A 10 GHz Compact Balun with Common Inductor on CMOS Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
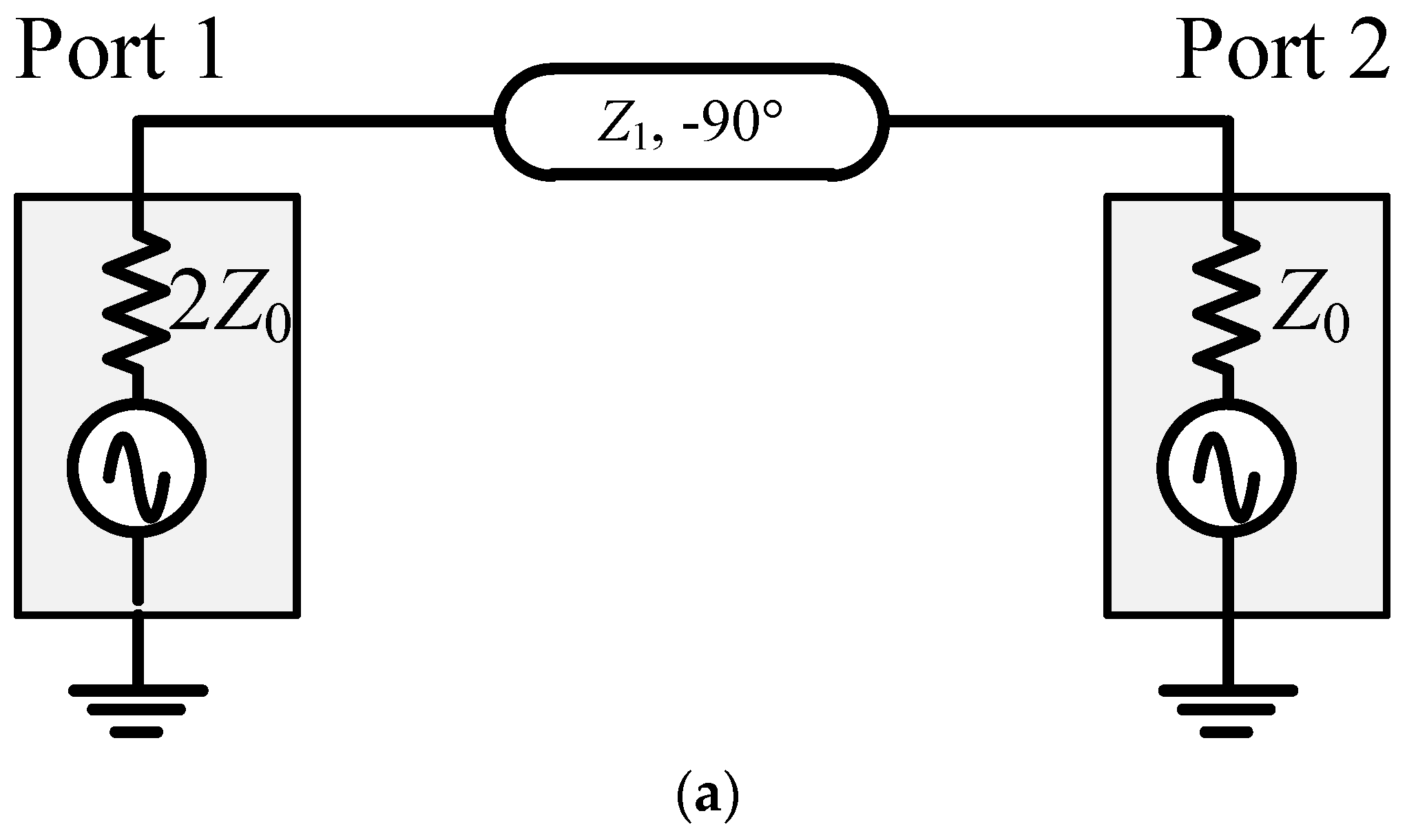
2. Conventional Wilkinson-Type Balun
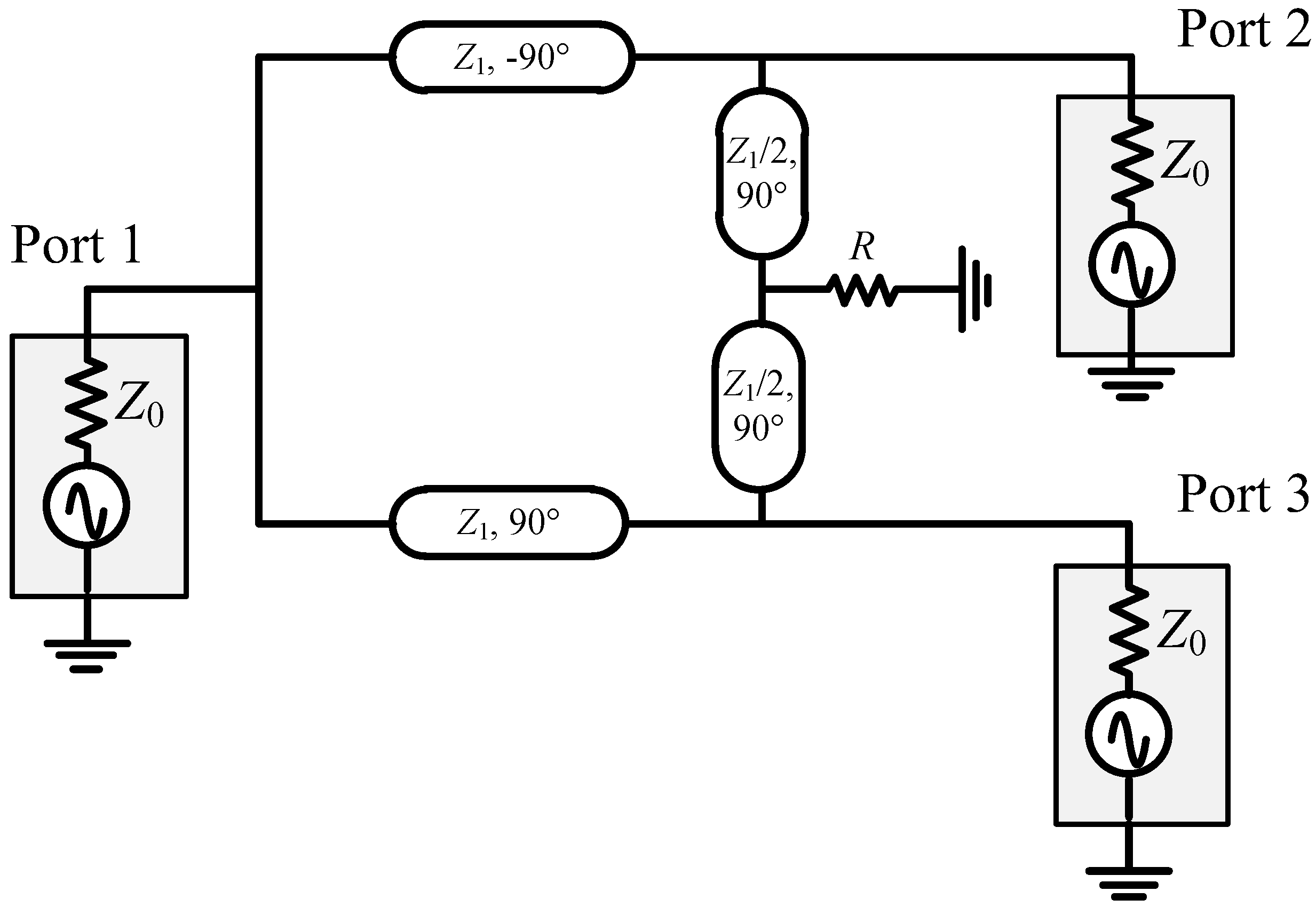
3. Balun with a Common Inductor
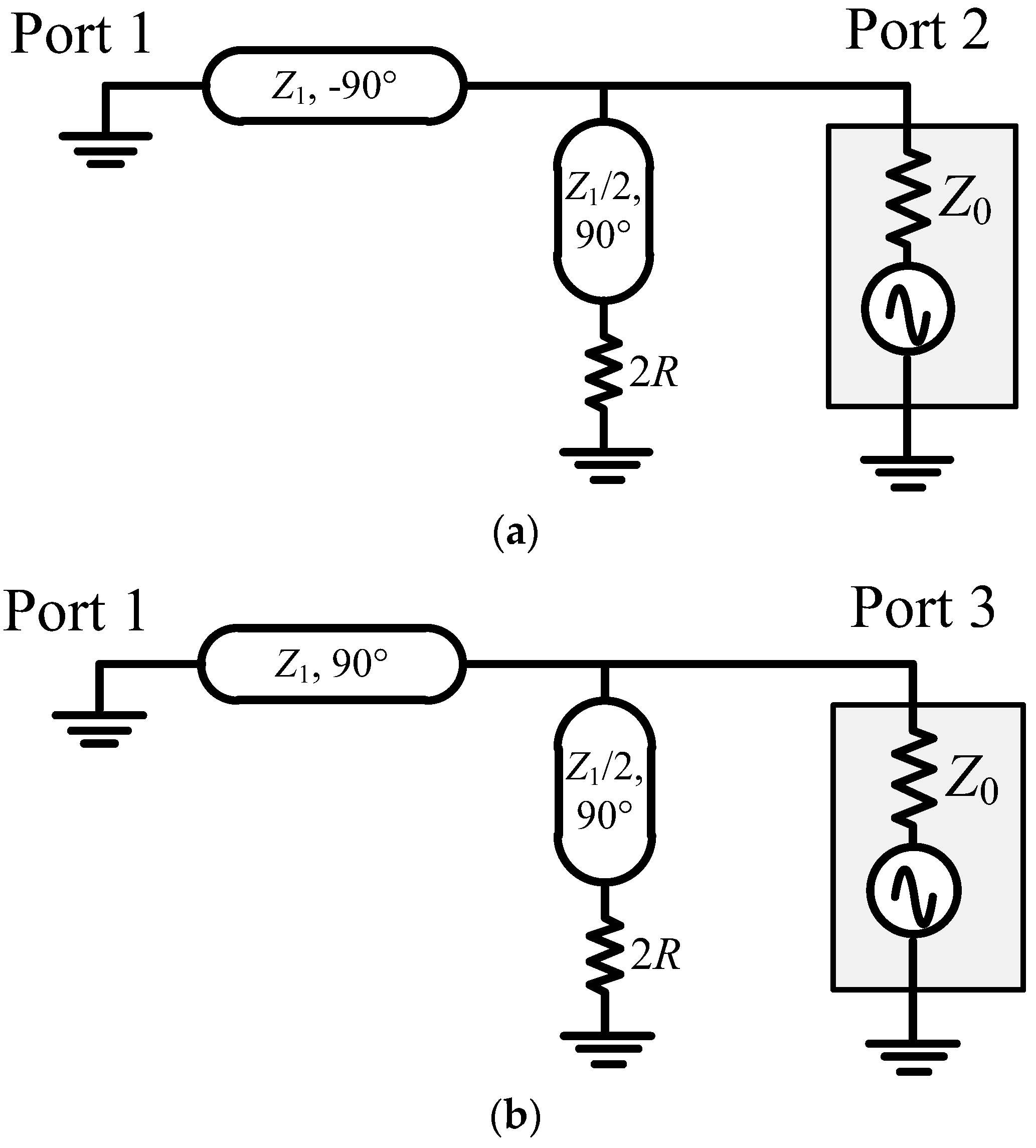
3.1. Phase Balance of Transmission Lines with Inductor Losses
3.2. Improvement of Phase Balance
3.3. Even-Mode Analysis of Balun with Common Inductor
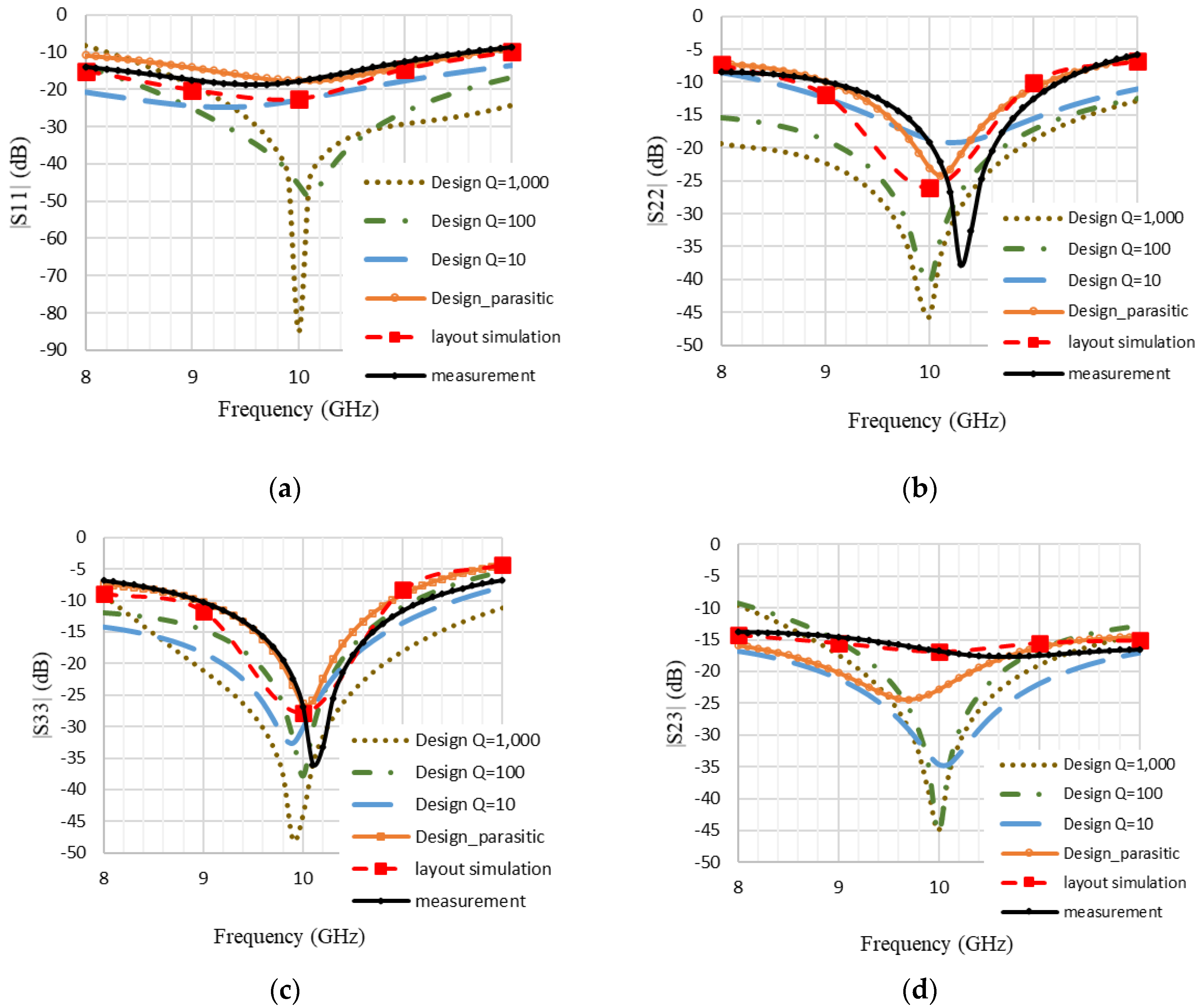
4. Simulated and Measured Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huynh, C.; Nguyen, C. Ultra-wideband active balun topology and its implementation on SiGe BiCMOS across DC-50 GHz. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2016, 26, 720–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-J.; Huang, B.-J.; Lin, K.-Y.; Wang, H. A 2–40 GHz active balun using 0.13 μm CMOS process. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2009, 19, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Jing, K. A 2–22GHz low-imbalanced active balun in 0.18μm SiGe BiCMOS technology. