Alternative Performance Indices-Based Control Technique for a Unity Power Factor Three-Phase Rectifier
Abstract
:1. Introduction
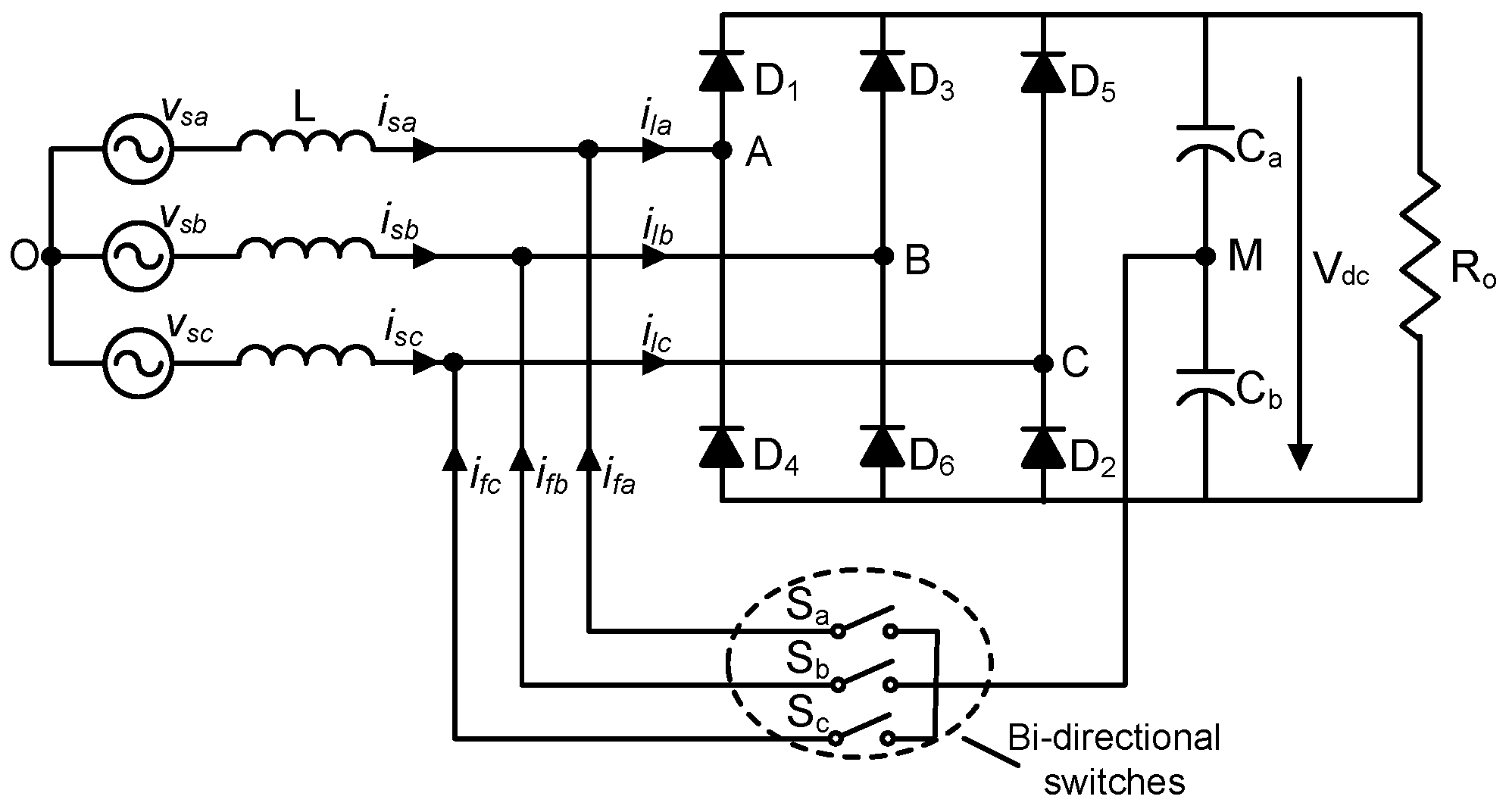
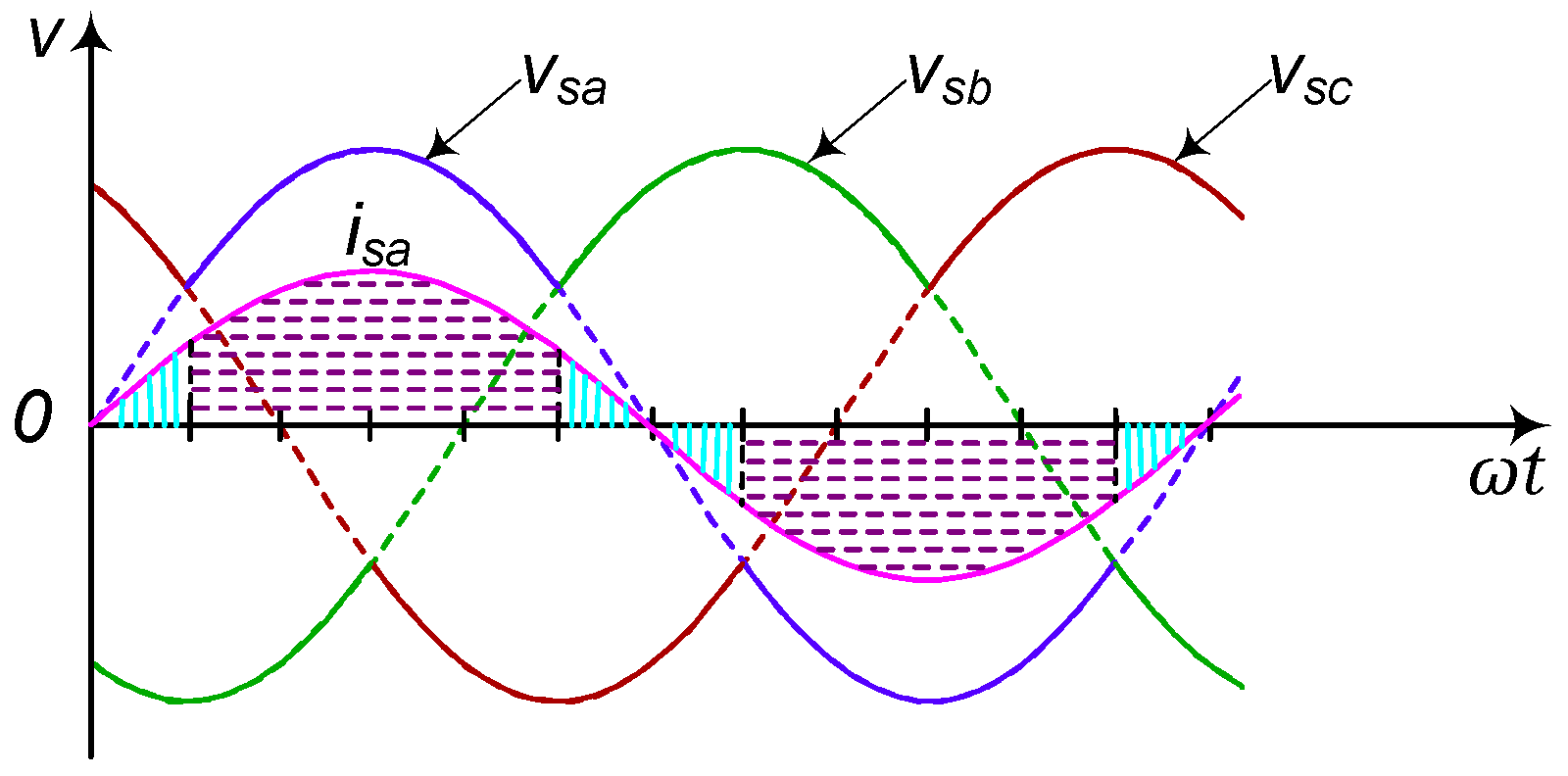
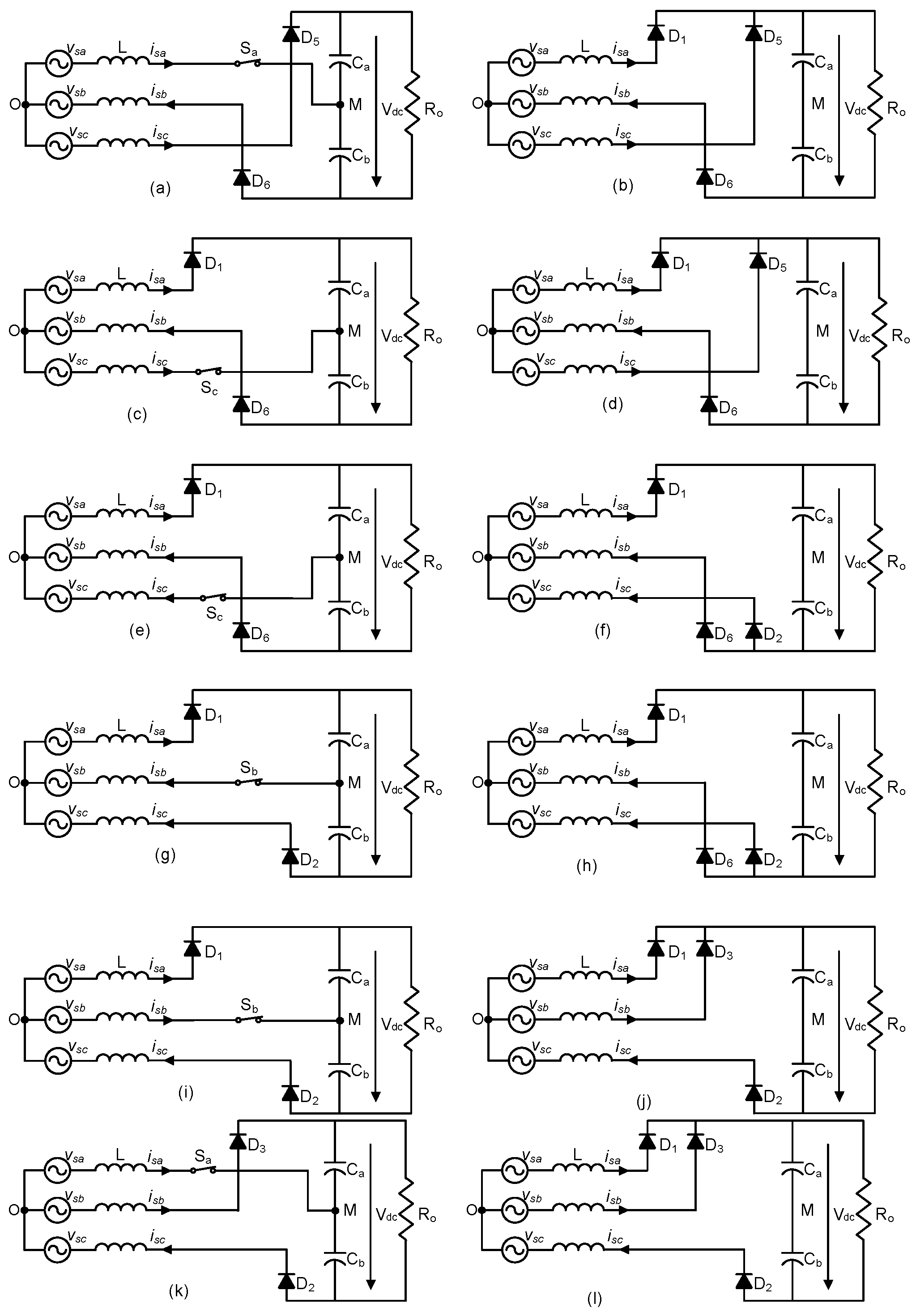
2. Operation Principle and Detailed Analysis of the Circuit
- Analysis of the operation of the scheme at interval I (0°–30°)
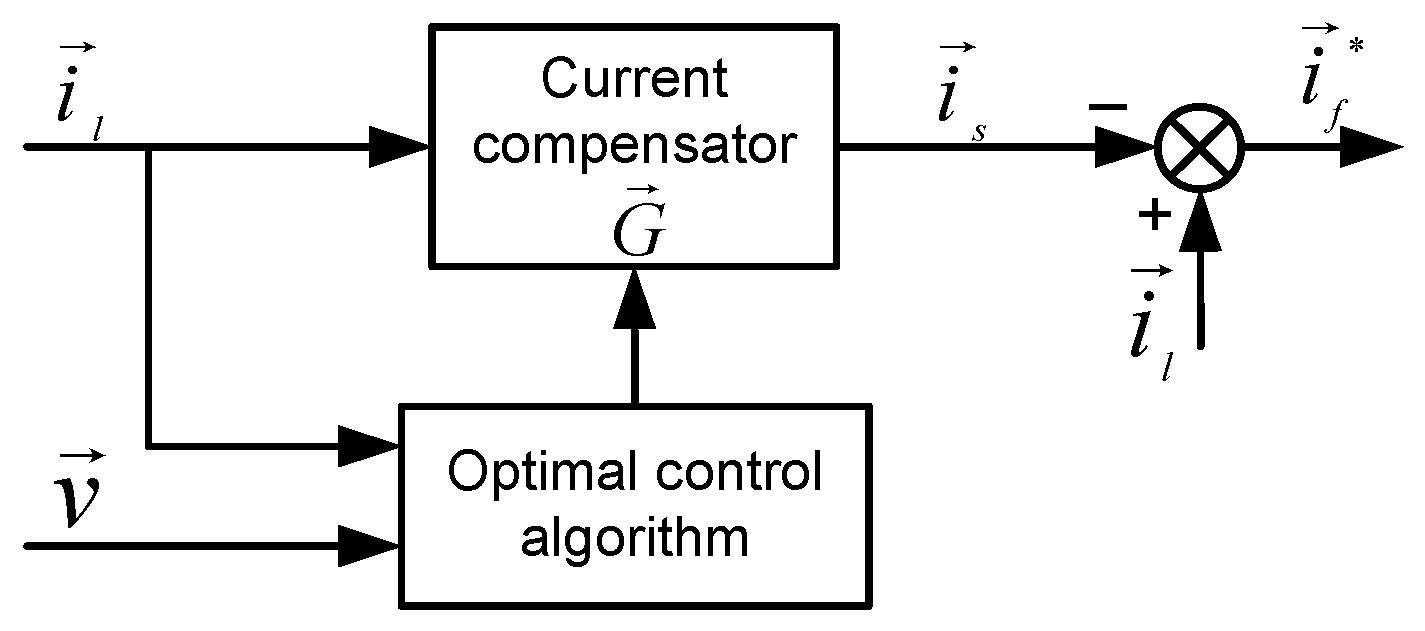
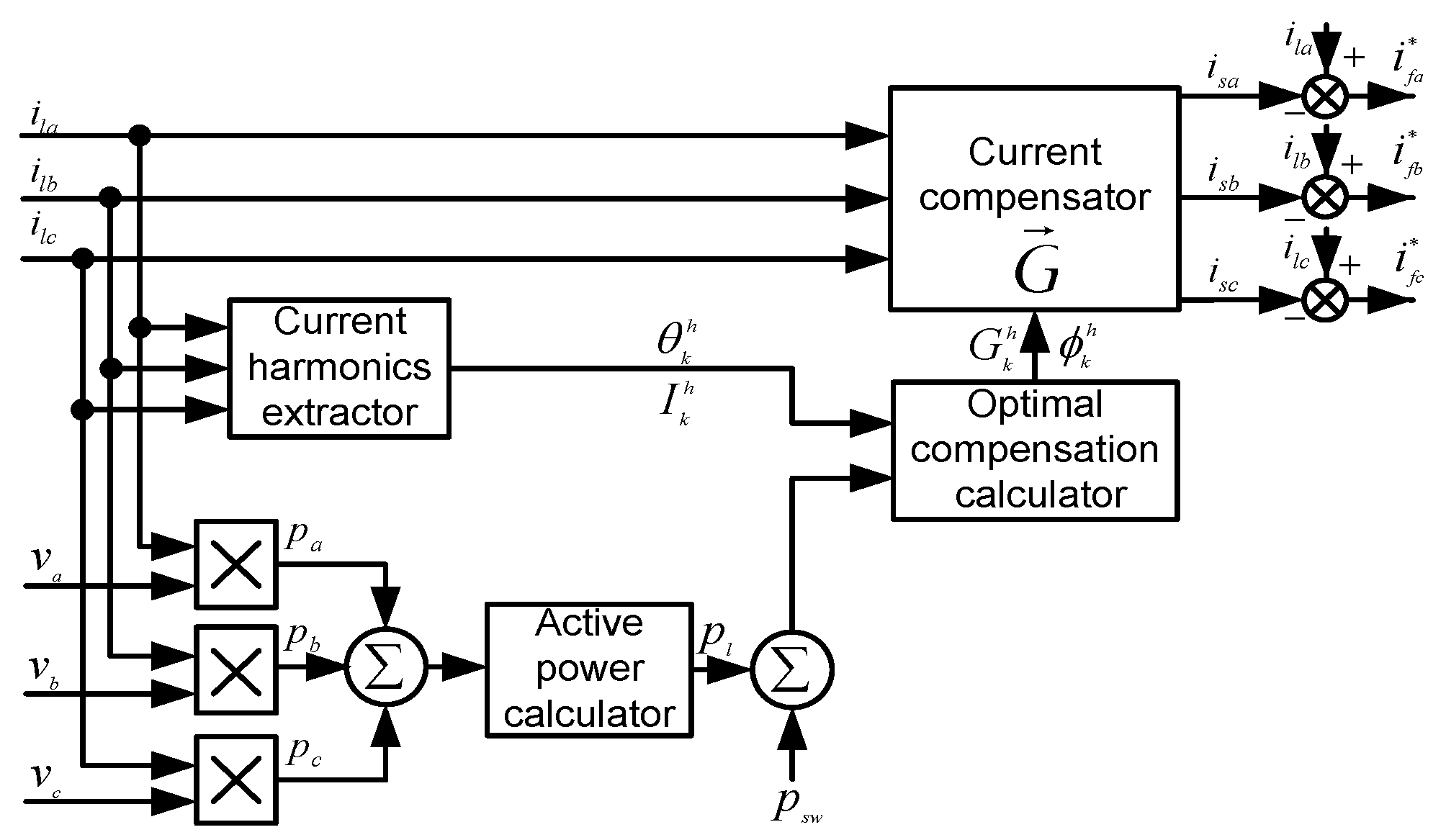
3. Proposed Optimal Control Technique for UPF Three-Phase Rectifier
3.1. Theoretical Calculation of Compensation Current
3.2. Constraints
3.2.1. Constraints on the Distortion of Single and Total Harmonics
3.2.2. Constraints on PF of the Load
3.2.3. Constraints on Consumption of Active Power
3.2.4. Objective Function
3.3. Method for Solving Constraints
4. Modeling the UPF Three-Phase Rectifier Using MATLAB
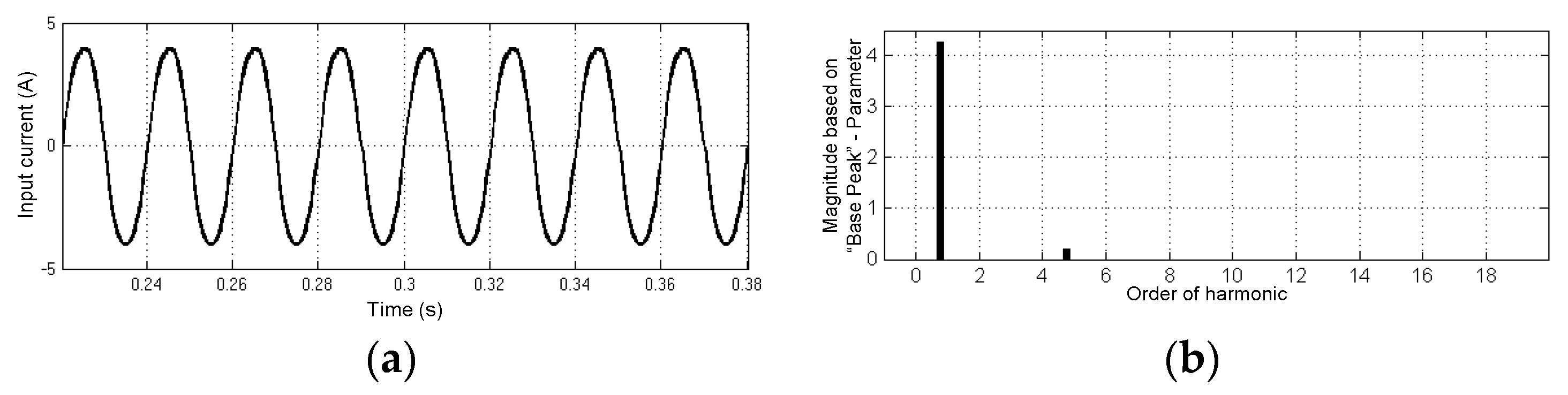
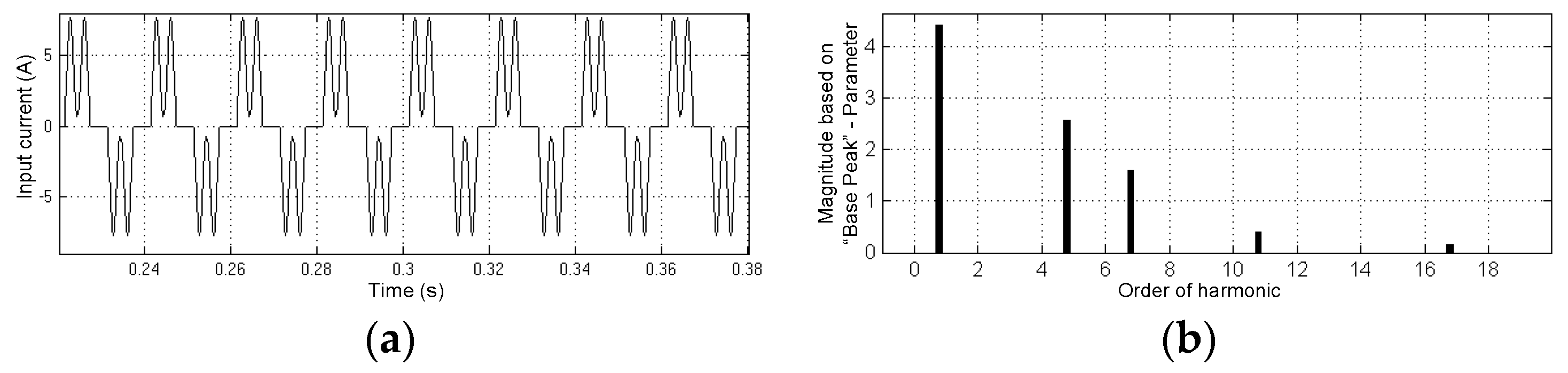
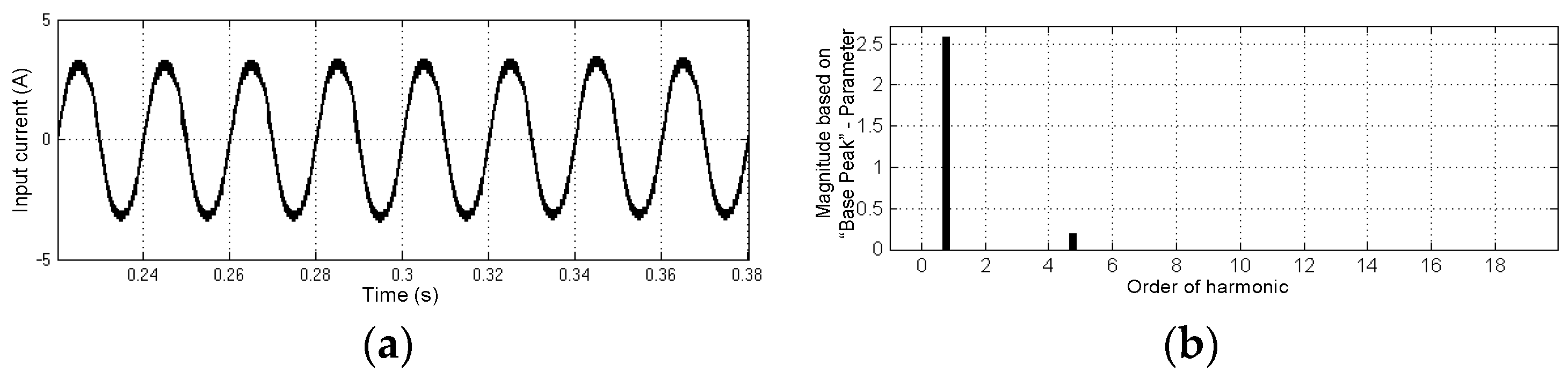
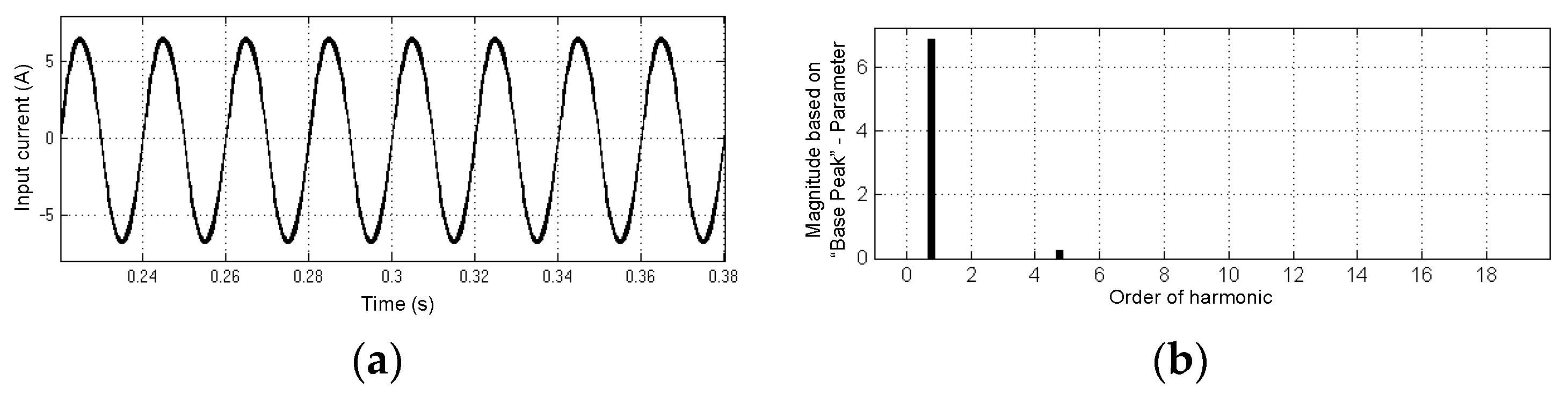
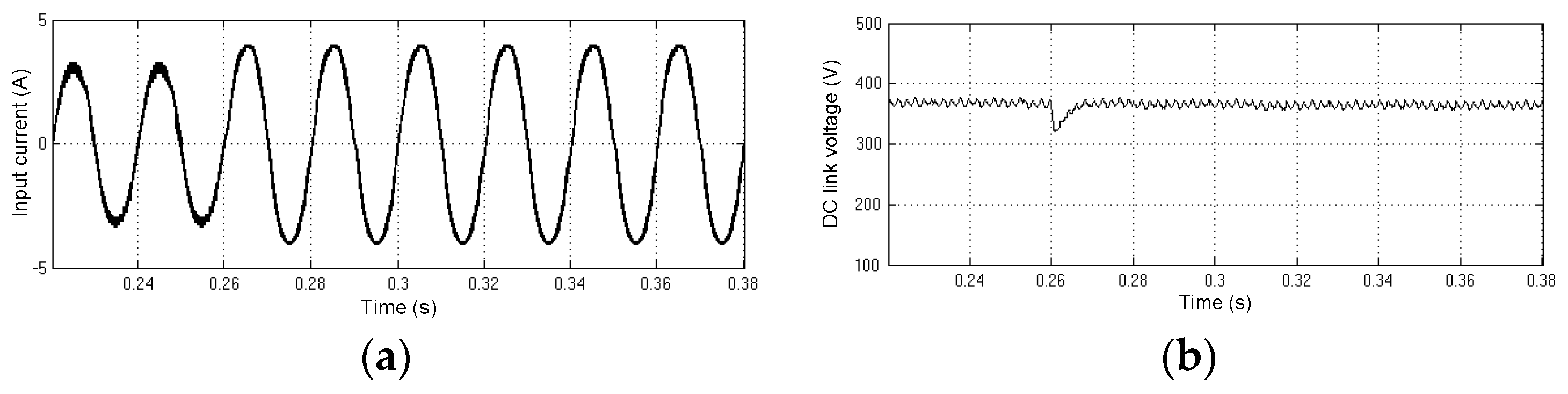
5. Simulation Results
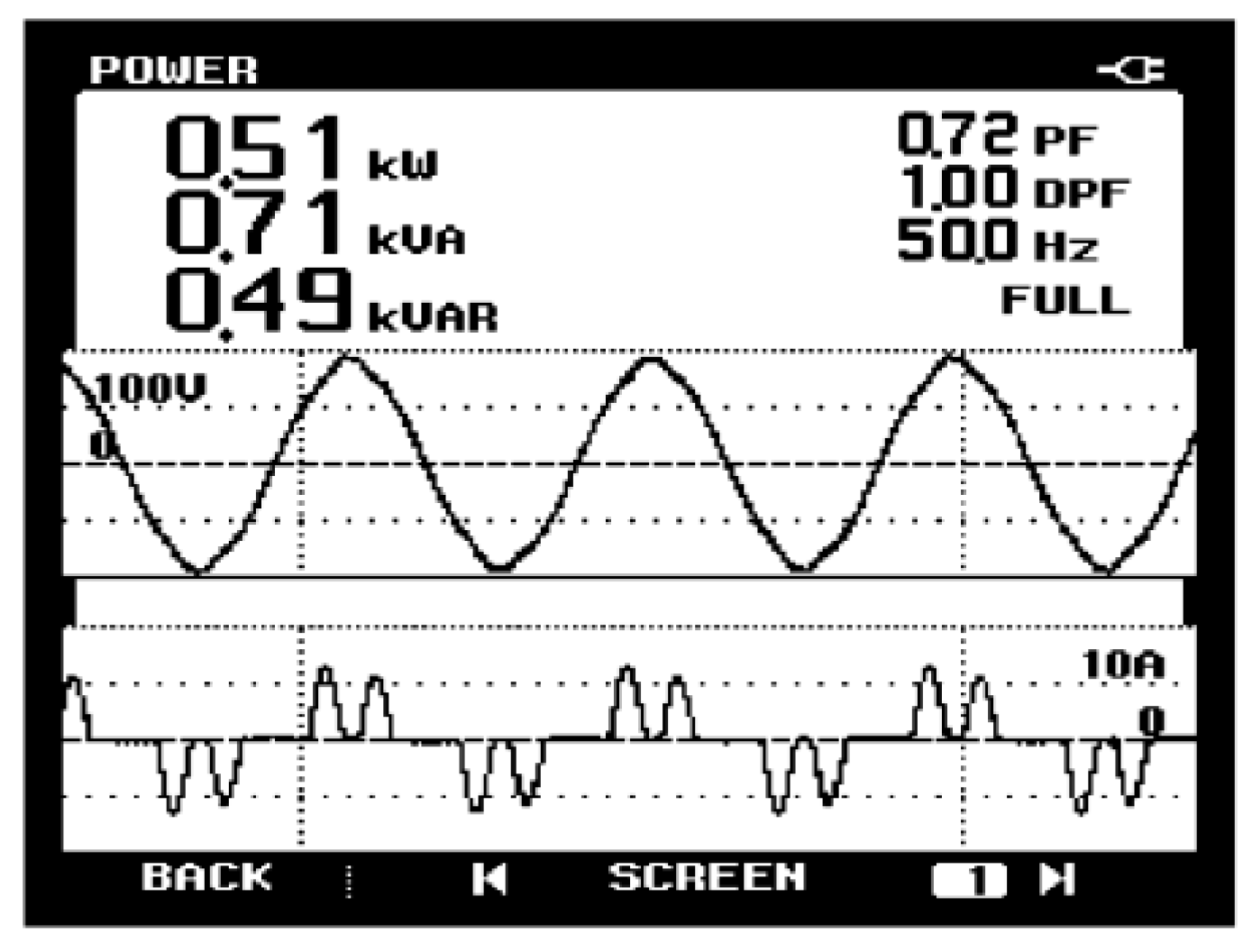
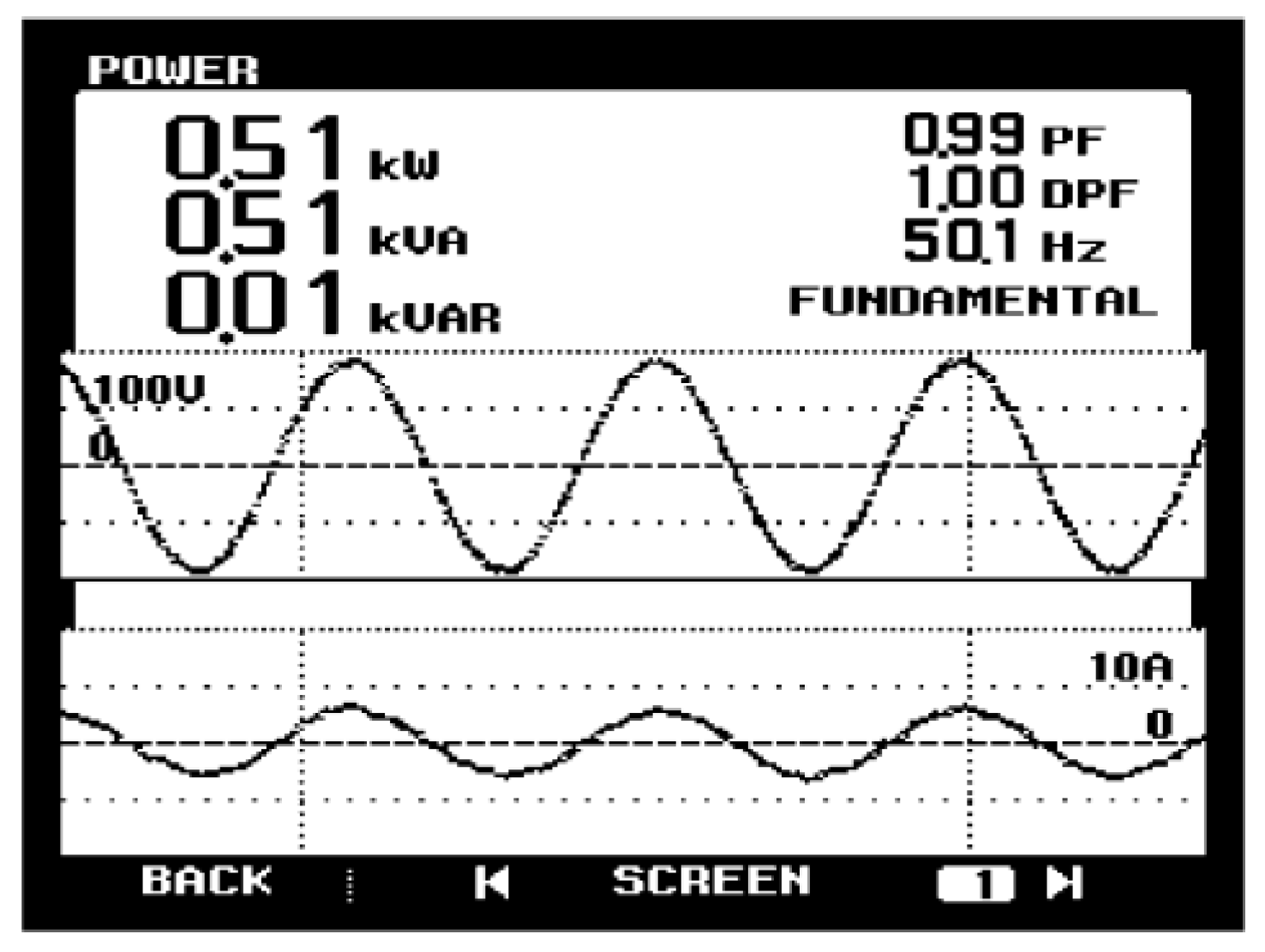
6. Experimental Results and Analysis
7. Discussion
- Adjustment of Power Factor: The proposed control technique demonstrated the capability to finely adjust the power factor within a specified target range.
- Reduction in Current Distortion: The research findings indicated that the proposed control technique effectively reduced the distortion in the power supply current.
- Improvements in Input Power Factor: The analysis revealed that the input power factor demonstrated significant improvement, even in the presence of fluctuations in input inductance, power, and varying load conditions.
