Abstract
With the rapid development of quantum computers, post-quantum cryptography (PQC) has become critical technology in the security field. PQC includes cryptographic techniques that are secure against quantum-computer-based attacks, utilizing methods such as code-based, isogeny-based, and lattice-based approaches. Among these, lattice-based cryptography is the most extensively studied due to its ease of implementation and efficiency. As quantum computing advances, the need for secure communication protocols that can withstand quantum computer-based threats becomes increasingly important. Traditional two-party AKE protocols have a significant limitation: the security of the entire system can be compromised if either of the communicating parties behaves maliciously. To overcome this limitation, researchers have proposed three-party AKE protocols, where a third party acts as an arbiter or verifier. However, we found that a recently proposed three-party AKE protocol is vulnerable to quantum-computer-based attacks. To address this issue, we propose a provably quantum secure three-party AKE protocol based on MLWE. The proposed scheme leverages the user’s biometric information and the server’s master key to prevent the exposure of critical parameters. We analyzed the security of the protocol using simulation tools such as the Burrows–Abadi–Needham (BAN) logic, Real-or-Random (RoR) model, and Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and Applications (AVISPA). Furthermore, comparative analysis with similar protocols demonstrates that our protocol is efficient and suitable.
1. Introduction
With the rapid advancement of quantum computing, the security of traditional cryptographic systems is increasingly under threat. The security of widely used cryptographic algorithms, such as Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA) and elliptic curve cryptography (ECC), largely relies on the difficulty of the factorization problem (FP) [1] and the discrete logarithm problem (DLP) [2]. However, as demonstrated by Shor [3] and Grover [4], both FP and DLP can be solved in polynomial time by quantum computers. This development makes the foundational mathematical problems underlying RSA and ECC vulnerable to quantum-based attacks. In response to this emerging threat, extensive research has been conducted on post-quantum cryptography (PQC), which aims to develop cryptographic methods resilient to quantum attacks [5,6,7,8,9].
There are several approaches, such as multivariate-based [5], hash-based [6], code-based [7], isogeny-based methods [8], and lattice-based [9], to defend these attacks. Lattice-based cryptography algorithms, first proposed by Ajtai in 1996 [10], are built on complex mathematical problems defined within a lattice. Notable advantages of these lattice-based algorithms are easy to implement, efficient in computation, and suitable for lightweight devices, because all operations can be executed using matrix multiplications and additions.
PQC is gaining attention in the research of three-party authentication and key exchange (AKE) protocols. While current three-party AKE schemes may resist classical attacks, they remain vulnerable to quantum-based threats. Unlike two-party AKE, which assumes honest behavior from both participants, three-party AKE protocols introduce a third party as a mediator, enhancing system reliability and reducing the risk of data leaks. Mutual authentication among all three parties is essential to prevent malicious impersonation and data manipulation, ensuring secure and trustworthy communication. However, many existing quantum-secure three-party AKE protocols still face performance and security challenges.
One popular cryptosystem used in three-party authentication and key exchange protocols is the lattice-based encryption algorithm learning with error (LWE). LWE is considered more secure than other cryptosystems because it relies on a worst-case hardness assumption, which greatly improves security. In 2009, Regev [11] was the first to propose using LWE problems to design public-key cryptosystems. However, LWE has the disadvantage of incurring a high overhead. In 2010, Lyubashevsky et al. [12] introduced the concept of ideal lattices and proposed ring-LWE (RLWE) based on it. RLWE is based on the worst-case intractability of the ideal lattice and allows for a more efficient implementation of public-key cryptosystems. However, RLWE is generally considered to be less secure than LWE. To address this, in 2015, Langlois et al. [13] proposed modular-LWE (MLWE), which combines the strengths of LWE and RLWE. MLWE has lower overhead compared to LWE and higher security compared to RLWE by introducing rings while maintaining the matrix structure. In addition, MLWE has flexible parameterization that can be adapted to different security levels by modifying the matrix size. Therefore, we conducted research on three-party AKE protocols with a focus on MLWE schemes that combine the strengths of LWE and RLWE.
While researching MLWE-based three-party AKE protocols, we came across a paper by Guo et al. in 2023 [14]. Guo et al. presented a three-party AKE protocol based on MLWE and claimed that their scheme is secure, efficient, and mutually authentic. However, we found that the scheme is vulnerable to replay attacks, user and server impersonation, authentication table leaks, insider attacks, and DoS attacks. In addition, mutual authentication was not fully guaranteed. Their scheme used a password-based AKE scheme. In this paper, we analyze which attacks Guo et al.’s scheme is vulnerable to and propose a three-factor AKE scheme that uses the user’s biometric information to improve the security and efficiency of the scheme.
1.1. Contribution
- We identified that the authentication and key exchange scheme proposed by Guo et al. exhibits correctness issues and security vulnerabilities, particularly in the mutual authentication process. To address these challenges, we propose a three-party authentication and key exchange scheme based on MLWE that incorporates biometric data.
- We provide a formal proof of the security and robustness of the proposed scheme using BAN logic, the Real-or-Random (RoR) model, and Automated Validation of Internet Security Protocols and Applications (AVISPA). Moreover, we demonstrate that the scheme is secure against various attacks, including insider, impersonation, replay, and man-in-the-middle attacks. Furthermore, we establish that our scheme ensures mutual authentication.
- We evaluate the security features and computational costs of the proposed scheme. Through comparative analysis, we demonstrate its superiority over the methods proposed by Guo et al. and other related schemes.
1.2. Paper Organization
In Section 2, we review the foundational works on LWE, RLWE, and MLWE, along with related research on public-key cryptography and key exchange protocols based on LWE. In Section 3, we describe MLWE, the mathematical techniques utilized in our proposed scheme, and introduce the error reconciliation scheme, biohash, attacker model, and notation. Next, in Section 4, we revisit the scheme proposed by Guo et al., and in Section 5, we detail the vulnerabilities identified in their scheme. In Section 6, we introduce our proposed scheme, followed by our security analysis using BAN logic, RoR models, and AVISPA tool in Section 7. The performance analysis, which includes security features, communication costs, and computational efficiency, is presented in Section 8. Finally, in Section 9, we conclude the paper and outline future research directions.
2. Related Works
Lattice-based cryptography is a promising field for achieving post-quantum security, particularly due to its reliance on worst-case hardness assumptions, which provide resistance against quantum attacks. In 2009, Regev [11] introduced the LWE problem, which became a foundation for constructing secure public-key cryptographic schemes based on the hardness of lattice problems. In 2010, Lyubashevsky et al. [12] introduced the RLWE problem, which incorporated ideal lattices and algebraic structures to enable more efficient public-key cryptosystems based on worst-case hardness assumptions in ideal lattices. Further advancing this field, Langlois et al. [13] proposed the MLWE problem in 2015, which bridges the gap between LWE and RLWE by combining ring polynomials with matrix structures. MLWE offers lower computational overhead than LWE and greater security compared to RLWE, along with the flexibility to adjust matrix dimensions for different security levels.
Building on these advances in lattice-based cryptography, various researchers have focused on developing practical and secure key exchange protocols, often inspired by the Diffie–Hellman approach, using LWE, RLWE, and their variants. In 2012, Ding et al. [15] introduced the first provably secure key exchange protocol based on the LWE problem, which is both computationally efficient and extendable to the RLWE framework. However, the shared key generated in their scheme is not uniformly random, leading them to recommend the use of an extractor, which unfortunately reduces the effective key length. While the protocol proposed by Ding et al. resembles the Diffie–Hellman key exchange, it does not inherently provide reliability. The key contribution of their work lies in presenting the first LWE and RLWE key exchange frameworks incorporating a novel error reconciliation mechanism. In 2014, Peikert [16] proposed a straightforward, low-bandwidth coordination technique that allows two parties to “roughly agree” on a secret value, ultimately enabling them to reach an exact agreement. However, this method, while grounded in LWE-based cryptographic techniques, is computationally more intensive. Essentially, this approach is a form of key encapsulation and does not guarantee reliability for users. The primary distinction between Ding et al. and Peikert is that the former employs a biased coordination mechanism, whereas the latter utilizes an unbiased one.
