Abstract
Video-based flame detection (VFD) aims to recognize fire events by using image features. Flame segmentation is an essential task in VFD, providing suspected regions for feature analysis and object recognition. However, the lack of positive flame samples makes it difficult to train deep-learning-based VFD models effectively. In this paper, we propose the assumption that we can train a segmentation model with virtual flame images and design experiments to prove it. We collected many virtual flame videos to extend existing flame datasets, which provide adequate flame samples for deep-learning-based VFD methods. We also apply a random-background-pasting method to distribute the flame images among different scenarios. The proposed method trains a flame segmentation model with zero real flame images. Moreover, we perform segmentation testing using real flame images, which the model has never used, to see if the model trained using ‘fake’ images can segment real objects. We trained four segmentation models based on FCN, U-Net, Deeplabv3, and Mask-RCNN using synthetic flame video frames and obtained the highest mPA of 0.783 and mIoU of 0.515. The experimental results on the FIRE-SMOKE-DATASET and the Fire-Detection-Image-Dataset demonstrate that the ‘fake’ flame samples generated by the proposed random-background-pasting method can obviously improve the performance of existing state-of-the-art flame segmentation methods using cross-dataset evaluation settings.
1. Introduction
For fire detection in spacious buildings with high ceilings, such as warehouses, factories, airports, and atrium buildings; forests; and grasslands, it will be difficult to install traditional fire detectors to detect fire events [1,2]. Video-based fire detection has become a prospective solution for fire protection in spacious buildings, forests, and grasslands [3,4,5] due to its advantages, such as being untouchable, not limited to the height of installation, fast response, and large view scope. With the tremendous progress that has been made in deep-learning-based video fire detection (VFD), one may expect that a video fire detection system based on a state-of-the-art neural network model can be easily deployed [6,7]. However, the biggest challenge of VFD research is the lack of an adequate annotated flame dataset for model training. As a kind of rare accident, collecting a large number of videos or images of real fire scenarios is difficult. In most fire detection studies, researchers use some small public datasets or design an experiment to shoot videos of simulated fire events [4] for data analysis, and the amount of data is very limited. However, deep learning networks are heavily dependent on big data in order to avoid overfitting. To model the training data perfectly, the networks have to learn a function from data with very high variance. Collecting a large number of training images becomes one of the main problems in VSD research. Based on the concept of object constancy in cognitive theory [8], children can learn to recognize objects using cartoon flashcards, and we think of the following: Can the segmentation model learn the information of an object by using virtual images? Therefore, we designed several experiments to train the segmentation model using fully synthetic images to see if using virtual images works. Deep-learning-based segmentation algorithms are significantly more accurate than traditional approaches [9]. The models used in this paper are all fully automatic segmentation models, and they can be classified under automatic video object segmentation (AVOS), as mentioned in [9].
Our main work is to generate synthetic training samples for object segmentation. We also propose a new random-background-pasting method to complement the data in the flame segmentation task. Inspired by how toddlers learn to recognize objects using drawn flashcards, we investigate the possibility of training a segmentation model with zero real flame images in this paper. We train a flame segmentation model with zero real flame images and then evaluate its performance on real-data target domains. We use four datasets: virtual flame videos [10], the FIRE-SMOKE-DATASET [11], the Fire-Detection-Image-Dataset [12], and the Non-smoke Images [13]. The training dataset from [10] has two types of data: the first comprises original virtual flame videos with a black background and white background, and the second comprises a virtual flame with a randomly pasted background. The segmentation model trained with virtual flame frames was used for the unseen real flame target domain to demonstrate benefits even when transferring between substantially different sources and target domains. Datasets FIRE-SMOKE-DATASET and Fire-Detection-Image-Dataset with real flame images provide a substantially challenging test. We present virtual video samples that are synthesized with good quality and show substantial improvement on segmentation tasks via FCN [14], UNET [15], Deeplabv3 [16], and Mask-RCNN [17] networks.
The experiment results demonstrate that it is possible to learn essential information from virtual flame videos generated by Blender, which shines the light that using virtual data may solve the problem of lacking data in deep-learning-based image segmentation or object detection. Our finding offers promise for VSD tasks such as flame detection, smoke detection, and segmentation using limited positive training samples.
The primary contributions of this paper are as follows:
- We train segmentation models using virtual images without manual annotation. By using fully synthetic video frames, we can learn significant information about the targets.
- We demonstrate a significant improvement in generalization performance in segmentation tasks. By training models using synthetic video frames, models can learn a particular approach from a source domain and then use that approach in a different target domain.
- We carry out the efficient augmentation of the training dataset using synthetic videos for any real test case. This study shows that training a segmentation model without using real training data is possible. This means that the problem of lacking data and time-consuming annotations can be solved with our method.
2. Materials and Methods
In this section, we will describe three aspects: related works, the method, and the experiment.
2.1. Related Works
To alleviate the lack of data for model training, data augmentation (DA), a data space solution for the problem of limited data, has been widely used in deep-learning-based research [18]. DA is a technique that can increase the variation in a dataset by applying transformations to the original data that preserve label information, with the validation of label integrity being performed by a human observer (a human observer can still recognize the object). Operations such as flip, translation, rotation, scale, crop, and adding noise are the easiest and most widely used techniques for DA in deep learning. Wong et al. [19] investigated the benefit of augmenting data by using synthetically created samples when training a machine learning classifier, such as CSVM (convolutional support vector machine), CNN, and CELM (convolutional extreme learning machine). The experiment on the MNIST dataset showed that augmentation in a data space using elastic deformations produced the best results, which were slightly worse than having additional real training samples. Taylor et al. [20] provided a comparative study on the effectiveness of geometric and photometric transformations (color space). The study demonstrates that DA is an effective method for increasing CNN (convolutional neural network) classification task performance. Additionally, experimental results indicate that altering the geometry of the images is more important than just changing the lighting and color in DA. This is the widely used DA method in many deep learning tasks; however, the transformations are based on the original image itself, and the generated variation is limited.
Except for DA with transformations, the adversarial approach is another possible research direction that can address the domain adaptation problem. It employs style transfer or cross-domain mapping networks to stylize the images in the source domain as the target and train the recognition [21] and segmentation models in this stylized space [22]. In [23], researchers trained a generative model (Data Augmentation Generative Adversarial Network (DAGAN)) to perform data augmentation, and it works well on Omniglot, EMNIST, and VGG-Face datasets. Experiments have proved that DAGAN can learn a representation and process it for data augmentation. The application of DAGAN to augment a standard classifier in the low-data regime demonstrated significant improvements in generalization performance with respect to all tasks. Xu et al. [24] built deep architectures based on domain adaptation to confuse the distributions of features extracted from synthetic and real smoke images for the purpose of video smoke detection. They report that the generation model is not stable, and sometimes, it does not work well.