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.G.; Xu, T.Y.; Xiang, L.P.; Wang, Q. Multi-phase interleaved parallel self-current-sharing high-gain DC/DC converter and its control strategy. J. Electr. Mach. Control 2021, 25, 27–37. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, J.; Hong, D.; Ren, R.W.; Li, X.Y. The effect of marine power generation technology on the evolution of energy demand for new energy vehicles. J. Coast. Res. 2020, 103, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, O.M.; Oliveira, D.; Diniz, A.S.A.C. Distributed photovoltaic generation and energy storage systems: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2010, 14, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.K.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.M.; Dong, J.Q. A simple and reconfigurable wireless power transfer system with constant voltage and constant current charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2022, 37, 4921–4925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.U.; Maswood, A.I.; Tariq, M.; Tafti, H.D.; Tripathi, A. Reliability and economic feasibility analysis of parallel unity power factor rectifier for wind turbine system. IET Renew. Power Gener. 2020, 14, 1184–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, J.H.; Liu, B.D.; Chen, S.M.; Yang, H.T. New power factor correction application for a small wind power system. IEICE Trans. Electron. 2016, E99C, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimshurst, A.; Willden, R.H.J. Analysis of a tip correction factor for horizontal axis turbines. Wind. Energy 2017, 20, 1515–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.R.; Ding, C.; Chen, W.H. Research on the diffusion model of electric vehicle quantity considering individual choice. Energies 2023, 16, 5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordic, M.; Stamenkovic, D.; Popovic, V.; Muzdeka, S.; Micovic, A. Electric vehicle conversion: Optimisation of parameters the design process. Teh. Vjesn.