Abstract
Modern processors often face challenges when handling instructions that overwhelm the branch target buffer (BTB), leading to front-end bottlenecks. As the BTB’s capacity increases, its prediction module can become slower and power-hungry. In this paper, we introduce a straightforward yet highly effective two-level prediction mechanism to mitigate the escalating power consumption in the BTB structure, achieved by reducing the number of accesses. Our approach incorporates two main elements: M-BTB and V-BTB. M-BTB encompasses the first-level prediction mechanism and a fully associative BTB, while V-BTB houses the second-level prediction mechanism and a set-associative BTB. To implement our prediction mechanism, we optimize the traditional two-level BTB structure. The first level employs the skew mechanism, and the second level dissects the tag bits to create the Partial tag. These two levels of prediction mechanism correspond to the bank/way prediction for the two-level BTB structure. Our experimental results show that the first-stage prediction mechanism reduces M-BTB accesses by 75%, while the second-stage prediction mechanism ensures that over 98% of addresses require just zero or one way of the V-BTB to achieve a hit result. Our proposed approach achieves a remarkable 86–97% reduction in power consumption, with a minimal impact on performance and an increase in overall area efficiency.
1. Introduction
Branch instructions play a critical role in the execution of programs by enabling jumps from the current instruction stream to other locations, thereby improving program flow and reducing execution delays. To expedite execution and minimize the stalls caused by branch instructions, branch prediction systems are employed. These systems forecast the destination of branch instructions, enhancing execution speed. The central components of branch prediction structures are the branch target buffer (BTB) and the branch predictor [1].
The branch predictor is responsible for determining whether a conditional branch will occur. Various conditional branch predictors, such as Bimodal, Gshare [2], Tournament [3], and TAGE [4], among others, have demonstrated exceptional performance. Meanwhile, the BTB records crucial information, including the current address of branch instructions, their target addresses, jump types, and more. To improve prediction performance, designers often combine multiple structures into an efficient branch prediction system, as studies have indicated that BTB-based schemes offer significant advantages in prediction performance [5,6,7].
In the pursuit of enhanced processor performance, designers have made efforts to optimize the structure of the BTB to reduce table miss rates. For example, certain BTB structures allocate different-sized target table entries to accommodate more branch instructions [8]. Asheim’s experiments demonstrated that gradually expanding the BTB structure can significantly reduce mispredictions [9]. However, the increased BTB capacity introduces more access latency, resulting in longer branch instruction prediction times and increase power consumption. Kaynak et al. introduced a BTB structure called AirBTB [10], which closely resembles an L1 cache and effectively reduces branch mispredictions. Nevertheless, its BTB table entries, exceeding 130 bits, and a high number of entries lead to substantial access latency, negatively affecting branch prediction performance.
A two-level BTB structure proposed by Burcea et al. [11] achieved a high success rate in branch prediction, addressing the performance losses due to missed branches. However, it suffered from excessive power consumption. The first-level BTB, housing 4 K entries, introduced resource overhead and decreased access speed, rendering the first-level BTB’s benefits largely ineffective. Additionally, because their BTB adopted a multiplexed group-connected structure, simultaneous accesses caused considerable energy consumption issues.
The previous schemes developed to reduce BTB power consumption mainly include adding redundant bits and modifying the structure. The increases in redundant bits increases the area and may reduce the prediction performance [12]. Modifying the BTB structure may also cause an increase in table entries, resulting in capacity waste. Therefore, the BTB prediction performance should not be affected by an advantageous power optimization scheme, and the balance between area and power consumption should be achieved.
In this paper, we present a simple and effective two-level prediction mechanism for addressing the high-power-consumption problem by reducing the number of BTB accesses. We base our design on the conventional two-level BTB structure and introduce two main modules: the M-BTB module and the V-BTB module. The M-BTB module comprises a first-level prediction mechanism and a fully associative BTB with 64 entries, while the V-BTB module includes a second-level prediction mechanism and a set-associative structure with 4 × 512 entries. Compared to a typical two-level BTB scheme, our prediction mechanism identifies which bank/way is accessed, reducing power consumption by reducing BTB accesses.
