Immersive Virtual Reality Enabled Interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
(This article belongs to the Section Artificial Intelligence)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Procedure and Criteria
2.2. Selection Procedure
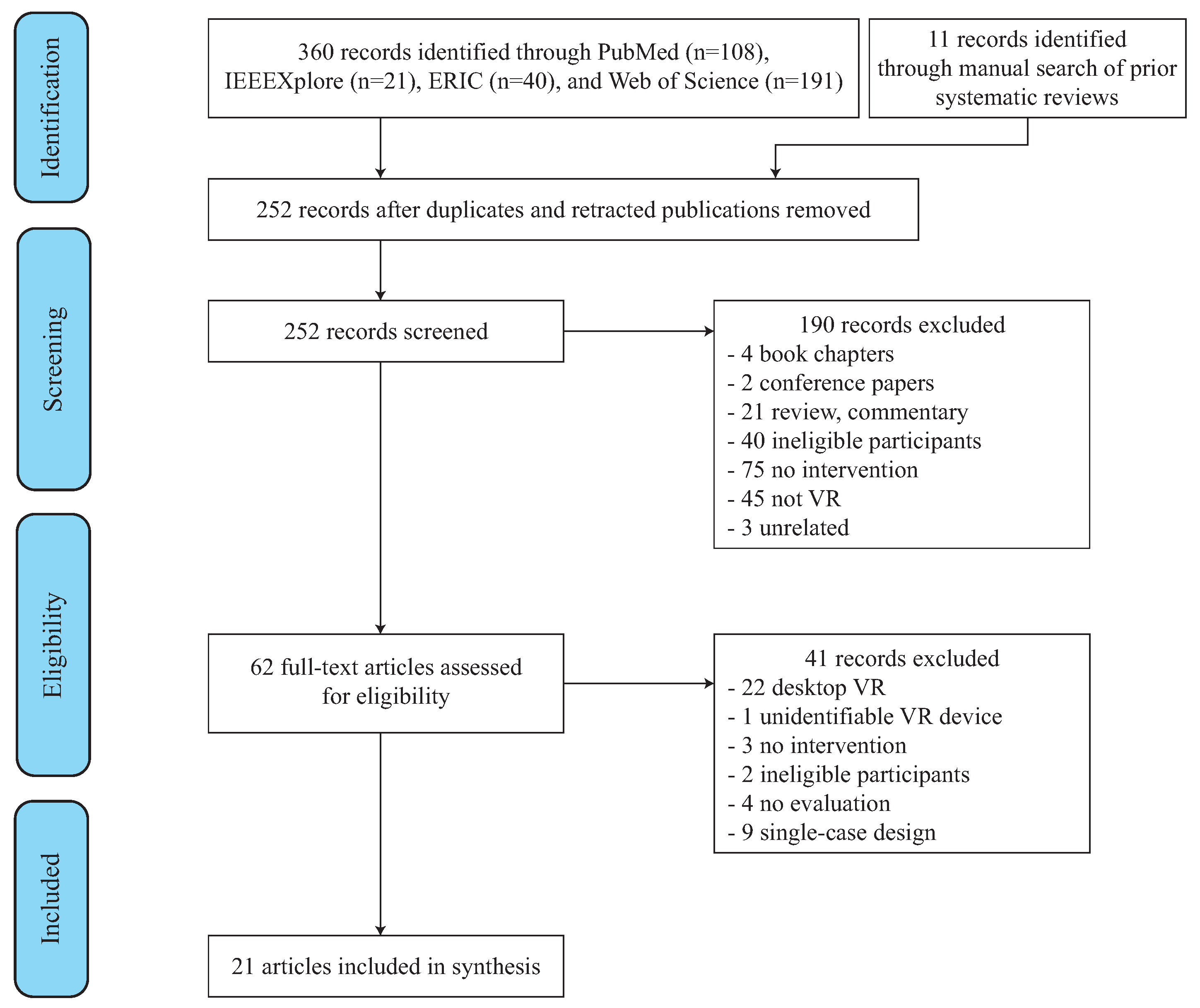
3. Results
3.1. Search Results
3.2. Descriptive Analysis
3.2.1. Areas of Intervention
3.2.2. Characteristics of Participants
3.2.3. Enabling Technology
3.2.4. Theoretical Foundations
3.2.5. Evaluation Approach and Measures
3.3. Meta-Analysis on the Effectiveness
4. Discussion
4.1. Area of Intervention
4.2. Affordances of Immersive VR
4.3. Theoretical Foundation
4.4. The Effectiveness of Intervention
4.5. Research Trends and Challenges
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABA | Applied Behavior Analysis |
| ABAS-II | Adaptive Behavior Assessment System Second Edition |
| ADDM | Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring |
| ASD | Autism Spectrum Disorder |
| ATEC | Autism Treatment Evaluation Checklist |
| BAI | Beck Anxiety Inventory |
| BCI | Brain-computer Interface |
| BDEFS | Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale |
| BDI | Beck Depression Inventory |
| BFNE | Brief Fear of Negative Evaluation Scale |
| BOT-2 | Bruininks--Oseretsky Test of Motor Proficiency Second Edition |
| CAVE | Cave Automatic Virtual Environment |
| CBT | Cognitive Behavior Therapy |
| CDC | Disease Control and Prevention |
| CGI-I | Clinical Global Impression-Improvement |
| CI | Confidence Intervals |
| DAS | Driving Attitude Scale |
| DCCS | NIH Dimensional Change Card Sort Test |
| DCQ | Driving Cognitions Questionnaire |
| EDA | Electrodermal Activity |
| EQ | Empathy Quotient |
| ERIC | Education Resources Information Center |
| ESPE | Emotions and Situations for Primary Emotions |
| ESSE | Emotions and Situations for Secondary Emotions |
| FEEST | Facial Expressions of Emotions: Stimuli and Tests |
| GAD-7 | General Anxiety Disorder Questionnaire-7 |
| GE | Graded Exposure |
| HADS | Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale |
| HMD | Head-mounted Display |
| I-CLE | College Living Experience Satisfaction Scale |
| JAA | Joint Attention Assessment |
| JAAT | Joint-attention Assessment Task |
| KELM | Kolb’s Experiential Learning Model |
| MASC | Movie for the Assessment of Social Cognition |
| NIH | National Institutes of Health |
| PECS | Picture Exchange Communication System |
| PEP-3 | Psychoeducational Profile Third Edition |
| PESE | Perceived Empathic Self-Efficacy Scale |
| PHQ-9 | Patient Health Questionnaire-9 |
| POMS | Profile of Mood States |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews |
| PSSE | Perceived Social Self-Efficacy Scale |
| RCPM | Raven’s Colored Progressive Matrices |
| RSPM | Raven’s Standard Progressive Matrices |
| SACQ | Student Adaptation to College Questionnaire |
| SCAS-C | Spence Children’s Anxiety Scale (child version) |
| SCAS-P | Spence Children’s Anxiety Scale (parent version) |
| SCERTS | Social-Communication, Emotional Regulation and Transactional Support |
| SE | Secondary Emotions |
| SIAS | Social Interaction Anxiety Scale |
| SISST | Social Interaction Self-Statement |
| SRS | Social Responsiveness Scale |
| STAI | State-Trait Anxiety Inventory |
| TEACCH | Treatment and Education of Autistic and Related Communication Handicapped Children |
| TMT | Trail Making Test |
| ToM | Theory of Mind |
| VABS | Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scale |
| VMI | Developmental Test of Visual-Motor Integration |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®); American Psychiatric Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Baio, J.; Wiggins, L.; Christensen, D.L.; Maenner, M.J.; Daniels, J.; Warren, Z.; Kurzius-Spencer, M.; Zahorodny, W.; Rosenberg, C.R.; Dowling, N.F. Prevalence of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years-autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2010. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. Surveill. Summ. 2014, 63, 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Elsabbagh, M.; Divan, G.; Koh, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kauchali, S.; Marcín, C.; Montiel-Nava, C.; Patel, V.; Paula, C.S.; Wang, C.; et al. Global prevalence of autism and other pervasive developmental disorders. Autism Res. 2012, 5, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron-Cohen, S.; Leslie, A.M.; Frith, U. Does the autistic child have a “theory of mind”? Cognition 1985, 21, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron-Cohen, S. Mindblindness: An Essay on Autism and Theory of Mind; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Baron-Cohen, S. Theory of mind and autism: A fifteen year review. In Understanding Other Minds: Perspectives from Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience; Baron-Cohen, S., Tager-Flusberg, H., Cohen, D.J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2000; Volume 2, pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Frith, U. Autism: Explaining the Enigma; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Frith, U.; Happé, F. Autism: Beyond “theory of mind”. Cognition 1994, 50, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozonoff, S.; Pennington, B.F.; Rogers, S.J. Executive function deficits in high-functioning autistic individuals: Relationship to theory of mind. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 1991, 32, 1081–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozonoff, S. Executive functions in autism. In Learning and Cognition in Autism; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1995; pp. 199–219. [Google Scholar]
- Foxx, R.M. Applied behavior analysis treatment of autism: The state of the art. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 17, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondy, A.S.; Frost, L.A. The picture exchange communication system. Focus Autistic Behav. 1994, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesibov, G.B.; Shea, V.; Schopler, E. The TEACCH Approach to Autism Spectrum Disorders; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin, E.; Prizant, B.M.; Laurent, A.C.; Wetherby, A.M. Social communication, emotional regulation, and transactional support (SCERTS). In Interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorders; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 107–127. [Google Scholar]
- Grynszpan, O.; Weiss, P.L.; Perez-Diaz, F.; Gal, E. Innovative technology-based interventions for autism spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis. Autism 2014, 18, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, H.H.; Li, C. Virtual reality-based learning environments: Recent developments and ongoing challenges. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Hybrid Learning and Continuing Education; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Rheingold, H. Virtual Reality: Exploring the Brave New Technologies; Simon & Schuster Adult Publishing Group: London, UK, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Steuer, J. Defining virtual reality: Dimensions determining telepresence. J. Commun. 1992, 42, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blascovich, J.; Loomis, J.; Beall, A.C.; Swinth, K.R.; Hoyt, C.L.; Bailenson, J.N. Immersive virtual environment technology as a methodological tool for social psychology. Psychol. Inq. 2002, 13, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, S.; Parsons, S.; Westbury, A.; White, K.; White, K.; Bailey, A. Sense of presence and atypical social judgments in immersive virtual environments: Responses of adolescents with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Autism 2010, 14, 199–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adjorlu, A.; Høeg, E.R.; Mangano, L.; Serafin, S. Daily living skills training in virtual reality to help children with autism spectrum disorder in a real shopping scenario. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR-Adjunct), Baltimore, MD, USA, 6–11 May 2007; pp. 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Karkhaneh, M.; Clark, B.; Ospina, M.B.; Seida, J.C.; Smith, V.; Hartling, L. Social Stories™ to improve social skills in children with autism spectrum disorder: A systematic review. Autism 2010, 14, 641–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vismara, L.A.; Rogers, S.J. Behavioral treatments in autism spectrum disorder: What do we know? Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2010, 6, 447–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, N.S. Specific and nonspecific factors in the effectiveness of a behavioral approach to the treatment of marital discord. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1978, 46, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandin, T. How does visual thinking work in the mind of a person with autism? A personal account. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, D.; Taylor, J. Interactive multimedia systems for students with autism. J. Educ. Media 2000, 25, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, H.H.; Wong, S.W.; Chan, D.F.; Byrne, J.; Li, C.; Yuan, V.S.; Lau, K.S.; Wong, J.Y. Enhance emotional and social adaptation skills for children with autism spectrum disorder: A virtual reality enabled approach. Comput. Educ. 2018, 117, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, D.; Marcus, L.M.; Mesibov, G.B.; Hogan, K. Brief report: Two case studies using virtual reality as a learning tool for autistic children. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1996, 26, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbutt, N.; Sung, C.; Kuo, H.J.; Leahy, M.J.; Lin, C.C.; Tong, B. Brief report: A pilot study of the use of a virtual reality headset in autism populations. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2016, 46, 3166–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yuan, S.; Ip, H. A Case Study on Delivering Virtual Reality Learning for Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder Using Virtual Reality Headsets. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Education and New Learning Technologies (EDULEARN18), Palma, Spain, 2–4 July 2018; IATED Academy: Valencia, Spain, 2018; pp. 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Neira, C.; Sandin, D.J.; DeFanti, T.A.; Kenyon, R.V.; Hart, J.C. The CAVE: Audio visual experience automatic virtual environment. Commun. ACM 1992, 35, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Neira, C.; Sandin, D.J.; DeFanti, T.A. Surround-screen projection-based virtual reality: The design and implementation of the CAVE. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, New York, NY, USA, 2–6 August 1993; pp. 135–142. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, M. Immersion and the illusion of presence in virtual reality. Br. J. Psychol. 2018, 109, 431–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, G.; Pomares, J.; Lledó, A. Inclusion of immersive virtual learning environments and visual control systems to support the learning of students with Asperger syndrome. Comput. Educ. 2013, 62, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsentidou, S.; Poullis, C. Immersive visualizations in a VR cave environment for the training and enhancement of social skills for children with autism. In Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications (VISAPP), Lisbon, Portugal, 5–8 January 2014; Volume 3, pp. 230–236. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, C.L.; Yang, C.S. Using a 3D immersive virtual environment system to enhance social understanding and social skills for children with autism spectrum disorders. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabil. 2015, 30, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozgeyikli, L.; Bozgeyikli, E.; Raij, A.; Alqasemi, R.; Katkoori, S.; Dubey, R. Vocational rehabilitation of individuals with autism spectrum disorder with virtual reality. ACM Trans. Access. Comput. 2017, 10, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, M.; Lowry, J.; Rodgers, J.; McConachie, H.; Parr, J.R. Reducing specific phobia/fear in young people with autism spectrum disorders (ASDs) through a virtual reality environment intervention. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskey, M.; Rodgers, J.; Grahame, V.; Glod, M.; Honey, E.; Kinnear, J.; Labus, M.; Milne, J.; Minos, D.; McConachie, H.; et al. A randomised controlled feasibility trial of immersive virtual reality treatment with cognitive behaviour therapy for specific phobias in young people with autism spectrum disorder. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 1912–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozgeyikli, L.; Raij, A.; Katkoori, S.; Alqasemi, R. A survey on virtual reality for individuals with autism spectrum disorder: Design considerations. IEEE Trans. Learn. Technol. 2017, 11, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, R.; Newbutt, N. Autism and virtual reality head-mounted displays: A state of the art systematic review. J. Enabling Technol. 2018, 12, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, G.; Lledó, A.; Arráez-Vera, G.; Lorenzo-Lledó, A. The application of immersive virtual reality for students with ASD: A review between 1990–2017. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2019, 24, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, G.; Zhao, L. A systematic review: The application of virtual reality on the skill-specific performance in people with ASD. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2020, 31, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 2009, 151, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brämer, G.R. International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems: Tenth revision. World Health Stat. Q. Rapp. Trimest. Stat. Sanit. Mond. 1988, 41, 32–36. [Google Scholar]
- White, S.W.; Richey, J.A.; Gracanin, D.; Coffman, M.; Elias, R.; LaConte, S.; Ollendick, T.H. Psychosocial and computer-assisted intervention for college students with autism spectrum disorder: Preliminary support for feasibility. Educ. Train. Autism Dev. Disabil. 2016, 51, 307. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, G.; Lledó, A.; Pomares, J.; Roig, R. Design and application of an immersive virtual reality system to enhance emotional skills for children with autism spectrum disorders. Comput. Educ. 2016, 98, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, D.J.; Brown, T.; Ross, V.; Moncrief, M.; Schmitt, R.; Gaffney, G.; Reeve, R. Can youth with autism spectrum disorder use virtual reality driving simulation training to evaluate and improve driving performance? An exploratory study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2017, 47, 2544–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, C.; Mouga, S.; Simões, M.; Pereira, H.C.; Bernardino, I.; Quental, H.; Playle, R.; McNamara, R.; Oliveira, G.; Castelo-Branco, M. A feasibility clinical trial to improve social attention in Autistic Spectrum Disorder (ASD) using a brain computer interface. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.N.V.; Ip, H.H.S. Using virtual reality to train emotional and social skills in children with autism spectrum disorder. Lond. J. Prim. Care 2018, 10, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, M.; Bernardes, M.; Barros, F.; Castelo-Branco, M. Virtual travel training for autism spectrum disorder: Proof-of-concept interventional study. JMIR Serious Games 2018, 6, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, C.; Cloutier, V.; Bouchard, S. The “Decoding of Social Interactions in Virtual Reality” Tasks for Autism Spectrum People: Development of an Intervention Protocol and Pilot Testing. Annu. Rev. Cyberther. Telemed. 2018, 2018, 148. [Google Scholar]
- Politis, Y.; Sung, C.; Goodman, L.; Leahy, M. Conversation skills training for people with autism through virtual reality: Using responsible research and innovation approach. Adv. Autism 2019, 6, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindran, V.; Osgood, M.; Sazawal, V.; Solorzano, R.; Turnacioglu, S. Virtual reality support for joint attention using the Floreo Joint Attention Module: Usability and feasibility pilot study. JMIR Pediatr. Parent. 2019, 2, e14429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, J.F.; Lorenzo, G. An immersive virtual reality educational intervention on people with autism spectrum disorders (ASD) for the development of communication skills and problem solving. Educ. Inf. Technol. 