‘Cut’ and ‘paste’ is another approach that can generate large, annotated instance datasets [25,26,27]. Dwibedi et al. [26] automatically segmented the object and augmented the data with rotation, and then they pasted the objects in the background scenes using different blending methods. The results show that these synthesized data are both competitive with respect to real data and contain complementary information. The instances are all obtained from segmentation, and the number is also limited.
Tremblay et al. [28] proposed a simulation system using parameters of the simulator—such as lighting, pose, object textures, etc.—that are randomized in order to force the neural network to learn the essential features of the object of interest and bridge the reality gap in synthetic images and real-world data. The approach was evaluated using the bounding box detection of cars in the KITTI dataset. Using only synthetic domain randomization data, the performance of car detection was comparable to more labor-intensive datasets.
These DA methods are designed to generate more data for model training; however, there are still many problems for specific applications. Shorten et al. [18] indicated that combining augmentations such as cropping, color shifts, and random erasing can result in massively inflated dataset sizes, but the method is not guaranteed to be advantageous. In domains with very limited data, this could result in further overfitting. In [29], researchers generated RGB images and point clouds with pixel-wise and point-wise annotations; then, they trained solely on synthetic data and tested on real-world RGB images. However, most methods in the paper are about data generation, and only subjective segmentation results are shown in the experiment. In this paper, we propose a flame segmentation based on fully synthetic videos and the random-background-pasting method for VFD.
2.2. Method
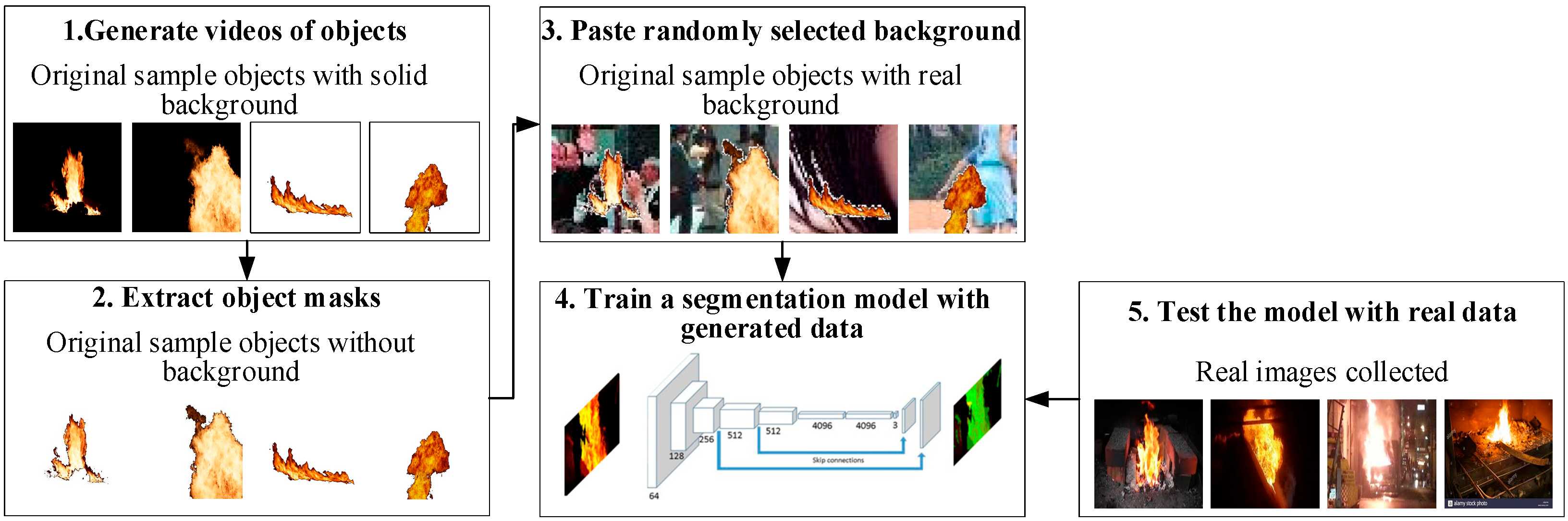
As mentioned above, the most commonly used data augmentation strategies are operations such as flip, translation, rotation, scale, crop, adding noise, and so on. However, all these operations need corresponding manually annotated labels in deep-learning-based segmentation model training. For many segmentation tasks, this comprises quite tedious and laborious work. Hence, we turn our attention to pursuing a method that provides abundant training data without annotations in order to make the automatic segmentation method more efficient and obtain better generalization performance. We assume that the model can learn flame features from fully virtual video frames, and the segmentation model will use zero real data for training in the proposed schema. The workflow of our proposal is shown in Figure 1:

Figure 1.
The approach to rapidly synthesizing datasets for object detection.
- Generate videos of objects.
In this work, the flame is a segmentation target. Blender [30] and Unity [31] were utilized to generate a bunch of flame videos with diverse viewpoints that contain solid backgrounds (black or white). Most synthetic videos were obtained from [10], and a small number of videos were obtained by ourselves.
- 2.
- Extract object masks.
We extract the flame regions separately from the background using threshold segmentation.
- 3.
- Paste a randomly selected background.
Background images are collected from real-world scenes. The segmented flames are pasted onto the randomly selected background images as our generated training data.
- 4.
- Train a segmentation model using generated data.
We train segmentation models using synthetic images.
- 5.
- Test the model using real flame images.
This is a fully automatic flame segmentation model. In the training stage, generated flame samples are used to learn the features and build the model. Then, we test the model by inputting real flame images to observe the learning ability of the model and the quality of generated data.
As Figure 1 shows, we start with a set of flame images extracted from synthetic videos. Then, we automatically extract the flame masks. The flames are pasted on the randomly selected real background images to ensure that the features of the background can also be learned by the detection model, which is important to guarantee the generalization of the model. Our results show that the synthesized data are both competitive with respect to real data and contain complementary information.
