Abstract
A large increase in distributed generation integrated within power system networks has resulted in power quality challenges and in the need to resolve complex system faults. The monitoring of the real-time state of the power parameters of the transmission and distribution grid helps to control the stability and reliability of the grid. In such a scenario, having current monitoring equipment that is flexible and easy to install can always be of great help to reduce the price of energy monitoring and to increase the dependability of a smart grid. Advances in magnetic sensor research offer measurement system accuracy that is less complex to install and that can be obtained at a lower less cost. Tunneling magnetoresistive (TMR) sensors can be used to measure the AC current by sensing the magnetic field that is generated by the current-carrying conductor in a contactless manner. This paper illustrates the results of a thorough investigation of factors that can influence the performance of the TMR sensors that are used for the current phasor measurements of a single-phase AC current application, such as the effects of distance, harmonics, and conductor insulation.
1. Introduction
The need for power quality measurements at various nodes in power system distribution and transmission networks is increasingly gaining importance because of the increasing number of distributed generations being added to the network. The time-stamped power parameters at each node are where multiple generations are connected to the power grid. Advances in electronics have transformed the old electromechanical meters into sophisticated phasor measurement units (PMU) that are able to be installed at the substations and power generation sites to provide comprehensive information about these time-stamped power parameters [1,2,3]. These PMUs need transducers to sense the currents and voltages of the grid. Conventional current transformers (CTs) are widely used since they have been used as current transducers for PMUs for many decades. These CTs are core wound and are appropriate for high-voltage applications when they are inside of oil filled containers, and therefore, they are prone to damage because of the temperature, moisture, and the faults that can take place at the substations. If their secondary channels are left open, then they can generate infinite potential across the open secondary terminals and that can explode and cause serious damage. The installation and maintenance of conventional CTs requires a long-term outage at the substation, increasing the cost of operations and affecting the performance of the substation. Moreover, they are susceptible to saturation because of the asymmetrical and symmetrical fault currents that can occur if their ratios and accuracy class are not adequately designed [4]. Higher accuracy demands a higher CT ratio and therefore higher costs [4,5]. As a result, digital CTs are a new alternative for researchers and industries [6,7,8,9,10]. In modern smart grids, compact and noninvasive current measurement sensors have proven to be beneficial for operation and cost efficiency. With the benefit of being noninvasive, these sensors can be installed at any required location in the power distribution and transmission network, including in substations as well as in distributed generation (DG) facilities; thus, it is possible to acquire an accurate real-time state of the entire power grid.
Recently, digital sensors that are based on advanced electronics such as Rogowski coils, Hall sensors, and digital fiber CTs have been researched in order to determine their application in current measurement processes [6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. These sensors are a good replacement for conventional CTs, but they cannot be applied to a wide frequency range or higher magnitude AC currents. The recent discovery of magnetoresistive (MR) sensors has encouraged many researchers to explore alternative current measurement and fault detection methods [13,14,15,16]. The work that has been conducted in these studies does account for any of the effects resulting from the presence of conductor insulation on the magnetic field that can be sensed by the sensors. Research based on the application of sensors to high-voltage transmission lines [16] has not covered the effect of various factors such as harmonics, the distance from the conductor, the sensor quality, and the effect of sag in long transmission lines as of yet. M. Shafiq et al. presented a study discussing electrical insulation diagnostics using magnetic sensors [15] where the defects in the insulation were studied with the help of magnetic sensors. Moreover, these studies used basic MR sensors that had the design and manufacturing limitations of hysteresis and sensitivity. In this research, a NVE TMR sensor that has high sensitivity and that is capable of sensing an AC current of up to 300 A is used. The price of this sensor is lower than that of the conventional CTs and is comparatively the same as that of Halls sensors [7]. To validate the applicability of this sensor for current measurements, it is important to study its performance based on various aspects such as its ability to accurately sense the magnetic field from particular distances in the presence of additional frequencies other than 60 Hz as well as in cases where there are insulated cables and bare aluminum conductors. The calibration of the TMR sensor that is based on these factors will help to achieve the maximum accuracy in terms of current measurement. This objective can be accomplished by testing these sensors in an experimental setting. This paper focuses on the experimental validation, calibration, and analysis of the effect of various factors on the performance of sensors.
Section 2 of this paper illustrates the current measurement method with the help of a magnetic field for a single-phase application. Section 3 describes the experimental set up that was used to test 12 TMR sensors in a resistive single-phase circuit that comprises a medium voltage aluminum conductor of the size 4/0. Section 4 provides the results and discussion regarding the response of the TMR sensors to the above-mentioned factors influencing the calibration process and measures that can be taken to increase the current measurement accuracy. Finally, the conclusions discussing the performance of all of the sensors are included in Section 6.
2. Current Measurement Using Magnetic Field
The magnetic field that is generated by a current carrying overhead conductors depends on the type of the current that generates the field. In case of a low-frequency alternating current with a medium- and high-voltage distribution and in transmission line networks, the Biot–Savart law can be applied to determine the magnetic field intensity, H, by assuming the conductor of an infinite length carrying a low-frequency current, such as a power frequency of 60 Hz. In such a case, the mathematical expression is given as
In the above equation, “I” is the current flowing through the conductor, and “d” is the distance from the center of the conductor to the point of measurement of the magnetic flux density. In the above equation, is the constant of proportionality. The magnetic flux density, B is given by the multiplication of the magnetic field intensity with the permeability of air and is expressed as
where μ0 is the permeability of air as a medium. Since the frequency is low (60 Hz), the time-varying magnetic field can be considered as a quasi-static magnetic field, and therefore, the effect of the resistivity of the conductors and the shielding effects caused by eddy currents can be assumed to be negligible.
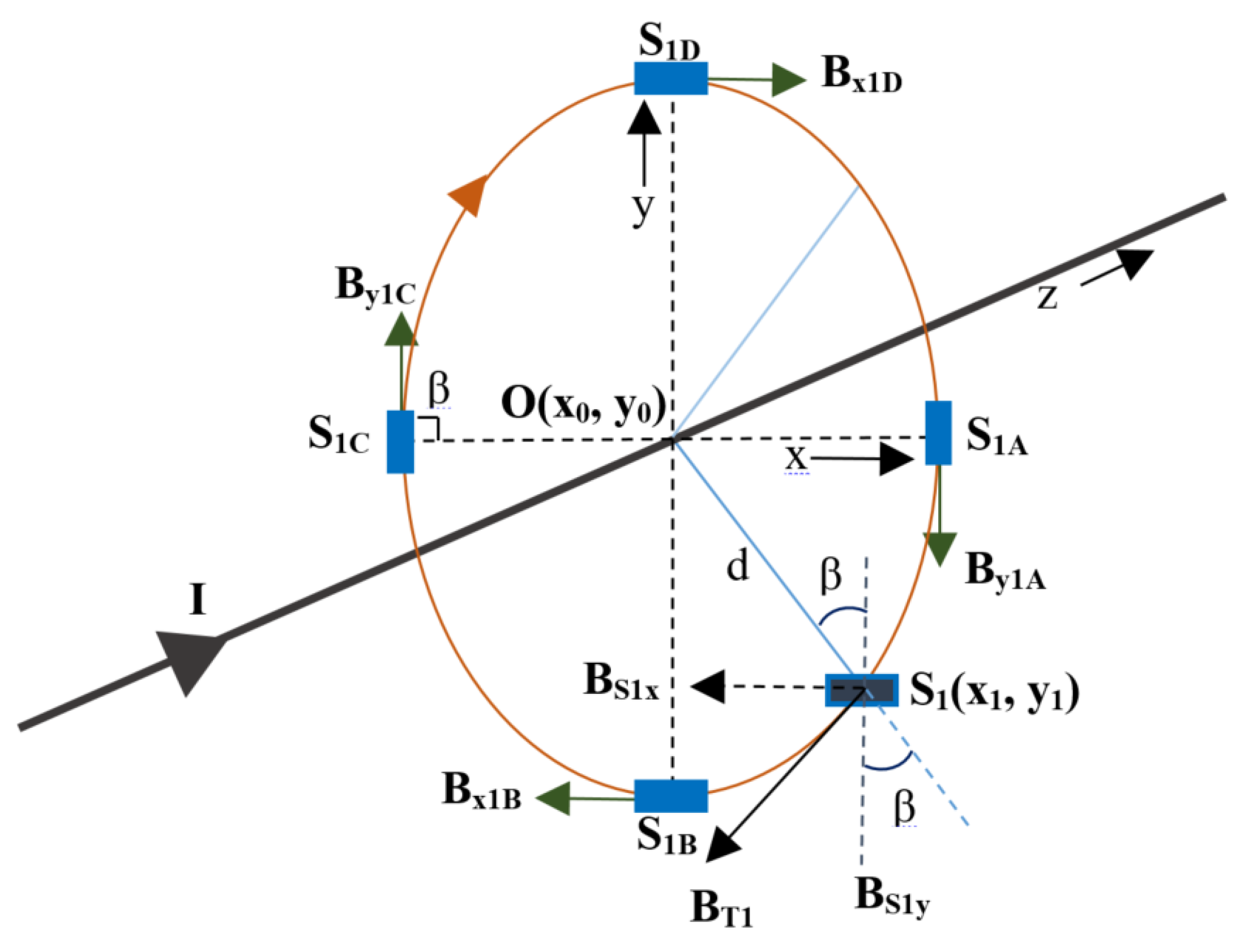
The magnetic field measurements can be considered by using the Cartesian coordinate system with the magnetic field components in the x, y, and z directions. Figure 1 illustrates a single-phase conductor with the magnetic field in the clockwise direction and a sensor, S1. This sensor is placed at a distance, “d”, from the center of the conductor at an angle of incidence, “β”. The magnetic field in the z-direction is parallel with the axis of the conductor or the current flow and can therefore be assumed to be negligible. Thus, at any angle of incidence, the magnetic field will only have two components, Bx and By. If it is assumed that the coordinates of S1 are (x1, y1) when the center of the conductor is at O(x0, y0), then the magnetic field that is sensed by the sensor at this location can be given as
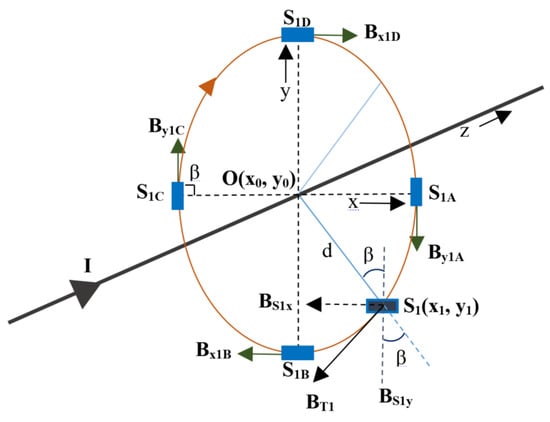
Figure 1.
TMR sensor placed at various locations (depicted by solid rectangles) around a single-phase conductor.
In the above equations, is the unit vector in the y direction, is the unit vector in the x direction, and β is the angle. The total magnetic field at the sensor location S1 is BT1 and is given as:
The magnetic field that is sensed by the sensor at S1 depends on the angle of orientation and the location. This field will be at its maximum if the angle β is 90°. It has been already demonstrated in [17] that the maximum magnetic field component will be achieved if the tangential component of the sensor is matched with that of the magnetic field, therefore bringing it to zero. By doing so, the component will produce the tangential component, and the will produce the perpendicular component. Thus, when is 90°, only one component is required. This will make the field resolve the x and y components to one single component and provides the maximum value of the magnetic field. The possible locations for the sensing maximum magnetic field for S1 can be at any angle of incidence, with one shown at angle β and other four locations at 90° such as S1A, S1B, S1C, and S1D. Following this theory and Equations (3) and (4), the tangential component of the magnetic field at location S1 will as By1A. Similarly, the tangential component of the magnetic field for the same sensor if placed at location S1B will be given as Bx1B.
The magnetic field that is sensed by the sensors is a function of the distance (d), the angle of incidence (, and the magnitude of current (I) and can be expressed as . By placing the sensors at various locations, the magnetic field can thus be sensed by multiple sensors at various locations b. If we assume the locations of the sensors S1, S2, … S12 to be at P1, P2,… P12 then the resultant magnetic field is expressed as:
The use of multiple sensors improves the measurement accuracy compared to a single sensor, and this has been researched and demonstrated by various groups in other research studies [13,14,15,16]. Additionally, it has been demonstrated that due to practical issues and manufacturing imperfections, the output of the sensors does not exactly follow the above-mentioned theoretical equations. Therefore, it becomes important to calibrate and prepare the sensors to improve the accuracy of the current measurements.
Current Calculation from Faraday’s Law
Equation (2) can be used in reverse to calculate the current if the magnetic field that is generated by the unknown current source is measured. This concept was tried and tested in the preliminary stage of the present research by conducting an experiment using a single-phase circuit where only one sensor was employed at a distance of 7 mm and 15 mm. single-phase AWG # 4/0 aluminum conductors with and without insulation with a resistive load of 1 kW were used, and the magnetic field was measured for the series of currents that passed through the conductor. The analog output of the sensor was then converted to the magnetic field density using the sensitivity relation of the sensor, and the multiplying factors (MFs) were calculated using Equation (2), which provided the current for each measurement, with the reverse equation expressed as:
Using SI units for the variables and the permeability value of the free space, the theoretical MF for distance, d = 7 mm is 318.18, and for d = 15 mm, it is 618.81. Using these MFs and the magnetic field values that had been converted from the analog voltage outputs of sensors for both the 7 mm distance and 15 mm distances, the currents were calculated for No-Insulation (NI) and With-Insulation (WI) cases. The percentage error was calculated by comparing these currents with a current transformer (CT) output (CT ratio = 1000:1). The resulting percentage errors are shown in Table 1. The percentage errors were observed to be high for the 7 mm NI case and were shown to be very high for the 15 mm, WI case. There is a big dissimilarity between the results of the NI and WI case even though they are for the same distance case and for the same sensor. This is because of the presence of insulation on the conductor that is affected by the permeability and because the free space permeability no longer applied.

Table 1.
Results of sensor S1 using Faraday’s law for various cases.
From the results of this method, it was inferred that a MF for a distance of 7 mm is not applicable to NI and WI cases nor was it applicable for the varying magnetic fields that were produced by a range of currents. The errors were beyond the acceptable limits, and therefore, the theoretical method that could be used to find the current based on the magnetic field proved to be ineffective. It became clear that other methods for sensor calibration and to test sensor performance under various scenarios need to be explored.
