-2008; National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. General Methods on Determination of Cosmetics—Determination of pH. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine: Beijing, China, 2008. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/GBT13531.1-2008 (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Costa, G.M.D.A.; Campos, P.M.B.G.M. Development of Cosmetic Formulations Containing Olive Extract and Spirulina sp.: Stability and Clinical Efficacy Studies. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 16886.10-2017; National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 10: Test for Irritation and Skin Sensitization. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/GBT16886.10-2017 (accessed on 5 August 2024).
- Li, J.; Huang, W.; He, H.; Shi, S.; Sun, X.; Xiao, J. Biocompatible and bioactive hydrogels of recombinant fusion elastin with low transition temperature for improved healing of UV-irradiated skin. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 6975–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariffin, N.H.M.; Hasham, R. Assessment of non-invasive techniques and herbal-based products on dermatological physiology and intercellular lipid properties. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdlaty, R.; Fang, Q. Skin erythema assessment techniques. Clin. Dermatol. 2021, 39, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Zhang, J.; Quan, S.; Yang, Y.; Yao, L.; Xiao, J. A highly biocompatible and bioactive transdermal nano collagen for enhanced healing of UV-damaged skin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 272 Pt. 1, 132857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yan, H.; Yao, L.; Xie, Y.; Liu, P.; Xiao, J. A highly bioactive THPC-crosslinked recombinant collagen hydrogel implant for aging skin rejuvenation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 266 Pt. 2, 131276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-J.; Chang, C.-C.; Lu, M.-E.; Wu, Y.-H.; Shen, J.-W.; Chiang, H.-M.; Lin, B.-S. Photoaging and Sequential Function Reversal with Cellular-Resolution Optical Coherence Tomography in a Nude Mice Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biernacki, M.; Brzóska, M.M.; Markowska, A.; Gałażyn-Sidorczuk, M.; Cylwik, B.; Gęgotek, A.; Skrzydlewska, E. Oxidative Stress and Its Consequences in the Blood of Rats Irradiated with UV: Protective Effect of Cannabidiol. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wölfle, U.; Esser, P.R.; Simon-Haarhaus, B.; Martin, S.F.; Lademann, J.; Schempp, C.M. UVB-induced DNA damage, generation of reactive oxygen species, and inflammation are effectively attenuated by the flavonoid luteolin in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Kong, C.; Cheng, S.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J. Succinoglycan riclin relieves UVB-induced skin injury with anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 235, 123717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, T. The Role of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor (MIF) in Ultraviolet Radiation-Induced Carcinogenesis. Cancers 2010, 2, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Torres, J.E.; Hakim, M.; Babiak, P.M.; Pal, P.; Battistoni, C.M.; Nguyen, M.; Panitch, A.; Solorio, L.; Liu, J.C. Collagen- and hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels and their biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2021, 146, 100641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Qin, D.; Wang, H.; Zhu, Y.; Bi, S.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, X. Effect and mechanism of fish scale extract natural hydrogel on skin protection and cell damage repair after UV irradiation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2023, 225, 113281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Group | UV Radiation | Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| blank | - | - |
| model | + | - |
| product | + | 0.1 g/day |
| THRC gel | + | 0.1 g/day |
| Time | pH (25 °C) | Centrifugation Test | Heat Test | Freeze Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 w | 6.43 ± 0.03 | no significant difference | no significant difference | no significant difference |
| 4 w | 6.57 ± 0.05 | no significant difference | no significant difference | no significant difference |
| 8 w | 6.44 ± 0.08 | no significant difference | no significant difference | no significant difference |
| 12 w | 6.50 ± 0.04 | no significant difference | no significant difference | no significant difference |
| Group | Score | PDII | The Intensity of Irritation |
|---|---|---|---|
| control | 0 | 0 | no irritating |
| normal | 0 | 0 | no irritating |
| damage | 0 | 0 | no irritating |
| positive control | 1.66 | 0.55 | mildly irritating |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Tian, B.; Xie, Y.; Liu, P.; Yao, L.; Xiao, J. Bioactive Triple-Helical Recombinant Collagen Gels for Improved Healing of Sunburned Skin. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11040138
Yang Y, Tian B, Xie Y, Liu P, Yao L, Xiao J. Bioactive Triple-Helical Recombinant Collagen Gels for Improved Healing of Sunburned Skin. Cosmetics. 2024; 11(4):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11040138
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yi, Bei Tian, Yi Xie, Peng Liu, Linyan Yao, and Jianxi Xiao. 2024. "Bioactive Triple-Helical Recombinant Collagen Gels for Improved Healing of Sunburned Skin" Cosmetics 11, no. 4: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11040138
APA StyleYang, Y., Tian, B., Xie, Y., Liu, P., Yao, L., & Xiao, J. (2024). Bioactive Triple-Helical Recombinant Collagen Gels for Improved Healing of Sunburned Skin. Cosmetics, 11(4), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11040138






