Image-Based Malware Classification Using VGG19 Network and Spatial Convolutional Attention
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first attention-based malware detection method working from 25 malware classification and benign class.
- The study proposes a transfer learning-based architecture that uses spatial convolutional attention to classify malware from multiple families through class weighting and without class balancing techniques.
- Lastly, we have performed extensive experiments testing using metrics such as precision, recall, F1- measure, confusion matrix ROC-AUC curves and produced above 97% result with and without class balancing.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
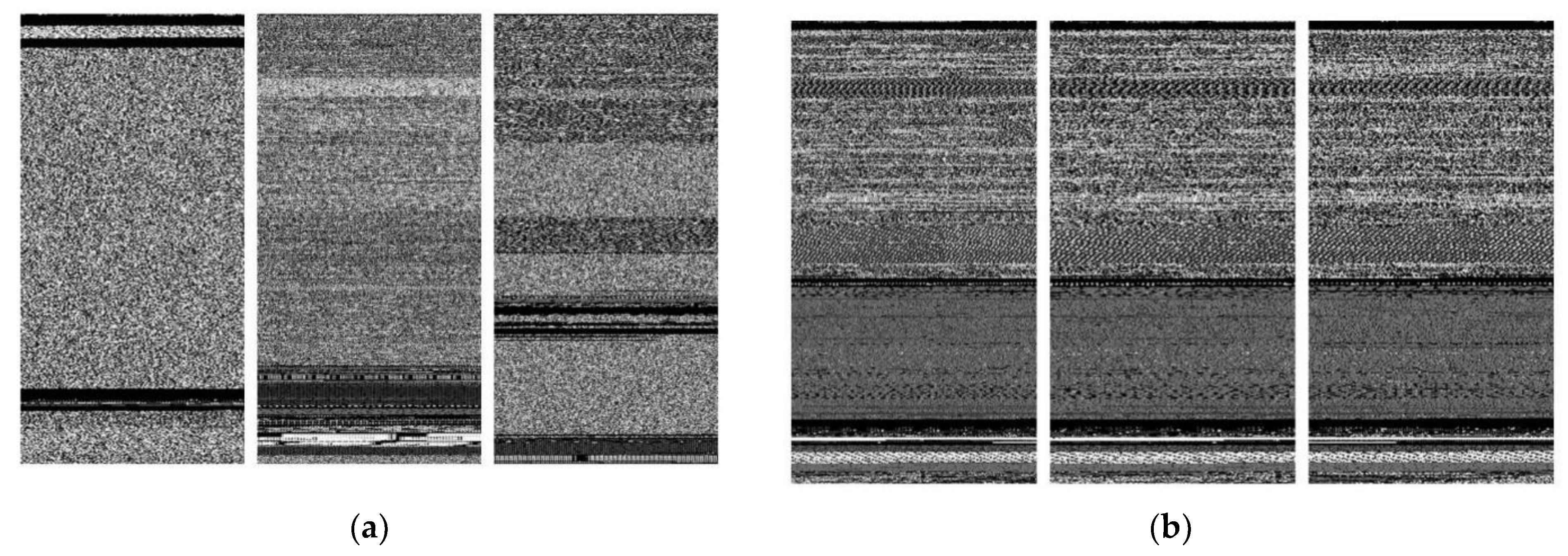
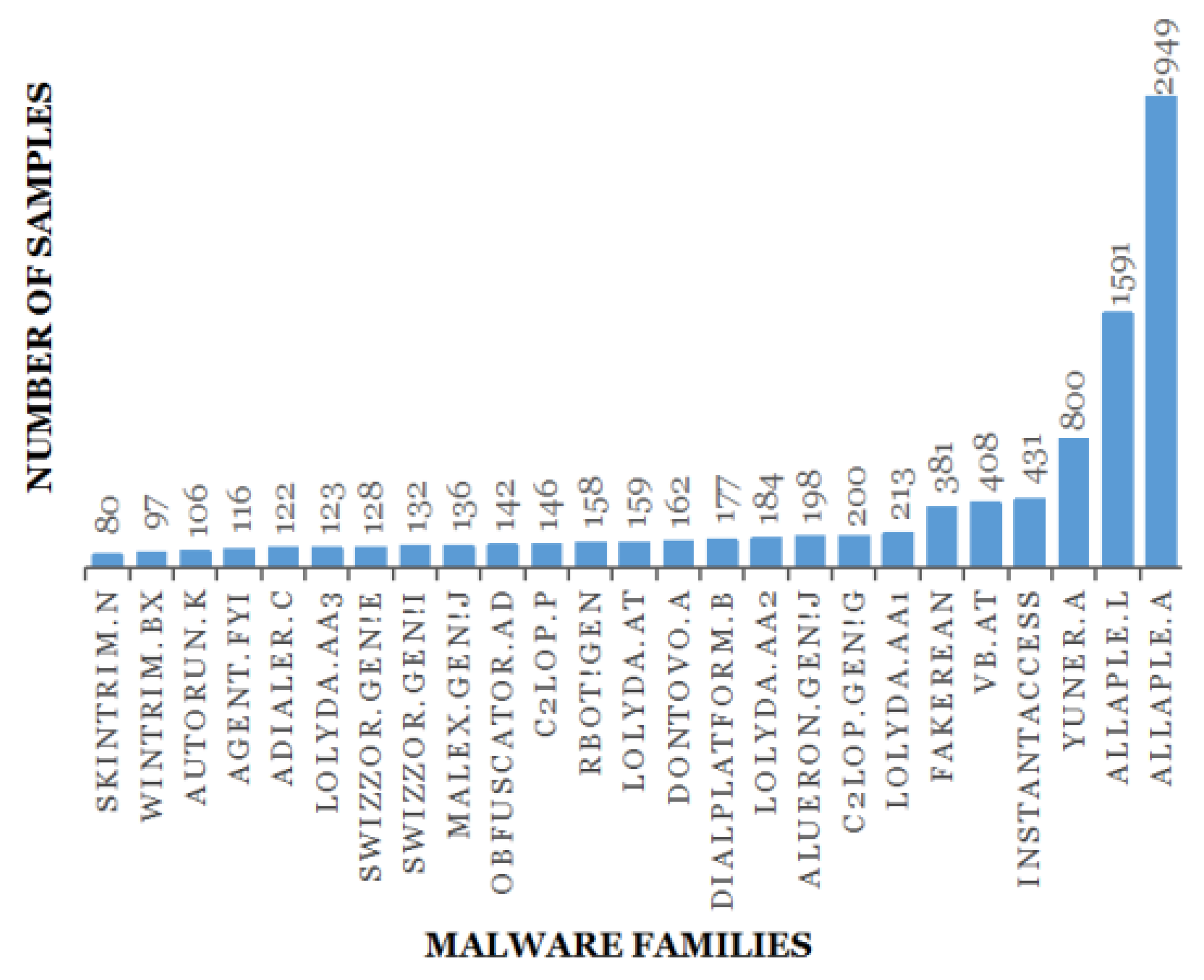
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Data Pre-Processing
3.3. Techniques
3.3.1. Convolutional Neural Networks
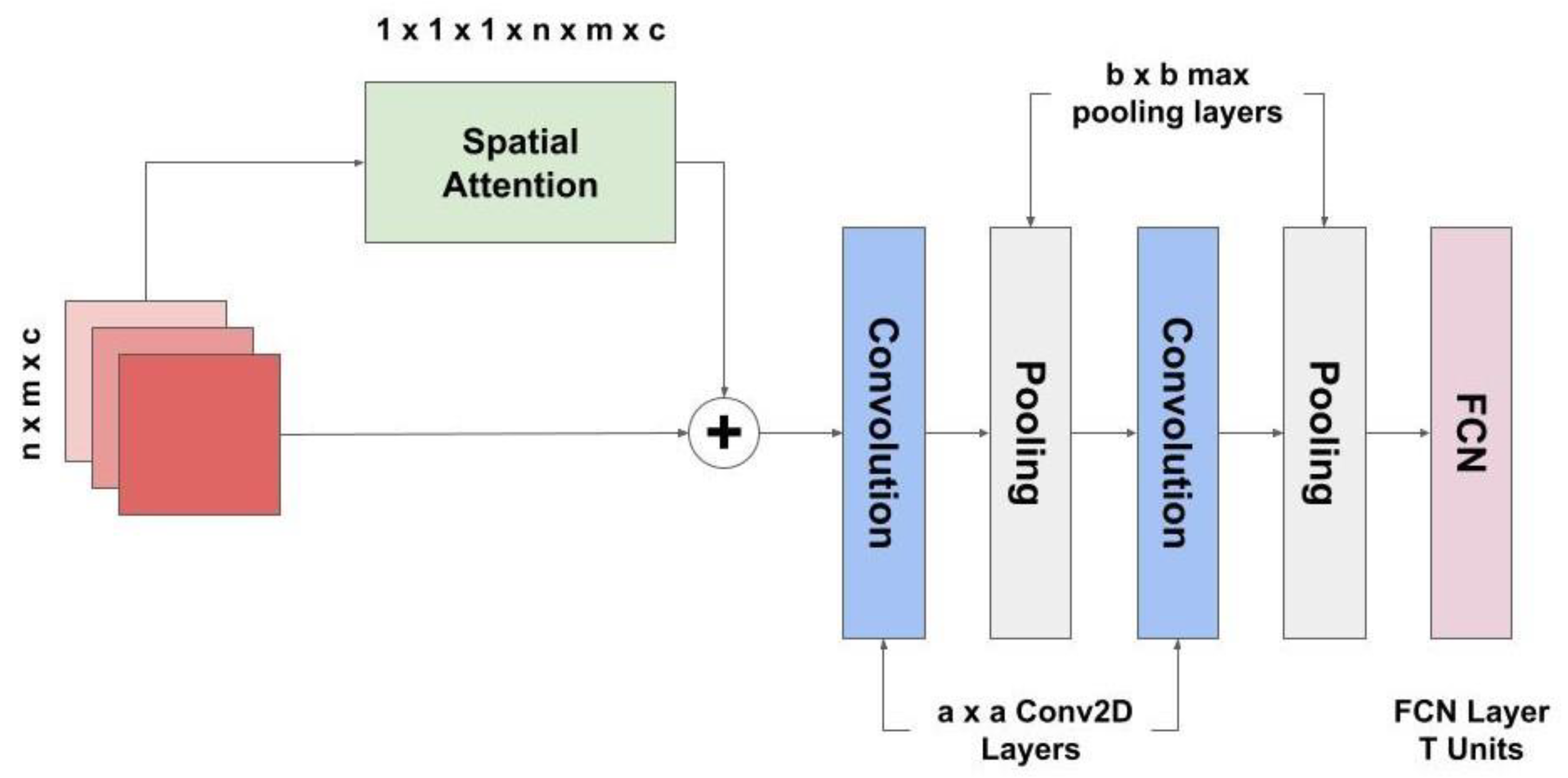
3.3.2. Spatial Attention Mechanism
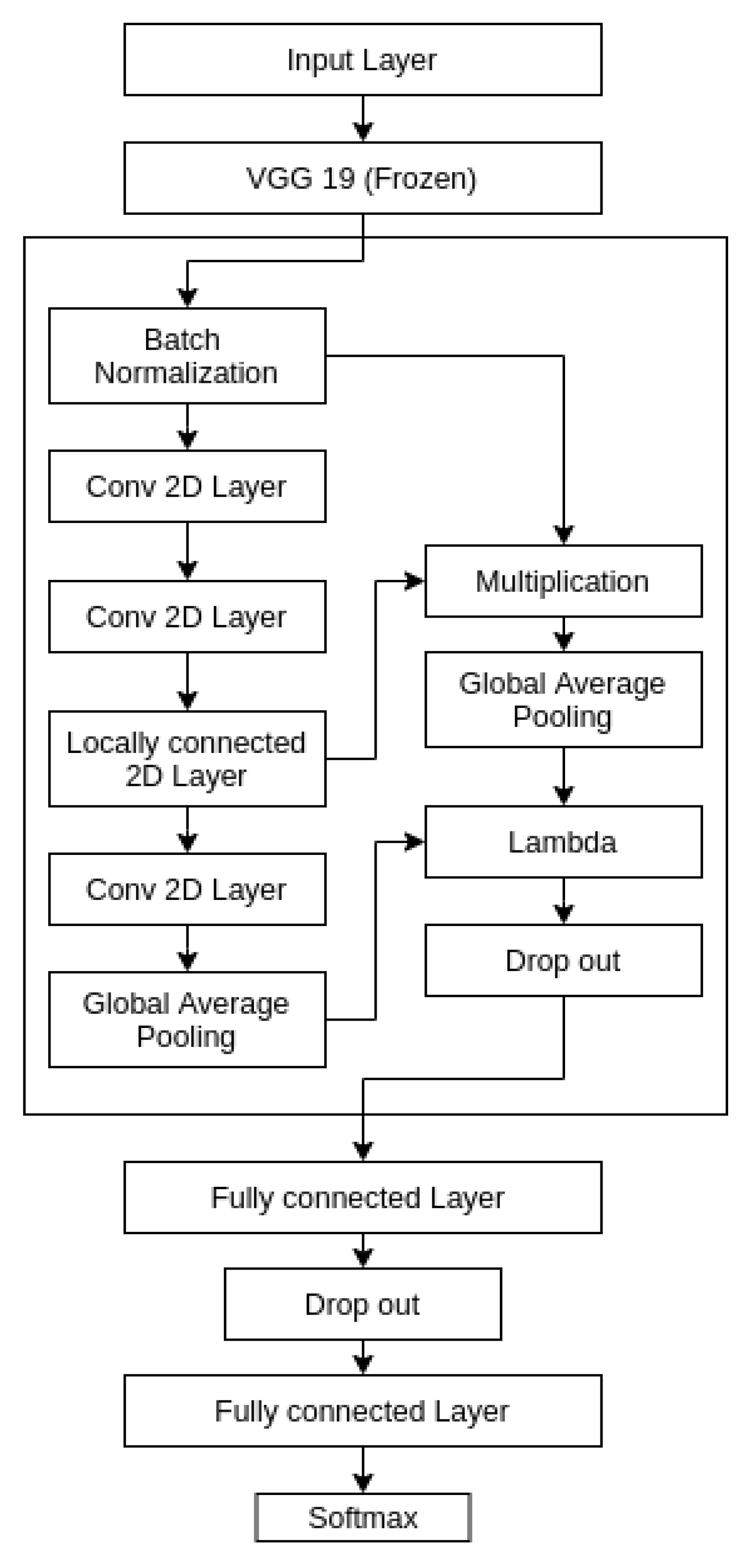
3.4. Our Proposed Architecture
4. Experimental Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
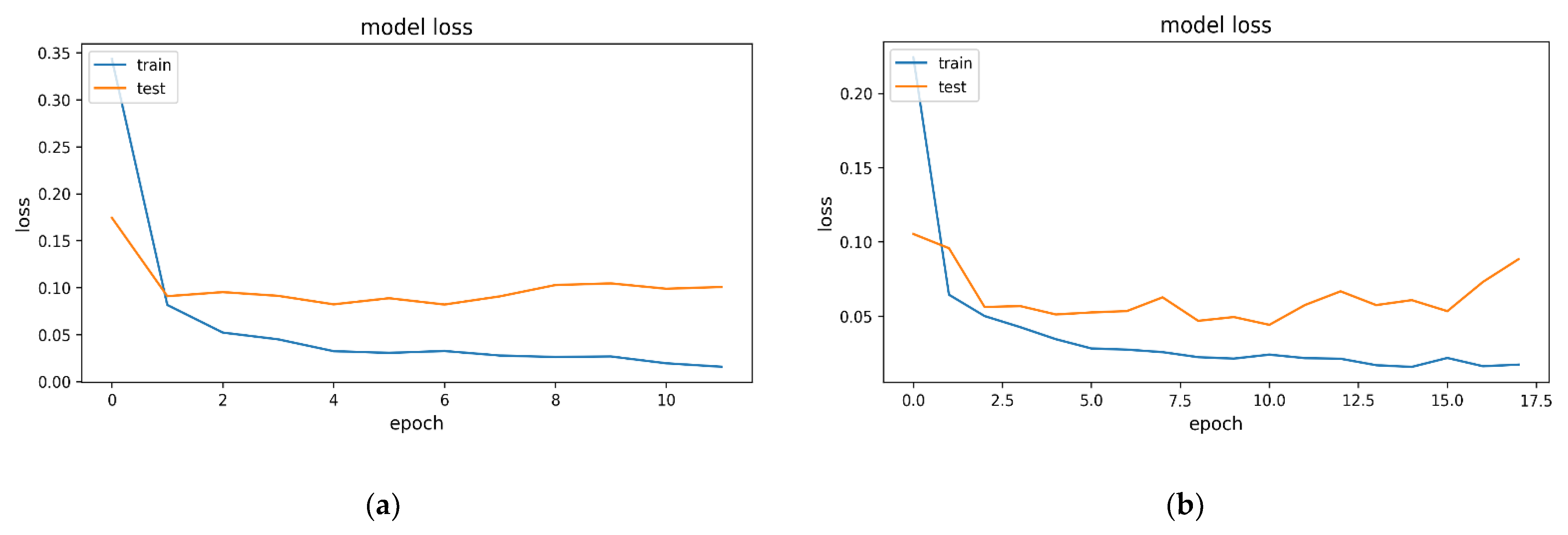
4.2. Evaluation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rieck, K.; Trinius, P.; Willems, C.; Holz, T. Automatic analysis of malware behavior using machine learning. J. Comput. Secur. 2011, 19, 639–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.J.; Farooq, U.; Babar, H.M.A.; Yasin, A.; Nobanee, H.; Hussain, M.; Hakeem, O.; Zain, A.M. Real-time DDoS attack detection system using big data approach. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferooz, F.; Hassan, M.T.; Awan, M.J.; Nobanee, H.; Kamal, M.; Yasin, A.; Zain, A.M. Suicide bomb attack identification and analytics through data mining techniques. Electronics 2021, 10, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbus, N.V.; Yeo, S.-S.; Cho, E.-S.; Kim, J.-A. Malware and antivirus deployment for enterprise IT security. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Ubiquitous Multimedia Computing, Hobart, Australia, 13–15 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Azeez, N.A.; Salaudeen, B.B.; Misra, S.; Damasevicius, R.; Maskeliunas, R. Identifying phishing attacks in communication networks using URL consistency features. Int. J. Electron. Secur. Digit. Forensics 2021, 12, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, B.; Wei, W.; Li, K.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wozniak, M.; Polap, D.; Damaševičius, R. Ensemble machine learning approaches for webshell detection in internet of things environments. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.A.; Ibrahim, D.A.; Salman, A.O. Adaptive intelligent learning approach based on visual anti-spam email model for multi-natural language. J. Intell. Syst. 2021, 30, 774–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehma, A.A.; Awan, M.J.; Butt, I. Comparison and evaluation of information retrieval models. VFAST Trans. Softw. 2018, 6, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Rhode, M.; Burnap, P.; Jones, K. Early-stage malware prediction using recurrent neural networks. Comput. Secur. 2018, 77, 578–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, T.M.; Awan, M.J. Domain analysis of information extraction techniques. Int. J. Multidiscip. Sci. Eng. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Adebayo, O.S.; Abdul Aziz, N. Improved malware detection model with apriori association rule and particle swarm optimization. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, Y.; Farooq, A.; Alam, T.M.; Farooq, M.S.; Awan, M.J.; Baig, T.I. Detection of schistosomiasis factors using association rule mining. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 186108–186114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, R.N.; Chen, H.; Lopez, J.; Sauveron, D.; Yang, L.T. Security, privacy and trust of user-centric solutions. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 80, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, H.S.; Kharkar, A.; Filar, B.; Roth, P. Evading machine learning malware detection. In Proceedings of the Black Hat, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 22–27 July 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Azeez, N.A.; Odufuwa, O.E.; Misra, S.; Oluranti, J.; Damaševičius, R. Windows PE malware detection using ensemble learning. Informatics 2021, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, B.A.; Mostafa, S.A.; Mustapha, A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Mahmoud, M.A.; Al-Rimy, B.A.S.; Abd Razak, S.; Elhoseny, M.; Marks, A. An adaptive protection of flooding attacks model for complex network environments. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anam, M.; Ponnusamy, V.A.; Hussain, M.; Nadeem, M.W.; Javed, M.; Gou, H.G.; Qadeer, S. Osteoporosis prediction for trabecular bone using machine learning: A review. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 67, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizan, A.H.; Mostafa, S.A.; Mustapha, A.; Foozy, C.F.M.; Abd Wahab, M.H.; Mohammed, M.A.; Khalaf, B.A. A machine learning approach for improving the performance of network intrusion detection systems. Ann. Emerg. Technol. Comput. (AETiC) 2021, 5, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.; Jain, R.; Arora, S.; Gupta, A.; Awan, M.J.; Chaudhary, G.; Nobanee, H. AI-enabled COVID-19 outbreak analysis and prediction: Indian states vs. union territories. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 67, 933–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaševičius, R.; Venčkauskas, A.; Toldinas, J.; Grigaliūnas, Š. Ensemble-based classification using neural networks and machine learning models for windows pe malware detection. Electronics 2021, 10, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.J.; Yasin, A.; Nobanee, H.; Ali, A.A.; Shahzad, Z.; Nabeel, M.; Zain, A.M.; Shahzad, H.M.F. Fake news data exploration and analytics. Electronics 2021, 10, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Rehman, S.U.; Shah, J.H.; Meraj, T.; Rauf, H.T.; Damaševičius, R.; Mohammed, M.A.; Abdulkareem, K.H. Adversarial attack and defence through adversarial training and feature fusion for diabetic retinopathy recognition. Sensors 2021, 21, 3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, A.; Alosaimi, W.; Alyami, H.; Rauf, H.T.; Damaševičius, R. Botnet attack detection using local global best bat algorithm for industrial internet of things. Electronics 2021, 10, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavifar, S.; Ghorbani, A.A. Application of deep learning to cybersecurity: A survey. Neurocomputing 2019, 347, 149–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, G.; Dean, E.; Sinda, M.; Sangster, B. Visual reverse engineering of binary and data files. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Visualization for Computer Security, Cambridge, MA, USA, 15 September 2008; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Nagi, A.T.; Awan, M.J.; Javed, R.; Ayesha, N. A Comparison of two-stage classifier algorithm with ensemble techniques on detection of diabetic retinopathy. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics (CAIDA), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 6–7 April 2021; pp. 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, A.; Awan, M.; Shehzad, M.; Ashraf, M. Fake news classification bimodal using convolutional neural network and long short-term memory. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Learn 2020, 11, 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Mujahid, A.; Awan, M.J.; Yasin, A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Damaševičius, R.; Maskeliūnas, R.; Abdulkareem, K.H. Real-time hand gesture recognition based on deep learning YOLOv3 Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, E.; Ruppert, G.; Carvalho, T.; Ramos, F.; De Geus, P. Malicious software classification using transfer learning of resnet-50 deep neural network. In Proceedings of the 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Cancun, Mexico, 18–21 December 2017; pp. 1011–1014. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, R.U.; Zhang, X.; Kumar, R. Analysis of ResNet and GoogleNet models for malware detection. J. Comput. Virol. Hacking Tech. 2019, 15, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, D.; Alazab, M.; Wassan, S.; Safaei, B.; Zheng, Q. Image-Based malware classification using ensemble of CNN architectures (IMCEC). Comput. Secur. 2020, 92, 101748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosinski, J.; Clune, J.; Bengio, Y.; Lipson, H. How transferable are features in deep neural networks? arXiv 2014, arXiv:1411.1792. [Google Scholar]
- Nataraj, L.; Karthikeyan, S.; Jacob, G.; Manjunath, B.S. Malware images: Visualization and automatic classification. In Proceedings of the 8th International Symposium on Visualization for Cyber Security, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 20 June 2011; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Agarap, A.F. Towards building an intelligent anti-malware system: A deep learning approach using support vector machine (SVM) for malware classification. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1801.00318 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Akarsh, S.; Poornachandran, P.; Menon, V.K.; Soman, K. A Detailed investigation and analysis of deep learning architectures and visualization techniques for malware family identification. In Cybersecurity and Secure Information Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 241–286. [Google Scholar]
- Akarsh, S.; Simran, K.; Poornachandran, P.; Menon, V.K.; Soman, K. Deep learning framework and visualization for malware classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Advanced Computing Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 15–16 March 2019; pp. 1059–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S. MCFT-CNN: Malware classification with fine-tune convolution neural networks using traditional and transfer learning in internet of things. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2021, 125, 334–351. [Google Scholar]
