Abstract
With the many applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in social judicial systems, false fact identification becomes a challenging issue when the system is expected to be more autonomous and intelligent in assisting a judicial review. In particular, private lending disputes often involve false facts that are intentionally concealed and manipulated due to unique and dynamic relationships and their nonconfrontational nature in the judicial system. In this article, we investigate deep learning techniques to identify false facts in loan cases for the purpose of reducing the judicial workload. Specifically, we adapt deep-learning-based natural language processing techniques to a dataset over 100 real-world judicial rules spanning four courts of different levels in China. The BERT (bidirectional encoder representations from transformers)-based classifier and T5 text generation models were trained to classify false litigation claims semantically. The experimental results demonstrate that T5 has a robust learning capability with a small number of legal text samples, outperforms BERT in identifying falsified facts, and provides explainable decisions to judges. This research shows that deep-learning-based false fact identification approaches provide promising solutions for addressing concealed information and manipulation in private lending lawsuits. This highlights the feasibility of deep learning to strengthen fact-finding and reduce labor costs in the judicial field.
1. Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) has led to vigorous development in many aspects of our daily lives from level generation in video games [1] and students’ performance evaluation in intelligent education [2] to critical applications in digital health [3] and cybersecurity [4]. Social conflicts between stakeholders have frequently occurred with the rapid development of the economy and society in recent years [5]. Litigation has become a primary method of dispute resolution [6]. In addition, there have been numerous cases where false lawsuits have been constructed to take advantage of the court’s power of adjudication and enforcement for illegal profit [7]. False litigation refers to an action in which the actor, individually or maliciously conspiring with others, forges evidence and makes false statements, fabricates the basic facts of a civil case, or fictionalizes a civil dispute and files a civil lawsuit with the people’s court [8]. According to statistics, nearly 90% of false litigation cases are confirmed through a retrial, with only 11.9% and 1.86% confirmed in the first- and second-instance proceedings, respectively [9].
AI has been used in various aspects of the judiciary system [10]. The significance of factual determination in judicial decision-making is well recognized in the generation of legal AI [11]. In this article, we focus on the specific AI application scenario of false facts in private loan cases and investigate the ability of two deep-learning-based techniques, namely, the BERT model (bidirectional encoder representations from transformers) [12] and the T5 model (Text-To-Text Transfer Transformer) [13], to identify false facts. Both the BERT and T5 models are pretrained models for dealing with natural language processing (NLP) problems in the current AI field. BERT is a pretrained language model based on a Transformer architecture that improves the performance of various NLP tasks. It employs a bidirectional (two-way) training approach and utilizes pre- and post-contextual information for comprehension and processing. Compared with previous models, such as traditional recurrent neural networks (RNNs) [14] and convolutional neural networks (CNNs) [15], BERT can better capture long-distance dependencies through the attention mechanism of the Transformer [16], thus improving language modeling [17]. Unlike traditional NLP models, T5 adopts a general framework that treats all NLP tasks as text-to-text transformation problems [13]. The core idea is to use a single model to solve multiple NLP tasks, including text categorization, machine translation, and Q&A systems. The consistent framework simplifies the model design and training process. It can be fine-tuned to fit specific tasks [18].
By exploiting the aforementioned BERT and T5 techniques, we researched “what kind of lending fact is a false fact that can be judged?” as shown in Figure 1. We used sample data from real-world open data resources in Chinese language modes of “China Judgment Online”, “Peking University Law Database”, and “Wolters Kluwer”. We studied cases from the years 2020 and 2023, and the type of document was set to “Judgment document”, with the subject matters of “civil” and “private lending”. The data cover four levels of courts in China, and priority was given to cases with revised judgments at the retrial and second-instance levels. We ultimately selected over 100 real cases to test the applicability of the T5 model to the small sample classification problem for a single task. We compare the two models and show their performance with real-world data. Since the empirical data are full of general adjudication rules in the national range and hold characteristics of fake descriptions [19], the results indicate the possibility of a general application of deep learning techniques in false fact identification in legal texts [20]. However, the prediction results only provide decision support to judges, who will decide the adjudication [21].
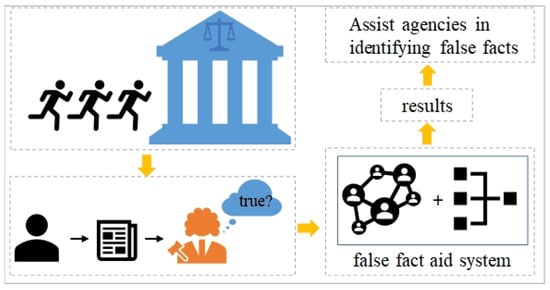
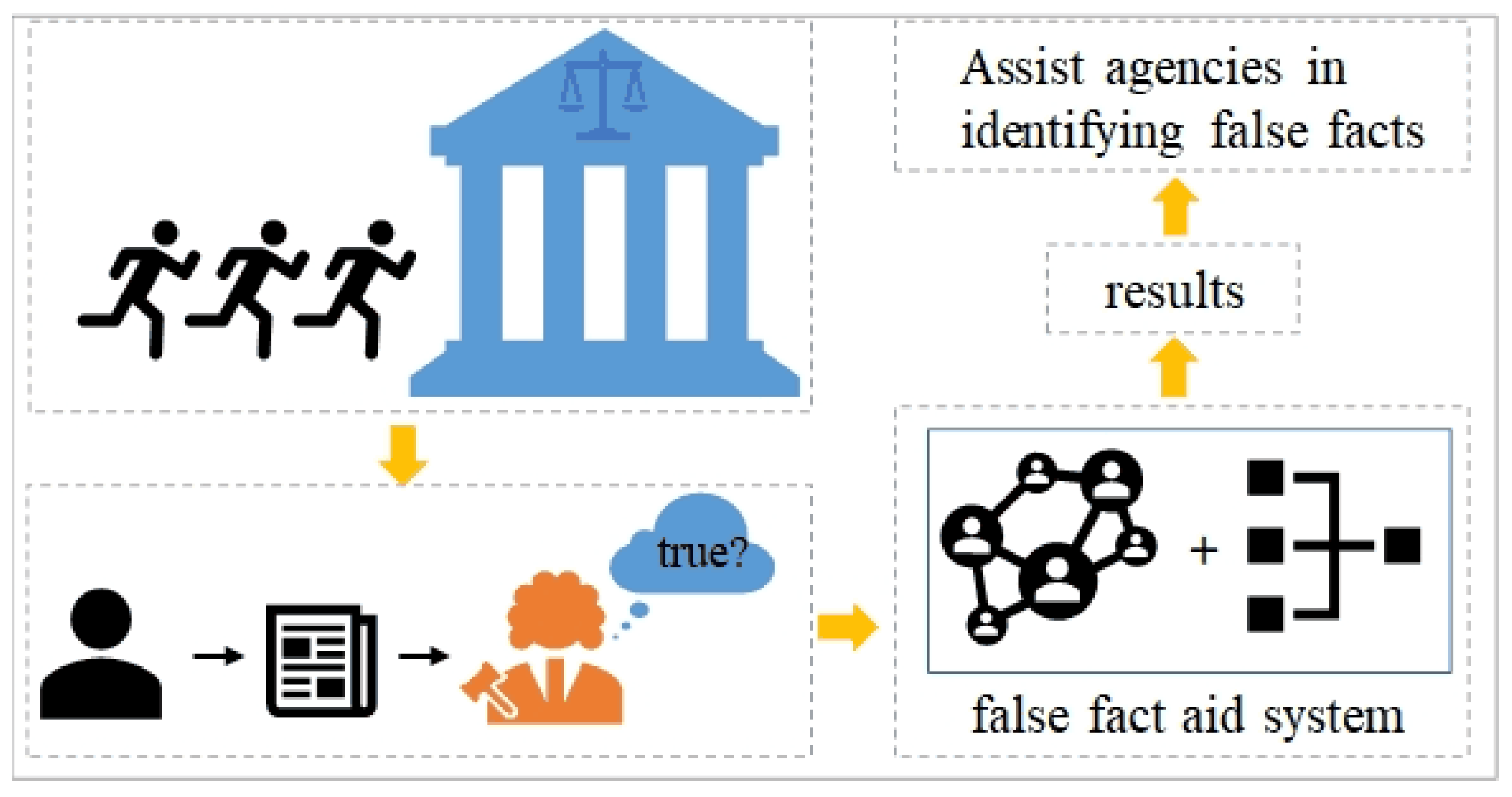
Figure 1.
The AI in the loop of identifying legal facts in social judicial systems.
In this article, we first review the related AI techniques in social judicial systems in Section 2. Subsequently, in Section 3, we introduce the BERT and T5 models as adjudication technologies for identifying false facts in Chinese judicial practice. The core of identifying “false” is the proof and determination of the disputed facts in the lawsuit. After that, we develop the “false facts” labeling system on the basis of the BERT and T5 models. Section 4 describes the conducted experiments and compares the performance of the two models. Finally, we conclude this research and discuss future directions.
