Abstract
Forest fires are caused naturally by lightning, high atmospheric temperatures, and dryness. Forest fires have ramifications for both climatic conditions and anthropogenic ecosystems. According to various research studies, there has been a noticeable increase in the frequency of forest fires in India. Between 1 January and 31 March 2022, the country had 136,604 fire points. They activated an alerting system that indicates the location of a forest fire detected using MODIS sensor data from NASA Aqua and Terra satellite images. However, the satellite passes the country only twice and sends the information to the state forest departments. The early detection of forest fires is crucial, as once they reach a certain level, it is hard to control them. Compared with the satellite monitoring and detection of fire incidents, video-based fire detection on the ground identifies the fire at a faster rate. Hence, an unmanned aerial vehicle equipped with a GPS and a high-resolution camera can acquire quality images referencing the fire location. Further, deep learning frameworks can be applied to efficiently classify forest fires. In this paper, a cheaper UAV with extended MobileNet deep learning capability is proposed to classify forest fires (97.26%) and share the detection of forest fires and the GPS location with the state forest departments for timely action.
1. Introduction
Data on the provincial effects of forest fires on ambient air quality are collected across the globe in areas such as Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America, among others. Advanced remote sensing (RS) is used to locate wildland fires and assess air quality. This type of work is useful for researchers and forest officers to find out the needs and make recommendations for wildfires and air pollution. Advanced fire and air quality techniques are required to characterize the fire classes [,]. Automatic fire detection systems have the capability to examine environmental factors. Researchers attempt to minimize the sensors, which results in the improvement of speed and accuracy of diagnosis. Wildfire detection using a single method is feasible but too expensive due to the combination of sensors. It is necessary to focus on soft computing methods for separate fire detection []. The relationship between wildfire and lightning has been analyzed, and 25 percent of lightning strokes result in wildfire ignitions without connected rainfall. The suggestion makes no perceptible links between rainfall and the holdover period. The survival phase following lightning ignition shows the everyday cycle of solar heating []. The impact of particulate matter (PM) results in everyday mortality in Spain when wildfires burn biomass. However, wildfires are becoming more common, which contributes to climate change, necessitating a thorough investigation []. Firefighters must have precise information about wildfires, and arriving at the fire scene on time is critical to putting out the fire. To take an exact decision, the firefighting department needs digital information about forests and fires that describes fire behavior and severity. Two novel extraction methods have been used, namely, geometric parameter calculation and triangle contour [].
Drones with remote sensing result in low operational costs, optimal spatial and temporal resolution, and the absence of risky crews. Drones with forest applications are currently in the experimental stage, but they are expected to progress quickly []. The advanced remote sensing techniques in the area of landslide analysis permit easy, rapid, and updated data acquisition. Improving the conventional capabilities of detection, monitoring, and mapping becomes a challenging task in the area of optimization when investigating hazardous materials. However, the investigative capacity instruments required and accordingly enlarged application are needed []. The INPE burn database was used as the remote sensing method for forest dynamic spots from 1998 to 2016. In 2017, burnt scar detection using the radiance domain considering the atmospheric illumination conditions and the viewing geometry was presented in the study []. The most affected areas were spotted using the normalized burn ratio spectral index. Fire severity is one of the factors that shapes the landscape region while slowing regeneration progression in preferred areas []. Nowadays, remote sensing is used for emergency mapping, part of the disaster management cycle. Satellite imagery is generally used to guide crisis response actions. There are new possibilities with geospatial data, and resources are needed to perform the analysis of the time frame as well as emergency response activities [,,]. Fire severity mapping is an important source for land management agencies, forest officers, and fire scientists across the globe. The severity of large wildfires is measured using the difference normalized burn ratio () and the pre- and post-fire difference severity index (). GEE (Google Earth Engine)-based classification is used in the land management group framework for the rapid production of fire severity maps []. GEE (Google Earth Engine)-based classification is used in the land management group framework for the rapid production of fire severity maps []. The analysis of wildfires expands the knowledge of planning, supervision techniques, and tools to diminish their effects. The quantitative approach is important to improve the full view of the WUI (wildland–urban interface). However, using LiDAR data in forest analysis and satellite imagery to find forest and urban areas is not possible with this approach []. The radio coverage tool enhances the response to emergencies such as wildfire events. Excess attenuation results in a cold plasma barrier near wildfires.
Wildfires and their effects are mapped using a variety of machine learning algorithms. However, improving the accuracy of the mapping of wildfire effects using hyperspatial drone imagery is still challenging. The addition of texture results in an improvement in the post-fire effect classifier accuracy. Additional evaluation is required for imagery, especially when evaluating scenes with high tree canopy cover []. A deep learning-based wildfire monitoring technique was introduced, in which images are retrieved using a UAV with the help of an optical sensor. The method was designed to be able to make judgments similar to humans. The result shows whether a fire exists or not in the forest area. The system does not support infrared thermal cameras [,]. The fuzzy clustering technique of modified Fuzzy C-Means clustering is used for fire identification and region extraction. The detection and segmentation of wildfires are performed using high-resolution satellite images. The method needs further improvement with hybrid methods that combine fuzzy and genetic algorithms []. SVM and ANN are used to process the information collected from satellite images over large regions and extort insights from them to predict the incidence of wildfires and circumvent such disasters. Remote sensing data related to the positions of the crops, meteorological conditions, and fire indicators are used in this approach, “MODIS” []. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (“MODIS”) is the key technique aboard the Terra and Aqua satellites [,].
The use of UASs (unmanned aerial systems) in the area of photogrammetry and remote sensing (PaRS) has become popular in the last couple of years []. A UAV can obtain information using visual cameras or on-board infrared automatic cameras. UAVs, similar to helicopters, can hover, and drones are extremely useful. Moreover, more UAVs can combine, which results in improved fire monitoring services, such as coverage of a big fire, fire severity assessment, and complementary view of fires. A deep learning method for forest fire detection can be introduced into the fire classifier using a CNN, which extracts more features to train.
