Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control with Compensated Current Controller Dynamics on Active Magnetic Bearings with Large Air Gap
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Modeling
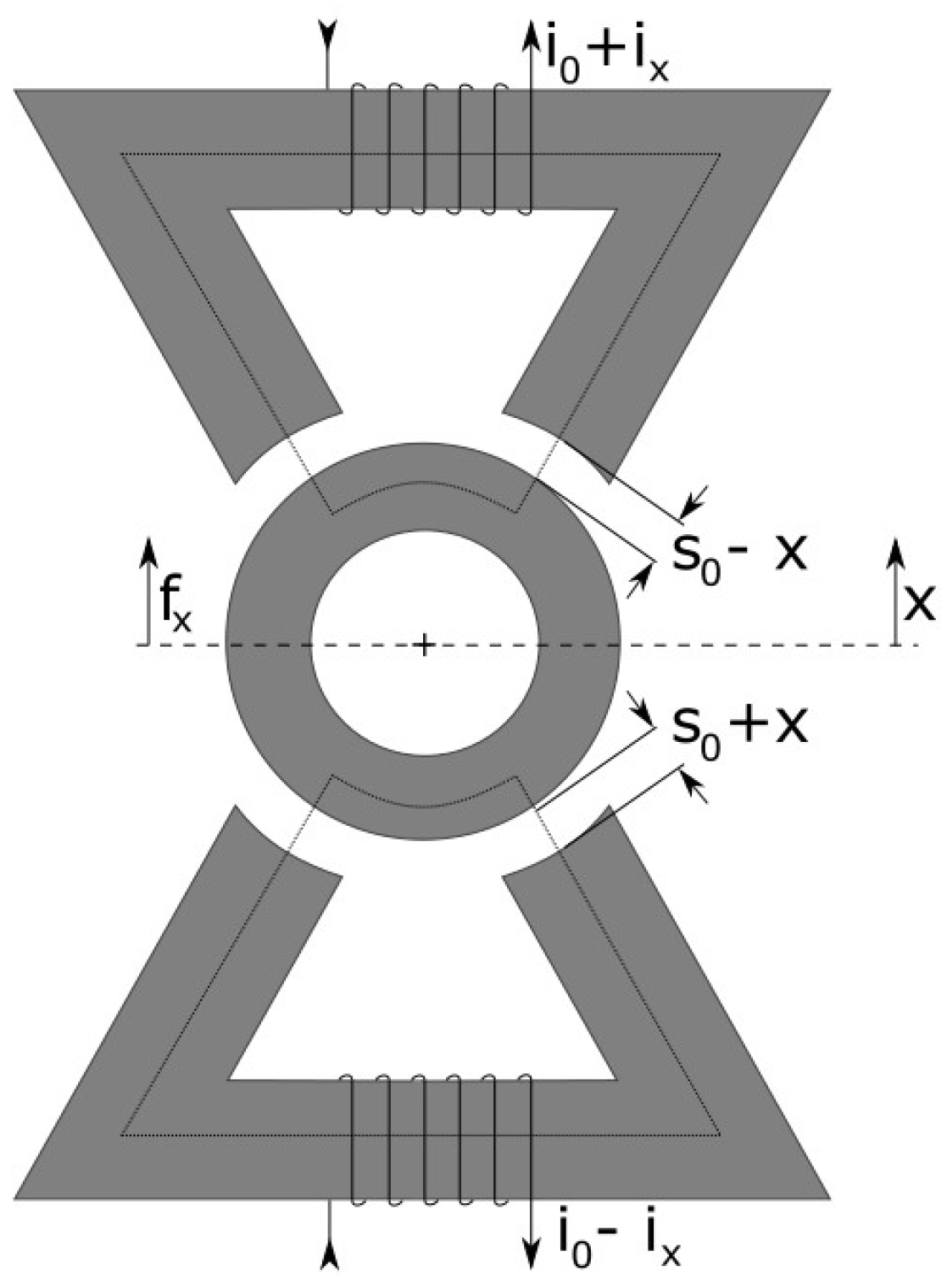
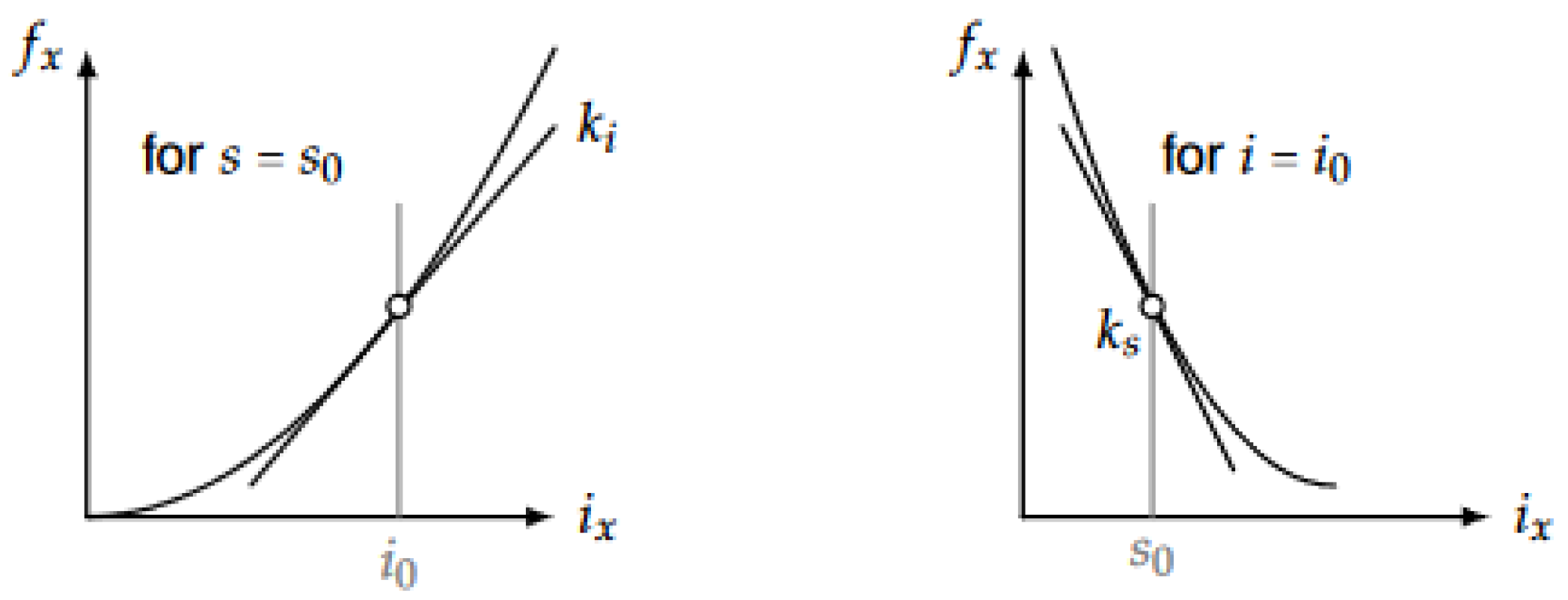
2.1. Modelling of AMBs
2.2. Integrating the Current Controller Dynamics
- PI Controller: with the controller gain and the time constant tuned according to the modulus optimum criterion.
- H-bridge Voltage Amplifier: with the time constant where is the PWM frequency of the H-bride.
- Current Sensor: with its time constant , where is the sensors sampling frequency.
- Coil: with is resistance R, inductance L, gain and its electric time constant .
