Abstract
Exosomes, a subtype of extracellular vehicles (EVs), play a pivotal role in cellular communication and have gained considerable attention in dermatological research. Formed through the inward budding of the endosomal membrane, exosomes facilitate the transfer of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, including microRNAs (miRNAs), thereby influencing the behavior and function of recipient cells. These vesicles are secreted by various cell types, including keratinocytes, and are crucial for maintaining skin homeostasis, regulating immune responses, and promoting wound healing. Exosomes have demonstrated therapeutic potential in addressing dermatological conditions such as hair disorders, skin cancers and photoaging through enhanced regeneration and reduced oxidative stress. However, they are also implicated in disease progression, with pathogens utilizing exosome release to evade host immune responses. Recent studies highlight the diverse origins and functions of exosomes, suggesting their promise as innovative therapeutic agents in dermatology. As research continues to elucidate their multifaceted roles, exosomes represent a frontier in understanding intercellular communication and developing novel treatments for skin-related diseases, underscoring their potential impact on both health and clinical applications. This review synthesizes the existing literature on exosome biology and isolation with a focus on their implications in dermatological contexts.
1. Introduction
Exosomes are a specific subtype of EVs (EVs) measuring between 30 and 150 nm in diameter [1,2]. Among the various types of EVs, exosomes have garnered significant interest as a focal point in dermatological research due to their significant role in cellular communication and their potential therapeutic applications.
2. Role of Exosomes in Human Health
Exosomes are formed through the inward budding of the endosomal membrane, leading to the creation of multivesicular bodies (MVBs) that release exosomes into the extracellular space upon fusion with the plasma membrane [3,4].
Exosomes are secreted by a wide range of cell types and are involved in the transfer between cells of proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids, including microRNAs (miRNAs) [5].
miRNAs have the capacity to affect recipient cells by altering gene expression and influencing various cellular activities such as cell growth, programmed cell death, and movement [6,7,8]. The resilience of miRNAs within exosomes protects them from degradation, boosting their utility as biomarkers for diagnosing and predicting outcomes in diseases, especially cancer [9,10].
The content of exosomes, especially in terms of miRNA, strongly influences the behavior and function of recipient cells, making exosomes important mediators in both health and disease [11].
First of all, it is widely recognized that exosomes play a role in communication within the immune system and facilitate immune modulation [12].
They are also essential for cell communication within brain tissue [13] and are released by the cardiovascular system for normal function [14].
Interestingly, skin cells, particularly keratinocytes, continuously release exosomes to regulate intercellular communication and maintain homeostasis. Exosome release from the skin system exerts a wide range of functions, such as wound healing [15], regulation of the immune response, modulation of pigmentation [16], control of microbiome balance [17] and responses to oxidative stress [18,19].
Besides their typical beneficial roles, exosomes are also implicated in the pathological development and progression of various diseases [11]. Current research is highlighting that pathogens can exploit exosome release to infect host cells, manipulating these host-derived exosomes to evade immune responses [20].
Exosomes have also been recognized for their pivotal roles in various diseases, particularly concerning abnormalities in production and signaling pathways like Notch and Sonic Hedgehog (SHH) [21].
In neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), exosomes’s role in the production of abnormalities have been linked to disease pathology [22]. In liver diseases such as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma, EVs are significant for disease progression because they carry microRNAs and proteins that modulate cellular responses [22]. This underscores their potential as therapeutic targets and biomarkers, particularly in conditions involving aberrant SHH signaling.
Additionally, exosomes are associated with several other conditions, including heart failure [23] and cancer [24,25,26].
Indeed, the diverse origins of exosomes contribute to their unique characteristics and therapeutic potential in addressing various dermatological issues [27,28].
Treatment with exosomes has been reported to be effective in skin tumors, especially as a drug carrier [29,30], as well as in wound healing [31,32,33,34] and in reducing photo-oxidative stress [35,36,37,38], including disorders affecting the scalp and hair follicles [39,40,41,42].
Research has shown that exosomes can transport hydrophobic Wnt proteins on their surface, facilitating the activation of β-catenin [43]. This process plays a crucial role in the signaling pathway that regulates hair morphogenesis and regeneration [44].
Exosomes derived from platelet-rich plasma (PRP) have gained interest due to their potential to stimulate hair growth, particularly in conditions like androgenetic alopecia [41,45]. PRP is abundant in growth factors and cytokines essential for maintaining hair follicle health [46]. Recent research indicates that exosomes released from PRP can promote the proliferation and survival of dermal papilla cells (DPCs), which are crucial for hair follicle development and cycling [47,48,49]. Specifically, these exosomes are known to transport microRNAs and growth factors that can influence signaling pathways such as the Wnt/β-catenin pathway while also antagonizing the inhibitory effect of dihydrotestosterone on HF growth [50,51]. Moreover, the use of PRP-derived exosomes has been linked to increased angiogenesis and an improved vascularization of follicles, thereby enhancing nutrient delivery to support hair growth [52,53] (Figure 1).
