A Novel Fiducial Point Extraction Algorithm to Detect C and D Points from the Acceleration Photoplethysmogram (CnD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials
Database Selection
3. Detection Method
3.1. Data Preparation
3.2. Pre-Processing
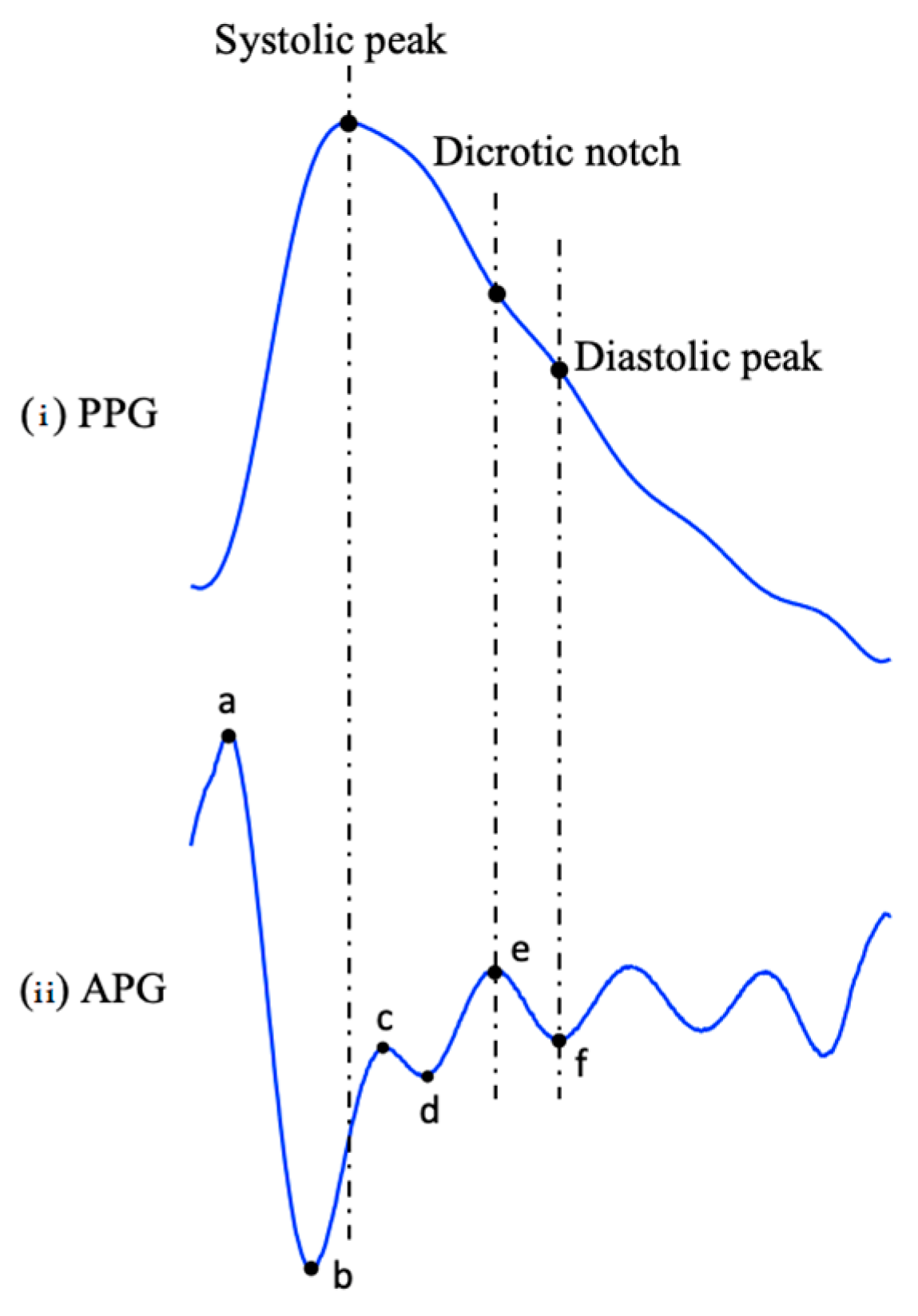
3.3. PPG Derivatives (VPG, APG, JPG)
3.4. Fiducial Points
3.5. Novel Fiducial Point Extraction Algorithm to Detect C and D Points from the Acceleration Photoplethysmogram (CnD)
4. Performance Evaluation of the CnD Algorithm
| Algorithm | N | TP | FP | FN | SN% | PPV% | Err% | Acc% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case I | 140 | 139 | 0 | 1 | 99.29 | 100 | 0.71 | 99.29 |
| Case II | 54 | 53 | 1 | 0 | 100 | 98.15 | 1.85 | 98.15 |
| Case III | 25 | 25 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | 0 | 100 |
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Allen, J. Photoplethysmography and Its Application in Clinical Physiological Measurement. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, R1-39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Goubran, R.A.; Liu, X.P. Secondary Peak Detection of PPG Signal for Continuous Cuffless Arterial Blood Pressure Measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 1431–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, W.; Raman, S.; Ansermino, J.M.; Dumont, G.A. Multiparameter Respiratory Rate Estimation from the Photoplethysmogram. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 1946–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.T.; Zabir, I.; Ahamed, S.T.; Yasar, M.T.; Shahnaz, C.; Fattah, S.A. A Time-Frequency Domain Approach of Heart Rate Estimation from Photoplethysmographic (PPG) Signal. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control 2017, 36, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, H.; Kawanaka, H.; Bhuiyan, M.S.; Oguri, K. Estimating Heart Rate Using Wrist-Type Photoplethysmography and Acceleration Sensor While Running. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBC, San Diego, CA, USA, 28 August–1 September 2012; pp. 2901–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, P.H.; Kyriaco, P.A.; Mant, J.; Marozas, V.; Chowienczyk, P.; Alastruey, J. Wearable Photoplethysmography for Cardiovascular Monitoring. Proc. IEEE Inst. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2022, 110, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Chu, Y.; Ryu, J.; Park, Y.J.; Yang, S.; Koh, S.B. Artificial Intelligence for Detection of Cardiovascular-Related Diseases from Wearable Devices: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Yonsei Med. J. 2022, 63, S93–S107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Sadhukhan, D.; Pal, S.; Mitra, M. Automated Myocardial Infarction Identification Based on Interbeat Variability Analysis of the Photoplethysmographic Data. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control 2020, 57, 101747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahri, N.; Gan, K.B.; Meswari, R.; Jaafar, M.H.; Mohd. Ali, M.A. Utilization of Second Derivative Photoplethysmographic Features for Myocardial Infarction Classification. J. Med. Eng. Technol. 2017, 41, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Liang, Y.; Ward, R. Toward Generating More Diagnostic Features from Photoplethysmogram Waveforms. Diseases 2018, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ab Hamid, H.; Nayan, N.A. Methods of Extracting Feature from Photoplethysmogram Waveform for Non-Invasive Diagnostic Applications. Int. J. Online Biomed. Eng. 2020, 16, 39–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Sadhukhan, D.; Mitra, M. An Automated Algorithm to Extract Time Plane Features from the PPG Signal and Its Derivatives for Personal Health Monitoring Application. IETE J. Res. 2019, 68, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almarshad, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Al-Ahmadi, S.; Bahammam, A.S. Diagnostic