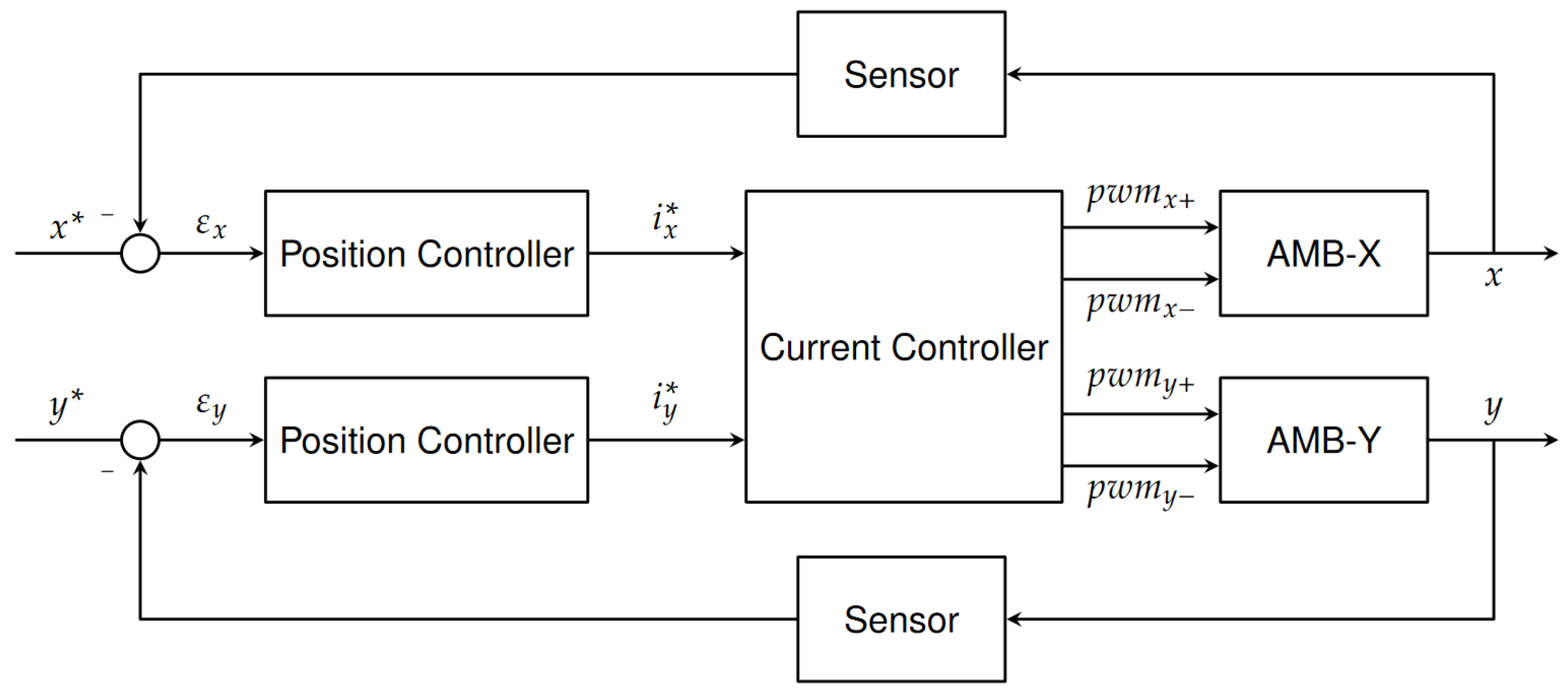
3. Controller Design
4. Results and Discussion
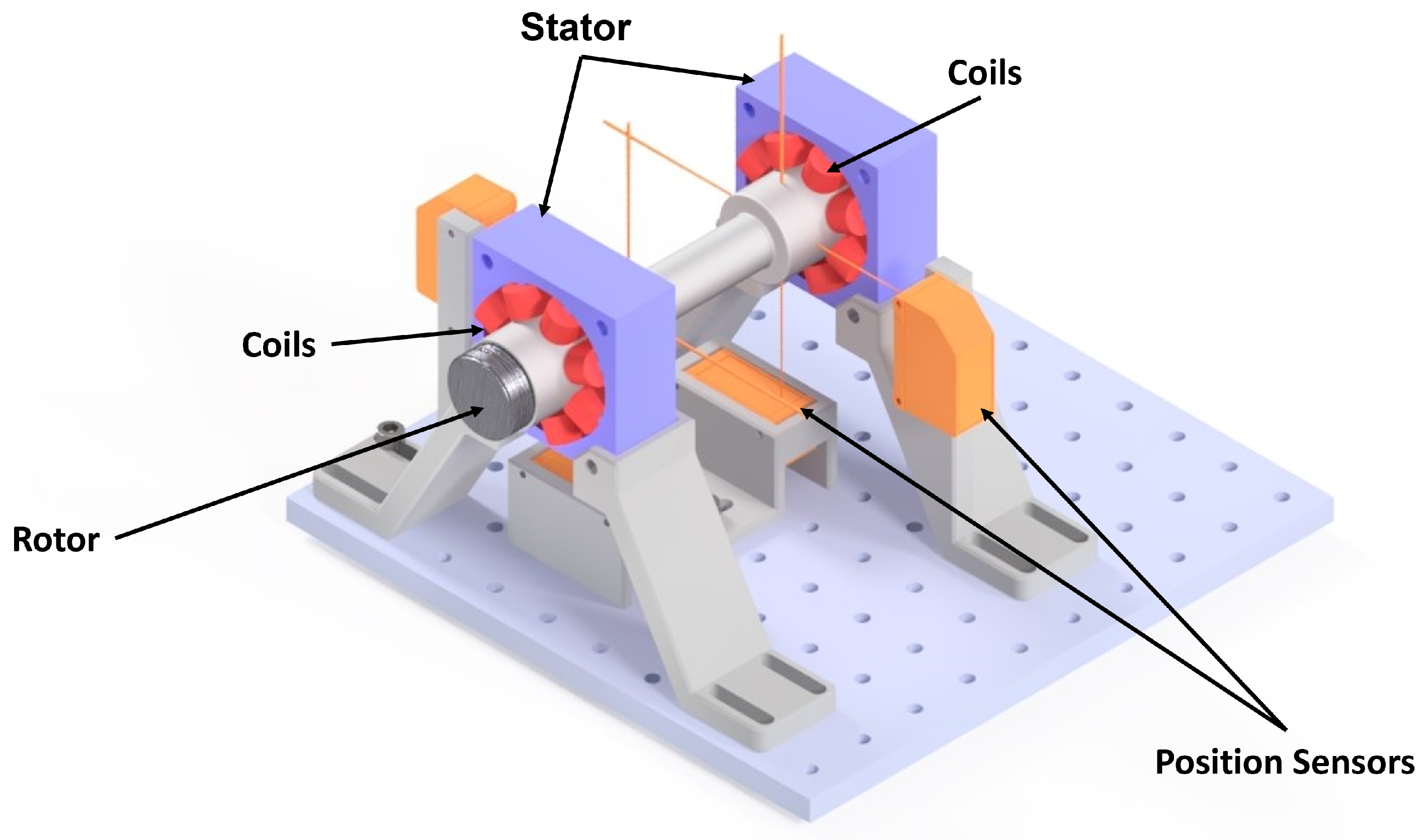
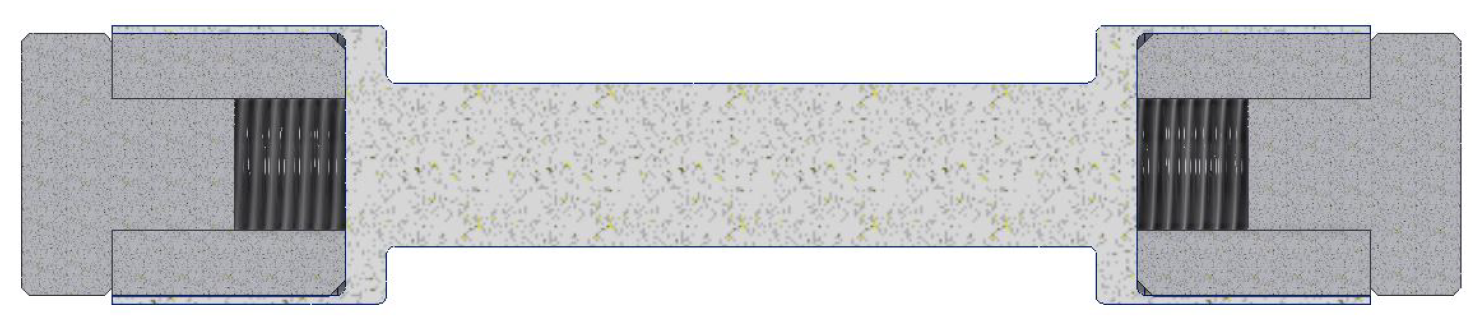
4.1. Test Bench Design
4.2. Experiment Current Controlled
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| reference displacement in x-direction | |
| x | displacement in x-direction |
| initial rotor displacement in x-direction | |
| reference displacement in y-direction | |
| y | displacement in y-direction |
| initial rotor displacement in y-direction | |
| control error | |
| u | controller output |
| i | current |
| bias current | |
| f | force |
| permeability of vacuum | |
| permeability of iron | |
| n | number of windings in a coil |
| cross-section area | |
| angle between the legs of the AMB | |
| length of the iron | |
| s | magnetic air gap |
| nominal magnetic air gap | |
| magnetic flux | |
| field energy | |
| volume in the air gap | |
| magnetic flux density in the air gap | |
| magnetic field in the air gap | |
| k | machine constant |
| force/current factor | |
| force/displacement factor | |
| v | velocity |
| m | mass of the rotor |
| L | inductance |
| R | resistance |
| time constant | |
| state vector | |
| sliding variable | |
| controller gain | |
| c | controller gain |
| b | controller gain |
| * | control reference |
| x | in x direction |
| y | in x direction |
| + | in positive direction |
| − | in negative direction |
| R | state space description in controllability form |
Appendix B
| Parameter | Symbol | Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| number of poles | 8 | - | |
| angle between pole and axis | rad | ||
| coil windings | n | 96 | - |
| maximum voltage | 24 | V | |
| maximum current | 5 | A | |
| bias current | A | ||
