A Temporal Filter to Extract Doped Conducting Polymer Information Features from an Electronic Nose
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
3. Results
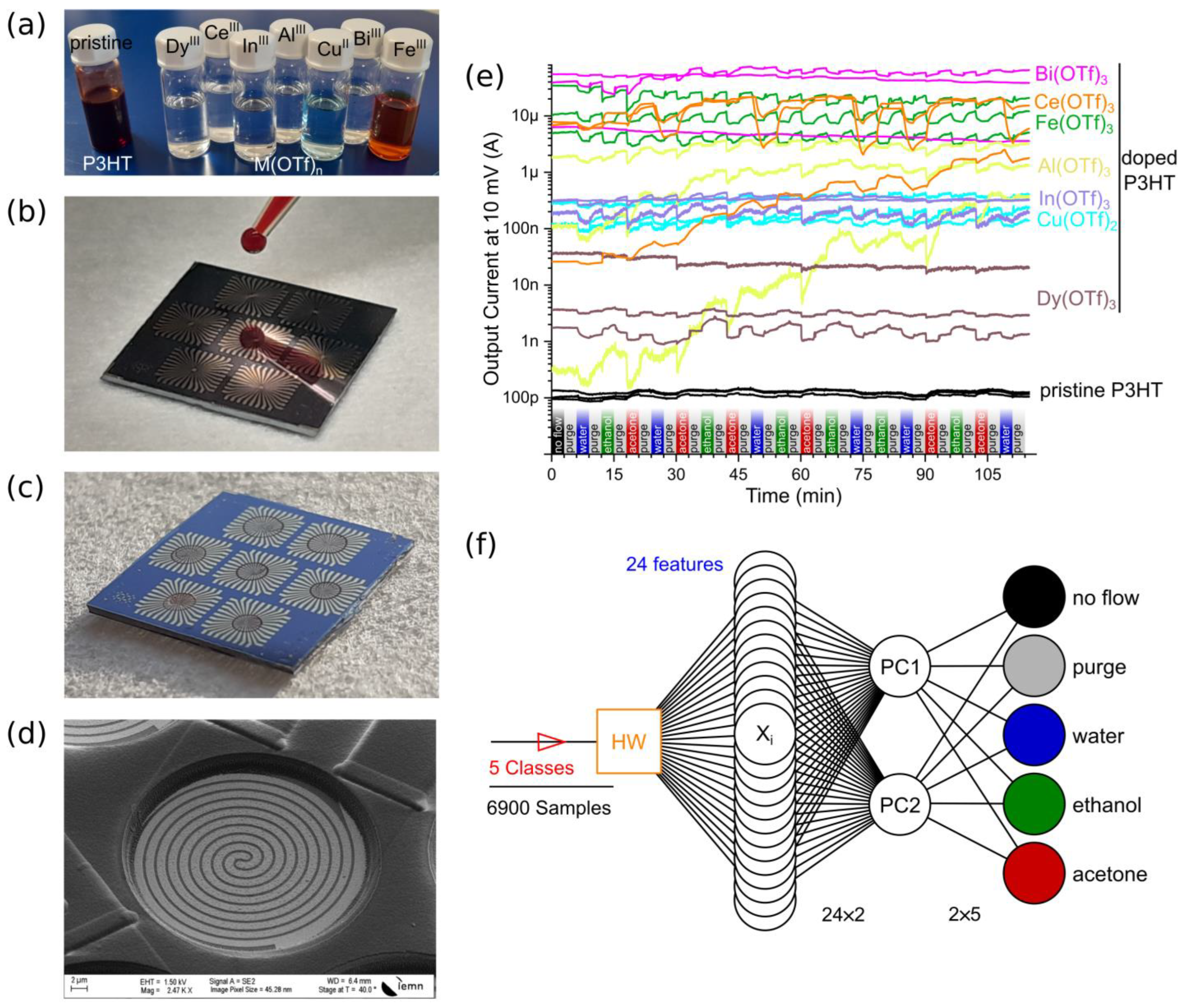
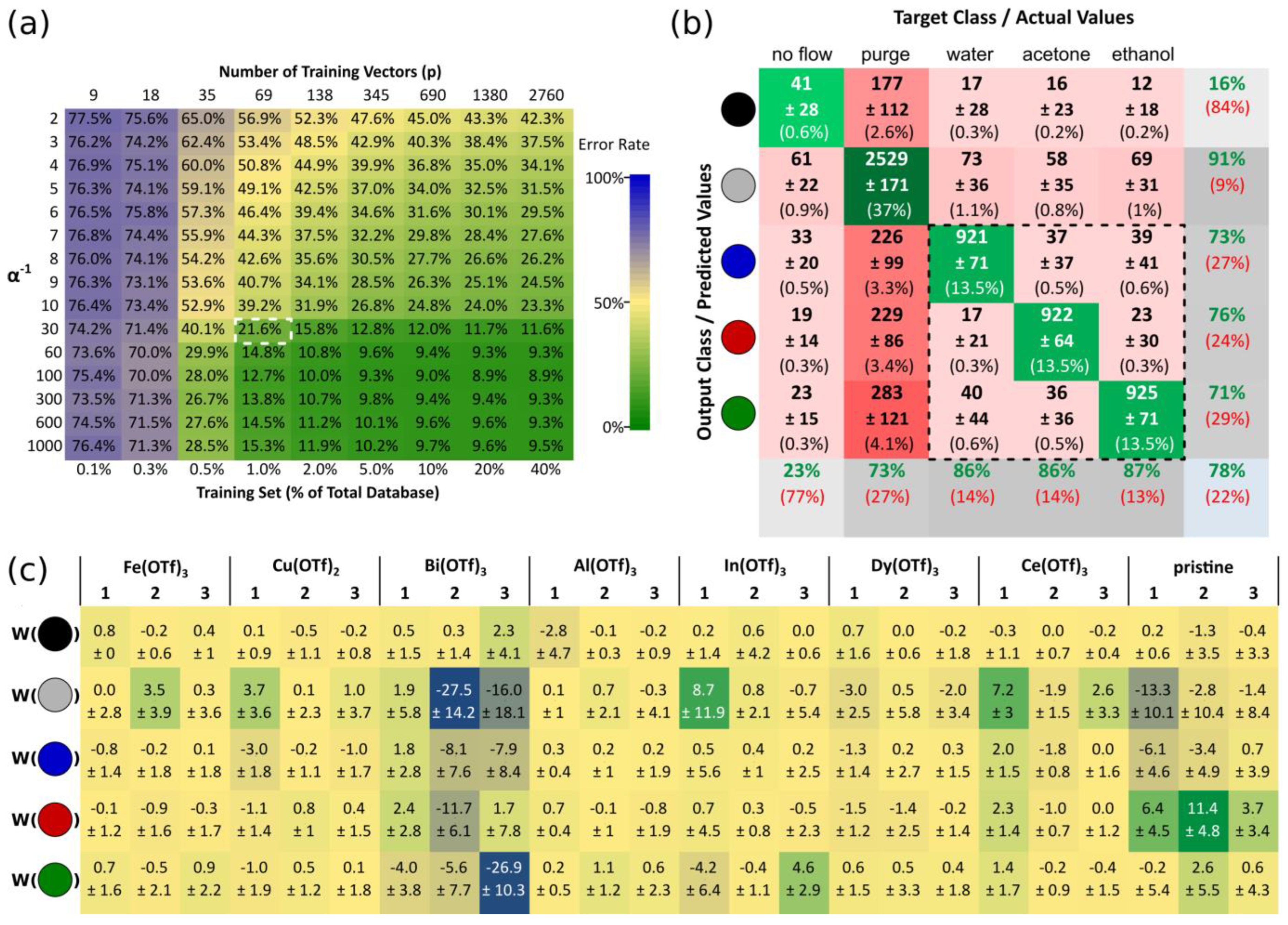
3.1. Data Collection and Feature Extraction
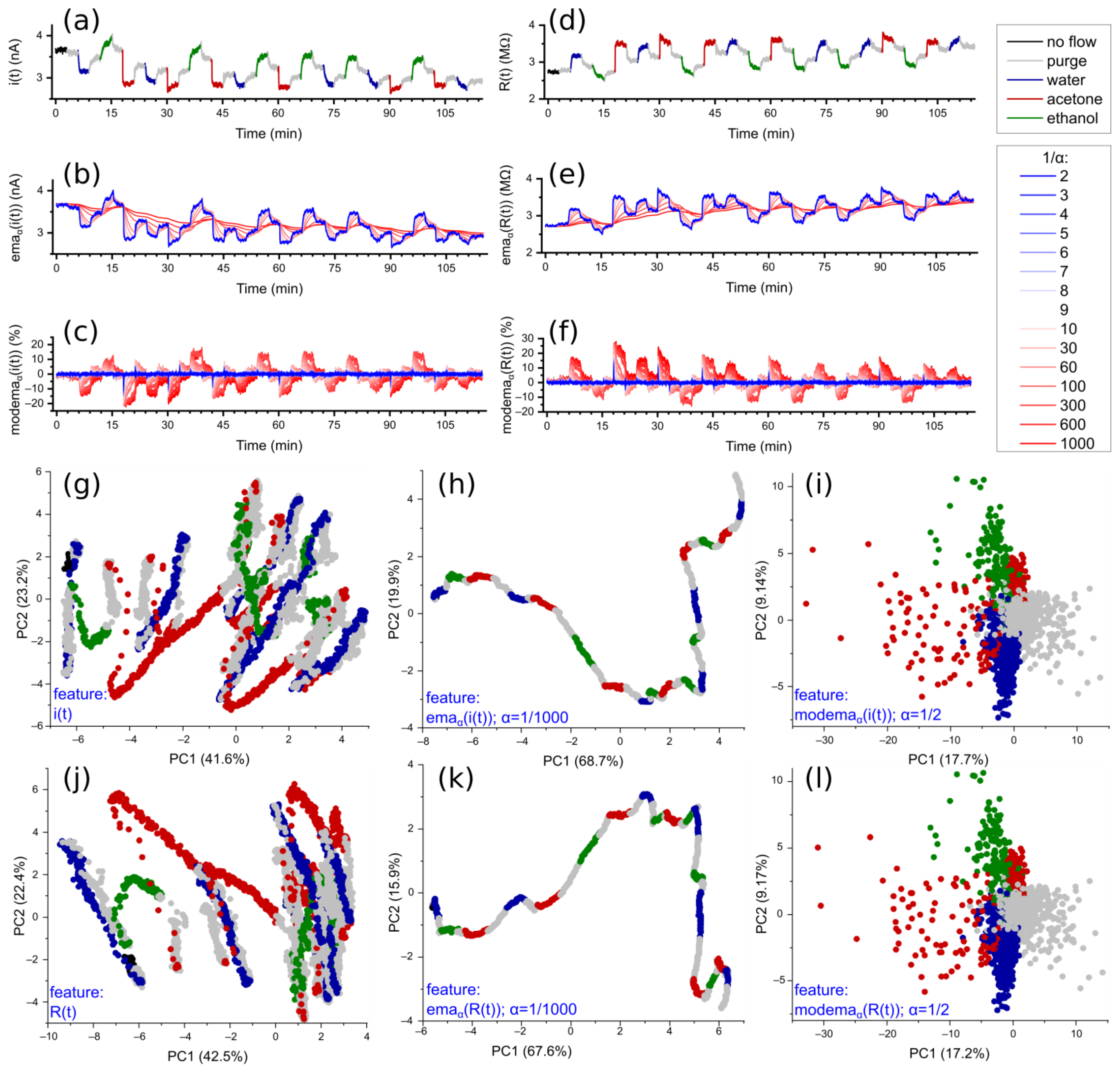
3.2. Exponential Moving Average as a Floating Reference
3.3. Relationship between Attenuation Coefficient and Environment Clustering
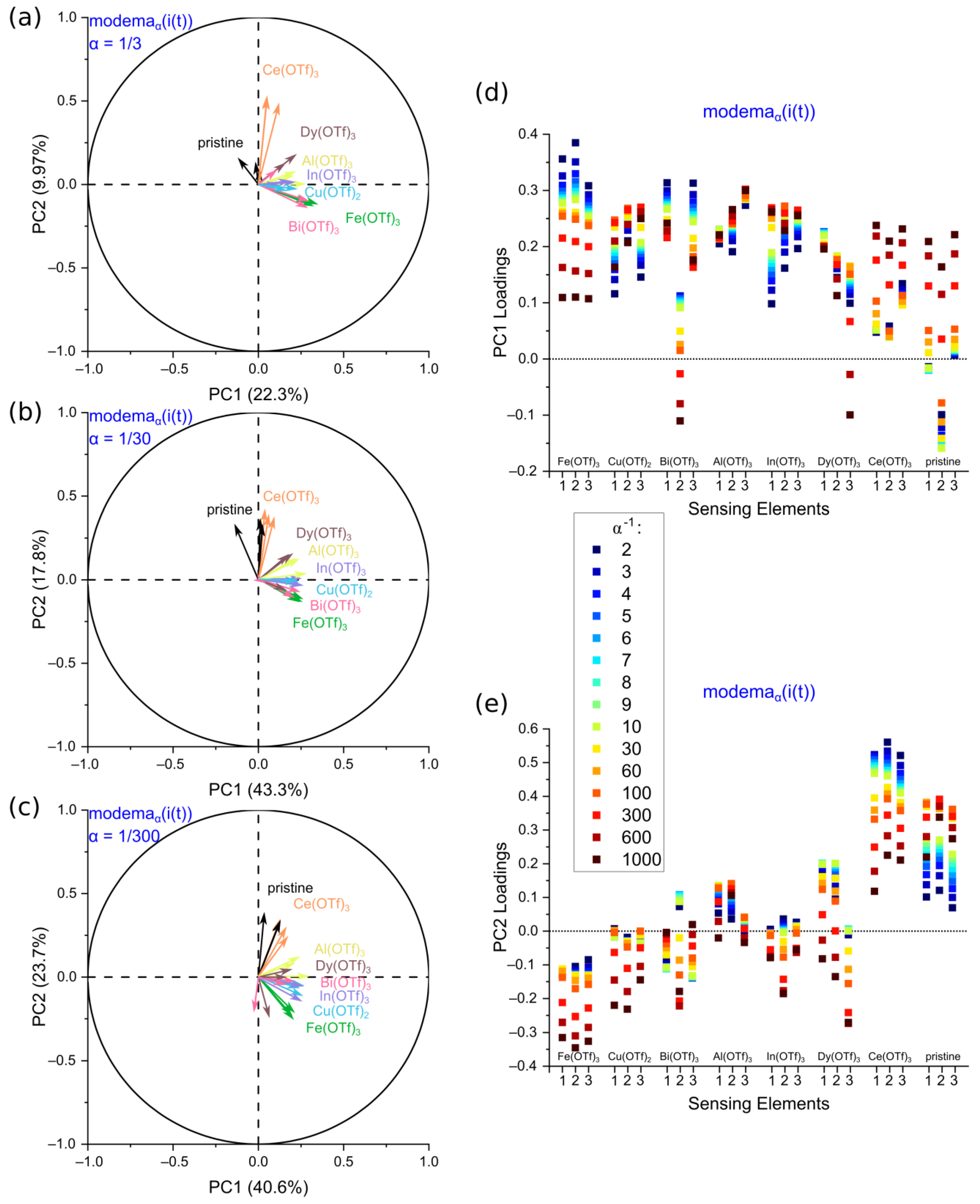
3.4. Conducting Polymer Doping Complementarity in the Principal Component Analysis
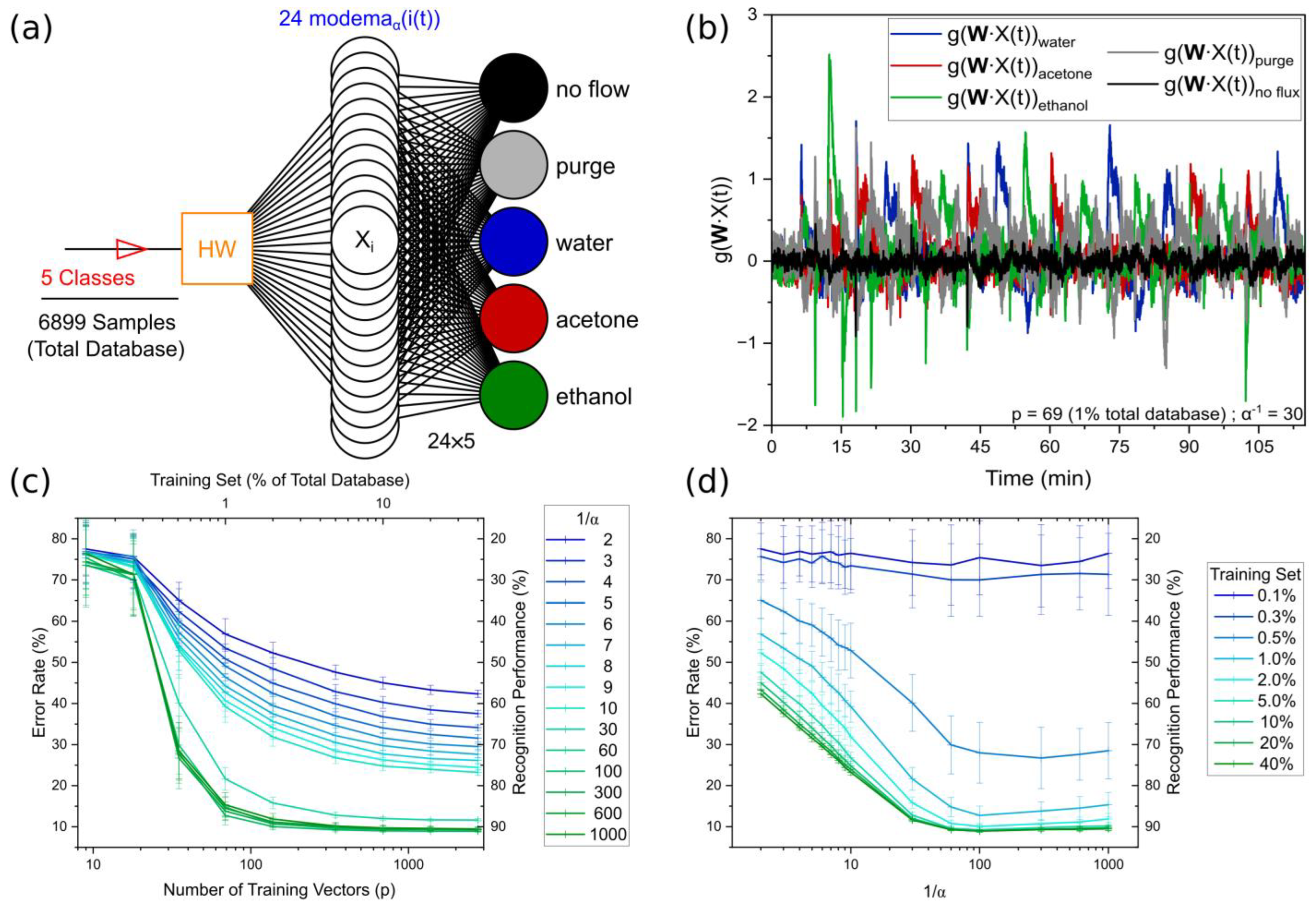
3.5. Supervised Training of Environment Recognition with Output Currents’ Modema
3.6. Conducting Polymer Doping Complementarity with the Moore–Penrose Pseudo-Inverse
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ullah, A.; Anwar, S.M.; Li, J.; Nadeem, L.; Mahmood, T.; Rehman, A.; Saba, T. Smart cities: The role of Internet of Things and machine learning in realizing a data-centric smart environment. Complex Intell. Syst. 2023, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xiao, G.; Liu, H.; Wei, H. Multi-sensor measurement and data fusion. IEEE Instrum. Meas. Mag. 2022, 25, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavi, A.; Mazzoleni, F.; Facello, A.; Prato, A. Metrology for next generation “Phygital Sensors”. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT (MetroInd4. 0&IoT), Brescia, Italy, 6–8 June 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.; Lee, K.K.; Kang, M.S.; Shin, D.-M.; Oh, J.-W.; Lee, C.-S.; Han, D.-W. Artificial olfactory sensor technology that mimics the olfactory mechanism: A comprehensive review. Biomater. Res. 2022, 26, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, P.M.; Olsson, M.J.; Cain, W.S. Quantification of odor quality. Chem. Senses 2000, 25, 429–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushdid, C.; Magnasco, M.O.; Vosshall, L.B.; Keller, A. Humans can discriminate more than 1 