Abstract
Direct current microgrids (DCMGs) are currently presented as an alternative solution for small systems that feed sensitive electrical loads into DC. According to the scientific literature, DCMG maintains good voltage regulation. However, when the system is in islanded mode, very pronounced voltage variations are presented, compromising the system’s ability to achieve reliable and stable energy management. Therefore, the authors propose a solution, connecting the electrical network through a grid-tied voltage source converter (GVSC) in order to reduce voltage variations. A coordinated control strategy between the DCMG and GVSC is proposed to regulate the DC voltage and find a stable power flow between the various active elements, which feed the load. The results show that the control strategy between the GVSC and DCMG, when tested under different disturbances, improves the performance of the system, making it more reliable and stable. Furthermore, the GVSC supports the AC voltage at the point of common coupling (PCC) without reducing the operating capacity of the DCMG and without exceeding even its most restrictive limit. All simulations were carried out in MATLAB 2020.
1. Introduction
Microgrids (MGs) were originally small-scale power systems composed of a limited number of sources and minimal loads with a storage system to support the operation. The connection between the MG and the power grid would depend directly on the system operator (SO) [1,2]. However, the MG did not have the option of operating in islanded mode. Today, research has focused on finding ways for the MG to be an active element in the network [3,4], in that it is able to exchange energy bi-\directionally, as well as having the capacity to operate in islanded mode [5,6].
Microgrids can be categorized into two general types: AC (ACMG) and DC (DCMG) [2]. The DCMG can be designed to provide energy to small rural areas, commercial, and residential buildings [7]. An advantage of the DCMG over its ACMG counterpart is that it is not necessary to have control over frequency, phase, or reactive power. For a stable operation in the DC system, achieving balance in the power flow at all times is necessary, enabling the DC bus voltage to remain constant [8]. Coordination between sources (dispatchable and non-dispatchable), load, and energy storage systems is achieved by the balancing of energy with a shared power control scheme [9]. The following section outlines the advantages and disadvantages of this control scheme.
This control strategy falls into two general types. In the first, the control references of the converters generate a central controller with real-time feedback from controlled terminals [10]; however, this solution has a number of disadvantages such as its dependence on stable communication (without delays or failures) and adequate scalability [8]. The second strategy is an autonomously controlled solution [11,12]. It is based on the detection of the local DC bus voltage, which is an indicator of the balance of power flow within the DCMG. To achieve this balance, a hybrid energy storage system (HESS) is used. This is composed of a battery supported by a supercapacitor (SC), allowing for the difference in energy between the non-dispatchable sources and the connected load to be delivered. When the batteries are only used as an energy storage system (due to their low power density), the charge and discharge rate is low, causing severe fluctuations in VDC in cases of rapid charging. This results in an increase in the number of charge/discharge cycles, which, in turn, reduces battery life [12]. SCs have a high power density and can react quickly to rapid load fluctuations. However, SCs alone cannot be used as an energy storage system, as they cannot supply charge over a sustained period [13,14]. A study by [15] explores a control design and stability analysis for DC microgrids under false data injection and denial of service. Nevertheless, a grid connection is not displayed, i.e., a grid–VSC is not used.
This paper proposes a coordinated control strategy between a voltage source converter (GVSC) and a DC microgrid (DCMG) in order to manage power flow sufficiently to reduce DC bus voltage variations within the DCMG in the case of events such as generation failures or load changes. The GVSC will maintain a constant voltage on the AC side at the point of common coupling (PCC), contributing to the control performance within the DCMG when compared with islanded and grid-connected modes of operation. The DCMG is composed of a battery and supercapacitor, forming a hybrid system (HESS), a photovoltaic array (PVA), and a DC load. The GVSC is connected to a passive LCL filter, an AC load, and the electrical system.
2. Microgrid System Configuration
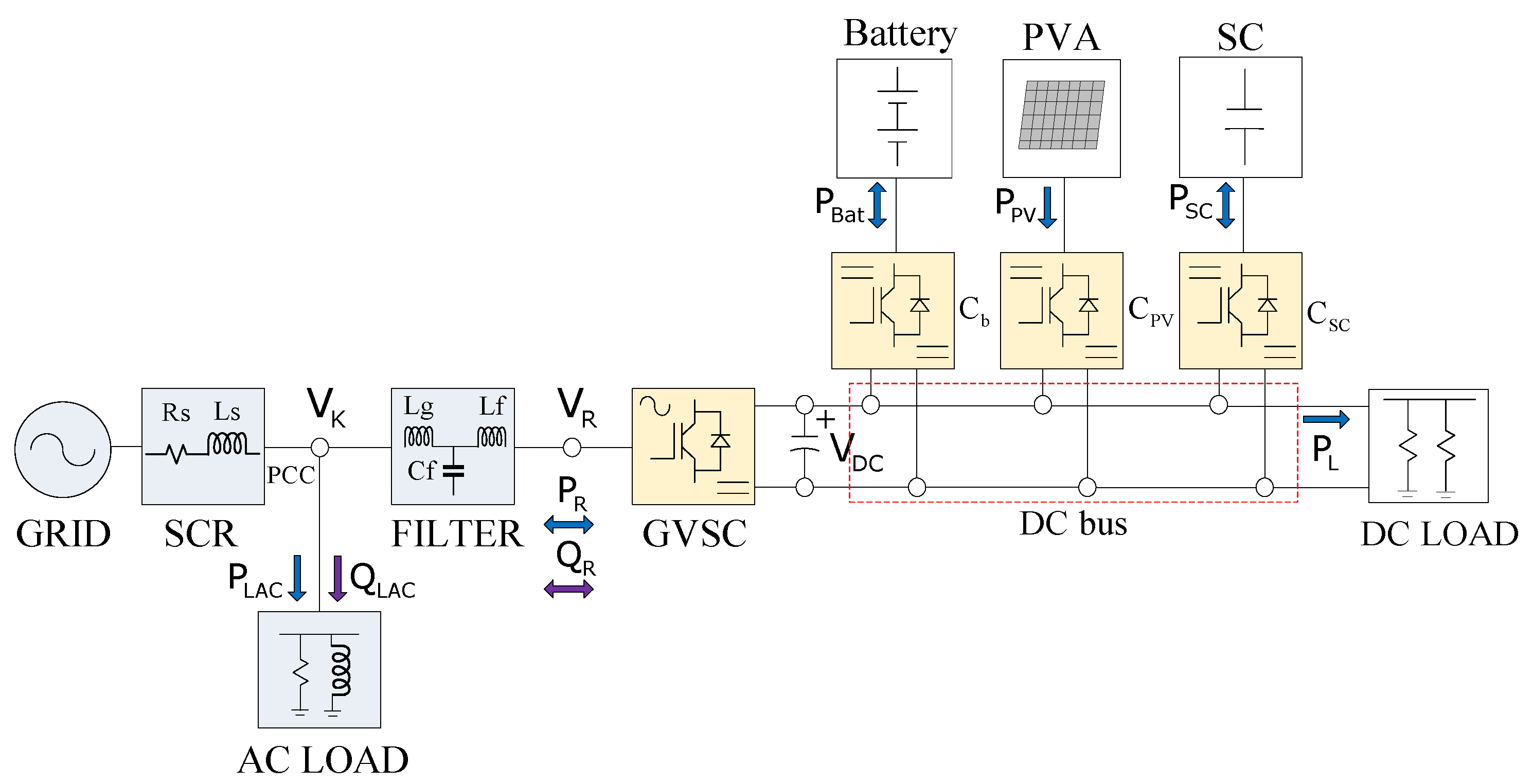
The topology of the DCMG studied is shown in Figure 1. This system comprises five subsystems: the storage system of battery with a Cb/DC–DC converter, the supercapacitor (SC) bank with a CSC/DC–DC converter, the photovoltaic generator (PVA) with a CPV/boost converter, and the load. The PVA is a non-dispatchable generator. All of them are supplied to the DC bus (see Figure 1). On the other side, the AC–DC bidirectional grid-tied voltage source converter (GVSC) is connected to the DC bus and to the AC bus through an LCL filter. The filter is connected to the AC side at the point of common coupling (PCC). This node is also connected to an AC load. In the proposed control strategy, each terminal into the DCMG functions as a P terminal or as a Gen terminal depending on the case study. P terminal does not actively contribute to the regulation of VDC in the DCMG.

