A Survey of Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
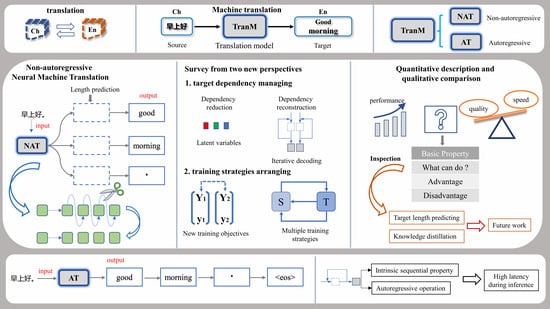
- We provide a concise retrospective on the technology evolving of non-autoregressive neural machine translation from the different viewpoints of target-side dependency management and training strategy arrangement.
- We made a comprehensive comparison among the methods applied in this field according to both effectiveness and accuracy via quantitative evaluation of the reported data and qualitative analysis based on the proposed theory.
- In addition to the review, the practices for fast decoding in corresponding tasks are also described, along with the challenges of NAMT and the prospects for future direction in this area.
2. Preliminary
- (a)
- Machine translation
- (b)
- Autoregressive neural machine translation
- (c)
- Non-autoregressive neural machine translation
3. Proposed Approaches
3.1. Dependency Management
3.1.1. Dependency Reducing for Fully NAD (FNAD)
3.1.2. Dependency Reconstructing for Iterative NAD (INAD)
3.2. Training Arrangement
3.2.1. New Training Objectives (NTO)
3.2.2. Multiple Training Strategies (MTS)
3.3. Multi-Mechanism Integrated (MI)
4. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis
4.1. Model Architectures and Results Overview
4.1.1. Transformer
4.1.2. Latent-Variable-Based Model for FNAD
4.1.3. Iterative Model for INAD
4.1.4. Models with New Training Objectives (NTO)
4.1.5. Models by Multiple Training Strategies (MTS)
4.1.6. Results Overview for All Models
4.2. Performance Description
4.3. Performance Analysis
- (1)
- On behalf of the original NAMT, FNAD achieves a favorable balance between translation quality and speed, though it is hard to train the model.
- (2)
- Restricted by the compromising contradiction, INAD yields limited benefits by substituting speed for quality.
- (3)
- NTO allows one-stop model training and bypasses the trade-off problem, but strong modules or means are needed to further promote translation accuracy.
- (4)
- MTS and MI all learn from other effective methods. However, the former focuses on correlative domains and tasks, thus requiring an extra adapting module or training schema. Additionally, the latter mainly integrates available mechanisms from the same field to complement each other. In general, MI seems to be a more promising way to gain further progress by combining the superiorities of others.
5. Problem Inspection
5.1. Target Sentence Length Prediction
5.2. Sequence-Level Knowledge Distillation
6. Discussions
7. Conclusions and Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sutskever, I.; Vinyals, O.; Le, Q.V. Sequence to Sequence Learning with Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 28th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 7–12 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.; Merrienboer, B.V.; Gülçehre, Ç.; Bahdanau, D.; Bougares, F.; Schwenk, H.; Bengio, Y. Learning Phrase Representations using RNN Encoder–Decoder for Statistical Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bahdanau, D.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y.J.C. Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.0473. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Schuster, M.; Chen, Z.; Le, Q.V.; Norouzi, M.; Macherey, W.; Krikun, M.; Cao, Y.; Gao, Q.; Macherey, K.; et al. Google’s Neural Machine Translation System: Bridging the Gap between Human and Machine Translation. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1609.08144. [Google Scholar]
- Gehring, J.; Auli, M.; Grangier, D.; Yarats, D.; Dauphin, Y. Convolutional Sequence to Sequence Learning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Sydney, Australia, 6–11 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.M.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the NIPS, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Narasimhan, K. Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training; OpenAI: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners; OpenAI: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models are Few-Shot Learners. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.14165. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.-W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K.J.A. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Heaton, J. Ian Goodfellow, Yoshua Bengio, and Aaron Courville: Deep learning. Genet. Program. Evolvable Mach. 2018, 19, 305–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, J.; Bradbury, J.; Xiong, C.; Li, V.O.K.; Socher, R.J.A. Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.02281. [Google Scholar]
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics, Univ Penn, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Wu, L.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Qin, T.; Liu, T.-Y. A Survey on Non-Autoregressive Generation for Neural Machine Translation and Beyond. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2204.09269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Indurthi, S.; Zaidi, M.A.; Lakumarapu, N.K.; Lee, B.; Kim, S.; Kim, C.; Hwang, I.J.A. Faster Re-translation Using Non-Autoregressive Model for Simultaneous Neural Machine Translation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.14681. [Google Scholar]