trillion olfactory stimuli. Science 2014, 343, 1370–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamlouk, A.M.; Martinetz, T. On the dimensions of the olfactory perception space. Neurocomputing 2004, 58, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulakov, A.A.; Kolterman, B.E.; Enikolopov, A.G.; Rinberg, D. In search of the structure of human olfactory space. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Smith, B.H.; Sharpee, T.O. Hyperbolic geometry of the olfactory space. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billesbølle, C.B.; de March, C.A.; van der Velden, W.J.C.; Ma, N.; Tewari, J.; del Torrent, C.L.; Li, L.; Faust, B.; Vaidehi, N.; Matsunami, H.; et al. Structural basis of odorant recognition by a human odorant receptor. Nature 2023, 615, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, J.B.; Ramanathan, A.; Chennubhotla, C.S. Categorical Dimensions of Human Odor Descriptor Space Revealed by Non-Negative Matrix Factorization. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, K.; Ramanathan, V. Predicting odor from molecular structure: A multi-label classification approach. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.K.; Mayhew, E.J.; Sanchez-Lengeling, B.; Wei, J.N.; Qian, W.W.; A Little, K.; Andres, M.; Nguyen, B.B.; Moloy, T.; Yasonik, J.; et al. A principal odor map unifies diverse tasks in olfactory perception. Science 2023, 381, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, L.; Miller, J.G. Odor incongruity and chirality. Science 1971, 172, 1044–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abate, A.; Brenna, E.; Fuganti, C.; Gatti, F.G.; Giovenzana, T.; Malpezzi, L.; Serra, S. Chirality and fragrance chemistry: Stereoisomers of the commercial chiral odorants Muguesia and Pamplefleur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, R. The nose as a stereochemist. Enantiomers and odor. Chem. Rev. 2006, 106, 4099–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gronenberg, W.; Raikhelkar, A.; Abshire, E.; Stevens, J.; Epstein, E.; Loyola, K.; Rauscher, M.; Buchmann, S. Honeybees (Apis mellifera) learn to discriminate the smell of organic compounds from their respective deuterated isotopomers. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 281, 20133089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genva, M.; Kemene, T.K.; Deleu, M.; Lins, L.; Fauconnier, M.-L. Is It Possible to Predict the Odor of a Molecule on the Basis of its Structure? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Panda, S. Polymer selection approaches for designing electronic noses: A comparative study. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, T.; Eom, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jang, H.W. Chemoresistive materials for electronic nose: Progress, perspectives, and challenges. InfoMat 2019, 1, 289–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, A.K.; Petit, C. Material Screening for Gas Sensing Using an Electronic Nose: Gas Sorption Thermodynamic and Kinetic Considerations. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 3808–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.; Neaves, P.; Hicks, P.; Persaud, K.; Travers, P. Towards an integrated electronic nose using conducting polymer sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 18, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freund, M.S.; Lewis, N.S. A chemically diverse conducting polymer-based “electronic nose”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 2652–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Padilla, A.; García-Guzmán, J.J.; López-Iglesias, D.; Palacios-Santander, J.M.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L. E-Tongues/Noses Based on Conducting Polymers and Composite Materials: Expanding the Possibilities in Complex Analytical Sensing. Sensors 2021, 21, 4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüssem, B.; Riede, M.; Leo, K. Doping of organic semiconductors. Phys. Status Solidi A 2013, 210, 9–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzmann, I.; Heimel, G.; Oehzelt, M.; Winkler, S.; Koch, N. Molecular Electrical Doping of Organic Semiconductors: Fundamental Mechanisms and Emerging Dopant Design Rules. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, N.; Warren, R.; Zhang, F.; Nayak, S.; Liu, J.; Kesava, S.V.; Lin, Y.-H.; Biswal, H.S.; Lin, X.; Grovenor, C.; et al. Adduct-based p-doping of organic semiconductors. Nat. Mater. 2021, 20, 1248–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boujnah, A.; Boubaker, A.; Kalboussi, A.; Lmimouni, K.; Pecqueur, S. Mildly-doped polythiophene with triflates for molecular recognition. Synth. Met. 2021, 280, 116890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boujnah, A.; Boubaker, A.; Pecqueur, S.; Lmimouni, K.; Kalboussi, A. An electronic nose using conductometric gas sensors based on P3HT doped with triflates for gas detection using computational techniques (PCA, LDA, and kNN). J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 27132–27146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, W.H.; Boujnah, A.; Boubaker, A.; Kalboussi, A.; Lmimouni, K.; Pecqueur, S. Steady vs. Dynamic Contributions of Different Doped Conducting Polymers in the Principal Components of an Electronic Nose’s Response. Eng 2023, 4, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriano, D.; Capelli, L. Evolution of Electronic Noses from Research Objects to Engineered Environmental Odour Monitoring Systems: A Review of Standardization Approaches. Biosensors 2019, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capelli, L.; Sironi, S.; Del Rosso, R. Electronic Noses for Environmental Monitoring Applications. Sensors 2014, 14, 19979–20007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.D. Review of Electronic-nose technologies and algorithms to detect hazardous chemicals in the environment. Procedia Technol. 