The primary use of UAVs is to detect fires in the early stages. Hence, the detection of fire at low-level intensity itself is necessary. The features extracted with traditional machine learning are limited and highly influence the classification accuracy. With the use of deep learning, numerous features can be extracted that can assist in improving accuracy. As UAVs are used for capturing the live stream of forest fire, the processing of images in real time is needed. Among the available ImageNets, MobileNetV2 [] is fast and designed for mobiles that have limited resources. As a result, we suggest a lightweight neural network architecture, X-MobileNet, that is appropriate for embedded and mobile applications and that performs well in real-time fire detection applications. The system operates on less powerful, more affordable single-board computers such as Raspberry Pi 3B and Arduino.
The major contributions of the proposed model are as follows:
- We propose a novel deep learning method based on the existing MobileNetV2 that is suitable for fast execution and low-resource devices such as drones.
- The pre-trained weights for all layers of the MobileNetv2 architecture are used in the proposed method, which reduces the number of trainable parameters needed. Our model is now well suited for use on drones with limited resources as a result.
- Unlike standard machine learning techniques, the proposed model may be trained and deployed end to end, eliminating the need for separate feature extraction and classification phases.
- To ensure that our model is robust, it was validated using two different fire datasets. The results of our experiments demonstrate that our method consistently outperformed other recent DL-based algorithms on fire datasets.
- A lightweight hexagon drone was designed at low cost and with flight control.
In this paper, the models based on deep learning are explored and analyzed. Section 2 of this paper presents detailed information on existing forest fire techniques and related work, and Section 3 presents the proposed methodology. In Section 4, the experimental results and discussion are presented. In Section 5, the conclusion and future work are described.
2. Related Works
UAVs for disasters are available, face a lot of challenges when in use, are likely limited computationally, and have energy and regulation issues. Nevertheless, UAVs with deep learning methods result in improved disaster modeling, when combining geotagged events that are used in geospatial applications [,]. Deep learning is very effective in high-level feature learning; however, a significant amount of training results in optimal results. A new saliency detection method was proposed; the method is useful for the fast location and segmentation of the aerial image of the wildfire. The method results in avoiding feature loss caused by direct resizing. In wrongly classified forest mist images, IR sensors may be used for better decision making []. A real-time forest fire monitoring system with UAVs was proposed; the system uses five sensors, namely, a GPS, a compass sensor, an inertial measurement unit (IMU), a temperature sensor, and a barometer. The drone can detect the temperature from 20 m above the ground surface. However, data loss during the data transmission from the drone to the web server needs to be improved []. Color feature extraction results in inaccuracy; to overcome the issue, a two-dimensional discrete wavelet transform (DWT) is used. The DWT is used to differentiate the flame and smoke region from high-frequency noise signals. The computational cost is lower, and improved fire detection accuracy is achieved using a UAV platform [,]. UAV-based fire detection based on utilizing color as well as motion was proposed. The color decision rule extracts the fire-colored pixels by producing a chromatic feature of the fire. The Horn–Schunck optical flow algorithm is used to compute motion vectors of the candidate regions. The method results in significantly improved performance in fire detection and reduction [,]. The near-real-time (NRT) method was proposed; the framework combination of digital image analysis and the visualization of web support results in the automatic updating of the results. Compared with existing methods, the NRT method results in low computational power []. UAVs with deep learning methods result in improved disaster modeling, when combining geotagged events that are used in geospatial applications. The R-CNN algorithm is used to detect not one or two objects, but hundreds of object types in nature. The CNN is used with UAVs; UAVs are particularly lightweight and low cost, while the CNN object detection algorithm has very large computational demands. In general, it requires high-end Graphics Processing Units (GPUs) that need a lot of power and weight, especially for a lightweight and low-cost drone []. A UAS platform with the support of a helicopter was proposed, namely, the Sky-Eye system. The system improves awareness by providing strategic support to the monitoring of wildfires in an easy way. Sky-Eye works with existing COTS (commercial off-the-shelf) techniques deployed in medium-sized helicopters. However, the UAS with an abstraction layer as service, defined as standard service, and the interrelations between them need further improvement [].
The use of UAVs (unmanned aerial vehicles) in the area of photogrammetry and remote sensing (PaRS) has become popular in the last couple of years [,]. UAVs can obtain information using visual cameras or on-board infrared automatic cameras. UAVs have hovering capabilities, similar to helicopters, and drones are very useful. However, more UAVs can combine, which results in improved fire monitoring services, such as coverage of big fires, fire severity assessment, and complementary view of fires [,]. UAV-based remote sensing is used in forests and farming to afford adequate decision support. However, better data pre-processing with various temporal and spatial data handling software applications is required. Software can be used effectively to take better decisions in the future [,]. In [], a review of fire detection using videos is presented. Improving computer vision and object detection is important when multiple diverse models are in use. UAVs with high-resolution cameras and faster transmission of video result in faster and more accurate footage. However, drones need to be programmed, and autonomous features with navigation are required [].
Extracting the characteristics of smoke by pre-training VGG-16 on the ImageNet dataset for feature transfer is explained in []. Inception-ResNet-v2 pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset was used for classifying fire and smoke []. The performance of the model can be improved substantially using backbone networks such as ResNet, VoVNet, and FBNetV3 in deep learning. It was used with Bayesian neural network and Faster R-CNN [], which improved the performance. Ft-ResNet50 [] was modeled by fine-tuning layers of ResNet with Adam and Mish functions, and the semantic information of fire images were effectively extracted. CNN-based Inception-V3 was used to improve accuracy in classifying fire/non-fire images []. A combination of EfficientNet-B5 and DenseNet-201 models for classification and EfficientSeg for segmentation, and two vision transformers were used to build a novel deep ensemble learning mode, which improved the performance [].