2. Related Works
As artificial intelligence technologies have rapidly advanced, NLP techniques have been increasingly applied in the legal domain, assisting tasks such as legal documentation, contract review, and case prediction [22]. In recent years, many related studies have made significant progress. With respect to the identification of facts from case materials, Hu [23] utilized long short-term memory (LSTM) networks and graph convolutional networks (GCNs) to predict crime rates and employed attention mechanisms to improve experimental results. Practitioners must effectively use complex NLP technologies to handle many publicly available legal texts for the benefit of society [24]. Chalkidis et al. [25] explored the task of legal judgment prediction, which involves automatically predicting case outcomes given descriptions of case facts. They proposed a hierarchical BERT model to overcome the length limitations of the BERT model when hashing long texts and applied the model to English legal judgment prediction. This study demonstrated the potential of neural networks in the task of legal judgment prediction.
Li et al. [26] constructed a decision support system for similar case matching through BERT. They proposed a multistage approach to enhance legal document retrieval and utilized large language models to improve retrieval accuracy. This study is important for developing valuable tools for legal practitioners. In their research, Duan et al. [27] introduced the Chinese Judicial Reading Comprehension (CJRC) dataset and constructed two powerful baseline models based on BERT and BiDAF. This research provides a beneficial exploration and application of introducing AI into the legal field. Azam et al. [28] noted that although models such as BERT have made significant progress in the judiciary domain, there is still room for improvement in predicting confidence levels. Hence, they proposed a Bayesian method, called BayesJudge, to quantify uncertainty in legal judgment predictions and demonstrated its advantages in prediction accuracy and confidence estimation, providing more reliable information for legal professionals.
Compared with the existing research, this study emphasizes the identification of false facts in private lending scenarios. We first introduce the principles related to the pretraining and fine-tuning of the BERT and T5 models. Then, we discuss relevant laws and how AI identifies false facts. The experiment compares the performance of the BERT and T5 models. The experimental results show that T5 has advantages over BERT on small, domain-specific corpora. The experiments also highlight the practical value of enhancing trial fairness through deep learning techniques.
3. Models for Identifying False Facts
In this section, we describe the development of the BERT and T5 models for identifying false facts. Although both models have been well studied, this is the first study in which they are used in social judicial systems.
3.1. The BERT Model
The training process of BERT consists of two phases, namely, pretraining and fine-tuning, as shown in Algorithms 1 and 2. In the pretraining phase, BERT is trained with large-scale unlabeled textual data to learn a generalized language representation. Specifically, BERT is trained on two tasks: masked language modeling (MLM) and next sentence prediction (NSP). BERT can learn to understand the relationship between words and sentences through these two tasks.
In the fine-tuning phase, BERT’s pretrained models are fine-tuned on specific NLP tasks such as text categorization, named entity recognition, and sentiment analysis. In the fine-tuning process, the model structure remains unchanged and only an appropriate task-specific output layer is added on the top. Supervised fine-tuning is performed through labeled data. In the BERT fine-tuning classification task, BERT uses a classifier to transform the BERT output into the prediction of specific classes. The output contains a unique token of [CLS], which is the representation vector obtained after all the input text sequences have gone through the BERT model. It represents the semantic information of the entire input text sequence. Suppose that we have a categorization task to classify the input text into K categories; then, the output representation vector of [CLS] is denoted as h in the BERT fine-tuning.
A classifier (usually a fully connected layer) is trained to transform the representation vector into a classification probability distribution.
where is the probability that the input belongs to the k-th category in the vector h. W and b are the classifier parameters that are learned in the training process. Finally, the category with the highest probability is selected as the model prediction result, e.g., , where is the categorized prediction result and is the index corresponding to the category with the highest probability.
Algorithm 1 elaborates the training process in the BERT model. It learns the model parameter through the embedding and attention mechanism. We first create the sequences of tokens (lines 1–4) from the input of the text corpus. Subsequently, we calculate the parameter values through masked language modeling and the next sentence prediction tasks (line 5). Finally, we output the pretrained BERT model that could be used for a new classification task.
| Algorithm 1 BERT Pretraining Process |
| Require:
Unlabeled text corpus: , where is a sentence. Ensure: Pretrained BERT model parameters
|
In the BERT fine-tuning classification task, the above core formulation maps the output representation vector h to the category probability distribution through the classifier and finalizes the classification prediction. Algorithm 2 describes the BERT fine-tuning process where we optimize the classifier’s parameters by comparing them with the labeled data. Hence, the model can achieve good performance on the classification task. Given the input of the labeled dataset, we consider the model as a classifier to process the sentences (line 2). Then, we compute the cross-entropy-based loss function to compare the true and predicted labels, and update the model parameters through backpropagation (line 3). The loss function is used to measure the difference between the model’s predictions and the true labels and is a commonly used loss function in classification tasks. The cross-entropy has relatively high sensitivity to prediction errors and encourages the model to converge rapidly.
The cross-entropy is a metric commonly used to measure the difference between two probability distributions. Assuming that we have two probability distributions, namely, the actual distribution P and the predicted distribution Q, the loss function based on the cross-entropy can be computed below.
where denotes the index of an event or category, represents the probability of event in the actual distribution, and signifies the probability of event in the predicted distribution.
| Algorithm 2 BERT Fine-tuning Process |
| Require: A labeled task-specific dataset: , where is an input sequence and is the corresponding label. Ensure: The fine-tuned BERT model parameter
|
During the fine-tuning process, the model parameters are adjusted by minimizing the cross-entropy loss, aiming to make the model’s output as close as possible to the distribution of actual labels. For binary classification, the cross-entropy is simplified.
where y represents the actual label (0 or 1) and p is the probability predicted by the model.
3.2. The T5 Model
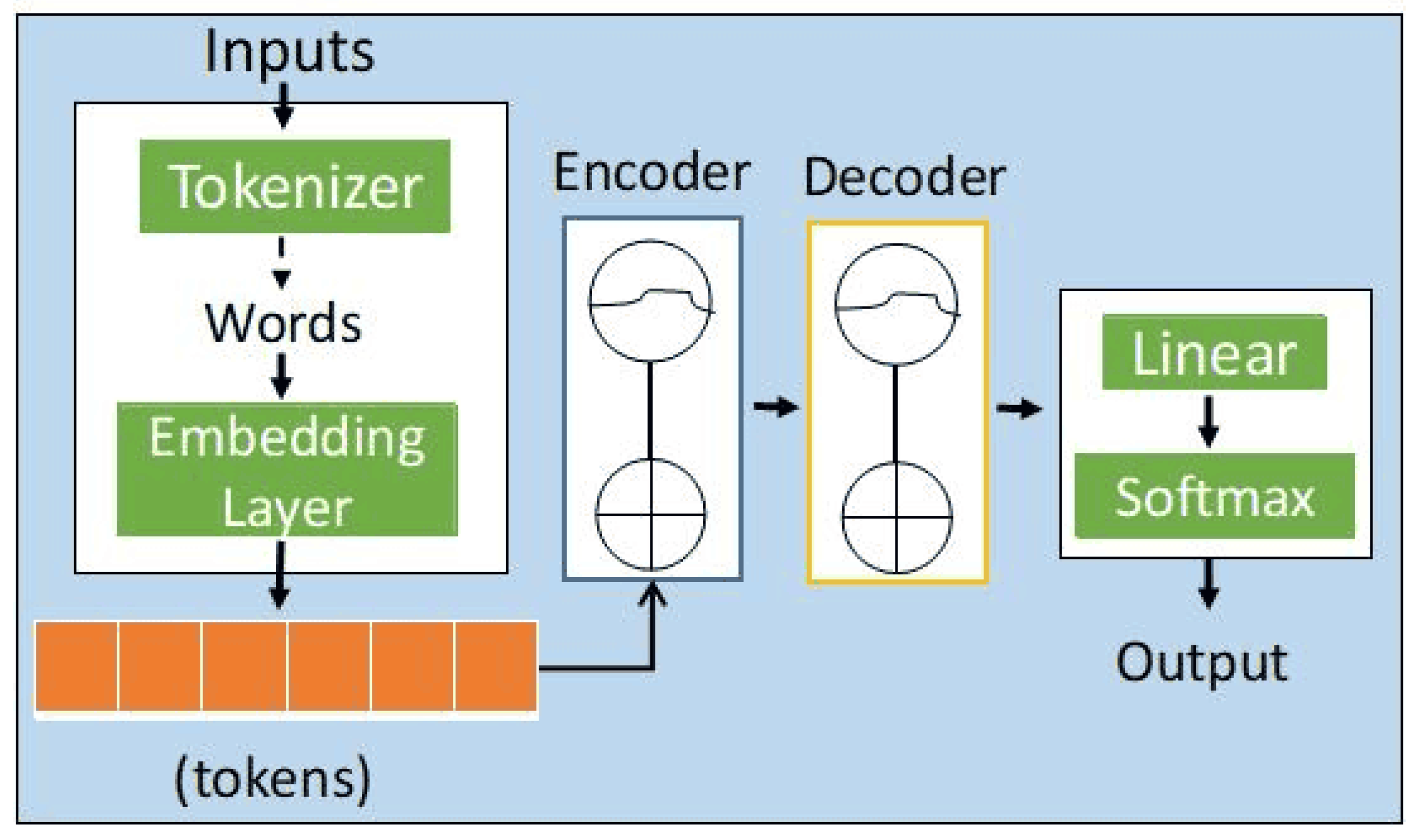
Similarly, the pretraining process of T5 consists of two phases: pretraining and fine-tuning. In the pretraining phase, T5 is trained with a large number of unlabeled text data to learn a generalized text representation, and the process is shown in Figure 2. In contrast to other models, T5 uses a paradigm called “Text-to-Text”, where the input is a sequence of text and the output is a transformation or generation of the sequence. This format allows T5 to handle various NLP tasks in a uniform way. T5 has a similar pretraining process as the BERT model in Algorithm 1. However, unlike BERT, T5 receives the input of text that would be processed in the encoding-and-decoding mechanism in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
T5 model architecture.