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2016, 70, 1367–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandari, R.; Ebrahimi, A.; Sobhi, J. A wideband noise cancelling balun LNA employing current reuse technique. Microelectron. J. 2018, 76, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manstretta, D. A broadband low-power low-noise active balun with second-order distortion cancellation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 407–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.-H.; Huang, F.-C.; Wang, C.-S.; Wang, C.-K. A 90 nm CMOS V-band low-noise active balun with broadband phase-correction technique. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2011, 46, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, H.-K.; Lin, J.-Y. Symmetric offset stack balun in standard 0.13-μm CMOS technology for three broadband and low-loss balanced passive mixer designs. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 2011, 59, 1529–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-S.; Lan, K.-S. Design and analysis of CMOS baluns for 94 GHz image radar and 28 GHz 5G communication system. Analog. Integr. Circ. Sig. Process 2020, 103, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Tang, K.; Wang, Z. 3.6–8.1 GHz CMOS balun with 1.8° in-band phase difference by using capacitive balance compensation technique. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2020, 62, 1548–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nithiporndecha, K.; Pakasiri, C. A UHF compact complex impedance-transforming balun with high isolation. Recent Adv. in Electr. Electron. Eng. 2020, 13, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.; Thorsell, M.; Enoksson, P. Design equations for lumped element balun with inherent complex impedance transformation. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 2017, 65, 5162–5170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Li, L.-Y.; Gu, J.-Z.; Sun, X.-W. A bandwidth improved broadband compact lumped-element balun with tail inductor. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2013, 23, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, H.-K.; Lin, H.