3. Experimental Setup
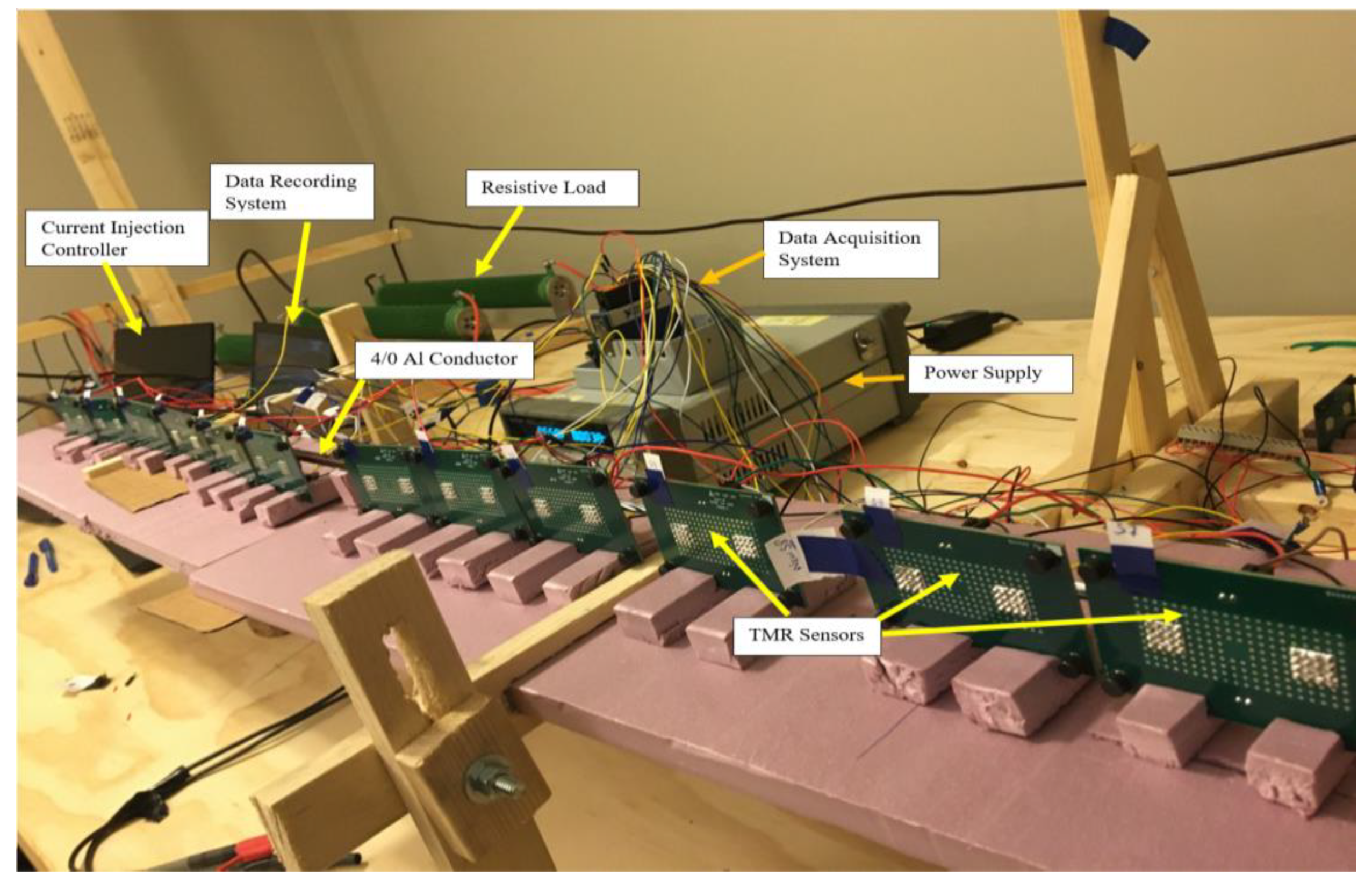
For this experiment, twelve TMR sensors and a multi-stranded XLPE aluminum cable of size 4/0 AWG was selected. The experiment was performed for a range of magnitudes of alternating currents that ranged from 1 A to 29 A, with sensors at various distances from the conductor. This was achieved by placing the sensors at a right angle from the conductor at the distances 7 mm, 15 mm, 25 mm, and 35 mm. One of the performance factors was the effect of insulation on the ability of the sensor to detect the magnetic field. Therefore, the insulation on some parts of the cables was removed in order to use the same cable as a bare aluminum conductor. Six sensors are placed near the bare part, and the remaining six sensors were placed near the insulated part of the conductor during the experiment. The sensors were then interchanged to the record magnetic fields that were sensed for the same current value. Figure 2 shows the arrangement of the experimental setup for 12 sensors.
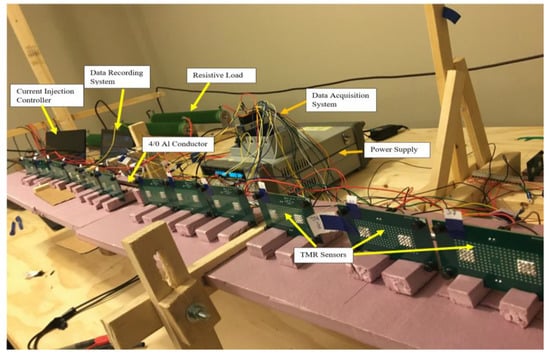
Figure 2.
Experimental setup with twelve sensors.
The (TMR) sensors are one of three types of anisotropic magnetoresistance sensors [18,19]. These sensors have multilayer ferromagnetic electrodes that are separated by a thin insulating barrier that helps the electrons tunnel from one layer to another under the application of a magnetic field. The tunneling effect depends on the orientation of the magnetic field. Under the application of a parallel magnetic field, the magnetoresistance reduces and results in electrons tunneling from one layer to another. When there is an anti-parallel magnetic field, the electrons will have alternating strong and weak scattering effect, resulting in a highly magnetoresistive state [13]. The TMR sensors that were used in this research operate at a voltage of 5.5 VDC. Their sensitivity is 20 mV/V/mT typical. This sensitivity is inclusive of the gain because of the sensor, the Wheatstone bridge, and all of the electronic components that are a part of the circuit that is embedded onto the sensor chip. This means that for various current values, the magnetic field that is produced will be equal to 110 times the voltage output of the sensor.
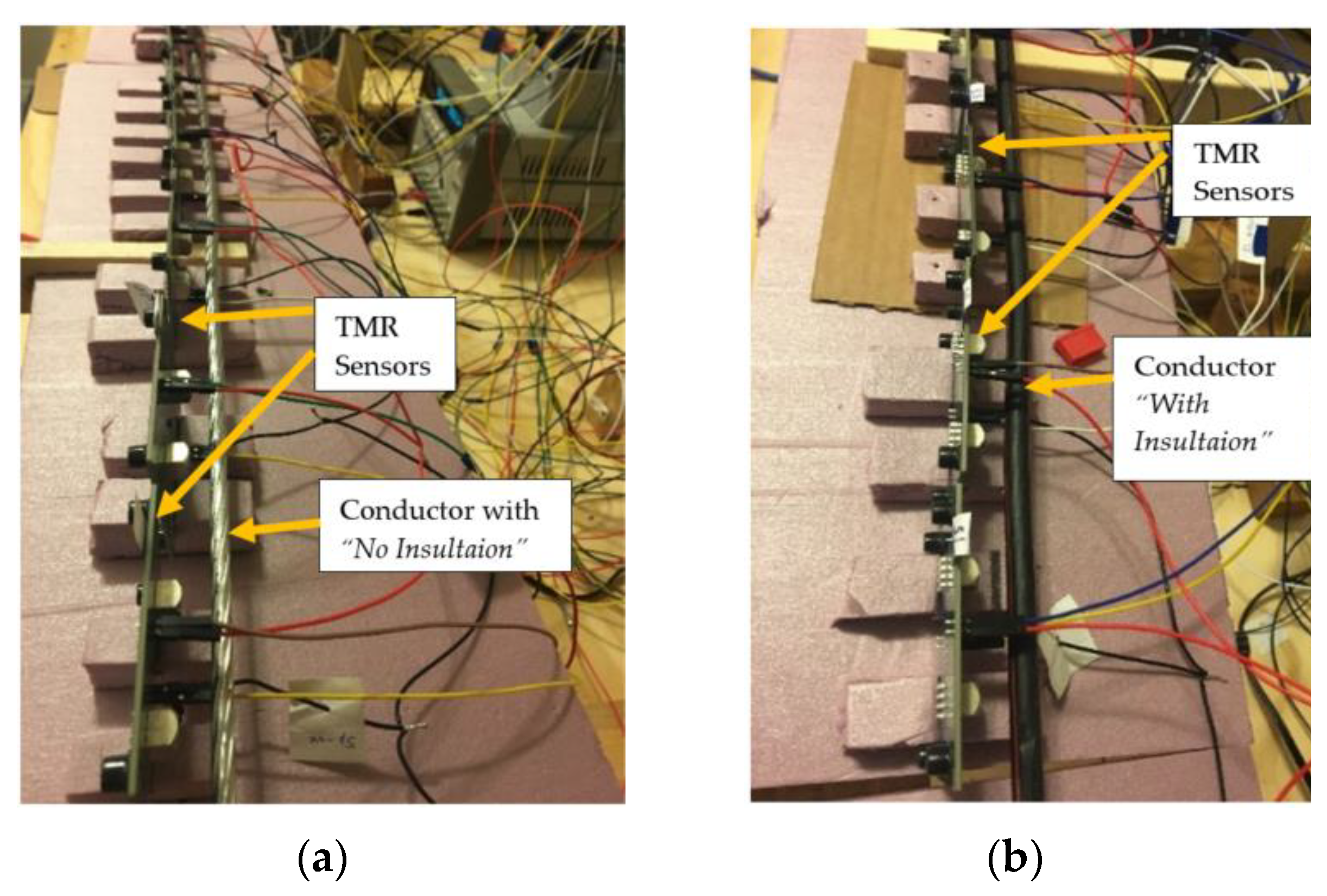
The experiments were conducted in two sets, each with five stages and four parts. These stages and parts were repeated for the No-Insulation and With-Insulation cases, as shown in Figure 3a,b. In the first set and during Stage 1 of Part I, twelve sensors were placed at a distance of 7 mm from the center of the conductor, with six being located near the insulated part and six being located near the non-insulated part of the conductor. An alternating current with a frequency 60 Hz ranging from 1 A to 29 A with a step of 0.5 A was injected using an Omicron CMC356 current injection set [20]. The sensor output and the CT output were recorded using the NI cDAQ-9174 data acquisition system [21]. The sampling rate was kept at 7.2 kHz, and 10,000 samples were recorded for each value of the injected current. Thus, the outputs were recorded for each current value from 1 A to 29 A. For the second stage, the current injection setting was changed to inject a current of the second harmonic frequency. Thus, for Stage 2, the currents ranging from 1 A to 29 A had a second harmonic component, and the same steps were repeated as they were in Stage 1, and the outputs were recorded. For Stage 3, the injected currents were of the third harmonic, and this pattern continued until Stage 5, where fifth harmonic currents were injected. The completion of these steps denoted the end of Part I of the experiment. For Part II, the distance of the sensor was changed from 7 mm to 15 mm, and all five of the states that were described in Part I were repeated. This procedure continued for Part III, which took place at a distance of 25 mm, and for Part IV, wherein the sensors were located at a distance of 35 mm from the center of the conductor. The completion of Part IV denoted the end of Set 1. In Set 2, the location of the sensors was interchanged for the bare and insulated part of the conductor, and all five stages and four parts were repeated in the same manner as explained above for Set 1. This resulted in a total of 1160 variations of the experiment, and therefore, the same number of data files were recorded for the further analysis and calibration of the sensors. Once the calibration was completed using a part of the recorded data, the sensors were tested using the remaining recorded data to verify the calibration results.
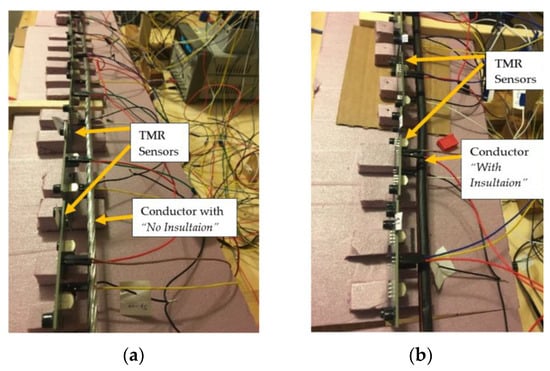
Figure 3.
Arrangement of the sensors for (a) No-Insulation portion and (b) With-Insulation part of the conductor.
While performing this experiment, measurement uncertainty was addressed. To reduce measurement errors during experimentation, the specifications of all of the devices that were involved in the experiment were checked for their performance accuracy. For the current generation test set, Omicron CMC 356 was found to have a resolution of 1 mA, an accuracy of less than 0.05% during magnitude amplification, and a 0.001° resolution for phase amplification. The phase error at 60 Hz was 0.02° for the voltage and 0.05° typical for the current. This test set had 1μs absolute timing accuracy for both voltage and current. The NI cDAQ-9174 A/D convertor (National Instruments, Austin, TX, USA) was found to have a timing resolution of 1 ns and a timing accuracy of 50 ppm for the sample rate, with a maximum sampling rate of 500 kHz. To minimize errors from occurring when recording the outputs from the sensor, the sampling rate was selected to be 7.2 kHz/channel, which is well below the limit of 25 kHz/channel. To minimize errors caused by increases in the temperature, the measurements were taken with a time gap of 1 min within each current magnitude for every stage in each part explained above. Thus, the measurement uncertainty was minimized as much as possible.
4. Performance Results and Analysis
The main objectives of testing the performance of these TMR sensors were to study and analyze the:
- Effect of variation on the sensor quality that is caused by any slight variation that may occur during manufacturing;
- Effect of distance on sensing the magnetic field that is generated by the current-carrying conductor;
- Effect of insulation and the absence of insulation on magnetic field sensing;
- Effect of harmonics on the current estimation accuracy.
To achieve these objectives, the data that were measured during the experiment for all of the sensors for all 1160 cases described in the previous section was used. The sensor outputs were converted from voltage to magnetic field density using the sensitivity conversion formula given by the manufacturer. In order to calculate the currents from these magnetic fields, these sensors needed calibration, as it was determined as well as explained in Section 3 that the measured magnetic field did not exactly obey the theoretical expressions provided by Equation (2) in Section 2. The purpose of calibration is to determine the multiplying factor that can convert the measured magnetic field into the injected current. The availability of offline data in a discrete form made it possible to apply digital filtering methods such as the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) method to obtain the multiplying factors. This method applied Discrete Fourier transform directly to any of the unfiltered data that may have had a DC offset. For this analysis, the data samples were used to estimate the current phasors using the DFT algorithm, which also calculated the multiplying factor (MF) for each case. A separate set of data was gathered by repeating the experiments for all 1160 cases, and 5000 samples were used from each case to test of the MFs that were obtained using previous experiments. The sampling rate of 7.2 kHz for the measurement of the sensor output helped to obtain sufficient samples to apply the orthogonal functions to in the DFT algorithm so as to complete the calculation of the phasors for one complete cycle, and this method was then repeated accordingly for the rest of the data. The multiplying factors that were obtained during the testing and validation phase were used for the final verification stage of the calibration. This was achieved by repeating a few selected cases and by computing the current phasors using previously obtained multiplying factors.
A computational program was developed in MATLAB to implement the DFT algorithm and to perform the steps that were mentioned above for all 1160 cases. The algorithm computed the multiplying factors for the individual currents for each case, and these multiplying factors, along with the resulting calculated current phasors, were stored in separate data files. For analysis, a separate MATLAB program was developed that was able to read these data files for further analysis. The following subsections provide a detailed analysis of the performance of each sensor, the effect of the sensor quality, the effect of distance from the conductor, harmonics, and the state of insulation. The following subsections provide the results of the analysis that are based on each factor.
