Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching Memory Based on Molybdenum Disulfide for Reduction of Leakage Current in Synapse Arrays
Abstract
:1. Introduction
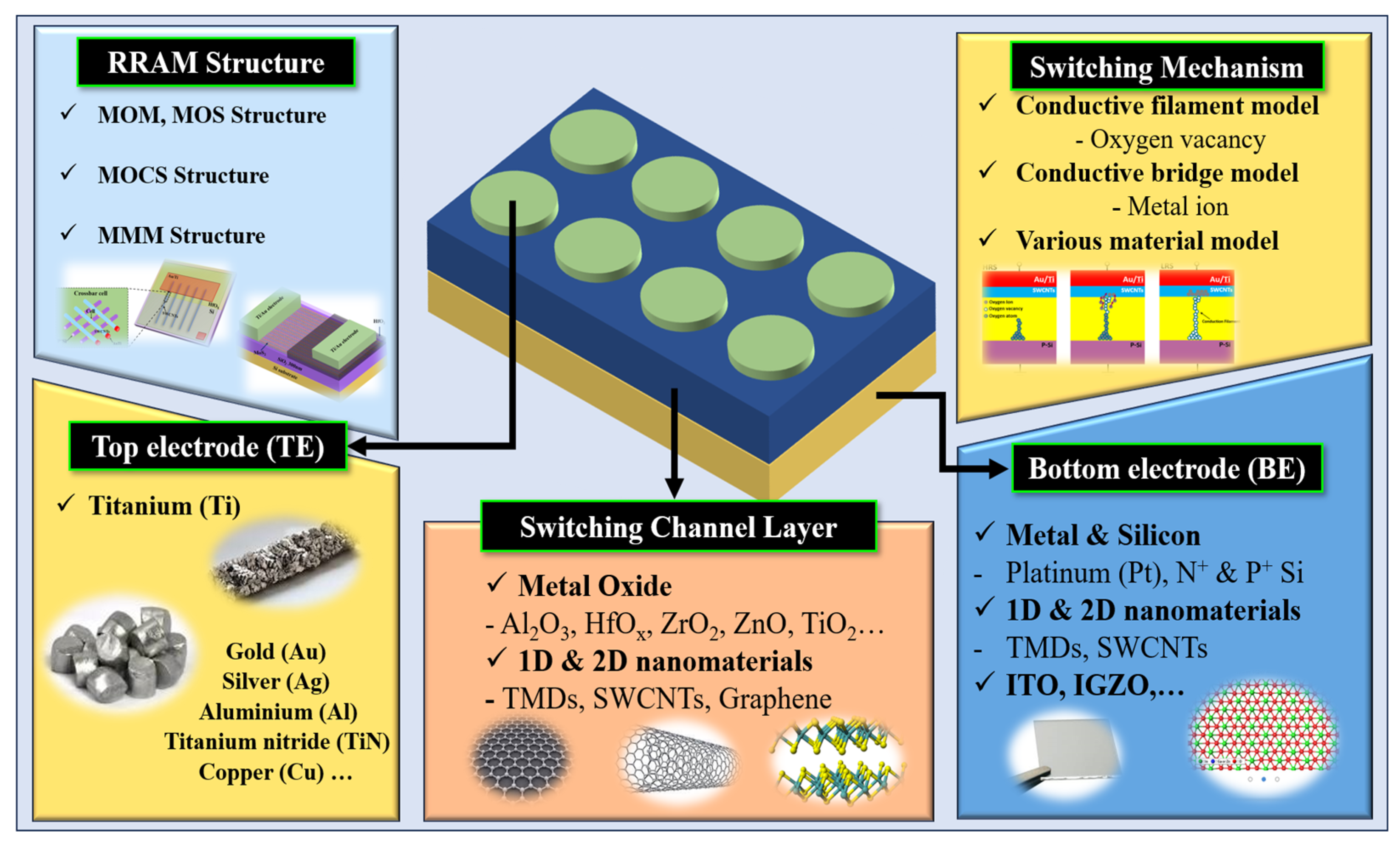
2. Nanomaterials for Switching Channel Layer
3. Experimental Details
3.1. Fabrication Process
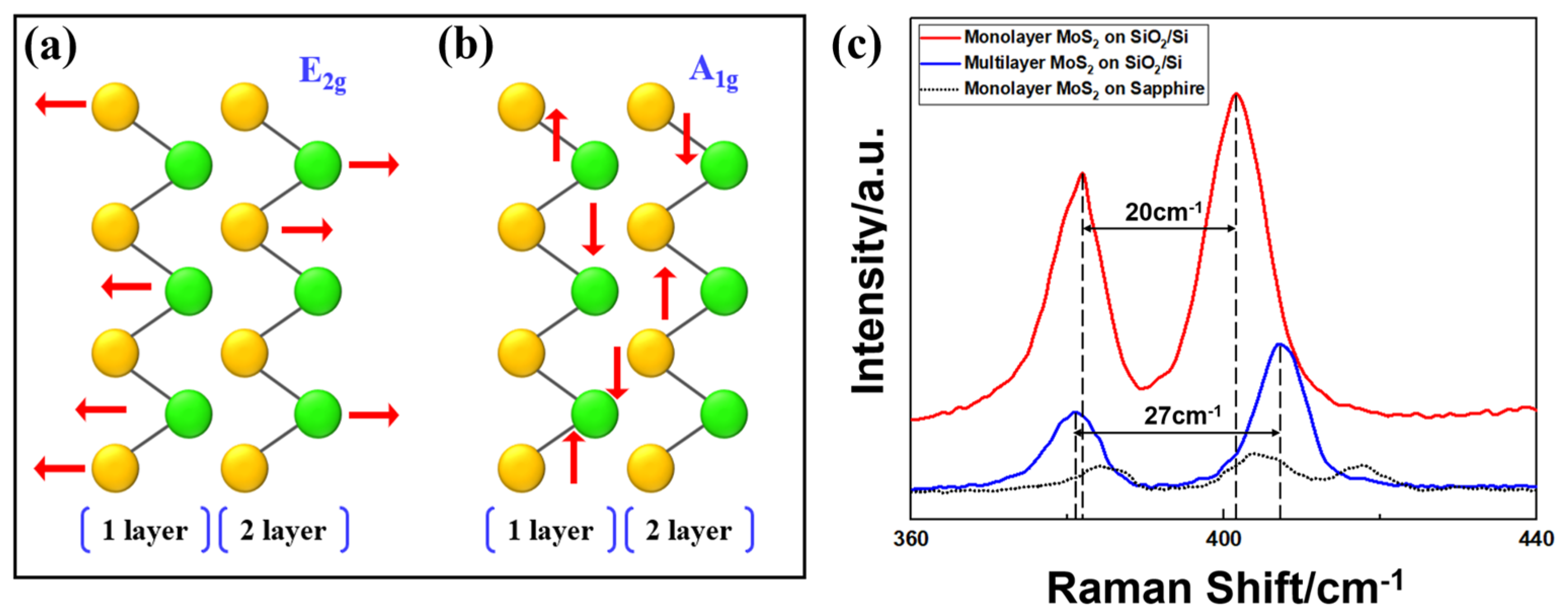
3.2. Raman Spectroscopy
3.3. Photoluminescence Mapping
4. Results and Discussion
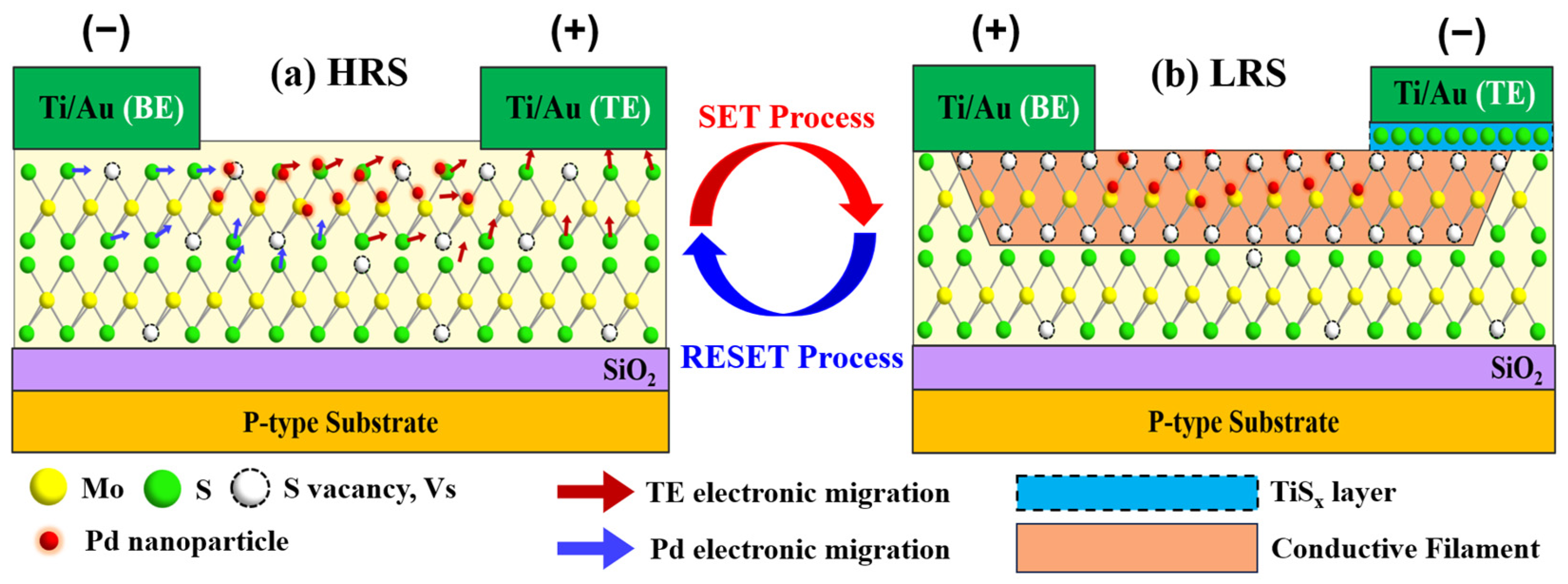
4.1. Resistive Switching Mechanisms
4.2. I–V Measurement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Kim, K.-H.; Lu, W. Crossbar RRAM arrays: Selector device requirements during read operation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2014, 61, 1369–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cosemans, S.; Wouters, D.J.; Groeseneken, G.; Jurczak, M.; Govoreanu, B. On the optimal ON/OFF resistance ratio for resistive switching element in one-selector one-resistor crosspoint arrays. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2015, 36, 570–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.-F.; Tian, H.; Zhao, H.-M.; Zhang, T.-Y.; Mao, W.-Q.; Qiao, Y.-C.; Pang, Y.; Li, Y.-X.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.-L. Interface engineering with MoS2–Pd nanoparticles hybrid structure for a low voltage resistive switching memory. Small 2018, 14, 1702525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govoreanu, B.; Crotti, D.; Subhechha, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.Y.; Clima, S.; Paraschiv, V.; Hody, H.; Adelmann, C.; Popo, M.; et al. A-VMCO: A novel forming-free, self-rectifying, analog memory cell with low-current operation, nonfilamentary switching and excellent variability. In Proceedings of the 2015 Symposium on VLSI Technology (VLSI Technology), Kyoto, Japan, 16–18 June 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Gong, T.; Xu, X.; Yuan, P.; Ma, H.; Dong, D.; Lv, H.; Long, S.; et al. Self-rectifying and forming-free resistive-switching device for embedded memory application. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2018, 39, 664–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Eshraghian, J.K.; Shipley, I.; Weiss, M. Analog synaptic behaviors in carbon-based self-selective RRAM for in-memory supervised learning. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 71st Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), San Diego, CA, USA, 1 June 2021–4 July 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, K.; Wu, R.; Song, L.; Li, T.