-H.; Chang, C.-Y. Lumped-element compensated high/low-pass balun design for MMIC double-balanced mixer. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 1997, 7, 248–250. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, P.-C.; Liu, W.-C.; Chiou, H.-K. Compact 28-GHz subharmonically pumped resistive mixer MMIC using a lumped-element high-pass/band-pass balun. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2005, 15, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Meng, F.-Y.; Wang, C.; Adhikari, K.K.; Qiang, T.; Wu, Q.; Wu, Y. Design analysis of integrated passive device-based balun devices with high selectivity for mobile application. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 23169–23176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z. A wideband transformer balun with center open stub in CMOS process. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2014, 24, 614–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotella, F.M.; Cismaru, C.; Tkachenko, Y.G.; Cheng, Y.; Zampardi, P.J. Characterization, design, modeling, and model validation of silicon on-wafer M:N balun components under matched and unmatched conditions. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2006, 41, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, H.-M.; Huang, J.-S.; Chen, S.-Y.; Lai, S.-H. Design of an on-chip balun with a minimum amplitude imbalance using a symmetric stack layout. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 2010, 58, 814–819. [Google Scholar]
- Park, U. A Wilkinson-type balun using a composite right/left-handed transmission line. J.Inf. Commun. Converg. Eng. 2013, 11, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakasiri, C.; Kongchayasukwat, T. Improvement of transmission line circuit on lossy substrate with application on phase shifter design. In Proceedings of the 2019 7th International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Hua Hin, Thailand, 6–8 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Caloz, C.; Itoh, T. Novel Microwave Devices and Structures Based on the Transmission Line Approach of Meta-Materials. IEEE MTT-S Int. Microw. Symp. Dig. 2003, 1, 195–198. [Google Scholar]