4.1. Sensor Quality
The performance uniformity for each sensor is worth investigating because these sensors are manufactured on microscale in order to arrange the layers of magnetoresistive material and to be integrated with an internal gain with Whetstone bridge configuration. This is an important step to account for because this will provide the capacity of an individual sensor to sense the same magnetic field that is generated by a finite current in the conductor. Moreover, the results of the algorithm in terms of the multiplying factor for each sensor will depend on its characteristics and measured magnetic field. Consequentially, this will help to define further steps by determining whether the same multiplying factor applies to all sensors or whether each sensor has their individual multiplying factor in order to calculate the current from the same magnitude of the magnetic field. Therefore, this section focuses on the analysis and the test results that were obtained from the sensors through various factors, such as variation in the multiplying factors, the amount of magnetic field sensed at the same distance for the same conductor situation, and the current that was able to be estimated with the help of the DFT algorithm. The following subsections discuss the performance details of each sensor accordingly.
4.1.1. Multiplying Factors of Sensors
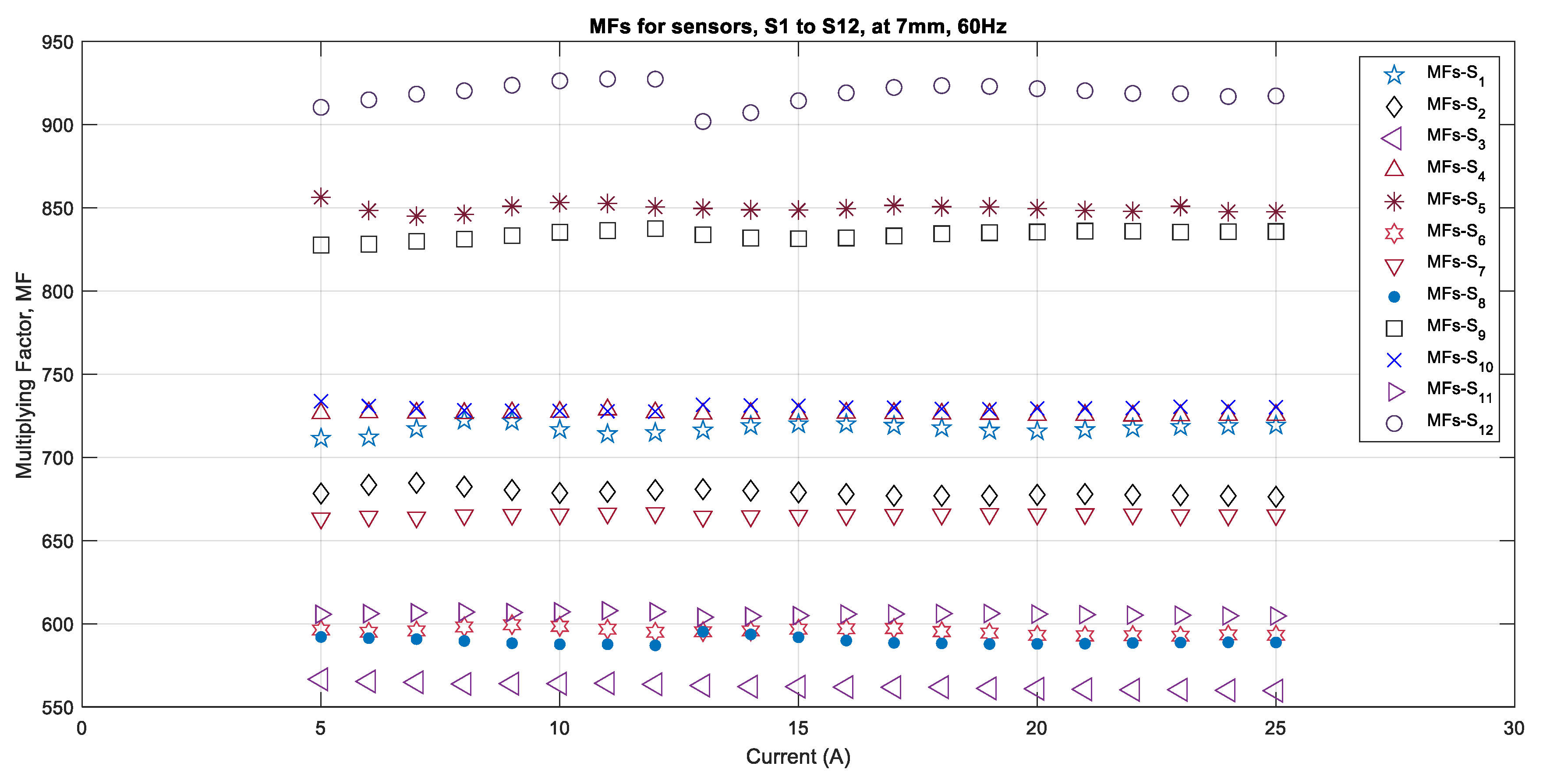
To study the effect of sensor quality, it was determined that measurements would be taken for all of the sensors that were placed the distance that was the closest to the source and for the fundamental frequency of 60 Hz. The algorithm calculated the multiplying factors by using the DFT algorithm for each sensor and for each current value of 60 Hz that varied in peak value from 1 A to 25 A in steps of 1 A when the sensors were placed at a distance of 7 mm from the center of the conductor. Since the sensors have the capacity to measure up to 300 A, it was found that their sensitivity for 1 A current is very low. Therefore, it was decided the currents ranging from 5 A to 25 A would be considered for performance analysis. The multiplying factors that were obtained for the twelve sensors are shown in Figure 4. It is evident from this figure that each sensor has a different multiplying factor (MF) and that it varies from 565 to 921 for the same amount of source current. Three sensors, S6, S8, and S11, have MFs in that are in the close range from 590 to 616. Similarly, sensors S1, S4, and S10 show values that are close to each other and that are in the range from 716 to 738. Sensors S2 and S7 have MFs that are almost the same, with a variation of 15. Only sensor S12 showed a very high MFs value for all currents ranging from 5 A to 25 A, and the individual MFs for each current were less consistent compared to all of the other sensors. It is also evident from Figure 4 that the MFs become very consistent when there is less variation for the increasing value of current from 10 A onwards. It is therefore anticipated that all of the sensors will provide consistent performance for all of the magnetic fields that are generated by currents that are higher than 20 A.
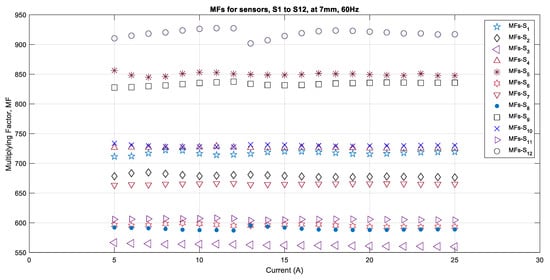
Figure 4.
Multiplying actors for all sensors for case of 7 mm, 60 Hz.
4.1.2. Sensor Outputs
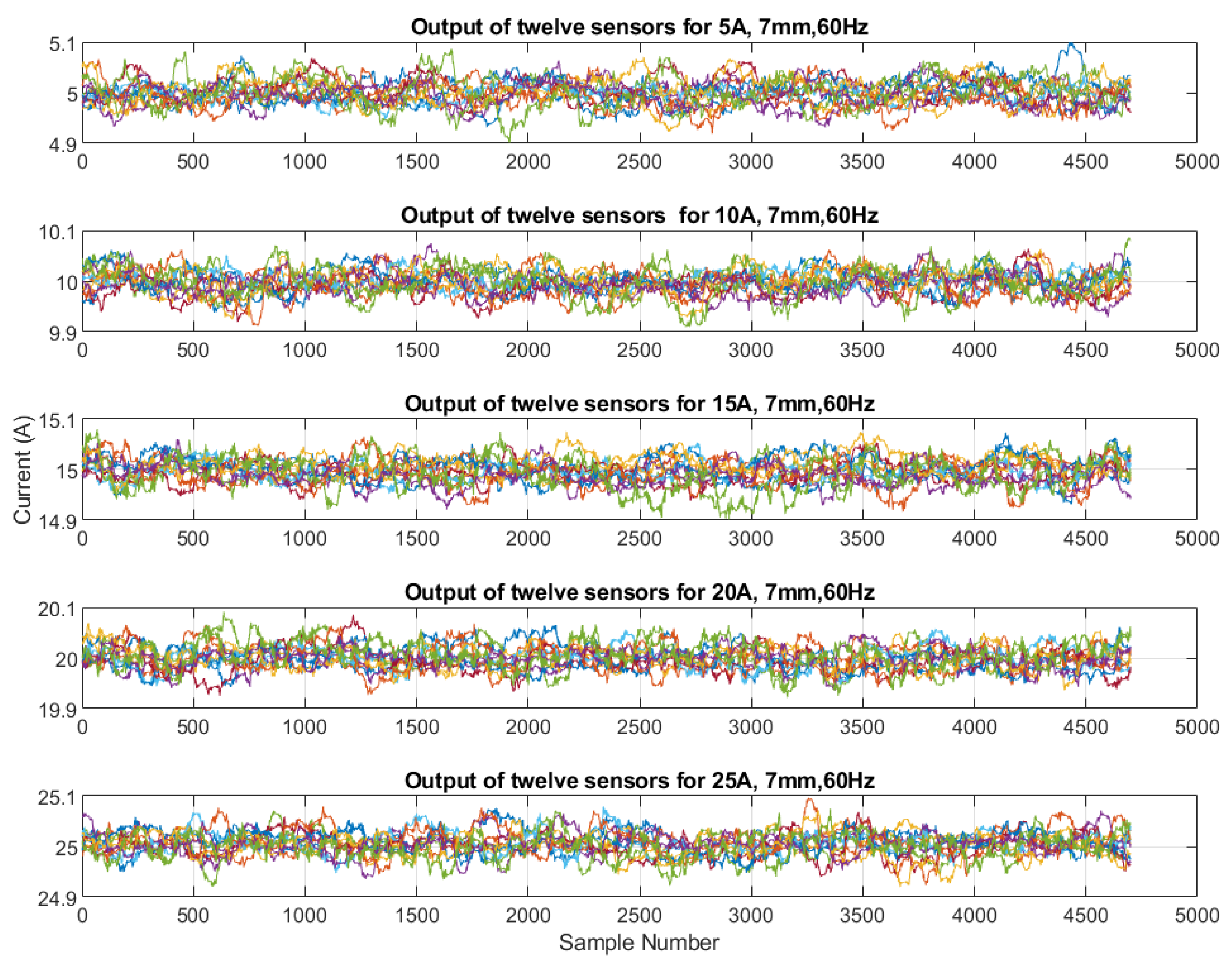
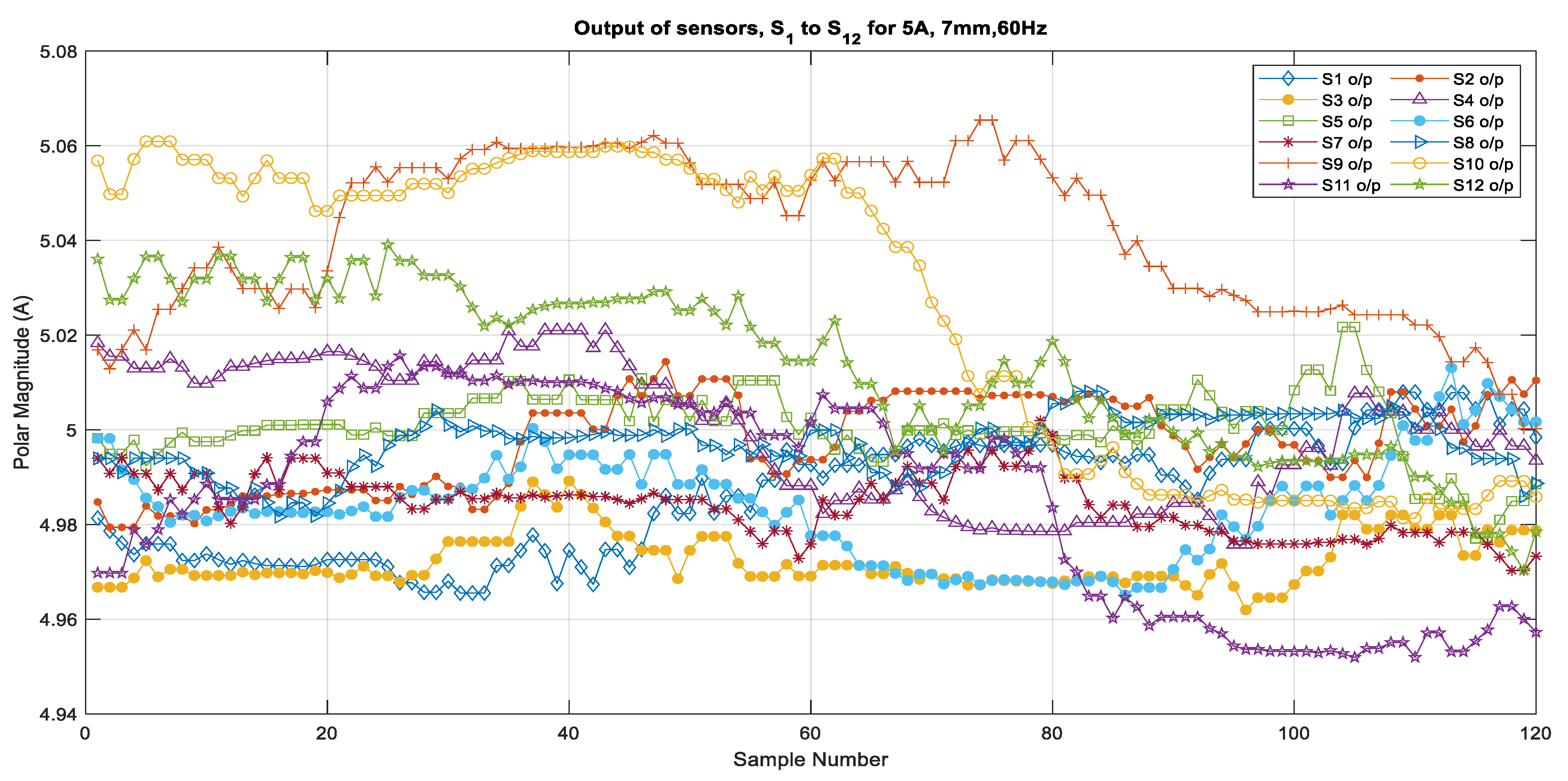
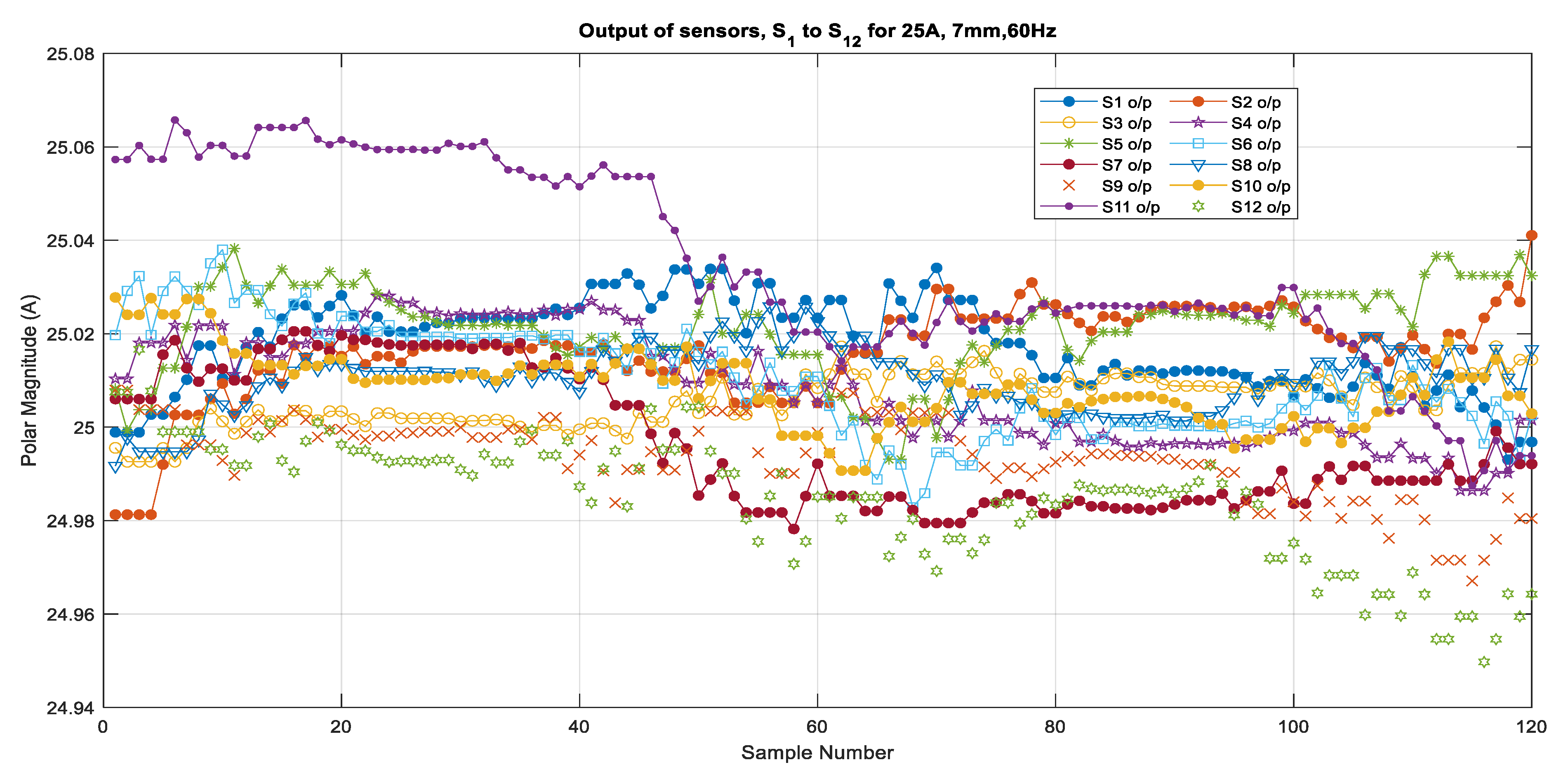
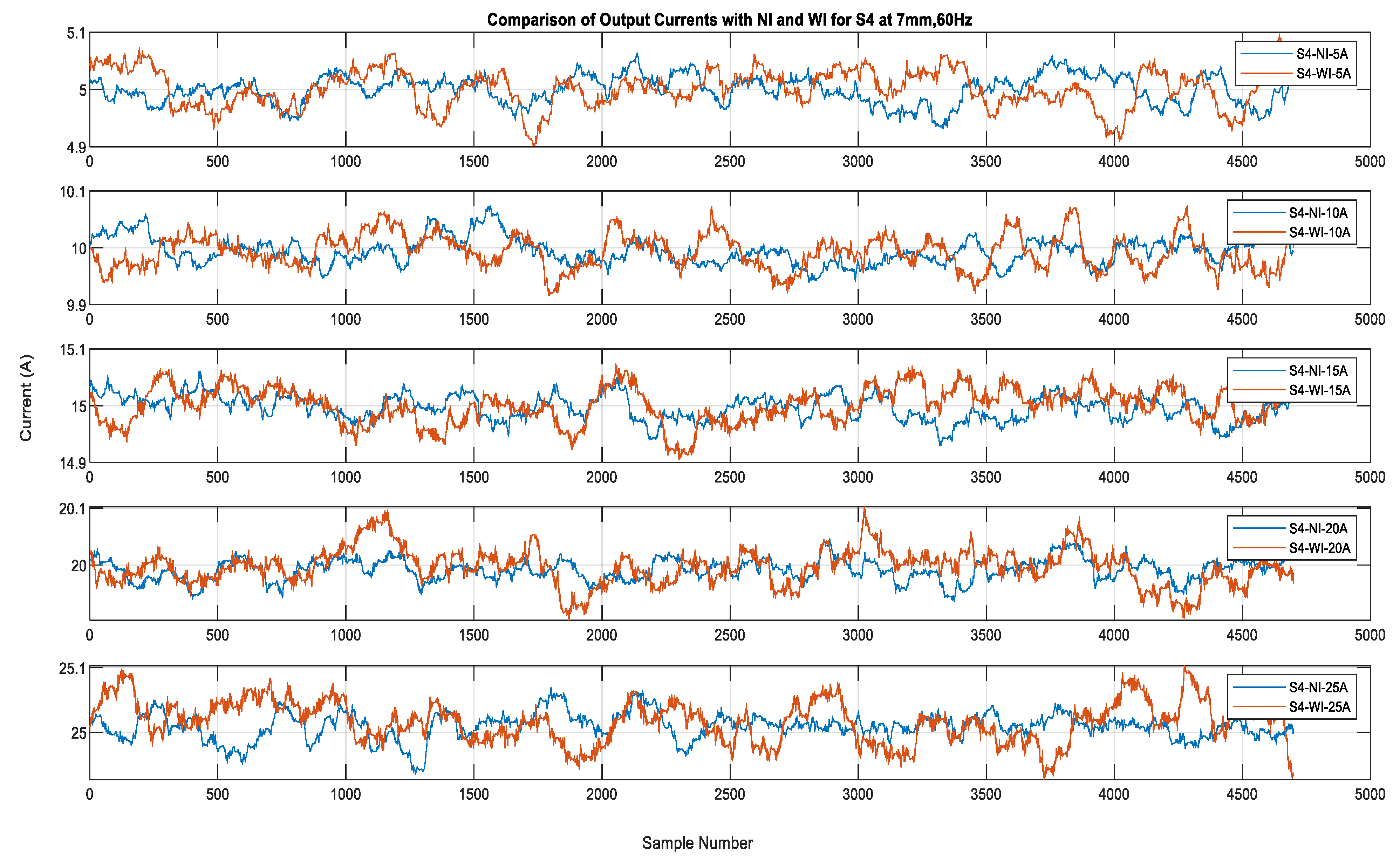