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Qian, H. Stacked 3D RRAM array with graphene/CNT as edge electrodes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Wu, J.; He, G.; Zhang, J.; Deng, T.; He, P.; Wang, H. Physical mechanism and performance factors of metal oxide based resistive switching memory: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.H.; Kim, S. Artificial synaptic characteristics of TiO2/HfO2 memristor with self-rectifying switching for brain-inspired computing. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 140, 110236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Fernandez, A.; Aldana, S.; Campabadal, F.; Sune, J.; Miranda, E.; Jimenez-Molinos, F.; Roldan, J.B.; Gonzalez, M.B. Resistive switching with self-rectifying tunability and influence of the oxide layer thickness in Ni/HfO2/n+-Si RRAM devices. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 3159–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, H.; Kim, S. Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching and Short-Term Memory Characteristics in Pt/HfO2/TaOx/TiN Artificial Synaptic Device. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chand, U.; Huang, K.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Tseng, T.Y. Mechanism of nonlinear switching in HfO2-based crossbar RRAM with inserting large bandgap tunneling barrier layer. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2015, 62, 3665–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, M.K.; Ismail, M.; Mahata, C.; Kim, S. Effect of interlayer on resistive switching properties of SnO2-based memristor for synaptic application. Results Phys. 2020, 18, 103325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.D.; Kim, S.; Yun, M.J. Self-rectifying resistive switching behavior observed in Al2O3-based resistive switching memory devices with p-AlGaN semiconductor bottom electrode. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 742, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Gao, B.; Yu, S.; Liang, J.; Yang, Y.; Xie, D.; Kang, J.; Ren, T.-L.; Zhang, Y. Monitoring Oxygen Movement by Raman Spectroscopy of Resistive Random Access Memory with a Graphene-Inserted Electrode. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wu, Y.; Wong, H.-S.P. Investigating the switching dynamics and multilevel capability of bipolar metal oxide resistive switching memory. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 103514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullani, N.; Ali, I.; Dongale, T.D.; Kim, G.H.; Choi, B.J.; Basit, M.A.; Park, T.J. Improved resistive switching behavior of multiwalled carbon nanotube/TiO2 nanorods composite film by increased oxygen vacancy reservoir. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2020, 108, 104907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.L.; Jung, H.Y.; Park, S.; Li, B.; Liu, F.; Hao, J.; Kwon, Y.K.; Jung, Y.J.; Kar, S. Voltage-switchable photocurrents in single-walled carbon nanotube silicon junctions for analog and digital optoelectronics. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, C. Pt-activated TiO2-MoS2 nanocomposites for H2 detection at low temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 747, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Caruso, E.; McEvoy, N.; Coileáin, C.; O’Neill, K.; Ansari, L.; Duesberg, G.S.; Nagle, R.; Cherkaoui, K.; Gity, F.; et al. Insights into Multilevel Resistive Switching in Monolayer MoS2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 6022–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Lu, A.Y.; Fang, W.; Lee, Y.H.; Hsu, A.L.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.K.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, L.J.; et al. Van der Waals epitaxy of MoS2 layers using graphene as growth templates. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 2784–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shi, M. Thermal Evaporation Deposition of Few-layer MoS2 Films. Nano-Micro Lett. 2013, 5, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Dwivedi, A.; Lodhi, A.; Khandelwal, A.; Tiwari, S.P. Resistive switching behavior of TiO2/(PVP: MoS2) nanocomposite hybrid bilayer in rigid and flexible RRAM devices. Mem.-Mater. Devices Circuits Syst. 2023, 4, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, N.S.; Mitra, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Roy, A. Nonvolatile memristive devices based on in situ functionalized layered rGO-MoS2 nanocomposites. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2022, 11, 071003. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Sarkar, P.K.; Prajapat, M.; Roy, A. Electrical reliability, multilevel data storage and mechanical stability of MoS2-PMMA nanocomposite-based non-volatile memory device. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 265103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-Y.; Huang, J.-J.; Lai, C.