Single-Branch Wide-Swing-Cascode Subthreshold GaN Monolithic Voltage Reference
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Previous Art
2.1. Schottky-Diode-Based GaN Voltage Reference
2.2. Reference Voltage Generators Based on Current Mirrors
2.3. 2-T Voltage Reference
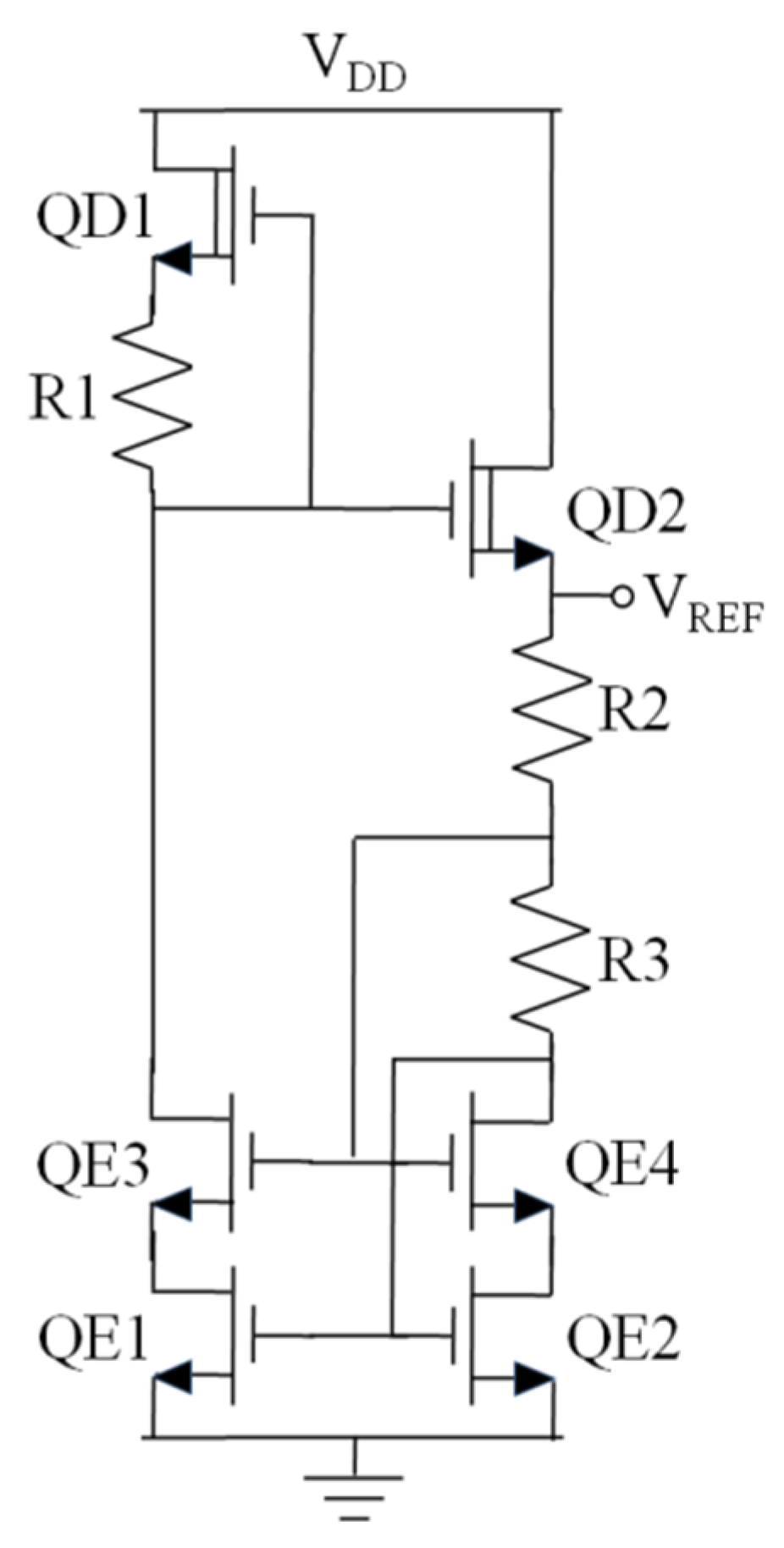
3. Proposed Voltage Reference Generator
3.1. Circuit Description
3.2. Analysis and Design Strategy
4. Validation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Widlar, R.J. New developments in IC voltage regulators. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1971, 16, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsividis, Y.P.; Ulmer, R.W. A CMOS voltage reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1978, 13, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittoz, E.A.; Neyroud, O. A low-voltage CMOS bandgap reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1979, 14, 573–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorian, R.; Wegner, G.A.; Nicholson, W.E., Jr. An integrated single-chip PCM voice codec with filters. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1981, 16, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banba, H.; Shiga, H.; Umezawa, A.; Tanzawa, T.; Atsumi, S.; Sakui, K. A CMOS Bandgap Reference Circuit with Sub-1 -V Operation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1999, 34, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leug, K.N.; Mok, P.K.T. A Sub-1-V 15-ppm/°C CMOS Bandgap Voltage Reference without Requiring Low Threshold Voltage Device. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2002, 37, 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Boni, A. Op-Amps and Startup Circuits for CMOS Bandgap Referecnces with Near 1-V Supply. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2002, 37, 1339–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giustolisi, G.; Palumbo, G.; Criscione, M.; Cutri, F. A low-voltage low-power voltage reference based on subthreshold MOSFETs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2003, 38, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, G.; Iannaccone, G. A Sub-1-V, 10 ppm/°C, Nanopower Voltage Reference Generator. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueno, K.; Hirose, T.; Asai, T.; Amemiya, Y. A 300 nW, 15 ppm/°C, 20 ppm/V CMOS Voltage Reference Circuit Consisting of Subthreshold MOSFETs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2009, 44, 2047–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnelli, L.; Crupi, F.; Corsonello, P.; Pace, C.; Iannaccone, G. A 2.6 nW, 0.45 V Temperature-Compensated Subthreshold CMOS Voltage Reference. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 46, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, M.; Kim, G.; Blaauw, D.; Sylvester, D. A Portable 2-Transistor Picowatt Temperature-Compensated Voltage Reference Operating at 0.5 V. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 2534–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A.; Finocchiaro, A.; Papotto, G.; Palmisano, G. Nano-Power CMOS Voltage Reference for RF-Powered Systems. IEEE Trans.Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 65, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassio, L.; Lin, L.; de Rose, R.; Lanuzza, M.; Crupi, F.; Alioto, M. Trimming-Less Voltage Reference for Highly Uncertain Harvesting Down to 0.25 V, 5.4 pW. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 3134–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Savaria, Y.; Sawan, M. GaN Integration Technology, an Ideal Candidate for High-Temperature Applications: A Review. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 78790–78802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghini, M.; Meneghesso, G.; Zanoni, E. (Eds.) Power GaN Devices: Materials, Applications and Reliability; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Meneghini, M.; Meneghesso, G.; Zanoni, E. (Eds.) Gallium Nitride Enabled High Frequency and High Efficiency Power Conversion; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.J.; Häberlen, O.; Lidow, A.; Tsai, C.L.; Ueda, T.; Uemoto, Y.; Wu, Y. GaN-on-Si power technology: Devices and applications. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 779–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kwan, A.M.H.; Jiang, Q.; Chen, K.J. A GaN pulse width modulation integrated circuit for GaN power converters. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, M.; Lueders, M.; Kaya, C.; Wicht, B. 18.2 A monolithic E-mode GaN 15 W 400 V offline self-supplied hysteretic buck converter with 95.6% efficiency. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–20 February 2020; pp. 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.; Noël, J.-P.; Savaria, Y.; Sawan, M. Circuit Techniques in GaN Technology for High-Temperature Environments. Electronics 2022, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimović, D.; Zhang, Y.; Rodríguez, M. Monolithic Very High Frequency GaN Switched-mode Power Converters. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), San Jose, CA, USA, 28–30 September 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Sun, R.; Bu, Q.; Liu, W.; Wen, H.; Li, A.; Liang, Y.C.; Zhao, C. Monolithic GaN Half-bridge Stages with Integrated Gate Drivers for High Temperature DC-DC Buck Converters. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 184375–184384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Bu, Q.; Cai, Y.; Sun, R.; Liu, W.; Wen, H.; Lam, S.; Liang, Y.C.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Taylor, S.; et al. Monolithic Integration Design of GaN-based Power Chip Including Gate Driver for High Temperature DC-DC Converters. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 58, 056505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Liang, Y.C.; Yeo, Y.-C.; Zhao, C.; Chen, W.; Zhang, B. All-GaN Power Integration: Devices to Functional Subcircuits and Converter ICs. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.; Kwan, A.M.H.; Wong, R.K.Y.; Lei, J.; Su, R.Y.; Yao, F.W.; Lin, Y.M.; Yu, J.L.; Tsai, T.; Tuan, H.C.; et al. Digital Integrated Circuits on an E-Mode GaN Power HEMT Platform. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2017, 38, 1282–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Lai, J.; Chen, W.; Zhang, B. GaN Power Integration for High Frequency and High Efficiency Power Applications: A Review. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 15529–15542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.-Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, K.J. Wide bandgap GaN smart power chip technology. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Compound Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology, Tampa, FL, USA, 18–21 May 2009; pp. 