| sampling frequency position sensor | 2 | kHz | |
| sampling frequency current sensor | 10 | kHz | |
| PWM frequency | 20 | kHz | |
| controller gain | C | - | |
| sliding surface gains | S | - |
References
- Maslen, E.H.; Schweitzer, G. (Eds.) Magnetic Bearings; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earnshaw, S. On the nature of the molecular forces which regulate the constitution of the luminferous ether. Trans. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1842, 7, 97. [Google Scholar]
- Benjak, O.; Gerling, D. Review of position estimation methods for IPMSM drives without a position sensor part II: Adaptive methods. In Proceedings of the XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines—ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjak, O.; Gerling, D. Review of Position Estimation Methods for PMSM Drives Without a Position Sensor, Part III: Methods based on Saliency and Signal Injection. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems, Incheon, Republic of Korea, 10–13 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Benjak, O.; Gerling, D. Review of position estimation methods for IPMSM drives without a position sensor part I: Nonadaptive methods. In Proceedings of the The XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines—ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strothmann, R. Fremderregte Elektrische Maschine. EP Patent EP1005716B1, 14 November 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mantala, C. Sensorless Control of Brushless Permanent Magnet Motors. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Bolton, Bolton, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Schuhmacher, K.; Grasso, E.; Nienhaus, M. Improved rotor position determination for a sensorless star-connected PMSM drive using Direct Flux Control. J. Eng. 2019, 2019, 3749–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, T. Geberlose Rotorlagebestimmung in Elektrischen Maschinen; Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden: Wiesbaden, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, E.; Mandriota, R.; König, N.; Nienhaus, M. Analysis and Exploitation of the Star-Point Voltage of Synchronous Machines for Sensorless Operation. Energies 2019, 12, 4729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, E. Direct Flux Control—A Sensorless Technique for Star-Connected Synchronous Machines An Analytic Approach; Shaker Verlag: Düren, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Brasse, R.; Vennemann, J.; König, N.; Grasso, E.; Nienhaus, M. Design and Implementation of a Driving Strategy for Star-Connected Active Magnetic Bearings with Application to Sensorless Driving. Engergies 2023, 16, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, G. A Review of Active Magnetic Bearing Control Technology. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC), Nanchang, China, 3–5 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 2888–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, L. Fuzzy logic. Computer 1988, 21, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psonis, T.; Mitronikas, E.; Nikolakopoulos, P. Comparison of PID and Fuzzy PID Controller for a Linearised Magnetic Bearing. Tribol. Ind. 2017, 39, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Lin, F.J. Decentralized PID neural network control for five degree-of-freedom active magneticbearing. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2013, 26, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Agashe, S. Review of fractional PID controller. Mechatronics 2016, 38, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shata, A.M.A.H.; Hamdy, R.A.; Abdelkhalik, A.S.; El-Arabawy, I. A fractional order PID control strategy in active magnetic bearing systems. Alex. Eng. J. 2018, 57, 3985–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, J. Flatness-Based Control An Introduction; Shaker Verlag: Düren, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Lévine, J.; Lottin, J.; Ponsart, J.C. Control of Magnetic Bearings: Flatness with Constraints. IFAC Proc. Vol. 1996, 29, 2798–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Löwis, J.; Rudolph, J.; Thiele, J.; Urban, F. Flatness-Based Trajectory Tracking Control of a Rotating Shaft. In Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Magnetic Bearings, Zürich, Switzerland, 23–25 August 2000; pp. 299–304. [Google Scholar]
- Utkin, V. Variable structure systems with sliding modes. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1977, 22, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, P. Design and Analysis of Second-Order Sliding Mode Controller for Active Magnetic Bearing. Energies 2020, 13, 5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.S.; Lyou, J.; Lee, J.K. Sliding mode control for an active magnetic bearing system subject to base motion. Mechatronics 2010, 20, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Bandyopadhyay, B. (Eds.) Emerging Trends in Sliding Mode Control: Theory and Application; Springer: Singapore, 2021; Volume 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Amrr, S.M.; Saidi, A.S.; Banerjee, A.; Nabi, M. Finite-Time Adaptive Higher-Order SMC for the Nonlinear Five DOF Active Magnetic Bearing System. Electronics 2021, 10, 1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Amrr, S.M.; Nabi, M. Adaptive Second Order Sliding Mode Control for the Regulation of Active Magnetic Bearing. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2020, 53, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrr, S.M.; Alturki, A. Robust Control Design for an Active Magnetic Bearing System Using Advanced Adaptive SMC Technique. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 155662–155672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schweitzer, G.; Traxler, A.; Bleuler, H. Magnetlager: Grundlagen, Eigenschaften und Anwendungen berüHrungsfreier, Elektromagnetischer Lager; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiba, A.; Fukao, T.; Ichikawa, O.; Oshima, M.; Takemoto, M.; Dorrell, D. (Eds.) Magnetic Bearings and Bearingless Drives; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Newnes: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lunze, J. Regelungstechnik: Systemtheoretische Grundlagen, Analyse und Entwurf Einschleifiger Regelungen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lunze, J. Regelungstechnik 2: Mehrgrößensysteme, Digitale Regelung; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, D. Elektrische Antriebe—Regelung von Antriebssystemen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Shtessel, Y.; Edwards, C.; Fridman, L.; Levant, A. Sliding Mode Control and Observation; Control Engineering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, V.; Poznyak, A.; Orlov, Y.V.; Polyakov, A. Road Map for Sliding Mode Control Design; SpringerBriefs in Mathematics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





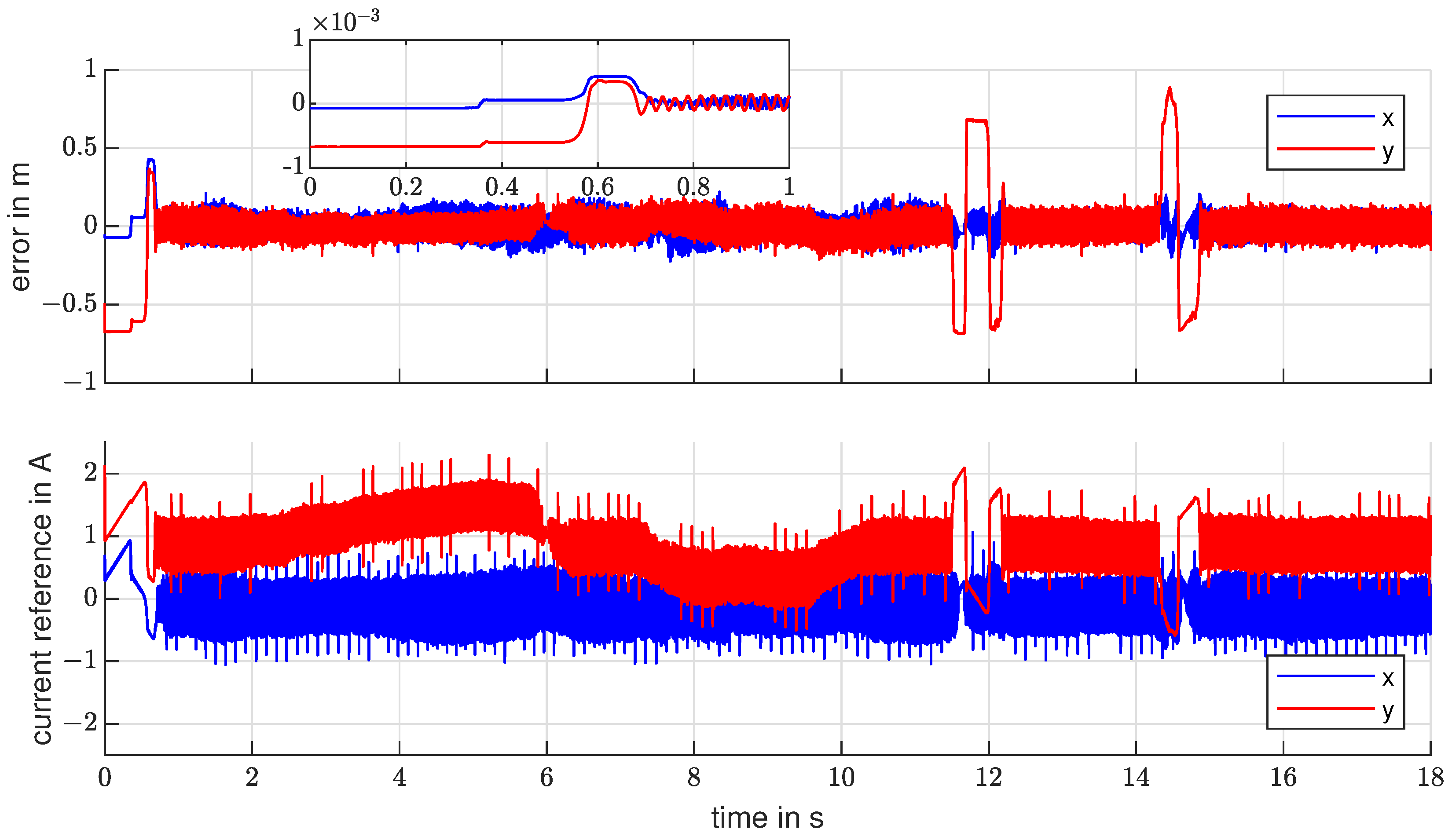
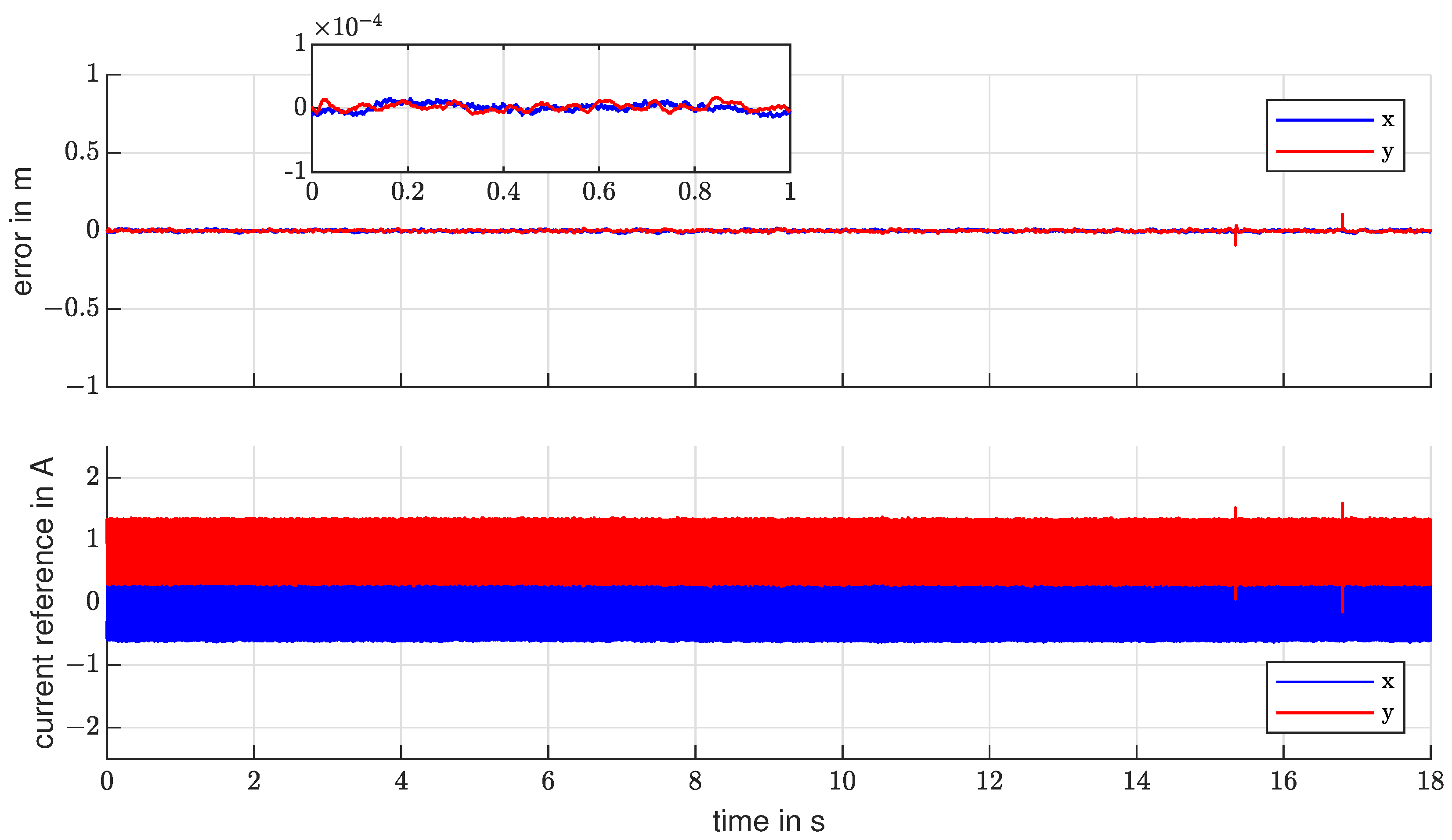

| Axis | Mean Error in % | Max Error in % | Max Error in mm | Settling Time in s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 0.9 | 21.18 | 0.21 | 0.7 |