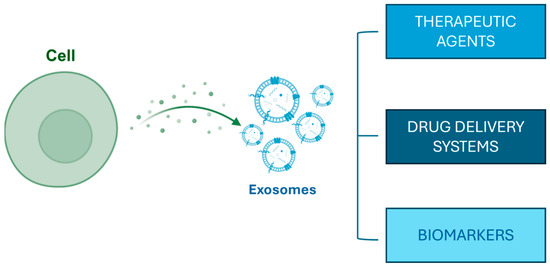
Figure 1.
Exosome biogenesis and their potential applications.
3. Types of Exosomes
The origin of human exosomes is notably diverse; studies have demonstrated that exosomes can be released from various biological fluids, including blood, saliva, urine, and breast milk, and they can be produced by a wide range of cells, such as immune cells, epithelial cells, and cancer cells [54].
For example, exosomes sourced from human umbilical cord MSCs have been reported to enhance skin wound healing by promoting angiogenesis and fibroblast activity through miRNA-mediated mechanisms [55,56].
Furthermore, exosomes derived from induced pluripotent stem cells have been found to mitigate skin aging by stimulating collagen production and lowering matrix metalloproteinase activity, which is crucial for maintaining skin elasticity and integrity [57,58].
In consideration of their strong immunomodulatory effects, they are also considered valuable for treating inflammatory skin conditions like psoriasis and atopic dermatitis [59]. Exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells alleviate psoriasis-like skin inflammation [60,61].
Another important source of human exosomes is breast milk. Milk exosomes (MI-Exos) were found to be particularly rich in bioactive molecules, including proteins, lipids, and various types of microRNAs (miRNAs), able to exert diverse biological functions and with potential health benefits [29]. The first study focused on exosomes derived from milk was published in 2007 [62]. MI-Exos possess an extraordinary ability to influence immune responses due to their richness in immune-related miRNAs that can enhance the development of regulatory T cells, which are essential for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing excessive inflammation [63,64]. This is mainly related to their capacity to deliver oligosaccharides to macrophages, thereby modulating the immune response and potentially offering protection against infections, including those caused by adherent–invasive Escherichia coli [65]. miR-148a-3p is the most prevalent miRNA found in human breast milk [66].
The immunomodulatory function of breast milk is especially advantageous for infants, aiding in the establishment of a balanced immune system during their early growth [67]. Additionally, studies suggest that miRNAs derived from milk can be absorbed by human intestinal cells, facilitating their bioavailability and their potential to have biological effects within the body [66,68]. Breast milk exosomes have shown protective effects against inflammatory disorders such as necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC), a severe gastrointestinal condition affecting premature infants [69]. Their protective properties also extend to skin health, where the anti-inflammatory effects of breast milk exosomes may alleviate conditions like atopic dermatitis and psoriasis by modulating local immune responses [70].
Significant attention has been given to investigating microRNA and mRNA within exosomes derived from colostrum [71].
Colostrum, the initial milk produced postpartum, is especially abundant in exosomes and has been found to contain a greater concentration of bioactive molecules than mature milk. Studies have shown that these exosomes can enhance the proportion of regulatory T cells, which are crucial for maintaining immune tolerance and preventing allergic reactions in infants [72].
Additionally, human colostrum-derived exosomes have also been found to survive digestion and be absorbed by intestinal cells, allowing them to exert systemic effects, including potential benefits for skin health [73].
The exosome system represents an archaic and highly conserved signaling system among all mammals. Exosomes originating from non-human cells, including those from rodents and other mammals, have been thoroughly investigated for their possible therapeutic uses [74]. MI-Exos have been successfully isolated from the milk of cows, pigs, mice, sheep, kangaroos, and yaks [75,76,77,78]. These animals can produce several liters of milk each day, resulting in substantial quantities of exosomes compared to those obtained from cell lines or other biological fluids. Notably, these exosomes exhibit a consistent particle size of around 100 nm, which is particularly advantageous for therapeutic applications.
One of the main features of MI-Exos is their capacity to affect immune responses mainly due to the presence of miRNAs [77,79].
Indeed, miRNAs found in bovine milk, for instance [80,81], are a type of single-stranded noncoding RNA that attach to the 3′ untranslated regions of target genes [82].
Through this mechanism, miRNAs regulate a variety of cellular processes, including cell differentiation, tissue development, and immune responses, which in turn influence various facets of health and disease [83,84,85,86].
Exosomal miRNAs exhibit a high degree of sequence homology across different species. The main advantage of MI-exos, as of those derived from breast milk, is their capability to pass through biological barriers, including the intestinal and blood–brain barriers, avoiding immune reactions. This low antigenic potential makes them especially attractive for therapeutic purposes, such as drug delivery systems for small interfering RNAs and other bioactive substances [74,87].
The minimal antigenicity of milk exosomes is linked to their composition, which is similar to that of cell membranes, leading to high biocompatibility and lowered immunogenicity [88].
This feature is essential because it enables the safe delivery of miRNAs to recipient cells without provoking negative immune responses. Therefore, research has shown that miRNAs from Mi-EXOs can easily preserve their integrity and functionality in the gastrointestinal environment, since they are not influenced by low pH and enzymatic breakdown [88,89].