Figure 1.
DCMG system configuration.
The Gen terminal is adjusted to compensate for power variations in the system and therefore actively regulates DC bus voltage, VDC. The terminals responsible for this regulation are the HESS and GVSC. The latter regulates the AC voltage, VK, at the point of common coupling (PCC), and keeps VDC constant in the bus of the DCMG [16]. Depending on the event studied, and according to Figure 1, only one of the terminals is responsible for maintaining constant VDC in the system, meaning that it functions as a Gen terminal.
2.1. Solar System Model (PV Array)
The PVA model was performed using the equations given in [17,18]. This method considers two models: an ideal and a real model. This model is derived from the classic I–V curves in which three remarkable points are highlighted: the short circuit current, (0, Isc), the open-circuit voltage, (Voc, 0), and the point of maximum power point tracking (MPPT) values (Vmp, Imp). The PVA is connected to the DC bus of the DCMG through a boost converter, which extracts the maximum power from PVA using an MPPT algorithm [16]. However, the PVA control strategy could change to a load-following algorithm, as will be seen in the following sections.
The boost converter average model is given by the following equation:
where LPV is the inductance of the converter inductor, VPV is the PVA voltage, iPV is the current through the inductor, and dPV is the duty cycle of the converter.
2.2. AC Utility Grid and VSC Model
A line–line (VLL) AC utility grid with a short circuit ratio (SCR) is modeled. The GVSC can operate as an inverter or as a rectifier (see Figure 1), depending on its voltage at the terminals (VR) and the voltage at the PCC (VK). This is formed by the bidirectional converter and connected to the utility grid by means of an LCL filter [16].
The approximate GVSC equations in the synchronous reference frame can be expressed by
where idk and iqk are dq currents in the LCL filter, disregarding the current of the capacitor, Leq is the equivalent inductance of LCL filter (Lf + Lg), Req is the equivalent resistance of the LCL filter (Rf + Rg), and δ is the angle between VK and VR.
The control of the GVSC is presented in [17]. This can regulate VDC on the side of the DCMG, ensuring that it always remains constant when there is an active power flow from the converter to the grid, meaning the converter can function as a Gen terminal. However, any fault in the network may cause a drop in AC voltage, reducing the power transmitted by the GVSC and potentially reaching, in severe cases, values equal to zero. In these conditions, the GVSC can be disconnected from the DCMG.
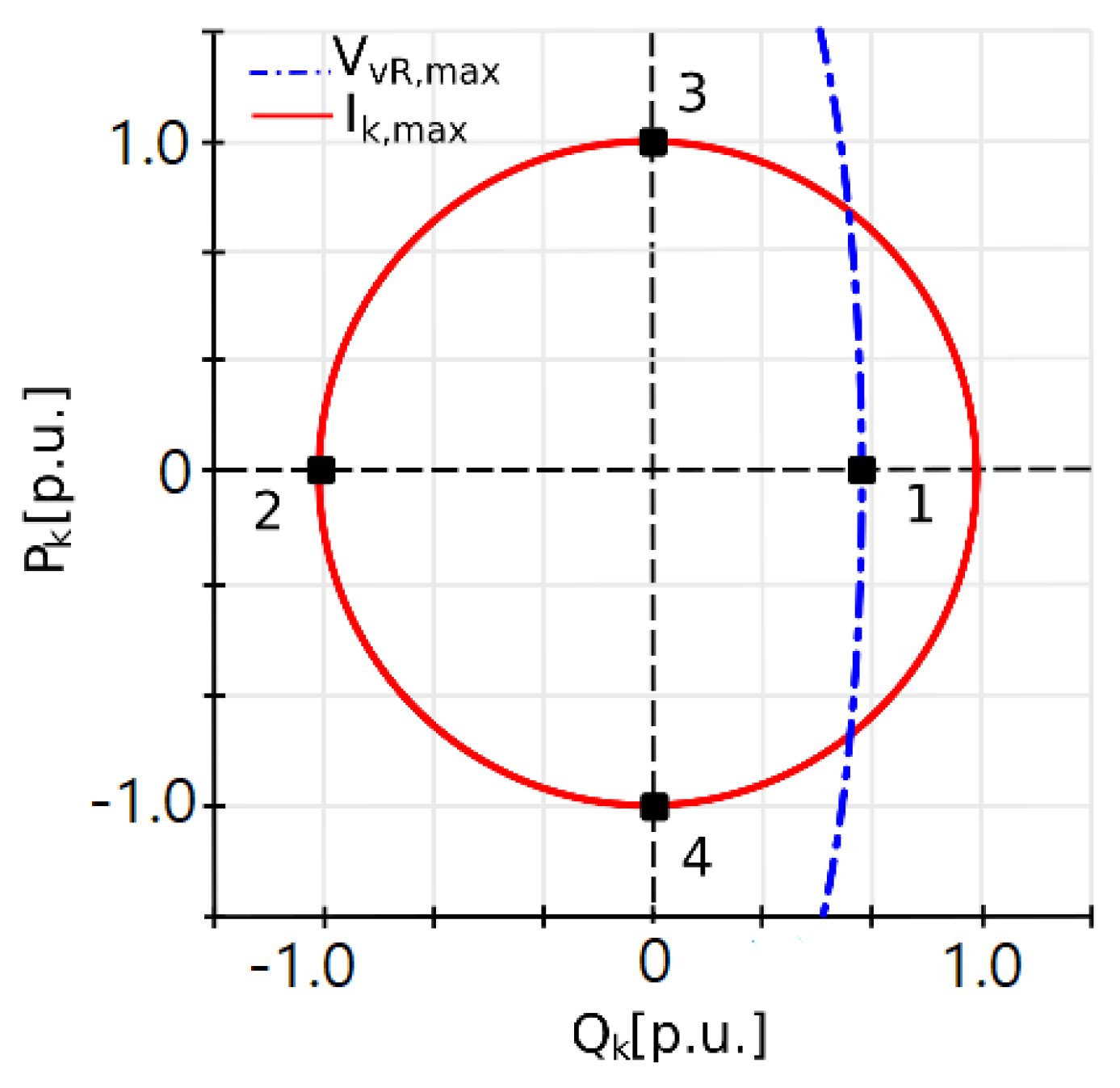
Figure 2 shows the PQ curves that limit the output AC voltage (in blue) of the converter and the maximum current that can circulate through the switches (in red). The two most relevant GVSC operation scenarios are highlighted: Points 1 and 2 are when the inverter delivers or receives reactive power (QK). In this case, the inverter would be regulating the voltage (VK) at the PCC, and when this occurs, the DCMG is able to operate in islanded mode, as the AC–DC converter does not need to deliver PK to the grid. At points 3 and 4, the inverter has the maximum active power that can be either delivered to or absorbed from the DCMG, depending on the case. When this occurs, the DCMG must provide this power and the entire system (GVSC–DCMG) is therefore interconnected.

Figure 2.
PQ curves at the GVSC.
2.3. Battery Energy Storage System Model
The selected battery model emulates a real lithium-ion (Li) battery according to [19] due to its great chemical potential of high density and low weight. The battery state of charge (SoC) cannot be measured by a sensor and therefore must be estimated. The SoC value can be computed using the Coulomb counting method [20]. This method measures the battery electrical current ibat. The SoC is expressed by Equation (4). Qb is the battery nominal capacity found at the datasheet, and SoC0 is the initial SoC value.
The SoC should be limited between a maximum and minimum value to conserve the life span of the battery [20]. When the SoC exceeds these values, it neither absorbs nor supplies current.
The battery is connected to the DCMG through a buck–boost converter (DC–DC). The average model of the buck–boost converter is given by
where Lb is the inductance of the converter inductor, Vb is the battery voltage, and db is the duty cycle.
The control of the buck–boost is a conventional cascade control that involves the use of two controllers, an inner current loop, and an outer voltage loop to regulate the DC bus [21].
2.4. Super Capacitor Energy Storage System Model
The supercapacitor energy storage (SC) was modeled as a three-branch circuit according to [22]. According to the manufacturer’s specifications [23], the self-discharge effect was modeled with a resistance. Losses are represented as an equivalent series resistor (ESR). The ideal loading and unloading curves of the SC were obtained from the manufacturer’s specifications sheet [23].