The first-level mechanism involves bank prediction. We evenly distribute the BTB into N banks, and bank selection is carried out through a decoder. To minimize conflicts arising from bank additions, we introduce the skew design to reduce entry replacement frequency. The second-level mechanism is way prediction, wherein we split the tag to generate the partial tag, facilitating advanced access prediction. The partial tag effectively blocks accesses from sequential instruction addresses and minimizes nonhit way accesses. Our analysis of various traces and experiments reveals that our proposed scheme achieves an impressive 86–97% reduction in power consumption, with a minimal impact on performance.
The main contributions of this article can be summarized as follows:
1. We propose an effective, practical approach for a two-level prediction mechanism that reduces access power consumption.
2. We propose bank/way-based prediction methods based on different BTB structures. The bank prediction method is used for the fully associative BTB structure, and the skew design is added to reduce entry conflicts. For the set associative BTB structure, the way prediction method is used to realize the filtering of nonbranch addresses.
The remained of this paper is organized as follows: In Section 2, the previous methods and introduce the two-level BTB structures. Section 3 introduces the structure of our methods. In Section 4, we evaluate the analysis of accesses, power, area, performance and way selection mechanism. Section 5 concludes this paper.
2. Background and Related Work
2.1. Branch Prediction and Its Significance
Branch prediction is a critical aspect for improving processor performance and has been a prominent research subject within the computer architecture field. Branch prediction consists of three primary components: the key features, BTB, and the branch predictor. The branch predictor is responsible for forecasting the outcomes of predicted conditional branch instructions, determining whether an instruction will jump to another location or continue sequentially. The BTB, on the other hand, stores information about the branch instruction address. Many studies have shown that processors equipped with BTB structures possess have performance advantages, as they lead to lower cycle times and have increased pipeline depths, both of which contribute to more efficient execution [13,14,15,16].
2.2. Historical Development of BTB
The inception of BTB structures dates back to the work of Sussenguth et al. [17] in 1971, who introduced the first BTB structure, laying the groundwork for subsequent research. In efforts to optimize table entry utilization, Seznec’s team [18] introduced the concept of virtualization to branch direction prediction.
Burcea et al. [11] proposed a virtual BTB structure to accommodate more branch table entries within limited storage space. Kumar et al. [19] presented a BTB structure design incorporating a traditional BTB structure at the first level and a second-level BTB shared across all cores.
A novel FDIP-X branch prediction scheme, introduced by Asheim et al. [20], took into account the varying distributions of offset lengths in branch instructions, enabling the storage of offsets instead of full target addresses, which effectively reduced area requirements and increased entry count.
2.3. Power Optimization and Capacity
With the increasing demands on BTB capacity as program loads grow, reducing power consumption in BTB design is becoming increasingly vital. Kaynak et al. proposed the AirBTB, a basic block BTB design that employs a branch bitmap for each branch table entry, simplifying the identification of branch instructions within cache blocks [10]. Chang et al. [21] proposed an energy-efficient BTB lookup scheme for embedded processors, emphasizing the filtering of sequential execution instructions to decrease BTB access. Levison et al. [22] introduced a microarchitectural method called shifted-index BTB with a set buffer, effectively reducing dynamic and static power. Xiong et al. [12] proposed a TG-BTB structure, which reduced the number of queries by counting the distance between adjacent branch instructions and accessing the BTB only when the target distance was reached, thus lowering query power consumption.
2.4. Innovations in Power Reduction
Previous schemes [21,22] aimed at power optimization often involved increasing the number of levels and marking bits, which included instruction intervals, instruction buffers, and more. In contrast, our approach introduces a prediction mechanism to reduce power consumption without extending table entry lengths. This represents a novel approach to mitigating power consumption in the BTB structure. Moreover, our design exhibits the advantage of simplicity in fault tolerance schemes. Previous approaches [12] that added extra bits within table entries necessitated more complex fault tolerance mechanisms, increasing system complexity. The experimental results from both approaches indicate some performance loss due to the inaccuracy of the instruction interval prediction and the swifter replacement of table entries resulting from shifting operations. Additionally, incorporating marking bits within table entries introduces extra area overhead. In comparison, our approach optimizes the structure by adding a prediction mechanism without increasing entry length, presenting a fresh approach to power consumption reduction.