2.2.1. Virtual Video Frames for Model Training
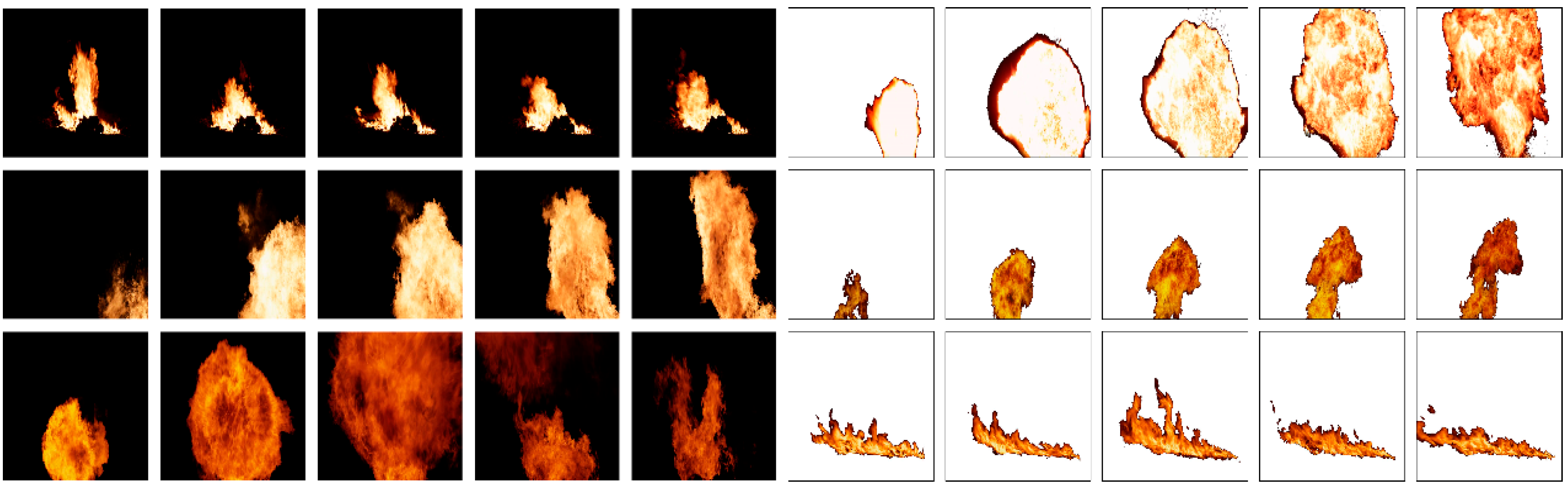
As mentioned above, we use four datasets in this study. The most important dataset contains virtual videos of flames [10]. Figure 2 shows examples of the virtual videos that were used for model training. As observed, the flame with a black background is more realistic, especially during the dynamic video playback. The color, texture, edge, and movement of the fire plume are obvious in movies. There are 140 virtual videos (22,090 frames) of flames in total, and they are created with the Blender software (version 3.5) for model training.

Figure 2.
Clipped frames from original virtual flame videos.
All of our operations are conducted within the RGB color space. Because the background of synthetic virtual flame videos is black (pixel value is 0) or white (pixel value is 255), setting the pixel value to obtain the corresponding binary masks for segmentation is easy. As shown in Equation (1), is the pixel value of the frame at location (x, y, z), and z indicates the RGB channel of the image, z = 0, 1, 2. is the extracted flame region, with the background set to 0.
With virtual video rendering software, including Blender 3.5 and Unity 3.2, we can quickly generate a large number of training data and masks by changing resolution parameters, lighting, color, texture, etc., which can beneficially improve generalization.
2.2.2. Bridging the Reality Gap with Background Paste
For real flame images or videos, the background will be not only black or white but will also contain different scenes based on the specific monitoring environment. We use the trained model to segment the flame in real shooting environments. In this study, the input’s distribution changes. The model experiences a covariate shift [32], which has a significant impact on the learning procedure in neural networks. To improve the segmentation model’s ability of adapting to various segmentation scenes, we proposed a random-background-pasting method here to bridge the reality gap between virtual videos and real flame videos. By randomly pasting the selected backgrounds from non-smoke images [13], we can narrow the gap between the training dataset and real flame images. The pasting operation is shown in Equation (2), where f is the virtual video frame, and b is the selected background. f’ is the pasted flame sample. Some of the examples of virtual images with pasted backgrounds are shown in Figure 3.

Figure 3.
Examples of flame video frames with randomly selected backgrounds.
After we obtain the prepared images, we use FCN [14], UNET [15], Deeplabv3 [16], and Mask-RCNN [17] methods and initialize the model that is pre-trained using object detection on the ImageNet [33] dataset.
2.3. Experiment
We trained four segmentation models with the same training data. All training data are virtually generated flame images. Then, we test the model with real flame images to test the effectiveness of our synthesized data. Firstly, we describe our standard experimental setup here.
2.3.1. Dataset for Model Training and Testing
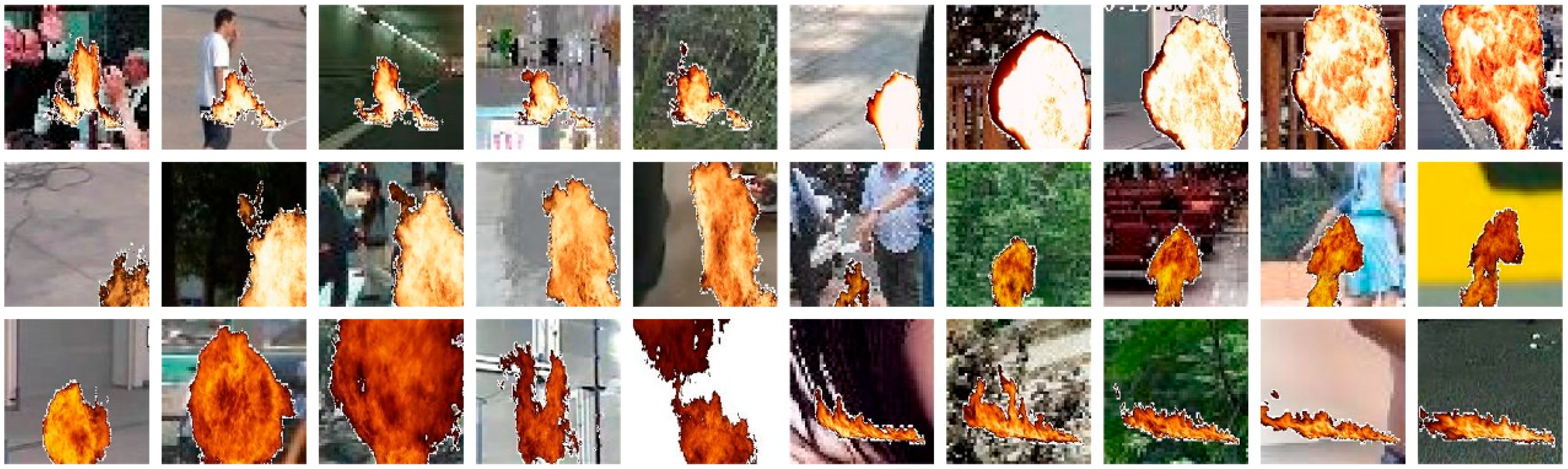
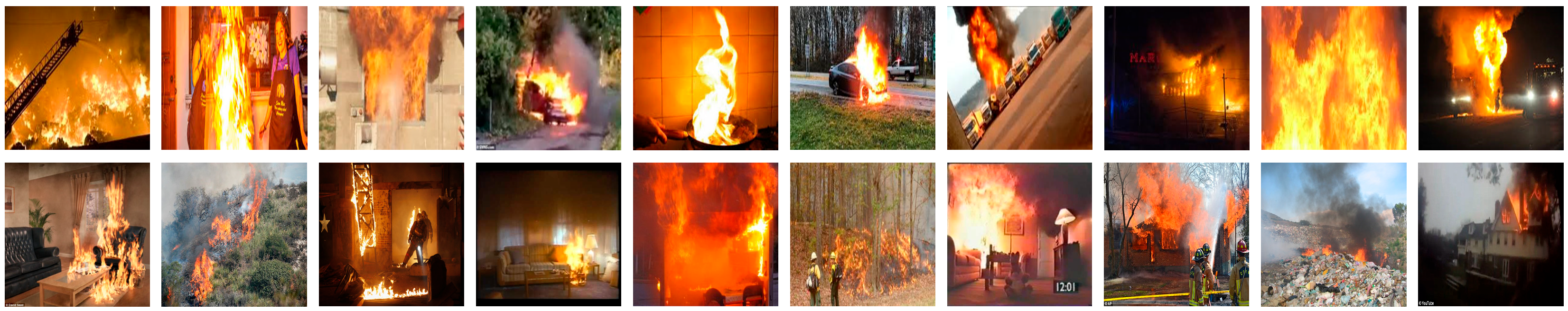