A new model, FT-ResNet50 [], based on transfer learning was proposed for forest fire identification using UAV images. A multi-oriented value conversion–attention mechanism (MVMNet) [] was discussed for forest fire detection. The issues of false smoke alarm and missed detection were also addressed in the same work. An artificial intelligence-based deep learning method [] was used for forest fire identification in smart cities. A deep learning method and vision transformers [] were used for classifying forest fires. Different methods used for forest fire detection were reviewed in []. Recently, MobileNets [] were used for applications related to mobiles for executing at faster rates and with improved performance. MobileNets are the first computer vision models built for mobiles. Due to their efficiency, MobileNets [,,] have been applied to the classification of fruits, skin images, diabetic retinopathy, etc. As on-board computation on UAVs needs to be minimized, MobileNets could be a way forward for forest fire detection.
Considering the efficacy of MobileNets, in this paper, we propose to use an extended MobileNet for classifying fire and non-fire images, as speedy and lightweight models for UAVs are highly needed. The cost-efficient UAV design and the lightweight MobileNet make the proposed model efficient in detecting forest fires.
3. Materials and Methods
Real-time, early forest fire detection is essential, since once it reaches a certain threshold, it is difficult to contain. The procedure followed in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV)-based forest fire detection is shown in Figure 1. UAV-based fire detection identifies the fire at a faster pace with higher precision than the satellite monitoring and detection of fire events. As a result, an unmanned aerial vehicle outfitted with a GPS and a high-resolution camera may capture photographs of the fire position that are of excellent quality. Additionally, deep learning frameworks are used to accurately categorize forest fires. Additionally, false alarms from smoke and files created by people can be avoided with UAV-based forest fire detection. From this point forward, we suggest an end-to-end CNN image classification extended MobileNet (X-MobileNet) to detect wildfires.
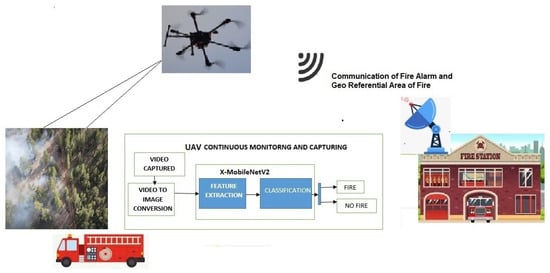
Figure 1.
Workflow of forest fire detection.
3.1. UAV and Its System Architecture
UAV-based forest fire detection systems contain two sections: hardware related to the UAV and software for detecting the fire. The UAV system architecture and its components are presented in Figure 2. UAV hardware consists of Arduino UNO, which is connected to sensors, flight controller, and receiver. Arduino is connected to several sensors that constantly monitor different subsystems of the UAV. The drone specifications used for the designed UAV, shown in Figure 3 are presented in Table 1.
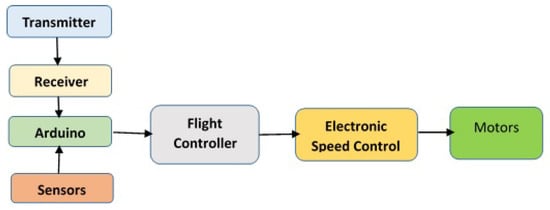
Figure 2.
UAV system architecture.

Figure 3.
The designed camera and UAV.

Table 1.
Specifications of the designed UAV.
The designed UAV is a hexacopter with 6 wings to allow it to go higher than the traditional quadcopter and increase flight time. The proposed UAV wings are provided with a fail-safe in case one motor dies mid-flight. An Arduino micro controller is used to make it autonomous when an obstacle is detected while hovering. The UAV is equipped with Mission Planner software to map way points and to fly from one place to another without any human intervention in between. Ublox is used to fix the GPS, and as the UAV waits for the GPS to be fixed, the drone is provided with a path/mission it has to follow. The Ublox device then sends the data obtained using telemetry via MAVLink (a communication protocol) to the drone. Once the UAV is armed with the mission of mapping and surveying the area, a video feed is provided as live transmission that detects forest fires.
Our suggested approach combines the IoT and deep learning with the goal of offering a comprehensive one-stop solution for spotting wildfires. CNNs and other sensors are used by MobileNet to identify the fire, evaluate the fire severity, and analyze weather information of the impacted area.
3.2. Dataset
There is no standard dataset for fire images. So, it is inevitable to create one. Images were collected using the designed UAV, and images were extracted from videos of forest fires collected in kaggle and FLAME; then, we added frames from videos taken with the drone. The dataset was divided into two parts: fire and non-fire. This fire dataset contains a total of 5313 fire images, and the non-fire dataset contains a total of 677 images. The accuracy of a model can be increased by increasing the size of the dataset by adding images extracted from live video stream; in this way, the size of the dataset will be ever growing, and the accuracy of a model increases every time the model is trained. The dataset is available at [].
3.3. Data Pre-Processing
Data needed to be pre-processed in order to make them the most suitable for subsequent processing. Often, images captured using drones have washout intensity, and sometimes, small-intensity fires are not visible. Hence, image enhancement is needed in order to enhance the image to remove washout features. Here, the histogram equalization technique was used, followed by power law transformation to highlight the fire region. The gamma value used for the considered dataset was 5 after trial and error.
Data are gold as far as deep learning is concerned. The model performs better if we have a larger number of samples in the training dataset, as there are variability and bias problems with smaller sample sizes. Variability is calculated using standard deviation; the standard deviation of a sample is how far the true results might be from the sample that we have. The larger the deviation is, the lesser the accuracy is, since smaller sample sizes get decreasingly representative of the entire population. Small sample sizes also affect the reliability of a model, because they lead to higher variability, which may lead to bias. If we only train a model for a certain gender or certain physical traits, or on an image that is straight, the model does not work well in all possible cases and does not produce accurate results.