In the fine-tuning phase, the pretrained model of T5 is fine-tuned on a specific task, similar to what other pretrained models do. By performing supervised fine-tuning on task-specific datasets, T5 can be adapted to different tasks, thus achieving better performance. The input and output sequences of the T5 model are text sequences consisting of a series of tokens. In the task of generating text, the input sequence is usually a unique start token (e.g., “<start>”) plus a piece of text indicating that the model generates the following textual content on the basis of this piece of text. The input goes through multiple layers of encoders and decoders to obtain the generated results. The encoder is responsible for encoding the input sequence into a contextual representation, whereas the decoder uses the contextual representation to generate the output sequence incrementally.
Specifically, the Transformer model captures the long-distance dependency in the input and output sequences through a self-attention mechanism, allowing it to perform well in the generative text task. In the fine-tuning classification task, the model learns that the output result is either or , indicating the corresponding semantic information comprises the classification of the input problem.
3.3. Legal Provisions and Points for Review of “False” Facts
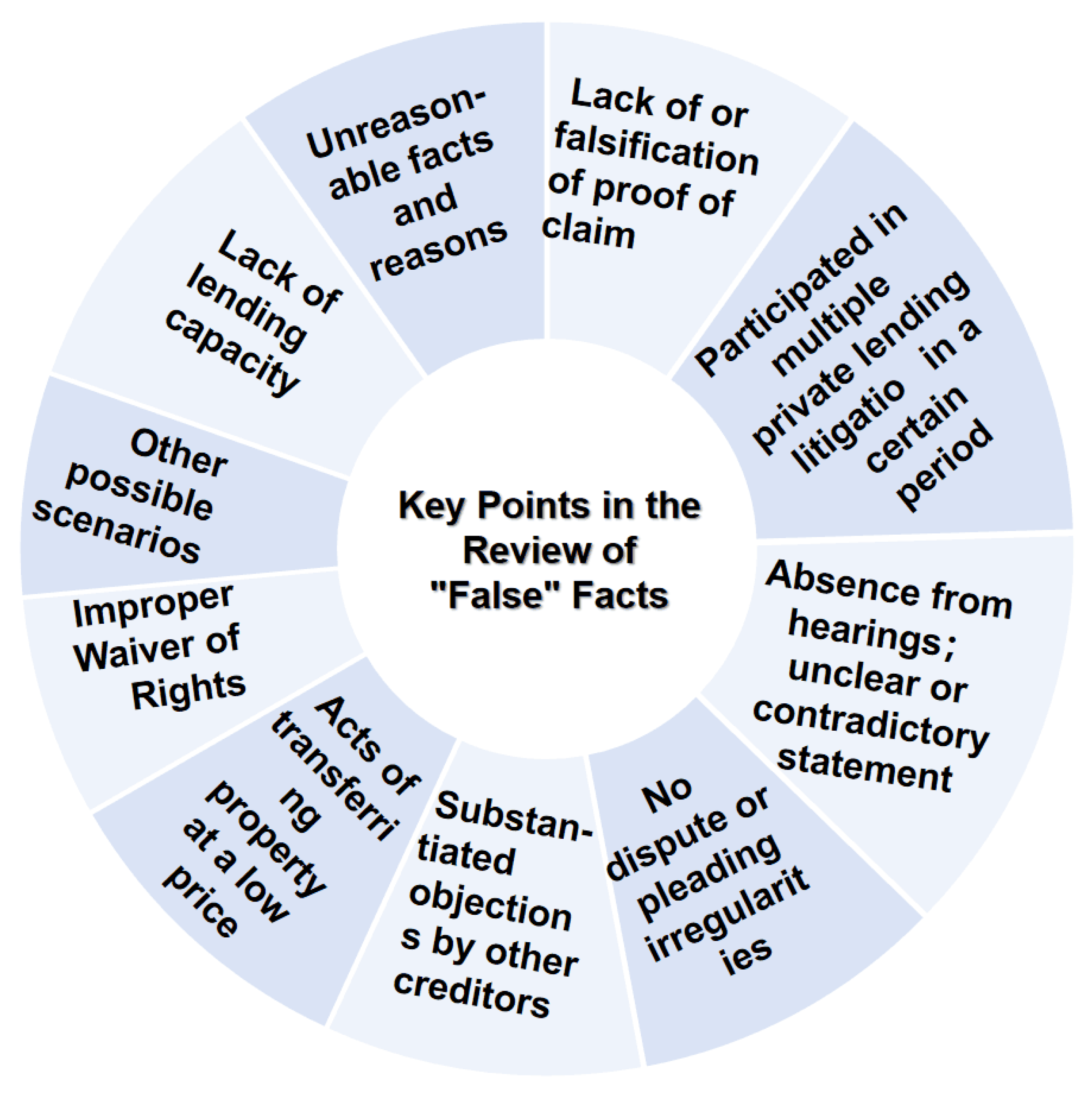
With the increasing adoption of AI in the judicial system, in this paper, we explore a deep learning technique for false fact identification in a social judicial system. Article 18 of the Provisions of the Supreme People’s Court on Several Issues Concerning the Application of Law in the Trial of Private Loan Cases stipulates that if the People’s Court finds one of the following circumstances in the trial of a private loan dispute case, it shall strictly examine the reasons for the occurrence of borrowing and lending. The review considers the time, place, source of money, mode of delivery, direction of money flow, and relationship between the two parties to borrowing and lending and their economic situation. Accordingly, a judge decides whether the civil litigation is false. We present such considerations in Figure 3. Hence, the BERT and T5 models have the ability to identify these words and their relationships; otherwise, identification becomes difficult.
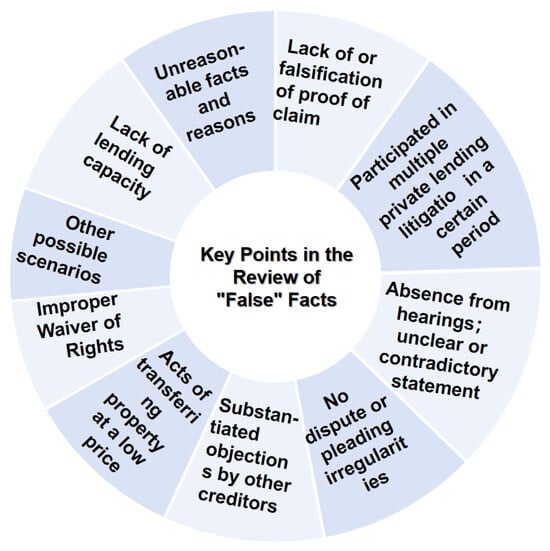
Figure 3.
The key points in the review of “false” facts.
In other countries and regions, false statements to government departments are often characterized as criminal acts [29]. The determination and identification of false facts in Chinese judicial practice focuses on the identification of false litigation rights: the identification and proof of the facts in dispute between the parties in the litigation [30]. In judicial practice, the penetrating trial method is emphasized for private lending cases through penetrating trial thinking to determine the real meaning of the parties and explores the real legal relationship. Its primary task is to restore the legal facts so that the rights and interests of real right holders can be fully protected and substantive justice can be achieved [31]. Hence, we focus on five levels of facts: the subject of the loan, the loan’s agreement, the loan’s delivery, the loan’s repayment, and special matters. In determining whether the essential facts of borrowing are “false”, it is necessary to conduct an authenticity determination on the transaction practices of private lending, the actual use of funds, and even the intensity of court defense [32].
3.4. Recognition of “False” Facts via Deep Learning
Fact determination is the starting point of judicial decision-making [33]. With the penetration of AI in the judicial field, the intelligence of civil litigation fact determination has become a problem worth studying. Its basic principle is that machines with knowledge of fact determination make legal and logical judgments on civil evidence, thereby automatically identifying the facts of the case [34].