Building on the DH-like structures discussed earlier, various researchers have proposed authentication and key exchange schemes to enhance security in different environments. Recently, Wang et al. [17] introduced a quantum-resistant two-factor authentication protocol optimized for mobile devices. Although this protocol is effective, it does introduce some overhead. In 2022, Dharminder et al. [18] proposed a security reconciliation mechanism based on lattice cryptography to facilitate key exchange in Internet of Things (IoT) environments. The following year, Kumar et al. [19] introduced a post-quantum key exchange protocol grounded in RLWE, a variant of lattice-based cryptography. Their protocol supports authenticated key exchange (AKE) with just two message exchanges, significantly enhancing efficiency.
However, all of the aforementioned protocols are two-party AKE schemes, which inherently suffer from certain limitations. In a two-party authentication protocol, two entities, commonly referred to as Alice and Bob, exchange messages to authenticate each other. This setup assumes that both parties will act honestly and securely. However, if either party is compromised or behaves maliciously, the security of the entire system can be jeopardized. This vulnerability underscores the need for a more robust solution. Introducing a third party, typically called Charlie, transforms the process into a three-party AKE protocol. In this setup, Charlie acts as a trusted intermediary, enhancing the overall security of the authentication process by mediating between Alice and Bob. Charlie’s role is critical, as it helps to mitigate risks associated with direct communication between the two parties and provides an additional layer of verification and trust. This added complexity not only strengthens the authentication process but also ensures that even if one party is compromised, the security of the system remains intact [20].
Given the inherent limitations of two-party AKE schemes, recent research has shifted focus towards three-party AKE protocols to enhance security and resilience. In 2023, Chaudhary et al. [21] proposed a three-party key agreement protocol using ECC encryption, providing authentication, anonymity, and forward secrecy. Rewal et al. [22] introduced a lattice-based key establishment protocol that enhances efficiency and resists password guessing but lacks anonymous communication and full three-factor security. Guo et al. [14] proposed a three-party AKE protocol based on MLWE. However, the scheme was found to be vulnerable to attacks such as replay, impersonation, insider, and DoS. In addition, mutual authentication was not fully guaranteed. As a result, designing a secure three-party quantum key agreement protocol that addresses these vulnerabilities remains a significant challenge.
Table 1 summarizes cryptographic technologies and contributions of various authentication schemes using LWE.

Table 1.
Post-quantum key exchange protocols overview.
3. Preliminaries
3.1. Module Learning with Error
The MLWE problem extends the LWE and RLWE problems by introducing a more flexible structure. Specifically, let represent a vector containing d ring polynomials in . Additionally, let denote a matrix of ring polynomials with rank k and dimension d. The MLWE problem generalizes both LWE and RLWE: when the ring is set to , it reduces to the LWE problem, and when , it reduces to the RLWE problem.
In 2015, Langlois and Stehlé [13] introduced the MLWE problem as a compromise between LWE and RLWE. By retaining the matrix format while incorporating algebraic structure, MLWE offers greater flexibility and simplicity in designing lattice-based cryptographic schemes for various security scenarios. The decision version of the MLWE problem is defined as follows:
Definition 1.
(MLWE problem). The MLWE problem is defined with parameters , where n represents the dimension of the vector, q is the modulus, k is the dimension of the polynomial matrix, and η specifies the distribution parameters for the error and the secret. Given these parameters, a polynomial matrix is selected randomly and uniformly. Subsequently, a secret and an error vector are also chosen randomly and uniformly. Using these, the vector is computed.
The MLWE problem then asks one to distinguish between two distributions: one where A and s are chosen uniformly at random and e follows the distribution , and another where A and b are chosen uniformly at random.
Definition 2.
(Decision MLWE problem). The decision MLWE problem involves determining whether a given pair originates from one of two specified distributions: one where for a uniformly chosen secret s and an error e sampled from the distribution , or another where b is uniformly random.
More specifically, given , where and , the decision MLWE problem requires deciding whether comes from the first distribution or whether Y is uniformly random in .
3.2. Reconciliation Mechanism
An error reconciliation mechanism helps ensure that two parties, each holding slightly differing values, can converge on the same final value through a combination of information exchange and computation. In 2014, Peikert introduced an enhanced error reconciliation mechanism, building on the earlier work of Ding. Suppose Alice and Bob possess approximate values and , respectively. To achieve reconciliation, Bob applies a modular rounding function and a cross-rounding function. The output of the modular rounding function serves as the shared key, while the cross-rounding function generates the signal value. The definitions of these two functions are as follows:
Definition 3.
Let q be an even modulus. The modular rounding function is defined as
and the cross-rounding function is defined as
Once Alice receives the signal value from Bob, she generates the shared key using the reconciliation function.
Definition 4.
(The reconciliation function). Given an element and the cross-rounding value of a close element , define the sets and . Let , and the reconciliation function is
3.3. Biohashing
The utilization of a user’s biometric information in an authentication system is an effective method for verifying the identity of the actual user. In 2004, Jin et al. [23] introduced biohashing, a technique that combines pseudorandom numbers with biometric features to enhance security. This approach, particularly in the context of fingerprint data, makes it challenging for an attacker to replicate the biohash code without access to the correct hash key.
- Feature extraction: Biometric data (e.g., a face image) are captured and processed to extract a feature vector . For instance, discrete cosine transform (DCT) coefficients can be utilized as features.
- Pseudo-random vector generation: A secret seed (hash key) K is used to generate a sequence of pseudorandom vectors . These vectors are ensured to be linearly independent. An example of an algorithm that generates such pseudorandom numbers is the Blum–Blum–Shub method.
- Orthonormalization: The generated vectors are transformed into an orthonormal set using the Gram–Schmidt orthonormalization procedure.
- Scalar product and threshold binarization: The inner product between the biometric feature vector x and each orthonormal vector is calculated: . Each result is compared to a threshold to produce a bit:
- BioHash code: The resulting bit vector is the BioHash code, which is unique to the user’s biometric data and the hash key.
- Matching: During authentication, the BioHash code is compared using Hamming distance for similarity matching.
3.4. Adversary Model
The adversary’s capabilities are defined based on the “Dolev–Yao (DY) model” [24], which is commonly used for protocol security analysis [25,26]. The adversary is assumed to possess the following abilities:
- The adversary can eavesdrop on, intercept, modify, delete, and fabricate messages transmitted over public channels.
- The adversary can make educated guesses regarding either the legitimate user’s identity or password but cannot correctly guess both at the same time.
- The adversary can launch various attacks, including impersonation, replay, and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- The adversary may also operate as an insider within the system.
3.5. Notations
Table 2 provides the symbols and their descriptions used throughout this paper.

Table 2.
Notations.
4. Revisiting Guo et al.’s Scheme
4.1. System Initialization Phase
In the password-based AKE scheme proposed by Guo et al., R and are used to denote and , respectively. In this context, lowercase italics are used to denote column vectors whose elements belong to the ring R or , while uppercase italics are used to denote matrices. The open parameters are , where n is a power of 2, and q is an odd prime number that satisfies . The notation represents a matrix sampled uniformly from . Similarly, represents a private key and noise sampled uniformly from .
4.2. Registration Phase
Before generating a session key for communication, users must register with the server through a secure channel. The detailed procedure is outlined below:
- Step 1:
- chooses and , then calculates . subsequently sends and to the server as a registration request through a secure channel.
- Step 2:
- Upon receiving and from the user, the server generates a random number and calculates . The server then sends to through a secure channel.