2.5. The Two-Level BTB Structure
As program sizes continue to grow, the demand for larger BTB capacities is increasing. To strike a balance between performance and power consumption, researchers have explored various BTB architecture designs [23,24,25]. However, as directional predictors become more complex, the BTB needs to provide addresses for prediction and prefetching.
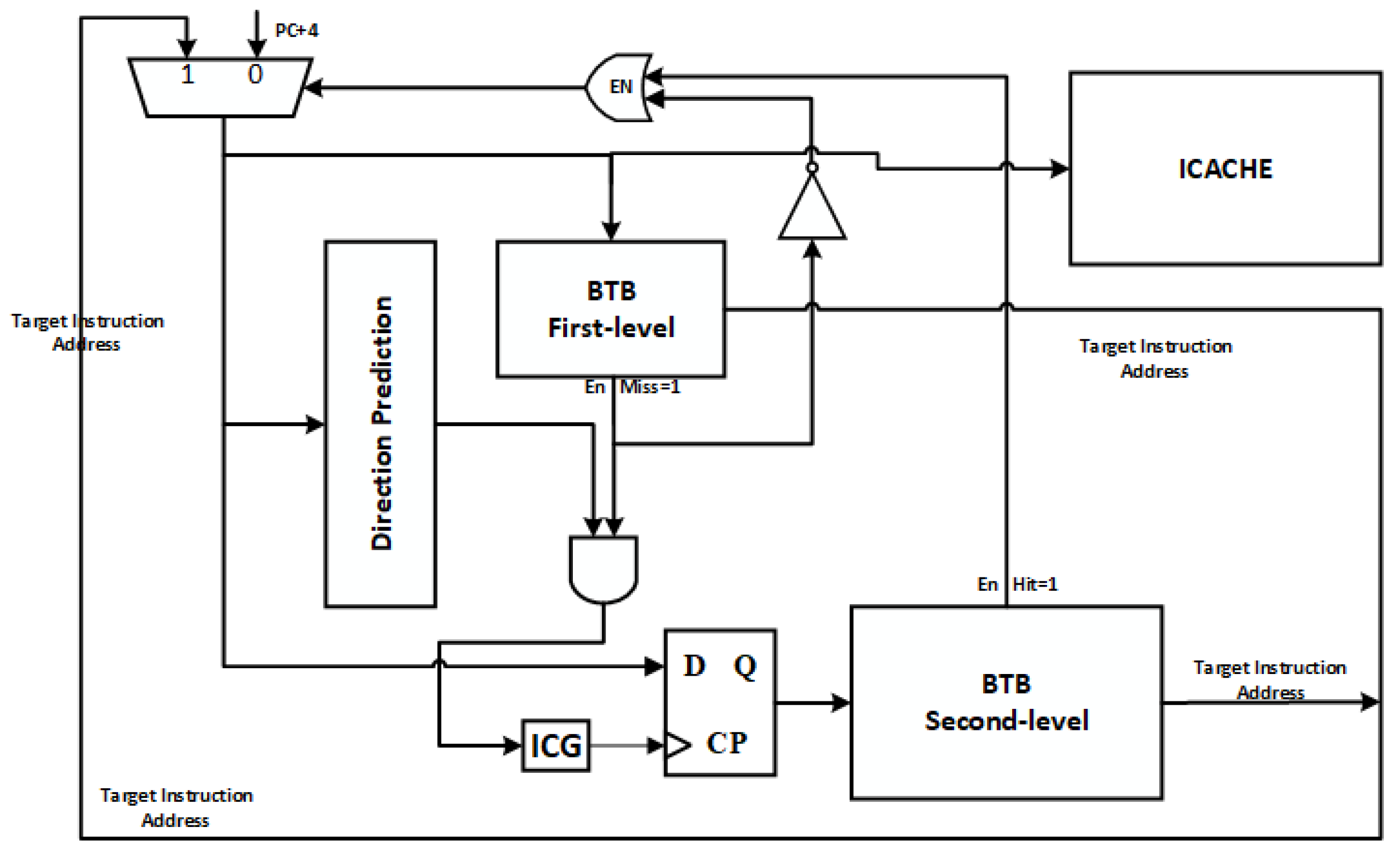
This section delves into the analysis of the serial two-level BTB architecture [26]. Figure 1 illustrates the microarchitecture of the serial two-level BTB design. As shown in Figure 1, ICG stands for gating clock. BTB is used to predict the branch instruction’s address, the direction predictor is used to indicate which direction is to be taken, and the instruction cache is used to fetch the target instruction. During the read phase, the instruction cache, branch direction predictor, and first-level BTB (FB) are accessed simultaneously. If the branch is predicted to be unoccupied or if the branch is predicted to be occupied and the FB hits, the branch address forecast (BAF) does not involve the second-level BTB (SB) in the next cycle. However, if the branch is predicted to be occupied and the FB lookup fails, the SB must be accessed in the following cycle. In such cases, the fetch logic either halts or inserts a no-operation (NOP) instruction (by supplying the address of a 0) until the result of the SB access becomes available.