The strong resilience of miRNAs during the digestive process and their capacity to enter systemic circulation highlight the therapeutic promise of milk exosomes as carriers for delivering genetic material and other therapeutic substances [90]. The stability of miRNAs found in Mi-EXOs is another significant factor that boosts their therapeutic promise, enabling them to exert biological effects beyond the gastrointestinal system [91]. These features imply that Mi-EXOs could be utilized for topical treatments, potentially delivering therapeutic miRNAs directly to skin cells to encourage healing and decrease inflammation [75,92].
Research also indicates that exosomes from bovine colostrum can stimulate cell proliferation and boost immune responses, proving beneficial for conditions like intestinal colitis [93,94]. Notably, certain miRNAs present in bovine colostrum exosomes, such as miR-30a-5p, are associated with anti-inflammatory properties, which highlights their potential in the treatment of inflammatory skin disorders [95].
Exosomes can also originate from a variety of non-human sources. In plants, they facilitate the communication between plant cells and the surrounding environment and mediate the stress responses by releasing signaling molecules that help in the adaptation to adverse conditions, such as drought or pathogen attack [96]. Due to their functions, plant exosomes have proven to be useful in both the field of agriculture and human health.
Non-plant exosomes closely mimic human cell structures and pathways, allowing them to encapsulate and transport molecules like proteins, lipids, and RNAs more efficiently within animal and human systems. This results in more precise targeting and a reduced likelihood of immune response. Consequently, animal exosomes are particularly advantageous in areas like drug delivery, disease diagnostics, and regenerative medicine. Therefore, animal exosomes are frequently regarded as superior to plant exosomes for specific medical and therapeutic uses, mainly because of their high biocompatibility [77].
When it comes to isolating plant-derived EVs, the outcomes recorded in different studies often differ based on factors such as the plant source, the isolation method used, the plant’s physiological condition, and the composition of the extracted nanoparticles. This variability is largely due to the absence of a standardized isolation protocol [97].
Furthermore, there is a significant gap in knowledge regarding the biogenesis of plant-derived EVs [97,98], and the scarcity of specific protein markers for EVs complicates the biological characterization of these exosomes. More research is needed to identify the surface markers and other defining features of plant exosomes, which remain largely unknown.
Another non-human sources of exosomes are bacteria. In bacteria, exosomes are often referred to as outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) [99,100]. These vesicles are released by Gram-negative bacteria and contain various virulence factors, including toxins and enzymes that can modulate host immune responses [101]. One of the most fascinating discoveries concerning the release of EVs from Gram-positive bacteria is the identification of EVs released by mycobacteria [102,103]. Interestingly, EVs containing mycobacterial materials can be produced by infected host cells, such as macrophages, which serve as the primary host cells for Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other pathogenic mycobacteria [104,105].
4. Exosome Isolation and Quality Control
Eosomes isolation is a critical step in harnessing their therapeutic potential. Given their small size and the complexity of biological fluids, effective methodologies for isolating exosomes must be robust and reproducible to ensure high yield and purity.
The choice of isolation method significantly influences the characterization of exosomal content, with various techniques leading to differences in concentration, purity, and size.
There is currently no established gold standard for isolating exosome, and it seems that new methods are constantly emerging. Ultracentrifugation, particularly in the form of differential centrifugation, continues to be the predominant method for the primary isolation of EVs and is the methodology utilized by over 80% of researchers in the field globally [106]. Unfortunately, this technique presents several limitations, including the simultaneous isolation of non-exosomal contaminants, issues with reproducibility, low yields of RNA, potential harm to the exosomes themselves, and limited throughput, making it less suitable for clinical applications [107].
Also, multiple isolation methods are used (e.g., density gradient followed by ultrafiltration and size-exclusion chromatography) [106].
Zhang and collaborators [108] recently developed a new technique for isolating exosomes using asymmetric-flow field-flow fractionation (AF4), which separates nanoparticles according to their density and hydrodynamic properties.
Research indicates that different isolation methods produce distinct mRNA profiles with unique miRNAs and altered levels of several proteins widely used as “markers” of exosomes, such as tetraspanins [109,110,111,112].
Once isolated, electron microscopy is the most widely used technique for verifying the quality of exosome isolation and confirming that the vesicles remain intact [113,114,115]. Even though effective, this technique is labor-intensive and not well suited for high-throughput analysis of exosome counts. Therefore, the actual number of exosomes can be underestimated due to the potential loss of vesicles during the sample preparation process.
5. Future Perspectives and Conclusions
The safety and tolerability of exosome-based therapies are critical factors in their clinical application. Although many studies have highlighted positive results with minimal side effects, continued research is necessary to develop standardized procedures for isolating, characterizing, and utilizing exosomes [116,117,118].
Additionally, the mechanisms of exosome uptake and action in target cells remain poorly understood, complicating the development of targeted therapies. Issues related to the large-scale isolation, purification, and characterization of exosomes also hinder their clinical translation. Developing stringent quality control measures is crucial for the consistent production of therapeutic exosomes. Innovations in characterization techniques to assess exosome size, concentration, and biological activity are key to establishing product standards. This will also facilitate the creation of a biorepository with well-defined exosome characteristics that can serve as a valuable resource for ongoing research.
Future research should focus on engineering exosomes for enhanced specificity and therapeutic effect, elucidating their interactions with host cells, and developing robust methods for their production and quality control, thereby addressing these critical gaps in knowledge and application.