-Tech. Gaz. 2017, 24, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Dudek, E. The flexibility of domestic electric vehicle charging: The electric nation project. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2021, 19, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanés-Montero, M.I.; Gallardo-Lozano, J.; Romero-Cadaval, E.; González-Romera, E. Hall-effect based semi-fast AC on-board charging equipment for electric vehicles. Sensors 2011, 11, 9313–9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caro, L.M.; Ramos, G.; Rauma, K.; Rodriguez, D.F.C.; Martinez, D.M.; Rehtanz, C. State of charge influence on the harmonic distortion from electric vehicle charging. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2021, 57, 2077–2088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.C.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, Q.G.; Wei, N.Q. Measurement-based harmonic modeling of an electric vehicle charging station using a three-phase uncontrolled rectifier. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, T.; Hao, F.; Srdic, S.; Lukic, S. Extreme fast charging of electric vehicles: A technology overview. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electr. 2020, 5, 861–878. [Google Scholar]
- Panchanathan, S.; Vishnuram, P.; Rajamanickam, N.; Bajaj, M.; Blazek, V.; Prokop, L.; Misak, S. A comprehensive review of the bidirectional converter topologies for the vehicle-to-grid system. Energies 2023, 16, 2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, Y.C.; Lin, Z.R.; Chen, M.C.; Hsieh, H.C.; Liu, Y.C.; Chiu, H.J. High-efficiency wireless power transfer system for electric vehicle applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II-Express Briefs 2017, 64, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwly, M.Y.; Abdel-Majeed, M.S.; Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Torki, M.; Hamdy, R.A.; Hamad, M.S.; Ahmed, S. IoT-based supervisory control of an asymmetrical nine-phase integrated on-board EV battery charger. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 62619–62631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnago, H.; Lucía, O.; Chhawchharia, S.; Menzi, D.; Kolar, J.W. Novel bidirectional universal 1-phase/3-phase-input unity power factor differential AC/DC converter. Electron. Lett. 2023, 59, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Li, Z.; Cheng, H.; Chen, T.; Kong, J.Y. Novel high-power triple line-voltage cascaded unity power factor rectifier. J. Power Electron. 2023, 23, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswood, A.I.; Al-Ammar, E.; Liu, F. Average and hysteresis current-controlled three-phase three-level unity power factor rectifier operation and performance. IET Power Electron. 2011, 4, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, E.L.M.; Barbi, I. An improved high power factor and low cost three-phase rectifier. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1997, 33, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolar, J.W.; Zach, F.C. A novel three-phase utility interface minimizing line current harmonics of high power telecommunications rectifiers modules. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1997, 44, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswood, A.I.; Liu, F. Unity power factor rectifier-inverter structure operating under unbalanced supply and variable dc bus voltage. IET Power Electron. 2011, 4, 899–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswood, A.I.; Yusop, A.K.; Rahman, M.A. A novel suppressed-link rectifier-inverter topology with unity power factor. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2002, 17, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drofenik, U.; Kolar, J.W. Comparison of not synchronized sawtooth carrier and synchronized triangular carrier phase current control for the VIENNA rectifier. In ISIE’99, Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics (Cat. No. 99TH8465), Bled, Slovenia, 12–16 July 1999; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Maswood, A.I.; Liu, F. A novel unity power factor input stage for AC drive application. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Smedley, K.M. Three-phase unity-power-factor star-connected switch (VIENNA) rectifier with unified constant-frequency integration control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2003, 18, 952–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Maswood, A.I. A novel variable hysteresis band current control of three-phase three-level unity PF rectifier with constant switching frequency. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2006, 21, 1727–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswood, A.I.; Liu, F. A unity power factor front-end rectifier with hysteresis current control. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2006, 21, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maswood, A.I.; Liu, F. A unity-power-factor converter using the synchronous-reference-frame-based hysteresis current control. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2007, 43, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std. 519-1992; IEEE Recommended Practices and Requirements for Harmonic Control in Electric Power Systems. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1993.