The basic premise of the control scheme shown in [23] is that the SC manages the high-frequency power component, while the battery manages the average power component. It is important to control the stress levels in the battery to improve its life span. The control scheme is based on the decoupling of low and high-frequency power components and utilizes the error current of the battery to control the SC [13,22]. The SC control does not directly control VDC into DCMG, but it helps extend the battery life.
3. Control Strategy in the DCMG System
The control strategy in the DCMG system seeks to maintain a constant VDC, continuously feeding the DC loads and keeping a stable VK at the PCC through the GVSC. Unbalanced energy flow can cause an abnormal VDC and interrupt the operation in the DCMG. To guarantee normal operation, VDC must be kept constant, thus ensuring that the energy flow is balanced. Maintaining VDC at its nominal value involves establishing a coordinated control of the active elements included in the DCMG, adhering at all times to the following expression:
where PGEN is the power generated by the PVA, PR is the power generated or consumed by the GVSC, PHESS is the power generated or consumed by the battery–SC (PBAT + PSC), PL is the power consumed by the load, and CDC the equivalent capacitor in the DC loop in the DCMG according to Figure 1.
This control strategy was carried out by the HESS and GVSC controllers. Each controller is explained separately below.
The objective of the HESS controller is to reduce the stress on the battery and hence increase the lifetime of the battery [22]. The control strategy is explicated in [22], and it is shown again here.
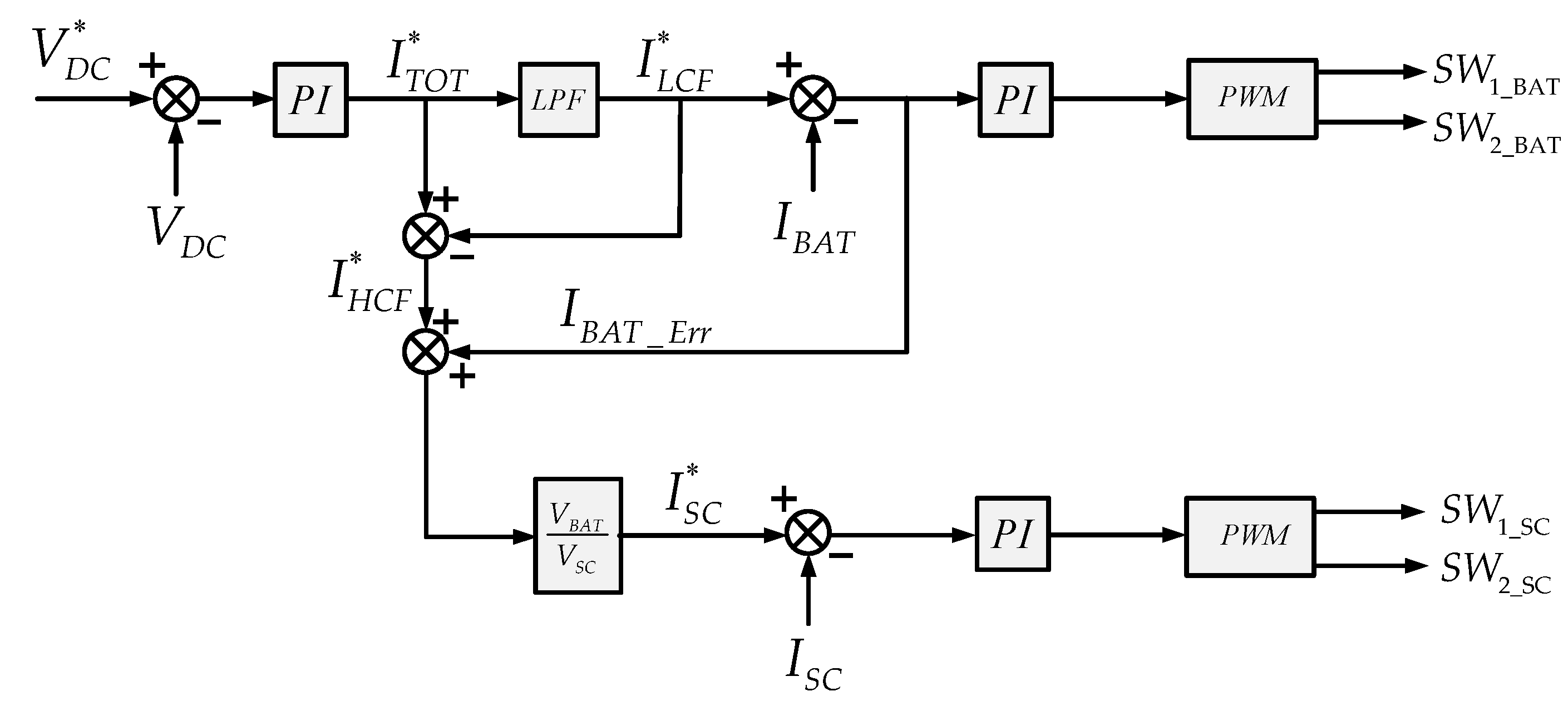
The method is based on decoupling of low- and high-frequency power components of demand–generation mismatch and utilizes the error current of the battery to control the SC. At the top of Figure 3, VDC is compared with a reference voltage (VDC*), and the error is given to the proportional–integral (PI) controller. The PI controller generates the total current required (ITOT*) from HESS. This current is separated into a low-frequency component (ILCF*) and a high-frequency component (IHCF*). ILCF* is compared with IBAT, and the error (IBAT_Err) is given to another PI controller. This PI controller generates (via PWM) switching pulses corresponding to the battery switches (SW1_BAT, SW2_BAT).

Figure 3.
HESS Controller.
At the bottom of Figure 3, the SC control is shown. The battery has a slow dynamic that makes the IBAT unable to track the IBAT* instantly. Therefore, an uncompensated battery power (PBAT_uncomp) has to be compensated by SC. The reference current of SC is given as
ISC* is compared with the measured SC current (ISC), and the error is given to the PI controller. This PI controller generates (via PWM) switching pulses, corresponding to the SC switches (SW1_SC, SW2_SC).
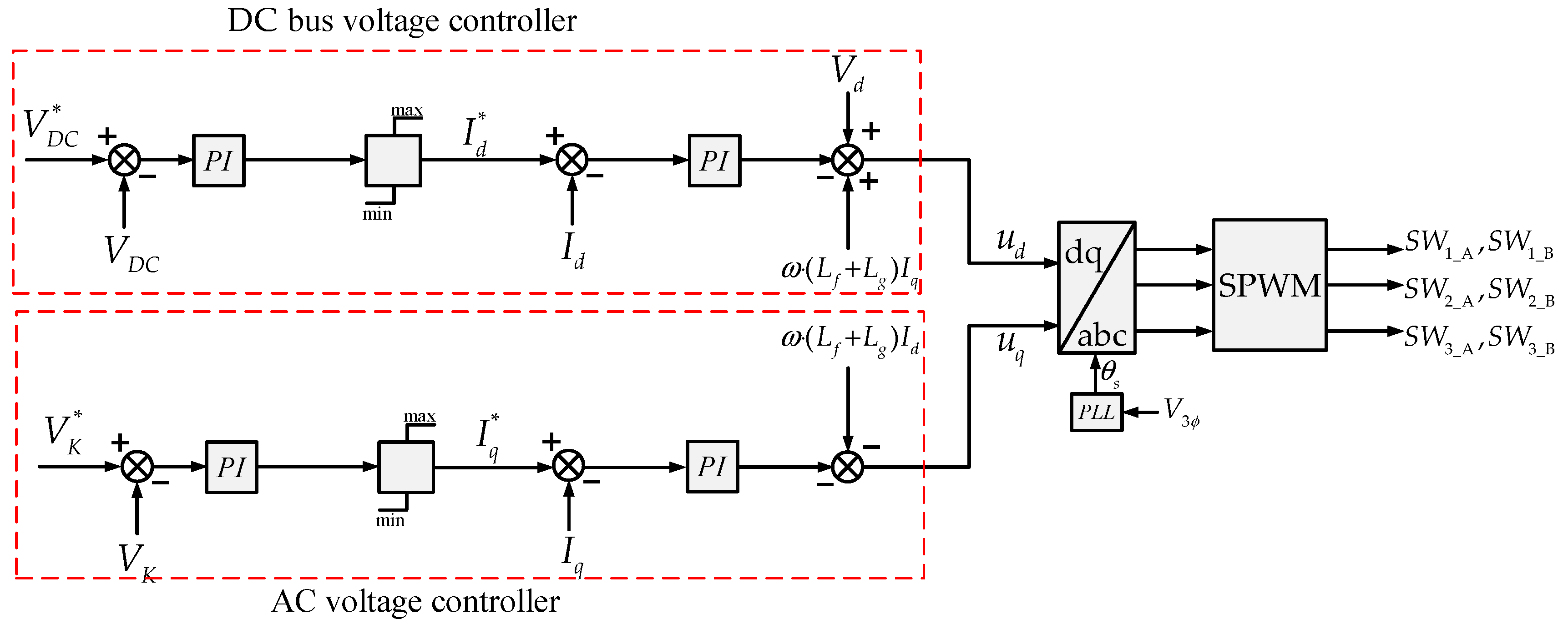
For the control of the GVSC, the cascade type control strategy was used to regulate the DC voltage and the AC voltage [17]. The upper part of Figure 4 shows the DC voltage controller and the bottom shows the AC voltage controller. The DC voltage–control in Figure 4 compares the DC bus voltage (VDC) with a voltage VDC*, and the error is given to the PI controller. This PI controller computes Id*. Therefore, the DC voltage can be controlled by controlling Id*. The AC voltage VK can be controlled by controlling Iq*. The AC VK* voltage is compared with the measured VK on the K bus. This error is given to the PI controller that computes Iq*. Both Id* and Iq* are limited to avoid overload.