4.3. Authentication and Key Exchange Phase
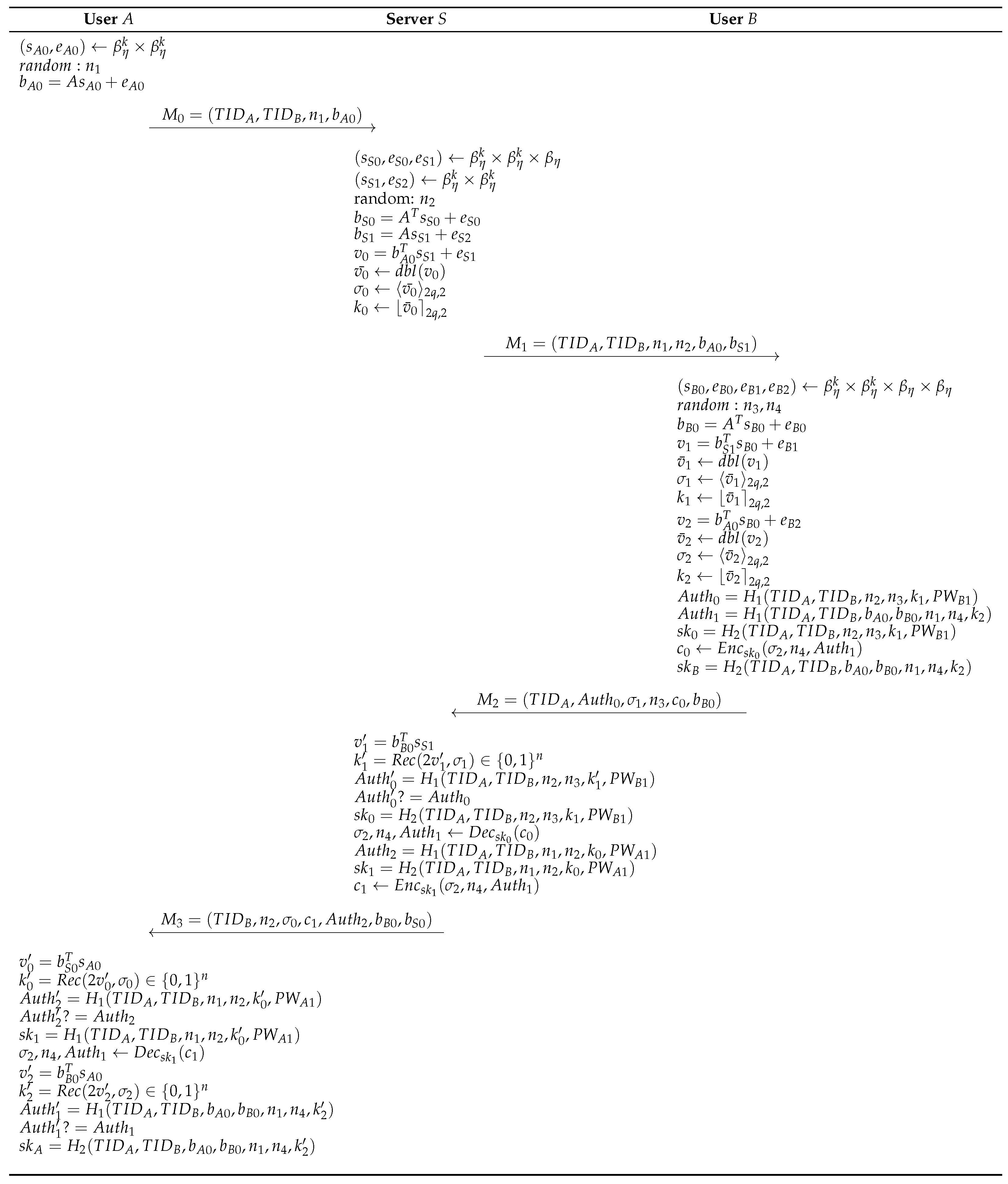
For User A and User B to securely share a session key for communication, they must first mutually authenticate with a trusted server to verify the legitimacy of their identities. The detailed process is outlined below and is illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
AKE phase of Guo et al.’s scheme.
- Step 1:
- uniformly samples and generates a random number . Then, computes . After finding its own and the counterpart it wants to communicate with, creates the message and sends it to the server.
- Step 2:
- Upon receiving from , the server verifies the user’s identity using the and . The server then samples and and generates the random number and computes , , and . Finally, the server uses the randomized function, cross-rounding function, and modular rounding function to compute , , , and sends the message to .
- Step 3:
- After receiving from the server, samples , generates two random numbers, and , computes , , , and calculates , , , , , using the randomized function, cross-rounding function, and modular rounding function. computes , the authentication information between and the server, and the shared key , and computes , the authentication information between and , and the shared key . Finally, encrypts (, , ) with and generates the message and sends it to the server.
- Step 4:
- The server computes and using Peikert error reconciliation function, and calculates , the authentication information between the server and . By checking , the server verifies that is a legitimate user, then computes , the shared key between the server and , and uses to decrypt to obtain (). The server then computes , the authentication information between the server and , and computes the shared key . Finally, the server encrypts () with and generates a message and sends it to .
- Step 5:
- computes and using the Peikert error reconciliation function, and calculates , the authentication information between the server and . By verifying , confirms the server’s credibility. Then computes , the shared key between the server and , and uses to decrypt to obtain . Using the decrypted information, computes and with the Peikert error reconciliation function. then computes and compares it with . If , then is verified, and both and obtain the same session key .
5. Cryptanalysis of Guo et al.’s Scheme
As described in Section 3, Attacker can eavesdrop on, intercept, and forge transmitted messages, as well as extract parameters from the server. This information can be leveraged to launch various security attacks, including replay attacks, user impersonation, server impersonation, verification table leakage attacks, privileged insider attacks, and DoS attacks, all of which are described in more detail below.
5.1. Replay Attack
If an attacker eavesdrops on messages sent or received over a public channel, can impersonate you by resending the intercepted messages from a previous session. The detailed process is as follows:
- Step 1:
- records a message from user A to the server, replaces in with his public key , and sends it to the server.
- Step 2:
- The server cannot distinguish whether is from User A or . Therefore, can start a session by impersonating User A.
- Step 3:
- User B cannot tell whether it is User A or who wants to generate the session key. Therefore, User B uses to compute , , and .
- Step 4:
- can use his secret key to compute the session key with the server, and decrypt to get and . can use , user B’s public key and his own secret key to generate and , and can generate a session key with user B.
Guo et al. cannot verify the freshness of the message and cannot verify the identity of the sender of the message.
Therefore, Guo et al.’s scheme cannot resist replay attack.
5.2. Impersonation Attack
Attacker can attempt user and server impersonation attacks. The process is as follows:
- User impersonation: The attacker must generate a message to impersonate the user. chooses a secret key and an error random number and computes a public key . Then generates a message and sends it to the server to initiate a session. The server does not know whether is a legitimate message or from an attacker.
- Server impersonation: The attacker needs to generate message to impersonate the server. chooses a secret key , an error , and a random number , and computes a public key . Then generates a message and sends it to user B, with whom user A wants to communicate. User B does not know whether is a legitimate message or a message from an attacker.
Therefore, Guo et al.’s scheme cannot resist impersonation attack.
5.3. Verification Table Leakage Attack
If the attacker extracts the server’s verification table, can perform an impersonation attack. After receiving the message , sets the secret key and error values , , and according to the protocol, then calculates and accordingly. Using , can generate , the authentication information with the server, as well as the session key . Using , can generate and , the authentication information with User A. It then creates a message and sends it to the server. The server cannot distinguish whether the message it receives is legitimate or from an attacker.
Therefore, Guo et al.’s scheme cannot resist verification table leakage attacks.
5.4. Privileged Insider Attack
An attacker can obtain sensitive values such as from the registration message with the help of a privileged insider. Based on these values, can attempt a user impersonation attack.
generates its own secret key and error values , , and , and computes and . Using , can calculate the authentication information with the server, , and the session key, . Using , can calculate the authentication information with user A, , and the session key . If generates a message using the value generated using his secret key and sends it to the server, the server will not know whether is a legitimate message or a message from the attacker.
Therefore, Guo et al.’s scheme cannot resist privileged insider attack.
5.5. Lack of Mutual Authentication
Guo et al. asserted that their protocol offers mutual authentication. In the AKE phase, is used by the server to authenticate User B, while is used by User A to authenticate User B. However, the protocol lacks a mechanism for the server to authenticate User A and for User B to authenticate both the server and User A. Therefore, the scheme proposed by Guo et al. does not fully achieve mutual authentication.
5.6. Correctness
There was a problem with the structure proposed by Guo et al. that prevented two users from generating a session key in a normal way, which is detailed below.
- To generate MLWE-based secret and public keys, the equation needs to be modified to . This change is necessary to avoid inconsistency issues during the calculation process.
- When the session key between the server and user A is generated, the hash function is used by the server, but when user A generates the session key , the hash function is used. This means that the session key between the server and user A is not generated properly, so the ciphertext cannot be decrypted normally. As a result, the session key between user A and user B cannot be generated normally.
5.7. DoS Attack
A malicious attacker can attempt to send the message repeatedly. Since no login is required to generate , and the server does not authenticate the user who sent it, the scheme proposed by Guo et al. is vulnerable to DoS attacks.
Therefore, Guo et al.’s scheme cannot effectively resist DoS attacks.