Data Augmentation
To overcome the issue of having a smaller dataset, we used the augmentation method by applying a number of random transformations, so that the model that was built could never have taken the same image twice. This helped in preventing the overfitting of the model and eventually helped the model to generalize. Below are some of the features that can be passed as parameters to the augmentation function:
- Rotation range: It is a value in the range of (0–180) degrees, a range within which the picture is rotated randomly.
- Width shift and height shift: To shift an image means moving all pixels of the image in one direction, such as horizontally or vertically, while keeping the same image dimensions.
- Zoom range: It is used for zooming the pictures.
- Horizontal flip: It flips half of the image in the horizontal direction.
- Fill mode: It fills the newly produced pixels that appear after rotation and width or height shift.
The sample dataset and the augmented dataset are shown in Figure 4.
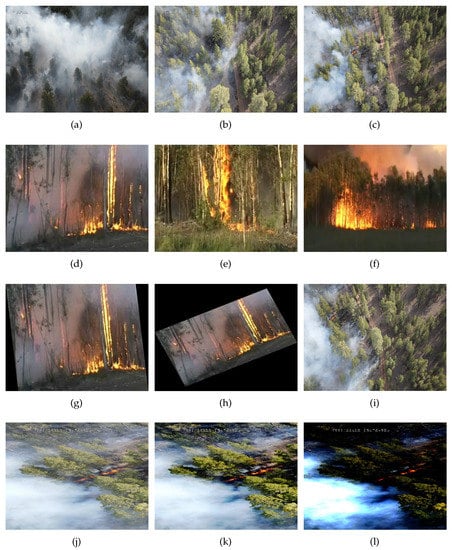

Figure 4.
Images in row 1 (a–c) indicate Image2443, Image5835, and Image6577; row 2 (d–f) indicates frame89, frame318, and frame507; row 3 (g–i) shows shear, shear rotated, and horizontally flipped images of the dataset; and row 4 (j–l) shows the original, histogram-equalized and power law-transformed images.
4. Proposed Enhanced MobileNet Model
The overall architecture of the proposed model is presented in Figure 5. The images are pre-processed and then fed to X-MobileNet for classification with the customized output layer for classifying fire or no fire.
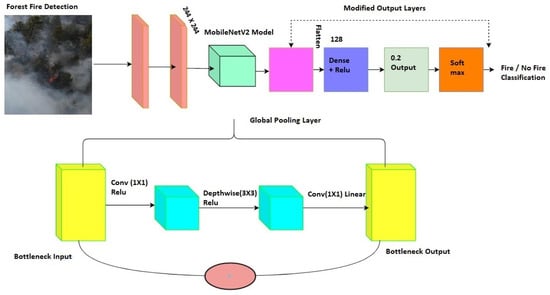
Figure 5.
Workflow of extended MobileNet for forest fire detection.
One of the often-used methods for computer vision tasks such as classification and segmentation is transfer learning. It consists in the exchange of weights or in using the expertise gained from tackling one challenge to solve other connected issues. Transfer learning typically results in less training, if the application domains are connected, in terms of time. There are two typical methods to carry out transfer learning: using pre-trained models and defining custom output layers. In the proposed model, to cut down on computational costs, the pre-trained MobileNet is modified to be used, and transfer learning is preformed with global average pooling as the output layer, as shown in Figure 6.
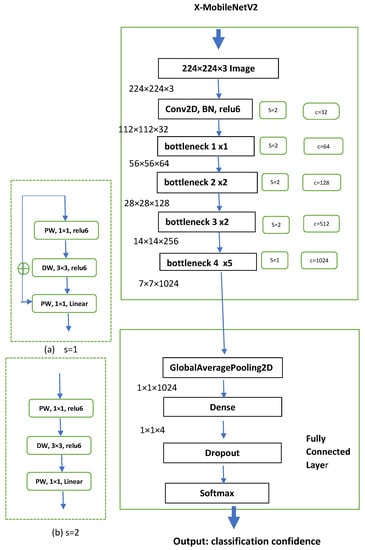
Figure 6.
Layers of extended MobileNet for forest fire detection.
4.1. Pre-Trained Model Usage
Pre-trained models such as AlexNet, ZFNet, GoogleNet, VGG, and MobileNet, etc., can be used, as they are already proved models with a large number of images. MobileNet is a lightweight model that is designed for mobiles considering its low power consumption, fast execution, and low memory usage; hence, MobileNet was considered.
4.2. Customized Output Layer
This approach considers the pre-trained model without the output layer, which serves as a feature extractor. Using a unique output layer, these features can be applied to the needed classification task. Last but not least, training the custom model is necessary to improve the classification outcomes. Here, transfer learning with global pooling is devised at the output layer, as fire detection is a binary classification problem rather than a 1000-class problem in MobileNet.
4.3. Global Average Pooling
Global pooling is used to reduce the multi-dimensional feature map to a one-dimensional feature vector , where is the size of image and N is the number of filters. Here, global average pooling is used to obtain the average value of the features. The filer acts as a flattening layer, and overfitting is prevented in this layer because there are no parameters. The flattened layer is connected to a dense layer with 128 neurons in a fully connected manner.
4.4. Depth-Wise Separable Convolution
The core of the MobileNet model is depth-wise separable convolution. In order to lower computing costs and model sizes, it factors filters. The two layers of a depth-wise separable convolution are as follows:
- Depth-wise convolution: This technique performs layer filtering by applying a single filter to each input channel. In Figure 7, it can be seen that the filter is depth-wise separated with a single filter and applied to each layer. With this, 9 parameters in the filter can be represented with 6 parameters, as shown in Figure 7.