Based on the calibration for individual sensors, the current output was calculated from the measured magnetic field that was generated by the 60 Hz source currents varying from 5 A to 25 A when the sensors were placed at a distance of 7 mm from the center of the conductor. The algorithm then used the multiplying factors that were obtained from the calibration to compute the current phasors for the selected samples from the validation set of measurements. Figure 5 shows the outputs of all of the sensors for 5 A, 10 A, 15 A, 20 A, and 25 A as subplots. Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the outputs for all of the sensors for 5 A and 25 A for 120 samples (1 cycle of 60 Hz). These figures show an enlarged view of the outputs of each sensor. Figure 6 shows that the outputs are scattered over a bigger range from 4.95 A to 5.06 A and that the outputs are not very consistent, the reason being that the magnetic field is weak when it is generated by a 5 A source. However, it can be observed in Figure 7 that the outputs are very close to each other and are very close to the 25 A value, with a very minor variation that ranges from 24.98 to 25.04 for all of the sensors, except S1 and S12, which also show a larger variation for 5 A. From these figures, it can be seen that all of the sensors except S1 and S12 show very good and similar performance for higher current values. It can be seen that the outputs are well within the limits of ±0.2 A. This means that irrespective of the sensor quality, the output of the sensors does not vary from the actual value too much because of the use of the multiplying factors of each sensor.
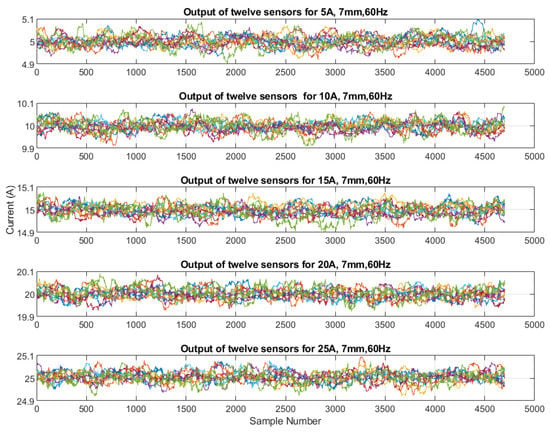
Figure 5.
Output of all sensors for 5 A to 25 A for 7 mm, 60 Hz.
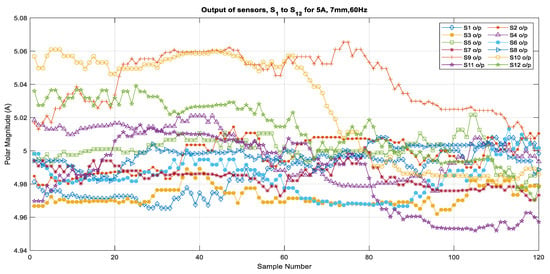
Figure 6.
Output of all sensors for 5 A, 7 mm, 60 Hz.
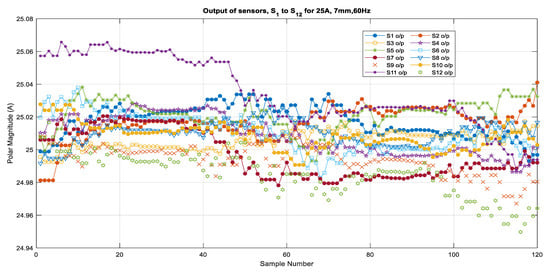
Figure 7.
Output of all sensors for 25 A, 7 mm, 60 Hz.
The outputs for each individual sensor were thus found to vary and were not found to be very similar to each other because of the variation in the sensor quality; therefore, the algorithm calibrates the sensors individually using individual multiplying factors. The sensors with lower MF values show that they are more accurate in sensing the magnetic field and need smaller multiplying factor values to estimate the current phasors from the measured magnetic field. Based on this study, the conclusion is that the remaining factors will be studied using the multiplying factors for individual sensors and for each current value instead of a mean value for all of the currents in order to obtain a more accurate analysis for the effects of distance, harmonics, and insulation.
4.2. Distance from Source
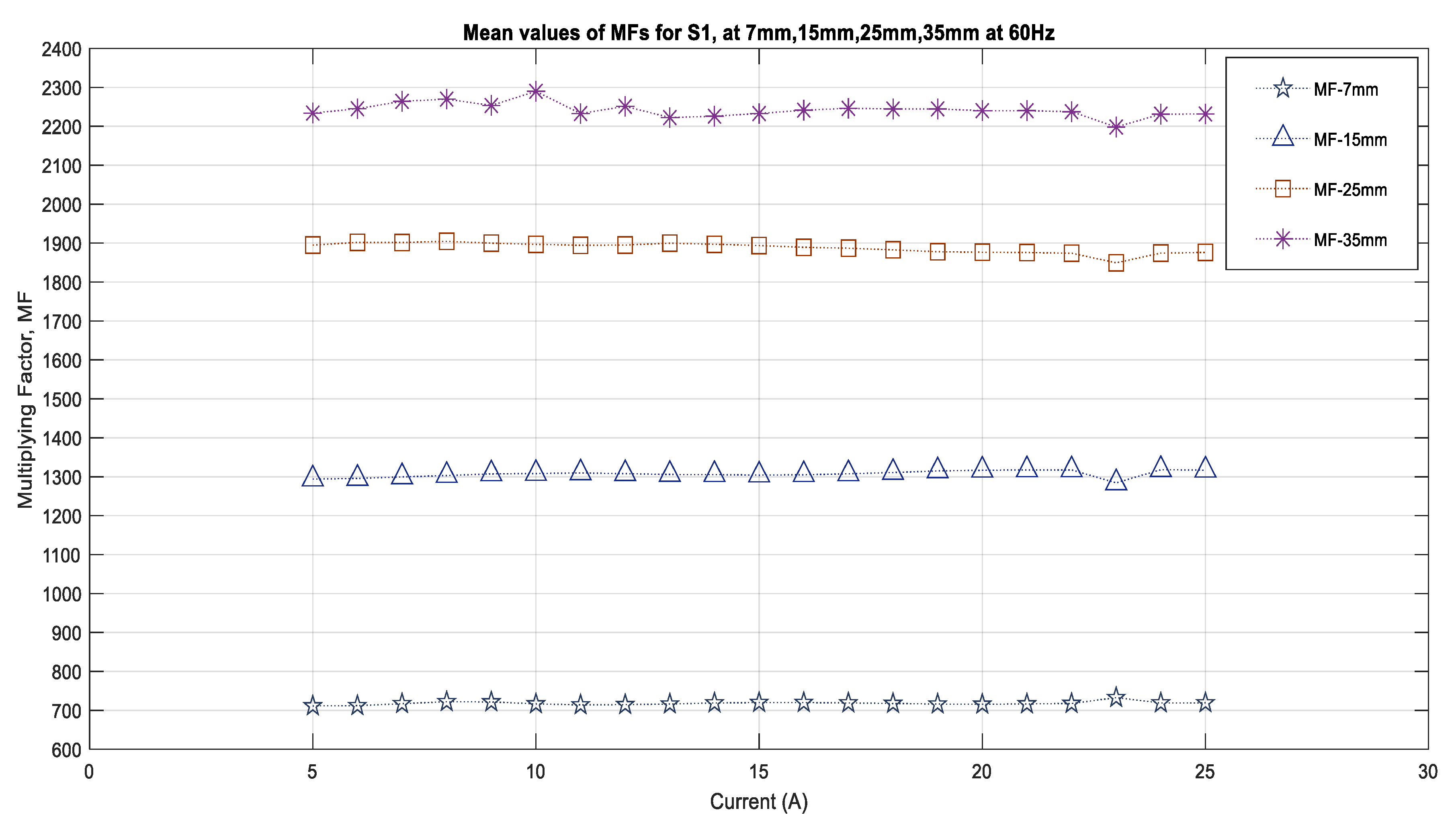
According to Equation (1), the strength of the magnetic field decreases as the distance from the source increases. In order to study this factor as well as to explore whether there is a fixed relationship between the distance and the multiplying factors for each sensor, the measurements were used for a set of distances, i.e., 7 mm, 15 mm, 25 mm, and 35 mm from the center of the conductor. In this study, the current for all cases had a frequency of 60 Hz, and the conductor did not have insulation. This is because the overhead conductors that were used in the medium- and high-voltage overhead power system applications were bare conductors. The computational program used the DFT algorithm to calibrate the sensors for the magnetic fields that were sensed for this set of distances and computes the multiplying factors for each current varying from 5 A to 25 A for each distance. The results that were obtained for the MFs are shown in Figure 8 for the sensor S1. This figure shows that the multiplying factor increases with the distance from the source. For 7 mm, the MFs are in the range of 718 to 730 for 15 mm, and for the same amount of currents and sensors, these MFs have range of 1300. For 25 mm, the MFs are in the range of 1895 to 1900, and for the 35 mm distance, these values jump from 1900 to 2250. There is no fixed relationship between these distances and for the MFs for each sensor for the same distance, and currents show variation based on the sensor quality. Therefore, the sensors will have range of MFs that are dependent on the distance and the current.