6. Proposed Scheme
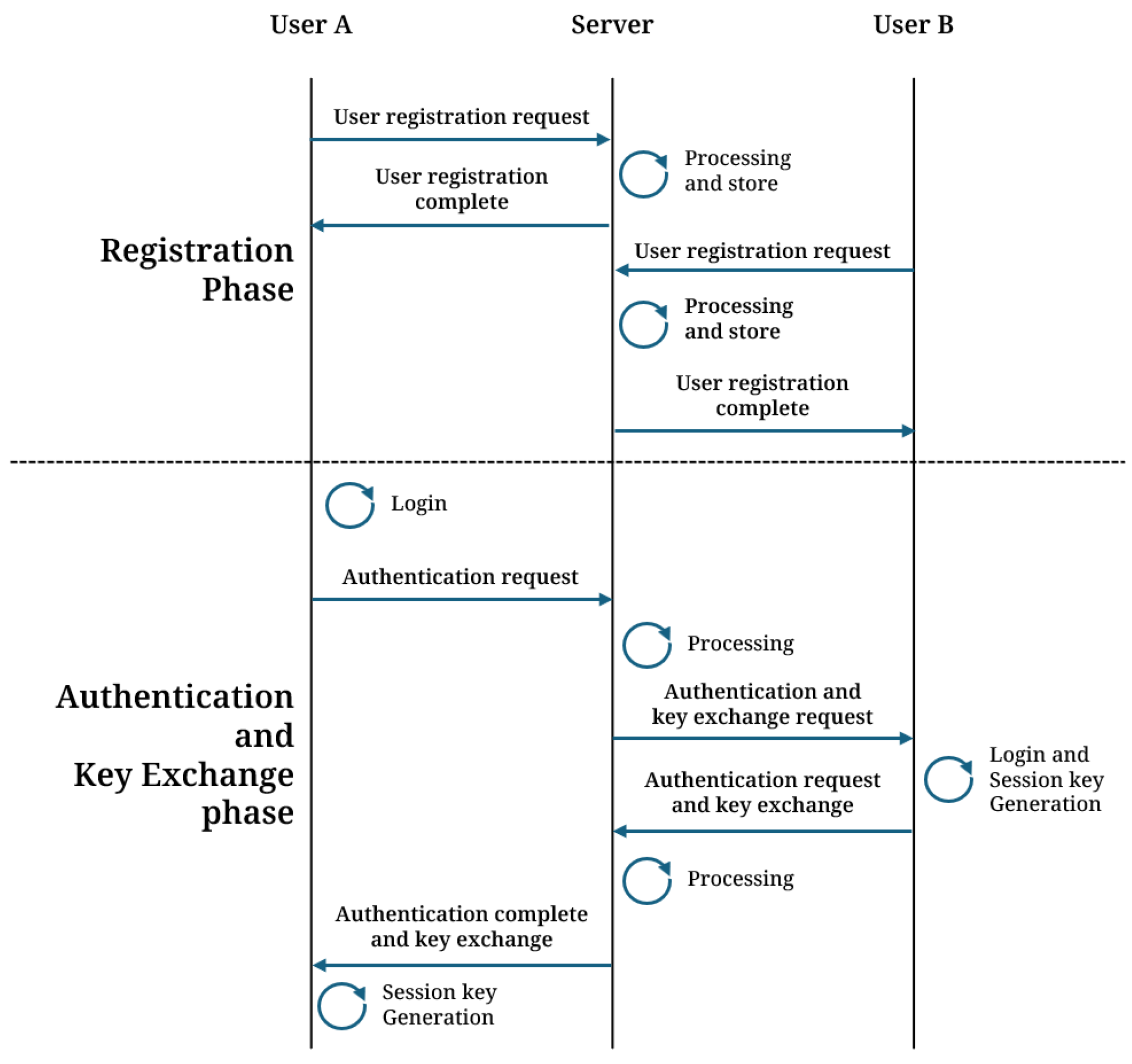
In this section, we propose a three-party mutual authentication and key exchange protocol using MLWE. The proposed scheme consists of system initialization, registration, authentication, and key exchange phases. Figure 2 illustrates the flowchart of the proposed scheme.
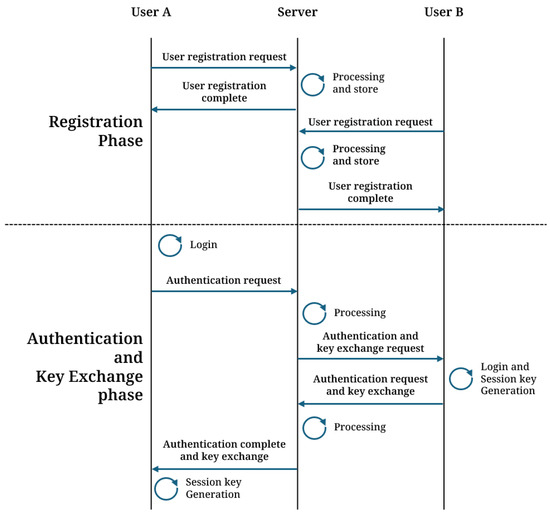
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the proposed scheme.
6.1. System Initialization Phase
In our proposed protocol, we use the same open parameters and initialization process as those in the password-based AKE scheme proposed by Guo et al. Specifically, R and denote and , respectively. Lowercase italics represent column vectors with elements in the ring R or , while uppercase italics represent matrices. The open parameters are defined, where n is a power of 2 and q is an odd prime number that satisfies . For instance, is a matrix sampled uniformly from , and represents a private key and noise sampled uniformly from . The parameter A, which is used to generate the user’s public key during the session, is a value that is prepublished by the server.
6.2. Registration Phase
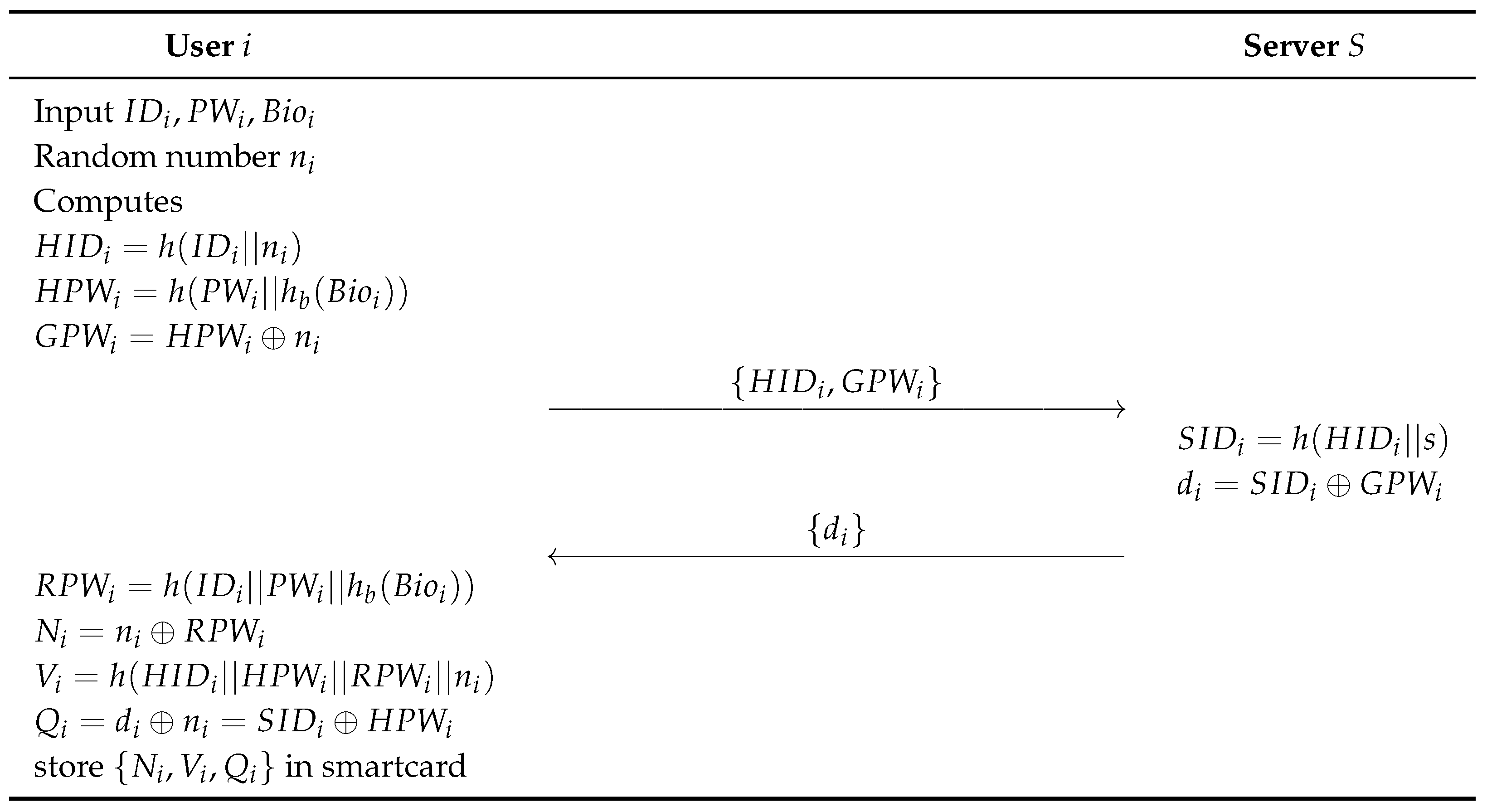
Before the authentication and session key generation process for communication, the user must complete a registration process with the server through a secure channel. During this process, the user registers information such as their identity, password, and biometric data. The detailed process is outlined below and illustrated in Figure 3.