- Point-wise convolution: This technique uses 1X1 convolution to create linear collective output.
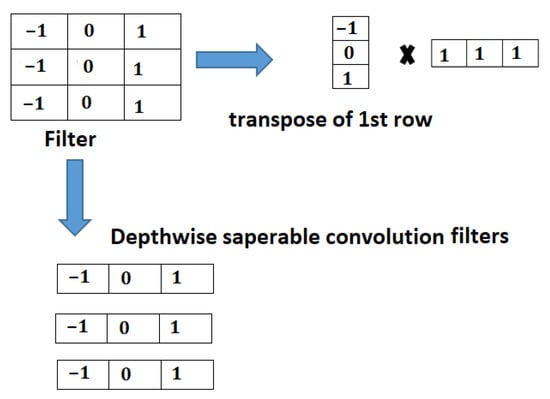
Figure 7.
Depth-wise separable convolution.
If depth-wise convolution is applied to an output layer of , then we obtain parameters (27), and point-wise convolution results in parameters, as well as 1 final parameter, for a total of 31 parameters. If it is applied to 3 layers, then for 3 layers, parameters result in (27) parameters, and point-wise convolution results in 3 times , i.e., 9 parameters, for a total of 36 parameters; on the other hand, standard convolution would result in , i.e., 81 parameters. Hence, if input image F is of size , the filter size is ; when applied to channels, the standalone convolution computation complexity is given by Equation (1).
The depth-wise computation cost is given by
The comparative ration of both computational costs is
The ratio shown in Equation (3) indicates that MobileNetV2 reduces the computational cost.
Regular convolution, shown in Figure 6, is replaced with depth-wise convolution in Figure 6a,b and is explained with input image F. Here, S indicates the stride, and C indicates the channel outputs. Outputs F1, F2, and F3 can be expressed with the following equations:
where value represents the ReLu function, is point-wise convolution, is depth-wise convolution, and represents the linear activation function. In the case of short form path on bottleneck implementation,
and when there is no short form path on bottleneck implementation,
4.5. Fire Classification
In the fire dataset, fine-tuning was carried out on the network top layer. The retraining of the layers was performed using the target dataset results in the updating of the top-layer weights. The classification layer was swapped in the extended MobileNet model with a new layer that contained the 2 classifications of the fire dataset. Retraining the layer with the dataset for fire detection updated the weights of the output layer.
In the extended MobileNetV2, the downsampling technique is implemented such that feature extraction is delayed until the resolution of the image becomes lower. Applying depth-wise separable convolutions in quick order at the network start results in faster downsampling. Max pooling is not used in this situation, because we discovered that it does not improve efficiency but instead adds unnecessary computation. The proposed X-MobileNet takes images up to 224 × 224 pixels in size and downsamples 4 times in the first 2 layers and 32 times in 12 layers, whereas the original MobileNet downsamples 4 times in 24 layers. The detailed layers and the structure of X-MobileNet are presented in Figure 4. Bottlenecks 1, 2, and 3 contain depth-wise separable convolution, as shown in figure (a), with s = 1. Bottlenecks 2 and 3 are repeated twice, for a total of 5 depth-wise separable downsampling. Finally, bottleneck 4 is repeated 5 times for feature extraction using depth-wise convolution, as shown in figure (b), with s = 2.
5. Experimental Results and Discussion
The experimental setup of the proposed model is presented in this section. The experiments were executed on an Intel i7 processor with 16 GB GPU, and they were executed in Python and tensor flow.
5.1. Training the Model
Supervised learning algorithm MobileNetV2 was used to train the model. After data augmentation, the function for the data generator was used to divide the dataset into training (80%) and test (20%) sets. One hot encoding was used to generate the value as 1 if the input image was fire and 0 if it was a non-fire image.
The experiment was conducted using the packages TesnsorFlow and Keras for loading the images and transforming them randomly. A batch size of 32 was used for the experiment. The images were resized to 224 × 224 and fed to MobileNetV2. In Figure 6, the detailed architecture of the proposed methodology is shown. The outcome of MobileNetV2 was , which was a 1028 classifier.
An additional global average pooling layer with a filter was used to reduce the dimensionality of the data. A dense layer for fully connected neurons was fed to a 0.25 dropout layer in order to avoid overfitting. In the architecture, S indicates the stride; BN indicates batch normalization; DW indicates depth-wise normalization; and PW indicates point-wise normalization (Figure 7). The set of hyperparameters used in the execution of the model is presented in Table 2. In total, 30 epochs were used to train each model. Binary cross entropy loss was adapted during the training of the model. In order to adapt the learning rate towards the optimum value, the Adam optimizer was used. The Adam optimizer is a basic, simple, yet fast optimizer for deep learning algorithms. Hence, the Adam optimizer was applied during the execution of the proposed model. These hyperparameters were used based on the trial and error method and with reference to the existing literature. These parameters refer to the current running instance of the model.

Table 2.
Parameters used in the model.
5.2. Evaluation Measures
In order to measure the performance of the proposed model, the following coefficients were used (Equations (9)–(13)):
where is true positive, i.e., the fire images that are predicted as fire images; is true negative, which represents the number of fire images predicted as non-fire ones; is false negative, i.e., the non-fire images that are predicted as non-fire images; is false positive, i.e., the non-fire images that are predicted as fire images.