2020, 25, 1689–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jialiang, H.; Haiyan, Z.; Huiying, Z. Research on the auxiliary treatment system of childhood autism based on virtual reality. J. Decis. Syst. 2021, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, R.; Naro, A.; Colucci, P.V.; Pranio, F.; Tardiolo, G.; Billeri, L.; Le Cause, M.; De Domenico, C.; Portaro, S.; Rao, G.; et al. Improvement of brain functional connectivity in autism spectrum disorder: An exploratory study on the potential use of virtual reality. J. Neural Transm. 2021, 128, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker-Ericzén, M.J.; Smith, L.; Tran, A.; Scarvie, K. A cognitive behavioral intervention for driving for autistic teens and adults: A pilot study. Autism Adulthood 2021, 3, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frolli, A.; Savarese, G.; Di Carmine, F.; Bosco, A.; Saviano, E.; Rega, A.; Carotenuto, M.; Ricci, M.C. Children on the autism spectrum and the use of virtual reality for supporting social skills. Children 2022, 9, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, H.H.; Wong, S.W.; Chan, D.F.; Li, C.; Kon, L.L.; Ma, P.K.; Lau, K.S.; Byrne, J. Enhance affective expression and social reciprocity for children with autism spectrum disorder: Using virtual reality headsets at schools. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2022, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Pelt, B.; Nijman, S.; van Haren, N.; Veling, W.; Pijnenborg, G.; van Balkom, I.; Landlust, A.; Greaves-Lord, K. Dynamic Interactive Social Cognition Training in Virtual Reality (DiSCoVR) for adults with Autism Spectrum Disorder: A feasibility study. Res. Autism Spectr. Disord. 2022, 96, 102003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hocking, D.R.; Ardalan, A.; Abu-Rayya, H.M.; Farhat, H.; Andoni, A.; Lenroot, R.; Kachnowski, S. Feasibility of a virtual reality-based exercise intervention and low-cost motion tracking method for estimation of motor proficiency in youth with autism spectrum disorder. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavale, K.A.; Forness, S.R. Social skill deficits and learning disabilities: A meta-analysis. J. Learn. Disabil. 1996, 29, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.L.; Braun, K.V.N.; Baio, J.; Bilder, D.; Charles, J.; Constantino, J.N.; Daniels, J.; Durkin, M.S.; Fitzgerald, R.T.; Kurzius-Spencer, M.; et al. Prevalence and characteristics of autism spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years-autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2012. MMWR Surveill. Summ. 2018, 65, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrington, J.; Oliver, R. Critical characteristics of situated learning: Implications for the instructional design of multimedia. In Proceedings of the ASCILITE 1995 Conference, Melbourne, Australia, 4–6 December 1995; Australian Society for Computers in Learning in Tertiary Education: Queensland, Australia, 1995; pp. 253–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hawton, K.E.; Salkovskis, P.M.; Kirk, J.E.; Clark, D.M. Cognitive Behaviour Therapy for Psychiatric Problems: A Practical Guide; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Cohn, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences; Lawrence Earlbam Associates: Hillsdale, NJ, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Cooper, H.; Hedges, L.V.; Valentine, J.C. The Handbook of Research Synthesis and Meta-Analysis; Russell Sage Foundation: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer, R.L.; Kroenke, K.; Williams, J.B.; Löwe, B. A brief measure for assessing generalized anxiety disorder: The GAD-7. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 1092–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronson, E.; Wilson, T.D.; Akert, R.M. Social Psychology; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2005; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, B.P.; Stephenson, J.; Carter, M. Cognitive—Behavioural approach for children with autism spectrum disorder: A literature review. J. Intellect. Dev. Disabil. 2015, 40, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, D.A. Experiential Learning: Experience as the Source of Learning and Development; FT Press: Bergen, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]