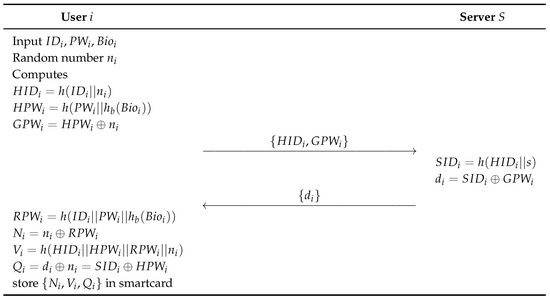
Figure 3.
Registration process of proposed scheme.
- Step 1:
- User i enters , , and and selects a random number . After that, i calculates , , , and sends , to the server as a registration request message via a secure channel.
- Step 2:
- After receiving the user’s registration request, the server calculates , , and sends {} to the user through a secure channel.
- Step 3:
- After receiving from the server, the user calculates , , , , and stores in the smartcard.
6.3. Authentication and Key Exchange Phase
In this process, the user logs in and uses the server to authenticate and generate a shared session key. The detailed process is as follows and is illustrated in Figure 4.

Figure 4.
AKE phase of proposed scheme.
- Step 1:
- inputs , , , and calculates , . , , . to authenticate the user, sample uniformly, and compute the public key . A random number and timestamp are generated, then the following is computed: , , . Finally, sends the message to the server over an open channel.
- Step 2:
- After receiving ’s message, the server checks the timestamp . If the timestamp is valid, the server computes , , . And to be certain that message came from user . The server then chooses a random value and timestamp . The server calculates , , , generates message , and sends it to user over an open channel.
- Step 3:
- checks the timestamp . If the timestamp is valid, takes , , , computes , , , , , and authenticates the user via . After the login process, computes , , and verifies that message came from the server via . After verification, is sampled uniformly and the public key is computed. computes , , , using a randomized doubling function, a cross-rounding function, and a modular rounding function. generates random numbers , and timestamp , and calculates , , ,, . Here, is the session key between and . generates a message and sends it to the server over the open channel.
- Step 4:
- After receiving the message from , the server checks the timestamp . If the timestamp is valid, the server computes , , and to verify that message came from user . The server then chooses a random value and timestamp . The server calculates , , generates message , and sends it to user over the open channel.
- Step 5:
- After receiving message from the server, checks the timestamp . If the timestamp is valid, computes , and uses to verify that message came from the server. After that, uses Peikert’s error reconciliation function to compute , , computes , , and uses to verify that is the one with whom wants to create a session key. Finally, computes the session key .
7. Security Analysis
7.1. Formal Analysis Using the BAN Logic
In the proposed scheme, users and a server perform mutual authentication to prove that they are valid entities of the system. To demonstrate the mutual authentication of the proposed scheme, we utilize a widely recognized formal verification technique called BAN logic [27]. Many researchers have affirmed the mutual authentication of their approaches using BAN logic [28,29]. The BAN logic analysis is performed sequentially by setting protocol goals, idealized form of the protocol, establishing assumptions, and proof using BAN logic. To incorporate our approach with BAN logic, we provide the following notations and descriptions. Table 3 is the notation used in BAN logic.

Table 3.
BAN logic notations.
7.1.1. BAN Logic Rules
- Message meaning rule (MMR):
- Nonce verification rule (NVR):
- Jurisdiction rule (JR):
- Belief rule (BR):
- Freshness rule (FR):
7.1.2. Goals
The goals are to show that and believe that they agreed upon the same session key.
- Goal 1:
- Goal 2:
- Goal 3:
- Goal 4:
7.1.3. Idealized Forms
The idealized forms of the messages exchanged during the authentication can be described as follows.
- :
- :
- :
- :
7.1.4. Assumptions
The basic assumptions for the BAN logic proof are as follows:
- :
- :
- :
- :
- :
- :
- :
- :
- :
- :
- :
- :
7.1.5. BAN Logic Proof
We perform the BAN logic proof of the proposed protocol as below:
- Step 1:
- S receives .
- Step 2:
- S can recognize that is from by .
- Step 3:
- S can consider that the message is fresh by and the FR.
- Step 4:
- S can apply the NVR using and .
- Step 5:
- receives .
- Step 6:
- can recognize that is from S by .
- Step 7:
- can consider that the message is fresh by and the FR.
- Step 8:
- can apply the NVR using and .
- Step 9:
- S receives .
- Step 10:
- S can recognize that is from by .
- Step 11:
- S can consider that the message is fresh by and the FR.
- Step 12:
- S can apply the NVR using and .
- Step 13:
- receives .
- Step 14:
- can recognize that is from S by .
- Step 15:
- S can consider that the message is fresh by and the FR.
- Step 16:
- can apply the NVR using and .
- Steps 17 and 18:
- considers that is from and considers that is from by and , respectively. Therefore, and can believe that the other party can calculate
- Steps 19 and 20:
- The JR can be applied to and using and , respectively.
Finally, the user and the server have mutually authenticated each other.
7.2. Formal Analysis Using the RoR Model
We prove the semantic security of the proposed protocol using the RoR model [30]. Under the RoR model, an adversary A can attempt passive and active queries (i.e., attacks) to obtain information about the session key . The notations and queries used in the RoR model are as follows. is a participant with the instance. For example, , , and represent participants , S, with , , and instances, respectively. Table 4 presents queries executed by A under the RoR model.

Table 4.
Queries of the RoR model.
A can obtain the output value of the hash function for the input by performing the query. When is the probability of the advantage for A to break the session key, we prove the following equation:
where represents the number of hash queries performed by A, represents the range space of cryptographic hash function, represents the number of queries performed by A, and and , respectively, represent the size of the password dictionary. represents the probability that A solves the MLWE problem in the polynomial time.
Proof.
Under the RoR model, A plays games . We denote that is a advantage of A to calculate after the end of .
- : A selects the bit c at the start of the game. In the first game, A has no information about and no queries to perform. By the definition of semantic security, we can induce the following equation.
- : A attempts query (i.e., eavesdropping attack) in this game. Then, A can obtain the transmitted messages through wireless channels. After that, A performs query and receives the return value. Finally, A tries to guess whether the return value is or a random number. To win the game, A should be able to calculate , which is computed by , , , , and . Among these values, A cannot obtain , which is a Diffie–Hellman key between and . Therefore, A has no advantage in this game, and the advantage function of A after at the end of has no change.
- : In this game, A uses the and queries to compromise . From the transmitted messages, A can obtain , , , and . A must obtain , , , , and to calculate the session key. However, A cannot obtain from the transmitted messages in the public channel; therefore, the only way for A to compromise the session key is to find the hash collision. The advantage function at the end of is as follows by the birthday paradox.
- : A can conduct query. For WLOS, we assume that A obtains the smart card of and A extracts from the smart card. However, these values are masked with and , and A must succeed in guessing and simultaneously to login to the smart card. At the end of , we can induce the following equation.