- Han, H.; Ahn, S.; Choi, Y.; Chung, I.; Kim, S.; Cho, K. Monotonic Simultaneous Translation with Chunk-wise Reordering and Refinement. In Proceedings of the Conference on Machine Translation, online and in the Barceló Bávaro Convention Centre, Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 7–11 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Z.K.; Yi, J.Y.; Tao, J.H.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wen, Z.Q. Spike-Triggered Non-Autoregressive Transformer for End-to-End Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech Conference, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Omachi, M.; Chang, X.K. Insertion-Based Modeling for End-to-End Automatic Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the Interspeech Conference, Shanghai, China, 25–29 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Leng, Y.C.; Tan, X.; Zhu, L.C.; Xu, J.; Luo, R.Q.; Liu, L.Q.; Qin, T.; Li, X.Y.; Lin, E.; Liu, T.Y. FastCorrect: Fast Error Correction with Edit Alignment for Automatic Speech Recognition. In Proceedings of the 35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Online, 6–14 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Inaguma, H.; Kawahara, T.; Watanabe, S. Source and Target Bidirectional Knowledge Distillation for End-to-end Speech Translation. In Proceedings of the Conference of the North-American-Chapter of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics-Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT), Online, 6–11 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Inaguma, H.; Dalmia, S.; Yan, B.; Watanabe, S. FAST-MD: Fast Multi-Decoder End-To-End Speech Translation with Non-Autoregressive Hidden Intermediates. In Proceedings of the IEEE Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding Workshop (ASRU), Cartagena, Colombia, 13–17 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tokarchuk, E.; Rosendahl, J.; Wang, W.Y.; Petrushkov, P.; Lancewicki, T.; Khadivi, S.; Ney, H. IIntegrated Training for Sequence-to-Sequence Models Using Non-Autoregressive Transformer. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Spoken Language Translation (IWSLT), Online, 5–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.T.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.X.; He, X.J.; Jiang, J.; Lu, H. Non-Autoregressive Image Captioning with Counterfactuals-Critical Multi-Agent Learning. In Proceedings of the 29th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 7–15 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mallinson, J.; Severyn, A.; Malmi, E.; Garrido, G.J.A. FELIX: Flexible Text Editing Through Tagging and Insertion. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2003.10687. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, D.; Kedzie, C.; Ladhak, F.; Carpuat, M.; McKeown, K. Incorporating Terminology Constraints in Automatic Post-Editing. In Proceedings of the Conference on Machine Translation, Online, 19–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.J.; Carpuat, M. EDITOR: An Edit-Based Transformer with Repositioning for Neural Machine Translation with Soft Lexical Constraints. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2021, 9, 311–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Carpuat, M. An Imitation Learning Curriculum for Text Editing with Non-Autoregressive Models. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Niwa, A.; Takase, S.; Okazaki, N.J.J.I.P. Nearest Neighbor Non-autoregressive Text Generation. J. Inf. Process. 2022, 31, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Crego, J.M.; Yvon, F. Bilingual Synchronization: Restoring Translational Relationships with Editing Operations. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Abu Dhabi, UAE, 7–11 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. A Survey of Large Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.18223. [Google Scholar]
- ArXiv, O.J. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Weaver, W. Machine Translation of Languages: Fourteen Essays; Locke, W.N., Booth, A.D., Eds.; Technology Press of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Cambridge, MA, USA; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1955; pp. 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Koehn, P.; Och, F.J.; Marcu, D. Statistical Phrase-Based Translation. In Proceedings of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Edmonton, Canada, 27 May–1 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Martínez, F.; Pérez-Ortiz, J.A. Philipp Koehn, Statistical machine translation. Mach. Transl. 2010, 24, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, L.; Roy, A.; Vaswani, A.; Parmar, N.; Bengio, S.; Uszkoreit, J.; Shazeer, N. Fast Decoding in Sequence Models Using Discrete Latent Variables. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Oord, A.v.d.; Vinyals, O.; Kavukcuoglu, K.J.A. Neural Discrete Representation Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.00937. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, L.; Bengio, S.J.A. Discrete Autoencoders for Sequence Models. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1801.09797. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, A.; Vaswani, A.; Neelakantan, A.; Parmar, N.J.A. Theory and Experiments on Vector Quantized Autoencoders. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.11063. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.Z.; Zhou, C.T.; Li, X.; Neubig, G.; Hovy, E. FlowSeq: Non-Autoregressive Conditional Sequence Generation with Generative Flow. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing/9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Kim, S.; Yoon, S. AligNART: Non-autoregressive Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Estimate Alignment and Translate. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 7–11 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, D.; Choi, H.J.A. Shared Latent Space by Both Languages in Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.03511. [Google Scholar]
- Akoury, N.; Krishna, K.; Iyyer, M. Syntactically Supervised Transformers for Faster Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhang, J.G.; Zhao, W.T.; Yu, P.S. Enriching Non-Autoregressive Transformer with Syntactic and Semantic Structures for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European-Chapter-of-the-Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (EACL), Kyiv, Ukraine, 19–23 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Huang, S.J.; Xiao, T.; Wang, D.Q.; Dai, X.Y.; Chen, J.J. Non-Autoregressive Translation by Learning Target Categorical Codes. In Proceedings of the Conference of the North-American-Chapter of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics—Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT), Online, 6–11 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Q.; Lin, Y.K.; Li, P.; Zhou, J. Guiding Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation Decoding with Reordering Information. In Proceedings of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence/33rd Conference on Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence/11th Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2–9 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Feng, J.; Wang, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, J.; Lei, L.J.A. Non-autoregressive Transformer by Position Learning. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.10677. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Mansimov, E.; Cho, K. Deterministic Non-Autoregressive Neural Sequence Modeling by Iterative Refinement. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, R.; Lee, J.; Nakayama, H.; Cho, K. Latent-Variable Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation with Deterministic Inference Using a Delta Posterior. In Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence/32nd Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference/10th AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Shu, R.; Cho, K. Iterative Refinement in the Continuous Space for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.Q. Semi-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stern, M.; Chan, W.; Kiros, J.; Uszkoreit, J. Insertion Transformer: Flexible Sequence Generation via Insertion Operations. In Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kasai, J.; Cross, J.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Gu, J.T. Non-autoregressive Machine Translation with Disentangled Context Transformer. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vienna, Austria, 12–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, Q.; Lin, Y.K.; Li, P.; Zhou, J. Learning to Recover from Multi-Modality Errors for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.; Xiao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.J.A. RenewNAT: Renewing Potential Translation for Non-Autoregressive Transformer. In Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazvininejad, M.; Levy, O.; Liu, Y.H.; Zettlemoyer, L. Mask-Predict: Parallel Decoding of Conditional Masked Language Models. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing/9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kreutzer, J.; Foster, G.; Cherry, C. Inference Strategies for Machine Translation with Conditional Masking. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Xu, R.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Qin, T.; Liu, Y.-T.; Zhang, M.J.A. AMOM: Adaptive Masking over Masking for Conditional Masked Language Model. In Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Libovicky, J.; Helcl, J. End-to-End Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation with Connectionist Temporal Classification. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Graves, A.; Fernández, S.; Gomez, F.; Schmidhuber, J. Connectionist temporal classification: Labelling unsegmented sequence data with recurrent neural networks. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Machine Learning, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 25–29 June 2006; Association for Computing Machinery: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2006; pp. 369–376. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.R.; Tian, F.; He, D.; Qin, T.; Zhai, C.X.; Liu, T.Y. Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation with Auxiliary Regularization. In Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence/31st Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference/9th AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Lin, Z.; He, D.; Tian, F.; Qin, T.; Wang, L.W.; Liu, T.Y. Hint-Based Training for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing/9th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (EMNLP-IJCNLP), Hong Kong, China, 3–7 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.Z.; Zhang, J.C.; Feng, Y.; Meng, F.D.; Zhou, J. Minimizing the Bag-of-Ngrams Difference for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence/32nd Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference/10th AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ghazvininejad, M.; Karpukhin, V.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Levy, O. Aligned Cross Entropy for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Vienna, Austria, 12–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, L.F.; Pang, R.Y.Z.; Wiseman, S.; Gimpel, K. ENGINE: Energy-Based Inference Networks for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.X.; Tu, Z.P.; Jiang, J. Order-Agnostic Cross Entropy for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), Online, 18–24 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Meng, F.D.; Zhou, J. Sequence-Level Training for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. Comput. Linguist. 2021, 47, 891–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, J.C.; Meng, F.D.; Chen, X.L.; Zhou, J. Retrieving Sequential Information for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, B.Z.; Wang, M.X.; Zhou, H.; Lin, J.Y.; Sun, X. Imitation Learning for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.Q.; Li, Z.H.; Wang, H.Q.; He, D.; Lin, Z.; Deng, Z.H. Fast Structured Decoding for Sequence Models. In Proceedings of the 33rd Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kasner, Z.; Libovický, J.; Helcl, J.J.A. Improving Fluency of Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.03227. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, X.; Lu, H.J.A. Fast Sequence Generation with Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.09698. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.; Feng, Y.; Shao, C.Z. Modeling Coverage for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Online, 18–22 July 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.L.; Tan, X.; Xu, L.L.; Qin, T.; Chen, E.H.; Liu, T.Y. Fine-Tuning by Curriculum Learning for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence/32nd Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence Conference/10th AAAI Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.L.; Ren, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhang, C.; Qin, T.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, T.Y. Task-Level Curriculum Learning for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 29th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Yokohama, Japan, 7–15 January 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, L.; Wei, H.-R.; Chen, B.; Chen, E.J.A. Incorporating BERT into Parallel Sequence Decoding with Adapters. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.06138. [Google Scholar]
- Su, Y.X.; Cai, D.; Wang, Y.; Vandyke, D.; Baker, S.; Li, P.J.; Collier, N. Non-Autoregressive Text Generation with Pre-trained Language Models. In Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European-Chapter-of-the-Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (EACL), Online, 19–23 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.F.; Li, L.Y.; Zhang, M.; Wu, M.H.; Liu, Q. Universal Conditional Masked Language Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.L.; Tan, X.; He, D.; Qin, T.; Xu, L.L.; Liu, T.Y. Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation with Enhanced Decoder Input. In Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Kong, X.J.A. Fully Non-autoregressive Neural Machine Translation: Tricks of the Trade. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2012.15833. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Huang, M.J.A. Directed Acyclic Transformer for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML 2022), Baltimore, MD, USA, 17–23 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.; Ma, Z.; Feng, Y.J.A. Viterbi Decoding of Directed Acyclic Transformer for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Shao, C.; Gui, S.; Zhang, M.; Feng, Y.J.A. Fuzzy Alignments in Directed Acyclic Graph for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR2023), Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Ke, P.; Huang, M.J.A. Directed Acyclic Transformer Pre-training for High-quality Non-autoregressive Text Generation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.11791. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Feng, Y.J.A. Rephrasing the Reference for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI2023), Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, L.H.; Zhou, H.; Bao, Y.; Wang, M.X.