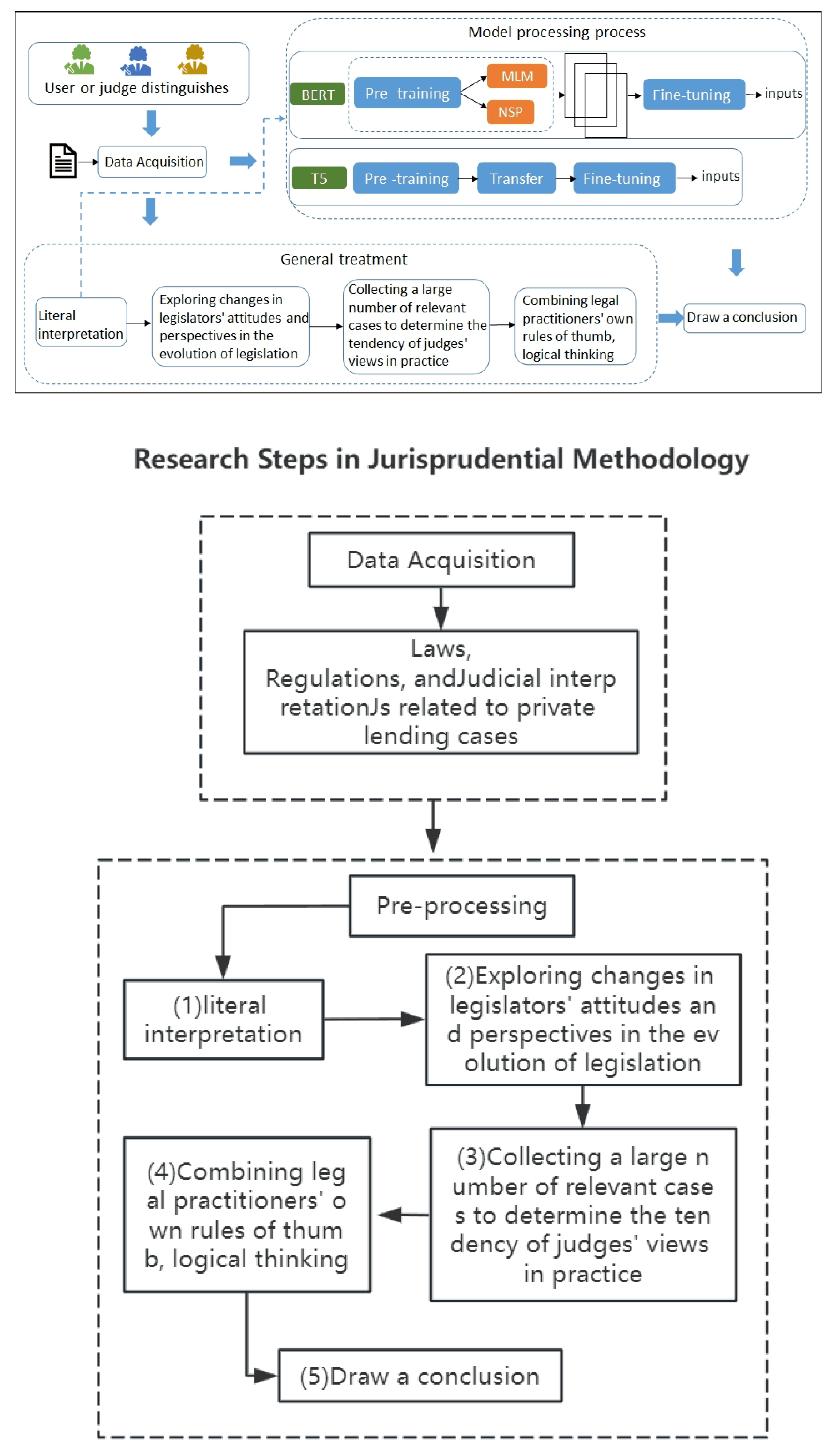
The T5 model is suitable for addressing scenarios containing multiple tasks within specific samples for each task, entirely using the data and fine-tuning the same model with different cue words. The implementation steps of using the T5 model to analyze the legal text of “false facts” in private lending cases can be divided into data acquisition, legal text preprocessing, and model training. We adapt both the BERT and T5 models in the determination process, as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
The recognition process for “false” facts.
The first step is to build a fact-finding streaming database and knowledge base. Considering the model training and training costs, we used three datasets with different text lengths in the experiments. The sample data were selected from real-world open data resources in Chinese from 2020 to 2023. We extracted the “false facts” from more than one hundred specific judgment documents and studied the critical factors in the judgment documents that can assist in determining whether they were “false facts”. Second, in terms of text preprocessing, we made the most direct textual evaluation of the legal text [35] and traced it back along a historical line to determine the changes in the legislator’s attitudes and viewpoints from the changes in the words and phrases in the legal text. We collected a large number of relevant cases for empirical analyses and determined the tendency of judges’ viewpoints in practice. Finally, we drew conclusions by combining the rules of thumb with logical thinking of the legal practitioners themselves.
We further elaborate how the T5 model identifies false facts in the judicial process. In the pretraining phase, the T5 model learns linguistic patterns, semantic associations, and textual representations from a large amount of textual data through large-scale unsupervised learning, which enables the T5 model to understand natural language to a certain extent and capture the semantic relationships between texts. In the fine-tuning phase, the T5 model performs supervised learning on legal text-related tasks end-to-end. Both the inputs and outputs are constructed as text-sequence questions. For classification problems, the outputs are constructed as “yes” and “no”, and the model is then asked to predict the outputs on the questions. Specifically, “fact” is a word in the legal text, whereas “fact” in the judgment document is presented as a specific fact found by the trial. The two are classified with different labels for the model to learn, enabling the model to understand their different semantics according to the context. After learning many mapping relationships between the inputs and outputs, the model can automatically extract the features of the input legal text and generate “yes” or “no” conclusions—the intelligent judgment of generative “false facts.”
4. Experimental Results
In this section, we first conduct a text analysis of the statement and then present the experimental results of the BERT and T5 model comparisons. The BERT implementation follows the codes (https://github.com/sleepingcat4/bert-textgeneration (accessed on 20 August 2024)) whereas the T5 model adapts the implementation (https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer (accessed on 20 August 2024)).
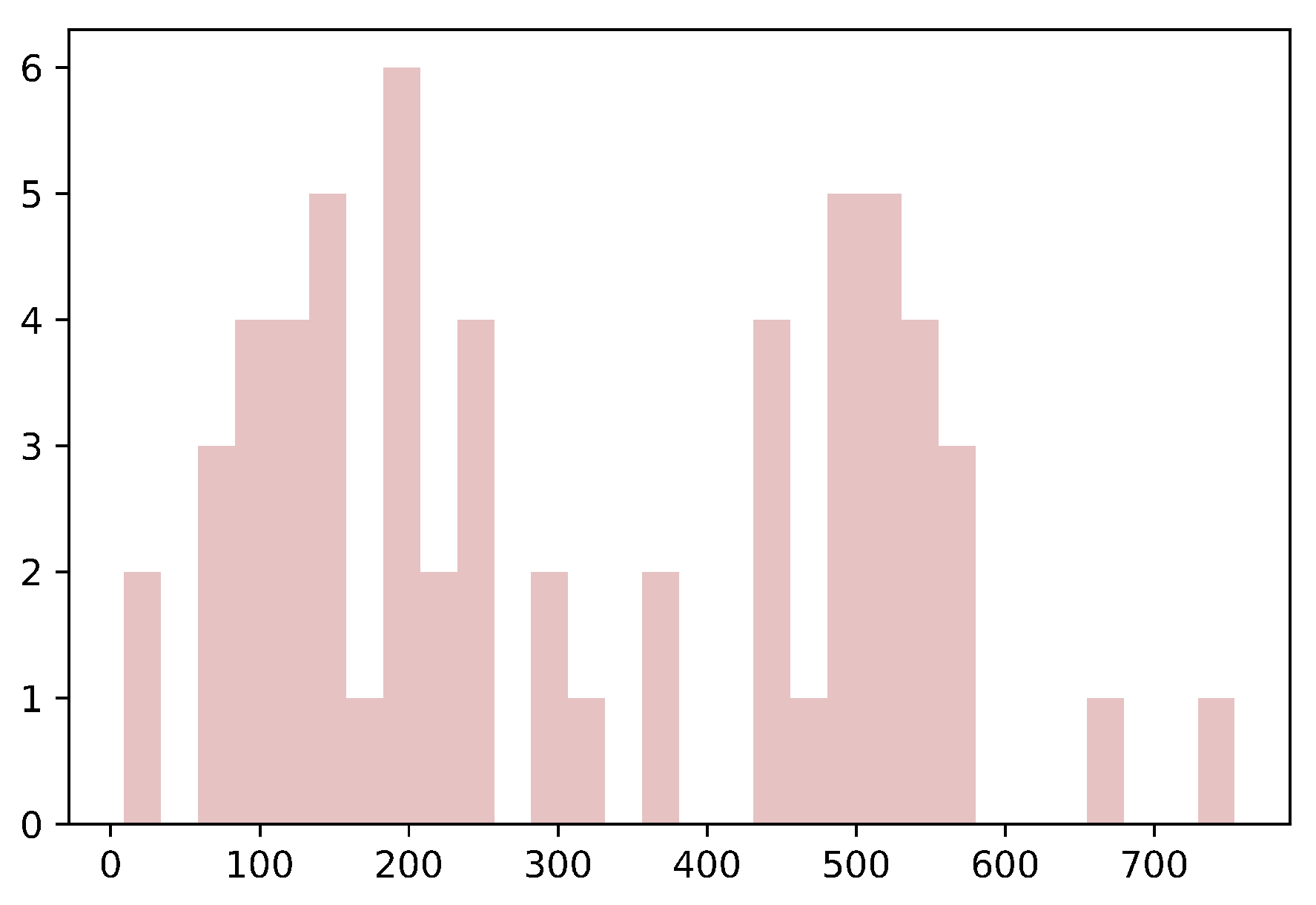
4.1. Text Length Distribution Map
Calculating the distribution of text length can help us better understand the characteristics of the original text data. Understanding the distribution of the text length, such as the average, most extended, and shortest, is helpful for appropriate data preprocessing and cleaning. In the generation task, it may be necessary to truncate or fill in the text to achieve similar lengths for deep learning model training and processing. Moreover, in the generation task, the text length is an important indicator for evaluating the quality of the generated results [36]. If the length of the generated text significantly deviates from the length distribution of the original data, it may indicate a problem with the model or require further optimization [37]. Therefore, the text length distribution can be used to evaluate the performance and effectiveness of the generated model. We conducted the analysis of the input of the text length and noticed that nearly one-third of the text lengths fell between 400 and 600, and most of them were distributed between 100 and 250. We show the results in Figure 5. Accordingly we chose a staging scheme of 128 or 512. Without considering the performance and accuracy, we selected the truncation scheme with the highest accuracy.