5.3. Forest Fire Detection Results
The forest fire classification results are presented in Table 3. The results show that the training and validation accuracy were good and that the loss was also negligible, making the model efficient. The classification loss values for the test dataset and the validation dataset are presented in Figure 8; the classification accuracy of training and validation are shown in Figure 9; and the AUC ROC curve is shown in Figure 10. As the number of iterations increase, the training accuracy (train_acc) and the validation accuracy (val_acc) converge and achieve almost equal accuracy, around 0.97; similar is the case with the AUC. The validation loss (val_loss) and the training loss (train_loss) decrease, converge, and result in minimum loss. From the convergence of the curves, it can be stated that the model was not overfitted nor underfitted. This also indicates that data augmentation improved the training accuracy as the number of images was increased. The method used 65 percent of images for training and 35 percent of images for testing. We even reduced the training percentage to 65; the model performed well, with 97.22 percentage of accuracy. The confusion matrix of the classification of the test and training data is shown in Table 4.

Table 3.
Loss and accuracy results.
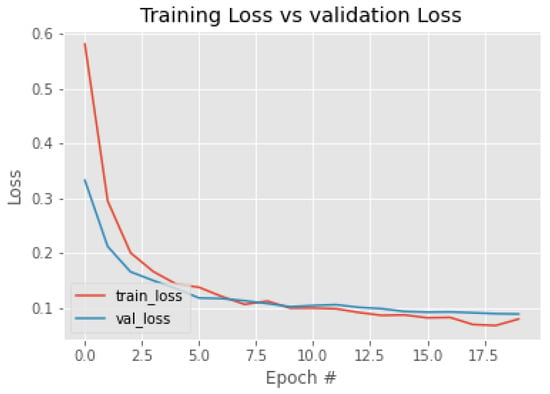
Figure 8.
Training and validation loss.
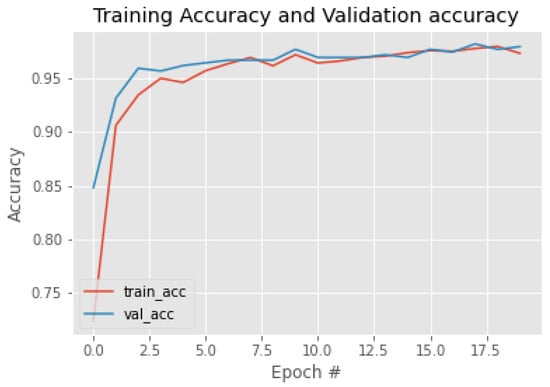
Figure 9.
Training and validation accuracy.
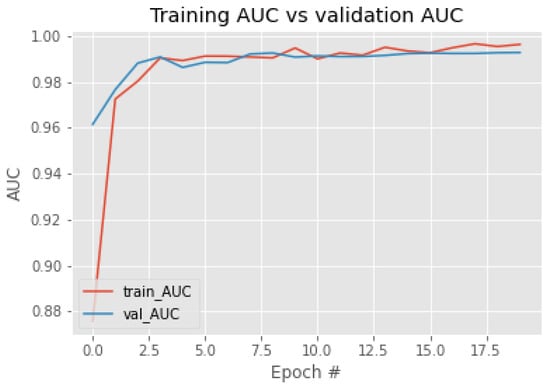
Figure 10.
Training and validation AUC ROC curve.

Table 4.
Confusion matrix of classification.
The depth-wise separable convolution used in the MobileNet tremendously improved the accuracy; even though the depth of layers increased by three, the accuracy improved greatly. Still, there was no increase in time complexity, and the output layer was flattened with global pooling for binary classification.
The optimizer used for a model and the activation function also impact the accuracy of a model. It has been observed in many deep learning studies that the Adam optimizer proves to be more efficient than other optimizers and that the ReLu activation function is preferred over other activation functions. The proposed model’s impact factor was also improved with the Adam optimizer.
The proposed algorithm was compared with the results of the other ImageNet models, such as ResNet50, VGG, and Inception. From the comparison in Table 5, it can be observed that the proposed model outperformed the other ImageNet models. The visual representation of the performance measures in comparison with other ImageNet models is reported in Figure 11, which shows that the proposed model outperformed the other models.

Table 5.
Performance comparison with other ImageNet models.
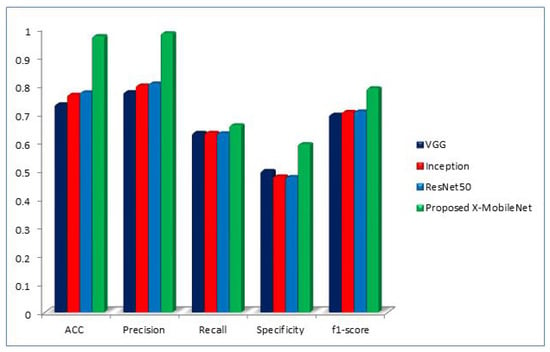
Figure 11.
Performance measure comparison of proposed X-MobileNet with other existing models.
6. Conclusions
The detection of wildfires using UAVs with the help of image processing is crucial to extinguish fire in the early stage. Forest fire detection using deep learning has been a promising research area. Considering MobileNet’s advantages, it was used as the base framework to develop X-MobileNet. The proposed model identifies forest fires, and augmentation methods are used to enhance the dataset. The augmentations assists in the generalizing of the model for all images. The proposed depth-wise separable convolution, global pooling at the output layer, and the addition of the Adam optimizer make the model optimal. The performance results of the model prove that X-MobileNet recognizes forest fires, showing high performance. Further, to increase the performance, Field Programmable Gate Arrays can be adapted to design a chip that can be placed on board the UAV.
Author Contributions
A.N., conceptualization, methodology, supervision, and writing draft—review and editing; P.S., validation and writing—original draft; S.M., supervision and writing draft—review and editing; S.R., supervision and writing draft—review and editing; E.T.E., supervision and writing draft—review and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The project was supported by RGEMS internal seed funding by VIT-AP University.