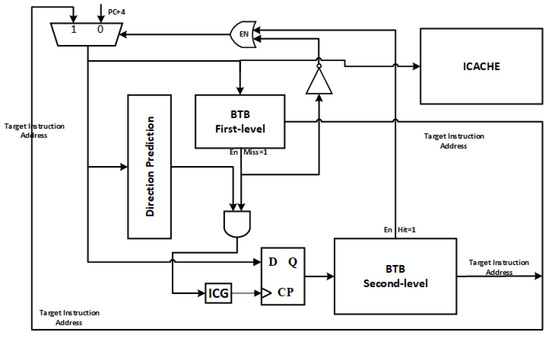
Figure 1.
Schematic of the two-level BTB structure.
To enhance processor performance, some processors opt to synchronize predictions with the FB and branch predictors. The first cycle utilizes the FB results, and the subsequent cycle is adjusted based on the SB and direction predictor results, LOOP predictor, and so on. This optimization strategy enhances processor performance since the FB structure can quickly access and promptly predict the target instruction address. Additionally, FB’s simple structure and fast access speeds contribute to improved performance. While parallel accesses result in a limited increase in access latency, the multilevel parallel structure leads to more unnecessary BTB accesses, consequently resulting in additional BTB energy consumption.
In this study, we addressed branch-target buffers designed for low-power embedded processors. We employed the serial two-stage BTB structure as a benchmark and reduced BTB structure access by introducing a prediction mechanism to lower the power consumption associated with BTB access. We describe the proposed structure in detail in the subsequent section.
3. The Proposed Structure
3.1. Structure Overview
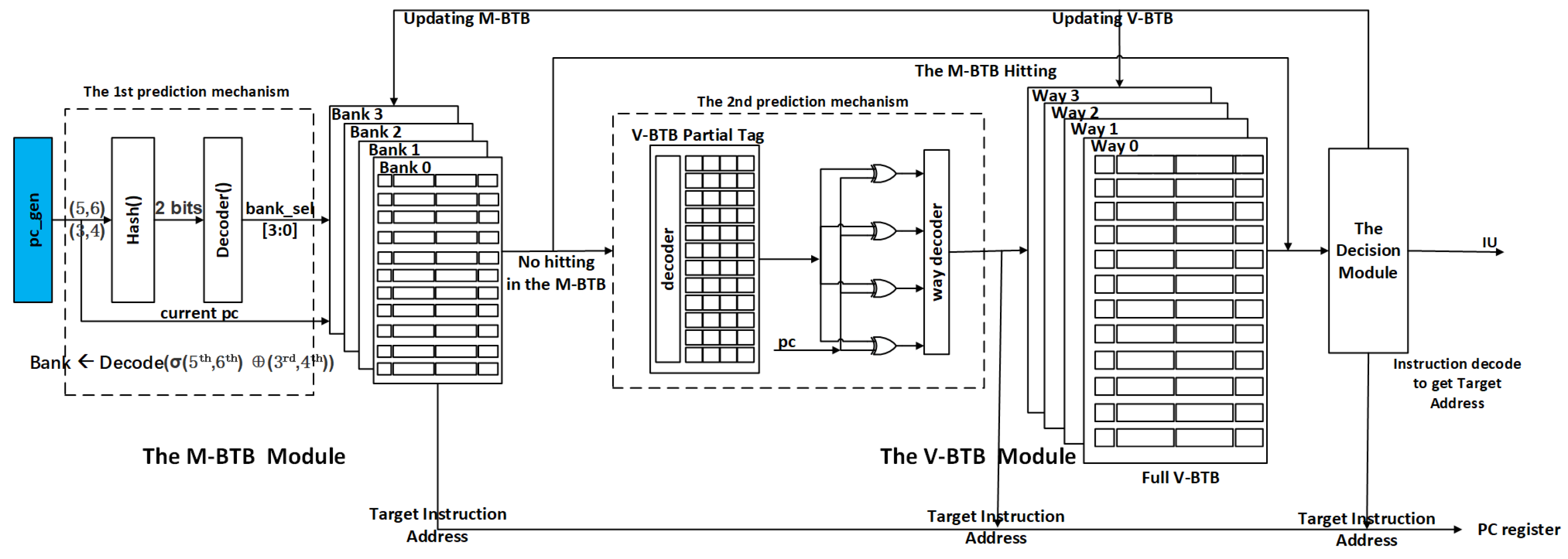
