Influence of the Cast Iron Frame on the Distribution of the Magnetic Field in the Stator Yoke and Additional Power Losses in the Induction Motor
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Objects for Investigation
3. Field-Circuit Analysis
4. Analytical Calculation
ELIC = −0.233 Bkd + 1.614 for Bkd ≥ 0.8 T,
HLIC = 0.684 Bkd + 0.961 for the entire Bkd range.
5. Calculation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olivo, M.; Bortolozzi, M.; Tessarolo, A.; Luise, F. A New Method for the Accurate Prediction of On-Load Power Factor in Two-Pole Induction Motors Considering Shaft Eddy Currents. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2020, 35, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinlein, M.; Hubert, T.; Kremser, A.; Bauer, T. Magnetic flux distribution between rotor and shaft in two-pole induction machines with axial cooling vents. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE 5th International Conference on Power Engineering, Energy and Electrical Drives (POWERENG), Riga, Latvia, 11–13 May 2015; pp. 485–490. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, W.; Huang, J.; Qu, R.; Kang, M.; Yang, J. Nonsinusoidal Power Supply Analysis for Concentrated-Full-Pitch-Winding Multiphase Induction Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, B.; Piao, R.-h.; Lu, W. Time-stepping finite element analysis on iron loss distribution of cage induction motors. In Proceedings of the 2014 17th International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems (ICEMS), Hangzhou, China, 22–25 October 2014; pp. 2043–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Document 32021R0341. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2021/341/oj (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Cao, W. Comparison of IEEE 112 and New IEC Standard 60034-2-1. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 24, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEC/EN, 60034-30-1; Rotating Electrical Machines—Part 30-1: Efficiency Classes of Line Operated AC Motors (IE Code). ABB: Zürich, Switzerland, 2014.
- De Almeida, A.T.; Ferreira, F.J.T.E.T.E.; Fong, J.A.C. Standards for Efficiency of Electric Motors. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2011, 17, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, L.; Troncon, D. Design of Electric Motors and Power Drive Systems According to Efficiency Standards. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2021, 68, 9287–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dems, M.; Komeza, K. Designing an Energy-Saving Induction Motor Operating in a Wide Frequency Range. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2022, 69, 4387–4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Badri, M.; Pillay, P. Modified Efficiency Estimation Tool for Three-Phase Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2023, 38, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiscia, O.; Rubino, S.; Vaschetto, S.; Cavagnino, A.; Tenconi, A. Accurate Induction Machines Efficiency Mapping Computed by Standard Test Parameters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2022, 58, 3522–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshandel, E.; Mahmoudi, A.; Kahourzade, S.; Soong, W.L. Efficiency Maps of Electrical Machines: A Tutorial Review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2023, 59, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dąbrowski, M. Projektowanie Maszyn Elektrycznych Prądu Przemiennego; Wydawnictwo Naukowo-Technicze: Warszawa, Poland, 1994; ISBN 83-2-041662-0. [Google Scholar]
- Śliwiński, T. Metody Obliczania Silników Indukcyjnych, t.1 Analiza; PWN: Warszawa, Poland, 2008; ISBN 978-8-30115-468-4. [Google Scholar]
- Frejtich, Z. Vypocet Magnetickeho Odlehceni Nasyceneho Indukcniho Motoru. Technika Electrickych Stroju 1972, 2, 90–98. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, G.; Vogt, K.; Ponick, B. Berechnung Elektrischer Maschinen; Technische Universitat Dresden, Elektrotechnisches Institut: Dresden, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toliyat, H.A.; Kliman, G.B. Handbook of Electric Motors—Second EDITION, Revised and Expanded; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 978-1-42003-038-9. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, B.; Tao, D.; Ge, B.; Wang, L.; Hou, P. Analysis of Eddy Current Loss of 120-kW High-Speed Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor. Machines 2022, 10, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, K.; Fukushima, W. Loss Analysis of Induction Motors by Considering Shrink Fitting of Stator Housings. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaria, R.; Lehikoinen, A.; Arkkio, A.; Belahcen, A. Effects of Manufacturing Processes on Core Losses of Electrical Machines. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stermecki, A.; Biro, O.; Bakhsh, I.; Rainer, S.; Ofner, G.; Ingruber, R. 3-D Finite Element Analysis of Additional Eddy Current Losses in Induction Motors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Bian, X.; Yu, H.; Li, C. Finite-Element Evaluation and Eddy-Current Loss Decrease in Stator End Metallic Parts of a Large Double-Canned Induction Motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6779–6785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bompou, E.; Mijatovic, N.; Træholt, C.; Willén, D.W.A.; Thidemann, C. Loss in Steel Armour Wires for Submarine Power Cables. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Power & Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralj, L.; Miljavec, D. Stray losses in power transformer tank walls and construction parts. In Proceedings of the XIX International Conference on Electrical Machines—ICEM 2010, Rome, Italy, 6–8 September 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheaytani, J.; Benabou, A.; Tounzi, A.; Dessoude, M.; Chevallier, L.; Henneron, T. End-Region Leakage Fluxes and Losses Analysis of Cage Induction Motors Using 3-D Finite-Element Method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohand Oussaid, W.M.A.; Tounzi, A.; Romary, R.; Benabou, A.; Laloy, D.; Boughanmi, W. Investigation of Losses in Fingers and Clamping Plates of High-Power Electrical Machines. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Valencia, Spain, 5–8 September 2022; pp. 2187–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohand Oussaid, W.M.A.; Tounzi, A.; Romary, R.; Benabou, A.; Laloy, D.; Boughanmi, W. Influence of Thickness on Eddy Current Losses in Materials Used as Clamping Structures in High-Power Electrical Machines. Proceedings of 2023 IEEE International Magnetic Conference—Short Papers (INTERMAG Short Papers), Sendai, Japan, 15–19 May 2023; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlala, E. Comparison of models for estimating magnetic core losses in electrical machines using the finite-element method. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2009, 45, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Properties of Electrical Steel M400-50A. Available online: https://www.tatasteeleurope.com/sites/default/files/m400-50a.pdf (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Properties of Grey Cast Iron. Available online: https://www.steel-foundry.com/news/grey-cast-iron-magnetic-properties/ (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Brauer, J. Simple equations for the magnetization and reluctivity curves of steel. IEEE Trans. Magn. 1975, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollet, Y.; Barbierato, G.; Gyselinck, J. Finite-element and magnetic-equivalent-circuit modelling of brushed wound-field DC machines with cross-saturation. In Proceedings of the 2018 XIII International Conference on Electrical Machines (ICEM), Lausanne, Switzerland, 4–7 September 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Savini, A.; Turowski, J. Dependence of forces, eddy current and stray losses on screening in power transformers. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Electrical Machines and Systems ICEMS’2001, Shenyang, China, 18–20 August 2001; Volume 1, pp. 