- : A failed to compromise through the above queries. Finally, A can defeat the cryptosystem by solving the MLWE problem in the polynomial time. The probability can be represented as follows:
After all the games are over, A should guess the correct bit c from query. It follows that
From Equations (2) and (3), we can obtain the following equation:
We can apply the triangular inequality to Equation (8).
We can obtain the following equation using Equations (8) and (9).
which is the same as Equation (1). Finally, we prove the semantic security of the proposed protocol using the RoR model. □
7.3. Formal Analysis Using AVISPA Tool
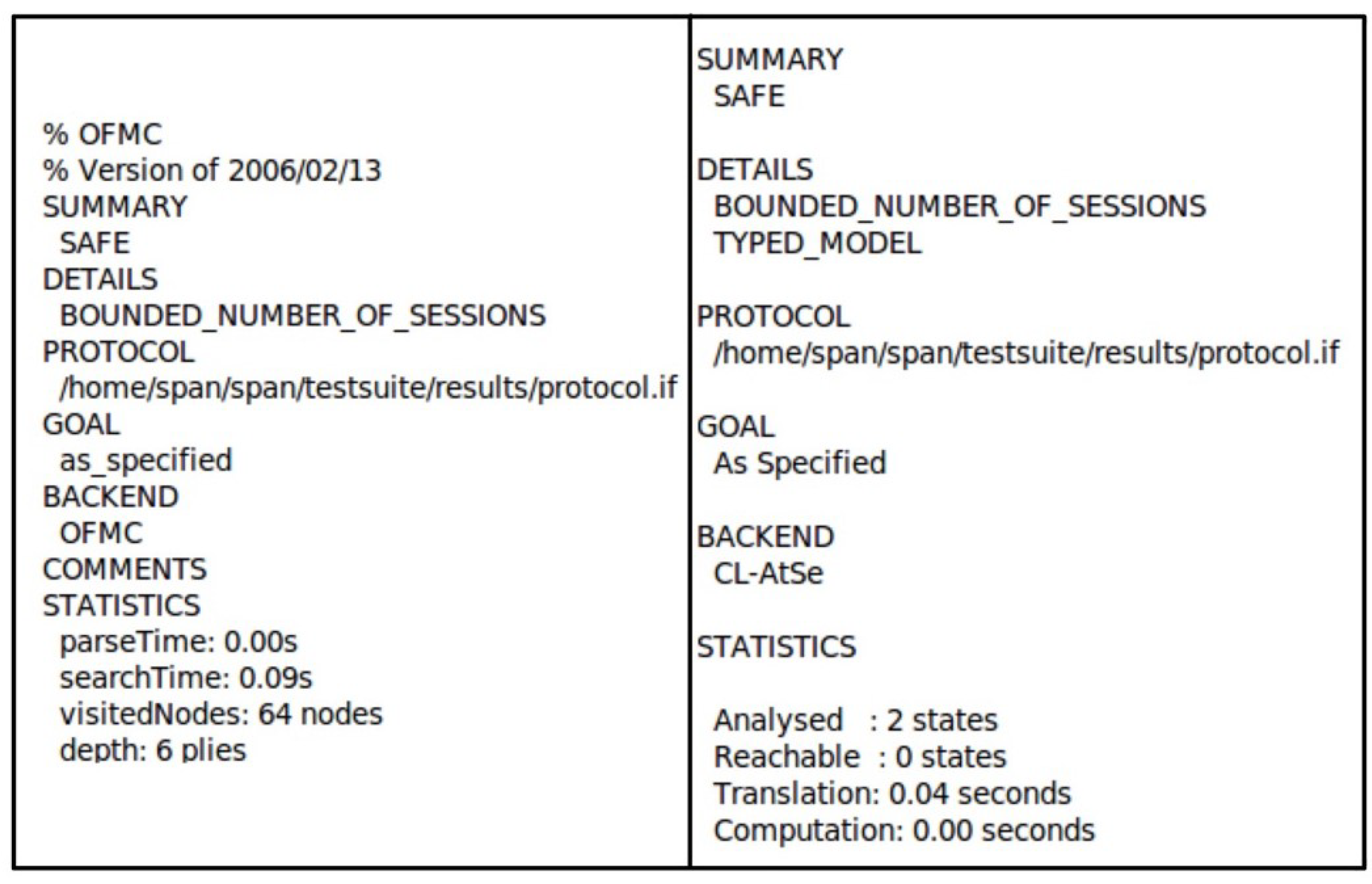
We conduct a formal verification of our proposed protocol using the AVISPA tool (v1.0) [31], employing code written in Higher Level Protocol Specification Language (HLPSL). AVISPA is a widely recognized simulation tool used for validating the security of Internet protocols and applications, particularly assessing protocols’ resistance to man-in-the-middle (MITM) and replay attacks.
AVISPA evaluates protocol safety through four backends: On-the-Fly Model Checker (OFMC), Constraint Logic-based Attack Detector (CL-AtSe), SAT-based Model Checker (SATMC), and Automatic Approximation-based Tree Automata for Security Protocol Analysis (TA4SP). Among these, the OFMC and CL-AtSe backends are predominantly used. OFMC is responsible for verifying resistance to MITM attacks, while CL-AtSe checks for replay attack resilience. The simulation results using AVISPA for the proposed protocol are presented in Figure 5, confirming that the protocol is secure against both MITM and replay attacks.
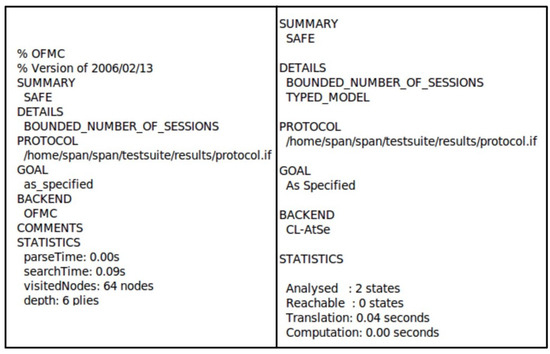
Figure 5.
Analysis of AVISPA simulation using OFMC and CL-AtSe.
7.4. Informal Security Analysis
7.4.1. Insider Attack
A malicious actor , who has gone through the registration phase as a legitimate user, might attempt to launch an insider attack using the obtained information. However, since the user’s public and secret keys are generated anew for each session, the attacker cannot determine the user’s secret key and, therefore, cannot compute . Additionally, the attacker cannot know the values of the random numbers , which are also generated anew for each session. Furthermore, the attacker cannot compute because they do not have access to the user’s biometric information or the server’s secret key. Therefore, the proposed scheme is secure against insider attacks.
7.4.2. Impersonation Attack
- User impersonation: For an attacker to impersonate the legitimate user , they must generate a valid message . However, since cannot obtain ’s biometric information, they cannot derive , and, consequently, cannot compute . Without , the attacker cannot generate the message to send to the server. Therefore, the proposed scheme is secure against user impersonation attacks.
- Server impersonation: To execute this attack, would need to send a message to user while pretending to be the server. However, even if intercepts the transmission of over an open channel, they cannot generate the required and for the message without knowing . Therefore, the proposed scheme is secure against server impersonation attacks.
7.4.3. Replay Attack
All users and servers validate the received messages using , and . Additionally, different public and private keys are used for each session, and freshness is ensured through the use of random numbers. Therefore, the proposed scheme is secure against replay attacks.
7.4.4. Man-in-the-Middle Attack
When an attacker intercepts a message and attempts to tamper with it, the user or server receiving the message uses , , , , and to verify that the message was sent by a legitimate user or server. As a result, it is impossible for an attacker to send a message while pretending to be a legitimate user or to modify it in transit. Therefore, the proposed protocol is secure against MITM attacks.
7.4.5. Privileged Insider Attack
In this attack scenario, attacker is considered an authorized insider, meaning they have access to confidential values such as the user’s enrollment request message . However, without the user’s exact biometric information, ID, or password (PW) value, it is impossible to calculate or . As a result, the proposed scheme is secure against privileged insider attacks.
7.4.6. Stolen Smartcard Attack
If a malicious attacker obtains the user’s smartcard, they can extract the values of . However, without the user’s biometric information, the value of cannot be determined from these parameters. Therefore, the proposed scheme is secure against stolen smartcard attacks.
7.4.7. DoS Attack
For two users to mutually authenticate with the server and generate a session key for communication, they must first complete the login process. Afterward, the messages are generated and sent, and the receiver validates the received messages. Therefore, the proposed scheme is secure against DoS attacks.