Figure 4.
GVSC Controller.
In Figure 4, the current control scheme is shown. It has two separate control loops that are capable of independently controlling Id and Iq. In each of the control loops, the Id and Iq measured is subtracted from the current reference (Id* and Iq*), and the resulting error signal is fed into a PI controller, respectively. These PI controllers generate (via cross-coupling terms) ud and uq. An inverse Park’s transformation block converts the adjusted desired values of ud and uq into three sinusoidal modulating signals. These signals are given to the SPWM block. This block generates switching pulses corresponding to GVSC switches (SW1_A, SW1_B, SW2_A, SW2_B, SW3_A, SW3_B).
Four modes of operation were proposed for studying the performance of the control:
In Mode 1, the DCMG system does not require power from the grid. The Gen terminal is the battery responsible for regulating VDC, thereby balancing the energy difference between that supplied by the PVA and the energy demanded by the load. The SC is used to support battery performance and smooth the response in energy. Alternatively, the GVSC can be used to regulate AC voltage (VK) at the PCC.
In Mode 2, the DCMG is connected to the grid through a GVSC. Again, the battery regulates VDC. However, the GVSC assists the DCMG system by regulating the VDC bus voltage with an injection of active power from the grid. In this mode of operation, the coordination between the GVSC and the DCMG is clearly seen.
The GVSC controls the VK voltage, supplying QR reactive power, and the DCMG controls VDC voltage with the help of the active power (PR) delivered by the grid.
In Mode 3, the battery energy storage system does not regulate VDC, thus converting from a Gen terminal to a P terminal. The condition for this to occur is when the battery’s SoC falls outside of the 25–85% range. The new Gen terminal within the DCMG will then be the GVSC. Therefore, the objectives of this converter are to maintain a constant VDC through the exchange of active power with the network while also regulating VK, injecting reactive power into the PCC [16].
In Mode 4, neither the HESS nor the GVSC is able to function as Gen terminals, meaning neither is responsible for keeping VDC constant. The two conditions required to reach this scenario are (a) that the demand on the loads is higher than generation, thereby creating a partial shedding of the less sensitive loads and enabling the PVA to deliver all its energy using MPPT; (b) the generation exceeds the load, so the supply source (PVA) is regulated using load-following control.
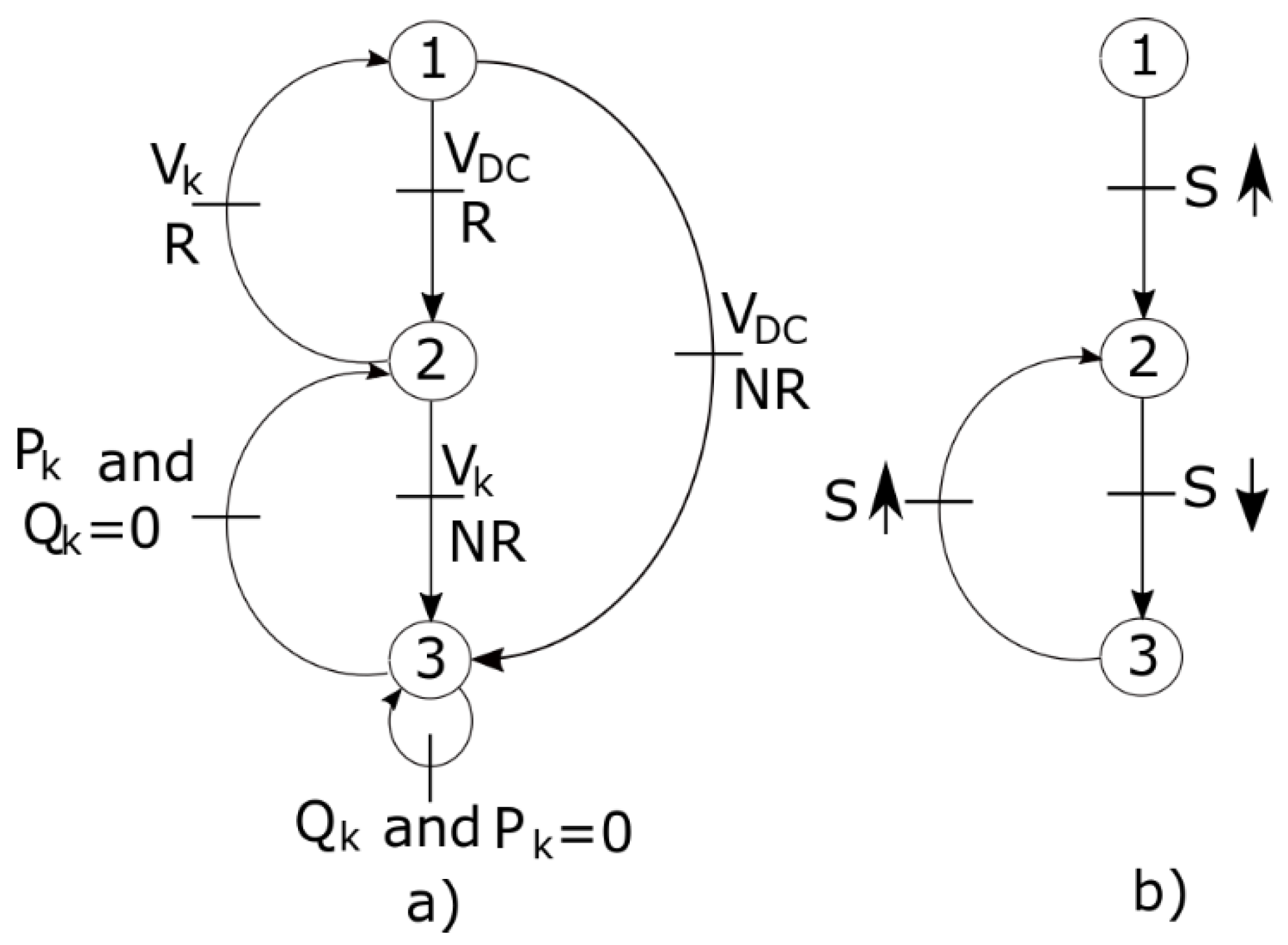
Finally, in Figure 5, the state diagram of the system is presented. In Figure 5a, it is observed how depending on the regulation conditions of the DC bus (VDC) or the AC bus (VK) in the PCC, the system can remain with HESS active (State 1: HESS ON), GVSC active (state 2: GVSC ON) or GVSC inactive (state 2: GVSC OFF).

Figure 5.
Hybrid system state diagram: (a) HESS–GVSC interaction; (b) PVA.