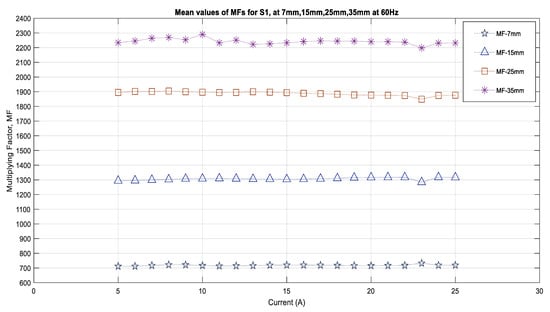
Figure 8.
Multiplying factors for the sensor S1 for various distances.
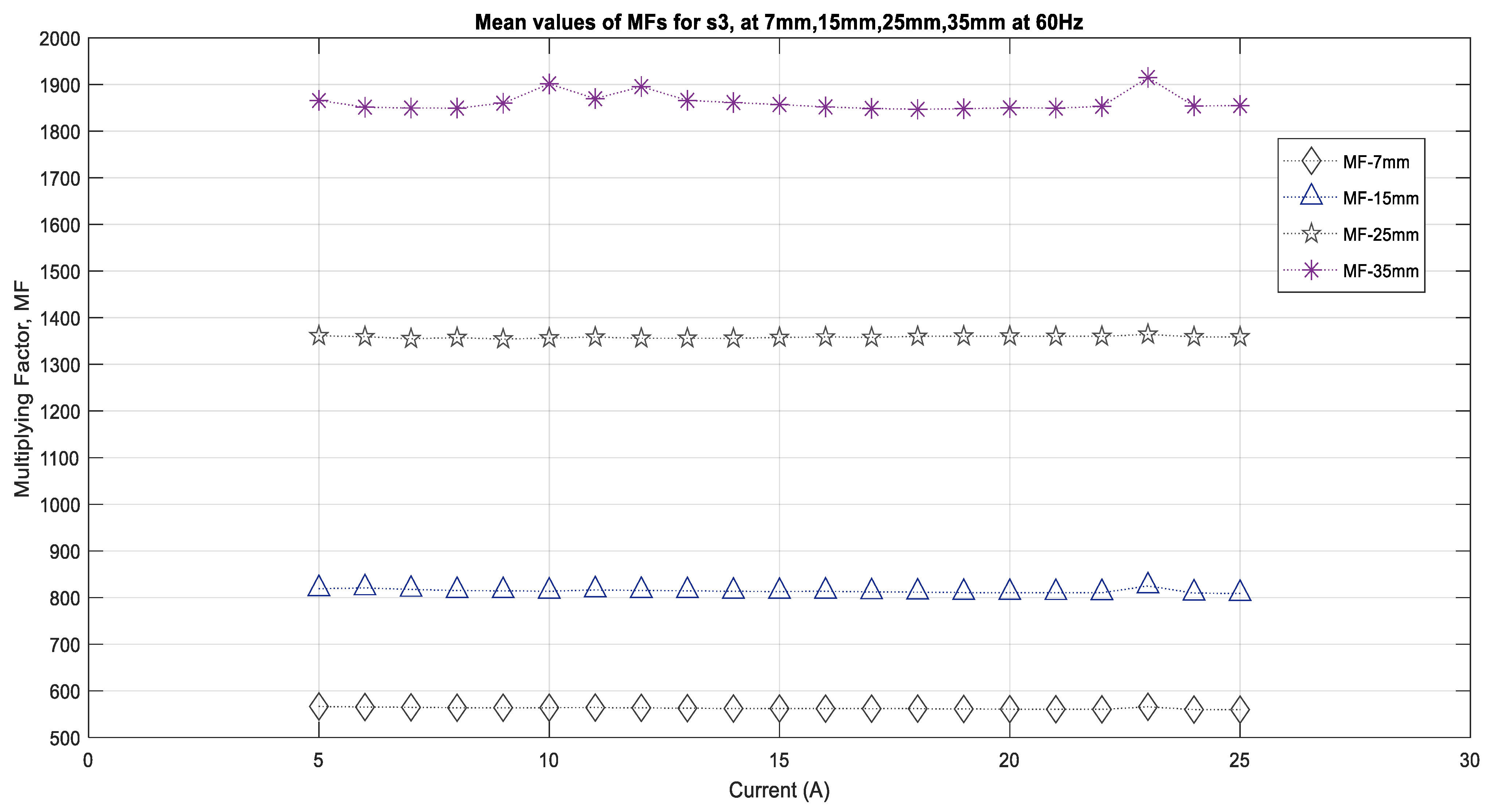
Figure 9 shows the results of the multiplying factors that were obtained for the sensor S3, which were similar those obtained in the different cases for S1. This figure also shows that sensor S3 has smaller values for the MF current and for the sensor distance from the source compared to those of S1. For 7 mm, the range of the MFs is between 550 and 560. For 15 mm, the MFs have almost equal values, all of which are close to 800. For 25 mm, these MFs increase significantly and are in the range of 1360 to 1370, whereas for 35 mm, the values are in the range of 1870 to 1880. As explained in Section 4.1 the sensors will have varying MFs based on their quality and their distance from the source, but it is clear that the outputs do not exactly follow the theoretical relationships between the current and the sensor distance from the current source. It can be concluded from the analysis in this section that when the sensors are closer to the source (conductor), the magnetic field is strong, and therefore, the sensors will provide consistent results, whereas when the magnetic field becomes weaker when the distance increases, it is only the higher currents that will produce better results.
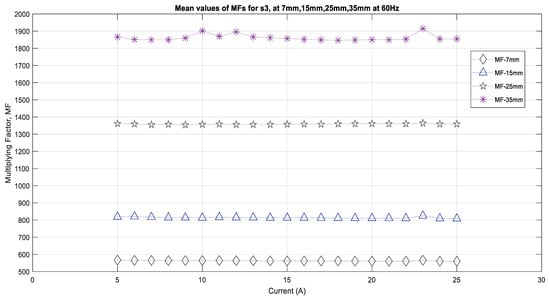
Figure 9.
Multiplying factors for the sensor S3 for various distances.
4.3. Insulation
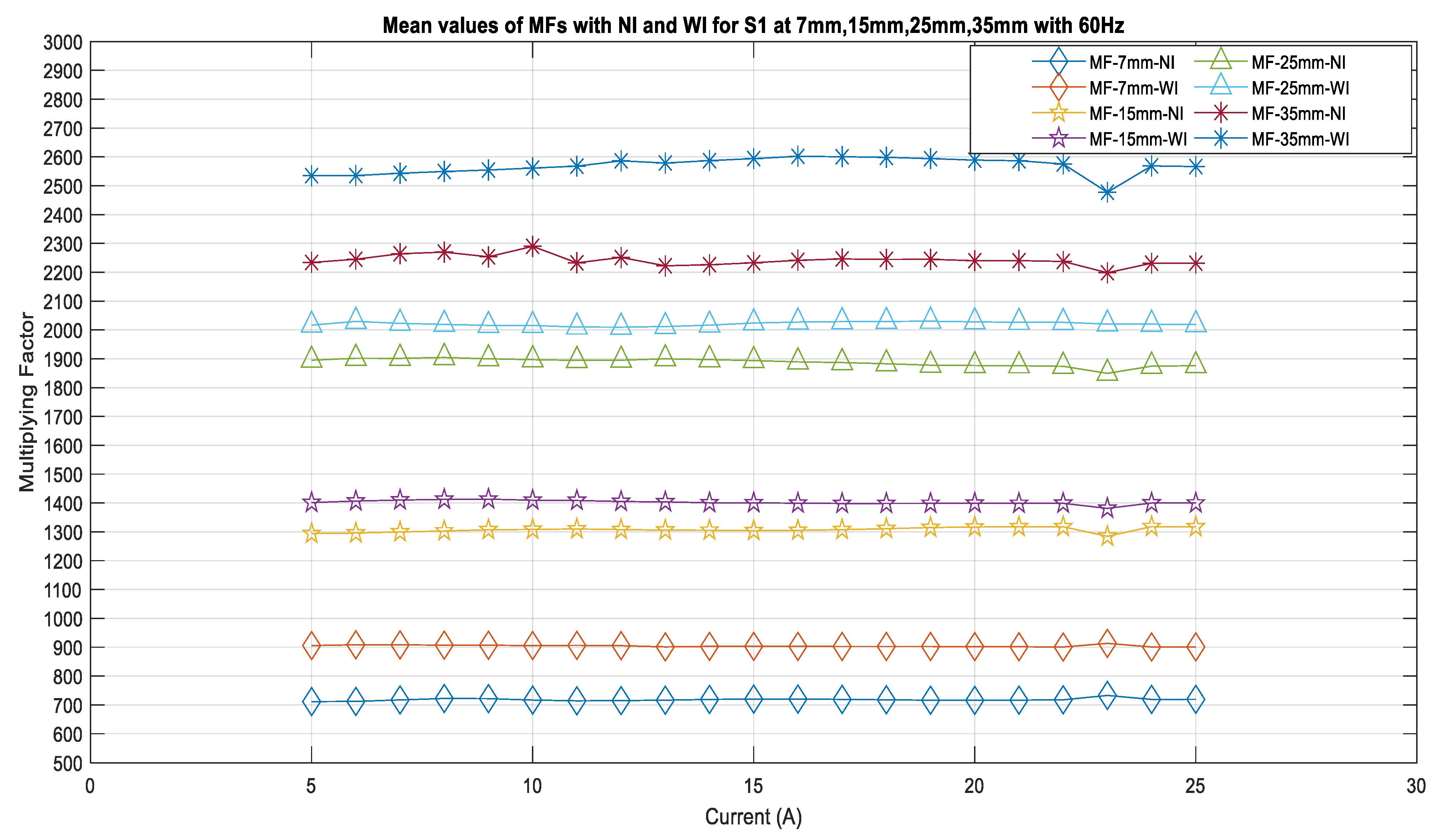
To check the ability of the sensors to sense the magnetic fields from an insulated conductor compared to a bare conductor, the measurements for both of these cases were used to calibrate the sensors separately and to compute the current phasors within the range of 5 A to 25 A using a computational program. These results are compiled and designated as No-Insulation (NI) and With-Insulation (WI). The results of the calibration provided multiplying factors, such as those shown in Figure 10, for various sensor distances from the center of the conductor and for the conductors with No-Insulation and With-Insulation. From this figure, it is evident that with the inclusion of insulation, the multiplying factor value increases for the same distance from the source and for the same set of currents. This was observed for all of the sensors. Figure 10 shows that the MFs at 7 mm for NI are in the range of 700, and for WI, they increase to 900 for all currents. Similarly, for the 15 mm distance, the MFs for the NI case are in the range of 1300, and they increase to 1400 in the WI case. It is observed that these values are 1900 and 2000, respectively, for the 25 mm distance. For the 35 mm distance, the magnetic field intensity decreased compared to at 7 mm, resulting in a higher difference between the NI and WI values. It can be observed that these values are 2200 and 2600 for the NI and WI cases, respectively.
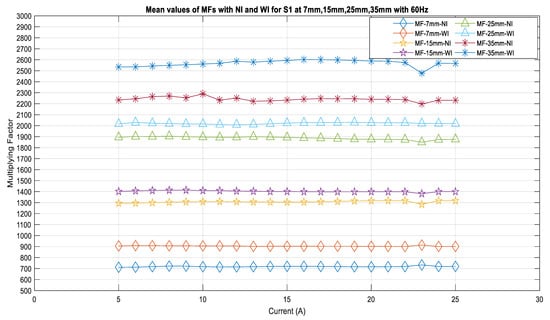
Figure 10.
Multiplying factors of the sensor S1 for various distances.
From these results, it can be observed that insulation affects the strength of the magnetic field sensing capability of the sensor, and therefore, the multiplying factors require higher values in order to obtain the same current magnitude, even when the sensor is kept at the same distance.