We performed two groups of experiments in this study: We trained the segmentation model using originally generated images (as shown in Figure 2) and used images that have been pasted onto real backgrounds (as shown in Figure 3). Virtually generated flame images with and without randomly pasted backgrounds are used as our training data (140 videos with black and white backgrounds (22,090 frames) and 140 videos with randomly pasted backgrounds (22,090 frames); in total, 22,090 × 2 images). Then, we tested the model using real flame images from FIRE-SMOKE-DATASET and Fire-Detection-Image-Dataset. Some examples of the test data are shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
Examples of flame video frames with randomly selected backgrounds. The first row shows samples from FIRE-SMOKE-DATASET. The second row shows images from Fire-Detection-Image-Dataset.
2.3.2. Segmentation Models
We use FCN [14], U-Net [15], Mask-RCNN [17], and Deeplabv3 [16] as segmentation models. FCN is designed for end-to-end, pixel-to-pixel semantic segmentation. Additionally, we tried to use synthetic video frames, which are similar in appearance to the real frame, to train the segmentation model in order to observe whether the model can learn effective information from the synthetic foreground pixels of synthetic data. The architecture of U-Net consists of a contracting path that captures the context and a symmetrically expanding path that enables precise localization. The network is trained end-to-end to obtain the segmentation result. Mask R-CNN extends Faster R-CNN [34] by adding a branch to predict an object mask that is parallel to the existing branch for the bounding box proposal. It outputs the mask of the segmentation objects. Deeplabv3 [16] employs atrous convolution in a cascade or in parallel to capture multi-scale contexts by adopting multiple atrous rates, and it is also designed for semantic image segmentation.
3. Results
3.1. Quality Assessment
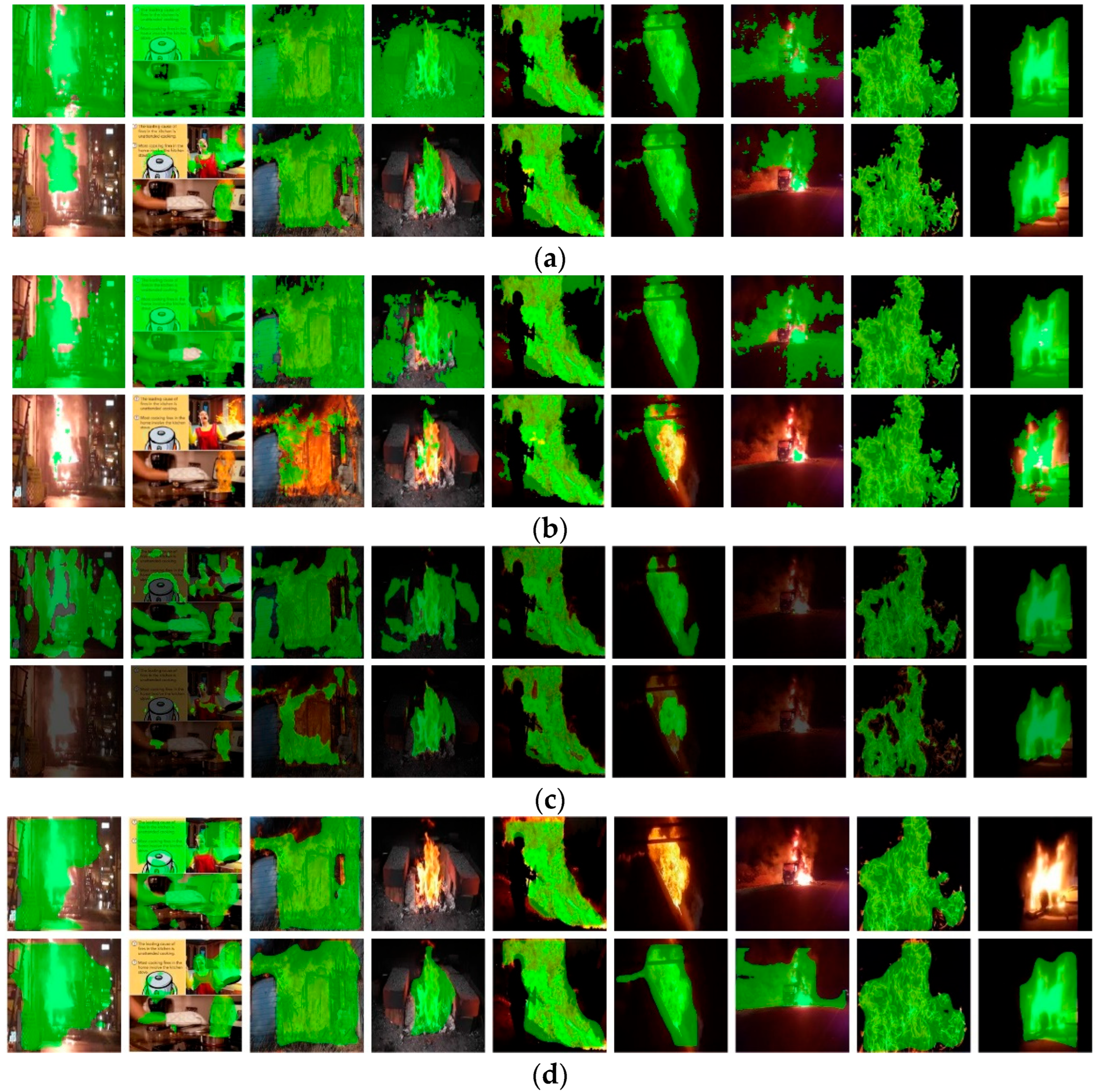
Before diving into the results, we would like to inspect the preliminary result found during the search to obtain a better understanding the operations were used. Using the original virtual images shown as examples in Figure 2, we trained several segmentation models, and the test results are shown in the first rows of Figure 5a–d. Green masks are used to show the segmentation result. From the first rows, we can observe that for the models trained using original virtual images with only a black and white background, almost all flame regions can be segmented. In the testing stage, if the background of real images is black or white and does not have texture, which is similar to the training data, the segmentation result looks much better, as shown in the fifth, sixth, eighth, and ninth images in each row. All models can handle these images very well due to the similar distribution of testing data and training data. However, for images with a complex background, over-segmentation is obvious (the first rows). We observe that no matter what segmentation model is used, this phenomenon always exists because, during the training stage, the model has never seen images with various backgrounds; moreover, the model tends to treat all pixels with a brighter grayscale as flames. Therefore, over-segmentation always occurs when segmenting real images with different scenes.