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, K.; Chen, W.; Chen, K.J. Integrated Voltage Reference Generator for GaN Smart Power Chip Technology. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2010, 57, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Yang, S.H.; Liao, M.Y.; Chung, K.C.; Kumari, N.; Chen, K.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Lin, S.R.; Tsai, T.Y.; Juang, Y.Z. 3.8 A 23.6 ppm/°C Monolithically Integrated GaN Reference Voltage Design with Temperature Range from −50 °C to 200 °C and Supply Voltage Range from 3.9 to 24 V. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–20 February 2020; pp. 72–74. [Google Scholar]
- Li, A.; Shen, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Mitrovic, I.Z.; Wen, H.; Lam, S.; Liu, W. A Monolithically Integrated 2-Transistor Voltage Reference with a Wide Temperature Range Based on AlGaN/GaN Technology. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2022, 43, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, S.; Pulvirenti, F.; Samperi, K. Frequency Compensation Scheme for a Full GaN OpAmp driving 1-nF load. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems—(ISCAS), Austin, TX, USA, 28 May–1 June 2022. [Google Scholar]









| Thresholds | Typ | SS | FF |
|---|---|---|---|
| VTH,E (V) | 1.62 | 2.28 | 0.918 |
| VTH,D (V) | −0.691 | −0.287 | −1.10 |
| Device | W (µm) | L (µm) | Multiplicity | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| QD1–QD2 | 5 | 0.5 | 1 | |
| QE1 | 250 | 1 | 8 | |
| QE2 | 200 | 1 | 3 | |
| R1 | 2 | 1000 | 1 | 320.22 kΩ |
| R2 | 2 | 1400 | 1 | 448.42 kΩ |
| R3 | 2 | 400 | 1 | 128.20 kΩ |
| Ref. Year | This Work * 2022 | [21] 2022 | [31] 2022 | [30] 2020 | [29] 2010 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply (V) | 3.9~24 | 4~16 | 4.8~50 | 3.9~24 | −4.3~−10 |
| VREF (V) | 2.7 | 2.3 | 2.53 | 3.19 | −2.1 |
| Tot. current (µA) | 2.7 (5, worst case) | 43 | 60 | 6.2 | 800 |
| Line Regul. (%V) | 0.105 | NA | 0.063 | 0.32 | N/A |
| PSR @100Hz (dB) | −45 (worst case) | NA | −42.8 | −45 | −35 |
| Temp. Range (°C) | −40~190 | 25~550 | −25~250 | −50~200 | 25~250 |
| TC (ppm/°C) | 200 + (worst case) | 242 + | 26.2 | 23.6 | 238 + |
| Area (mm2) | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.104 | 0.52 (0.31 w/o PADs) | 0.164 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bimbi, C.; Pennisi, S.; Privitera, S.; Pulvirenti, F. Single-Branch Wide-Swing-Cascode Subthreshold GaN Monolithic Voltage Reference. Electronics 2022, 11, 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11121840
Bimbi C, Pennisi S, Privitera S, Pulvirenti F. Single-Branch Wide-Swing-Cascode Subthreshold GaN Monolithic Voltage Reference. Electronics. 2022; 11(12):1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11121840
Chicago/Turabian StyleBimbi, Cesare, Salvatore Pennisi, Salvatore Privitera, and Francesco Pulvirenti. 2022. "Single-Branch Wide-Swing-Cascode Subthreshold GaN Monolithic Voltage Reference" Electronics 11, no. 12: 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11121840
APA StyleBimbi, C., Pennisi, S., Privitera, S., & Pulvirenti, F. (2022). Single-Branch Wide-Swing-Cascode Subthreshold GaN Monolithic Voltage Reference. Electronics, 11(12), 1840. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11121840