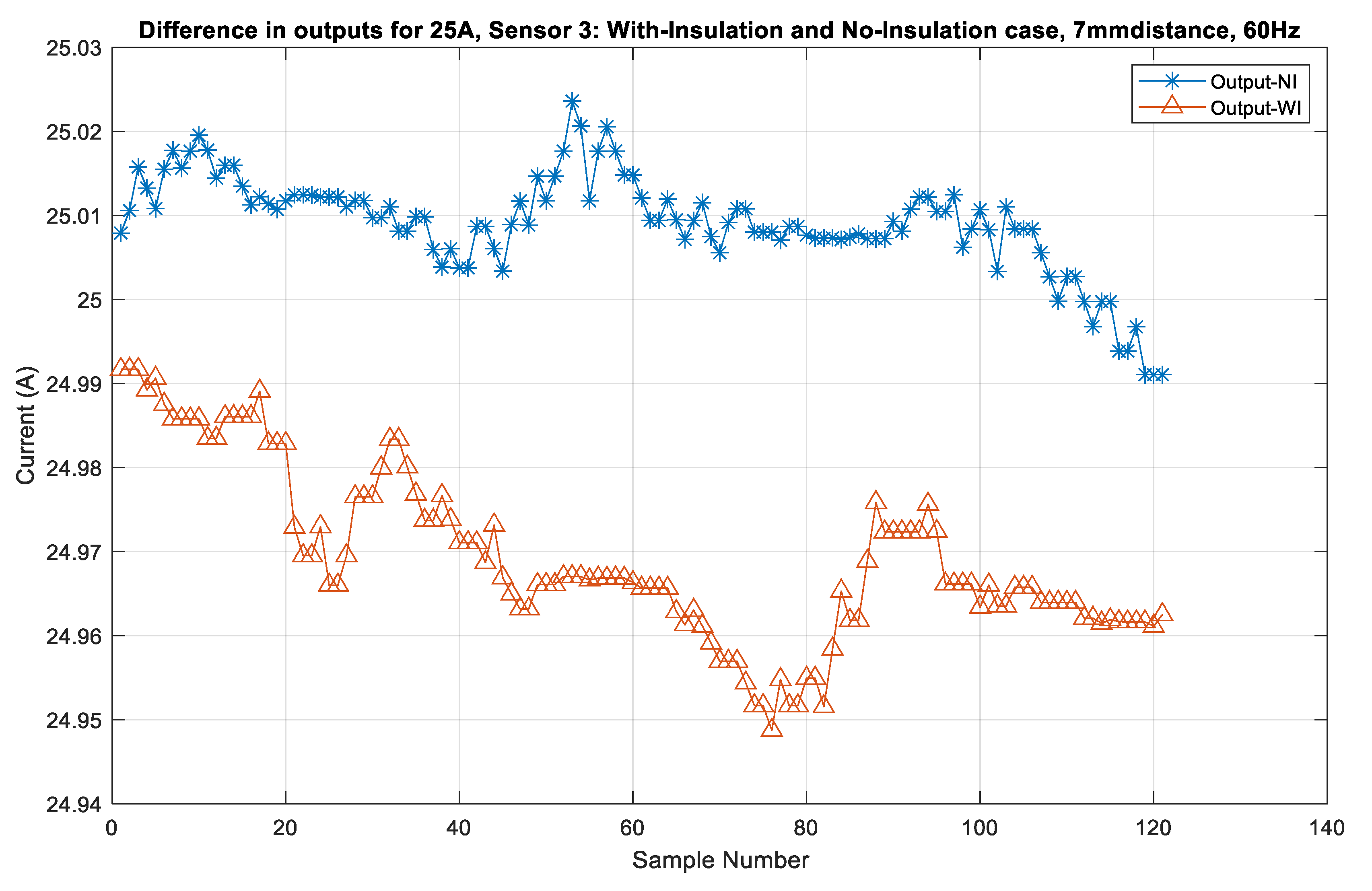
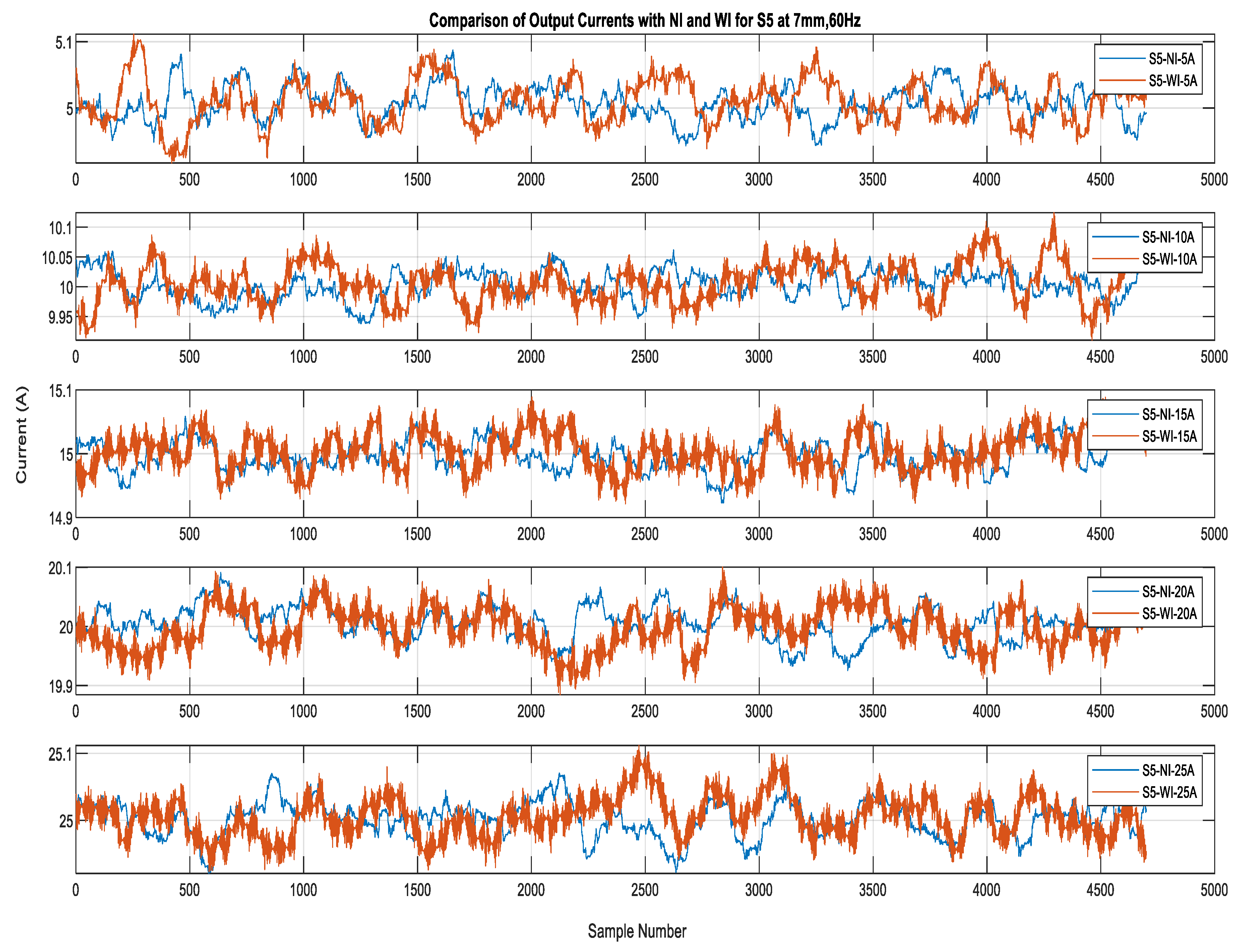
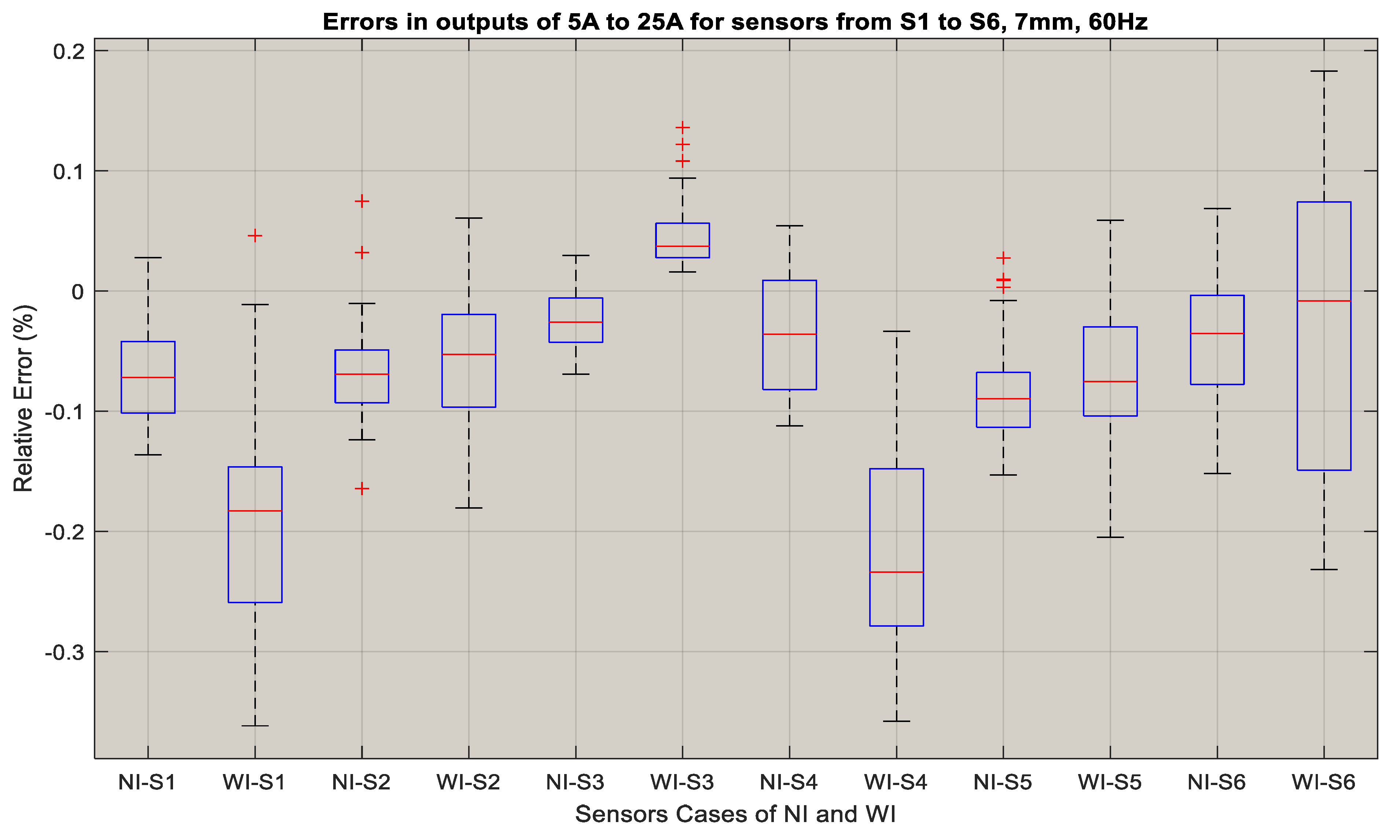
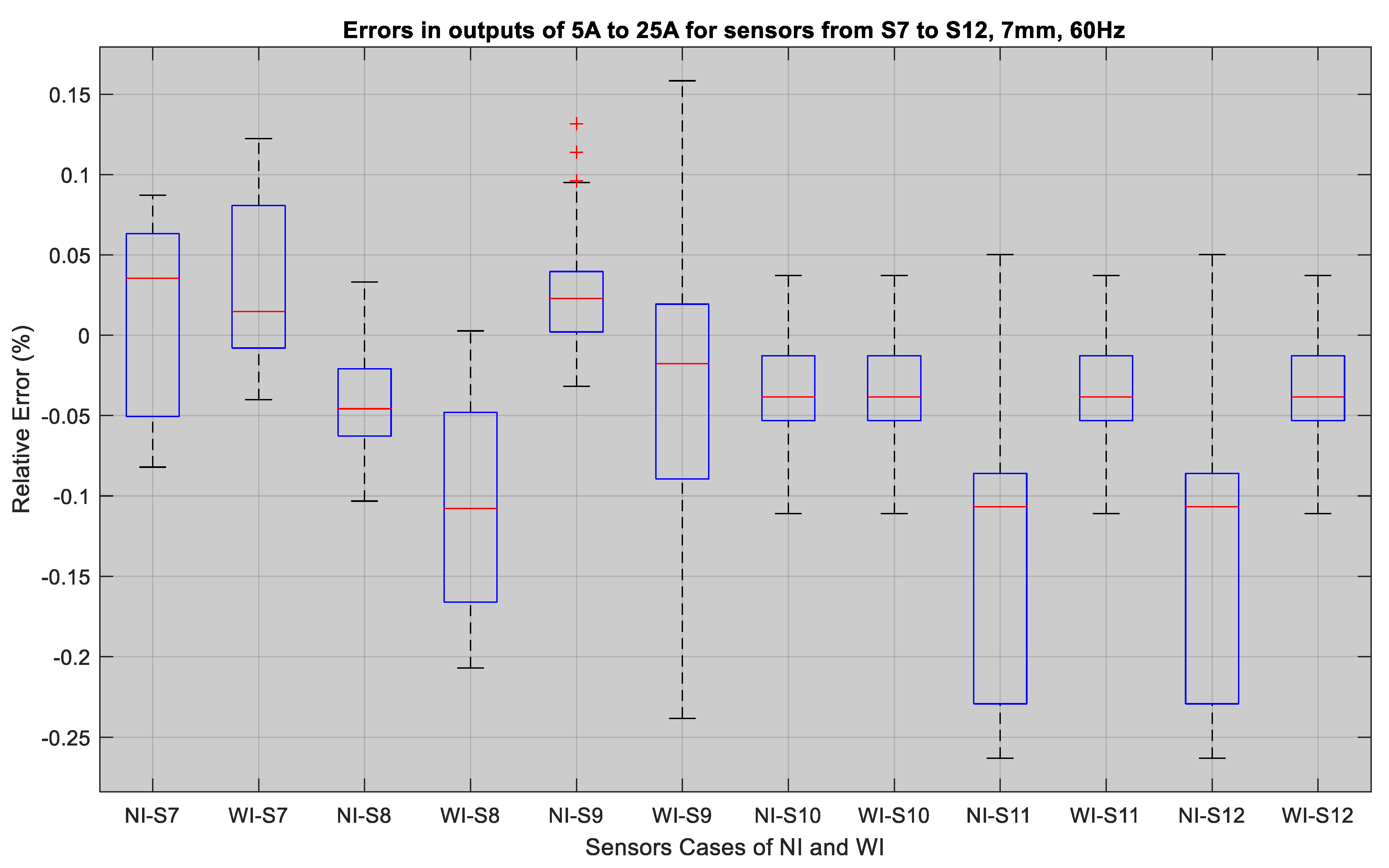
Figure 11 shows the output of sensor S3 for currents obtained in the No-Insulation compared to the With-Insulation case. The performance of sensors S5 and S4 for the c 5 A, 10 A, 15 A, 20 A, and 25 A currents is shown in Figure 12 and Figure 13. It can be seen that the output errors do not cross the limit of ± 0.1 A for five of the current values in both the No-Insulation and With-Insulation cases. However, more accurate values can be obtained for the No-Insulation case compared to the With-Insulation case. The relative percentage errors between the CT output and the sensor outputs were calculated for both the WI and NI cases for all of the sensors by considering the distance of 7 mm and input current frequency of 60 Hz. The results for all of the sensors are shown in Figure 14 and Figure 15 as box and whisker plots.
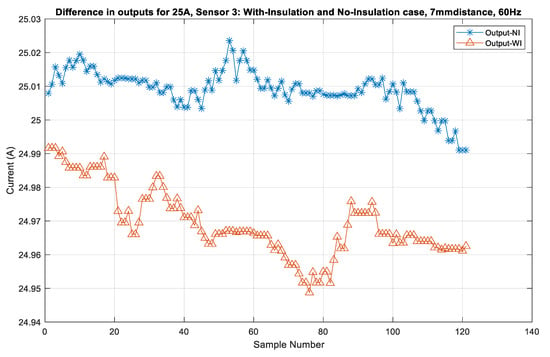
Figure 11.
Sensor S3 output for 25 A: With-Insulation and No-Insulation case.
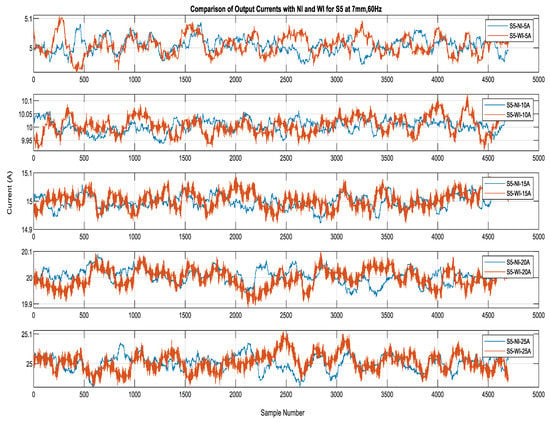
Figure 12.
Sensor S5 outputs for currents of 5 A to 25 A: WI and NI cases.
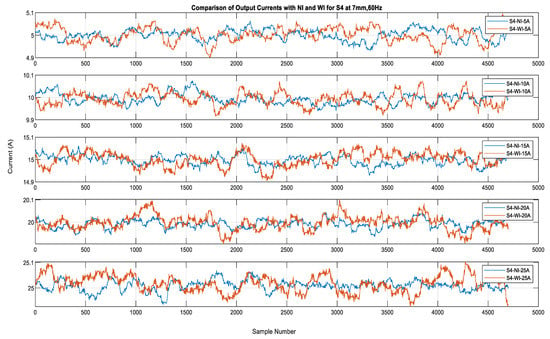
Figure 13.
Sensor S4 outputs for currents of 5 A to 25 A: WI and NI cases.