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turowski, J.; Turowski, M. Engineering Electrodynamics: Electric Machine, Transformer, and Power Equipment Design, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opera—Electromagnetic and Electromechanical Simulation. Available online: https://www.3ds.com/products-services/simulia/products/opera/ (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Dems, M.; Komeza, K. Modeling of Static and Dynamic Operating States of Induction Motors; Monograph of the Lodz University of Technology Publishing House: Lodz, Poland, 2011; pp. 1–332. ISBN 978-8-37283-449-2. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Gallandat, N.A.; Mayor, J.R.; Habetler, T.G.; Harley, R.G. Calculating the Electromagnetic Field and Losses in the End Region of a Large Synchronous Generator Under Different Operating Conditions With 3-D Transient Finite-Element Analysis. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 3281–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Haavisto, A.; Arkkio, A. Axial Flux and Eddy-Current Loss in Active Region of a Large-Sized Squirrel-Cage Induction Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2010, 46, 3933–3938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J. Research on End Structure Losses and Its Suppression Method of High-Speed Canned Induction Motor. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 49913–49923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, F.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, C.; Li, Y. Numerical Calculation and Analysis of Three-Dimensional Transient Electromagnetic Field in the End Region of Large Water–Hydrogen–Hydrogen Cooled Turbogenerator. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Wang, L.; Zhan, Y.; Zhao, H. Loss Distribution in Stator End Region of Turbo-generators During Asynchronous Operation after Loss of Field. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting (IAS), Detroit, MI, USA, 9–14 October 2022; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huo, F.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Guan, C. Influence of Metal Screen Materials on 3-D Electromagnetic Field and Eddy Current Loss in the End Region of Turbogenerator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke, T.; Schwarz, B.; Ponick, B. A Fast Calculation Approach for Pressure Finger Losses in Large Salient-Pole Synchronous Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2021, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavagnino, A.; Vaschetto, S.; Ferraris, L.; Gmyrek, Z.; Agamloh, E.B.; Bramerdorfer, G. Striving for the Highest Efficiency Class with Minimal Impact for Induction Motor Manufacturers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
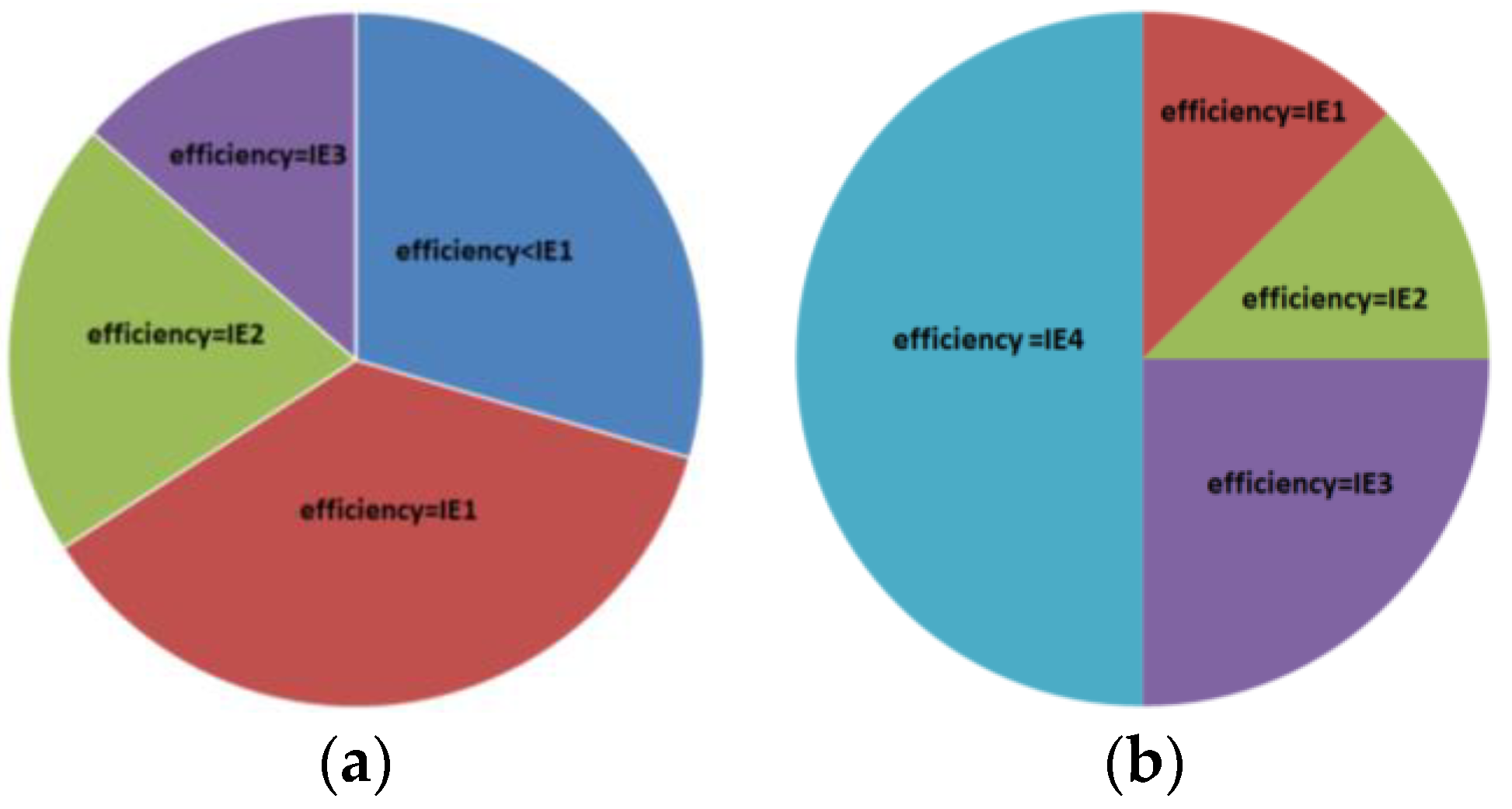

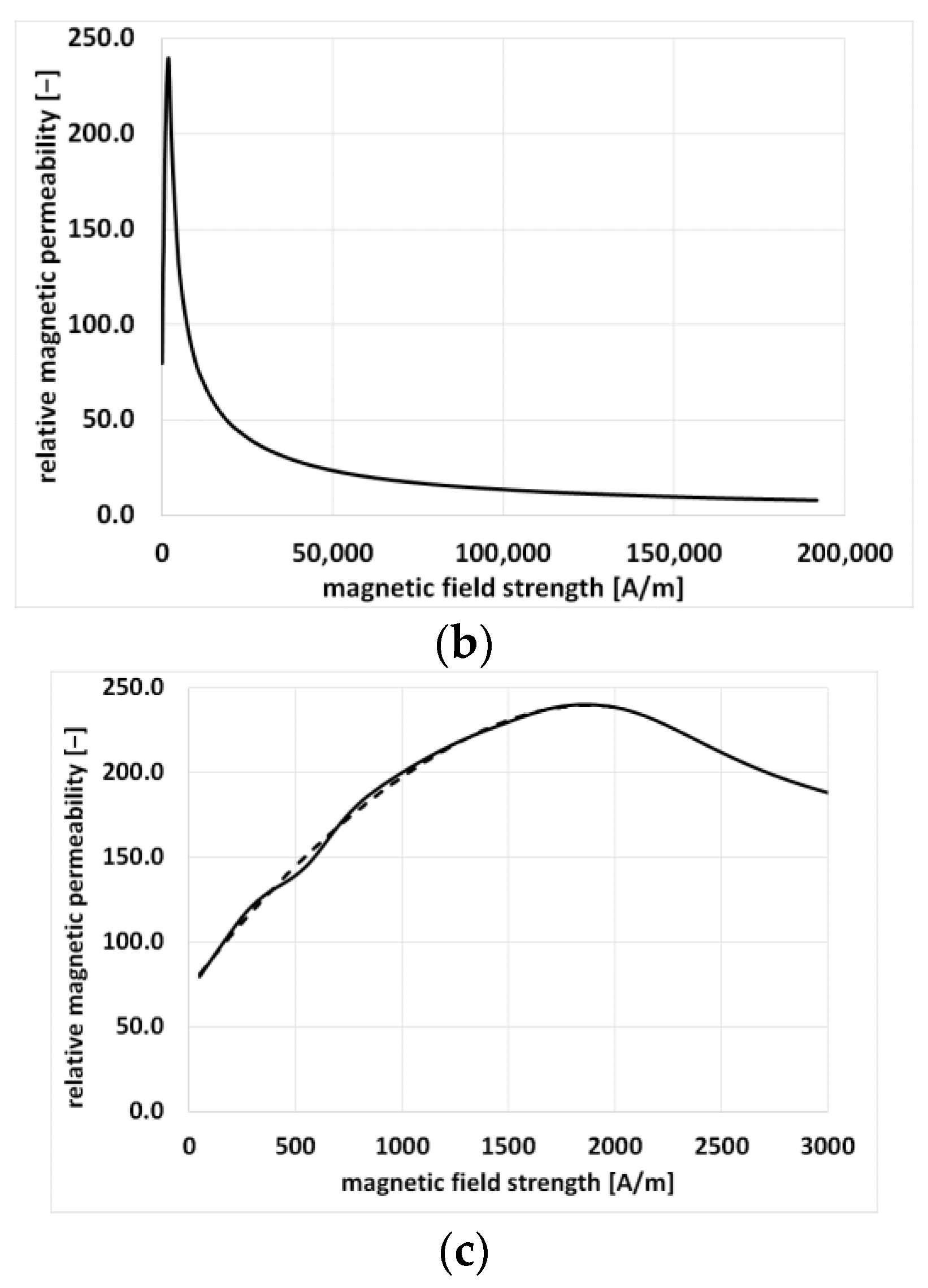