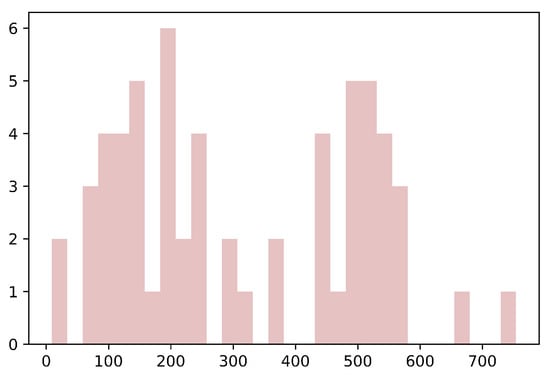
Figure 5.
The text length distribution in the dataset.
4.2. Word Cloud Diagram
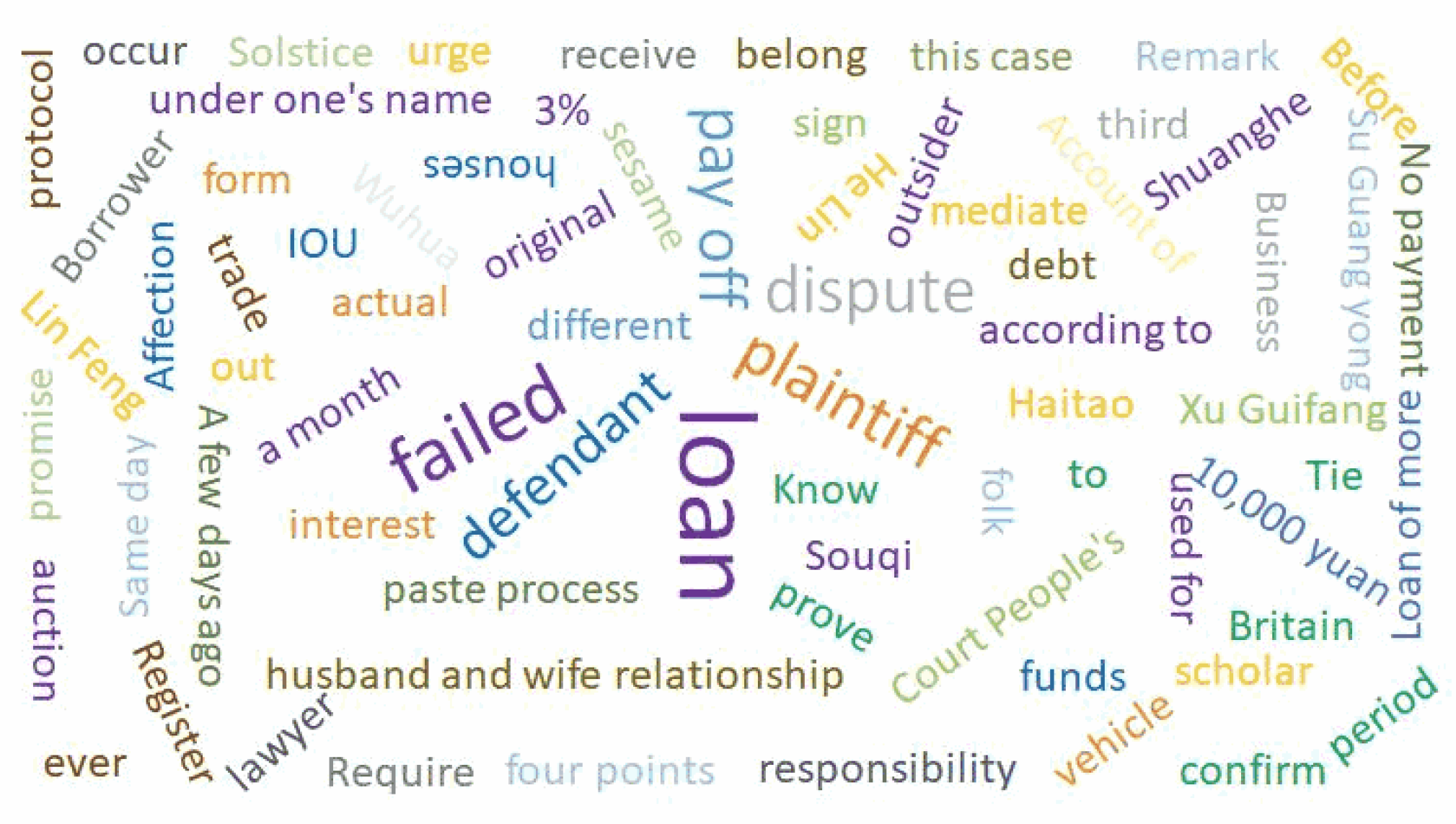
A word cloud graphically displays keywords in text data on the frequency or importance of words. In the word cloud diagram, words that appear more frequently are displayed in larger fonts, whereas words that appear less frequently are displayed in smaller fonts, thus intuitively reflecting the importance and distribution of words in the text data [38]. This visualization method is often used to analyze text data and can quickly comprehend the topics, keywords, and frequently occurring words of the text.
For the training test text, the vocabulary frequency is counted, and a word cloud map is created to present the importance and frequency of words in a visual way, which can intuitively highlight the keywords or famous words in the legal text and help in comprehending its main body and core content. As shown in Figure 6, the keywords highlighted in the text include plaintiff, defendant, borrowing, transferring cash payments, monthly interest, annual interest, etc. We adopted these keywords when testing traditional machine learning techniques that require the inputs of associated features.

Figure 6.
The word cloud map of the training test text.
4.3. Performance Comparison
The previous keyword and text analysis provides a good basis for using traditional machine learning approaches to conduct “false fact” identification. Keywords naturally become features/attributes in machine learning models. To test the strength of traditional machine learning, we adopted a naive Bayesian model [39] in the first experiment. We trained the model with 70% of the total data while testing it through the remaining data. The model could achieve a low identification accuracy. In addition, the results depended greatly on the input features, which is similarly shown in BERT and T5 below. These results are not surprising since the features are considered separately in the model. The model cannot truly understand their relationships, which is very important in the logical investigation of judicial cases. This is exactly what motivates the application of deep learning-based approaches in this research. Hence, we demonstrate the ability of BERT and T5 in the experiments below.