Features and Potential Applications of PPG Signal in Healthcare: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2022, 10, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Avalos, G.; Cruz-Ramos, N.A.; Alor-Hernández, G.; Sánchez-Cervantes, J.L.; Rodríguez-Mazahua, L.; Guarneros-Nolasco, L.R. Wearable Devices for Physical Monitoring of Heart: A Review. Biosensors 2022, 12, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, G.; Cooper, R.; Hosanee, M.; Welykholowa, K.; Kyriacou, P.A.; Zheng, D.; Allen, J.; Abbott, D.; Lovell, N.H.; Fletcher, R.; et al. Multi-Site Photoplethysmography Technology for Blood Pressure Assessment: Challenges and Recommendations. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, E.; Orini, M.; Bailón, R.; Vergara, J.M.; Mainardi, L.; Laguna, P. Photoplethysmography Pulse Rate Variability as a Surrogate Measurement of Heart Rate Variability during Non-Stationary Conditions. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 1271–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, H.J.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, B.; Park, K.S. Enhancing the Estimation of Blood Pressure Using Pulse Arrival Time and Two Confounding Factors. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takada, H.; Washino, K.; Harreil, J.S.; Iwata, H. Acceleration Plethysmography to Evaluate Aging Effect in Cardiovascular System Using New Criteria of Four Wave Patterns. Med. Prog. Technol. 1996, 21, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suboh, M.Z.; Jaafar, R.; Nayan, N.A.; Harun, N.H.; Mohamad, M.S.F. Analysis on Four Derivative Waveforms of Photoplethysmogram (PPG) for Fiducial Point Detection. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 920946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, A.; Ryu, K. Feature Selection Method for Estimating Systolic Blood Pressure Using the Taguchi Method. IEEE Trans. Industr. Inform. 2014, 10, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S. Biomedical Signal Analysis for Connected Healthcare; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 1–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok Ahn, J. New Aging Index Using Signal Features of Both Photoplethysmograms and Acceleration Plethysmograms. Healthc. Inform. Res. 2017, 23, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendi, M.; Norton, I.; Brearley, M.; Abbott, D.; Schuurmans, D. Systolic Peak Detection in Acceleration Photoplethysmograms Measured from Emergency Responders in Tropical Conditions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillante, D.G.; O’sullivan, A.J.; Howes, L.G. Arterial Stiffness Indices in Healthy Volunteers Using Non-Invasive Digital Photoplethysmography. Blood Press. 2008, 17, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elgendi, M.; Fletcher, R.; Liang, Y.; Howard, N.; Lovell, N.H.; Abbott, D.; Lim, K.; Ward, R. The Use of Photoplethysmography for Assessing Hypertension. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhaddi, F.; Kazemi, K.; Azimi, I.; Cao, R.; Niela-Vilén, H.; Axelin, A.; Liljeberg, P.; Rahmani, A.M. A Comprehensive Accuracy Assessment of Samsung Smartwatch Heart Rate and Heart Rate Variability. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.N.; Dong, M.C.; Vai, M.I. On an Automatic Delineator for Arterial Blood Pressure Waveforms. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control 2010, 5, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Liu, G.; Elgendi, M. A New, Short-Recorded Photoplethysmogram Dataset for Blood Pressure Monitoring in China. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Görges, M.; Jenkins, S.A. University of Queensland Vital Signs Dataset: Development of an Accessible Repository of Anesthesia Patient Monitoring Data for Research. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 114, 584–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Villarroel, M.; Reisner, A.T.; Clifford, G.; Lehman, L.W.; Moody, G.; Heldt, T.; Kyaw, T.H.; Moody, B.; Mark, R.G. Multiparameter Intelligent Monitoring in Intensive Care II: A Public-Access Intensive Care Unit Database. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 39, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlen, W.; Kobayashi, K.; Ansermino, J.M.; Dumont, G.A. Photoplethysmogram Signal Quality Estimation Using Repeated Gaussian Filters and Cross-Correlation. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 1617–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Elgendi, M.; Chen, Z.; Ward, R. Analysis: An Optimal Filter for Short Photoplethysmogram Signals. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Chen, D.; Yang, J. Pulse Rate Estimation from Forehead Photoplethysmograph Signal Using RLS Adaptive Filtering with Dynamical Reference Signal. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control 2022, 71 Part B, 103189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Qing, K.; Yang, D.; Hong, K.S. Real-Time Motion Artifact Removal Using a Dual-Stage Median Filter. Biomed. Signal. Process. Control 2022, 72 Part A, 103301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Liu, H.; Wang, W. A Comb Filter Based Signal Processing Method to Effectively Reduce Motion Artifacts from Photoplethysmographic Signals. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 2159–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Fang, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, T.; Xia, S. Cuff-Less Blood Pressure Measurement Using Pulse Arrival Time and a Kalman Filter. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2017, 27, 024002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, P.H.; Celka, P.; Farukh, B.; Chowienczyk, P.; Alastruey, J. Assessing Mental Stress from the Photoplethysmogram: A Numerical Study. Physiol. Meas. 2018, 39, 054001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghufran, K.S.; Jufen, Z.; Fei, C.; Dingchang, Z. Blood Pressure Estimation Using Photoplethysmography Only: Comparison between Different Machine Learning Approaches. J. Healthc. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1548647. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, S.; Debnath, B.; Biswas, S.; Al-Hossain, M.J.; Anika, A.; Khaled, S.Z.N. Estimation of Blood Glucose from PPG Signal Using Convolutional Neural Network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Engineering, Computer and Information Technology for Health (BECITHCON), Dhaka, Bangladesh, 28–30 November 2019. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdullah, S.; Hafid, A.; Folke, M.; Lindén, M.; Kristoffersson, A. A Novel Fiducial Point Extraction Algorithm to Detect C and D Points from the Acceleration Photoplethysmogram (CnD). Electronics 2023, 12, 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051174
Abdullah S, Hafid A, Folke M, Lindén M, Kristoffersson A. A Novel Fiducial Point Extraction Algorithm to Detect C and D Points from the Acceleration Photoplethysmogram (CnD). Electronics. 2023; 12(5):1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051174
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdullah, Saad, Abdelakram Hafid, Mia Folke, Maria Lindén, and Annica Kristoffersson. 2023. "A Novel Fiducial Point Extraction Algorithm to Detect C and D Points from the Acceleration Photoplethysmogram (CnD)" Electronics 12, no. 5: 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051174
APA StyleAbdullah, S., Hafid, A., Folke, M., Lindén, M., & Kristoffersson, A. (2023). A Novel Fiducial Point Extraction Algorithm to Detect C and D Points from the Acceleration Photoplethysmogram (CnD). Electronics, 12(5), 1174. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12051174