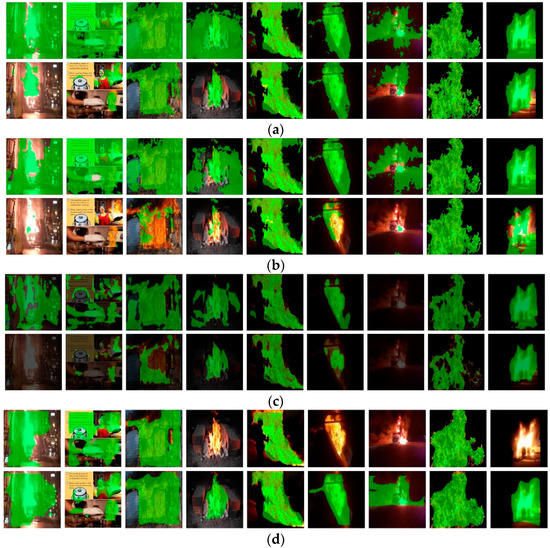
Figure 5.
Flame segmentation results of different models. For each model, we train it with original virtual images and images with pasted backgrounds, and the results are shown in two rows. The first row shows the results of the model trained with the original training data. The second row shows the results of the model trained with images with a background. (a) Segmentation result of FCN, (b) segmentation result of U-Net, (c) segmentation result of Deeplabv3, and (d) segmentation result of mask-RCNN.
To solve this problem, we proposed a random-background-pasting method to narrow the gap between the training data and testing data, as mentioned in Section 3.2. The second rows of Figure 5a–d show the results of the segmentation model trained using virtual flames pasted with a real background. Compared to the first rows, over-segmentation significantly improved, especially in Figure 5a. Except for the last image in the second row of Figure 5a, all segmentation results look pretty good. The reason may be that the brightness of the flame in this image is substantially higher than the ordinary flame, which is much harder for the model to segment.
Comparing the models horizontally, the performance of FCN is much better than U-Net and Deeplabv3 in this experiment. We feel that U-Net is improper for flame segmentation; hence, the variation in the target is much greater than in medical images with similar structures. Deeplabv3 did not work as well as we expected. However, the simple model FCN works better than the more developed and complex segmentation model Deeplabv3. In this study, the images of the training and testing dataset are not from the same domain. In other words, there is a dataset shift between the training and testing dataset. To obtain better segmentation results on the testing dataset, the generalization ability should be improved. It is also known that the easier the model, the better it can be model generalized. This may be the reason why FCN has better segmentation performance than the other two more complex models. In Figure 5d, the segmentation result of mask-RCNN is comparable to FCN. However, the segmentation procedures are different. In the mask-RCNN-based method, RPN (region proposal network) works ahead of segmentation, and if the target has not been detected, we cannot obtain a segmentation result. If the flame can be detected first, then the segmentation performance will be better than other models. This can be observed in the last row of Table 1. We shall discuss this later.

Table 1.
Comparison of four different state-of-the-art object segmentation models trained on original virtual images versus virtual images using a randomly pasted background.
3.2. Quantity Assessment
3.2.1. Analysis of the Segmentation Result
Here, we use PA (pixel accuracy) and IoU (intersection over union) as our evaluation metrics, and they are calculated using Equations (3) and (4):
In Equations (3) and (4), TP (true positive) counts the number of pixels that we predict as the region that is part of the flame and the region that is really a part of a segment. FP (false positive) counts the number of pixels that we predict as part of a segment but that is not part of the flame. TN (true negative) counts the number of places for which we predict a pixel is not part of a flame, and indeed, the pixel is not part of a segment. FN (false negative) counts the predicted number of pixels that are not part of a segment but are part of the flame. mPA (mean PA) and mIoU (mean IoU) are the mean values of all test images.
Table 1 lists the comparison results of the FCN, U-Net, Deeplabv3, and Mask-RCNN of the two different training datasets. In total, 832 test images are from FIRE-SMOKE-DATASET and the Fire-Detection-Image-Dataset. Our random-background-pasting method using mask-RCNN achieved an mPA of 0.783 and an mIoU of 0.515. Here, we calculate the mean value of mPA and mIoU, respectively. As mentioned above, mask-RCNN uses RPN to detect the object first, which causes mis-segmentation *, **. For the training dataset using original virtual images, the flame was not detected in 16 images; for the dataset with a pasted background, the flame was not detected in 149 images. mPA and mIoU were calculated only for images that have segmentation results. The assumption of this study is that the model can learn features of the flame only from virtual video frames, and the segmentation model can use zero real images for training to obtain the segmentation ability. What we want to emphasize is the shift of the dataset between the training and testing set. Although there are some related works on data synthesis [26,35], the training and testing datasets are independent and identically distributed (i.i.d.), and there is no dataset shift. Although we cannot compare the method under the same condition, the results can be referred to. In [26], an mAP (mean Average Precision) of 0.365 was obtained using the synthetic GMU Kitchen Scenes dataset for object detection. In [35], an mIoU of about 0.73 was obtained for smoke segmentation using a composited smoky image. However, the training and testing images are from the same dataset, and it is much easier to train a segmentation model with better performances than our experiment.