The state transitions depend on: the regulation of the DC bus (VDC regulated: VDC R) or VDC not regulated (VDC NR), on the regulation of the AC bus (PCC) with VK regulated (VK R) or VK not regulated (VK NR). As the PVA is not responsible for regulating the VDC voltage, its operation is limited to whether or not power is injected into the DC bus; its operation is illustrated in Figure 5b, where state 1 corresponds to the start of the operation, state 2 if PVA is active, and state 3 if PVA is inactive; transitions occur depending on the irradiance (S), and the up or down arrows indicate whether or not there is enough irradiance. The GVSC OFF condition indicates that the DCMG is in isolated mode, while the GVSC ON condition indicates that the DCMG is connected to the network through the GVSC and the LCL filter.
4. Case Study
This section demonstrates the flexibility and capacity of the DCMG by simulation using MATLAB/Simulink®. The control variable is the VDC magnitude using the control strategies proposed in the previous section. For this study, a common base power Sbase (in AC and DC) of 20 kVA was chosen as
The specifications and parameters used for testing the proposed system are found in Table 1.

Table 1.
Systems parameters.
4.1. First Mode of Operation
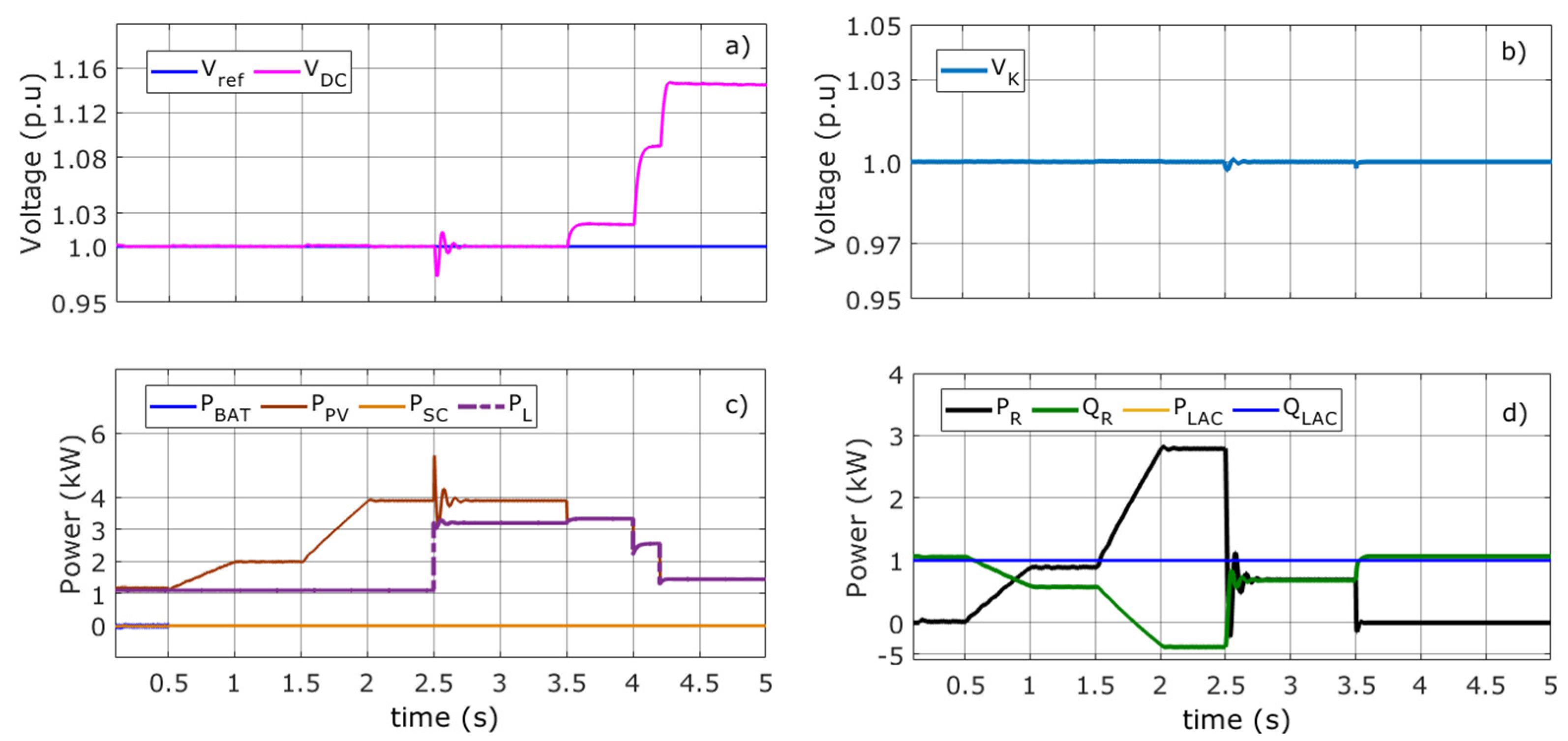
Here, the DCMG operates in an islanded mode without receiving or delivering active power to the network, i.e., the DCMG and GVSC are totally disconnected from each other. The battery power (PBAT) supported by the power of the SC (PSC) balances out the power difference between PPV and PL, meaning the HESS (battery–SC) acts as a Gen terminal. It can be observed that the GVSC supplies or absorbs reactive power QR to maintain a constant VK. In order to study the permanent and transitory regimes at this level of operation, Table 2 shows an approximate difference in generation and load. The DC load absorbs 1100 W until t = 2.5 s. At t > 2.5 s, the DC load changes to 3200 W.

Table 2.
Mode of operation 1.
Figure 6a shows the reference and DC voltages into the DCMG. Conditions have been initially simulated at 25°C with an irradiance of 300 W/m2, which is gradually decreased at 0.5 s and 1.5 s to 200 W/m2 and 0 W/m2, respectively (see Figure 6c). In observing the average value generated by the PVA (PPV), the difference in energy produced by the imbalance of VDC in the DCMG is shown (see Table 2). Therefore, the battery is responsible for providing the energy difference, thus assuming its function as a Gen terminal. The HESS reduces the DC voltage very close to the reference voltage (1.0 p.u.). The SC does not deliver any energy due to the low density of power required, i.e., there are no sudden changes in the load and source.

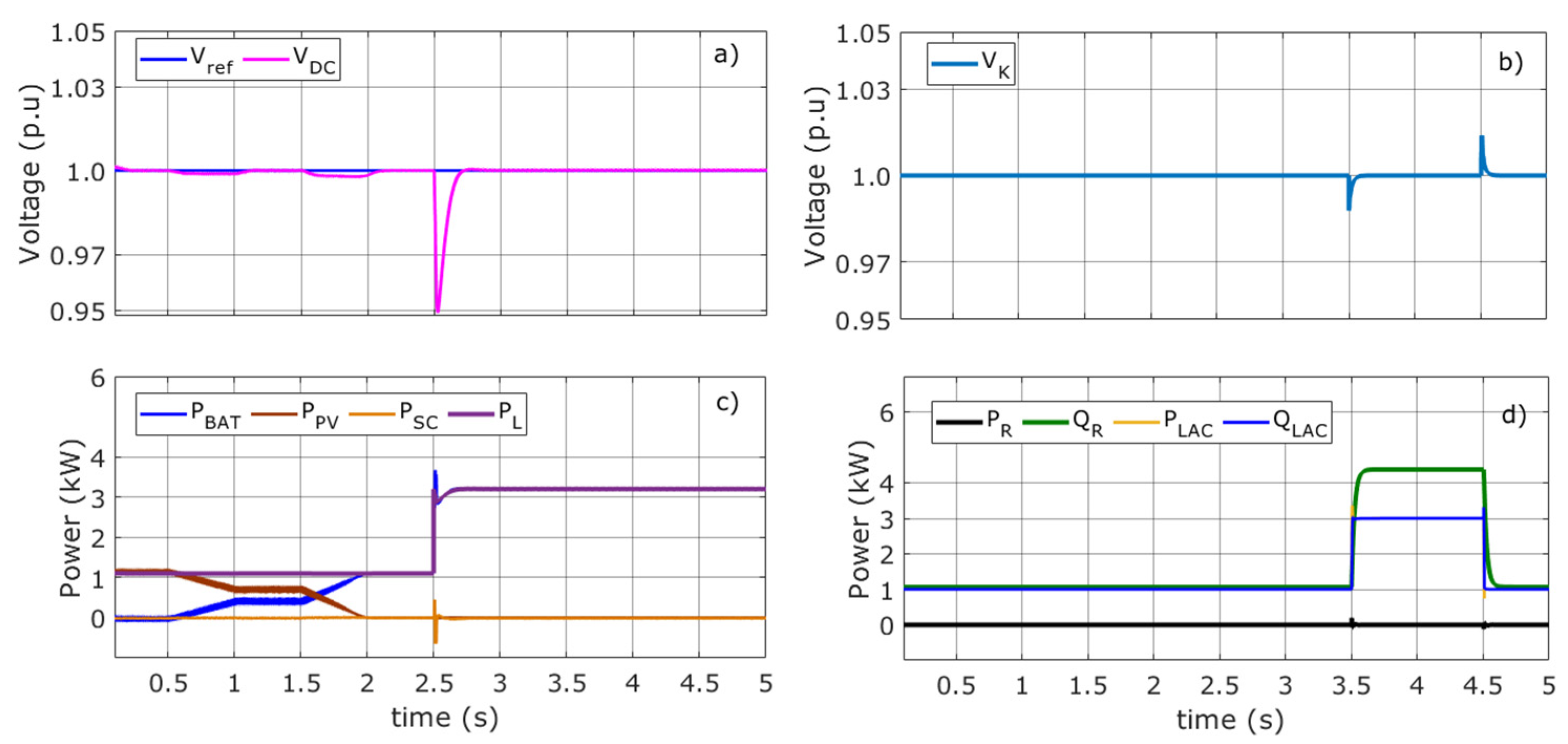
Figure 6.