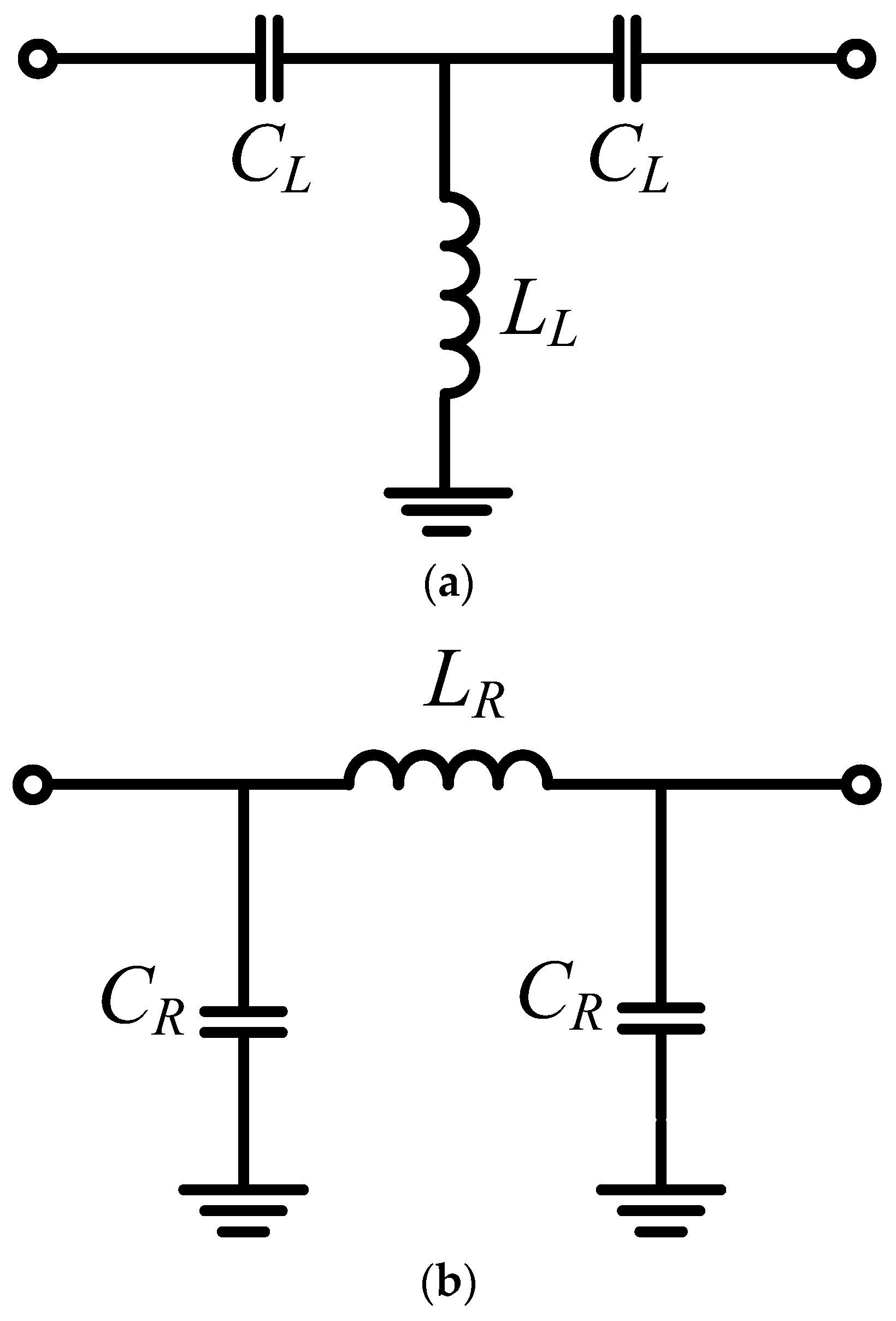


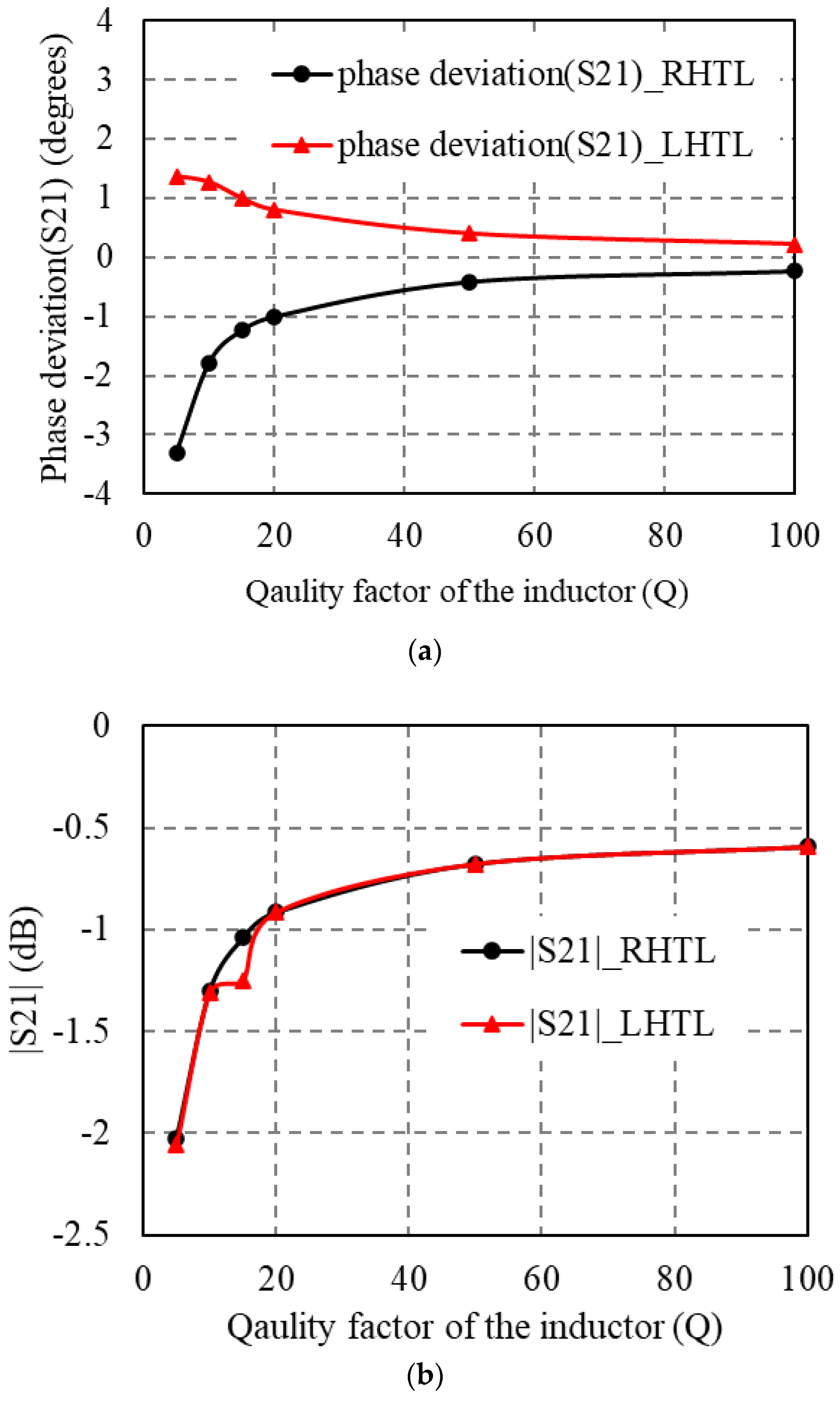
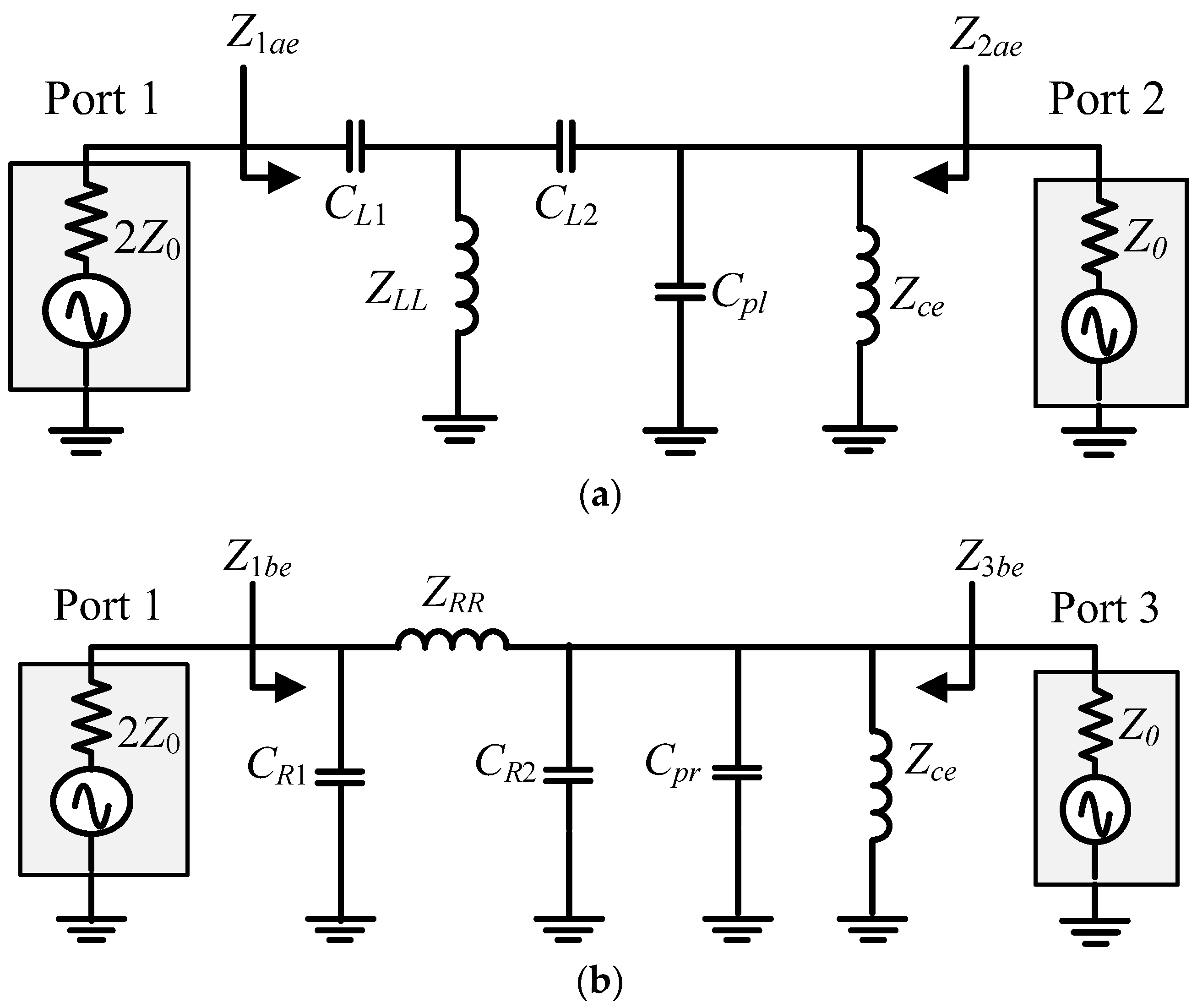

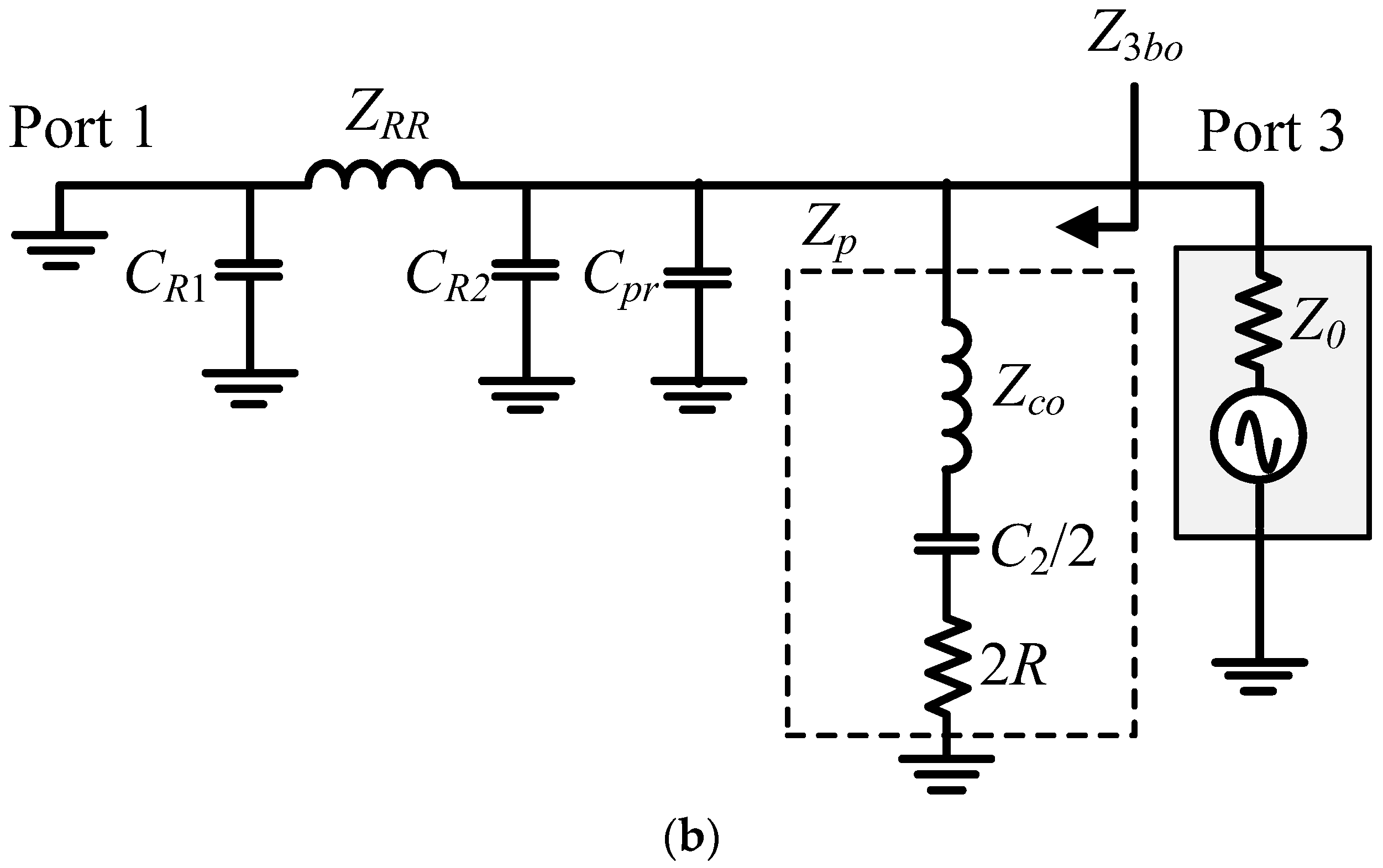

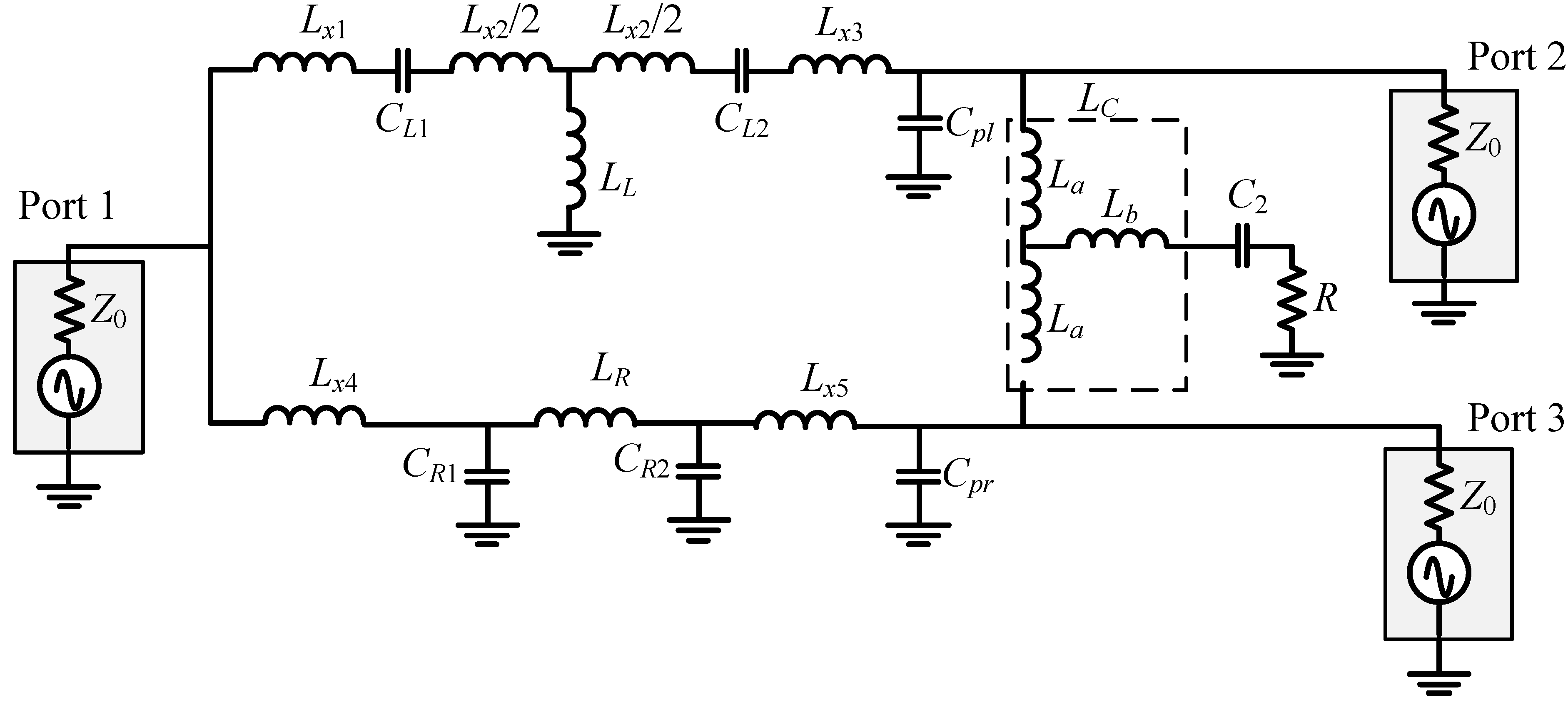

| Q | CR1 (pF) | CR2 (pF) | CL1 (pF) | CL2 (pF) | |S21,LHTL|and |S21, RHTL| (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 0.16 | 0.33 | 0.18 | 0.33 | −2.46 |
| 10 | 0.29 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.29 | −1.49 |
| 20 | 0.19 | 0.28 | 0.29 | 0.17 | −1.10 |
| 50 | 0.18 | 0.28 | 0.20 | 0.27 | −0.82 |
| 100 | 0.17 | 0.28 | 0.19 | 0.27 | −0.75 |
| Design | Left-Handed Transmission Line | Right-Handed Transmission Line | Common Inductor | Other Components | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL1 (pF) | CL2 (pF) | LL (nH) | Cpl (pF) | CR1 (pF) | CR2 (pF) | LR (nH) | Cpr (pF) | La (nH) | Lb (nH) | C2 (pF) | Rp (Ω) | |
| 1 (Q = 1000) | 0.27 | 0.19 | 0.95 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.47 | 0.95 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.22 | 0.94 | 12.87 |