3.2.2. Measurements of the Dataset for Learning
For model training using synthetic data, the parameters of the dataset are significant for describing the segmentation procedure. In order to measure the uncertainty of the dataset, we used the ratio of the flame’s size to image a, mean value of intensity im, and hue value hm of the flame region to indicate the flame’s size, light, and color with respect to the dataset. The image size is . F is the original flame image, and M is a two-dimensional binary mask of the flame image (the foreground is set to 1, and the background is set to 0). is the area of the flame. For the calculation of im and hm, first, we transform original image F into a gray image and use an HSV color space. The gray image is G, and the hue image is H. Then, we apply a binary mask to F and H, and we obtain two single-channel images, Gflame and Hflame. The measurements of the dataset are shown in Equations (5)–(7).
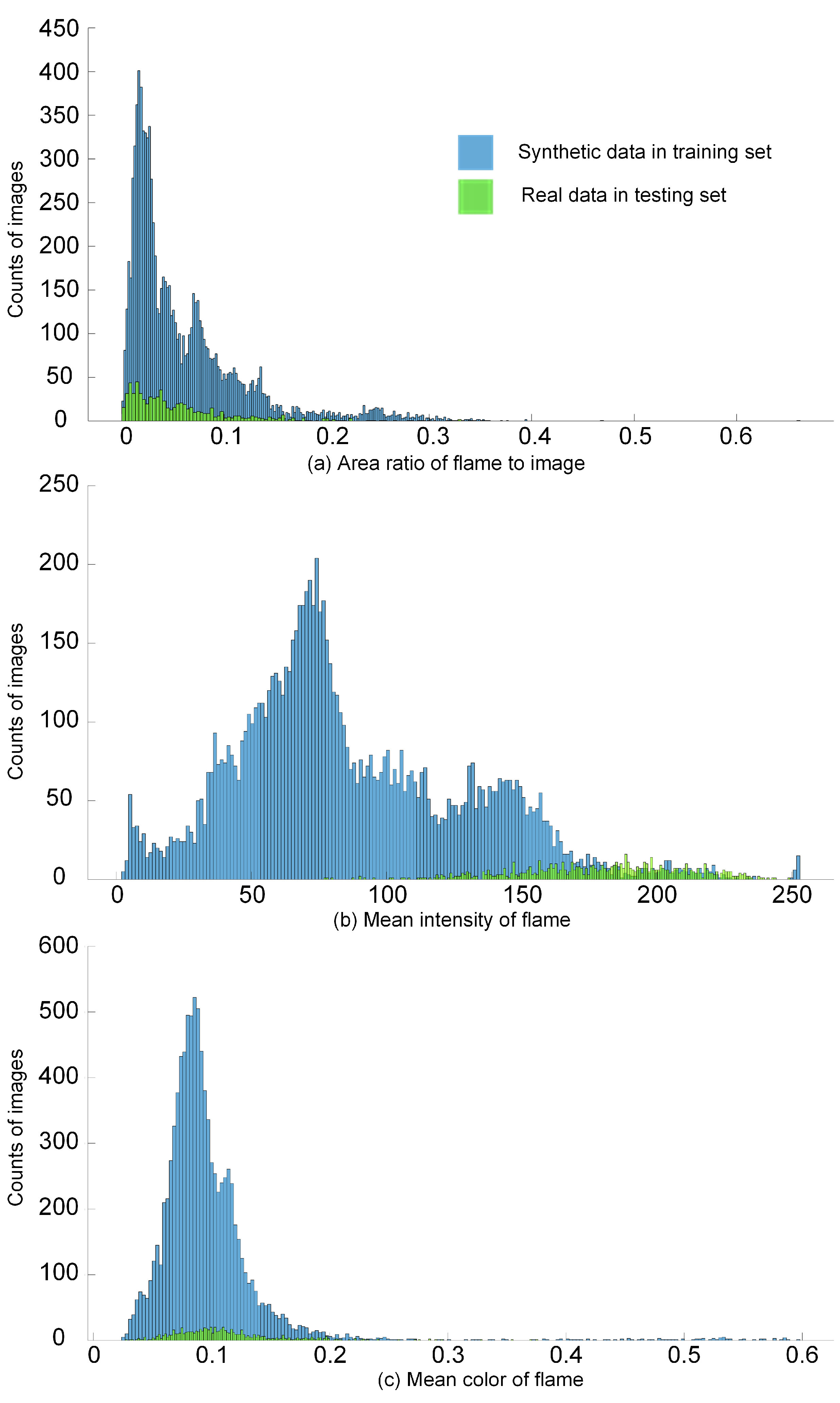
The results of the measurements are shown in Figure 6. The size of the training image and testing image is different; for example, the synthetic flame image is 1920 × 1080, while the real flame image is 290 × 173. However, all images are resized to the same size. Therefore, we used the ratio a describe the size of the flame. In Figure 6, blue shows synthetic data in the training set, and green shows the real flame data in the testing set. Because the number of images in the training set is much greater than that of the testing set, along with the y-axis, the number of synthetic data images is greater than real data. It will not affect the analysis of the dataset because we focused on the distribution of the measurement and not the number of images. It can be observed that the distributions of real data overlaid that of the synthetic data. This shows that synthetic flame images cover the variation of real flames in the testing set in terms of flame size, light, and color.
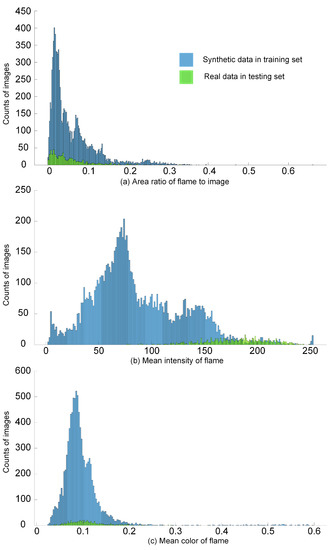
Figure 6.
Measurement of the dataset. (a–c) are distributions of the area ratio of the flame to image, the mean of the flame’s intensity, and the mean of flame color obtained from synthetic data and real data.