7.4.8. Session Key Disclosure Attack
To compute the session key , the attacker would need access to the values of , , , , and . However, the value of is known only to the two users who are generating the session key, as it is used temporarily and exists only within a single session. Therefore, the proposed scheme is secure against session key disclosure attacks.
7.4.9. Mutual Authentication
In the AKE phase, the values , , , , and contained in messages , , , and enable the verification of identity between the user and the server, as well as between the users themselves. The transparency of authentication is ensured because the open channel prevents an attacker from exploiting , values, or arbitrary values. Therefore, the proposed scheme provides mutual authentication.
8. Performance Analysis
8.1. Security Features Comparison
We visually compared the security features of our proposed scheme with those of related schemes [14,20,21,22,32], and the results are summarized in Table 5. The table includes various security aspects such as “Insider Attack”, “Impersonation Attack”, “Replay Attack”, “MITM Attack”, “Privileged Insider Attack”, “Stolen Smartcard Attack”, “DoS Attack”, “Session Key Disclosure”, and “Mutual Authentication”. The comparison suggests that our proposed scheme not only offers more security features than Guo et al.’s scheme but also presents fewer instances of unidentified or unavailable features when compared with other related schemes.

Table 5.
Security and functionality features (SFFs) comparison.
8.2. Communication Costs Comparison
We conducted a comparative analysis of the communication costs between the proposed scheme and other related schemes [14,20,21,22,32].
To represent the communication costs of existing authentication protocols, we assume that each binary string, including passwords, nonces, timestamps, and identities, is 256 bits in size. For the hashing process, we use the Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA-512) with a 512-bit output. Symmetric encryption and decryption are performed using a 256-bit key with the AES-256 algorithm. An elliptic curve point is assumed to be 320 bits, and each element from has a 4094-bit size. In the RLWE-based scheme, the public key is 7424 bits using the NowHope512 algorithm, whereas the MLWE-based scheme uses a 6400-bit public key with the Kyber512 algorithm.
Therefore, the message exchanged in the AKE phase of the proposed scheme contains bits). The message requires (512 + 4096 + 512 + 160 + 64 = 5344 bits), requires (512 + 512 + 4096 + 512 + 512 + 512 + 160 + 160 + 64 = 7040 bits), and requires (512 + 4096 + 512 + 512 + 512 + 160 + 160 + 64 = 6528 bits).
Table 6 summarizes the communication costs of related schemes [14,20,21,22,32] and the proposed scheme.

Table 6.
Comparison analysis of communication costs.
8.3. Computation Costs Comparison
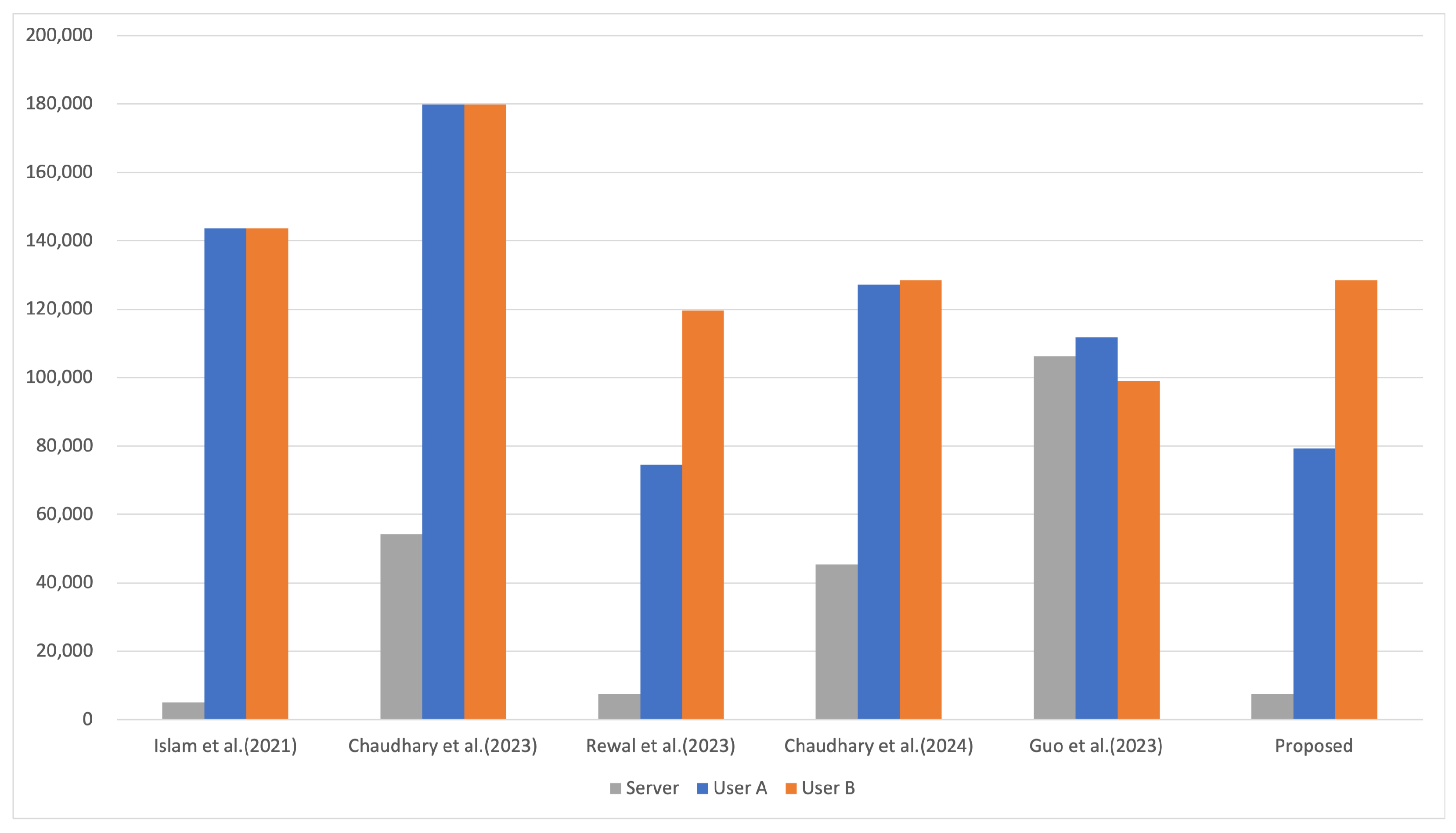
We performed a comparative analysis of computation costs during the AKA phase of the proposed scheme and other related schemes [14,20,21,22,32]. Experiments were conducted on an Ubuntu 22.04.3 system with a 12th Gen Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-12400F CPU and 3.8 GB of RAM, utilizing OpenSSL [33], NewHope [34], and Crystal-Kyber [35], all part of NIST’s “Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization” project [36]. Hash functions are denoted as , and AES-256 encryption/decryption as /. For RLWE and MLWE protocols, , , , and , , represent key generation, encapsulation, decapsulation, and sampling times. Elliptic curve point multiplication is denoted as . The average execution time for each operation is detailed in Table 7, with protocol computation times shown in Table 8 and Figure 6.

Table 7.
Average run time in nanoseconds.

Table 8.
Comparison analysis of computation costs in nanoseconds.
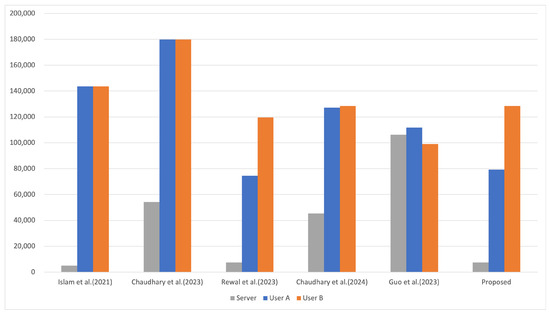
Figure 6.
Computation costs comparison on the user’s side [14,20,21,22,32].
As shown in Table 8, the total computation cost of the proposed scheme is more efficient than that of other schemes. Even though the cost of [22] is better than the proposed scheme, it is vulnerable to impersonation attacks and privileged insider attacks. To ensure robustness against these vulnerabilities, our proposed protocol incorporates additional hash functions, resulting in a marginal increase in computational cost. From the perspective of user B, the proposed protocol requires slightly more computations compared to those of [14,20], but, overall, the computational cost makes the proposed approach far more efficient.