- Vinayakumar, R.; Alazab, M.; Soman, K.; Poornachandran, P.; Venkatraman, S. Robust intelligent malware detection using deep learning. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 46717–46738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, K. MalFCS: An effective malware classification framework with automated feature extraction based on deep convolutional neural networks. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020, 141, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Xue, F.; Cai, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, G.-G.; Chen, J. Detection of malicious code variants based on deep learning. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2018, 14, 3187–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Du, L.; Wang, P.; Cai, X.; Zhang, W. Malicious code detection based on CNNs and multi-objective algorithm. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2019, 129, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Andreopoulos, W.; Stamp, M. CNN vs ELM for image-based malware classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.13820. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, H.; Ullah, F.; Naeem, M.R.; Khalid, S.; Vasan, D.; Jabbar, S.; Saeed, S. Malware detection in industrial internet of things based on hybrid image visualization and deep learning model. Ad Hoc Networks 2020, 105, 102154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatraman, S.; Alazab, M.; Vinayakumar, R. A hybrid deep learning image-based analysis for effective malware detection. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2019, 47, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.-L.; Nguyen, T.-K.; Nguyen, T.V.; Nguyen, T.N.; Massacci, F.; Phung, P.H. A convolutional transformation network for malware classification. In Proceedings of the 2019 6th NAFOSTED Conference on Information and Computer Science (NICS), Hanoi, Vietnam, 12–13 December 2019; pp. 234–239. [Google Scholar]
- El-Shafai, W.; Almomani, I.; Alkhayer, A. Visualized malware multi-classification framework using fine-tuned CNN-based transfer learning models. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussas, V.; Andreatos, A. Malware detection based on code visualization and two-level classification. Information 2021, 1, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roseline, S.A.; Geetha, S.; Kadry, S.; Nam, Y. Intelligent vision-based malware detection and classification using deep random forest paradigm. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 206303–206324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Muttoo, S.K.; Singh, V.B. Multiclass malware classification via first-and second-order texture statistics. Comput. Secur. 2020, 97, 101895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çayır, A.; Ünal, U.; Dağ, H. Random CapsNet forest model for imbalanced malware type classification task. Comput. Secur. 