4.3.1. Impact of Different Sentence Lengths on the Prediction Accuracy
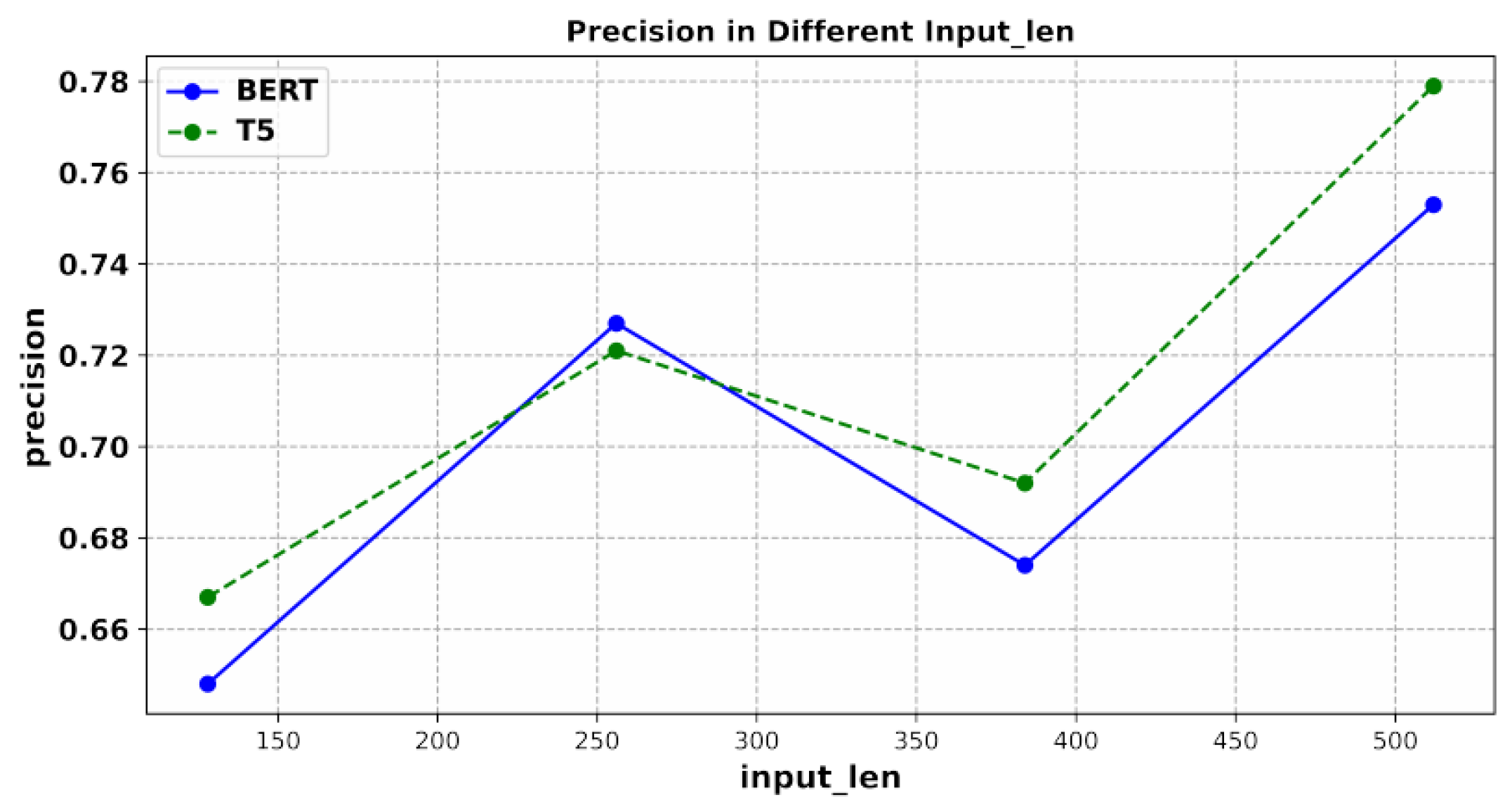
This comparison experiment focuses on testing the changes in the classification accuracy of the BERT and T5 models. With the sentences of different lengths, we intercepted four text lengths of 128, 256, 384, and 512 according to the original text length for experiments, as shown in Table 1. With the change in the input length, we compared the accuracy of the BERT and T5 models in the test set under the different lengths of the restricted input sentences, as shown in Figure 7.

Table 1.
Test text with different lengths.

Figure 7.
The accuracy of BERT and T5 on the test text with different sentence lengths.
According to the experimental results, the sensitivities of the BERT and T5 models to the length of the sentence are similar. With the addition of the information that the sentence can provide (in the case of insufficient sentence length, there is also a lack of original information, which can also reflect that the side of the model has a particular understanding of sentence semantics), the accuracy of the test text gradually increases. However, the accuracy decreases when the length is 384. This is expected since insufficient training data with such long sentences do not provide enough information in the classification. Generally, the T5 model is better than the BERT model, especially in the case of long sentences. This may be because T5 can use different prompt words to train the same model at the same time, and make better use of very limited data information. Moreover, T5 addresses the entire sentence and can exploit the hidden relationships among different keywords. In contrast, the BERT model separates the keywords and their relationships can be easily lost when more confusing words appear.
4.3.2. The Impact of Different Prompt Words on Accuracy
Cue words are the starting point of the text generation task, and they set the topic, direction, or constraints for the generated text. With the cue words, the model can be explicitly told what type of text should be generated, e.g., writing a poem, writing a story, or answering a question. In a text generation task, the cue words can guide the model to generate relevant content [40]. The model determines the content of the generated text on the basis of the semantic and contextual information. This ensures that the generated results are associated with the cue words. For long text generation tasks, gradually providing cue words can increase the consistency of the text. With the gradual introduction of new cue words, the model can articulate the subsequent text according to the previous content in the generation process, making the generated text more coherent. Moreover, cue words can help resolve ambiguities, and sometimes, models may face ambiguous situations in the text generation tasks. By using cue words in multitask learning, the model can focus more on the characteristics of different tasks, improving the model’s generalization performance across tasks. The cue words provide additional information that helps the model distinguish the differences between tasks, allowing the model to better adapt to the characteristics of individual tasks. In multitask learning, if there are similarities between multiple tasks, the same input can be used, and different tasks can be specified with different cue words. By doing so, we can reduce the need for labeled data and increase data utilization efficiency. This also determines that text generation can fully utilize the data and better understand the task in scenarios with multiple tasks and limited data.
In the experiments, we set up different cue words to prompt the model for the task to be processed in the training and testing phases. To maintain fairness, we added the cue words into the BERT model to help understand the information. We present the experimental results in Table 2. When the prompt words were “whether it is determined to be a false lawsuit” and “whether there is a real lending relationship”, the T5 model was significantly better than BERT in terms of prediction accuracy. T5 took advantage of the prompt words to further optimize the prediction accuracy. When the prompt word was empty, BERT could give full play to the advantages of its own prediction and outperformed T5. This finding demonstrates that T5 can better utilize prior information and optimize for specific tasks with the help of prompt words. Moreover, it shows the powerful ability of BERT itself in reasoning tasks.

Table 2.
The accuracy of BERT and T5 on the test set for different prompt words.
4.3.3. Loss Curve Change Chart Analysis
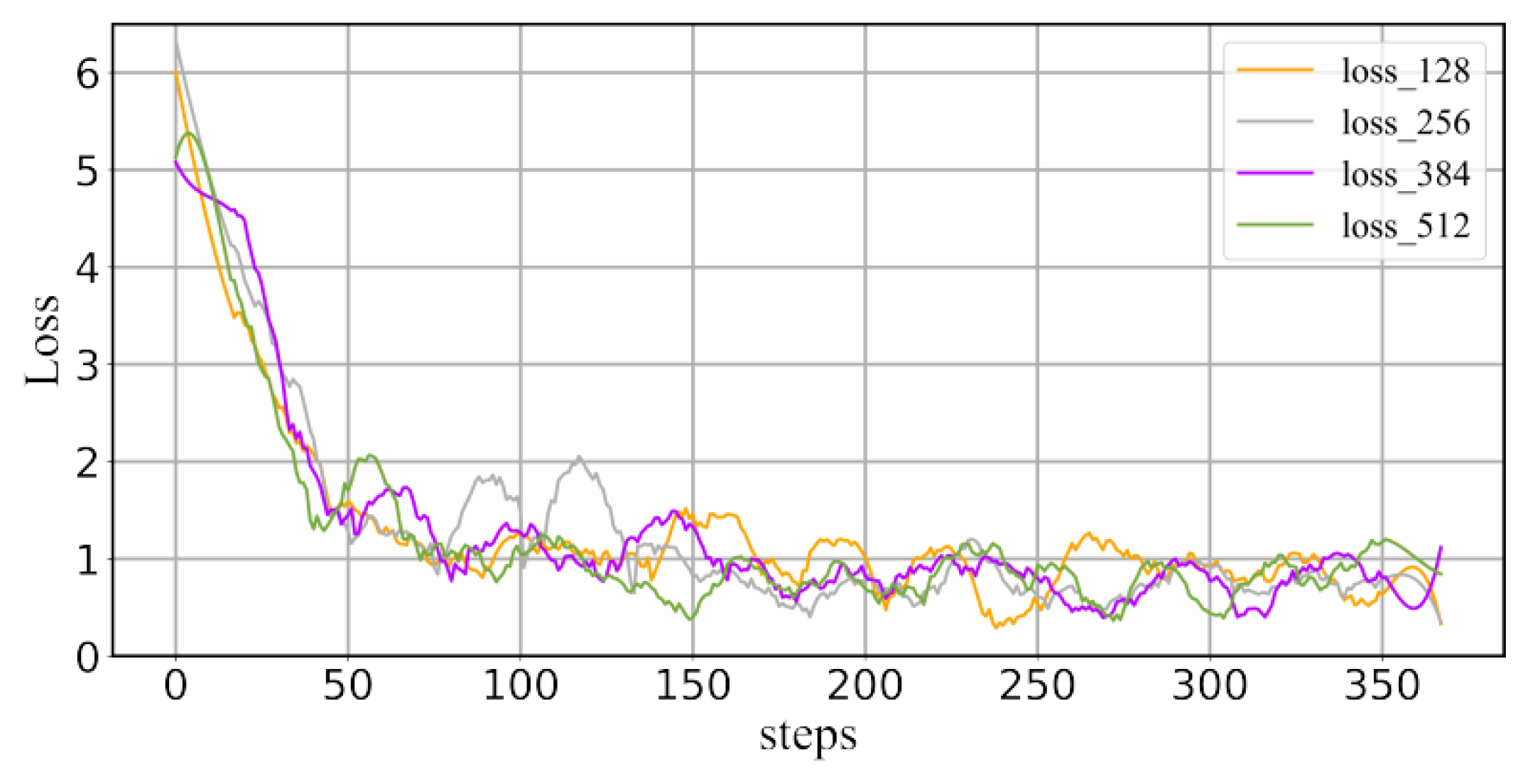
We analyzed the convergence speed of the loss function in the generation task at the end of training by examining the loss curves. The four curves in Figure 8 correspond to different lengths of the T5 loss-constrained text. We observed that the model’s loss decreased rapidly in the initial stages, stabilizing dynamically around the 100th step. However, it is worth noting that the loss of the generative model somewhat fluctuated, showing an overall downward trend and eventually converging to a fixed range. The loss curve trends of different lengths of text were similar, indicating that the model has a certain degree of robustness to the text length. Additionally, training could be terminated early at approximately the 200th step. Hence, we can consider ending the training early to prevent overfitting.