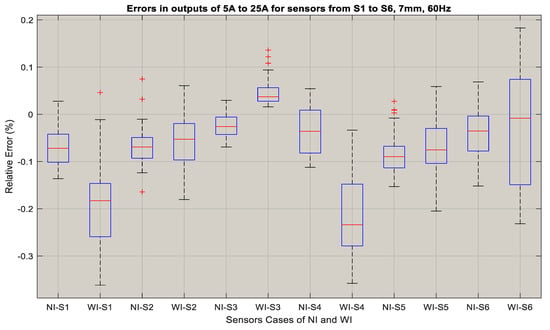
Figure 14.
Relative errors in outputs of the sensors S1 to S6: WI and NI case.
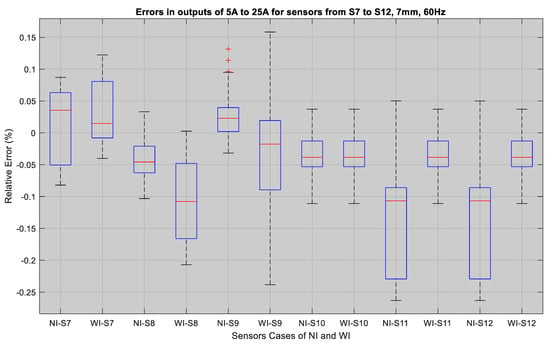
Figure 15.
Relative errors in outputs of the sensors S7 to S12: WI and NI case.
The sensor errors that are shown in Figure 14 range from −2.57–0.067% for the NI case, whereas the percentage errors vary from −0.38–0.18% for the WI case. The median values for all of the sensors in the NI case in this figure indicate that the errors are between 0.04% and −0.09%, implying that for higher currents, the error rate is lower. This is also evident for sensors 7 to 12 from Figure 15. The median value of the errors for the NI case was in between 0.05–−0.05%, whereas these values varied from 0.1–−0.15% for the WI cases. Overall, both of these figures show that the TMR sensors have very low errors in both cases, and that the medians show that their output is very close to the actual current. Therefore, these sensors can be used for both underground cables with insulation as well as with overhead bare conductors for an alternating current sensing application up to 300 A.
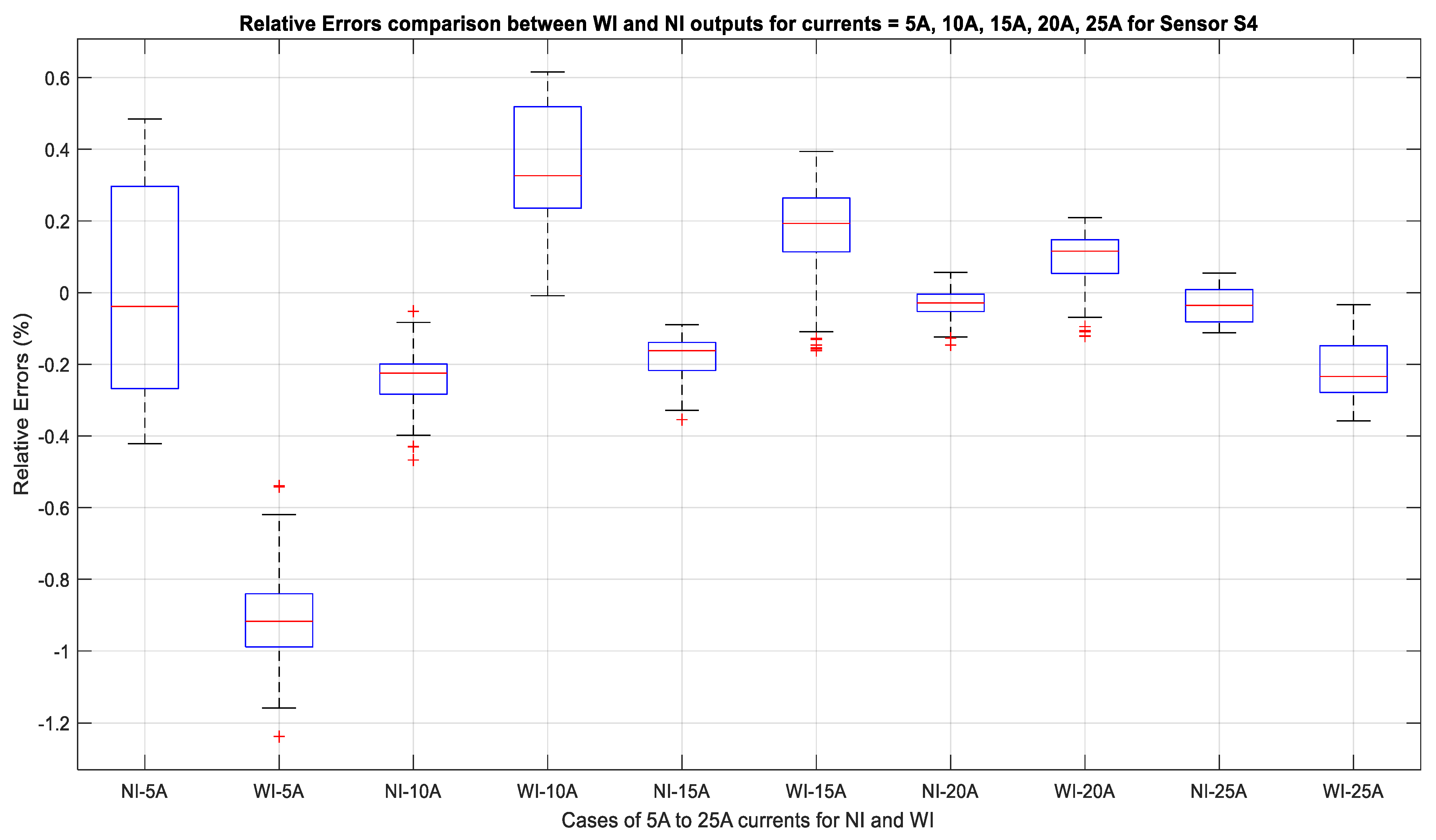
These relative errors were also compared on the basis of the performance of each sensor for a specific source current value as well as for the WI and NI cases. The results are shown by the box and whisker plot in Figure 16. The median value for all of the currents for NI the case shown in Figure 16 is very close to 0%, whereas the median varies with the range from 0.3–−0.2% for the WI case. In all of the NI cases, the error for 5 A was 0.5% when considering the fact that the sensors are less accurate at lower current values since their rating is for 300 A. It is evident that for 25 A, the error rate for all of the sensors is 0.01%. In case of WI, the error value is 0.6% for 10 A; however, it is −0.001% for 25 A. This indicates that the sensors will be accurate when they are used for higher current applications.
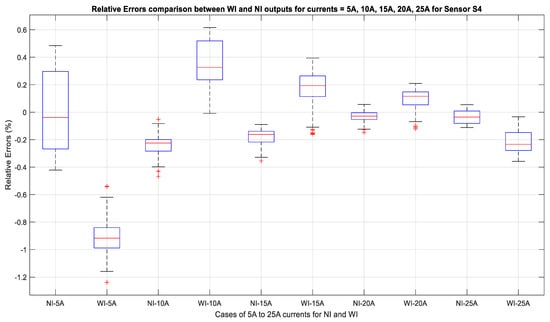
Figure 16.
Output of all sensors for 25 A, 7 mm, 60 Hz: No-Insulation case.
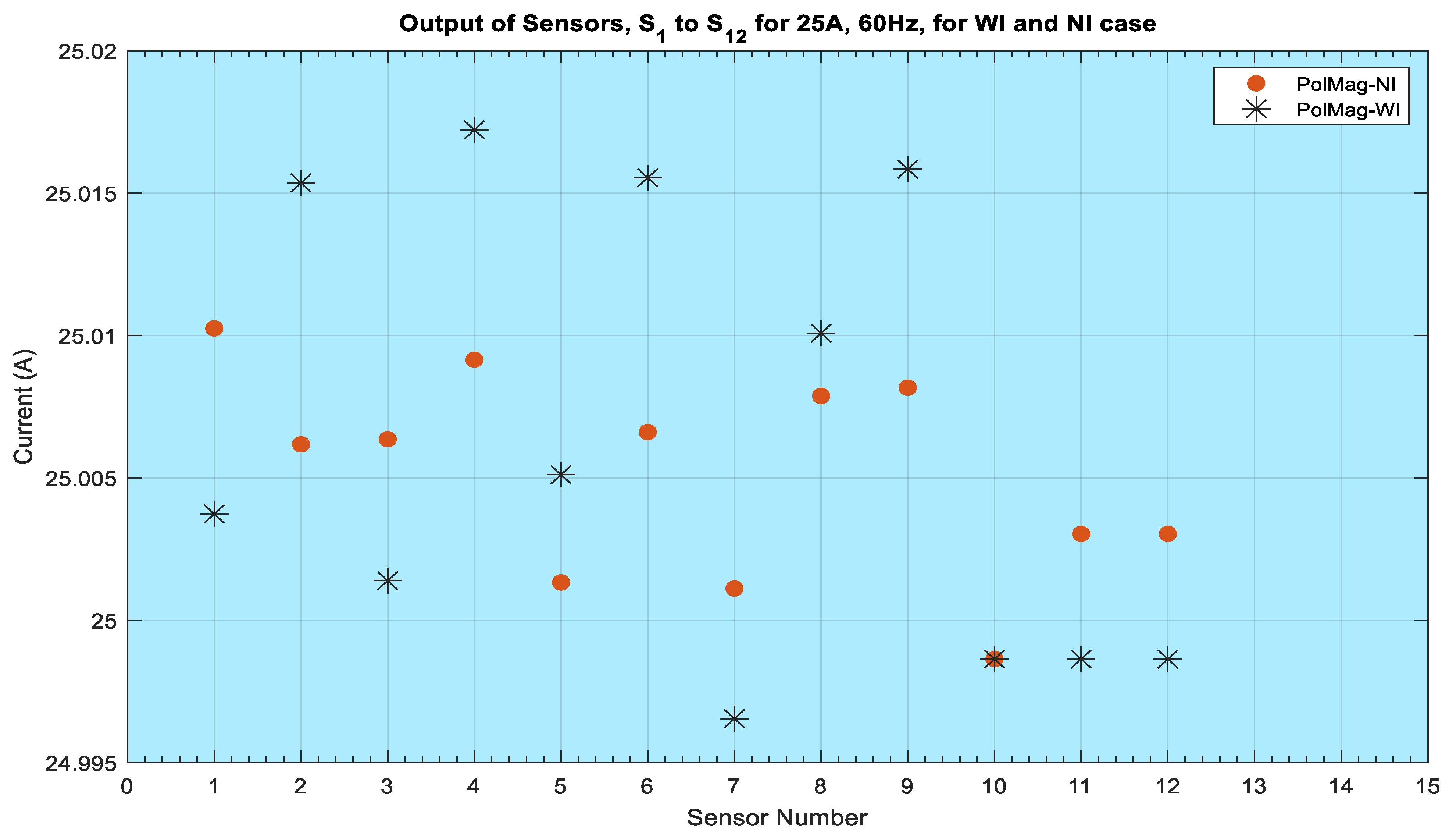
The performance for all of the sensors also needs to be confirmed when considering the presence or absence of insulation for higher currents in order to validate that these sensors will always perform better for higher currents. In this experiment, the maximum value of the source current was limited to 25 A. Therefore, the output of all of the sensors for 25 A for both the WI and NI cases was taken as reference. Figure 17 shows these outputs, and it can be observed that all of the sensors demonstrate more consistent output that is very close to 25 A for the NI case compared to the WI case. The output of sensor S5 was 25.018 A, and the minimum value that was obtained was 24.995 A in the With-Insulation case. For the no-insulation case, the output for all of the sensors was in the range of 25.001 A to 25.01 A. The results of the DFT algorithm for the multiplying factors for both the WI and NI cases showed a variation of 110 to 120 for each sensor. However, the final output of the current phasors was very close to the actual current that was injected by the Omicron current injection set, with the errors shown above. The algorithm that is proposed in this paper demonstrates the accuracy of the chosen method in determining the currents from a magnetic field for a range of currents from 5 A to 25 A. It is anticipated that the accuracy of the sensors at higher currents will be better for both NI and WI cases due to the stronger magnetic fields. A detailed performance analysis on the insulation infers that the insulation affects the sensing ability of the magnetic field, and therefore, the accuracy of the current calculation is affected as well. The path of the magnetic field lines is different for air compared to air with an insulation medium, and therefore, the magnetic field is weaker due to the insulation.
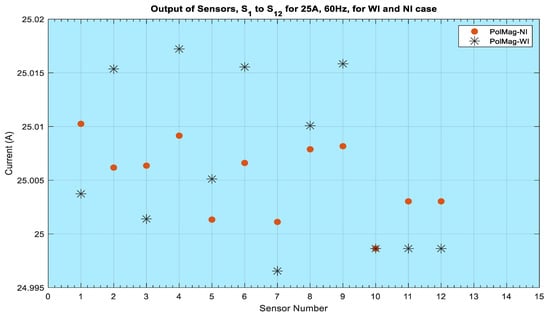
Figure 17.
Output of all sensors for 25 A, 7 mm, 60 Hz: WI and NI cases.