Additionally, the regulatory landscape for exosome therapies is intricate; currently, no exosome products have received FDA approval for clinical applications, underscoring the need for further investigation into their long-term safety and effectiveness [107].
The FDA categorizes exosomes as biologics, necessitating thorough regulatory oversight, which includes extensive preclinical data on safety and efficacy prior to clinical trial approval. Although the FDA has issued guidance on cell-based therapies, specific protocols for exosome therapies continue to evolve, highlighting the need for researchers to remain updated on regulatory changes.
In an international context, disparate standards across countries pose challenges for the development and market access of exosome products. To address this, it is crucial to establish harmonized guidelines for the characterization, safety assessment, and clinical evaluation of exosomes. Collaboration with global regulatory agencies, such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the World Health Organization (WHO), is vital to create cohesive evaluation processes that can expedite the transition from research to clinical application and promote broader acceptance of exosome therapies worldwide.
To facilitate clinical translation, it would also be important to improve communication between researchers, product developers, and regulatory bodies to help clarify regulatory pathways and identify challenges early in the development process. Lastly, providing educational resources and training for stakeholders on regulatory standards and best practices will enhance the likelihood of successful market entry for exosome-based products.
In summary, exosomes are emerging as an innovative and promising area for human health, including the dermatological field. Their ability to facilitate intercellular communication and modulate cellular responses makes them highly valuable in regenerative medicine.
Human and milk-derived exosomes show great potential due to their high biocompatibility and resemblance to natural cellular processes within the human body. These exosomes can be tailored to deliver specific therapeutic agents, thereby providing targeted and personalized treatments. Milk-Exos are plentiful, easy to extract, and have demonstrated effectiveness in enhancing gut health and systemic immunity, making them suitable for a broad range of therapeutic applications.
The production process for both human and Milk-Exos is crucial, as it ensures the preparations are pure, functional, and consistent. Implementing standardized protocols and strict quality control measures is essential to creating exosomes that are both safe and effective for clinical use. In vitro studies are crucial for understanding the underlying biological mechanisms and optimizing formulations, while in vivo experiments are necessary to assess therapeutic performance and safety in living organisms.
This comprehensive approach to research and development is vital for transforming the potential of exosomes into practical medical solutions.
Additionally, the characterization of miRNA content within exosomes is of significant importance. miRNAs play a key role in regulating gene expression and influencing cellular behavior, so a detailed profiling of exosomal miRNAs can provide insights into their therapeutic potential. This enables the development of more precise and effective treatments.
As research continues to uncover the mechanisms behind exosome functionality and their clinical applications, exosome-based therapies have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of dermatological conditions, leading to improved patient outcomes and an enhanced quality of life.
To advance this field, focused research on EXs from diverse origins could unveil new, biocompatible options for therapeutic delivery. Additionally, optimizing delivery systems for targeted skin treatments can enhance the efficacy and specificity of exosome-based therapies, ultimately improving clinical outcomes.
Author Contributions
F.R., D.P. and G.G. conceptualized this study. D.P. and G.M. wrote the original draft. D.P., F.R. and G.G. reviewed and edited the manuscript. F.R. and G.G. acquired the funding. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not require ethical approval.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
D.P. and G.M. are employed by Giuliani S.p.A. F.R. serves as a consultant for Giuliani S.p.A. G.G. is on the board of directors of Giuliani S.p.A.
References
- Zaborowski, M.P.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lai, C.P. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. Bioscience 2015, 65, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, H.A.; Varsano, I.; Kahan, E.; Sarrell, E.M.; Uziel, Y. Effectiveness of an herbal preparation containing echinacea, propolis, and vitamin C in preventing respiratory tract infections in children. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2004, 158, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Dragoumani, K.; Mitsis, T.; Chrousos, G.P.; Vlachakis, D. Milk exosomes and a new way of communication between mother and child. EMBnet J. 2024, 29, e1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Gahan, P.B. MicroRNA shuttle from cell-to-cell by exosomes and its impact in cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2019, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Odenthal, M.; Fries, J.W. Exosomes as miRNA carriers: Formation–function–future. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Shi, K.; Yang, S.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, G.; Song, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, W. Effect of exosomal miRNA on cancer biology and clinical applications. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thind, A.; Wilson, C. Exosomal miRNAs as cancer biomarkers and therapeutic targets. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 31292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Tan, Z.; Guan, F. Tumor-derived exosomes mediate the instability of cadherins and promote tumor progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadaran, P.; Madhyastha, H.; Madhyastha, R.; Rajendran, R.L.; Nakajima, Y.; Watanabe, N.; Velikkakath, A.K.G.; Hong, C.M.; Gopi, R.V.; Muthukalianan, G.K.; et al. The emerging role of exosomes in innate immunity, diagnosis and therapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1085057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, C.; Raimondo, S.; Chiesi, A.; Ciccia, F.; De Leo, G.; Alessandro, R. Exosomes as intercellular signaling organelles involved in health and disease: Basic science and clinical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5338–5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fröhlich, D.; Kuo, W.P.; Frühbeis, C.; Sun, J.J.; Zehendner, C.M.; Luhmann, H.J.; Pinto, S.; Toedling, J.; Trotter, J.; Krämer-Albers, E.M. Multifaceted effects of oligodendroglial exosomes on neurons: Impact on neuronal firing rate, signal transduction and gene regulation. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Knowlton, A.A. HSP60 trafficking in adult cardiac myocytes: Role of the exosomal pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H3052–H3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Shah, D.; Rai, D.; Parra, D.C.; Pathikonda, S.; Kurilova, S.; Cili, A. Therapeutic values of exosomes in cosmetics, skin care, tissue regeneration, and dermatological diseases. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.L.; Delevoye, C.; Gilles-Marsens, F.; Loew, D.; Dingli, F.; Guéré, C.; André, N.; Vié, K.; Van Niel, G.; Raposo, G. Exosomes released by keratinocytes modulate melanocyte pigmentation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Chang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, W.; Song, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, C. Interactions between extracellular vesicles and microbiome in human diseases: New therapeutic opportunities. iMeta 2023, 2, e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Jian, Z.; Baskys, A.; Yang, J.; Li, J.; Guo, H.; Hei, Y.; Xian, P.; He, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. MSC-derived exosomes protect against oxidative stress-induced skin injury via adaptive regulation of the NRF2 defense system. Biomaterials 2020, 257, 120264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajialiasgary Najafabadi, A.; Soheilifar, M.H.; Masoudi-Khoram, N. Exosomes in skin photoaging: Biological functions and therapeutic opportunity. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cestari, I.; Ansa-Addo, E.; Deolindo, P.; Inal, J.M.; Ramirez, M.I. Trypanosoma cruzi immune evasion mediated by host cell-derived microvesicles. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1942–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, C.C.; Wang, H. Pathogenic and therapeutic role of exosomes in neurodegenerative disorders. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ateeq, M.; Broadwin, M.; Sellke, F.W.; Abid, M.R. Extracellular Vesicles’ Role in Angiogenesis and Altering Angiogenic Signaling. Med. Sci. 2024, 12, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Yan, Y.; Tan, Y. Role of exosomes in chronic liver disease development and their potential clinical applications. J. Immunol. Res. 2022, 2022, 1695802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadli, A.S.; Parasor, A.; Gomes, K.P.; Shandilya, R.; Patel, V.B. Exosomes in cardiovascular diseases: Pathological potential of nano-messenger. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 767488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefańska, K.; Józkowiak, M.; Angelova Volponi, A.; Shibli, J.A.; Golkar-Narenji, A.; Antosik, P.; Bukowska, D.; Piotrowska-Kempisty, H.; Mozdziak, P.; Dzięgiel, P.; et al. The role of exosomes in human carcinogenesis and cancer therapy—Recent findings from molecular and clinical research. Cells 2023, 12, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maqsood, Q.; Sumrin, A.; Saleem, Y.; Wajid, A.; Mahnoor, M. Exosomes in cancer: Diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Clin. Med. Insights Oncol. 2024, 18, 11795549231215966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandrey, M.; Jablonska, J.; Stauber, R.H.; Gül, D. Exosomes in cancer progression and therapy resistance: Molecular insights and therapeutic opportunities. Life 2023, 13, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, O.; Botsali, A.; Caliskan, E. Role of exosomes in skin diseases. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Feng, H.; Zeng, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, J.; Hou, K.; Wu, M. Exosomes: The emerging mechanisms and potential clinical applications in dermatology. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 20, 1778–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbichler, T.B.; Dudás, J.; Riechelmann, H.; Skvortsova, I.-I. The role of exosomes in cancer metastasis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 44, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhou, X. Application of exosome as a chemical drug carrier in tumor treatment. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Biological Engineering and Medical Science (ICBioMed2023), Online, 2–9 September 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Meng, Y.; Qian, M.; Zhang, G. Epidermal stem cell-derived exosomes promote skin regeneration by downregulating transforming growth factor-β1 in wound healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Song, H.; Wang, W. Exosomes derived from TSG-6 modified mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate scar formation during wound healing. Biochimie 2020, 177, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Hu, L.; Zhou, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhang, C.; Shehada, H.M.; Hu, B.; Song, J.; Chen, L. Exosomes secreted by human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote scarless cutaneous repair by regulating extracellular matrix remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1332. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, X.L.; Lu, Y.J.; Lu, S.T.; Cheng, J.; Fu, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhang, N.Y.; Li, P.X.; et al. Combined topical and systemic administration with human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hADSC) and hADSC-derived exosomes markedly promoted cutaneous wound healing and regeneration. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Li, Z.; Cores, J.; Huang, K.; Su, T.; Dinh, P.U.; Cheng, K. Needle-free injection of exosomes derived from human dermal fibroblast spheroids ameliorates skin photoaging. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 11273–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zhang, B.; Han, X.; Sun, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, L.; Zhou, X.; Jin, Q.; Fu, P.; Xu, W.; et al. HucMSC exosome-delivered 14-3-3ζ alleviates ultraviolet radiation-induced photodamage via SIRT1 pathway modulation. Aging 2021, 13, 11542–11563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.; Wang, X.; Si, Y.; Pang, J.