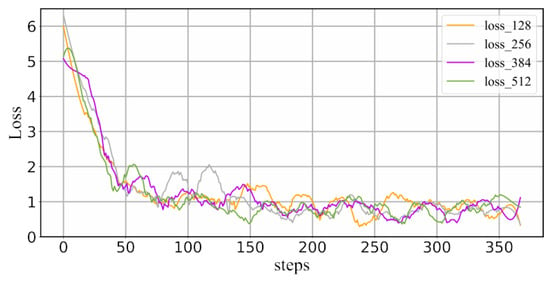
Figure 8.
The loss curves of the T5 model under different text lengths.
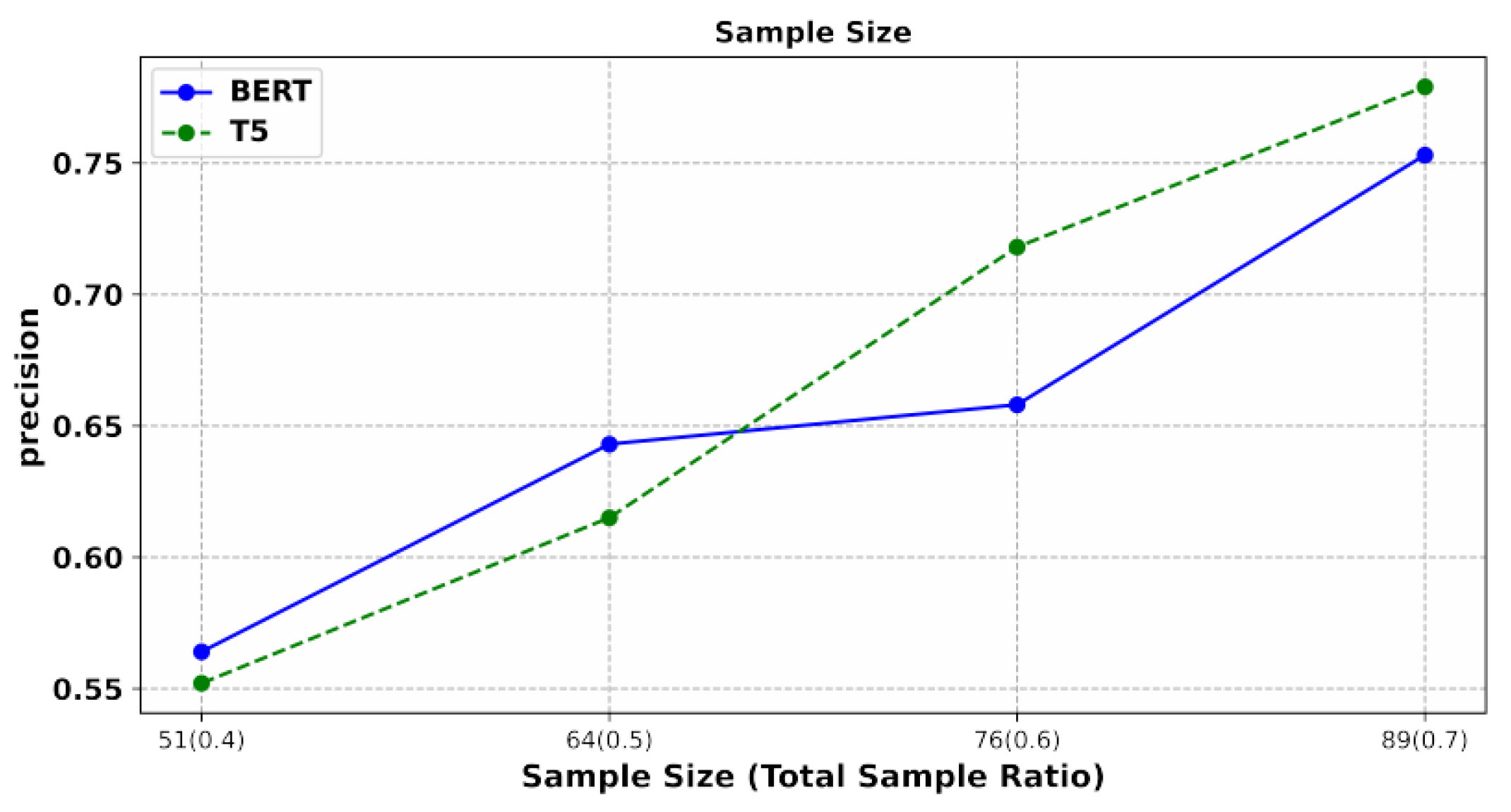
4.3.4. Effect of Sample Size on Accuracy
Under consistent parameter settings where the test sample is controlled at 30% of the total data, we adjusted the proportion of training samples. The x-axis represents the increasing number of training samples, with the proportion of this quantity to the total number of samples indicated in parentheses. The axes denote the classification accuracy of the test data. We show the experimental results in Figure 9. The results demonstrate a clear upward trend in the classification performance of both the T5 and BERT models as the dataset size increased.
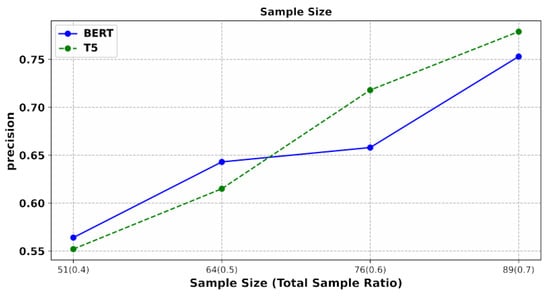
Figure 9.
The impact of different sample sizes on the classification accuracy.
Notably, with an increasing sample size, T5 achieves a superior classification accuracy. This highlights that insufficient training data directly impact classification effectiveness [41]. Currently, with just over one hundred data points, an accuracy of over 70% can be achieved. With a more comprehensive dataset, even higher accuracy rates can be attained [42]. This, in turn, suggests the potential to replace manual labor with automated processes, which will significantly reduce the labor cost.
4.4. Potential Engineering Applications
On the basis of the T5 model, we can implement a “false fact” identification system. The system includes modules for data crawling, text preprocessing, model training, and deployment. The frontend provides user interfaces for users to input case text. The back-end server handles model prediction and returns results. The system extracts key elements from the input text, generates “yes/no” conclusions of “false facts”, and highlights related pieces of evidence. The system can be integrated into a local court’s assisted judgment system. The statistical data show that the system flags key misleading claims and falsified evidence in most false litigation cases. Automating tedious screening work enables judges to focus more on in-depth trials and controversial cases. Significant labor cost savings could be achieved. The system provides strong technical support for penetrating trials of private loans, and prevents judgments from being misguided by concealment.