- Chen, D.; Lin, Y.; Xiao, L.; Xu, Z.; Lian, H. A harmonics detection method based on improved comb filter of sliding discrete Fourier for grid-tied inverter. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Optimization Toolbox User’s Guide for Use with Matlab; Version 2; The Math Works, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 1999.




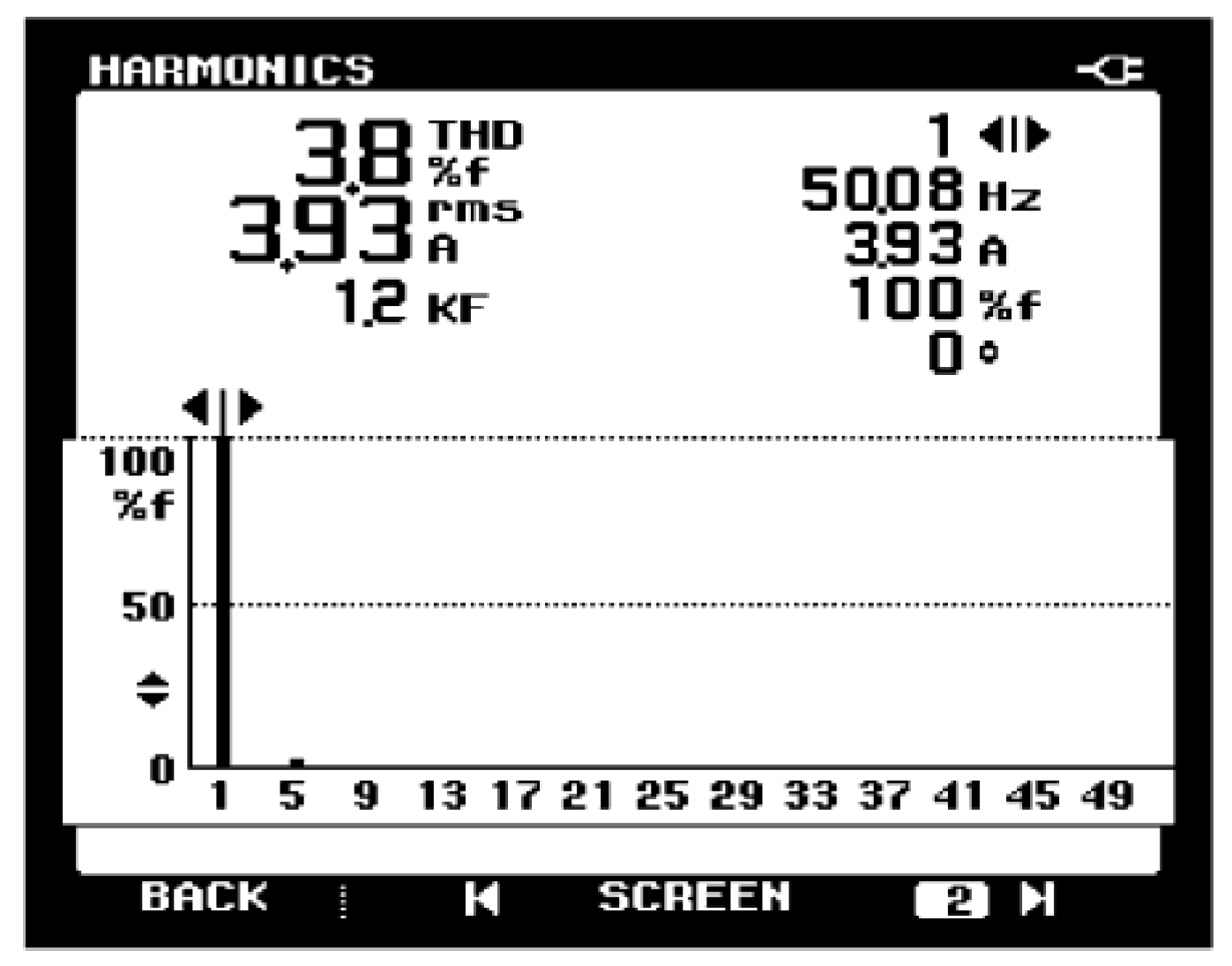

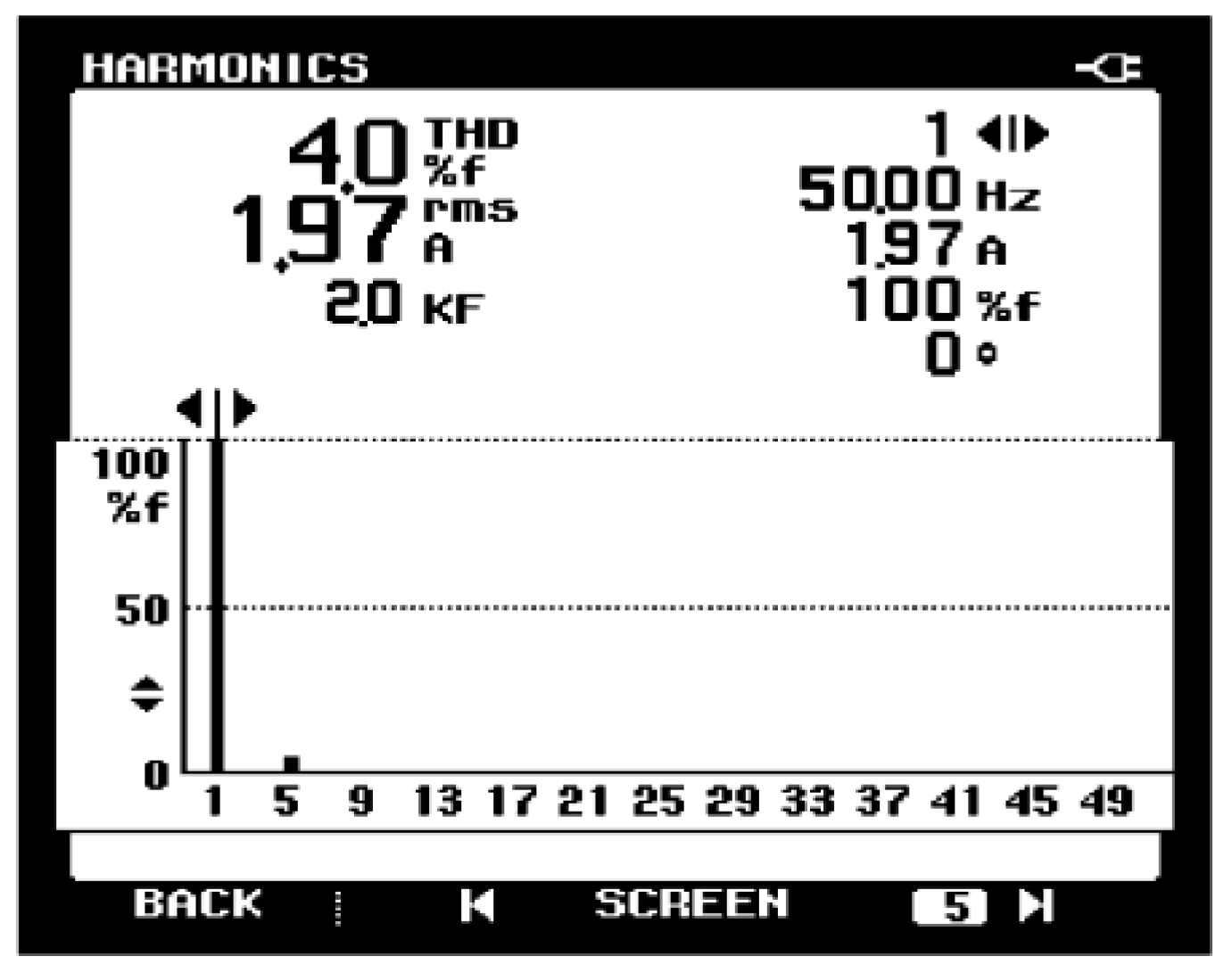
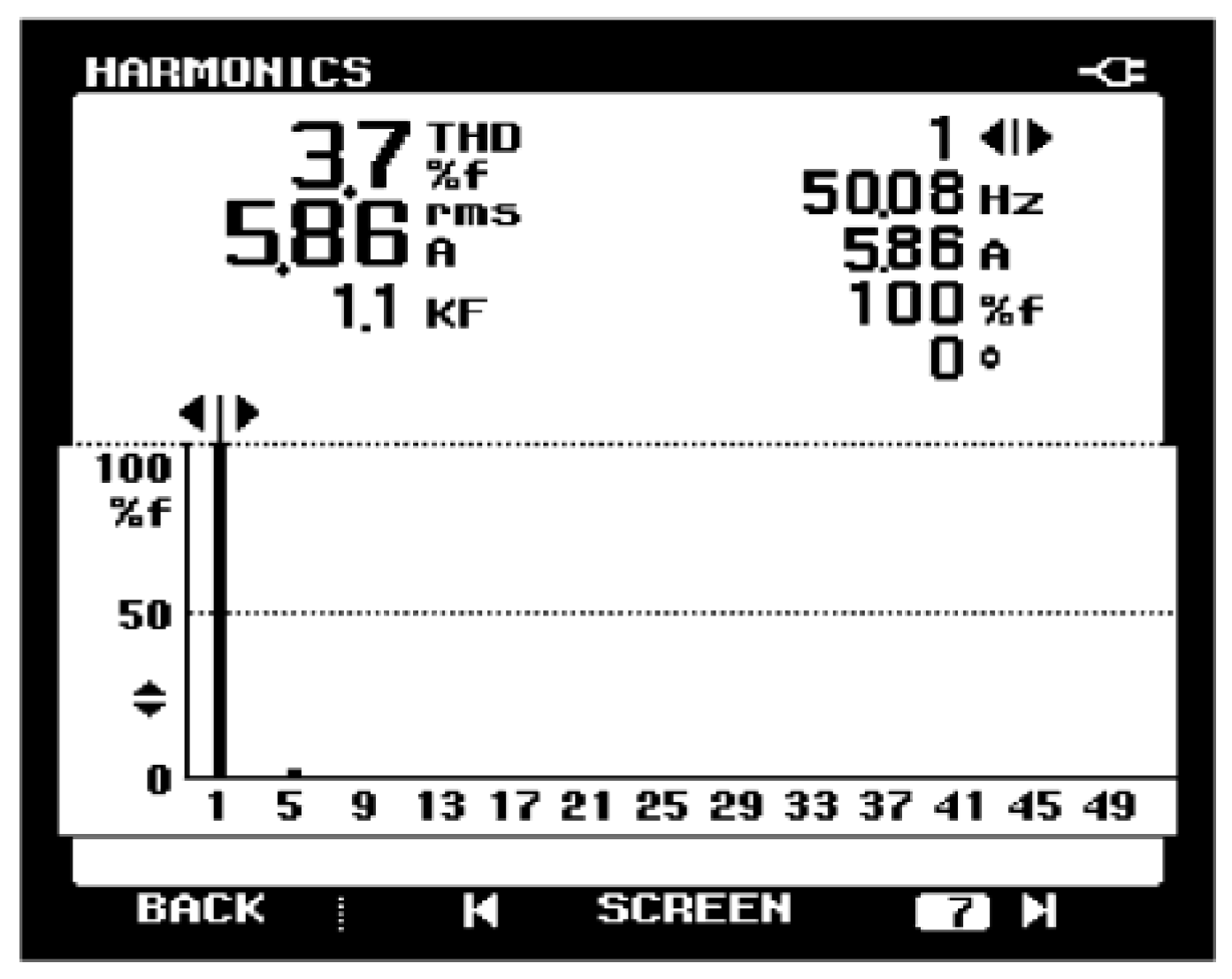
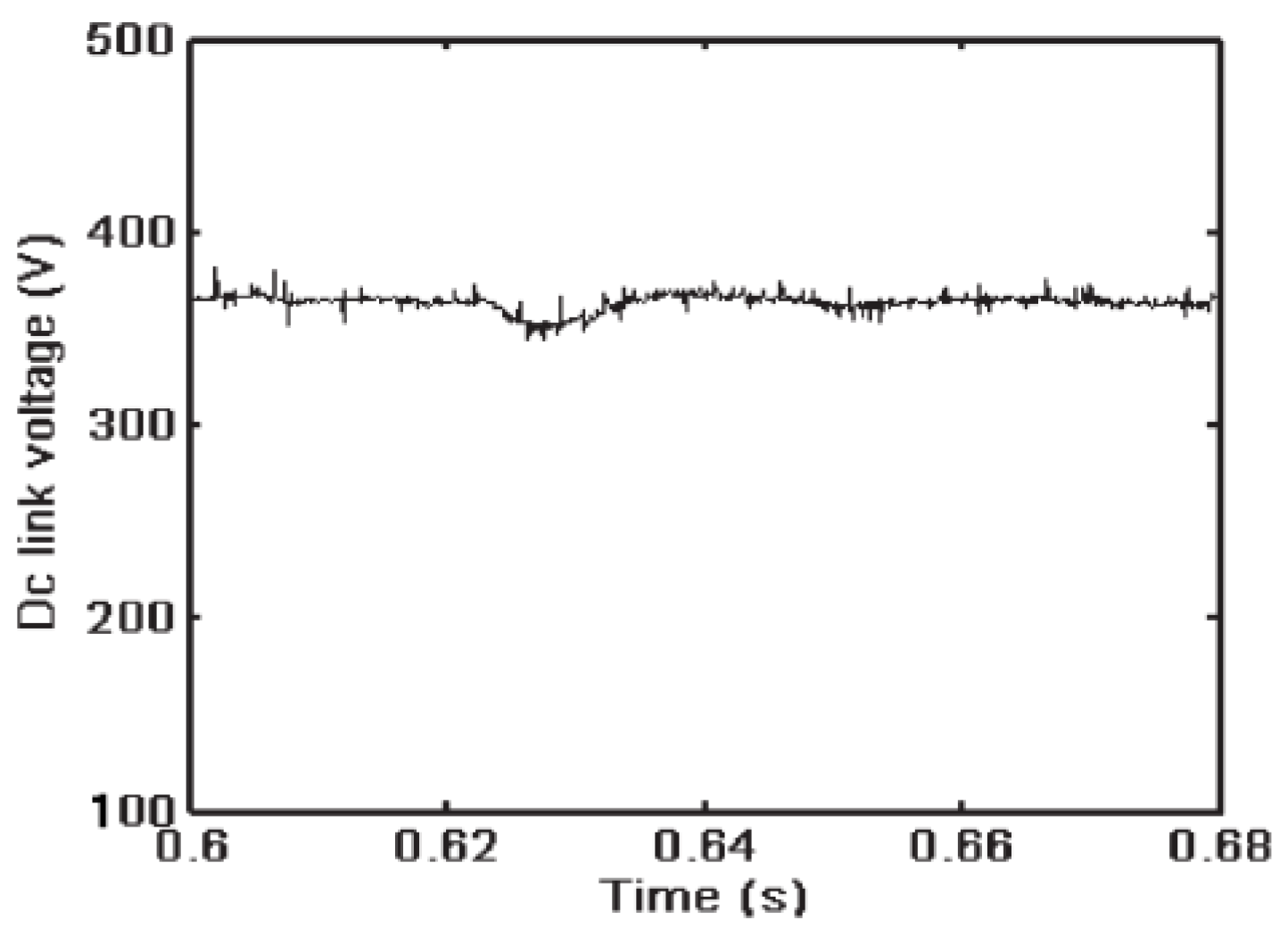
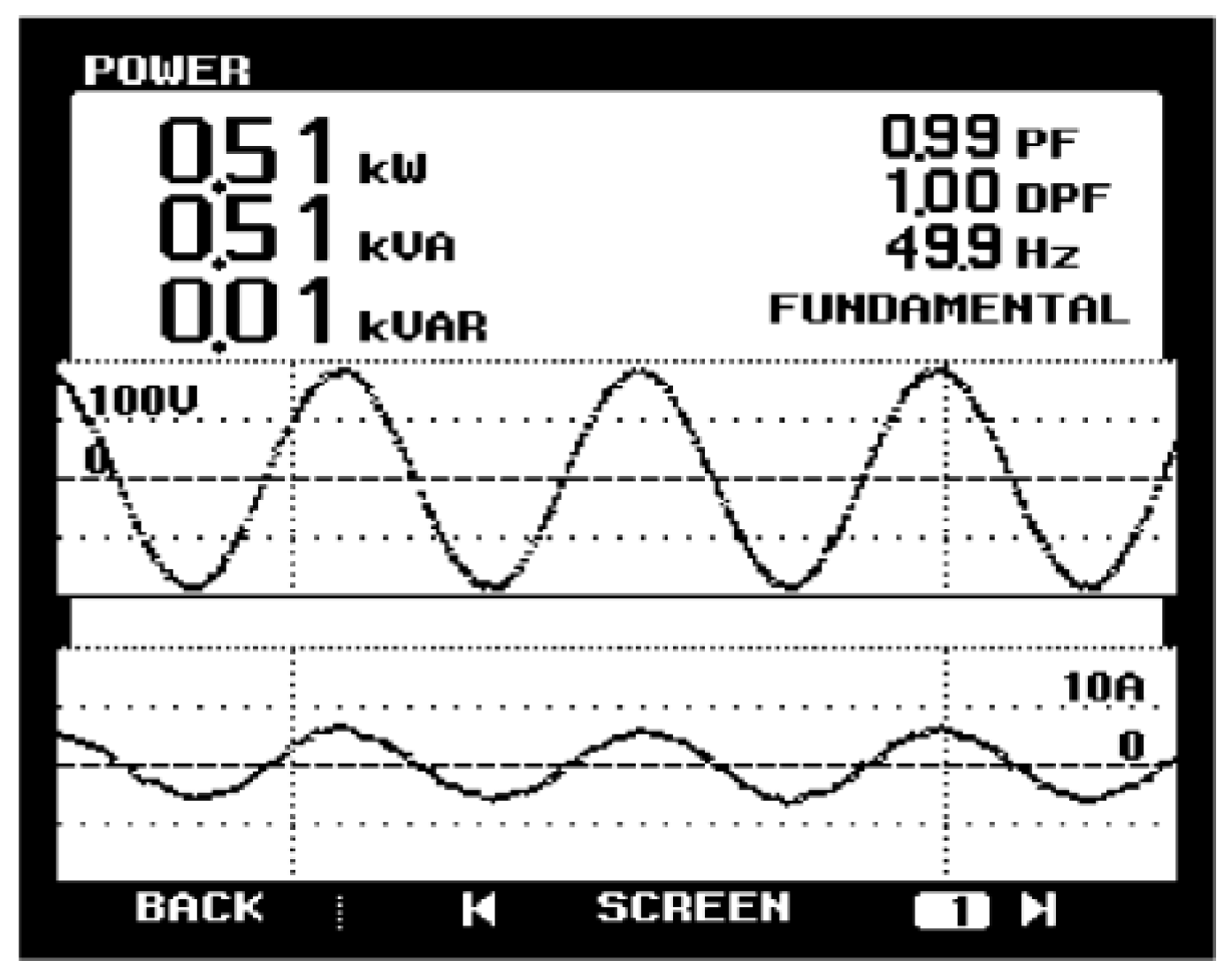
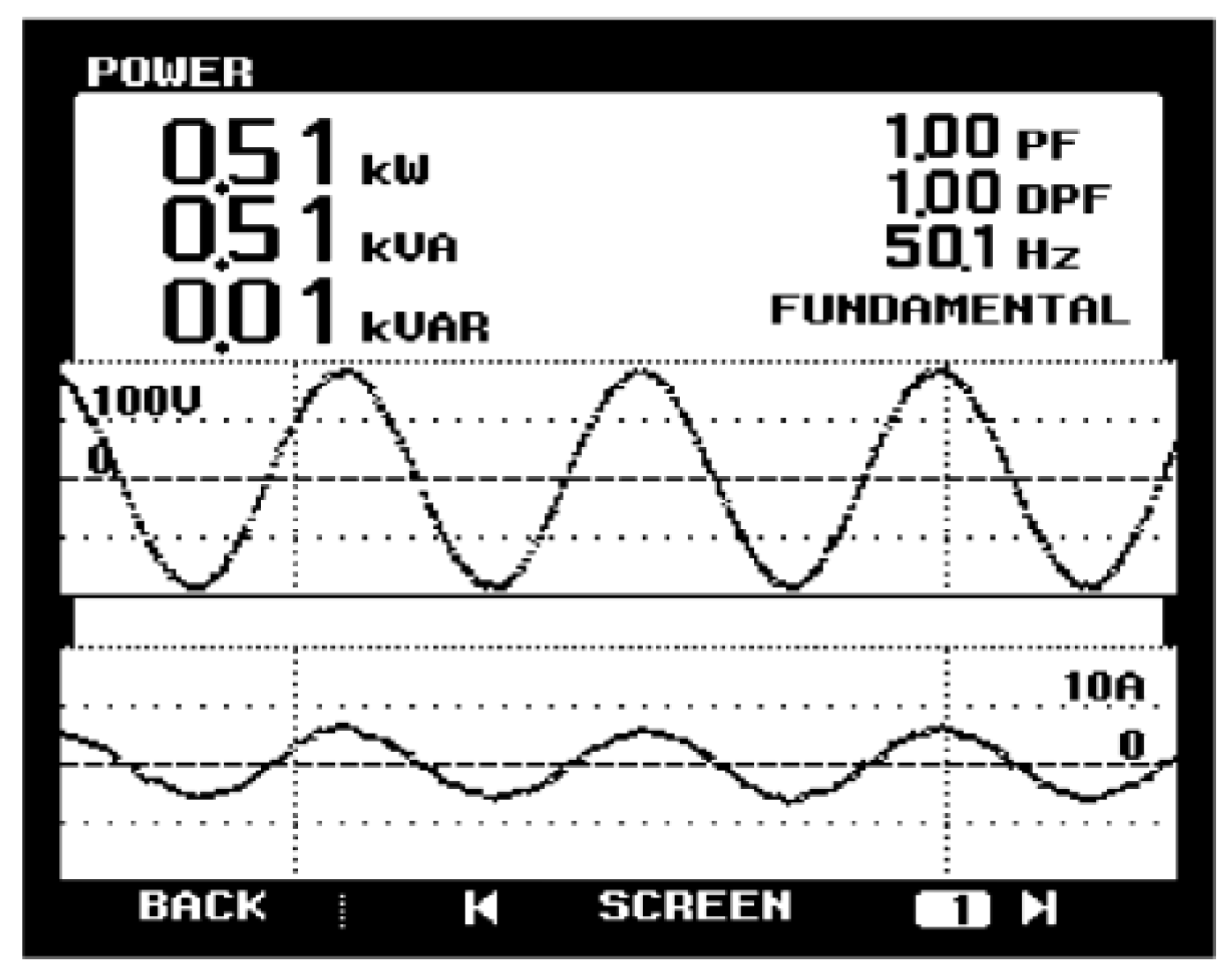
| Indicator | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Rated output power | 1 kW |
| Input inductor | 5 mH |
| DC link voltage | 370 V |
| Input voltage of line-to-line | 220 V |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Jia, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Alternative Performance Indices-Based Control Technique for a Unity Power Factor Three-Phase Rectifier. Electronics 2024, 13, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030604
Zhang S, Liu X, Jia Y, Wang P, Wang J, Zhang J. Alternative Performance Indices-Based Control Technique for a Unity Power Factor Three-Phase Rectifier. Electronics. 2024; 13(3):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030604
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Shaoru, Xiaoyan Liu, Yikun Jia, Pingjun Wang, Jingmin Wang, and Jielu Zhang. 2024. "Alternative Performance Indices-Based Control Technique for a Unity Power Factor Three-Phase Rectifier" Electronics 13, no. 3: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030604
APA StyleZhang, S., Liu, X., Jia, Y., Wang, P., Wang, J., & Zhang, J. (2024). Alternative Performance Indices-Based Control Technique for a Unity Power Factor Three-Phase Rectifier. Electronics, 13(3), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13030604