9. Conclusions
In this study, we analyzed the three-party AKE protocol proposed by Guo et al. and identified several vulnerabilities, including susceptibility to impersonation attacks, replay attacks, privileged insider attacks, DoS attacks, verification table leakage attacks, and a lack of user mutual authentication. To address these vulnerabilities, we proposed a three-party secure AKE protocol based on MLWE.
The proposed protocol leverages the user’s biometric information and the server’s master key to prevent the exposure of sensitive parameters and to ensure security against various attacks. We verified the security of mutual authentication and the resulting session key using the BAN logic, RoR model, and AVISPA. Additionally, we assessed the protocol’s resistance to insider attacks, impersonation attacks, replay attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, privileged insider attacks, stolen smartcard attacks, DoS attacks, and session key disclosure attacks through informal analysis, confirming the effectiveness of mutual authentication. Comparative analysis with other protocols demonstrated that the proposed protocol offers reasonable security features, communication cost, and computational cost.
In conclusion, the proposed scheme offers strong security against quantum-computer-based attacks while maintaining computational efficiency, making it suitable for securely providing real-time services to users. Future work will focus on applying the proposed three-party AKE protocol to specific environments and developing a comprehensive security system that remains secure against quantum-computer-based attacks.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.P. (Youngho Park) and Y.P. (Yohan Park); validation, Y.P. (Yohan Park); formal analysis, S.S.; investigation, H.P. and Y.P. (Yohan Park); resources, H.P.; data curation, S.S.; writing—original draft preparation, H.P.; writing—review and editing, Y.P. (Yohan Park); supervision, Y.P. (Youngho Park) and Y.P. (Yohan Park); project administration, Y.P. (Yohan Park); funding acquisition, Y.P. (Yohan Park). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Bisa Research Grant (No. 20230649) of Keimyung University in 2023.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MDPI | Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute |
| DOAJ | Directory of open access journals |
| TLA | Three-letter acronym |
| LD | Linear dichroism |
References
- Yan, S.Y. Primality testing and integer factorization in public-key cryptography. In Advances in Information Security; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Adleman, L. A subexponential algorithm for the discrete logarithm problem with applications to cryptography. In Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (SFCS 1979), San Juan, PR, USA, 29–31 October 1979; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 1979; pp. 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Shor, P.W. Algorithms for quantum computation: Discrete logarithms and factoring. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, Santa Fe, NM, USA, 20–22 November 1994; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 1994; pp. 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Grover, L.K. A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 22–24 May 1996; pp. 212–219. [Google Scholar]
- Ikematsu, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Takagi, T. Recent progress in the security evaluation of multivariate public-key cryptography. IET Inf. Secur. 2023, 17, 210–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, K.; Soni, D.; Nabeel, M.; Karri, R. Nist post-quantum cryptography—A hardware evaluation study. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2019, 2019, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Baldi, M.; Bodrato, M.; Chiaraluce, F. A new analysis of the McEliece cryptosystem based on QC-LDPC codes. In Proceedings of the Security and Cryptography for Networks: 6th International Conference, SCN 2008, Amalfi, Italy, 10–12 September 2008; Proceedings 6. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 246–262. [Google Scholar]
- Dam, D.T.; Tran, T.H.; Hoang, V.P.; Pham, C.K.; Hoang, T.T. A survey of post-quantum cryptography: Start of a new race. Cryptography 2023, 7, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.; Cho, H. Post-Quantum Cryptography and Research Trend Analysis. In Proceedings of the 2023 Korean Institute of Information Scientists and Engineers Conference, Jeju, Republic of Korea, 17–20 June 2023; pp. 1244–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Ajtai, M. Generating hard instances of lattice problems. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 22–24 May 1996; pp. 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Regev, O. On lattices, learning with errors, random linear codes, and cryptography. J. ACM (JACM) 2009, 56, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubashevsky, V.; Peikert, C.; Regev, O. On ideal lattices and learning with errors over rings. In Proceedings of the Advances in Cryptology–EUROCRYPT 2010: 29th Annual International Conference on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques, French Riviera, France, 30 May–3 June 2010; Proceedings 29. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Langlois, A.; Stehlé, D. Worst-case to average-case reductions for module lattices. Des. Codes Cryptogr. 2015, 75, 565–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Song, Y.; Guo, S.; Yang, Y.; Song, S. Three-Party Password Authentication and Key Exchange Protocol Based on MLWE. Symmetry 2023, 15, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Xie, X.; Lin, X. A simple provably secure key exchange scheme based on the learning with errors problem. Cryptol. ePrint Arch. 2012, 2012, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Peikert, C. Lattice cryptography for the internet. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Post-Quantum Cryptography, Waterloo, ON, Canada, 1–3 October 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 197–219. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Cheng, C.; He, D. Quantum2FA: Efficient quantum-resistant two-factor authentication scheme for mobile devices. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 2021, 20, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharminder, D.; Reddy, C.B.; Das, A.K.; Park, Y.; Jamal, S.S. Post-quantum lattice-based secure reconciliation enabled key agreement protocol for IoT. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 2680–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Garg, M.; Kumari, S.; Dharminder, D. A construction of post quantum secure and signal leakage resistant authenticated key agreement protocol for mobile communication. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2023, 34, e4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.; Dadsena, P.K.; Padmavathi, A.; Hassan, M.M.; Alkhamees, B.F.; Kumar, U. Anonymous Quantum Safe Construction of Three Party Authentication and Key Agreement Protocol for Mobile Devices. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 74572–74585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, D.; Kumar, U.; Saleem, K. A construction of three party post quantum secure authenticated key exchange using ring learning with errors and ecc cryptography. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 136947–136957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewal, P.; Singh, M.; Mishra, D.; Pursharthi, K.; Mishra, A. Quantum-safe three-party lattice based authenticated key agreement protocol for mobile devices. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2023, 75, 103505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, A.T.B.; Ling, D.N.C.; Goh, A. Biohashing: Two factor authentication featuring fingerprint data and tokenised random number. Pattern Recognit. 2004, 37, 2245–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolev, D.; Yao, A. On the security of public key protocols. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1983, 29, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.; Park, Y.; Das, A.K. Design of blockchain-based lightweight V2I handover authentication protocol for VANET. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Park, Y. Provably Secure Lightweight Mutual Authentication and Key Agreement Scheme for Cloud-Based IoT Environments. Sensors 2023, 23, 9766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, M.; Abadi, M.; Needham, R. A logic of authentication. ACM Trans. Comput. Syst. (TOCS) 1990, 8, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Yu, S.; Jho, N.; Park, Y. Provably secure PUF-based lightweight mutual authentication scheme for wireless body area networks. Electronics 2022, 11, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Ryu, D.; Kwon, D.; Park, Y. Provably secure mutual authentication and key agreement scheme using PUF in internet of drones deployments. Sensors 2023, 23, 2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.; Fouque, P.A.; Pointcheval, D. Password-based authenticated key exchange in the three-party setting. In Proceedings of the Public Key Cryptography-PKC 2005: 8th International Workshop on Theory and Practice in Public Key Cryptography, Les Diablerets, Switzerland, 23–26 January 2005; Proceedings 8. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 65–84. [Google Scholar]
- Armando, A.; Basin, D.; Boichut, Y.; Chevalier, Y.; Compagna, L.; Cuéllar, J.; Drielsma, P.H.; Héam, P.C.; Kouchnarenko, O.; Mantovani, J.; et al. The AVISPA tool for the automated validation of internet security protocols and applications. In Proceedings of the Computer Aided Verification: 17th International Conference, CAV 2005, Edinburgh, UK, 6–10 July 2005; Proceedings 17. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 281–285. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, S.H.; Basu, S. PB-3PAKA: Password-based three-party authenticated key agreement protocol for mobile devices in post-quantum environments. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2021, 63, 103026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Project, OpenSSL OpenSSL Releases. Available online: https://github.com/openssl/openssl/releases (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Team, NewHope Project NewHope Post-Quantum Cryptography Project. Available online: https://newhopecrypto.org/ (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Team, PQC Crystals PQC Crystals Project. Available online: https://pq-crystals.org/ (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Post-Quantum Cryptography Standardization. Available online: https://csrc.nist.gov/pqc-standardization (accessed on 13 August 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).