Real-Time RGBT Target Tracking Based on Attention Mechanism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- i.
- To achieve real-time tracking of RGBTs, we suggest a real-time tracking network based on the attention mechanism; the network uses the attention mechanism to achieve feature enhancement, which increases speed and guarantees tracking accuracy at the same time, as well as enhancement fusion operation at the last layer to decrease computational complexity and redundant information;
- ii.
- We design a feature selection enhancement module that makes use of the channel attention mechanism to adaptively select and fuse the features learned from various convolutional kernels; in addition, we combine this module with the Transformer, which can be useful for exploring rich contextual information, thereby enhancing and strengthening the useful information and suppressing the unimportant information to enhance tracking performance;
- iii.
- In order to better direct the tracker and produce better tracking results, we built the spatial channel adaptive adjustment fusion module; this module can adjust and fuse the information previously received from both spatial and channel dimensions.
2. Related Work
2.1. RGBT Target Tracking
2.2. MDNet Target Tracking Algorithm
2.3. Attention Mechanisms
3. Methods
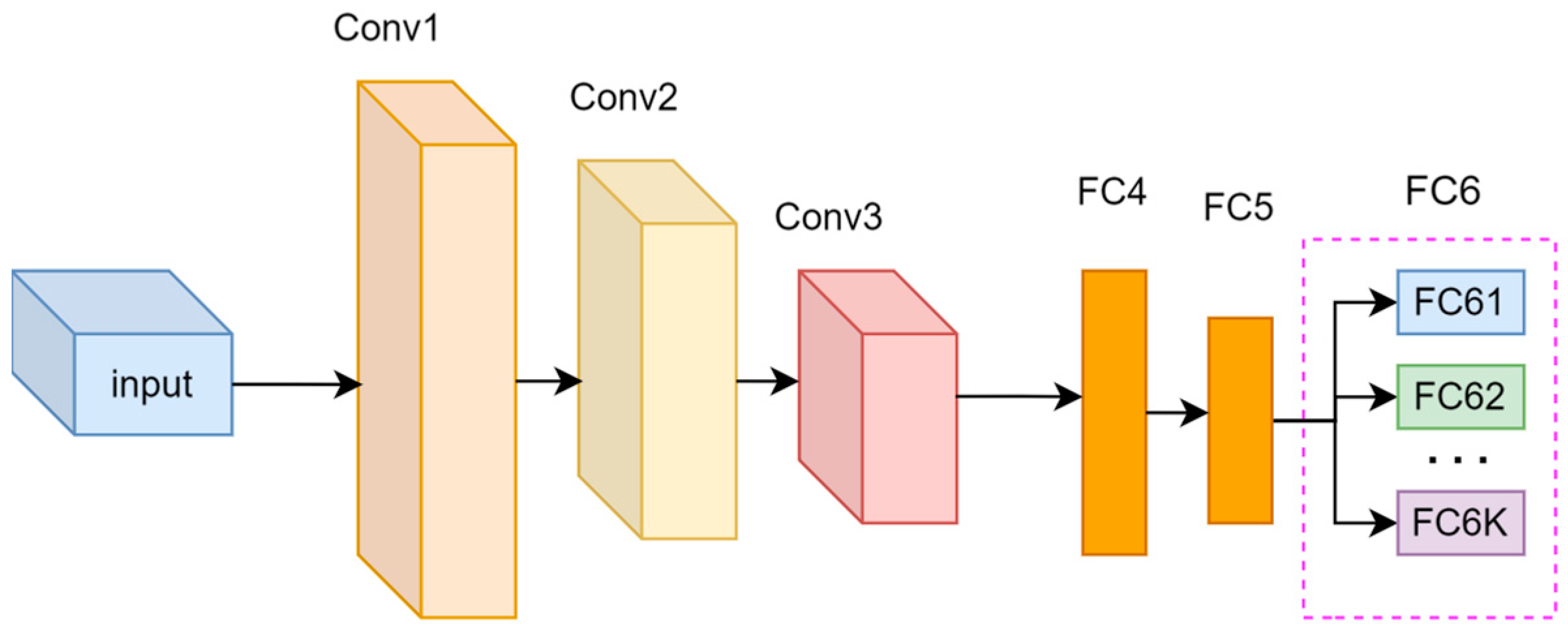
3.1. An Attention-Based Real-Time Tracking Network Framework
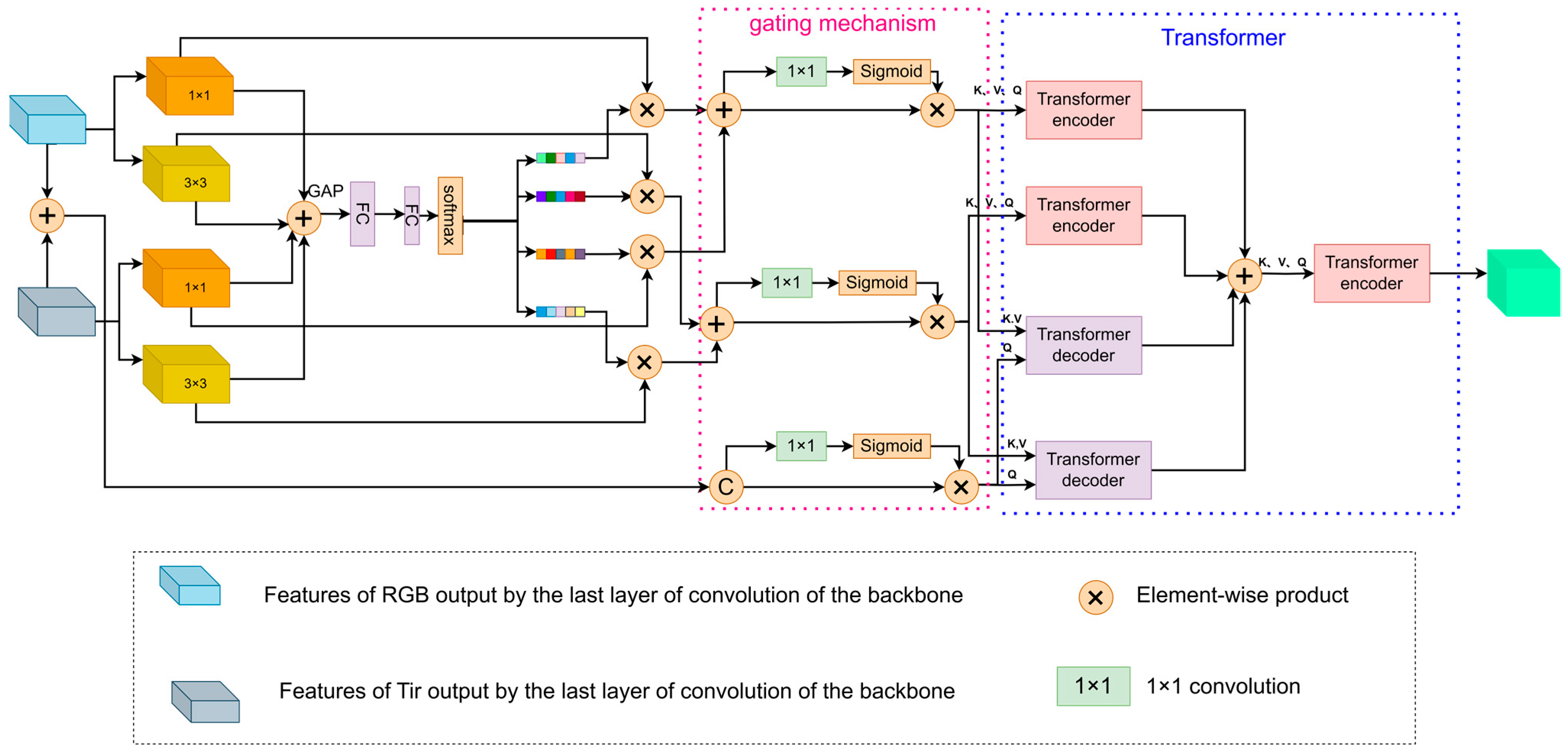
3.2. Feature Selection Enhancement Module
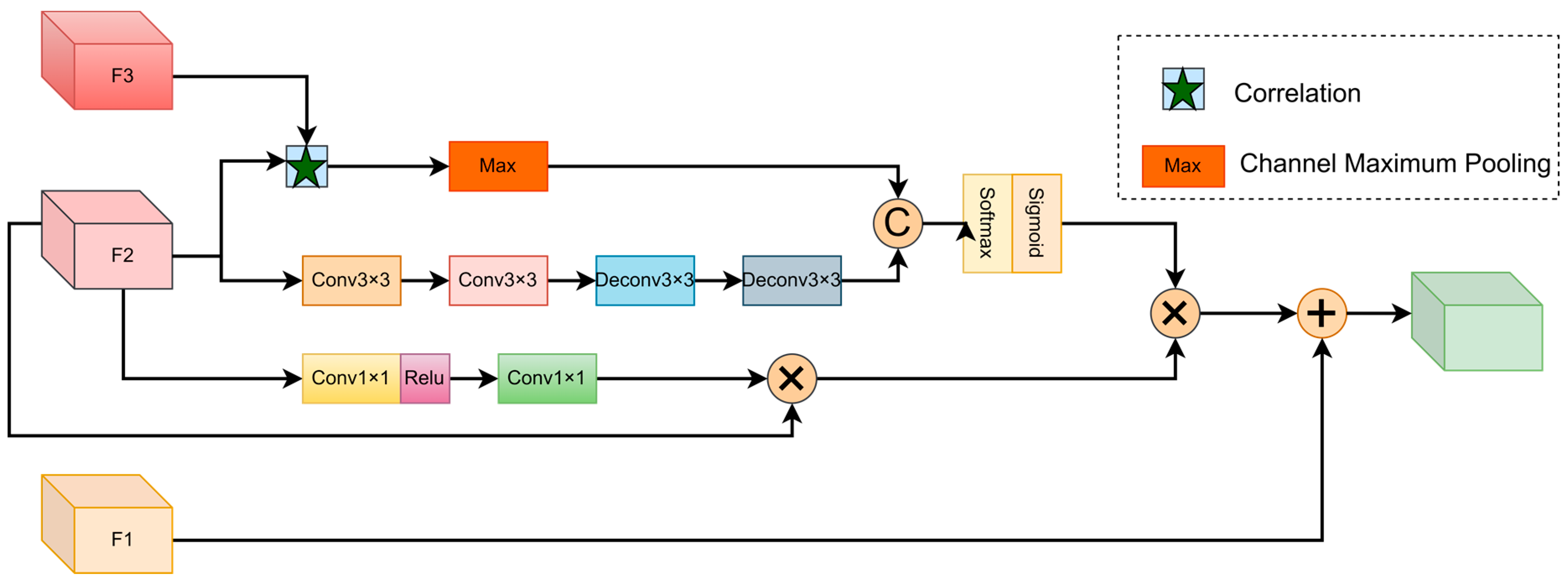
3.3. Spatial Channel Adaptive Adjustment Fusion Module
4. Experiments
4.1. Implementation Details
4.2. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