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, W.N.; Yu, Y.; Li, L. Glancing Transformer for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Joint Conference of 59th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL)/11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing (IJCNLP)/6th Workshop on Representation Learning for NLP (RepL4NLP), Bangkok, Thailand, 1–6 August 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.J.A. MvSR-NAT: Multi-view Subset Regularization for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.08447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savinov, N.; Chung, J.; Binkowski, M.; Elsen, E.; Oord, A.v.d.J.A. Step-unrolled Denoising Autoencoders for Text Generation. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR 2022), Online, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.Y.; Zhou, H.; Zaiane, O.R.; Mou, L.L.; Li, L. Non-autoregressive Translation with Layer-Wise Prediction and Deep Supervision. In Proceedings of the 36th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence/34th Conference on Innovative Applications of Artificial Intelligence/12th Symposium on Educational Advances in Artificial Intelligence, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Wei, D.; Shang, H.; Su, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tao, S.; et al. Diformer: Directional Transformer for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the European Association for Machine Translations Conferences/Workshops, Ghent, Belgium, 1–3 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, T.; Xia, H.; Sun, X.; Chen, S.-Q.; Wei, F.J.A. Lossless Acceleration for Seq2seq Generation with Aggressive Decoding. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.10350. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, B.; Jia, A.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Pan, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, M. The RoyalFlush System for the WMT 2022 Efficiency Task. In Proceedings of the EMNLP 2022 Seventh Conference on Machine Translation, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Zheng, Z.; Huang, S. Helping the Weak Makes You Strong: Simple Multi-Task Learning Improves Non-Autoregressive Translators. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP2022), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Saharia, C.; Chan, W.; Saxena, S.; Norouzi, M. Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation with Latent Alignments. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP 2020), Online, 16–20 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, W.; Saharia, C.; Hinton, G.; Norouzi, M.; Jaitly, N. Imputer: Sequence Modelling via Imputation and Dynamic Programming. In Proceedings of the 25th Americas Conference on Information Systems of the Association-for-Information-Systems (AMCIS 2019), Cancun, Mexico, 15–17 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.X.; Wang, R.; Tan, X.; Guo, J.L.; Ren, Y.; Qin, T.; Liu, T.Y. A Study of Syntactic Multi-Modality in Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Conference of the North-American-Chapter-of-the-Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (NAAACL)—Human Language Technologies, Seattle, WA, USA, 10–15 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.; Feng, Y.J.A. Non-Monotonic Latent Alignments for CTC-Based Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Sixth Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS 2022), New Orleans Convention Center, New Orleans, LA, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Du, C.; Tu, Z.; Jiang, J.J.A. ngram-OAXE: Phrase-Based Order-Agnostic Cross Entropy for Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics (Coling 2022 Oral), Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 12–17 October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Granularity Optimization for Non-Autoregressive Translation. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP2022), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lafferty, J.D.; McCallum, A.; Pereira, F.C.N. Conditional Random Fields: Probabilistic Models for Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Data. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 June–1 July 2001; pp. 282–289. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Yang, Y. An EM Approach to Non-autoregressive Conditional Sequence Generation. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Online, 13–18 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, K.J.A. Noisy Parallel Approximate Decoding for Conditional Recurrent Language Model. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.03835. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.; Rush, A.M.J.A. Sequence-Level Knowledge Distillation. In Proceedings of the EMNLP 2016, Austin, Texas, USA, 1–5 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, G.E.; Vinyals, O.; Dean, J.J.A. Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1503.02531. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Neubig, G.; Gu, J.J.A. Understanding Knowledge Distillation in Non-autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, New Orleans, LA, USA, 6–9 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Ma, S.; Zhang, D.; Carpuat, M. How Does Distilled Data Complexity Impact the Quality and Confidence of Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation? In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL 2021), Online, 1–6 August 2021.