-H. Resistive switching characteristics of a Pt nanoparticle-embedded SiO2-based memory. Thin Solid Film. 2012, 529, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.H.; Wu, M.C.; Lin, C.H.; Tseng, T.Y. Resistive switching characteristics and mechanisms of Pt-embedded SrZrO3 memory devices. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 107, 124117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.T.; Chang, T.C.; Lin, C.C.; Chen, S.C.; Chen, C.W.; Sze, S.M.; Yeh, F.S.; Tseng, T.Y. Influence of nanocrystals on resistive switching characteristic in binary metal oxides memory devices. Electrochem. Solid-State Lett. 2010, 14, H135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, B.; Geng, X.; Debliquy, M. Hydrogen sensors based on noble metal doped metal-oxide semiconductor: A review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 20386–20397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, U.J.; Jang, D.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, T.; Jo, B.; Kim, R.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, M.-W. A Palladium-Deposited Molybdenum Disulfide-Based Hydrogen Sensor at Room Temperature. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yan, H.; Brus, L.E.; Heinz, T.F.; Hone, J.; Ryu, S. Anomalous lattice vibrations of single-and few-layer MoS2. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2695–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Li, W.; Yang, X.; Cai, M.; Yang, K. Probing the Optical Properties of MoS2 on SiO2/Si and Sapphire Substrates. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, P.K.; Singh, E.; Viana, B.C.; Gao, J.; Luo, J.; Li, J.; Lin, Z.; Elías, A.L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Z. Wetting of mono and few-layered WS2 and MoS2 films supported on Si/SiO2 substrates. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 3023–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.M.; Rehman, H.M.M.U.; Gul, J.Z.; Kim, W.Y.; Karimov, K.S.; Ahmed, N. Decade of 2D-materials-based RRAM devices: A review. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2020, 21, 147–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, F.; Hu, K.; She, Y.; Song, S.; Song, Z.; Zhang, K. Improvement of resistive switching performance in sulfur-doped HfOx-based RRAM. Materials 2021, 14, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wu, B.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Ryu, B.; Lu, W.D.; Lu, W.; Liang, X. MoS2 memristors exhibiting variable switching characteristics toward biorealistic synaptic emulation. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 9240–9252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Ren, S.; Guo, J.; Kang, X.; Zhao, X. Robust resistive switching in MoS2-based memristor with Ti top electrode. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 605, 154698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monama, N.O. Electronic Structure Studies of Pallandium Sulphide (PdS) and Platinum (pt) Ternaries. Master’s Thesis, University of Limpopo, Polokwane, South Africa, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bessonov, A.A.; Kirikova, M.N.; Petukhov, D.I.; Allen, M.; Ryhänen, T.; Bailey, M.J.A. Layered memristive and memcapacitive switches for printable electronics. Nat. Mater. 2014, 14, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangwan, V.K.; Jariwala, D.; Kim, I.S.; Chen, K.-S.; Marks, T.J.; Lauhon, L.J.; Hersam, M.C. Gate-tunable memristive phenomena mediated by grain boundaries in single-layer MoS2. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2015, 10, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| TE and BE | Switching Layer | On/Off Ratio | Rectifying Ratio | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ITO and ITO | HfOx/Pd-MoS2 | ≈102 | - | [3] |
| Au and Au | MoS2 | ≈105 | - | [28,29,30,31] |
| Au/Ti and Au/Ti | MoS2 | ≈101 | - | [36] |
| Ti and Pt | MoS2 | ≈102 | - | [37] |
| Ag and Ag | MoS2/MoOx | ≈106 | - | [39] |
| Au and TiN | HfOx/MoS2/TiOx | ≈106 | - | [40] |
| Au/Ti and Ti/Au | Pd-MoS2 | ≈103 | >6 × 10 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jang, D.; Kwon, M.-W. Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching Memory Based on Molybdenum Disulfide for Reduction of Leakage Current in Synapse Arrays. Electronics 2023, 12, 4650. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224650
Jang D, Kwon M-W. Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching Memory Based on Molybdenum Disulfide for Reduction of Leakage Current in Synapse Arrays. Electronics. 2023; 12(22):4650. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224650
Chicago/Turabian StyleJang, DongJun, and Min-Woo Kwon. 2023. "Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching Memory Based on Molybdenum Disulfide for Reduction of Leakage Current in Synapse Arrays" Electronics 12, no. 22: 4650. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224650
APA StyleJang, D., & Kwon, M.-W. (2023). Self-Rectifying Resistive Switching Memory Based on Molybdenum Disulfide for Reduction of Leakage Current in Synapse Arrays. Electronics, 12(22), 4650. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12224650