2012, 1, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y. Electronic nose and its application in the food industry: A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 250, 21–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Xu, J. Applications of electronic nose (e-nose) and electronic tongue (e-tongue) in food quality-related properties determination: A review. Artif. Intell. Agric. 2020, 4, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Zhang, M.; Adhikari, B. Advances of electronic nose and its application in fresh foods: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 58, 2700–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Meng, Q.-H.; Lilienthal, A.J.; Qi, P.-F. Development of compact electronic noses: A review. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2021, 32, 062002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiele, A.; Wicaksono, A.; Ayyala, S.K.; Covington, J.A. Development of a compact, IoT-enabled electronic nose for breath analysis. Electronics 2020, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeschke, C.; Padilla, M.; Turppa, E.; Polaka, I.; Gonzalez, O.; Richardson, K.; Pajukanta, J.; Kortelainen, J.M.; Shani, G.; Shuster, G.; et al. Overview on SNIFFPHONE: A portable device for disease diagnosis. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Symposium on Olfaction and Electronic Nose (ISOEN), Fukuoka, Japan, 26–29 May 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Recent progress in smart electronic nose technologies enabled with machine learning methods. Sensors 2021, 21, 7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faleh, R.; Othman, M.; Gomri, S.; Aguir, K.; Kachouri, A. A transient signal extraction method of WO3 gas sensors array to identify polluant gases. IEEE Sens. J. 2016, 16, 3123–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Guo, X.; Duan, S.; Jia, P.; Wang, L.; Peng, C.; Zhang, S. Electronic nose feature extraction methods: A review. Sensors 2015, 15, 27804–27831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muezzinoglu, M.K.; Vergara, A.; Huerta, R.; Rulkov, N.; Rabinovich, M.I.; Selverston, A.; Abarbanel, H.D.I. Acceleration of chemo-sensory information processing using transient features. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 137, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergara, A.; Vembu, S.; Ayhan, T.; Ryan, M.A.; Homer, M.L.; Huerta, R. Chemical gas sensor drift compensation using classifier ensembles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 166, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, A.D. Lange’s handbook of chemistry. In Universitas of Tennese Knoxville, 15th ed.; Mc. Graw Hill Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Cong, W.; Zhang, J.A. Biobutanol Production from Acetone–Butanol–Ethanol Fermentation: Developments and Prospects. Fermentation 2023, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, S.-X.; Gandionco, K.A.; Bond, A.M.; Zhang, J. Electrocatalytic carbon dioxide reduction: From fundamental principles to catalyst design. Mater. Today Adv. 2020, 7, 100074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metsalu, T.; Vilo, J. ClustVis: A web tool for visualizing clustering of multivariate data using Principal Component Analysis and heatmap. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W566–W570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecqueur, S.; Talamo, M.M.; Guérin, D.; Blanchard, P.; Roncali, J.; Vuillaume, D.; Alibart, F. Neuromorphic time-dependent pattern classification with organic electrochemical transistor arrays. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2018, 4, 1800166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferchichi, K.; Bourguiga, R.; Lmimouni, K.; Pecqueur, S. Concentration-control in all-solution processed semiconducting polymer doping and high conductivity performances. Synth. Met. 2020, 262, 116352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Chai, Y. Near-sensor and in-sensor computing. Nat. Electron. 2020, 3, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Liao, F. Near-sensor and In-sensor Computing. Nat. Electron. 