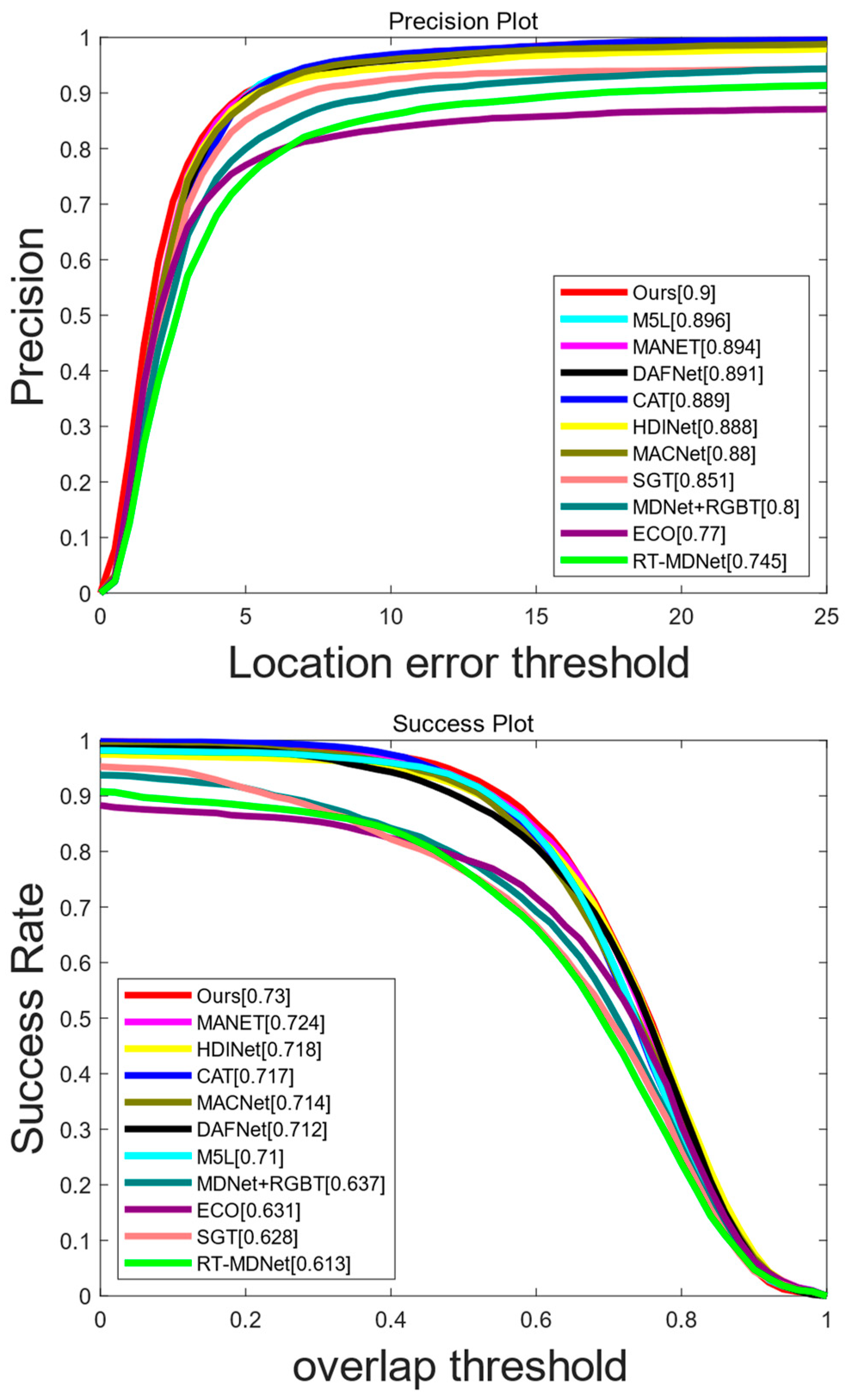
4.3. Results Comparisons
4.3.1. Evaluation of GTOT Dataset
4.3.2. Evaluation of RGBT234 Dataset
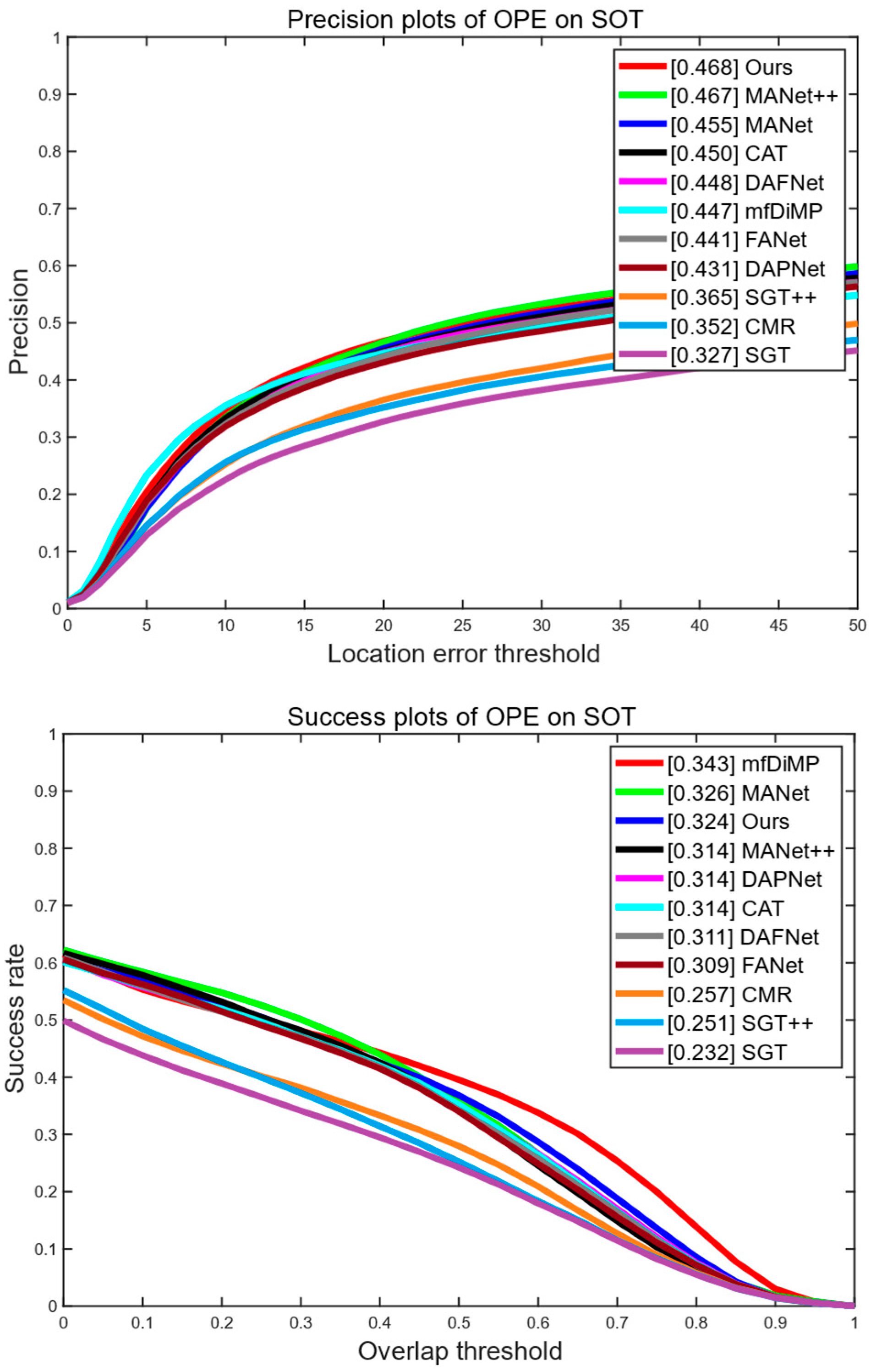
4.3.3. Evaluation of LasHeR Dataset
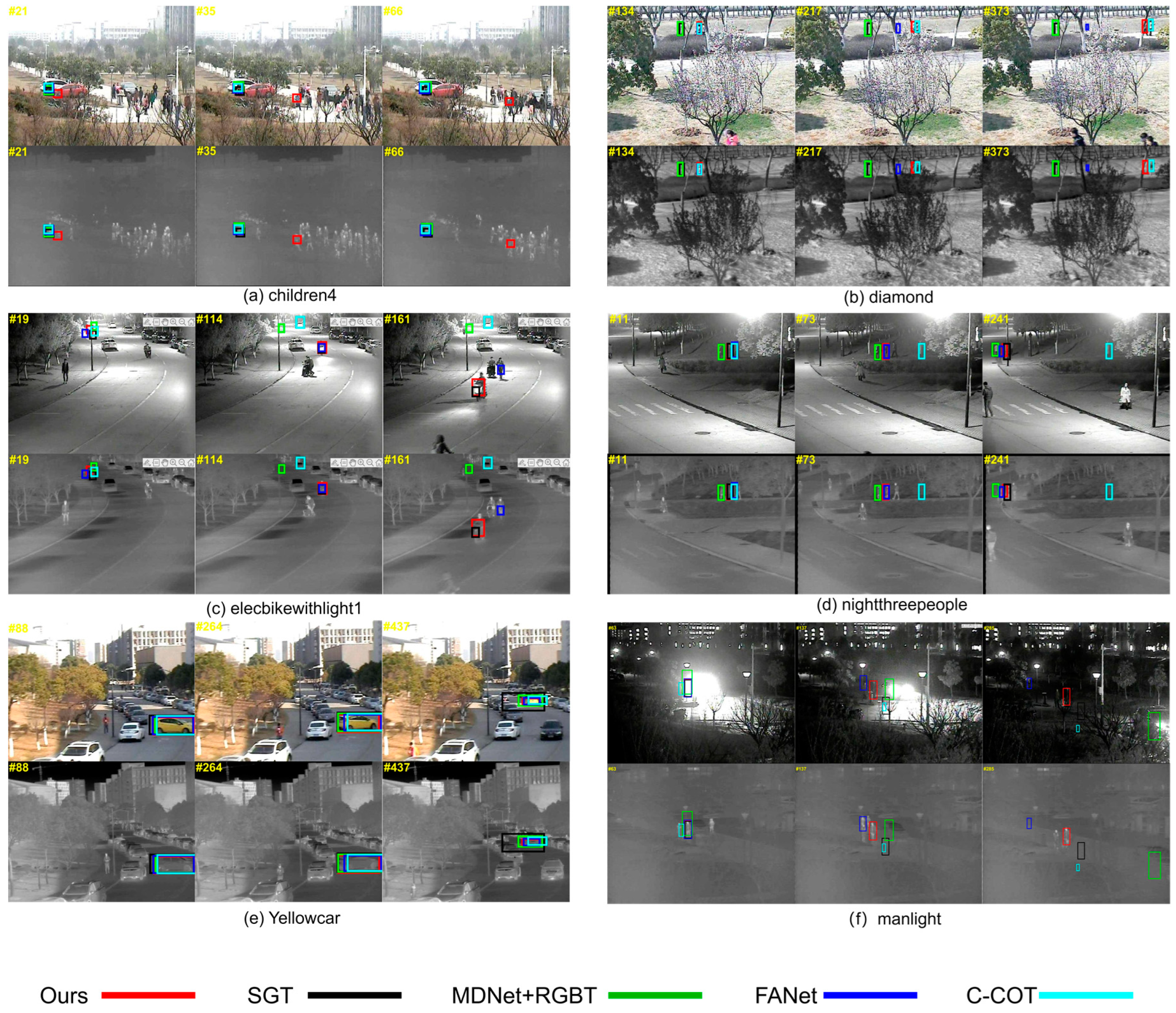
4.4. Implementation Detail Analysis of Visualization Comparison Results
4.5. Ablation Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, Z.; Xu, T.; Wu, X.-J. A survey for deep rgbt tracking. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2201.09296. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Zhang, H.; Shu, X.; Liu, Q.; Chang, X.; He, Z.; Shi, G. Thermal Infrared Target Tracking: A Comprehensive Review. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 73, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnelle, S.R.; Chan, A.L. Enhanced target tracking through infrared-visible image fusion. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Information Fusion, Chicago, IL, USA, 5–8 July 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.L.; Schnelle, S.R. Fusing concurrent visible and infrared videos for improved tracking performance. Opt. Eng. 2013, 52, 017004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ye, P.; Peng, S.; Liu, J.; Xiao, G. DSiamMFT: An RGB-T fusion tracking method via dynamic Siamese networks using multi-layer feature fusion. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2020, 84, 115756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Qian, C.; Li, C.; Tang, J.; Wang, L. Duality-gated mutual condition network for RGBT tracking. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Chen, M.; Chen, X.; Han, J.; Bai, L. Siamdl: Siamese Dual-Level Fusion Attention Network for RGBT Tracking; SSRN 4209345; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wei, X.; Tang, X.; Wu, J.; Fang, J. Response map evaluation for RGBT tracking. Neural Comput. Appl. 2022, 34, 5757–5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, C.; Tang, J. Learning soft-consistent correlation filters for RGB-T object tracking. In Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition and Computer Vision: First Chinese Conference, PRCV 2018, Guangzhou, China, 23–26 November 2018; Proceedings, Part IV 1. pp. 295–306. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, S.; Shao, P.; Liang, X.; Wang, X. Fast RGB-T tracking via cross-modal correlation filters. Neurocomputing 2019, 334, 172–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.; Han, B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 4293–4302. [Google Scholar]
- Bertinetto, L.; Valmadre, J.; Henriques, J.F.; Vedaldi, A.; Torr, P.H. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–10, 15–16 October 2016; Proceedings, Part II 14. pp. 850–865. [Google Scholar]
- Bhat, G.; Danelljan, M.; Gool, L.V.; Timofte, R. Learning discriminative model prediction for tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6182–6191. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, Ł.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30, 11. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, J.; Zhou, D.; Cao, J.; Nie, R.; He, K. Differential reinforcement and global collaboration network for rgbt tracking. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 7301–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Sui, X.; Gu, G. Multi-modal multi-task feature fusion for RGBT tracking. Inf. Fusion 2023, 97, 101816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, C.; Xiao, Y.; Ruan, R.; Fan, M. Rgbt tracking via challenge-based appearance disentanglement and interaction. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2024, 33, 1753–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Z.; Li, C.; Huo, B.; Zhang, Y. SiamCAF: Complementary Attention Fusion-Based Siamese Network for RGBT Tracking. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Song, K.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y. Exploring the potential of Siamese network for RGBT object tracking. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2023, 95, 103882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Cheng, H.; Hu, S.; Liu, X.; Tang, J.; Lin, L. Learning collaborative sparse representation for grayscale-thermal tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2016, 25, 5743–5756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Huang, J. A Hierarchical Registration Method of the Chang’E-1 Stereo Images; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. Quality-aware feature aggregation network for robust RGBT tracking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2020, 6, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Luo, B.; Tang, J.; Wang, X. Dense feature aggregation and pruning for RGBT tracking. In Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, NY, USA, 21–25 October 2019; pp. 465–472. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, J.; He, T.; Wang, F. Deep adaptive fusion network for high performance RGBT tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Liu, L.; Lu, A.; Ji, Q.; Tang, J. Challenge-aware RGBT tracking. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 222–237. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Yang, X. Learning adaptive attribute-driven representation for real-time RGB-T tracking. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 2714–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, C.; Liu, L.; Tang, J. Attribute-based progressive fusion network for rgbt tracking. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Online, 22 February–1 March 2022; pp. 2831–2838. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Zhang, P.; Wu, F.; Li, X. Fcanet: Frequency channel attention networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 783–792. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Natarajan, T.; Rao, K.R. Discrete cosine transform. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1974, 100, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Zhu, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, W.; Hu, Q. ECA-Net: Efficient channel attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11534–11542. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Wang, W.; Hu, X.; Yang, J. Selective kernel networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 510–519. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Heess, N.; Graves, A. Recurrent models of visual attention. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, Y.; Liu, W. Ccnet: Criss-cross attention for semantic segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 603–612. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, BC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Bao, J.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N.; Yuan, L.; Chen, D.; Guo, B. Cswin transformer: A general vision transformer backbone with cross-shaped windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 12124–12134. [Google Scholar]