2021, 102, 102133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, M.; Silka, J.; Wieczorek, M.; Alrashoud, M. Recurrent neural network model for IoT and networking malware threat detection. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2021, 17, 5583–5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, M.; Shah, J.H.; Kanwal, S.; Raza, M.; Khan, M.A.; Damaševičius, R.; Blažauskas, T. Hybrid malware classification method using segmentation-based fractal texture analysis and deep convolution neural network features. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemalatha, J.; Roseline, S.A.; Geetha, S.; Kadry, S.; Damaševičius, R. An efficient densenet-based deep learning model for malware detection. Entropy 2021, 23, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toldinas, J.; Venčkauskas, A.; Damaševičius, R.; Grigaliūnas, Š.; Morkevičius, N.; Baranauskas, E. A novel approach for network intrusion detection using multistage deep learning image recognition. Electronics 2021, 10, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, F.; Li, Q. A novel malware detection and family classification scheme for IoT based on DEAM and DenseNet. Secur. Commun. Netw. 2021, 2021, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.J.; Raza, A.; Yasin, A.; Shehzad, H.M.F.; Butt, I. The customized convolutional neural network of face emotion expression classification. Ann. Rom. Soc. Cell Biol. 2021, 25, 5296–5304. [Google Scholar]
- Mubashar, R.; Awan, M.J.; Ahsan, M.; Yasin, A.; Singh, V.P. Efficient residential load forecasting using deep learning approach. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 5998–6008. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Awan, M.J.; Bilal, M.H.; Yasin, A.; Nobanee, H.; Khan, N.S.; Zain, A.M. Detection of COVID-19 in chest X-ray images: A big data enabled deep learning approach. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, E.; Cheng, Y.; Xiao, C.; Liu, Z.; Yu, W. Efficient attention mechanism for dynamic convolution in lightweight neural network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed Awan, M.; Mohd Rahim, M.S.; Salim, N.; Mohammed, M.A.; Garcia-Zapirain, B.; Abdulkareem, K.H. Efficient detection of knee anterior cruciate ligament from magnetic resonance imaging using deep learning approach. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.M.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. Survey on deep learning with class imbalance. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.J.; Rahim, M.S.M.; Salim, N.; Ismail, A.W.; Shabbir, H. Acceleration of knee MRI cancellous bone classification on google colaboratory using convolutional neural network. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. 2019, 8, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, P.; Dai, X.; Xiao, B.; Yuan, L.; Gao, J. Focal self-attention for local-global interactions in vision transformers. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.00641. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, V.-N.; Lee, S.-H.; Le, H.-S.; Kwon, K.-R. High Performance deepfake video detection on CNN-based with attention target-specific regions and manual distillation extraction. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.J.; Khan, R.A.; Nobanee, H.; Yasin, A.; Anwar, S.M.; Naseem, U.; Singh, V.P. A Recommendation engine for predicting movie ratings using a big data approach. Electronics 2021, 10, 1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.J.; Rahim, M.S.M.; Nobanee, H.; Munawar, A.; Yasin, A.; Zain, A.M. Social media and stock market prediction: A big data approach. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2021, 67, 2569–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.M.; Awan, M.J.; Khan, N.S.; Yasin, A.; Shehzad, H.M.F. Sentiment analysis of online food reviews using big data analytics. Elem. Educ. Online 2021, 20, 827–836. [Google Scholar]
- Aftab, M.O.; Awan, M.J.; Khalid, S.; Javed, R.; Shabir, H. Executing spark BigDL for leukemia detection from microscopic images using transfer learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 1st International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Data Analytics (CAIDA), Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, 6–7 April 2021; pp. 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Awan, M.J.; Khan, M.A.; Ansari, Z.K.; Yasin, A.; Shehzad, H.M.F. Fake profile recognition using big data analytics in social media platforms. Int. J. Comput. Appl. Technol. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.J.; Rahim, M.S.M.; Nobanee, H.; Yasin, A.; Khalaf, O.I.; Ishfaq, U. A big data approach to black friday sales. Intell. Autom. Soft Comput. 2021, 27, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awan, M.J.; Gilani, S.A.H.; Ramzan, H.; Nobanee, H.; Yasin, A.; Zain, A.M.; Javed, R. Cricket match analytics using the big data approach. Electronics 2021, 10, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Parameter | Attention CNN with VGG19 |
|---|---|
| Batch Size | 263 |
| Dropout Rate | 0.5 |
| Epochs | 10 |
| Learning Rate | 0.1 to 0.001 |
| Trainable parameters | 173,482 |
| Non-trainable parameters | 20,025,920 |