Voltage and power in Mode 1. (a) Reference and DC bus voltage (b) AC voltage (c) Battery, photovoltaic, SC, and load powers (d) Active and reactive VSC powers, active and reactive load powers.
Figure 6b,d show the VK voltage at the PCC and the active and reactive powers of the GVSC and AC load, respectively. The VK voltage is regulated by the GVSC. It is worth noting that the GVSC works as a STATCOM, supplying or absorbing reactive power, QR, to keep the voltage constant at node K. Initially, the AC load absorbs 1000 W and 1000 var, respectively. At t = 3.5 s, the AC load changes to 3000 W and 3000 var, respectively (see Figure 6d). Finally, at t = 4.5 s, the AC load returns to its initial values. The GVSC controller regulates the voltage VK at its reference value (1.0 p.u.), as shown in Figure 6b. Here, the GVSC has no influence on the power balance of the DCMG and therefore does not control the VDC bus voltage.
To study the DCMG in a critical state, the PVA is disconnected at t = 2 s as shown in Figure 6c. Note that there is a power balance in the DCMG, and therefore, there is no VDC voltage variation as shown in Figure 6a. At t = 2.5 s, the DC load changes to 3200 W. This causes a pronounced VDC voltage drop that should be regulated by HESS. Table 2 shows the power variations that should be compensated by HESS.
In Figure 6c, it can be inferred how the battery provides all the energy demanded by the load and the losses that occur in the filters used by the elements that comprise the DCMG system. The SC delivers some energy due to the power required by DC load, thereby extending battery life. Notably, the SC does not regulate VDC here because its role is to support the battery. However, the SC supplies PSC momentarily until it reaches zero, as shown in Figure 6c. The PBAT takes a while to reach a steady state due to the output voltage error (VDC) minimized by the control system in Figure 3.
It should be noted that the DCMG system requires an extra element of support to avoid deep drops in VDC voltage. The next section shows how a GVSC helps the DCMG system to regulate VDC voltage without these pronounced drops in voltage.
4.2. Second Mode of Operation
In the second mode of operation, the DCMG operates with a GVSC. Here, the HESS is the Gen terminal, as shown in Figure 7. The DCMG will no longer be islanded from the grid and, as a result, part of the power to compensate is given or absorbed by the grid through the AC–DC converter. In addition, the GVSC can also act as a reactive power compensator at the AC side, if it is within its operating range. The generating powers of the PVA, those of the load consumption connected to the DCMG, and the compensation powers are shown in Table 3. The initial conditions and PVA’s irradiance in this mode of operation are the same as in the previous operating mode.

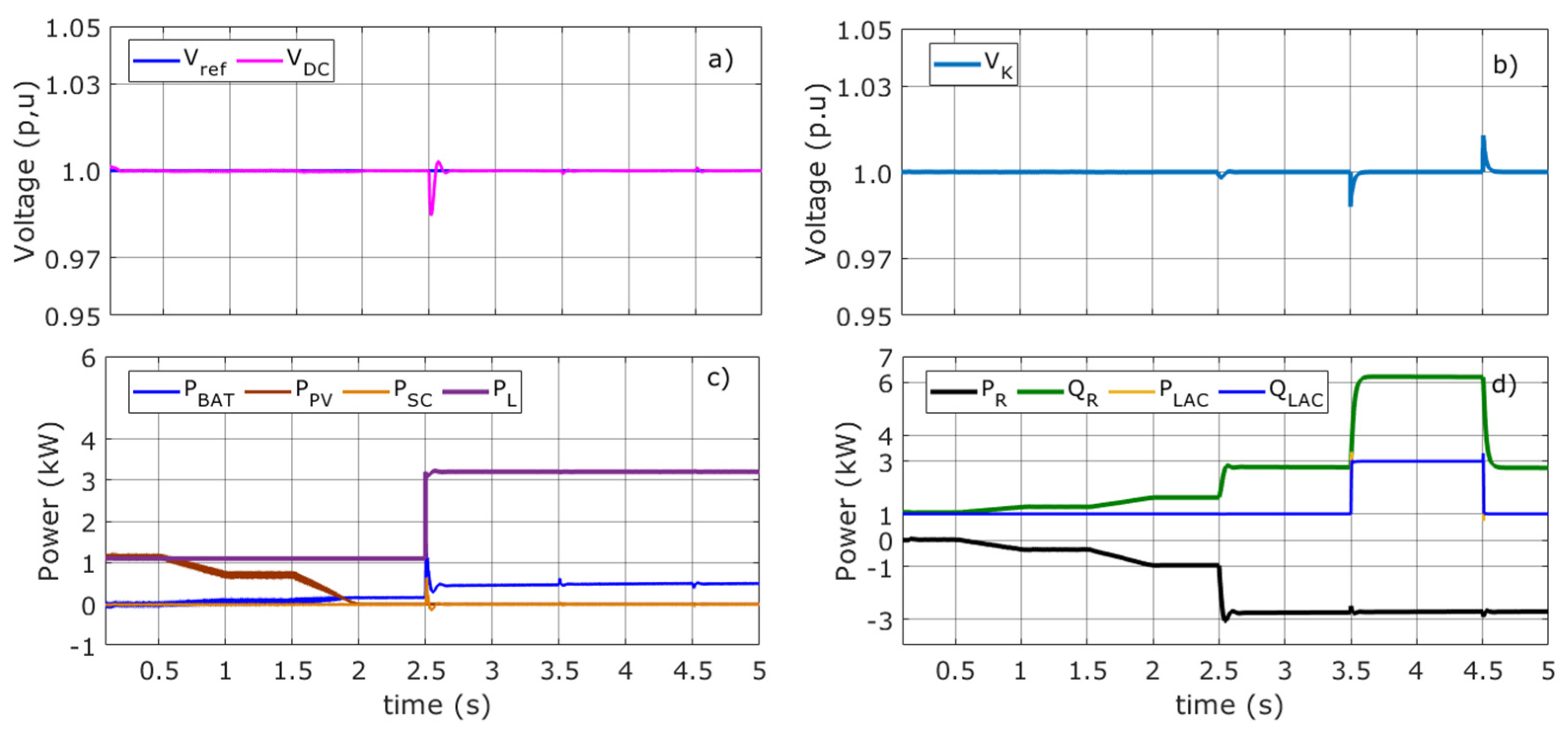
Figure 7.
Voltage and power flow in Mode 2. (a) Reference and DC bus voltage (b) AC voltage (c) Battery, photovoltaic, SC, and load powers (d) Active and reactive VSC powers, active and reactive load powers.

