An Interfacial Study of Sucrose Ester-Stabilized Water-Free Foams
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sucrose Ester/Oil Mixture Preparation
2.2. Sucrose Ester/Oil Characterization
2.2.1. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
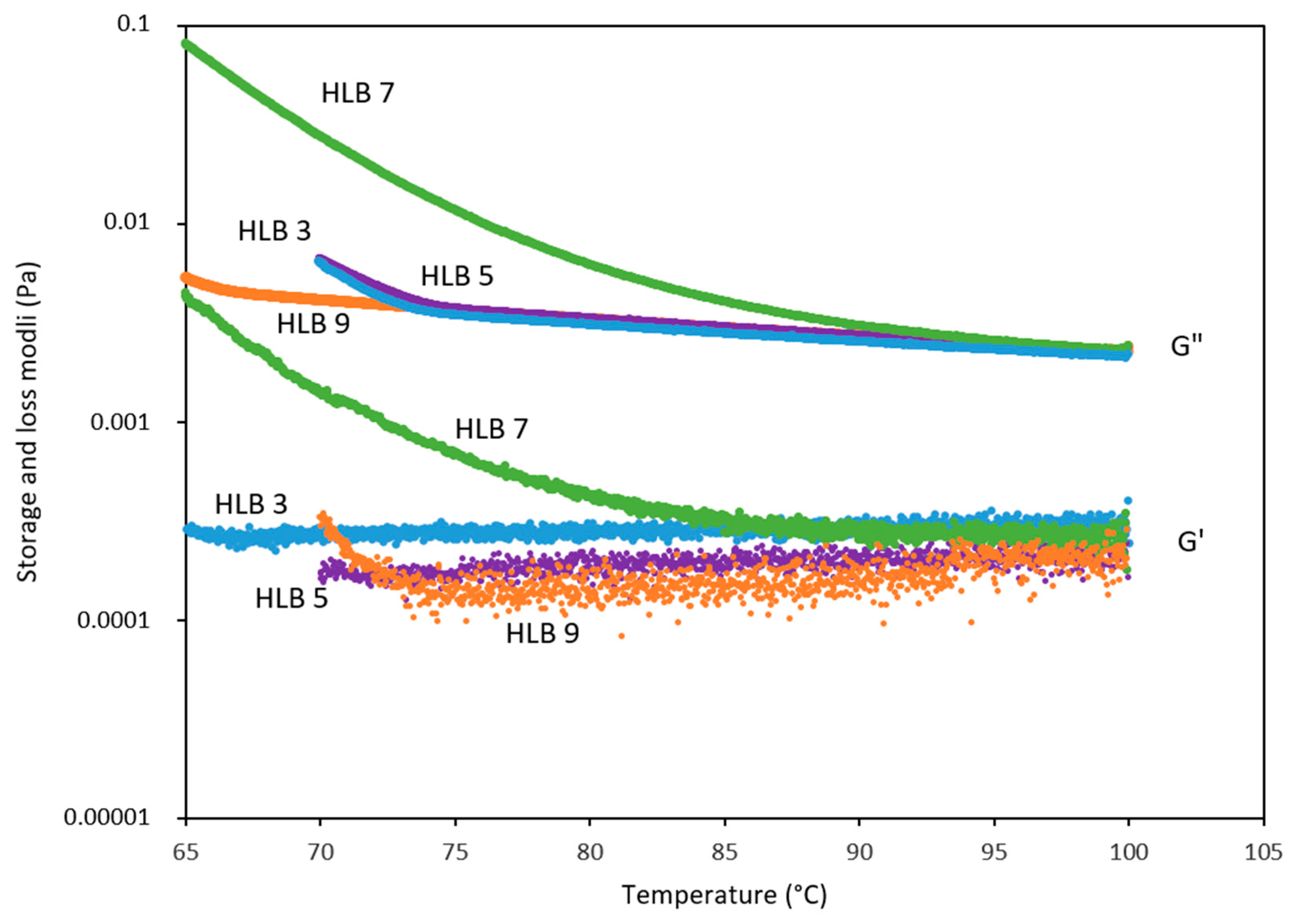
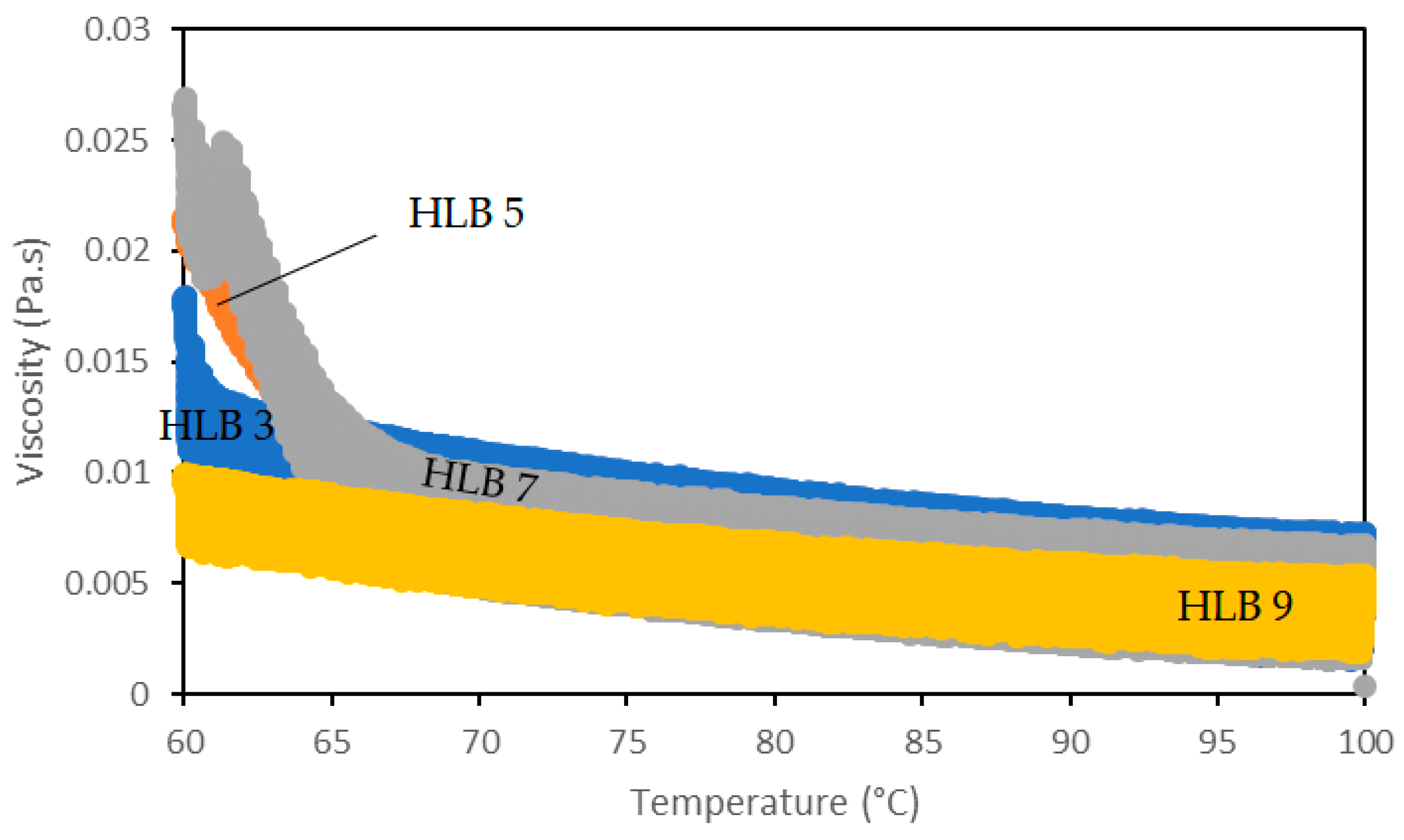
2.2.2. Rheology
2.2.3. Surface Tension
2.3. Foam Preparation
2.4. Foam Characterization
2.4.1. Over-Run
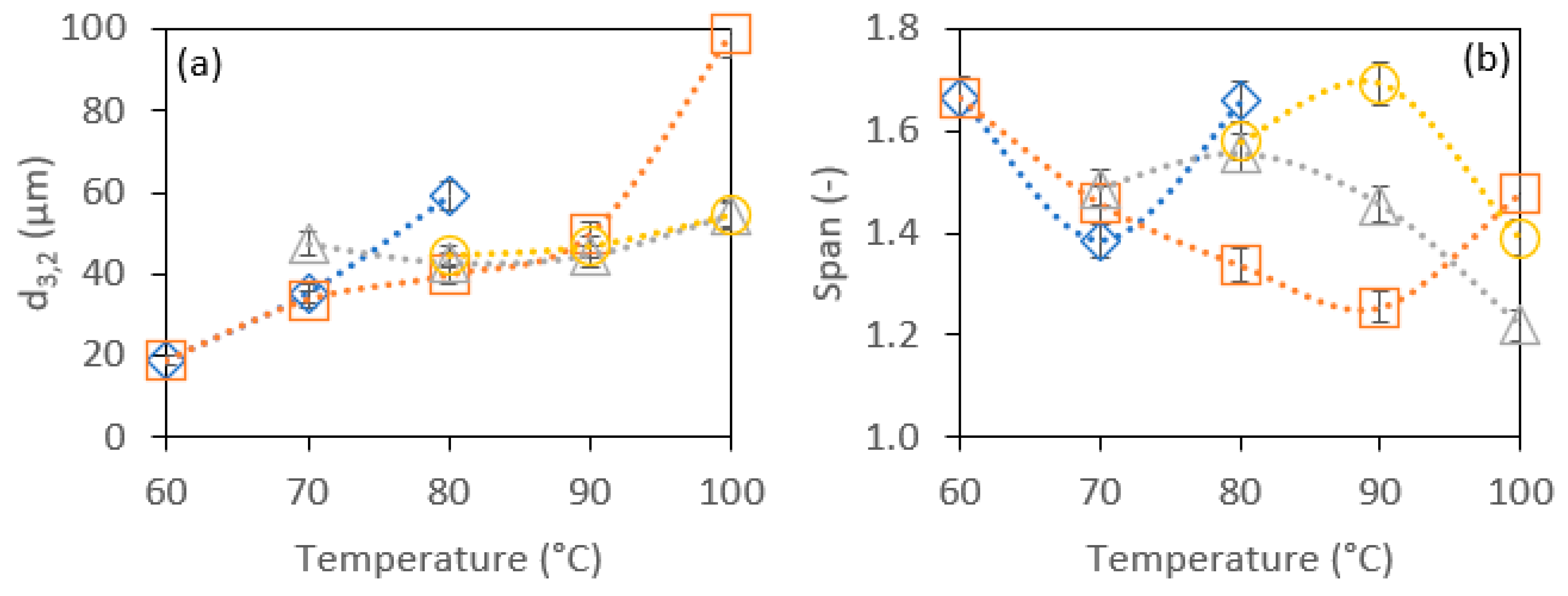
2.4.2. Bubble Size and Size Distribution
2.4.3. Stability at 60 °C
2.5. Triglyceride Mixtures
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SE and SE/MCT Characterization
3.2. Foam’s Physical Properties Characterization
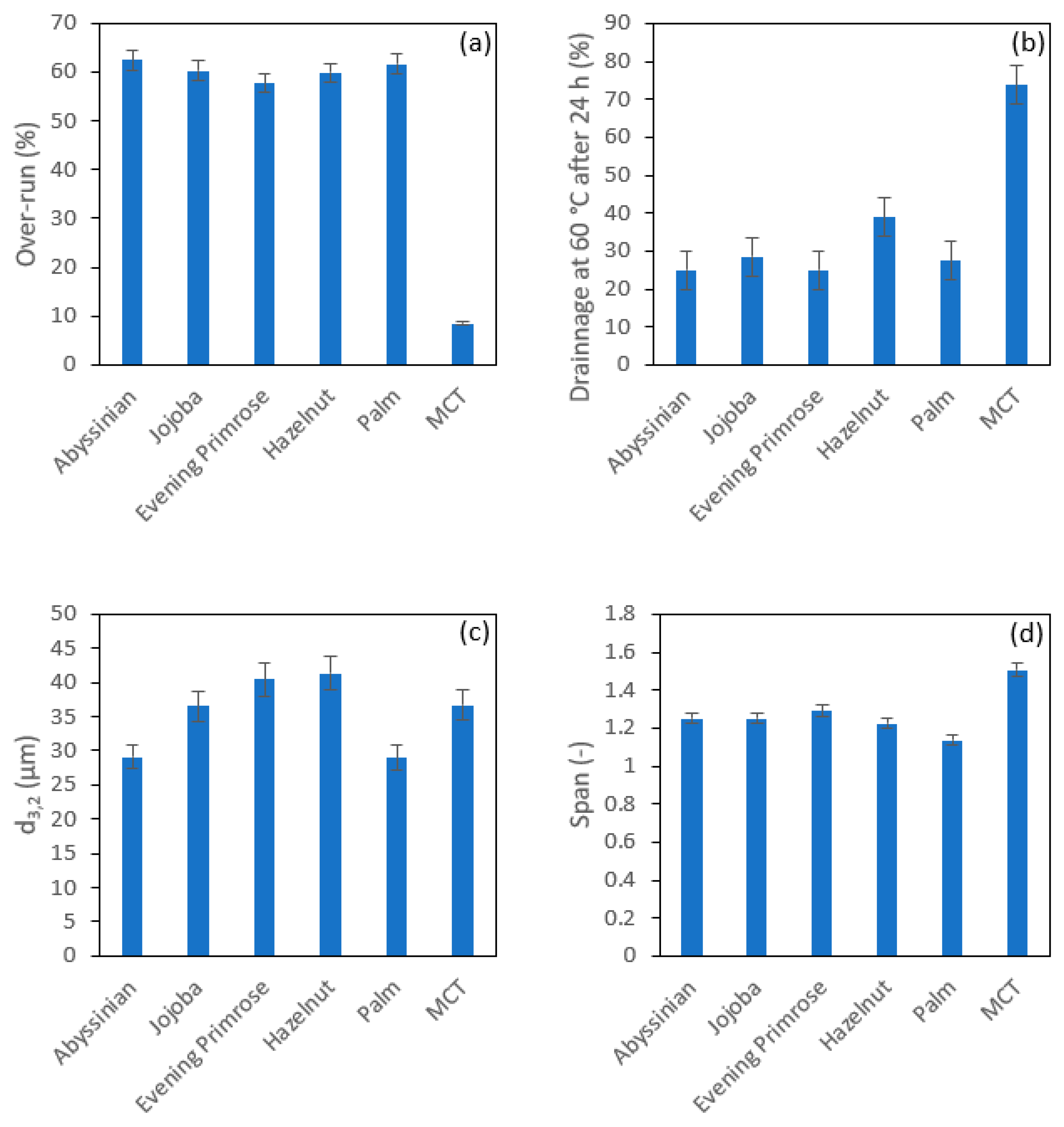
3.2.1. Effect of SE HLB Values and Whipping Temperature on the Foams’ Physical Properties
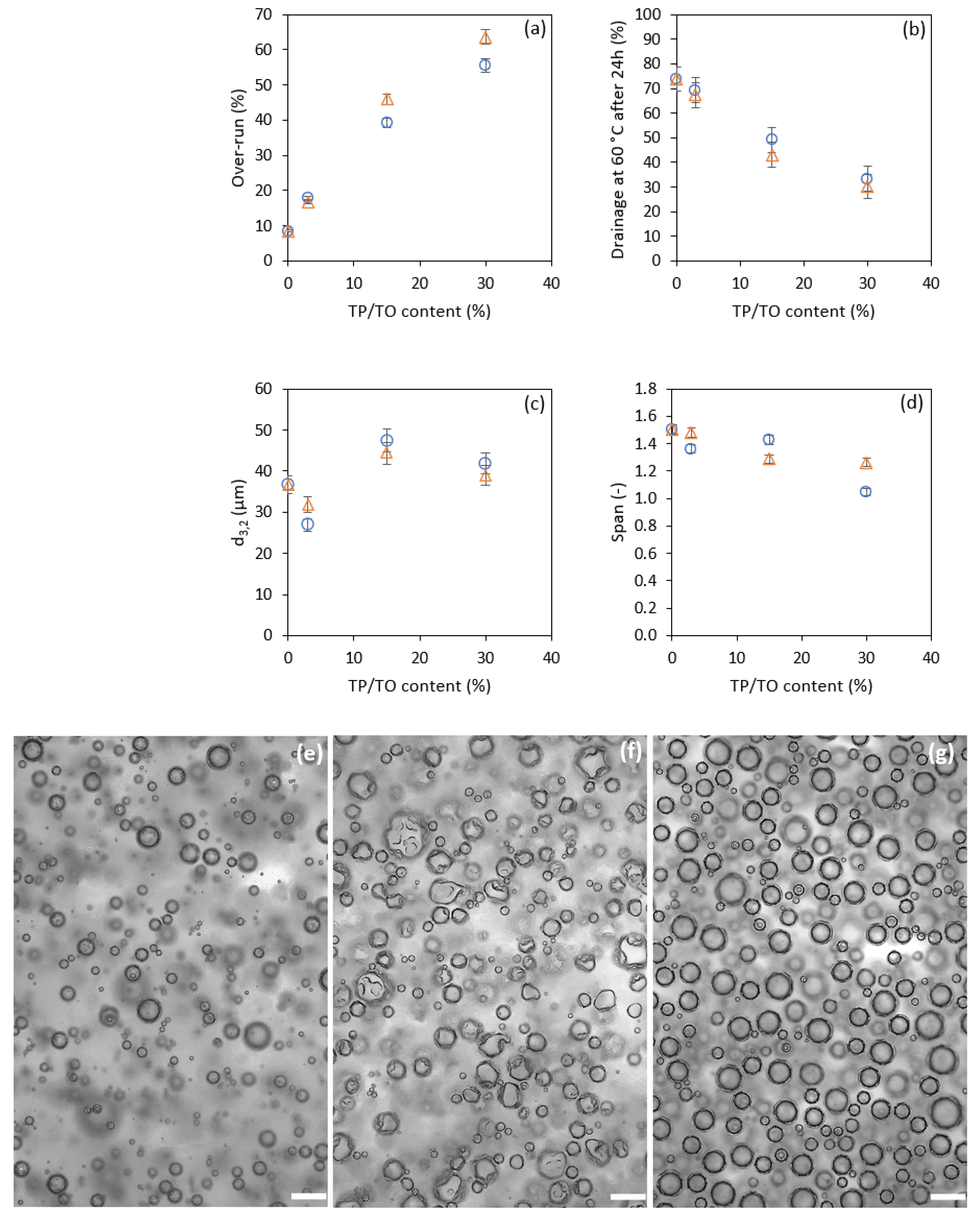