- Ren, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Tan, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, S.; Liu, T.Y. A Study of Non-autoregressive Model for Sequence Generation. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.W.; Keung, P.; Assoc Computat, L. Assoc Computat. Improving Non-autoregressive Neural Machine Translation with Monolingual Data. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Wang, M.; Wei, D.; Shang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Su, C.; et al. Self-Distillation Mixup Training for Non-autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.11640. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, C.; Wu, X.; Feng, Y. One Reference Is Not Enough: Diverse Distillation with Reference Selection for Non-Autoregressive Translation. In Proceedings of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Seattle, WA, USA, 10–15 July 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Bao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Huang, S.J.A. Selective Knowledge Distillation for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.17910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkowski, M.; Donahue, J.; Dieleman, S.; Clark, A.; Elsen, E.; Casagrande, N.; Cobo, L.C.; Simonyan, K.J.A. High Fidelity Speech Synthesis with Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1909.11646. [Google Scholar]
- Kasai, J.; Pappas, N.; Peng, H.; Cross, J.; Smith, N.A. Deep Encoder, Shallow Decoder: Reevaluating Non-autoregressive Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Online, 26 April–1 May 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Helcl, J.; Haddow, B.; Birch, A.J.A. Non-Autoregressive Machine Translation: It’s Not as Fast as it Seems. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.01966. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, R.M.; Pires, T.; Peitz, S.; Lööf, J.J.A. Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation: A Call for Clarity. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.10577. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, A.V.M.; Helcl, J.; Sennrich, R.; Haddow, B.; Birch, A.J.A. Deep architectures for Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the WMT 2017 Research Track, Copenhagen, Denmark, 7–8 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, B.; Xiao, T.; Zhu, J.B.; Li, C.L.; Wong, D.F.; Chao, L.S. Learning Deep Transformer Models for Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics (ACL), Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Junczys-Dowmunt, M.; Hassan, H.; Heafield, K.; Grundkiewicz, R.; Bogoychev, N. From Research to Production and Back: Ludicrously Fast Neural Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Hong Kong, China, 4 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Batanović, V.; Cvetanović, M.; Nikolić, B.J.P.O. A versatile framework for resource-limited sentiment articulation, annotation, and analysis of short texts. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draskovic, D.; Zecevic, D.; Nikolic, B. Development of a Multilingual Model for Machine Sentiment Analysis in the Serbian Language. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennrich, R.; Haddow, B.; Birch, A.J.A. Improving Neural Machine Translation Models with Monolingual Data. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (Volume 1: Long Papers), Berlin, Germany, 7–12 August 2016; Association for Computational Linguistics: Berlin, Germany; pp. 86–96. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.; Xia, Y.; Qin, T.; Wang, L.; Yu, N.; Liu, T.-Y.; Ma, W.-Y. Dual learning for machine translation. In Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates Inc.: Barcelona, Spain, 2016; pp. 820–828. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. J. Commun. ACM 2020, 63, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostić, M.; Batanović, V.; Nikolić, B. Monolingual, multilingual and cross-lingual code comment classification. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 124, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Feng, J.; Zhao, C.; Wang, M.; Li, L. Counter-Interference Adapter for Multilingual Machine Translation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Online and Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 7–11 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.H.; Gu, J.T.; Goyal, N.; Li, X.; Edunov, S.; Ghazvininejad, M.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L. Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2020, 8, 726–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.W.; Dong, L.; Ma, S.M.; Huang, S.H.; Mao, X.L.; Huang, H.Y.; Wei, F.R. mT6: Multilingual Pretrained Text-to-Text Transformer with Translation Pairs. In Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Online and Punta Cana, Dominican Republic, 7–11 November 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, L.T.; Constant, N.; Roberts, A.; Kale, M.; Al-Rfou, R.; Siddhant, A.; Barua, A.; Raffel, C. mT5: A Massively Multilingual Pre-trained Text-to-Text Transformer. In Proceedings of the Conference of the North-American-Chapter of the Association-for-Computational-Linguistics—Human Language Technologies (NAACL-HLT), Online, 6–11 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, S.; Kreutzer, J.; Cherry, C.J.A. Can Multilinguality benefit Non-autoregressive Machine Translation? arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.08570. [Google Scholar]










| Vielen Dank | ||
|---|---|---|
| Reference | Thank you very much | (standard translation) |
| Over-translated | Thank you much much | (repeated translation) |
| Under-translated (1) | Thanks you very much | (mistaken semantic) |
| Under-translated (2) | Thank  very much very much | (missing semantic) |
| WMT14 En-De | Latency Speedup | BLEU Gains | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FNAD-[43] | 27.48/24.64/27.50 | 1.00×/22.6×/9.3× | −2.84/+0.02 |
| INAD-[53] | 27.17/26.32/27.11 | 1.00×/4.31×/2.16× | −0.85/−0.06 |
| NTO-[66] | 27.42/23.90/25.54 | 1.00×/15.6×/15.6× | −3.52/−1.88 |
| MTS-[75] | 28.04/28.08/28.69 | 1.00×/4.7×/2.4× | +0.04/+0.65 |
| MI-[90] | 27.38/28.73/28.89 | 1.00×/3.0×/3.6× | +1.35/+1.51 |
| WMT14 En-De | Latency Speedup | BLEU Gains | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FNAD-base [12] | 23.45/17.35/19.17 | 1.00×/15.6×/2.36× | −6.10/−4.28 |
| [43] | 27.48/24.64/27.50 | 1.00×/22.6×/9.3× | −2.84/+0.02 |
| [44] | 27.33/25.56/26.60 | 1.00×/10.37×/5.59× | −1.77/−0.73 |
| [40] | 27.40/25.70/26.40 | 1.00×/13.9×/13.0× | −1.70/−1.00 |
| [88] | 27.48/ null /27.02 | 1.00×/ null /14.8× | null/−0.46 |
| AVG B | - | - | −3.10/−1.29 |
| AVG S | - | 1.00×/15.62×/9.01× | - |
| WMT14 En-De | Latency Speedup | BLEU Gains | |
|---|---|---|---|
| INAD-base [47] | 24.57/13.91/21.61 | 1.00×/8.9×/1.2× | −10.66/−2.96 |
| [50] | 27.11/23.93/26.90 | 1.00×/5.58×/1.51× | −3.18/−0.21 |
| [53] | 27.17/26.32/27.11 | 1.00×/4.31×/2.16× | −0.85/−0.06 |
| [49] | 28.30/25.70/27.40 | 1.00×/15.0×/6.20× | −2.60/−0.90 |
| [57] | 28.41/ null /27.57 | 1.00×/ null /2.3× | null/−0.84 |
| AVG B | - | - | −4.32/−1.00 |
| AVG S | - | 1.00×/8.45×/2.67× | - |
| WMT14 En-De | Latency Speedup | BLEU Gains | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NTO-base [58] | 22.94/12.51/17.68 | 1.00×/5.8×/3.4× | −10.43/−5.26 |
| [60] | 27.30/20.65/24.61 | 1.00×/27.6×/15.1× | −6.65/−2.69 |
| [61] | 27.30/21.11/25.20 | 1.00×/30.2×/17.8× | −6.19/−2.10 |
| [62] | 24.57/16.05/20.90 | 1.00×/10.76×/10.77× | −8.52/−3.67 |
| [66] | 27.42/23.90/25.54 | 1.00×/15.6×/15.6× | −3.52/−1.88 |
| AVG B | - | - | −7.06/−3.12 |