Table 3.
Mode of operation 2.
Figure 7a shows VDC voltage in the DCMG. From t = 1 s until t = 1.5 s, the battery controller adjusts the VDC voltage to its reference value. It is worth noting that the voltage variations in the DCMG are very small (see Figure 7a). In Figure 7c, PBAT increases slightly up to about 20 W to compensate for source power (PPV). In these conditions, the GVSC also compensates for the imbalance between the PVA and DC load with a PR equal to 350 W (Figure 7d). Therefore, the GVSC helps the battery controller to keep VDC very close to its reference value. As is observed in the previous operating mode, the SC does not deliver any energy due to the low density of power required. Figure 7d shows the QR reactive power to be the same to keep VK constant, as shown in Figure 7b.
To study a critical state, the PVA is disconnected at t = 2 s, as shown in Figure 7c. Once again, PBAT boosts up to 150 W to compensate for the lack of PVA power (Figure 7c). However, this increase is low in comparison to the previous case (Figure 6). This is due to the power (950 W) coming from the grid delivered by the GVSC to DCMG. The GVSC is within the operating limits, as shown in Figure 2.
At t = 2.5 s, the DC load changes to 3200 W. Figure 7a shows that the voltage drop is not very deep. Therefore, the GVSC improves the performance of the battery controller in a coordinated manner. PR power reaches 2750 W, and PBAT power is set at 480 W. It is worth that despite a change in the AC load (see Figure 7d) equal to 3200 W and 3200 var, the GVSC continues delivering the same PR active power. The reactive power given by the GVSC in the time period t = 3.5 s to t = 4.5 s is equal to 6220 var. Again, the GVSC’s powers fall within the operating limits of the inverter.
4.3. Third Mode of Operation
In the third mode of operation, the DCMG system operates without HESS and, only the GVSC is the Gen terminal. The DCMG is no longer be islanded from the grid and, as a result, all power to compensate is given or absorbed by the grid through the AC–DC converter. The generating powers of the PVA and those of the load consumption connected to the DCMG are shown in Table 4.

Table 4.
Mode of operation 3.
As seen in the previous modes of operation, the AC load increases its active power and reactive power from 1000 W and 1000 var to 3000 W and 3000 var, respectively.
In Figure 8c. the power demanded by the active elements connected to the DCMG and the power generated by the PVA are shown, which have been initially simulated at a temperature of 25 °C and an irradiance of 300 W/m2, both of which are gradually reduced at 0.5 s and 1.5 s to 200 W/m2 and 0 W/m2, respectively. Notably, in this period of time, the VDC voltage is regulated by the GVSC, as shown in Figure 8a,d. At t = 1 s, the GVSC absorbs energy from the general grid to compensate for the difference between demand and generation within the DCMG. The power delivered by the grid to the DCMG is 370 W (see Table 4). Thus, the AC–DC converter operates as a Gen terminal and keeps VDC at its nominal value, without the storage devices operating.

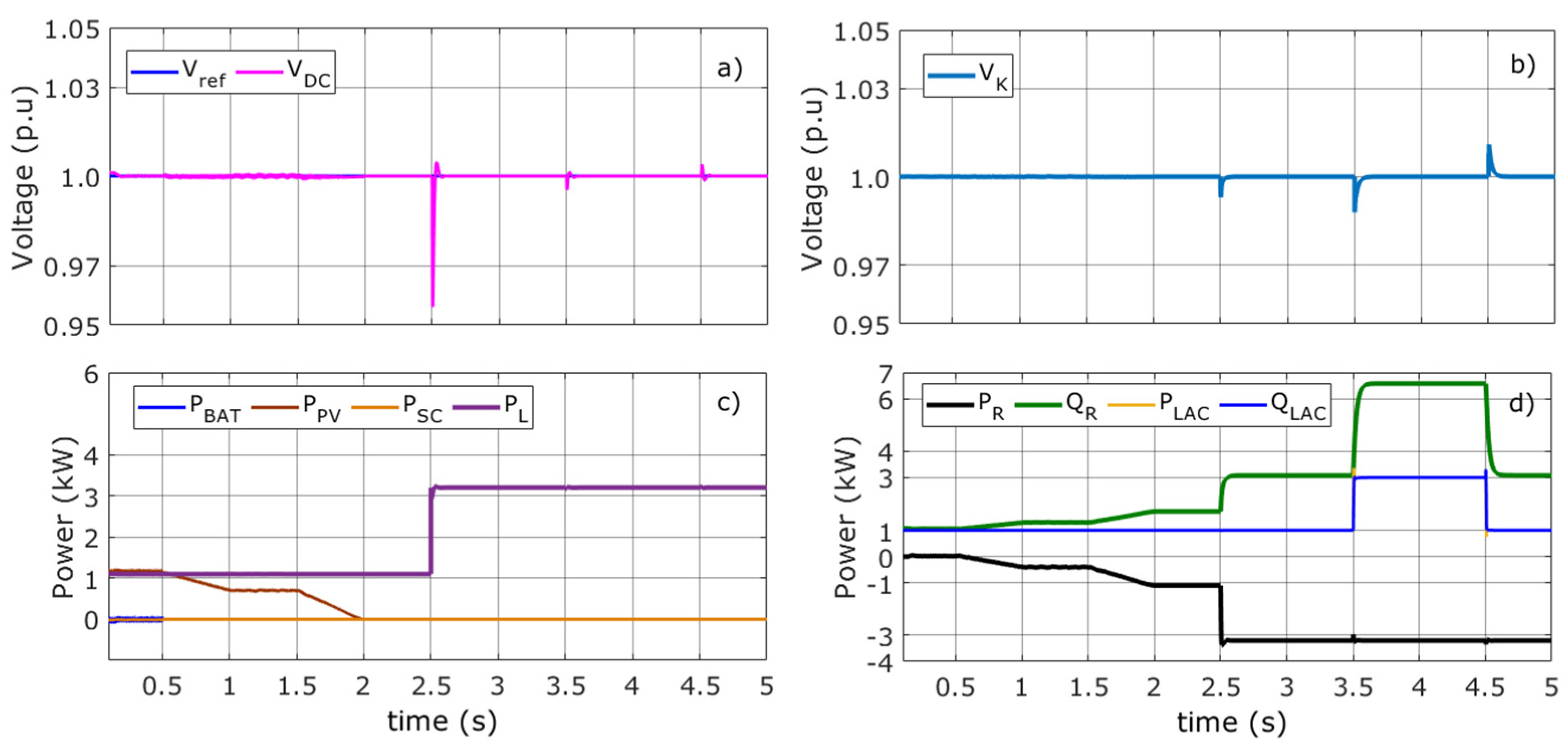
Figure 8.
Voltage and power flow in Mode 3. (a) Reference and DC bus voltage (b) AC voltage (c) Battery, photovoltaic, SC, and load powers (d) Active and reactive VSC powers, active and reactive load powers.
As a critical case, at t = 2 s, the disconnection of the PVA and its consequences for the performance of the other devices of the DCMG are analyzed, as shown in Figure 8b. Here, the absorbed power of the grid is greater due to the disconnection of the PVA (1100 W, see Table 4 and Figure 8d). The performance of the GVSC will be identical to that of the previous case; providing the additional real power it must supply does not result in it exceeding its physical limits. At t = 2.5 s. the DC load is increased to 3200 W. A greater drop in VDC is observed in Figure 8a. However, this variation is quickly regulated by the GVSC controller. In Figure 8d, the power of the DC load (3200 W) is delivered by the grid. The GVSC is capable of responding to this contingency because it is functioning within its operating range without exceeding its most restrictive limit, in this case, the converter voltage.
Figure 8b,d show the variations of VK voltage and powers at the grid. At t = 3.5 s, the AC load changes and, QR is shown to increase slightly due to the increase in PR that the GVSC must provide in the DCMG. With this increase in QR, the VK voltage at the PCC is maintained at its nominal value, as shown in Figure 8b. At t = 4.5 s, the AC load returns to its initial value, as shown in Figure 8d.
4.4. Fourth Mode of Operation
The final mode of operation addresses the most critical case possible, where the grid cannot provide power to the DCMG due to an energy blackout and the storage devices cannot maintain VDC at the nominal value because they also experience an energy blackout, as shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9.