3.2.2. Effect of Triglyceride Content on the Foams’ Physical Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, Y.; Ren, Z.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Y.; Weng, W. Effects of Pre-Emulsion Prepared Using Sucrose Esters with Different Hydrophile-Lipophile Balances on Characteristics of Soy Protein Isolate Emulsion Films. Food Res. Int. 2023, 165, 112542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, D.; Cai, Y.; Liu, T.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, Q. Effect of Hydrophobic Sucrose Esters with Different Fat Acid Composition and Esterification Degree on Whipped Cream Properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Binks, B.P.; Cui, Z. High Internal Phase Emulsions Stabilized by Adsorbed Sucrose Stearate Molecules and Dispersed Vesicles. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 121, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, L.N.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.V.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; et al. Safety Assessment of Saccharide Esters as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2021, 40, 52S–116S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin Sintang, M.D.; Danthine, S.; Patel, A.R.; Rimaux, T.; Van De Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K. Mixed Surfactant Systems of Sucrose Esters and Lecithin as a Synergistic Approach for Oil Structuring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 504, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szuts, A.; Pallagi, E.; Regdon, G.; Aigner, Z.; Szabó-Révész, P. Study of Thermal Behaviour of Sugar Esters. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 336, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Binks, B.P. A Novel Strategy to Fabricate Stable Oil Foams with Sucrose Ester Surfactant. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 594, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, C.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lee, W.J.; Fu, J.; Binks, B.P.; Wang, Y. Stabilisation of Oleofoams by Lauric Acid and Its Glycerol Esters. Food Chem. 2022, 386, 132776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Binks, B.P. Foams of Vegetable Oils Containing Long-Chain Triglycerides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 583, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saremnejad, F.; Mohebbi, M.; Koocheki, A. Practical Application of Nonaqueous Foam in the Preparation of a Novel Aerated Reduced-Fat Sauce. Food Bioprod. Process. 2020, 119, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettlaufer, T.; Flöter, E. Wax Based Oleogels and Their Application in Sponge Cakes. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 9419–9433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaade, W.; Huc-Mathis, D.; Drouet, L.; Dousset, C.; Blumenthal, D.; Daniellou, R. An Experimental Design Approach to Modeling Water-Free Foams. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2024, 699, 134700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, B.; Riba, J.R.; Baquero, G.; Rius, A.; Puig, R. Temperature Dependence of Density and Viscosity of Vegetable Oils. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 42, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholakova, D.; Tcholakova, S. Sucrose Ester Surfactants: Current Understanding and Emerging Perspectives. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 73, 101832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delahaije, R.J.B.M.; Sagis, L.M.C.; Yang, J. Impact of Particle Sedimentation in Pendant Drop Tensiometry. Langmuir 2022, 38, 10183–10191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- L’Estimé, M.; Schindler, M.; Shahidzadeh, N.; Bonn, D. Droplet Size Distribution in Emulsions. Langmuir 2024, 40, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, M.; Fang, B.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Oleofoams Stabilized by Monoacylglycerides: Impact of Chain Length and Concentration. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Binks, B.P. Fabrication of Stable Oleofoams with Sorbitan Ester Surfactants. Langmuir 2022, 38, 14779–14788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
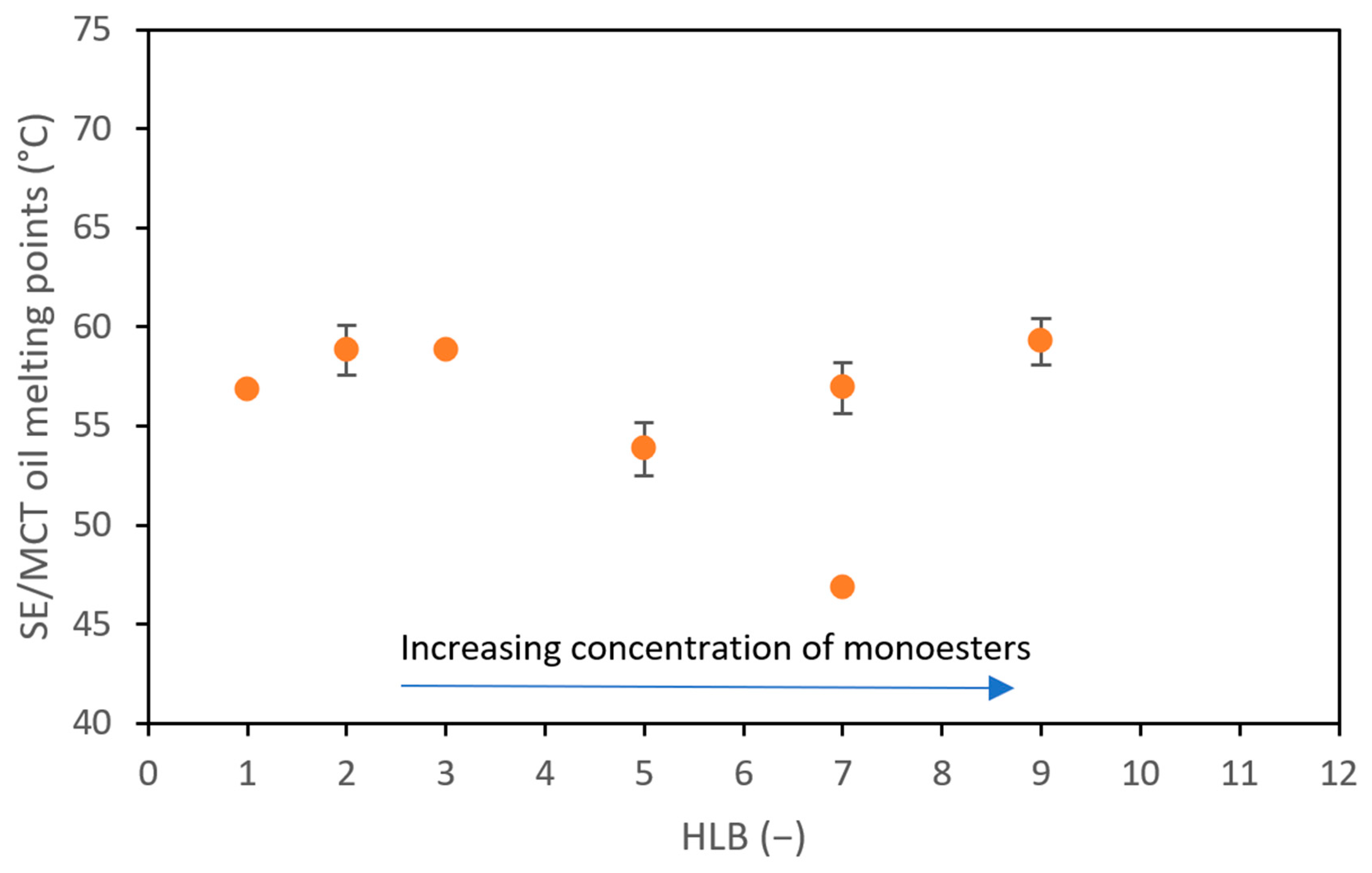


 : di, tri, poly ester
: di, tri, poly ester  : monoester;
: monoester;  : triglyceride chain; yellow background: MCT oil.