| Authors | Year | Theoretical Foundation | VR Device |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lorenzo et al. [34] | 2013 | Task-based learning | L-shaped screen |
| Maskey et al. [38] | 2014 | GE | Blue room |
| White et al. [46] | 2016 | CBT with mindfulness | Desktop, tablet, and HMD a |
| Lorenzo et al. [47] | 2016 | N/P | L-shaped screen |
| Cox et al. [48] | 2017 | Learn from simulation | Curved screen |
| Amaral et al. [49] | 2018 | N/P | HMD (Rift DK2) |
| Ip et al. [27] | 2018 | Situated learning | CAVE |
| Yuan & Ip [50] | 2018 | N/P | CAVE |
| Simões et al. [51] | 2018 | Gamification | HMD (Rift DK2) |
| Jacques et al. [52] | 2018 | N/P | CAVE |
| Politis et al. [53] | 2019 | N/P | N/P b |
| Ravindran et al. [54] | 2019 | N/P | Cardboard VR |
| Maskey et al. [39] | 2019 | CBT with GE | Blue room |
| Herrero & Lorenzo [55] | 2020 | Situated learning | HMD (Rift) |
| He et al. [56] | 2021 | N/P | HMD (VIVE) |
| De Luca et al. [57] | 2021 | N/P | Multiple screens |
| Baker-Ericzén et al. [58] | 2021 | Simulation and CBT | Customised driving simulator |
| Frolli et al. [59] | 2022 | N/P | Stereoscopic screen |
| Ip et al. [60] | 2022 | Experiential learning | HMD (Rift) |
| van Pelt et al. [61] | 2022 | Situated learning | HMD (Rift S) |
| Hocking et al. [62] | 2022 | N/P | HMD (VIVE Pro) |
| Article | Characteristics of Participants | Interventional Area | Sample Size | Measures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Mean (SD) | IQ Mean (SD) | ||||
| [38] | 11.2 (2.0) | N/P | Specific Phobia | 4 | SCAS; Confidence rating |
| [49] | 22.17 | 102.53 (11.64) | Social Skills | 15 | HADS; BDI; POMS; JAAT; ATEC; VABS |
| [52] | N/P | N/P a | Social Skills | 3 | Social decoding; CPS; CPI; SISST |
| [53] | N/P | N/P | Social Skills | 3 | PESE; PSSE; GAD-7 |
| [54] | 13.5 | N/P | Social Skills | 12 | JAA |
| [39] | N/P | N/P | Specific Phobia | 8 | PHQ-9; BAI; GAD-7 |
| [57] | 11 (3) | 26 (1.7) b; 31 (1.7) c | Cognitive Functions | 20 | RCPM; RSPM; VMI; BAI-Y |
| [58] | 20.53 (4.4) | N/P d | Life Skills-Driving | 17 | STAI; DCQ; DAS; Computerized DSE e |
| [61] | 27.62 (11.50) | 103.00 (14.39) | Social Skills | 22 | MASC; FEEST; TMT; SIAS; BFNE; SRS; EQ |
| [62] | 14.0 (2.6) | N/P | Motor Skills | 10 | BOT-2; DCCS |
| Article | Characteristics of Participants | Interventional Area | Sample Size | Measures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age Mean (SD) | IQ Mean (SD) | ||||
| [46] | CTRL: 20.25 (1.71) | CTRL: 115.75 (22.28) | Social Skills | CTRL: 4 | I-CLE; SACQ |
| EXP: 20.75 (1.71) | EXP: 126.75 (5.62) | EXP: 4 | |||
| [27] | 8.86 (1.13) | 95 (17.79) | Social and Affective Skills | CTRL: 36 | PEP-3; Faces test; Eyes test; |
| EXP: 36 | ABAS-II | ||||
| [56] | N/P a | N/P | Social Skills b | CTRL: 6 | Computerized evaluation c |
| EXP: 6 | |||||
| [59] | CTRL: 9.4 (0.49) | CTRL: 103.13 (2.04) | Affective Skills | CTRL: 30 | SE; ESPE; ESSE |
| EXP: 9.3 (0.63) | EXP: 103 (1.70) | EXP: 30 | |||
| [60] | CTRL: 112 (19.5) d | CTRL: 92.5 (16.5) | Social and Affective Skills | CTRL: 59 | PEP-3 |
| EXP: 101 (19.9) d | EXP: 93 (15.6) | EXP: 48 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Belter, M.; Liu, J.; Lukosch, H. Immersive Virtual Reality Enabled Interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Electronics 2023, 12, 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12112497
Li C, Belter M, Liu J, Lukosch H. Immersive Virtual Reality Enabled Interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Electronics. 2023; 12(11):2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12112497
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chen, Meike Belter, Jing Liu, and Heide Lukosch. 2023. "Immersive Virtual Reality Enabled Interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Electronics 12, no. 11: 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12112497
APA StyleLi, C., Belter, M., Liu, J., & Lukosch, H. (2023). Immersive Virtual Reality Enabled Interventions for Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Electronics, 12(11), 2497. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12112497