| 2 (Q = 100) | 2.99 | 0.23 | 1.13 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.51 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 0.57 | 0.24 | 0.75 | 7.97 |
| 3 (Q = 10) | 0.42 | 0.26 | 1.19 | 0.10 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 1.19 | 0.24 | 1.93 | 0.11 | 0.28 | 15.00 |
| Parasitic | 0.268 | 0.362 | 0.953 | 0.3 | 0.31 | 0.14 | 0.953 | 0.411 | 1.926 | 0.11 | 0.29 | 0.1 |
| Layout | 0.462 | 0.265 | 0.953 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.953 | 0.276 | 1.926 | 0.11 | 0.246 | - |
| Parasitic Inductor | Resistance (Ω) | Inductance (nH) |
|---|---|---|
| Lx1 | 0.273 | 0.072 |
| Lx2 | 0.319 | 0.012 |
| Lx3 | 1.246 | 0.142 |
| Lx4 | 0.371 | 0.038 |
| Lx5 | 0.935 | 0.09 |
| Refs. | [2] Balun | [2] Miniature Balun | [8] | [15] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process | 0.18 μm CMOS | 0.18 μm CMOS | 0.18 μm CMOS | IPD | 0.18 μm CMOS |
| f0(GHz) | 37.8 | 36.9 | 94 | 2.4 | 10 |
| |S21|, |S31|(dB) | >−6.281 | >−5.809 | >−6.178 | −3.25 | >−4.99 |
| |S11|, |S22|, |S33| (dB) | <−9.6 | <−14.5 | <−6.3 | −21 | <−17.8 |
| |S23| (dB) | −20.9 | −16.8 | −6 * | N/A | <−16.8 |
| Amplitude balance (dB) | 1.227 | 0.637 | 0.098 | 0.45 | 0.045 |
| Phase difference deviation (degrees) | 0 | 0 | −4.9 | 2.6 | 5.1 |
| Size (λ0 × λ0) | 1.1 × 10−3 | 1×10−3 | 3.5 × 10−3 | 1.12 × 10−3 | 8.662 × 10−4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pakasiri, C.; Xu, J.-L.; Wang, S. A 10 GHz Compact Balun with Common Inductor on CMOS Process. Electronics 2023, 12, 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12020468
Pakasiri C, Xu J-L, Wang S. A 10 GHz Compact Balun with Common Inductor on CMOS Process. Electronics. 2023; 12(2):468. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12020468
Chicago/Turabian StylePakasiri, Chatrpol, Jian-Long Xu, and Sen Wang. 2023. "A 10 GHz Compact Balun with Common Inductor on CMOS Process" Electronics 12, no. 2: 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12020468
APA StylePakasiri, C., Xu, J.-L., & Wang, S. (2023). A 10 GHz Compact Balun with Common Inductor on CMOS Process. Electronics, 12(2), 468. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12020468