| Quantity | Unit | Motor A | Motor B |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power PN | kW | 150 | 1250 |
| Rated line voltage UN | V | 1000 (Y) | 6000 (Y) |
| Rated current IN | A | 110 | 149 |
| Number of poles 2p | - | 4 | 10 |
| Power factor cos φR | - | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| Rated efficiency ηR | % | 94.0 | 96.2 |
| Rotation speed nR | rpm | 1472 | 596 |
| The outer diameter of the stator core Dse | mm | 520 | 1230 |
| The inner diameter of the stator core Dsi | mm | 334 | 950, |
| Stator core length Ls | mm | 232 | 540 |
| Stator yoke height hsy0 | mm | 36.7 | 61.0 |
| Number of stator slots | - | 72 | 120 |
| Number of rotor slots | - | 60 | 140 |
| Number of serial turns | - | 78 | 200 |
| Air gap thickness | mm | 1 | 3 |
| Quantity | Unit | Motor A | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Calculation | Field-Circuit Simulation | ||
| Induction in the yoke without field penetration into the frame Bsy0 | T | 2.076 | - |
| Reducing the induction in the stator yoke | T | 0.214 | |
| Induction in the yoke with field penetration into the frame Bsy | T | 1.862 | 1.874 |
| Field strength Hsy | A/m | 16614 | 16444 |
| Magnetic induction in the frame Bkd | T | 1.106 | 1.143 |
| Penetration depth | m | 0.00835 | 0.00817 |
| Hysteresis losses in the frame | W | 290 1/499 | 300 1/523 |
| Eddy-current losses in the frame | W | 4571 1/6200 | 4494 1/6057 |
| Total frame losses | W | 4861 1/6699 | 4794 1/6580 |
| Stator yoke height without field penetration into the frame hsy0 | m | 0.03673 | 0.03673 |
| Equivalent stator yoke height hsy | m | 0.04096 | - |
| Magnetic permeability of the frame | H/m | 66.6 10−6 | 69.6 10−6 |
| Quantity | Unit | Motor B | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Analytical Calculation | Field-Circuit Simulation | ||
| Induction in the yoke without field penetration into the frame Bsy0 | T | 1.320 | - |
| Reducing the induction in the stator yoke | T | 0.012 | |
| Induction in the yoke with field penetration into the frame Bsy | T | 1.308 | 1.29 |
| Field strength Hsy | A/m | 450.2 | 600.8 |
| Magnetic induction in the frame Bkd | T | 0.077 | 0.115 |
| Penetration depth | m | 0.00517 | 0.00519 |
| Hysteresis losses in the frame | W | 4.8 1/4.9 | 5.5 1/5.0 |
| Eddy-current losses in the frame | W | 28.9 1/30.1 | 32.7 1/31.6 |
| Total frame losses | W | 33.7 1/35.0 | 38.2 1/36.6 |
| Stator yoke height without field penetration into the frame hsy0 | m | 0.0610 | 0.0610 |
| Equivalent stator yoke height hsy | m | 0.0615 | - |
| Magnetic permeability of the frame | H/m | 173.8 10−6 | 172.2 10−6 |
| Quantity | Calculation | Measurement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Frame | Non-Magnetic Frame | ||