3.3. Analysis of the Random-Background-Pasting Method
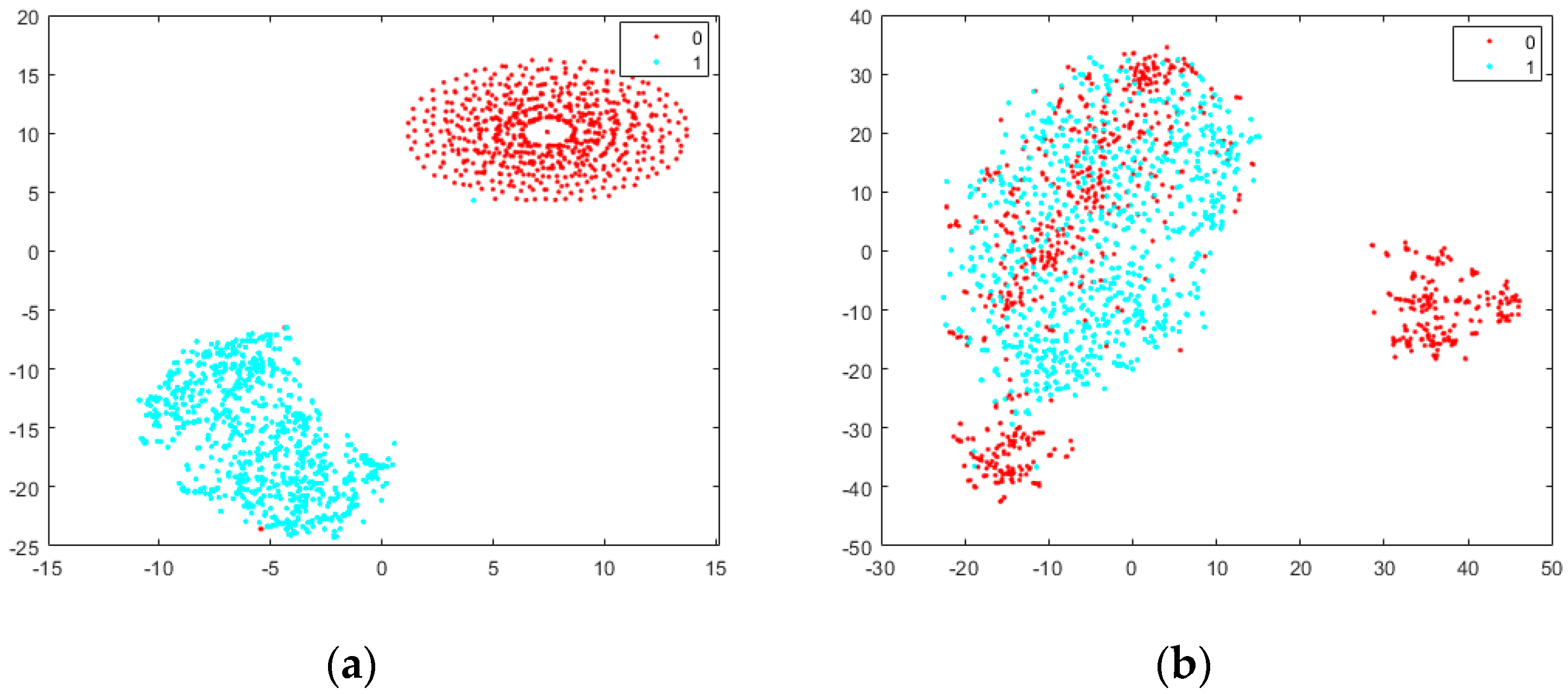
We proposed a random-background-pasting method to narrow the dataset shift between original synthetic images and real flame images. To show how much the pasting method contributes to the distribution’s bridging, t-SNE [36] is used to visualize high-dimensional data (images) in a 2D map. Figure 7 shows the results of applying t-SNE to the training and testing dataset (832 images). The cyan dots represent real flame images, and the red dots represent synthetic flame images. The two different types of synthetic images in the training dataset are original virtual images with a solid background and virtual images with a randomly pasted real background. t-SNE constructs a set of embedded points in a low-dimensional space with relative similarities that mimic the original high-dimensional points. For objects that look similar, the images are mapped to nearby points. We can observe that in Figure 7a, the distance between the original virtual images (red dots) and real flame images is far from each other, and the shift in the dataset is obvious. After we add a real background to the original synthetic images, as shown in Figure 7b, on the left side, the training and testing dataset are mixed well, and we can say that this method narrows the distance between synthetic data and real data. The small portion of red points on the right side may comprise the images pasted with a solid background. The background is selected from non-smoke images [13], which may be solid and may not look as real as the testing data. Overall, the dataset’s shift was eased to some degree, and the segmentation results indicate that this method is effective in improving performance.
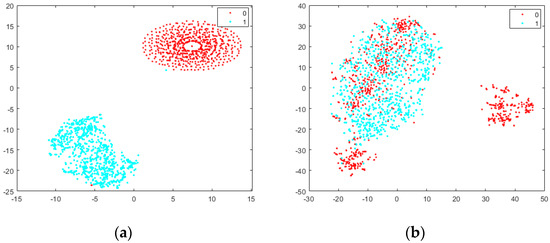
Figure 7.
Visualization of the training and testing dataset with t-SNE [36]. ‘1’ represents the real flame image (cyan dots), and ‘0’ represents the synthetic flame image (red dots). (a) Here, 832 randomly selected training images are original synthetic flame images with a solid background, as shown in Figure 2, and 832 testing images are the real images shown in Figure 4. (b) The 832 randomly selected training images are synthetic flame images with a randomly pasted background, as shown in Figure 2. The testing images are real images, as shown in Figure 4.
4. Discussion
The main goal of the study is to segment real flames with models trained using fully synthetic images. The study provides subjective and quantitative evaluations to support the assumption that models can learn information about real objects using virtual images. Although the study provides a segmentation method that can arrive at an mPA of 0.783 and an mIoU of 0.515, there were certain limitations when exploring the aim of the study. These points are expected to help future researchers in avoiding the same shortcomings.
During the study, all pasted backgrounds are randomly selected from one dataset [13], and it is certain that by pasting the randomly selected background images, the generalization of the model can be improved. However, we used 22,090 images from 70 videos for model training, and the variation in images from the same video is not large enough. More synthetic videos or images will contribute to better performances in the future. Additionally, more variations in luminance, wind, density, etc., will be added to synthetic data. In addition, the paste operation is random, and some combinations of the flame and background are illogical. For example, some background images comprise people, faces, water, etc. The pasted images will not appear in practical applications. Hence, a background dataset containing images more consistent with real fire situations is needed. Additionally, a better way is to generate or synthesize fire in a real scene using computer graphics methods. On the other hand, to apply the model in the future, we can collect background images of monitoring locations before system deployment. With this self-learning strategy, segmentation can perform better in a specific area.
The mis-segmentation phenomenon of mask-RCNN inspired the following: If we want to obtain better segmentation performance, we can detect the flame region first and then take advantage of the excellent segmentation ability of mask-RCNN to improve the final performance of the model. This is an attempt to train a segmentation model with zero manually annotated training data. Although the mPA of 0.783 and mIoU of 0.515 have substantial room for improvement, at least we know that it is possible to train the segmentation model using fully virtual images.