| y | 0.44 | 15.42 | 0.15 | 0.7 |
| Axis | Mean Error in % | Max Error in % | Max Error in mm | Settling Time in s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 0.007 | 1.86 | 0.018 | 0.6 |
| y | 0.03 | 1.86 | 0.018 | 0.6 |
| Axis | Mean Error in % | Max Error in % | Max Error in mm | Settling Time in s |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | 0.14 | 12.32 | 0.12 | 0.6 |
| y | 0.11 | 14.48 | 0.14 | 0.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vennemann, J.; Brasse, R.; König, N.; Nienhaus, M.; Grasso, E. Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control with Compensated Current Controller Dynamics on Active Magnetic Bearings with Large Air Gap. Electronics 2023, 12, 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040950
Vennemann J, Brasse R, König N, Nienhaus M, Grasso E. Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control with Compensated Current Controller Dynamics on Active Magnetic Bearings with Large Air Gap. Electronics. 2023; 12(4):950. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040950
Chicago/Turabian StyleVennemann, Jonah, Romain Brasse, Niklas König, Matthias Nienhaus, and Emanuele Grasso. 2023. "Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control with Compensated Current Controller Dynamics on Active Magnetic Bearings with Large Air Gap" Electronics 12, no. 4: 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040950
APA StyleVennemann, J., Brasse, R., König, N., Nienhaus, M., & Grasso, E. (2023). Super Twisting Sliding Mode Control with Compensated Current Controller Dynamics on Active Magnetic Bearings with Large Air Gap. Electronics, 12(4), 950. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12040950