| Rated power PN [W] | 150,000 | 150,000 | 150,000 |
| Losses in the stator windings Pus [W] | 3410 | 4117 | 3504 |
| Losses in the rotor windings Pur [W] | 3789 | 3778 | 3869 |
| Mechanical losses Pm [W] | 554 | 554 | 554 |
| Losses in the frame Pkd [W] | 6699 | - | - |
| Sum of core losses and additional losses (PFe + Pd) [W] (Losses in the frame Pkd non included in losses Pd) | 4324 | 4259 | 11,510 |
| Total losses ∑P [W] | 18,776 | 12,708 | 19,437 |
| Motor efficiency η [%] | 88.9 | 92.2 | 88.5 |
| Current in the stator winding Is [A] | 118.3 | 129.98 | 120.85 |
| Power factor cos φ [-] | 0.8246 | 0.7235 | 0.8103 |
| Quantity | Calculation | Measurement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Frame | Non-Magnetic Frame | ||
| Rated power PN [W] | 1,250,000 | 1,250,000 | 1,250,000 |
| Losses in the stator windings Pus [W] | 12,810 | 12,820 | 12,810 |
| Losses in the rotor windings Pur [W] | 7880 | 7880 | 7810 |
| Mechanical losses Pm [W] | 2690 | 2690 | 2690 |
| Losses in the frame Pkd [W] | 35 | - | - |
| Sum of core losses and additional losses (PFe + Pd) [W] (Losses in the frame Pkd non included in losses Pd) | 31,926 | 31,946 | 29,520 |
| Total losses ∑P [W] | 55,341 | 55,336 | 52,830 |
| Motor efficiency η [%] | 95.8 | 95.8 | 95.9 |
| Current in the stator winding Is [A] | 150.0 | 150.0 | 146.3 |
| Power factor cos φ [-] | 0.8380 | 0.8380 | 0.8573 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Komeza, K.; Dems, M.; Wiak, S.; Libera, R.; Pietrzak, J.; Stando, P.; Tomczyk, K. Influence of the Cast Iron Frame on the Distribution of the Magnetic Field in the Stator Yoke and Additional Power Losses in the Induction Motor. Electronics 2024, 13, 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13010119
Komeza K, Dems M, Wiak S, Libera R, Pietrzak J, Stando P, Tomczyk K. Influence of the Cast Iron Frame on the Distribution of the Magnetic Field in the Stator Yoke and Additional Power Losses in the Induction Motor. Electronics. 2024; 13(1):119. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13010119
Chicago/Turabian StyleKomeza, Krzysztof, Maria Dems, Slawomir Wiak, Rafal Libera, Jan Pietrzak, Patryk Stando, and Krzysztof Tomczyk. 2024. "Influence of the Cast Iron Frame on the Distribution of the Magnetic Field in the Stator Yoke and Additional Power Losses in the Induction Motor" Electronics 13, no. 1: 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13010119
APA StyleKomeza, K., Dems, M., Wiak, S., Libera, R., Pietrzak, J., Stando, P., & Tomczyk, K. (2024). Influence of the Cast Iron Frame on the Distribution of the Magnetic Field in the Stator Yoke and Additional Power Losses in the Induction Motor. Electronics, 13(1), 119. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13010119