2022, 3, 664–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, M.; Mansour, M.D.; Scholaert, C.; Dargent, T.; Coffinier, Y.; Pecqueur, S.; Alibart, F. Bio-inspired adaptive sensing through electropolymerization of organic electrochemical transistors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2022, 8, 2100891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholaert, C.; Janzakova, K.; Coffinier, Y.; Alibart, F.; Pecqueur, S. Plasticity of conducting polymer dendrites to bursts of voltage spikes in phosphate buffered saline. Neuromorphic Comput. Eng. 2022, 2, 044010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, D.T.; Rowley, J.C.; Jafek, B.W.; Lovell, M.A. The fine structure of the olfactory mucosa in man. J. Neurocytol. 1982, 11, 721–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malnic, B.; Godfrey, P.A.; Buck, L.B. The human olfactory receptor gene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2584–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghatpande, A.S.; Reisert, J. Olfactory receptor neuron responses coding for rapid odour sampling. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Hall, W.; LaMantia, A.-S.; McNamar, J.O.; Williams, S.M. Neurosciences, 3rd ed.; Sinauer Associates Inc.: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gerstner, W.; Kistler, W.M. Spiking Neuron Models: Single Neurons, Populations, Plasticity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pecqueur, S.; Lončarić, I.; Zlatić, V.; Vuillaume, D.; Crljen, Ž. The non-ideal organic electrochemical transistors impedance. Org. Electron. 2019, 71, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecqueur, S.; Vuillaume, D.; Crljen, Ž.; Lončarić, I.; Zlatić, V. A Neural Network to Decipher Organic Electrochemical Transistors’ Multivariate Responses for Cation Recognition. Electron. Mater. 2023, 4, 80–94. [Google Scholar]