| Loss Function | Categorical Cross entropy |
| Optimizer | Adam |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1 Score | Specificity | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SACNN VGG19 without class balancing | 97.62% | 97.68% | 97.5% | 97.20% | 97.68% | 97.66% |
| SACNN VGG19 with class balance | 97.42% | 97.11% | 96.95% | 97% | 97.33% | 97.32% |
| SACNN VGG19 with class balance on Benign class | 97.38% | 97.28% | 97.56% | 97.21% | 97.52% | 97.45% |
| Model | Accuracy | Precision | Recall | F1-Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Benign class SACNN class balancing | 100% | 100% | 100% | 100% |
| Architecture | Accuracy | Year & Reference |
|---|---|---|
| GoogleNET | 84.0% | (2018) [22] |
| ResNET (Avg) | 86.01% | |
| CNN-SVM | 77.22% | (2019) [26] |
| GRU-SVM | 84.92% | |
| MLP-SVM | 80.46% | |
| VGG16 + SVM | 92.97% | (2018) [20] |
| Linear-binary patterns and CNN (LBP + CNN) | 93.17% | (2017) [62] |
| Custom Deep Learning architecture + KNN (fast.ai) | 94.80% | (2019) [21] |
| SVM with T + C + L features | 95.23% | (2018) [24] |
| KNN with T + C + L features | 96.23% | |
| CNN-2 layer-LSTM (7:3) | 96.4% | (2019) [27] |
| CNN-2 layer-LSTM (9:1) | 96.8% | |
| SSPNet1 (with spatial pyramid pooling) | 96.60% | (2020) [63] |
| Multi-Objective learning | 96.86% | (2019) [34] |
| Capsule network model CapsNet | 96.58% | (2021) [44] |
| Kernel-based ELM with statistical texture features | 94.25% | (2020) [43] |
| Spatial Attention CNN with VGG16 without Class Balance Malware | 97.62% | Our study |
| Spatial Attention CNN with VGG16 with Class Balance Malware | 97.42% | |
| Spatial Attention CNN with VGG19 with Class Balance Benign | 97.38% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Awan, M.J.; Masood, O.A.; Mohammed, M.A.; Yasin, A.; Zain, A.M.; Damaševičius, R.; Abdulkareem, K.H. Image-Based Malware Classification Using VGG19 Network and Spatial Convolutional Attention. Electronics 2021, 10, 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10192444
Awan MJ, Masood OA, Mohammed MA, Yasin A, Zain AM, Damaševičius R, Abdulkareem KH. Image-Based Malware Classification Using VGG19 Network and Spatial Convolutional Attention. Electronics. 2021; 10(19):2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10192444
Chicago/Turabian StyleAwan, Mazhar Javed, Osama Ahmed Masood, Mazin Abed Mohammed, Awais Yasin, Azlan Mohd Zain, Robertas Damaševičius, and Karrar Hameed Abdulkareem. 2021. "Image-Based Malware Classification Using VGG19 Network and Spatial Convolutional Attention" Electronics 10, no. 19: 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10192444