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Ding, Q.; Wang, Y. Exosomes derived from ADSCs attenuate ultraviolet B-mediated photo-aging in human dermal fibroblasts. Photochem. Photobiol. 2021, 97, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.X.; Liao, X.; Li, S.H.; Jiang, X.; Li, Z.H.; Wu, Y.D.; Xiao, L.L.; Xie, G.H.; Song, J.X.; Liu, H.W. Antiaging properties of exosomes from adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in photoaged rat skin. Biomed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6406395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z.; Wu, T.; Yang, C. Hair follicle mesenchymal stem cell exosomal lncRNA H19 inhibited NLRP3 pyroptosis to promote diabetic mouse skin wound healing. Aging 2023, 15, 791–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Ma, C.; Chen, H.D.; Wu, Y.; Xu, X.G. The roles of exosomes in regulating hair follicle growth. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 17, 1603–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ersan, M.; Ozer, E.; Akin, O.; Tasli, P.N.; Sahin, F. Effectiveness of exosome treatment in androgenetic alopecia: Outcomes of a prospective study. Aesth. Plast. Surg. 2024, 48, 4262–4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Y.; Hou, X.; Su, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; Song, H. Treatment of androgenetic alopecia by exosomes secreted from hair papilla cells and the intervention effect of LTF. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 2996–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangoda, L.; Boukouris, S.; Liem, M.; Kalra, H.; Mathivanan, S. Extracellular vesicles including exosomes are mediators of signal transduction: Are they protective or pathogenic? Proteomics 2015, 15, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, A.R.; Bian, Q.; Gao, J.Q. Current advances in stem cell-based therapies for hair regeneration. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 881, 173197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.K.; Wang, T.; Rapaport, J.A. Systematic review of exosome treatment in hair restoration: Preliminary evidence, safety, and future directions. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 2424–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladulescu, D.; Scurtu, L.G.; Simionescu, A.A.; Scurtu, F.; Popescu, M.I.; Simionescu, O. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) in Dermatology: Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Action. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, B.; Dai, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X. Exosomes Derived from Dermal Papilla Cells Mediate Hair Follicle Stem Cell Proliferation through the Wnt3a/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 9042345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-L.; Qiu, X.-X.; Liao, X.-H. Dermal Papilla Cells: From Basic Research to Translational Applications. Biology 2024, 13, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; Ntege, E.H.; Sunami, H.; Inoue, Y. Regenerative medicine strategies for hair growth and regeneration: A narrative review of literature. Regen. Ther. 2022, 21, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Dai, Y.; Yang, N.; Bao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X. Exosomal miRNA-181a-5p from the cells of the hair follicle dermal papilla promotes the hair follicle growth and development via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 207, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Li, Z.; Lutz, H.; Huang, K.; Su, T.; Cores, J.; Dinh, P.C.; Cheng, K. Dermal exosomes containing miR-218-5p promote hair regeneration by regulating β-catenin signaling. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitua, E.; Troya, M.; Falcon-Pérez, J.M.; López-Sarrio, S.; González, E.; Alkhraisat, M.H. Advances in Platelet Rich Plasma-Derived Extracellular Vesicles for Regenerative Medicine: A Systematic-Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, G.H. Clinical Use of Extracellular Vesicles in the Management of Male and Female Pattern Hair Loss: A Preliminary Retrospective Institutional Review Board Safety and Efficacy Study. Aesth. Surg. J. Open Forum 2022, 4, ojac045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.; Yang, N.; Nadithe, V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: Current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Rao, S.S.; Wang, Z.X.; Cao, J.; Tan, Y.J.; Luo, J.; Li, H.M.; Zhang, W.S.; Chen, C.Y.; Xie, H. Exosomes from human umbilical cord blood accelerate cutaneous wound healing through miR-21-3p-mediated promotion of angiogenesis and fibroblast function. Theranostics 2018, 8, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtyar, N.; Jeschke, M.G.; Herer, E.; Sheikholeslam, M.; Amini-Nik, S. Exosomes from acellular Wharton’s jelly of the human umbilical cord promote skin wound healing. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Rhee, W.J.; Park, J.H. Exosomes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells ameliorate the aging of skin fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.M. Exosomes secreted from induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal stem cells accelerate skin cell proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Pei, S.; Ding, Y.; Tao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, W.; Yi, Y. Exosomes with overexpressed miR-147a suppress angiogenesis and inflammatory injury in an experimental model of atopic dermatitis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8904. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Li, Z.; Zheng, J.; Sun, Q. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2022, 42, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Admyre, C.; Johansson, S.M.; Qazi, K.R.; Filén, J.J.; Lahesmaa, R.; Norman, M.; Neve, E.P.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S. Exosomes with immune modulatory features are present in human breast milk. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torregrosa Paredes, P.; Gutzeit, C.; Johansson, S.; Admyre, C.; Stenius, F.; Alm, J.; Scheynius, A.; Gabrielsson, S. Differences in exosome populations in human breast milk in relation to allergic sensitization and lifestyle. Allergy 2014, 69, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, T.Y. The Role of MicroRNAs in Regulatory T Cells and in the Immune Response. Immune Netw. 2011, 11, 11–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaál, Z. Role of microRNAs in Immune Regulation with Translational and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; He, Z.; Leone, S.; Liu, S. Milk Exosomes Transfer Oligosaccharides into Macrophages to Modulate Immunity and Attenuate Adherent-Invasive E. coli (AIEC) Infection. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlberg, E.; Al-Kaabawi, A.; Thune, R.; Simpson, M.R.; Pedersen, S.A.; Cione, E.; Jenmalm, M.C.; Tingö, L. Breast milk microRNAs: Potential players in oral tolerance development. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1154211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, S.; Liao, Y.; Du, X.; Xu, W.; Li, J.; Lönnerdal, B. Exosomal MicroRNAs in Milk from Mothers Delivering Preterm Infants Survive in Vitro Digestion and Are Taken Up by Human Intestinal Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, e1701050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Du, X.; Li, J.; Lönnerdal, B. Human milk exosomes and their microRNAs survive digestion in vitro and are taken up by human intestinal cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1700082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, X. Human breast milk: A promising treatment for necrotizing enterocolitis. Early Hum. Dev. 2023, 184, 105833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Shen, J.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, W.; Gao, P.; Wang, X.; An, W. Large-Scale Isolation of Milk Exosomes for Skincare. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, T.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, X.; Gao, X.; Li, X. Immunerelated microRNAs are abundant in breast milk exosomes. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izumi, H.; Kosaka, N.; Shimizu, T.; Sekine, K.; Ochiya, T.; Takase, M. Bovine milk contains microRNA and messenger RNA that are stable under degradative conditions. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 4831–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munagala, R.; Aqil, F.; Jeyabalan, J.; Gupta, R.C. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuh, C.M.A.P.; Cuenca, J.; Alcayaga-Miranda, F.; Khoury, M. Exosomes on the border of species and kingdom intercommunication. Transl. Res. 2019, 210, 80–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.N.; Guo, H.Y.; Xie, X.L.; Wen, P.C.; Ren, F.Z. Yak milk-derived exosomes promote proliferation of intestinal epithelial cells in hypoxic environment. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 102, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.N.; Hu, H.; Wen, P.C.; Lian, S.; Xie, X.L.; Song, H.L.; Yang, Z.N.; Ren, F.Z. Yak milk-derived exosomes alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal inflammation by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/C3 pathway activation. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 8411–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, M.; Bijari, S.; Khazaei, A.H.; Shojaei-Ghahrizjani, F.; Rezakhani, L. The role of milk-derived exosomes in the treatment of diseases. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1009338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, M.I.; Gallardo, B.; Cerón, C.; Aguilera-Jiménez, E.; Cortes-Canteli, M.; Peinado, H.; Desco, M.; Salinas, B. Isolation of goat milk small extracellular vesicles by novel combined biophysical methodology. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1197780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, M.; Chisanga, D.; Liem, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Anand, S.; Ang, C.S.; Adda, C.G.; Versteegen, E.; Jois, M.; Mathivanan, S. Bovine milk-derived exosomes from colostrum are enriched with proteins implicated in immune response and growth. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikok, S.; Patchaneeb, P.; Boonyayatra, S.; Chuammitria, P. Potential role of MicroRNA as a diagnostic tool in the detection of bovine mastitis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 182, 105101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, A.R.; Salazar, N.A.; Ayoola, A.O.; Memili, E.; Thomas, B.N.; Morenikeji, O.B. Regulatory network of miRNA, lncRNA, transcription factor and target immune response genes in bovine mastitis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmoussa, A.; Provost, P. Milk microRNAs in health and disease. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 703–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, L.C. MicroRNAs in embryonic stem cells and early embryonic development. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.H.; Kaur, S.; Nielsen, L.B.; Størling, J.; Yarani, R.; Roursgaard, M.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Damm, P.; Svare, J.; Mortensen, H.B.; et al. Breast milk-derived extracellular vesicles enriched in exosomes from mothers with type 1 diabetes contain aberrant levels of microRNAs. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melnik, B.C.; Schmitz, G. Exosomes of pasteurized milk: Potential pathogens of western diseases. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.Y.; Hou, L.J.; Sun, J.J.; Zeng, B.; Xi, Q.Y.; Luo, J.Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.L. Porcine milk exosome miRNAs attenuate LPS-induced apoptosis through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB and p53 pathways in intestinal epithelial cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 9477–9491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, I.S.; Kim, S.H. Milk exosome-derived microRNA-2478 suppresses melanogenesis through the AKT-GSK3β pathway. Cells 2021, 10, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutai, E.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Zempleni, J. MicroRNAs in bovine milk exosomes are bioavailable in humans but do not elicit a robust pro-inflammatory cytokine response. ExRNA 2020, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Tong, C.; Ibeagha-Awemu, E.M.; Zhao, X. Exosomal bta-miR-185 and bta-miR-378 are potential markers for quality control of milk infected by Staphylococcus aureus. Res. Square 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Du, C.; Nan, L.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, S. Influence of estrus on dairy cow milk exosomal miRNAs and their role in hormone secretion by granulosa cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiferman, A.; Shu, J.; Grove, R.; Cui, J.; Adamec, J.; Zempleni, J. A diet defined by its content of bovine milk exosomes and their RNA cargos has moderate effects on gene expression, amino acid profiles and grip strength in skeletal muscle in C57BL/6 mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2018, 59, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.; Cho, H.; Kim, H.; Jang, Y.; Jang, H.; Kim, D.E.