Voltage and power flow in Mode 4. (a) Reference and DC bus voltage (b) AC voltage (c) Battery, photovoltaic, SC, and load powers (d) Active and reactive VSC powers, active and reactive load powers.
In this case, if the generation exceeds the demand, the MPPT of the PVA will cease to function, entering a load-following control system. Thus, the power balance is maintained, thereby maintaining VDC. However, if the PVA supplies more power than that demanded by the DC load, the option of load shedding will be implemented. Table 5 shows the different load changes in DCMG.

Table 5.
Mode of operation 4.
The initial irradiance of PVA is 300 W/m2, which is gradually increased at 0.5 s and 1.5 s to 500 W/m2 and 1000 W/m2, respectively, as shown in Figure 9c. Between t = 0.5 s and t = 3.5 s, the GVSC is the Gen terminal inside the DCMG. At t = 1 s, the power of the PVA is 1980 W. It is worth noting that this power exceeds the power demanded by the DC load. Therefore, excess power is delivered to the grid, as shown in Figure 9d. The DCMG decreases the reactive power (QR) required to keep VK at its nominal value, as shown in Figure 9b,d. This shows that coordination between the grid and DCMG is beneficial for both systems.
At t = 2 s, the power of PVA is 3900 W. Again, this power exceeds the power demanded by the DC load. The excess power delivered to the grid is 2800 W (Figure 9c). Here, the reactive power QR is absorbed by GVSC fall within the operating limits (Figure 2) of the inverter, as shown in Figure 9d. At all times, as Figure 7b shows, the GVSC keeps the VK voltage at its nominal value (1.0 p.u).
At t = 2.5 s, the DC load changes to 3200 W. The power of the PVA is still greater than the power absorbed by the DC load. However, this power is less than that of the previous times. The GVSC supplies 700 W (see Table 5) to the grid. Here, QR has the same value, as shown in Figure 7d.
To study the most critical case in the DCMG, at t = 3.5 s, the GVSC is disconnected from the DCMG. At this point, the PVA control system switches to a load-following strategy. Figure 9c shows this change in the power. The VDC voltage reaches a new operating point (1.02 p.u) slightly away from its reference value because there is no Gen terminal. However, the system remains stable since (6) is satisfied. Here, the power absorbed by DC load is no longer the nominal value (3200 W) but 3300 W, as shown in Table 4.
A partial load shedding (half load) is shown at t = 4 s. Again, the value of the DC voltage is increased to 1.082 p.u. This voltage distorts the actual value of the power absorbed by the DC load. Therefore, the load is halved again. The VDC voltage reaches 1.14 p.u. Although the system is stable, the voltage values are not acceptable. The load shedding without a slack bus does not work correctly, as shown in Figure 9a,c.
5. Conclusions
This paper presented a DC microgrid (DCMG) topology with a hybrid energy storage system consisting of a battery and a supercapacitor, which can operate in both an interconnected system through a grid-tied voltage source converter (GVSC) and in islanded mode. In different grid events such as the disconnection of passive elements as occurs in a load change, it has been shown that the DCMG has very pronounced voltage variation. However, when the DCMG is connected to the grid, the GVSC helps the DCMG to regulate the DC voltage without steep voltage drops and enables the whole system to remain stable. Therefore, the GVSC was shown to improve the performance of the battery controller via coordinated control. In addition, the GVSC supports the AC voltage at the PCC without reducing the operating capacity of the DCMG and without exceeding the converter voltage. Finally, the results show that load shedding without the Gen terminal does not work adequately: the DC voltage values are not acceptable due to the lack of voltage regulatory control. This final point could be the subject of potential future research.
Author Contributions
Data curation, J.L.R.-A. and S.A.; Investigation, M.M.-D., É.F.-M. and E.R.T.; Methodology, M.M.-D., É.F.-M. and E.R.T.; Validation, J.L.R.-A. and S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
This study did not report any data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Farrokhabadi, M.; Canizares, C.A.; Simpson-Porco, J.W.; Nasr, E.; Fan, L.; Mendoza-Araya, P.A.; Tonkoski, R.; Tamrakar, U.; Hatziargyriou, N.D.; Lagos, D.; et al. Microgrid Stability Definitions, Analysis, and Examples. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2020, 35, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justo, J.J.; Mwasilu, F.; Lee, J.; Jung, J.-W. AC-microgrids versus DC-microgrids with distributed energy resources: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 24, 387–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parhizi, S.; Lotfi, H.; Khodaei, A.; Bahramirad, S. State of the Art in Research on Microgrids: A Review. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 890–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.-J.; Park, J.-W.; Chung, I.-Y.; Moon, S.-I.; Kang, S.-H.; Nam, S.-R. Power-Sharing Method of Multiple Distributed Generators Considering Control Modes and Configurations of a Microgrid. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2010, 25, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocabert, J.; Luna, A.; Blaabjerg, F.; Rodriguez, P. Control of Power Converters in AC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 27, 4734–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, P.; Meng, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Multi-source coordinated control strategy based the battery SOC for islanded DC microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2017 20th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Sydney, Australia, 11–14 August 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Xu, L.; Yao, L. DC Voltage Variation Based Autonomous Control of DC Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2013, 28, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, D. Control and Operation of a DC Microgrid with Variable Generation and Energy Storage. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2011, 26, 2513–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Xu, L. Autonomous DC Voltage Control of a DC Microgrid with Multiple Slack Terminals. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2012, 27, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Francois, B. Energy Management and Power Control of a Hybrid Active Wind Generator for Distributed Power Generation and Grid Integration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2011, 58, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, D.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, M.; Deng, F.; Buja, G. Distributed Cooperative Control for Multiple DC Electric Springs with Novel Topologies Applied in DC Microgrid. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 10th International Symposium on Power Electronics for Distributed Generation Systems (PEDG), Xi’an, China, 3–6 June 2019; pp. 648–652. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, M.U.; Khan, M.M.; Hashmi, K.; Habib, S.; Jiang, H.; Tang, H. A Control Methodology for Load Sharing System Restoration in Islanded DC Micro Grid with Faulty Communication Links. Electronics 2018, 7, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sathishkumar, R.; Kollimalla, S.K.; Mishra, M.K. Dynamic energy management of micro grids using battery super capacitor combined storage. In Proceedings of the 2012 Annual IEEE India Conference (INDICON), Kochi, India, 7–9 December 2012; pp. 1078–1083. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, S.; Devaraj, D. Simulation and analysis of stand-alone photovoltaic system with boost converter using MATLAB/Simulink. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Circuits, Power and Computing Technologies [ICCPCT-2014], Nagercoil, India, 20–21 March 2014; pp. 814–821. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.-K.; Wen, C.; Xu, Q.; Wang, Y.-W. Resilient Control and Analysis for DC Microgrid System under DoS and Impulsive FDI Attacks. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2021, 12, 3742–3754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shania, F.; Rajakaruna, S.; Ghosh, A. Static Compensators (STATCOMs) in Power System; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Villalva, M.G.; Gazoli, J.R.; Filho, E.R. Comprehensive Approach to Modeling and Simulation of Photovoltaic Arrays. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2009, 24, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Yang, Y.A. Photovoltaic-Based DC Microgrid System: Analysis, Design and Experimental Results. Electronics 2020, 9, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aentron GmbH. Off-Grid-Lithium-Ion Battery System. Available online: http://www.aentron.com/ (accessed on 15 June 2021).
- Neto, P.J.D.S.; Barros, T.A.; Silveira, J.P.; Filho, E.R.; Vasquez, J.C.; Guerrero, J.M. Power management techniques for grid-connected DC microgrids: A comparative evaluation. Appl. Energy 2020, 269, 115057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Kang, R.; Cao, J.; Yang, T. Primary and secondary control in DC microgrids: A review. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2019, 7, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kollimalla, S.K.; Mishra, M.K.; Narasamma, N.L. A new control strategy for interfacing battery supercapacitor storage systems for PV system. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Students’ Conference on Electrical, Electronics and Computer Science, Bhopal, India, 1–2 March 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kollimalla, S.K.; Mishra, M.K.; Ukil, A.; Gooi, H.B. DC Grid Voltage Regulation Using New HESS Control Strategy. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 8, 772–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).