| AVG S | - | 1.00×/20.00×/12.53× | - |
| WMT14 En-De | Latency Speedup | BLEU Gains | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MTS-base [68] | 27.41/22.44/24.15 | 1.00×/18.6×/9.70× | −4.97/−3.26 |
| [69] | 27.41/20.27/26.80 | 1.00×/14.9×/4.39× | −7.14/−0.61 |
| [73] | 27.30/21.70/25.75 | 1.00×/28.9×/16.0× | −5.60/−1.55 |
| [74] | 27.30/21.94/25.37 | 1.00×/27.6×/16.0× | −5.36/−1.93 |
| [75] | 28.04/28.08/28.69 | 1.00×/4.7×/2.4× | +0.04/+0.65 |
| AVG B | - | - | −4.61/−1.34 |
| AVG S | - | 1.00×/18.94×/9.70× | - |
| WMT14 En-De | Latency speedup | BLEU gains | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MI-base [78] | 27.41/20.26/24.28 | 1.00×/24.3×/12.4× | −7.15/−3.13 |
| [93] | 27.80/25.80/28.20 | 1.00×/18.6×/3.9× | −2.00/+0.40 |
| [79] | 27.48/19.50/27.49 | 1.00×/17.6×/16.5× | −7.98/+0.01 |
| [87] | 27.30/27.94/28.46 | 1.00×/4.7×/1.4× | +0.64/+1.16 |
| [90] | 27.38/28.73/28.89 | 1.00×/3.0×/3.6× | +1.35/+1.51 |
| AVG B | - | - | −3.03/−0.01 |
| AVG S | - | 1.00×/13.64×/7.56× | - |
| Ranking | Translation Quality | Latency Speedup | Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | MI | NTO | 5 |
| 2 | INAD | MTS | 4 |
| 3 | FNAD | FNAD | 3 |
| 4 | MTS | MI | 2 |
| 5 | NTO | INAD | 1 |
| Methods | Properties | What can do | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MI | Multi-mechanism integrated | Allow multi-mechanism learning | Complement each other’s superiority | Need to integrate multi modules |
| FNAD | Pivot and latent-variable-based | Model any types of dependencies | Concise transfer flow | Model is hard to train and converge |
| NTO | Multimodality alignments regularized | accommodate coarse-grained match | Model training is end-to-end without intermediates | Lack of strong performance modules |
| MTS | Cross-domains transfer of ready methods | Enable one-stop training | With established performance basics | Require delicate adapting schema |
| INAD | Multi-pass decoding | Sentence-level autoregressive generation | Mechanism is distinct and tractable | Repeated decoding lags speed |
| BLEU Score without SKD | BLEU Score with SKD | BLEU Gains | |
|---|---|---|---|
| FNAD | |||
| [12] | 16.51/18.87 | 20.72/25.20 | 4.21/6.33 (25%/33%) |
| [38] | 21.40/22.40 | 26.40/26.70 | 5.00/4.30 (23%/19%) |
| [39] | 18.55/20.85 | 24.15/23.72 | 5.60/2.87 (30%/14%) |
| INAD | |||
| [47] | 20.91/23.65 | 26.17/27.11 | 5.26/3.46 (25%/15%) |
| [51] | 19.34/22.64 | 22.75/25.45 | 3.41/2.81 (18%/12%) |
| [55] | 10.64/24.61 | 18.05/27.03 | 7.41/2.42 (70%/10%) |
| NTO | |||
| [64] | 8.28 | 14.58 | 6.30 (76%) |
| [63] | 20.40 | 23.53 | 3.13 (15%) |
| [65] | 22.70 | 26.20 | 3.50 (15%) |
| MTS | |||
| [68] | 16.51/23.56 | 20.72/28.41 | 4.21/4.8(25%/21%) |
| MI | |||
| [93] | 15.6/24.7 | 25.4/27.9 | 9.80/3.20 (63%/13%) |
| [79] | 11.40 | 19.50 | 8.10 (71%) |
| [86] | 22.89/24.37 | 26.25/27.39 | 3.36/3.02 (15%/12%) |
| Avg. gains | 5.33/3.69(36%/17%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, F.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X. A Survey of Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. Electronics 2023, 12, 2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132980
Li F, Chen J, Zhang X. A Survey of Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. Electronics. 2023; 12(13):2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132980
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Feng, Jingxian Chen, and Xuejun Zhang. 2023. "A Survey of Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation" Electronics 12, no. 13: 2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132980
APA StyleLi, F., Chen, J., & Zhang, X. (2023). A Survey of Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation. Electronics, 12(13), 2980. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132980