4.4. Harmonics
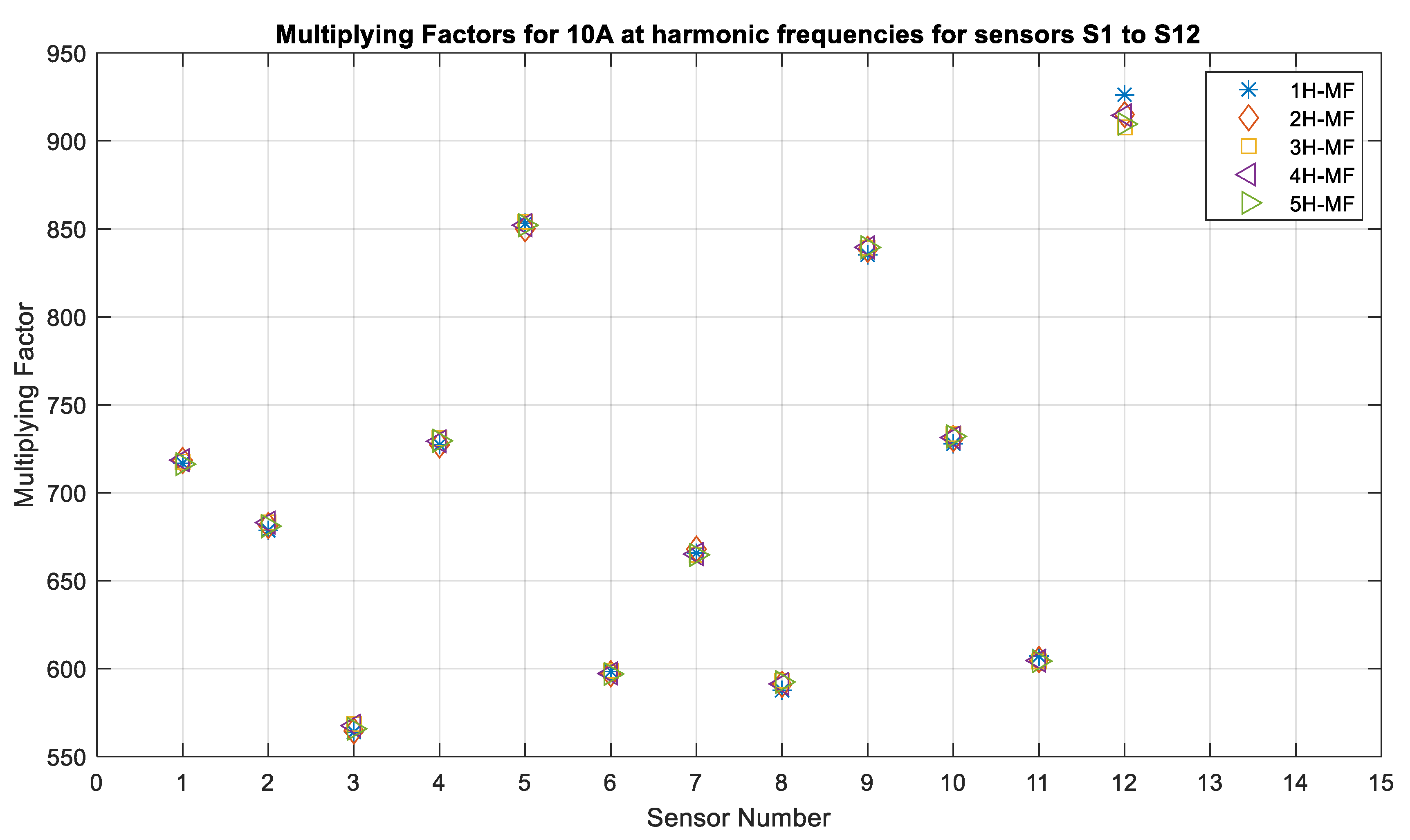
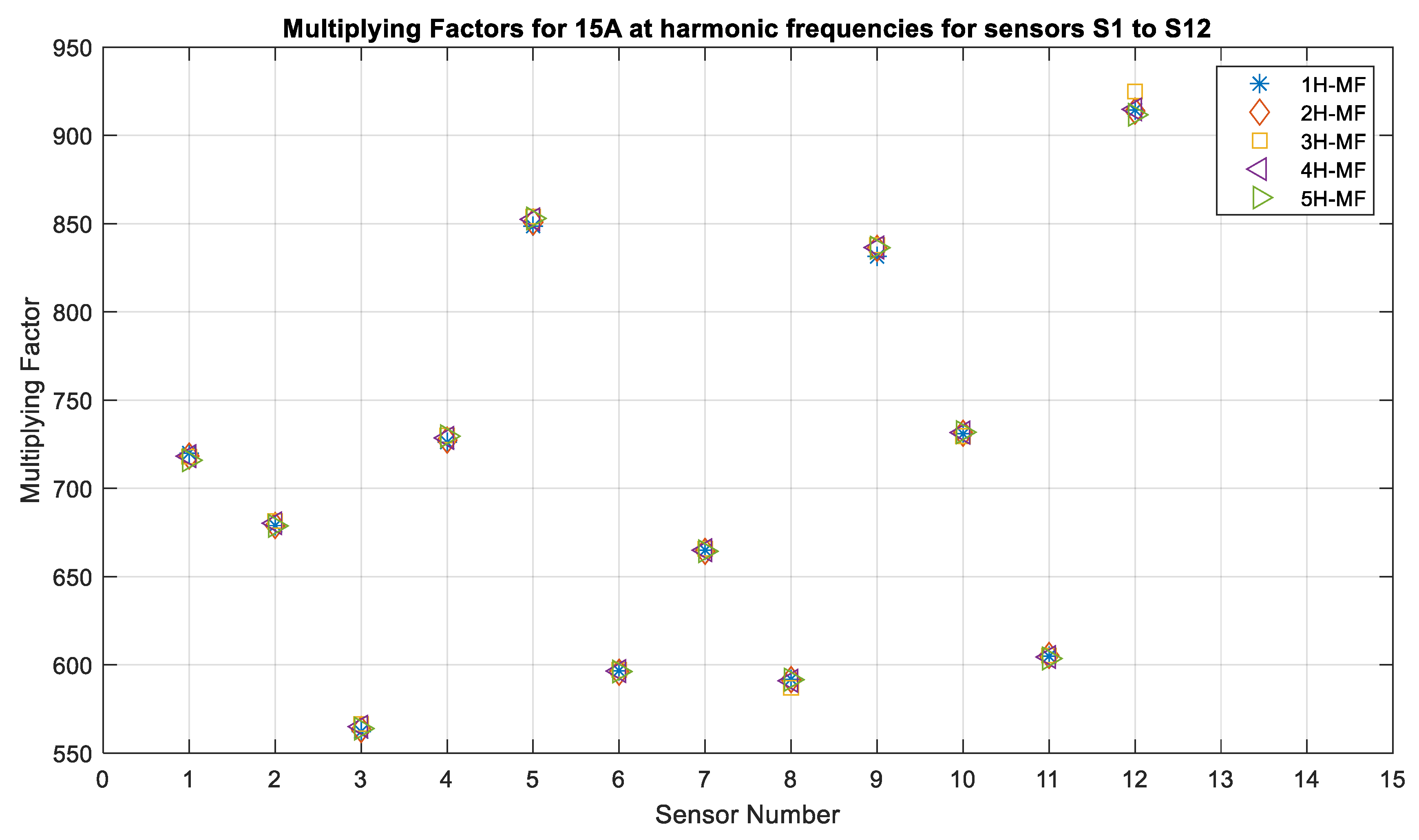
The last factor that was studied was the performance of individual sensors in the presence of harmonics. In this case, the application of the sensors is considered for medium-voltage power systems that often have the odd harmonic present in the system. Generally, the protection relays and instrumentation meters eliminate any harmonics that are above the 5th harmonic. Therefore, in this study, the sensor performance was tested for harmonics up to the 5th order. Figure 18 and Figure 19 show the multiplying factors that were obtained for twelve sensors for currents with the frequencies from 60 Hz to the 5th harmonic, and it can be seen that these are almost the same, with a very small variation for 10 A current being observed. There was less variation for 15 A compared to that for 10 A. It was observed that vibration was minimal for the higher currents. The sensors were able to measure the currents with harmonic frequencies as accurately as they were able to measure the fundamental frequency.
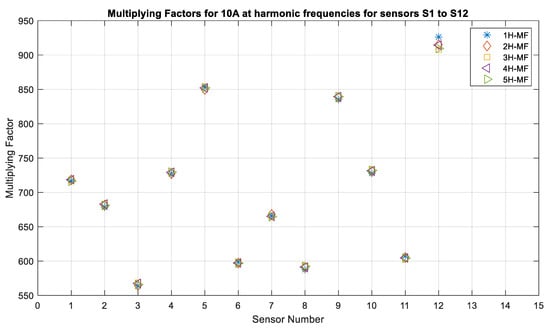
Figure 18.
Multiplying factors of all sensors for 10 A, 7 mm, 60 Hz and its harmonics: WI and NI cases.
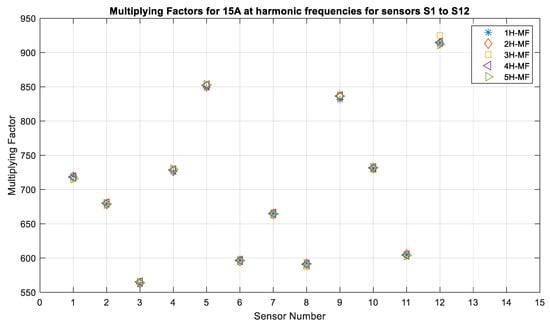
Figure 19.
Multiplying factors of all sensors for 15 A, 7 mm, 60 Hz and its harmonics: WI and NI cases.
The results of the multiplying factors for 5 A and 25 A are given in Table 2 and Table 3 in order to have a clear idea of the variation in their multiplying factors for each harmonic. Table 2 shows that sensor S12 has a maximum variation in the multiplying factor values ranging from 885 to 919, whereas sensor S8 shows the second highest variation, ranging from 889 to 604. The remaining sensors have a variation from 4 to 5 units between the multiplying factors for each harmonic. This demonstrates that the harmonics do not affect current measurement when TMR sensors are used.

Table 2.
Multiplying factors for all sensors with application of 5 A current for various harmonics.

Table 3.
Multiplying factors for all sensors with application of 25 A current for various harmonics.
Table 3 shows the multiplying factors that were obtained for all twelve at a current of 25 A. It can be seen that the MF values are almost the same, with a variation of two units being demonstrated for all sensors except sensor S5. This shows that the variation of the values is from 848 for 60 Hz to 853 to the 5th harmonic current. Sensor S12 shows the second highest variation of 4 from 913 to 917, and sensor S1 shows variation from 715 to 719. The remaining sensors have multiplying factors that are very close to each other, with a variation of one to two units between all values. The variation is already minimal, and the algorithm applies these to determine the output of the current phasor for each case, with a relative error of 0.005%. The investigation of the sensor performance for the effect of harmonics concluded that the MFs and the current outputs are fairly constant for all of the sensors, irrespective of the order of harmonic, except for sensors S8 and S12. The higher MF values for these two sensors are merely because of the sensor quality. Replacing these two sensors with those of a better quality will likely result in a similar performance as that of the other ten sensors. This further illustrates the need for proper sensor calibration before using them for current measurement.
5. Three-Phase Current Measurement
One of the objectives of this research was to validate the 12 sensors for the next phase of the experiment, which will be the extension of this single-phase experiment for a three-phase system [17]. There will be three similar conductors and two to four sensors will be used for each phase to measure the magnetic field that is produced by the current in the individual phase. The measured fields will be used to estimate the three-phase currents based on the algorithm explained in a previously published article that was based on the simulation of a three-phase system that includes a transmission line [17]. This research is ongoing, and the results will be reported in a future publication.
6. Conclusions
The performance of TMR sensors for current measurement was tested and studied with regard to the impact of variation in the sensor quality, distance from current source, the presence of insulation, and harmonics. The experiments were conducted with various parts and stages to record measurements in detail, and a thorough analysis was performed to study the behavior of the sensors under the four factors mentioned above. The less errors were produced when the sensor performance was compared for current-carrying conductors With-insulation and with No-insulation. Even though the sensor quality results showed variance in the performance of each individual sensor, for higher current values, they all exhibited similar behavior, with the exception of sensors S1 and S12. The variation in the output was not higher than 0.04 A for the 25 A current. The remaining sensors produced outputs with an error rate of 0.0013%, which was very satisfactory. It is expected that the difference of 0.04 A will reduce further when the magnitude in the source current increases. The variation in the distance for each sensor provided their individual multiplying factors, inferring that there is a need to calibrate each sensor separately in order to achieve an accuracy of 0.0001% for the current measurements. The calibration produced different values for the conductors with no-insulation and with-insulation, but eventually, the final outputs of the sensors were very close the injected current, with an error of 0.18% for the conductors with-insulation, and in some cases, the final outputs showed an error of −0.38%. For the conductors with no-insulation, the results were consistent for all sensors and for all current values from 5 A to 25 A, with errors ranging from 0.4% to −0.24%. The harmonics had no significant effects that were able to be observed on the performance of the TMR sensors. They showed very consistent outputs for all of the currents ranging from 5 A to 25 A when they were tested for currents with a fundamental frequency up to 5th harmonic. Thus, these sensors can be applied to measure currents containing harmonics. Once calibrated, it is possible to generate current measures using TMR sensors for three-phase current measurement that have no hysteresis and that have a higher measurement accuracy.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S.S.; methodology, T.S.S.; software, P.S.; validation, P.S. and T.S.S.; formal analysis, P.S.; investigation, P.S. and T.S.S.; resources, P.S. and T.S.S.; data curation, P.S. and T.S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, P.S. and T.S.S.; writing—review and editing, T.S.S.; visualization, P.S. and T.S.S.; supervision, T.S.S.; project administration, T.S.S.; funding acquisition, T.S.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received partial funding from Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Data Availability Statement
The data was created during the experiments that were carried out in the laboratory. The data is private and not to be shared with any third party.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Karnouskos, S.; Terzidis, O.; Karnouskos, P. An advanced metering infrastructure for future energy networks. In New Technologies, Mobility and Security; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 597–606. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, M.C. Electric Power Research Trends; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 68–148. [Google Scholar]
- Terzija, V.; Valverde, G.; Deyu, C.; Regulski, P.; Madani, V.; Fitch, J.; Skok, S.; Begovic, M.M.; Phadke, A. Wide-Area Monitoring, Protection, and Control of Future Electric Power Networks. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrave, A.; Thompson, M.; Heilman, B. Beyond the knee point: A practical guide to CT saturation. In Proceedings of the 2018 71st Annual Conference for Protective Relay Engineers (CPRE), College Station, TX, USA, 26–29 March 2018; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- IEEE Std. C37.110-2007. IEEE Guide for the Application of Current Transformers Used for Protective Relaying Purposes; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 13–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, W.F.; Hewson, C.R. High Performance Rogowski Current Transducers. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Industry Applications Conference, Thirty-Fifth IAS Annual Meeting and World Conference on Industrial Applications of Electrical Energy (Cat. No.00CH37129), Rome, Italy, 8–12 October 2000; pp. 3083–3090. [Google Scholar]
- Hall Effect Sensing and Application, Honeywell Book. Available online: https://sensing.honeywell.com/honeywell-sensing-sensors-magnetoresistive-hall-effect-applications-005715-2-en2.pdf (accessed on 15 January 2020).
- Costa, F.; Poulichet, P.; Mazaleyrat, F.; Labaoure, E. The current sensors in power electronics, a review. EPE J. 2001, 11, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, S.; Woodward, R.C.; Lu, H.H.C.; Borle, L.J. Investigation into static and dynamic performances of the copper trace current sense method. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripka, P. Advances in fluxgate sensors. Sens. Actuators A 2003, 106, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, J.; Edelstein, A.S. Magnetic sensors and their applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2006, 6, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binasch, G.; Grünberg, P.; Saurenbach, F.; Zinn, W. Enhanced magnetoresistance in layered magnetic structures with antiferromagnetic interlayer exchange. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 39, 4828–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vopalensky, M.; Platil, A.; Kaspar, P. Wattmeter with AMR sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2005, 123, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Lui, K.S.; Wong, K.K.Y.; Lee, W.K.; Hou, Y.; Huang, Q.; Pong, P.W.T. Novel Application of Magneto-resistive Sensors for High-Voltage Transmission-Line Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 2608–2611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafiq, M.; Hussain, G.A.; Kutt, L.; Lethonen, M. Electromagnetic Sensing for Predictive Diagnostics of Electrical Insulation Defects in MV Power Lines. 2015 Elsevier J. Meas. 2015, 73, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Weiss, R.; Weigel, R. Giant-Magnetoresistance-Based Galvanically Isolated Voltage and Current Measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 2048–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrawane, P.; Sidhu, T.S. Estimation of Three-Phase Currents in Overhead Power Line Conductors Using Numerical Model of Magnetic Fields. Prog. Electromagn. Res. C Pier C 2019, 97, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, T.; Jin, H. The Physics of Ferromagnetism; Springer series in Material Science: New York, NY, USA, 2009; Volume 158, pp. 204–249. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, P.P.; Ferreira, R.; Cardoso, S.; Cardoso, F. Magnetoresistive Sensors. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 165221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omicron Energy Website. Available online: https://www.omicronenergy.com/en/products/cmc-356/ (accessed on 24 April 2020).
- National Instruments Website. Available online: https://www.ni.com/pdf/manuals/372838e.pdf (accessed on 24 April 2020).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).