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, E.H.; Hwang, K.Y.; Kim, K.; et al. Bovine colostrum derived-exosomes prevent dextran sulfate sodium-induced intestinal colitis via suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 2076–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, M.; Chisanga, D.; Liem, M.; Keerthikumar, S.; Anand, S.; Ang, C.S.; Adda, C.G.; Versteegen, E.; Jois, M.; Mathivanan, S. Colostrum exosomes are reported to possess a broader range of oligosaccharides, which may further augment their immunomodulatory effects. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 519. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Zheng, J.; Han, X.; Zhao, J.; Cheng, S.; Li, A. Bovine Colostrum miR-30a-5p Targets the NF-κB Signaling Pathway to Alleviate Inflammation in Intestinal Epithelial Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 9164–9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sall, I.M.; Flaviu, T.A. Plant and mammalian-derived extracellular vesicles: A new therapeutic approach for the future. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1215650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, M.A. Overview and Update on Extracellular Vesicles: Considerations on Exosomes and Their Application in Modern Medicine. Biology 2022, 11, 804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwechheimer, C.; Kuehn, M.J. Outer-membrane vesicles from Gram-negative bacteria: Biogenesis and functions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulp, A.; Kuehn, M.J. Biological functions and biogenesis of secreted bacterial outer membrane vesicles. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2010, 64, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briaud, P.; Carroll, R.K. Extracellular vesicle biogenesis and functions in gram-positive bacteria. Infect. Immun. 2020, 88, e00433-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkoshek, K.S.; Wang, Y.; Athman, J.J.; Barton, M.R.; Wearsch, P.A. Interspecies communication between pathogens and immune cells via bacterial membrane vesicles. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, L.; Wolf, J.M.; Prados-Rosales, R.; Casadevall, A. Through the wall: Extracellular vesicles in Gram-positive bacteria, mycobacteria and fungi. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, S.; Shinagawa, K.; Castellino, F.J.; Schorey, J.S. Exosomes released from macrophages infected with intracellular pathogens stimulate a proinflammatory response in vitro and in vivo. Blood 2007, 110, 3234–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.P.; Li, L.; Schorey, J.S. Exosomal RNA from Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected cells is functional in recipient macrophages. Traffic 2015, 16, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, I.T.; Wilson, E.E.; Behfar, A.; Paradise, C.R.; Rohrich, R.J.; Wyles, S.P. Evolving Role of Exosomes in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery and Dermatology. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Global Open 2024, 12, e6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardiner, C.; Di Vizio, D.; Sahoo, S.; Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Wauben, M.; Hill, A.F. Techniques used for the isolation and characterization of extracellular vesicles: Results of a worldwide survey. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2016, 5, 32945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konoshenko, M.Y.; Lekchnov, E.A.; Vlassov, A.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Isolation of extracellular vesicles: General methodologies and latest trends. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8545347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Freitas, D.; Kim, H.; Fabijanic, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Mark, M.; Molina, H.; Martin, A.; Bojmar, L.; et al. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric-flow field-flow fractionation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Y.T.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zheng, L.; Qin, S.H.; Xu, X.P.; An, T.X.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.S.; Hu, X.M.; Ping, B.H.; et al. Comparison of isolation methods of exosomes and exosomal RNA from cell culture medium and serum. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 834–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, R.J.; Becker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Wong, C.S.F.; Wiegmans, A.P.; Leimgruber, A.; Möller, A. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stranska, R.; Gysbrechts, L.; Wouters, J.; Vermeersch, P.; Bloch, K.; Dierickx, D.; Andrei, G.; Snoeck, R. Comparison of membrane affinity-based method with size-exclusion chromatography for isolation of exosome-like vesicles from human plasma. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Pertierra, E.; Oliveira-Rodríguez, M.; Rivas, M.; Oliva, P.; Villafani, J.; Navarro, A.; Blanco-López, M.; Cernuda-Morollón, E. Characterization of plasma-derived extracellular vesicles isolated by different methods: A comparison study. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.K.; Mun, J.Y. Sample preparation and imaging of exosomes by transmission electron microscopy. JoVE J. Visualized Exp. 2018, 131, 56482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akers, J.C.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Nolan, J.P.; Duggan, E.; Fu, C.C.; Hochberg, F.H.; Chen, C.C.; Carter, B.S. Comparative analysis of technologies for quantifying extracellular vesicles (EVs) in clinical cerebrospinal fluids (CSF). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuo, S.T.Y.; Chien, J.C.Y.; Lai, C.P.K. Imaging extracellular vesicles: Current and emerging methods. J. Biomed. Sci. 2018, 25, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahm, W.J.; Thunga, S.; Yoo, J. Complications After Exosome Treatment for Aesthetic Skin Rejuvenation. Dermatol. Rev. 2024, 5, e242. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.K.; Tsai, T.H.; Lee, C.H. Regulation of exosomes as biologic medicines: Regulatory challenges faced in exosome development and manufacturing processes. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2024, 17, e13904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).