Data Availability Statement
The data will be made available upon request from the authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the efforts of Sankalp Saxena, Sammineni Saideep, and Gowtham Natarajan for designing the low-cost drone and generating the image datasets.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sherry, J.; Neale, T.; McGee, T.K.; Sharpe, M. Rethinking the maps: A case study of knowledge incorporation in Canadian wildfire risk management and planning. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytnerowicz, A.; Arbaugh, M.J.; Andersen, C.; Riebau, A.R. Chapter 26 Integrating Research on Wildland Fires and Air Quality: Needs and Recommendations. Dev. Environ. Sci. 2008, 8, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdipour, E.; Dadkhah, C. Automatic fire detection based on soft computing techniques: Review from 2000 to 2010. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2014, 42, 895–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda, N.; Rigo, T. The rainfall factor in lightning-ignited wildfires in Catalonia. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 239, 249–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linares, C.; Carmona, R.; Salvador, P.; Díaz, J. Impact on mortality of biomass combustion from wildfires in Spain: A regional analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Xu, X.; Han, N. A kind of identification method of geometric parameters for forest fire. In Proceedings of the ICSPS 2010—2nd International Conference on Signal Processing Systems, Dalian, China, 5–7 July 2010; Volume 1, pp. 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Shao, G. Drone remote sensing for forestry research and practices. J. For. Res. 2015, 26, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagli, N.; Frodella, W.; Morelli, S.; Tofani, V.; Ciampalini, A.; Intrieri, E.; Raspini, F.; Rossi, G.; Tanteri, L.; Lu, P. Spaceborne, UAV and ground-based remote sensing techniques for landslide mapping, monitoring and early warning. Geoenvironmental Disasters 2017, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayhan, B.; Kwan, C. On the use of radiance domain for burn scar detection under varying atmospheric illumination conditions and viewing geometry. Signal Image Video Process. 2017, 11, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, J.a.F.C.; Gleriani, J.M.; Velloso, S.G.S.; de Souza, G.S.A.; do Amaral, C.H.; Torres, F.T.P.; Medeiros, N.D.G.; dos Reis, M. Wildfires as a major challenge for natural regeneration in Atlantic Forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lollino, G.; Manconi, A.; Guzzetti, F.; Culshaw, M.; Bobrowsky, P.; Luino, F. Engineering Geology for Society and Territory-Volume 5: Urban Geology, Sustainable Planning and Landscape Exploitation; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 5, pp. 1–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherstjuk, V.; Zharikova, M.; Sokol, I. Forest Fire Monitoring System Based on UAV Team, Remote Sensing, and Image Processing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Data Stream Mining and Processing, DSMP 2018, Lviv, Ukraine, 21–25 August 2018; pp. 590–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherstjuk, V.; Zharikova, M.; Sokol, I. Forest Fire-Fighting Monitoring System Based on UAV Team and Remote Sensing. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 38th International Conference on Electronics and Nanotechnology (ELNANO), Kyiv, UKraine, 24–26 April 2018; Volume 7, pp. 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, L.; Griffioen, P.; Newell, G.; Mellor, a. The utility of Random Forests for wildfire severity mapping. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 216, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, A.; Pallares-Barbera, M.; Valldeperas, N.; Gisbert, M. Wildfires in the wildland-urban interface in Catalonia: Vulnerability analysis based on land use and land cover change. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 673, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, D.; Myers, B.; Branham, J.B. Evaluation of Texture as an Input of Spatial Context for Machine Learning Mapping of Wildland Fire Effects. Signal Image Process. Int. J. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, W.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, Y.T. Forest fire monitoring system based on aerial image. In Proceedings of the 2016 3rd International Conference on Information and Communication Technologies for Disaster Management—ICT-DM 2016, Vienna, Austria, 13–15 December 2016; pp. 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Fire detection using infrared images for UAV-based forest fire surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems—ICUAS 2017, Miami, FL, USA, 13–16 June 2017; pp. 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, P.; Sathish, B.S.; Sajiv, G. A comparative approach of identification and segmentation of forest fire region in high resolution satellite images. In Proceedings of the IEEE WCTFTR 2016—2016 World Conference on Futuristic Trends in Research and Innovation for Social Welfare, Coimbatore, India, 29 February–1 March 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, M.; Kwan, C.; Ayhan, B.; Tran, T.D. Burn scar detection using cloudy MODIS images via low-rank and sparsity-based models. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Global Conference on Signal and Information Processing (GlobalSIP), Washington, DC, USA, 7–9 December 2016; pp. 177–181. [Google Scholar]
- Sayad, Y.O.; Mousannif, H.; Al Moatassime, H. Predictive modeling of wildfires: A new dataset and machine learning approach. Fire Saf. J. 2019, 104, 130–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepaschenko, D.; Chave, J.; Phillips, O.L.; Lewis, S.L.; Davies, S.J.; Réjou-Méchain, M.; Sist, P.; Scipal, K. A global reference dataset for remote sensing of forest biomass. In The Forest Observation System approach; IIASA: Laxenburg, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Byrne, K. Digital Morphometry Applied to Geo-Hazard Risk Assessment: A Case Study from Germany. Technische Universitat Dresden. Faculty of Environmental Sciences. Inst. Cartogr. Master Sci. 2018, 1, 79–97. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F.X. Disaster Monitoring using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles and Deep Learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.11805. [Google Scholar]