- Chatfield, K.; Simonyan, K.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Return of the devil in the details: Delving deep into convolutional nets. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1405.3531. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Li, H. Transformer meets tracker: Exploiting temporal context for robust visual tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 1571–1580. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Woo, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. Bam: Bottleneck attention module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06514. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.-L.; Yang, Y.-B. Sa-net: Shuffle attention for deep convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021-2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 2235–2239. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Yan, B.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Yang, X.; Lu, H. Transformer tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 8126–8135. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, F.; Shao, L. Ranet: Ranking attention network for fast video object segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3978–3987. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Proceedings, Part III 18. pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2012, 25, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liang, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, N.; Tang, J. RGB-T object tracking: Benchmark and baseline. Pattern Recognit. 2019, 96, 106977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xue, W.; Jia, Y.; Qu, Z.; Luo, B.; Tang, J.; Sun, D. LasHeR: A large-scale high-diversity benchmark for RGBT tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 31, 392–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Tang, J. M 5 l: Multi-modal multi-margin metric learning for rgbt tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 31, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long Li, C.; Lu, A.; Hua Zheng, A.; Tu, Z.; Tang, J. Multi-adapter RGBT tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, J.; Zhou, D.; Cao, J.; Nie, R.; Guo, Y. Hdinet: Hierarchical dual-sensor interaction network for rgbt tracking. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 16915–16926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhuo, L.; Zhang, J. Object tracking in RGB-T videos using modal-aware attention network and competitive learning. Sensors 2020, 20, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, N.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Tang, J. Weighted sparse representation regularized graph learning for RGB-T object tracking. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Mountain View, CA, USA, 23–27 October 2017; pp. 1856–1864. [Google Scholar]
- Danelljan, M.; Bhat, G.; Shahbaz Khan, F.; Felsberg, M. Eco: Efficient convolution operators for tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6638–6646. [Google Scholar]
- Real-Time MDNet. Available online: https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ECCV_2018/html/Ilchae_Jung_Real-Time_MDNet_ECCV_2018_paper.html (accessed on 4 June 2024).