- Janzakova, K.; Ghazal, M.; Kumar, A.; Coffinier, Y.; Pecqueur, S.; Alibart, F. Dendritic organic electrochemical transistors grown by electropolymerization for 3D neuromorphic engineering. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2102973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzakova, K.; Kumar, A.; Ghazal, M.; Susloparova, A.; Coffinier, Y.; Alibart, F.; Pecqueur, S. Analog programing of conducting-polymer dendritic interconnections and control of their morphology. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teka, W.; Marinov, T.M.; Santamaria, F. Neuronal spike timing adaptation described with a fractional leaky integrate-and-fire model. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teka, W.W.; Upadhyay, R.K.; Mondal, A. Fractional-order leaky integrate-and-fire model with long-term memory and power law dynamics. Neural Netw. 2017, 93, 110–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Haj Ammar, W.; Boujnah, A.; Baron, A.; Boubaker, A.; Kalboussi, A.; Lmimouni, K.; Pecqueur, S. A Temporal Filter to Extract Doped Conducting Polymer Information Features from an Electronic Nose. Electronics 2024, 13, 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030497
Haj Ammar W, Boujnah A, Baron A, Boubaker A, Kalboussi A, Lmimouni K, Pecqueur S. A Temporal Filter to Extract Doped Conducting Polymer Information Features from an Electronic Nose. Electronics. 2024; 13(3):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030497
Chicago/Turabian StyleHaj Ammar, Wiem, Aicha Boujnah, Antoine Baron, Aimen Boubaker, Adel Kalboussi, Kamal Lmimouni, and Sébastien Pecqueur. 2024. "A Temporal Filter to Extract Doped Conducting Polymer Information Features from an Electronic Nose" Electronics 13, no. 3: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030497
APA StyleHaj Ammar, W., Boujnah, A., Baron, A., Boubaker, A., Kalboussi, A., Lmimouni, K., & Pecqueur, S. (2024). A Temporal Filter to Extract Doped Conducting Polymer Information Features from an Electronic Nose. Electronics, 13(3), 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030497





