Camouflaged Insect Segmentation Using a Progressive Refinement Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
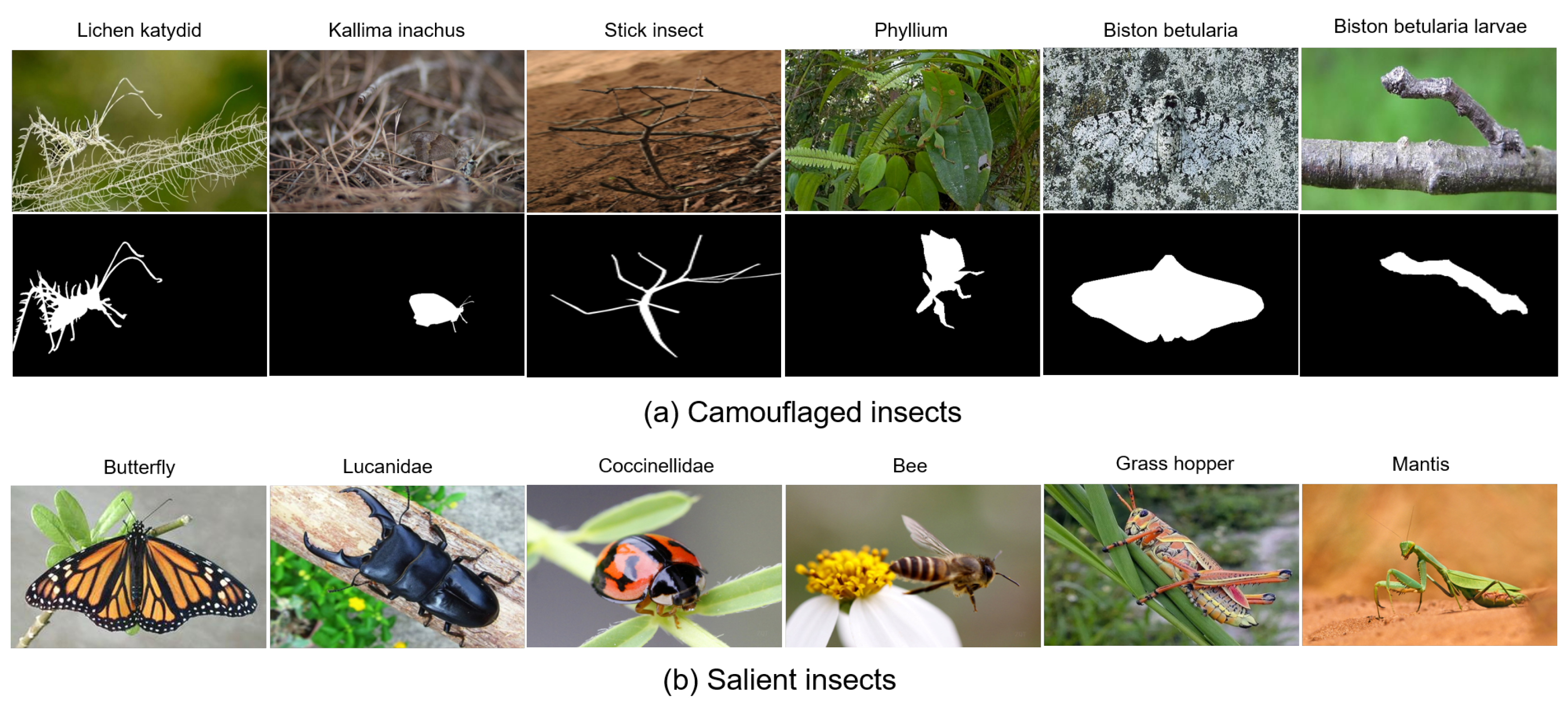
2. Dataset
3. Method
3.1. Asymmetric Receptive Field
3.2. Self-Refinement Module
3.3. Reverse Guidance Module
3.4. Implementation and Evaluation
4. Results
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
4.2. Comparisons with State-of-the-Art Detection Methods
4.3. Effectiveness Verification of Each Module
4.4. Generalization Verification
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Valan, M.; Makonyi, K.; Maki, A.; Vondráček, D.; Ronquist, F. Automated Taxonomic Identification of Insects with Expert-Level Accuracy Using Effective Feature Transfer from Convolutional Networks. Syst. Biol. 2019, 68, 876–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, M.; Merilaita, S. Animal camouflage: Current issues and new perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N. Context-aware Cross-level Fusion Network for Camouflaged Object Detection. In Proceedings of the Thirtieth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 19–27 August 2021; pp. 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mele, K. Insect Soup Challenge: Segmentation, Counting, and Simple Classification. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 1–8 December 2013; pp. 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyi, M.; Yimin, C.; Qiming, L.; Chen, H.; Sheng, X. Region Growing by Exemplar-Based Hand Segmentation under Complex Backgrounds. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Technol. 2012, 4, 432–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, X. Total Bregman divergencebased fuzzy local information Cmeans clustering for robust image segmentation. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 94, 106468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kong, F.; Wu, J.; Han, S.; Zhai, Z. Automatic image segmentation method for cotton leaves with disease under natural environment. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 1800–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shajahan, S.; Sivarajan, S.; Maharlooei, M.; Bajwa, S.; Harmon, J.; Nowatzki, J.; Igathinathane, C. Identification and Counting of Soybean Aphids from Digital Images Using Shape Classification. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2017, 60, 1467–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Li, C. Region-based color image segmentation of fishes with complex background in water. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Sci. Autom. Eng. 2011, 1, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Pan, S. A Cognitive Vision Method for Insect Pest Image Segmentation. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2018, 51, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, X. Deep learning techniques for automatic butterfly segmentation in ecological images. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Ji, G.; Zhou, T.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. PraNet: Parallel Reverse Attention Network for Polyp Segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, B. A computer vision for animal ecology. J. Anim. Ecol. 2017, 87, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Liu, C.; Qin, Z.; Luo, Z.; Wang, J. Structured Knowledge Distillation for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Tian, H.; Li, Y.; Bao, Y.; Fang, Z.; Lu, H. Dual Attention Network for Scene Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3141–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Xie, L.; Huang, G.; Du, D.; Wang, X. Attention-Guided Unified Network for Panoptic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7019–7028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Deng, Z.; Zhou, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Adaptive Pyramid Context Network for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7511–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Li, J.; Wang, S.; Tao, R.; Shen, J. MATNet: Motion-Attentive Transition Network for Zero-Shot Video Object Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2020, 29, 8326–8338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelhamer, E.; Long, J.; Darrell, T. Fully Convolutional Networks for Semantic Segmentation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 39, 640–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 833–851. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, J.; Qi, H.; Xiong, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y. Deformable Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 764–773. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. CCNet: Criss-Cross Attention for Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Cui, Y.; Tan, W.; Chen, Y. SG-Net: Spatial Granularity Network for One-Stage Video Instance Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual Conference, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 9811–9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, T.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Deep Hierarchical Semantic Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, W.; Konukoglu, E.; Van Goo, L. Rethinking Semantic Segmentation: A Prototype View. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2572–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthill, I.C. Camouflage. J. Zool. 2019, 308, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merilaita, S.; Stevens, M. Crypsis through background matching. In Animal Camouflage: Mechanisms and Function; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A. Camouflaged Object Detection and Tracking: A Survey. Int. J. Image Graph. 2020, 20, 2050028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.; Ruxton, G.D. The key role of behaviour in animal camouflage. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2019, 94, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merilaita, S.; Scott-Samuel, N.; Cuthill, I. How camouflage works. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Théry, M.; Gomez, D. Chapter 7—Insect Colours and Visual Appearance in the Eyes of Their Predators. In Advances in Insect Physiology: Insect Integument and Colour; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; Volume 38, pp. 267–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthill, I.C.; Allen, W.L.; Arbuckle, K.; Caspers, B.; Chaplin, G.; Hauber, M.E.; Hill, G.E.; Jablonski, N.G.; Jiggins, C.D.; Kelber, A.; et al. The biology of color. Science 2017, 357, eaan0221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuthill, I.C.; Matchette, S.R.; Scott-Samuel, N.E. Camouflage in a dynamic world. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2019, 30, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.P.; Ji, G.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Shao, L. Concealed Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 44, 6024–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.; Nguyen, T.V.; Nie, Z.; Tran, M.T.; Sugimoto, A. Anabranch network for camouflaged object segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 184, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubel, D.H.; Wiesel, T.N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat’s visual cortex. J. Physiol. 1962, 160, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Torr, P. Res2Net: A New Multi-Scale Backbone Architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y. Receptive Field Block Net for Accurate and Fast Object Detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.; Hinton, G.E. Rectified Linear Units Improve Restricted Boltzmann Machines. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, Haifa, Israel, 21–24 June 2010; pp. 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wu, X. Pyramid Feature Attention Network for Saliency Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3080–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, D.; Ji, G.; Sun, G.; Cheng, M.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Camouflaged Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2774–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, F.-e.; Lu, J. Coarse-to-fine: A dual-view attention network for click-through rate prediction. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2021, 216, 106767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.; Stevens, M.; Moon, J.; Lee, S.; Jablonski, P.G. Camouflage through behavior in moths: The role of background matching and disruptive coloration. Behav. Ecol. 2014, 26, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.J. Does disruptive camouflage conceal edges and features? Curr. Zool. 2015, 61, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, R.J.; Hassall, C.; Herdman, C.M.; Godin, J.G.J.; Sherratt, T.N. Disruptive camouflage impairs object recognition. Biol. Lett. 2013, 9, 20130501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Shuhui Wang, Q.H. F3Net: Fusion, Feedback and Focus for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Honolulu, HI, USA, 27 January–1 February 2019; pp. 12321–12328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornung, A.; Pritch, Y.; Krahenbuhl, P.; Perazzi, F. Saliency filters: Contrast-based filtering for salient region detection. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Gong, C.; Cao, Y.; Ren, B.; Cheng, M.M.; Borji, A. Enhanced-alignment Measure for Binary Foreground Map Evaluation. In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; pp. 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Cheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Borji, A. Structure-Measure: A New Way to Evaluate Foreground Maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4548–4557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolin, R.; ZelnikManor, L.; Tal, A. How to Evaluate Foreground Maps? In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Gao, C.; Dehghan, M.; Jagersand, M. BASNet: Boundary-Aware Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7471–7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Ji, G.; Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Wei, X.; Fan, D. Camouflaged Object Segmentation With Distraction Mining. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual Conference, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8772–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.; Tai, Y.; Kim, J. Deep Saliency with Encoded Low Level Distance Map and High Level Features. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Fan, D.; Cao, Y.; Yang, J.; Cheng, M. EGNet: Edge Guidance Network for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 8778–8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, T.; Qi, J.; Lu, H.; Wang, G. Progressive Attention Guided Recurrent Network for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shen, J.; Cheng, M.M.; Shao, L. An Iterative and Cooperative Top-Down and Bottom-Up Inference Network for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 5961–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.U.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All you Need. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Tan, X.; Wang, B.; Hu, X. Reverse Attention for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Han, J.; Yang, M. PiCANet: Learning Pixel-Wise Contextual Attention for Saliency Detection. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3089–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, C.; Tian, Y. Selectivity or Invariance: Boundary-Aware Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3798–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3213–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russakovsky, O.; Deng, J.; Su, H.; Krause, J.; Satheesh, S.; Ma, S.; Huang, Z.; Karpathy, A.; Khosla, A.; Bernstein, M.; et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2015, 115, 211–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannes, A.; Picon, A.; Alvarez-Gila, A.; Echazarra, J.; Rodriguez-Vaamonde, S.; Navajas, A.D.; Ortiz-Barredo, A. Automatic plant disease diagnosis using mobile capture devices, applied on a wheat use case. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2017, 138, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhold, G.; Ollmann, T.; Bulò, S.R.; Kontschieder, P. The Mapillary Vistas Dataset for Semantic Understanding of Street Scenes. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4990–4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kisantal, M.; Wojna, Z.; Murawski, J.; Naruniec, J.; Cho, K. Augmentation for small object detection. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Advances in Computing and Information Technology, Sydney, Australia, 21–22 December 2019; pp. 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liang, X.; Wei, Y.; Xu, T.; Feng, J.; Yan, S. Perceptual Generative Adversarial Networks for Small Object Detection. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1951–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talas, L.; Fennell, J.; Kjernsmo, K.; Cuthill, I.; Scott-Samuel, N.; Baddeley, R. CamoGAN: Evolving optimum camouflage with Generative Adversarial Networks. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2020, 11, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Wang, X.; Shen, C.; Cheng, B.; Shen, H.; Xia, H. End-to-End Video Instance Segmentation with Transformers. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Virtual Conference, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8737–8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Andriluka, M.; Andres, B.; Schiele, B. Multiple People Tracking by Lifted Multicut and Person Re-identification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3701–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xiao, T.; Jiang, Y.; Shao, S.; Sun, J.; Shen, C. Repulsion Loss: Detecting Pedestrians in a Crowd. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7774–7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Liang, J.; Li, S.; Zang, B.; Liu, C.H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, D. Causality Inspired Representation Learning for Domain Generalization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 8046–8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| Multiple Objects | Image contains at least two insects, e.g., Figure 3b |
| Small object | Ratio between insect area and whole image area is lower than 0.1., e.g., Figure 3e |
| Big Object | Ratio between insect area and whole image area is higher than 0.5., e.g., Figure 3d |
| Complex shape | Insect has thin parts and holes. e.g., Figure 3g |
| Indefinable boundaries | Insect has a similar color appearance, e.g., Figure 3c |
| Occlusion | Insect is partially occluded, e.g., Figure 3j |
| Out-of-View | Insect is clipped by image boundaries, e.g., Figure 3h |
| Method | Year | Field | Backbone | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BASNet [54] | 2019 | Camouflage | ResNet-50 | 0.068 | 0.770 | 0.692 | 0.483 |
| F3Net [49] | 2020 | Salient | ResNet-50 | 0.113 | 0.638 | 0.641 | 0.362 |
| SINet [44] | 2020 | Camouflage | ResNet-50 | 0.050 | 0.872 | 0.803 | 0.567 |
| PraNet [12] | 2020 | Camouflage | Res2Net-50 | 0.040 | 0.857 | 0.801 | 0.662 |
| SINet-V2 [36] | 2022 | Camouflage | Res2Net-50 | 0.033 | 0.889 | 0.836 | 0.719 |
| PFNet [55] | 2021 | Camouflage | ResNet-50 | 0.033 | 0.893 | 0.83 | 0.715 |
| C2FNet [3] | 2021 | Camouflage | Res2Net-50 | 0.035 | 0.887 | 0.833 | 0.712 |
| PRNet | 2021 | Camouflage | Res2Net-50 | 0.032 | 0.897 | 0.836 | 0.720 |
| No. | Module | MAE↓ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARF | SRM | RG | |||||
| 1 | √ | √ | 0.033 | 0.89 | 0.834 | 0.715 | |
| 2 | √ | √ | 0.040 | 0.897 | 0.831 | 0.657 | |
| 3 | √ | √ | 0.161 | 0.830 | 0.672 | 0.326 | |
| 4 | √ | √ | √ | 0.032 | 0.897 | 0.836 | 0.720 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Hong, M.; Hu, X.; Li, X.; Huang, S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, F. Camouflaged Insect Segmentation Using a Progressive Refinement Network. Electronics 2023, 12, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040804
Wang J, Hong M, Hu X, Li X, Huang S, Wang R, Zhang F. Camouflaged Insect Segmentation Using a Progressive Refinement Network. Electronics. 2023; 12(4):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040804
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jing, Minglin Hong, Xia Hu, Xiaolin Li, Shiguo Huang, Rong Wang, and Feiping Zhang. 2023. "Camouflaged Insect Segmentation Using a Progressive Refinement Network" Electronics 12, no. 4: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040804
APA StyleWang, J., Hong, M., Hu, X., Li, X., Huang, S., Wang, R., & Zhang, F. (2023). Camouflaged Insect Segmentation Using a Progressive Refinement Network. Electronics, 12(4), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040804