While there is considerable potential for adopting deep-learning-based “false fact” identification systems, we can perceive a number of challenges ahead. First, as we showed in the experiments, data do matter. This is particularly challenging in a judicial system since most cases are private and require ethical considerations in the application. To deploy such a legal AI system, how judicial data are maintained in a secured environment, and how learning techniques can cope with the partial information in the data, should be investigated. This may benefit from keyword analysis, in which we exploit useful, short sentences instead of entire ones. Second, we recognize the diversity of judicial cases/rules in a global environment. Generalizing the applications needs to explore sentence variations, including semantic relations, length, and so on. With the growing capability of deep learning techniques, there is a good chance to train models through heterogeneous sources, including different linguistics, cultures, and adjudications. Finally, we may explore the potential of large language models (LLMs) in a judicial system. LLMs could be natural assistants in decision support since they provide good question and answer styles. In addition, we may retrieve knowledge from available LLMs on which the BERT and T5 models can be sufficiently trained. However, it is still debatable whether LLMs could be trusted in a serious application.
5. Conclusions and Future Work
With the increasing adoption of AI in judicial systems, we explored data-driven techniques, particularly through the BERT and T5 models, to identify false facts in loan cases to reduce the judicial workload. In response to the unclear references and technical ambiguities of legal texts related to factual determinations in private lending, the T5 model was used to mine the legal texts and explore key element features in depth, thereby improving an understanding of uncertain legal concepts and legal ambiguities. At the same time, the ambiguities, evaluations, and search costs of legal practitioners were effectively reduced, providing a reference basis for legal research and judicial practice. In this work, we tested a “false fact” labeling system based on the T5 pretrained model; however, in the development and practice process, there are some areas for improvement. In future work, we will attempt to use generative models to address some classic legal problems, such as the Trolley problem and the case of Speluncean explorers, based on the empirical effects of the generative models. This work requires large-scale judicial data and pretrained models. We expect to exploit more knowledge from LLMs and investigate whether they could facilitate the T5 training process.
Author Contributions
Y.Z. developed the idea, initial draft and finalization. J.C. (Jiepin Chen) conducted the literature review and data collection. J.C. (Jiebin Cai) implemented the algorithms and analyzed the results. M.Z. implemented the algorithms. Y.P. refined the idea and polished the draft. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Guangdong Philosophy and Social 374 Science Planning Project: GD23XFX06.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This paper is part of the phase-in results of the Guangdong Philosophy and Social Science Planning Project “Trial Management Reform and Response under the Perspective of Digital Governance: A Study Based on the Practice in Guangdong” in 2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Todd, G.; Earle, S.; Nasir, M.U.; Green, M.C.; Togelius, J. Level Generation Through Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on the Foundations of Digital Games, Lisbon, Portugal, 11–14 April 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Zeng, Y.; Ma, B.; Pan, Y. Improving Knowledge Learning Through Modelling Students’Practice-Based Cognitive Processes. Cogn. Comput. 2024, 16, 348–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Fan, J.; Bekkering, E. MDFC–ResNet: An agricultural IoT system to accurately recognize crop diseases. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 115287–115298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cranford, E.A.; Ou, H.; Gonzalez, C.; Tambe, M.; Lebiere, C. Accounting for Uncertainty in Deceptive Signaling for Cybersecurity. In Proceedings of the 56th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, HICSS 2023, Maui, HI, USA, 3–6 January 2023; pp. 876–885. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X. The construction of legal knowledge graph for the application of artificial intelligence in civil justice: Based on the theory of factual civil judgment. Leg. Syst. Soc. 2018, 24, 66–80. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J. The procedural law dilemma and solution of Internet courts. Leg. Sci. (J. Northwest Univ. Political Sci. Law) 2021, 39, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, X. Typology of judicial measurement of the cost of private lending. J. Law Appl. 2022, 11, 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J. On the civil procedure regulation of unilateral false litigation. Mod. Law 2023, 45, 33–48. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, Y.; Liang, Z. Identification and regulation of false litigation—A study centered on judgment documents. J. Natl. Inst. Prosec. 2018, 26, 158–169+175. [Google Scholar]
- Black, N. The Case for ChatGPT: Why Lawyers Should Embrace AI. 2023. Available online: https://www.abajournal.com (accessed on 30 June 2023).
- Bench-Capon, T. Hypo’s legacy: Introduction to the virtual special issue. Artif. Intell. Law 2017, 25, 205–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.; Lee, K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2021, 21, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Lipton, Z.C.; Berkowitz, J.; Elkan, C. A critical review of recurrent neural networks for sequence learning. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1506.00019. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, M.; Chen, Q.; Yan, S. Network in network. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.4400. [Google Scholar]
- Gui, T.; Xi, Z.; Zheng, R. A review of robustness research in natural language processing based on deep learning. J. Comput. Sci. 2023, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, M.; Liu, Y.; Goyal, N. BART: Denoising Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training for Natural Language Generation, Translation, and Comprehension. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 5–10 July 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.; Sreenan, C.J.; Sitanayah, L.; Xiong, N.; Park, J.H.; Zheng, G. An emergency-adaptive routing scheme for wireless sensor networks for building fire hazard monitoring. Sensors 2010, 10, 6128–6148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, A.B.; Kumar, S.M.; Chacko, A.M. A systematic survey on explainable AI applied to fake news detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 122, 106087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlund, O.; Larsen, R.; Graves, L.; Kavtaradze, L.; Steensen, S. Technologies and Fact-Checking. A Sociotechnical Mapping. In Disinformations Studies: Perspectives from An Emerging Field; Universidade da Beira Interior: Covilhã, Portugal, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Z.; Schlichtkrull, M.; Vlachos, A. A Survey on Automated Fact-Checking. Trans. Assoc. Comput. Linguist. 2022, 10, 178–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.; Oswald, M. Assurance of Third-Party AI Systems for UK National Security: Research Report; The Alan Turing Institute: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J. A Hybrid GCN and LSTM Structure Based on Attention Mechanism for Crime Prediction. Converter 2021, 2021, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robaldo, L.; Villata, S.; Wyner, A.; Grabmair, M. Introduction for Artificial Intelligence and law: Special issue “natural language processing for legal texts”. Artif. Intell. Law 2019, 27, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalkidis, I.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Aletras, N. Neural legal judgment prediction in English. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.02059. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Wang, M. Design of intelligent legal text analysis and information retrieval system based on BERT model. Preprint 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, Z.; Ma, W.; Cui, Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, S.; Liu, T.; Huo, T.; Hu, Z.; et al. CJRC: A Reliable Human-Annotated Benchmark DataSet for Chinese Judicial Reading Comprehension. In Chinese Computational Linguistics; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, U.; Razzak, I.; Vishwakarma, S.; Hacid, H.; Zhang, D.; Jameel, S. BayesJudge: Bayesian Kernel Language Modelling with Confidence Uncertainty in Legal Judgment Prediction. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2404.10481. [Google Scholar]
- Rickeman, A.; Hagood, I.; Lewis, E. False Statements and False Claims. Am. Crim. Law Rev. 2022, 59, 793. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, D. On the definition and regulation of false litigation—Also on the coordination of criminal and civil procedures for regulating false litigation. Law Sci. 2016, 11, 136–144. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z. Application rules and boundary determination of penetrating trial thinking—Based on the theory of essential facts to outline the three-step and seven-step penetration method. J. Shandong Judges Train. Coll. 2022, 38, 126–135. [Google Scholar]
- Griffith, E. Searching for the truth in lending. Bayl. Law Rev. 2000, 52, 275. [Google Scholar]
- Long, K. Legal regulation research on the anomalies of generative artificial intelligence applications: From the perspective of Chat GPT and social robots. Orient. Law 2023, 4, 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q. Intelligence of fact determination in civil litigation. Contemp. Law 2021, 35, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, S. Interaction-Guided Joint Abstractive QAPs Generation Model. Chin. J. Comput. 2023, 47, 251–265. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, N.; Han, W.; Vandenberg, A. Green cloud computing schemes based on networks: A survey. IET Commun. 2012, 6, 3294–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jin, C.; Tang, Q.; Xiong, N.N.; Srivastava, G. Intelligent ubiquitous network accessibility for wireless-powered MEC in UAV-assisted B5G. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 2801–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattenberg, M.; Viegas, F. Tag clouds and the case for vernacular visualization. Interactions 2008, 15, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3rd ed.; Prentice Hall Press: Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, W.; Ding, Y.; Xiong, N. Computation offloading optimization for UAV-assisted mobile edge computing: A deep deterministic policy gradient approach. Wirel. Netw. 2021, 27, 2991–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Chen, R.S.; Xiong, N.; Chen, Y.C.; Hu, Y.X.; Chen, C.M. Selecting hyper-parameters of Gaussian process regression based on non-inertial particle swarm optimization in the Internet of Things. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 59504–59513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Xiong, N.; Vasilakos, A. A bare-metal and asymmetric partitioning approach to client virtualization. IEEE Trans. Serv. Comput. 2012, 7, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).