5. Conclusions
Deep learning has greatly improved segmentation performance using supervised training in many applications, such as organ segmentation [15], city landscape segmentation [16], and so on. However, for most model training, large-scale training sets are needed for improving performances, and obtaining annotations is also expensive and time-consuming. We proposed an assumption that, by learning synthetic data, the model can also learn the patterns of the target, similarly to teaching using cartoon flashcards. In this paper, we introduced synthetic video generation to improve the performance of segmentation networks. We proposed a novel approach to narrow the distance between training and testing sets using a random-background-pasting method, which helps improve the performance of the segmentation network. Experiments showed that our approach is efficient. The approach proved the hypothesis that was proposed before the experiment in that the model can learn the information of a real object using fully synthetic images. With the proposed method, we can train the model using zero samples to reach a certain accuracy. Thus, we believe that we have provided a case of training a segmentation model using fully synthetic data to improve deep learning techniques. Our work provides a new method for future research on video-based fire detection, especially for flame segmentation. Similarly, we can also use the method to process smoke using synthesized smoke images. With synthetic videos, we can not only train models for flame segmentation but also train models for object detection and recognition. Additionally, the videos can be used for both 3D and 2D models. With Blender and Unity, more virtual objects can be generated. This method can be applied in different fields. Our future work will explicitly add a similarity metric to data synthesis in order to improve the sense of reality further and improve efficiency for model training.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.J. and Z.M.; methodology, Y.J.; software, Y.J.; validation, Y.J., Z.M. and X.Z.; formal analysis, Y.K.; resources, Y.C.; data curation, Q.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.J.; writing—review and editing, Q.Z.; supervision, Y.C.; project administration, Y.J. and Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Industry-University-Research Collaboration Project of XUPT and XNIC262 (HX2021-496).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank all authors who contributed to this paper. They are key participants in this paper and have dedicated a lot of time and effort to experiments and data analysis. Their rigorous and serious working attitude, as well as their professional knowledge and skills, provided valuable support and assistance in this study. We also thank all institutions that supported us in this study for their cooperation and contributions. Additionally, we thank Xiaoxian Li, Ben Wang and Gang Wang from XNIC262, who support us to do this research for the future application. Their encouragement makes us feel confident of continuing this work all along.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jia, Y.; Du, H.; Wang, H.; Yu, R.; Fan, L.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Q. Automatic Early Smoke Segmentation based on Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks. Optik 2019, 193, 162879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, A.; Singh, A.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, A.; Kapoor, K. Video flame and smoke based fire detection algorithms: A literature review. Fire Technol. 2020, 56, 1943–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsoshoara, A.; Afghah, F.; Razi, A.; Zheng, L.; Fulé, P.Z.; Blasch, E. Aerial imagery pile burn detection using deep learning: The FLAME dataset. Comput. Netw. 2021, 193, 108001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Cao, Y.; Feng, X.; Lu, X. Global2Salient: Self-adaptive feature aggregation for remote sensing smoke detection. Neurocomputing 2021, 466, 202–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Hou, M.; Shu, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X. A Study on Forest Flame Recognition of UAV Based on YOLO-V3 Improved Algorithm. In Recent Advances in Sustainable Energy and Intelligent Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 497–503. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhao, W. Image fire detection algorithms based on convolutional neural networks. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2020, 19, 100625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purves, D. Cognitive Neuroscience; Sinauer Associates, Inc.: Sunderland, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, T.; Porikli, F.; Crandall, D.J.; Van Gool, L.; Wang, W. A Survey on Deep Learning Technique for Video Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 7099–7122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virtual Flame Videos. 2018. Available online: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ep411o7ao/?spm_id_from=333.999.0.0&vd_source=a3701280b4f33a1022c6b93f5360155f (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- FIRE-SMOKE-DATASET. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/DeepQuestAI/Fire-Smoke-Dataset (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Fire-Detection-Image-Dataset. 2017. Available online: https://github.com/cair/Fire-Detection-Image-Dataset (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Non-Smoke Images. 2023. Available online: http://staff.ustc.edu.cn/~yfn/non-smoke1_27707.rar (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Long, J.; Shelhamer, E.; Darrell, T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 3431–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.05587. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask R-CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.C.; Gatt, A.; Stamatescu, V.; McDonnell, M.D. Understanding data augmentation for classification: When to warp? In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications (DICTA), Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 30 November–2 December 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, L.; Nitschke, G. Improving deep learning with generic data augmentation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), Bangalore, India, 18–21 November 2018; pp. 1542–1547. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, P.; Zha, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Identity-aware facial expression recognition via deep metric learning based on synthesized images. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2021, 24, 3327–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankaranarayanan, S.; Balaji, Y.; Jain, A.; Lim, S.N.; Chellappa, R. Learning from synthetic data: Addressing domain shift for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3752–3761. [Google Scholar]
- Antoniou, A.; Storkey, A.; Edwards, H. Data augmentation generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.04340. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Lin, G.; Wang, J. Deep domain adaptation based video smoke detection using synthetic smoke images. Fire Saf. J. 2017, 93, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Oh, S.J.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Yoo, Y. Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6023–6032. [Google Scholar]
- Dwibedi, D.; Misra, I.; Hebert, M. Cut, paste and learn: Surprisingly easy synthesis for instance detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1301–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiasi, G.; Cui, Y.; Srinivas, A.; Qian, R.; Lin, T.-Y.; Cubuk, E.D.; Le, Q.V.; Zoph, B. Simple Copy-Paste is a Strong Data Augmentation Method for Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, J.; Prakash, A.; Acuna, D.; Brophy, M.; Jampani, V.; Anil, C.; To, T.; Cameracci, E.; Boochoon, S.; Birchfield, S. Training deep networks with synthetic data: Bridging the reality gap by domain randomization. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 969–977. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, R.; Ferreira, J.; Peixoto, P. SynPhoRest-Synthetic Photorealistic Forest Dataset with Depth Information for Machine Learning Model Training; Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Blender. 2023. Available online: https://www.blender.org/ (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Unity. 2023. Available online: https://unity.cn/ (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (PMLR), Lille, France, 6 July–11 July 2015; pp. 448–456. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Xia, X.; Huang, Q.; Li, X. A wave-shaped deep neural network for smoke density estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 2301–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Maaten, L.; Hinton, G. Visualizing data using t-SNE. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Yuan, J.; Wang, J.; Fang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y. A saliency-based method for early smoke detection in video sequences. Fire Technol. 2016, 52, 1271–1292. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).