: triglyceride chain; yellow background: MCT oil.
 : di, tri, poly ester
: di, tri, poly ester  : monoester;
: monoester;  : triglyceride chain; yellow background: MCT oil.
: triglyceride chain; yellow background: MCT oil.

| Sucrose Esters | HLB | Fatty Acids * | % Monoester | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP01-C | <1 | Stearic/palmitic | <1 | Sisterna * |
| SP10-C | 2 | Stearic/palmitic | 10 | Sisterna |
| C-1803 | 3 | Stearic | 20 | MKFC ** |
| C-1805 | 5 | Stearic | 30 | MKFC |
| C-1807 | 7 | Stearic | 40 | MKFC |
| S90 | 9 | Stearic | 50 | Synose *** |
| C-1811 | 11 | Stearic | 55 | MKFC |
| SP70-C | 15 | Stearic/palmitic | 70 | Sisterna |
| C-1816 | 16 | Stearic | 75 | MKFC |
| MCT Oil (%) | Tripalmitin (%) | MCT Oil (%) | Triolein (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 97 | 3 | 97 | 3 |
| 85 | 15 | 85 | 15 |
| 70 | 30 | 70 | 30 |
| Oil | Fatty Acid Content Reported by the Manufacturer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abyssinian (Aromazone) | 54.53% | Erucic acid | 22:1 | Monounsaturated |
| 16.15% | Oleic acid | 18:1 | Monounsaturated | |
| 2.21% | Palmitic acid | 16:0 | Saturated | |
| 8.23% | alpha-Linoleic acid | 18:3n3 | Polyunsaturated | |
| 3.16% | Linoleic acid | 18:2n6 | Polyunsaturated | |
| Jojoba (Aromazone) | 65–90% | Gadoleic acid | 20:1 | Monounsaturated |
| 5–30% | Erucic acid | 22:1 | Monounsaturated | |
| 5–15% | Oleic acid | 18:1 | Monounsaturated | |
| 0.5–5% | Nervonic acid | 24:1 | Monounsaturated | |
| Evening Primrose (Aromazone) | 74.21% | Linoleic acid | 18:2n6 | Polyunsaturated |
| 9.21% | gamma-Linolenic acid | 18:3n6 | Polyunsaturated | |
| 7.07% | Oleic acid | 18:1 | Monounsaturated | |
| 2.19% | Stearic acid | 18:0 | Saturated | |
| 6.47% | Palmitic acid | 16:0 | Saturated | |
| Hazelnut (Aromazone) | 82.59% | Oleic acid | 18:1 | Monounsaturated |
| 5.52% | Palmitic acid | 16:0 | Saturated | |
| 2.47% | Stearic acid | 18:0 | Saturated | |
| 7.62% | Linoleic acid | 18:2n6 | Polyunsaturated | |
| Palm (Aromazone) | 40–46% | Palmitic acid | 16:0 | Saturated |
| 36–44% | Oleic acid | 18:1 | Monounsaturated | |
| 3.5–6% | Stearic acid | 18:0 | Saturated | |
| 8–14% | Linoleic acid | 18:2n6 | Polyunsaturated | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaade, W.; Drouet, L.; Dousset, C.; Daniellou, R.; Huc-Mathis, D. An Interfacial Study of Sucrose Ester-Stabilized Water-Free Foams. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010015
Kaade W, Drouet L, Dousset C, Daniellou R, Huc-Mathis D. An Interfacial Study of Sucrose Ester-Stabilized Water-Free Foams. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaade, Wael, Lucille Drouet, Capucine Dousset, Richard Daniellou, and Delphine Huc-Mathis. 2025. "An Interfacial Study of Sucrose Ester-Stabilized Water-Free Foams" Cosmetics 12, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010015
APA StyleKaade, W., Drouet, L., Dousset, C., Daniellou, R., & Huc-Mathis, D. (2025). An Interfacial Study of Sucrose Ester-Stabilized Water-Free Foams. Cosmetics, 12(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12010015