- Shahbazi, M.; Théau, J.; Ménard, P. Recent applications of unmanned aerial imagery in natural resource management. GISci. Remote Sens. 2014, 51, 339–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, J.; Xu, L.; Guo, H. Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Forest Fire Detection; Atlantis Press: Guangzhou, China, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardihani, E.D.; Ramdhani, M.; Suharjono, A.; Setyawan, T.A.; Hidayat, S.S.; Helmy, S.W.; Widodo, S.; Triyono, E.; Saifullah, F. Real-time forest fire monitoring system using unmanned aerial vehicle. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 13, 1587–1594. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xin, J.; Yi, Y.; Liu, D.; Liu, H. Forest Fire Detection with Color Features and Wavelet Analysis Based on Aerial Imagery. In Proceedings of the 2018 Chinese Automation Congress—CAC 2018, Xi’an, China, 30 November–2 December 2018; pp. 2206–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Aerial Images-Based Forest Fire Detection for Firefighting Using Optical Remote Sensing Techniques and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. J. Intell. Robot. Syst. Theory Appl. 2017, 88, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Vision-based forest fire detection in aerial images for firefighting using UAVs. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems—ICUAS 2016, Arlington, VA, USA, 7–10 June 2016; pp. 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Ghamry, K.a.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Unmanned aerial vehicle based forest fire monitoring and detection using image processing technique. In Proceedings of the CGNCC 2016—2016 IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference, Nanjing, China, 12–14 August 2016; pp. 1870–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römer, H.; Kersten, J.; Kiefl, R.; Plattner, S.; Mager, A.; Voigt, S. Airborne near-real-time monitoring of assembly and parking areas in case of large-scale public events and natural disasters. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 682–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Wang, J.; Crandall, D.; Selma, S.; Selmašabanovic, S.; Fox, G. Real-Time Object Detection for Unmanned Aerial Vehicles based on Cloud-based Convolutional Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the First IEEE International Conference on Robotic Computing (IRC), Taichung, Taiwan, 10–12 April 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, E.; Barrado, C.; Royo, P.; Santamaria, E.; Lopez, J.; Salami, E. Architecture for a helicopter-based unmanned aerial systems wildfire surveillance system. Geocarto Int. 2011, 26, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned aerial systems for photogrammetry and remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Song, G.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Bilateral teleoperation of an unmanned aerial vehicle for forest fire detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation—ICIA 2017, Macao, China, 18–20 July 2017; pp. 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, L.; Caballero, F.; Martínez-de dios, J.R.; Maza, I.; Ollero, A. Automatic Forest Fire Monitoring and Measurement using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles. In Proceedings of the VI International Conference on Forest Fire Research, Coimbra, Portugal, 15–18 November 2010; p. 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajares, G. Overview and Current Status of Remote Sensing Applications Based on Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2015, 81, 281–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pádua, L.; Vanko, J.; Hruška, J.; Adão, T.; Sousa, J.J.; Peres, E.; Morais, R. UAS, sensors, and data processing in agroforestry: A review towards practical applications. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2017, 38, 2349–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrides, P.; Kolios, P.; Kyrkou, C. Smart Cities in the Mediterranean; Progress in IS; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetin, A.E.; Dimitropoulos, K.; Gouverneur, B.; Grammalidis, N.; Günay, O.; Habiboǧlu, Y.H.; Töreyin, B.U.; Verstockt, S. Video fire detection–Review. Digit. Signal Process. 2013, 23, 1827–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.; Kim, D.Y.; Kwok, E.; Ryan, M.; Tan, E.; Gamadia, R. Cloud computed machine learning based real-time litter detection using micro-uav surveillance. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE MIT Undergraduate Research Technology Conference (URTC), Cambridge, MA, USA, 5–7 October 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- WEI, X.; WU, S.; WANG, Y. Forest fire smoke detection model based on deep convolution long short-term memory network. J. Comput. Appl. 2019, 39, 2883. [Google Scholar]
- K Mohammed, R. A real-time forest fire and smoke detection system using deep learning. Int. J. Nonlinear Anal. Appl. 2022, 13, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar]
- Park, M.; Jeon, Y.; Bak, J.; Park, S. Forest-fire response system using deep-learning-based approaches with CCTV images and weather data. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 66061–66071. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, M.; Fu, Y.; Ding, Y. A Forest Fire Recognition Method Using UAV Images Based on Transfer Learning. Forests 2022, 13, 975. [Google Scholar]
- Vani, K. Deep learning based forest fire classification and detection in satellite images. In Proceedings of the 2019 11th International Conference on Advanced Computing (ICoAC), Chennai, India, 18–20 December 2019; pp. 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ghali, R.; Akhloufi, M.A.; Mseddi, W.S. Deep learning and transformer approaches for UAV-based wildfire detection and segmentation. Sensors 2022, 22, 1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhan, J.; Zhou, G.; Chen, A.; Cai, W.; Guo, K.; Hu, Y.; Li, L. Fast forest fire smoke detection using MVMNet. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2022, 241, 108219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Khan, A. FFireNet: Deep Learning Based Forest Fire Classification and Detection in Smart Cities. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yandouzi, M.; Grari, M.; Idrissi, I.; Moussaoui, O.; Azizi, M.; Ghoumid, K.; Elmiad, A.K. Review on forest fires detection and prediction using deep learning and drones. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2022, 2, 4565–4576. [Google Scholar]
- Akay, M.; Du, Y.; Sershen, C.L.; Wu, M.; Chen, T.Y.; Assassi, S.; Mohan, C.; Akay, Y.M. Deep learning classification of systemic sclerosis skin using the MobileNetV2 model. IEEE Open J. Eng. Med. Biol. 2021, 2, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahi, T.B.; Sitaula, C.; Neupane, A.; Guo, W. Fruit classification using attention-based MobileNetV2 for industrial applications. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0264586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Chaware, A. Transfer learning with fine-tuned MobileNetV2 for diabetic retinopathy. In Proceedings of the 2020 international conference for emerging technology (INCET), Belgaum, India, 5–7 June 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Nambur, A.; Sankalp Saxena, M.S.S.; Natarajan, M.G. Fire and Non Fire Image Dataset. 2022. Available online: hhttps://kaggle.com/datasets/f7517a19d918cae42ac1222937d07096179e663d7b8ed0a4c66deae33073b21d (accessed on 9 January 2023).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).