- Peng, J.; Zhao, H.; Hu, Z. Dynamic fusion network for RGBT tracking. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 24, 3822–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Xu, T.; Li, H.; Wu, X.-J.; Zhu, X.; Kittler, J. Exploring fusion strategies for accurate RGBT visual object tracking. Inf. Fusion 2023, 99, 101881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, C.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Cross-modal pattern-propagation for RGB-T tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 7064–7073. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Zhao, J.; Bo, C.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Yang, X. Jointly modeling motion and appearance cues for robust RGB-T tracking. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3335–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, A.; Li, C.; Yan, Y.; Tang, J.; Luo, B. RGBT tracking via multi-adapter network with hierarchical divergence loss. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 5613–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Danelljan, M.; Gonzalez-Garcia, A.; Van De Weijer, J.; Shahbaz Khan, F. Multi-modal fusion for end-to-end RGB-T tracking. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019. [Google Scholar]


| CAT | M5L | DFNet | DFAT | MDNet+RGBT | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCC | 89.9/69.2 | 87.1/66.6 | 88.7/68.9 | 86.3/68.7 | 82.9/64.1 | 90.4/70.3 |
| LSV | 85.0/67.9 | 91.0/70.2 | 84.2/69.7 | 92.4/75.0 | 77.0/57.3 | 86.1/70.3 |
| FM | 83.9/65.4 | 89.4/68.5 | 81.4/64.4 | 89.1/74.0 | 80.5/59.8 | 85.8/68.8 |
| LI | 89.2/72.3 | 91.7/73.0 | 89.6/73.3 | 92.2/74.1 | 79.5/64.3 | 91.1/74.2 |
| TC | 89.9/71.0 | 89.2/69.5 | 88.6/71.5 | 89.1/70.7 | 79.5/60.9 | 91.9/72.4 |
| SO | 94.7/69.9 | 96.0/70.2 | 94.3/71.3 | 94.4/71.9 | 87.0/62.2 | 94.6/71.8 |
| DEF | 92.5/75.5 | 92.2/74.6 | 92.8/74.8 | 91.9/73.5 | 81.6/68.8 | 92.1/75.4 |
| ALL | 88.9/71.7 | 89.6/71.0 | 88.1/71.9 | 89.3/72.3 | 80.0/63.7 | 90.0/73.0 |
| CAT | M5L | ADRNet | DFAT | APFNet | Ours | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC | 81.1/51.9 | 75.0/47.7 | 80.4/53.6 | 71.9/47.8 | 81.3/54.5 | 80.0/54.5 |
| CM | 75.2/52.7 | 75.2/52.9 | 74.3/52.9 | 74.2/54.7 | 77.9/56.3 | 78.8/57.1 |
| DEF | 76.2/54.1 | 73.6/51.1 | 74.3/52.8 | 76.0/57.6 | 78.5/56.4 | 79.2/56.9 |
| FM | 73.1/47.0 | 72.8/46.5 | 74.9/48.9 | 65.4/46.2 | 79.1/51.1 | 79.4/50.9 |
| HO | 70.0/48.0 | 66.5/45.0 | 71.4/49.6 | 63.9/45.5 | 73.8/50.7 | 74.8/53.3 |
| LI | 81.0/54.7 | 82.1/54.7 | 81.1/56.0 | 78.3/56.2 | 84.3/56.9 | 84.8/58.3 |
| LR MB NO PO SV TC ALL | 82.0/53.9 68.3/49.0 93.2/66.8 85.1/59.3 79.7/56.6 80.3/57.7 80.4/56.1 | 82.3/53.5 73.8/52.8 93.1/64.6 86.3/58.9 79.6/54.2 82.1/56.4 79.5/54.2 | 83.8/56.2 73.3/53.2 91.6/66.0 85.1/60.3 78.6/56.2 79.6/58.6 80.7/57.0 | 75.2/51.5 68.6/50.2 93.3/69.6 80.7/59.2 77.4/57.5 67.5/49.4 76.1/55.5 | 84.4/56.5 74.5/54.5 94.8/68.0 86.3/60.6 83.1/57.9 82.2/58.1 82.7/57.9 | 85.4/59.0 75.7/55.2 93.2/67.0 90.1/64.1 83.0/59.4 80.7/59.8 84.4/60.2 |
| Ours-FSEM | Ours-SCAAFM | Ours | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GTOT | PR | 0.886 | 0.878 | 0.900 |
| SR | 0.714 | 0.707 | 0.730 | |
| RGBT234 | PR | 0.836 | 0.822 | 0.844 |
| SR | 0.590 | 0.589 | 0.602 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Xiong, X. Real-Time RGBT Target Tracking Based on Attention Mechanism. Electronics 2024, 13, 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132517
Zhao Q, Liu J, Wang J, Xiong X. Real-Time RGBT Target Tracking Based on Attention Mechanism. Electronics. 2024; 13(13):2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132517
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Qian, Jun Liu, Junjia Wang, and Xingzhong Xiong. 2024. "Real-Time RGBT Target Tracking Based on Attention Mechanism" Electronics 13, no. 13: 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132517
APA StyleZhao, Q., Liu, J., Wang, J., & Xiong, X. (2024). Real-Time RGBT Target Tracking Based on Attention Mechanism. Electronics, 13(13), 2517. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132517