The core advantage of our structure, as depicted in Figure 2, lies in its two-level prediction mechanism. M-BTB incorporates a bank prediction mechanism along with the first level of a fully associative BTB, while V-BTB includes the prediction mechanism and the second level of a set associative structure. Before accessing the M-BTB and V-BTB, our approach integrates a two-level prediction mechanism to forecast potential banks/ways. The IU module serves as the executive execution component, tasked with calculating the instruction address and verifying it against the predicted address to determine the accuracy of the prediction. This approach minimizes the need for simultaneous accesses to multiple ways, effectively reducing power consumption. The detailed structure is delineated below.
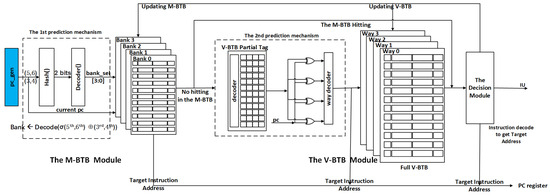
Figure 2.
Proposed low-power BTB design with a two-level prediction mechanism.
3.1.1. The M-BTB Module
The M-BTB branch prediction structure, depicted in Figure 2, comprises two parts: the bank prediction mechanism and a fully associative BTB with 64 entries.
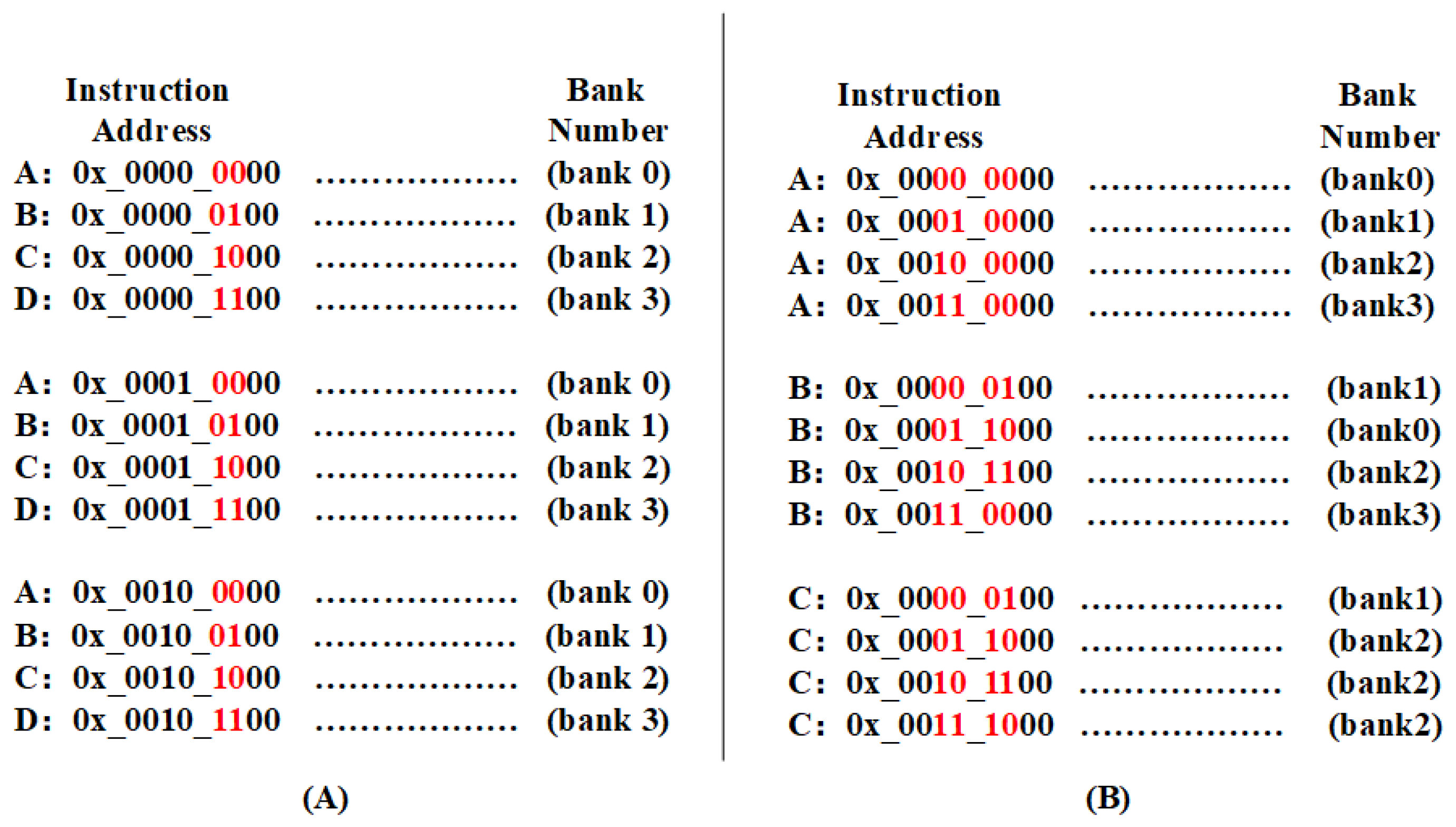
Bank Prediction Mechanism: In a fully associated BTB structure, every entry must be accessed for tag matching to ascertain the target entry. In the case of a structure housing 64 entries, 64 matches are required for a PC to determine whether it is a hit or not. To minimize the number of accesses, we evenly divide the BTB into multiple banks. Here, 64 entries are categorized into 4 banks, with a 2-to-4 decoder determining the hit bank. For instance, we use A, B, C, and D to represent the 3rd–4th of the addresses “00”, “01”, “10”, and “11”. When the address decoder identifies a hit on A, we directly access bank 0 in the M-BTB and avoid access to the other three banks.
However, a challenge arises when there is a correlation between the instruction addresses of each bank, specifically when bits 3–4 are the same. Such correlations can lead to uneven storage across the four banks, resulting in both idle and frequently replaced entries, which hampers prediction performance. To mitigate this, we introduced the skew design [27]. This design, inspired by Seznec et al., resolves way replacement issues in the set-associated caches by employing different hash functions to establish unique mapping relationships for each way. In our study, we designed a hash function to disperse entries and reduce the correlation within each bank.
As shown in Figure 3, we select the red bits in the address for address decoding and address hashing, where “00”, “01”, “10”, and “11” are all markers of addresses, which are used to distinguish groups. The bank assigned to each address after the hash function and decoding is presented in Figure 3B. This further disorganizes the addresses in the A, B, C, and D categories, diminishing the correlation of entries within each bank. As depicted in Figure 3A, this approach ensures that as long as the 3rd–4th bits are “00”, the decoding outcome is bank 0. Consequently, the number of entries in each bank remains balanced, preserving BTB hit performance.
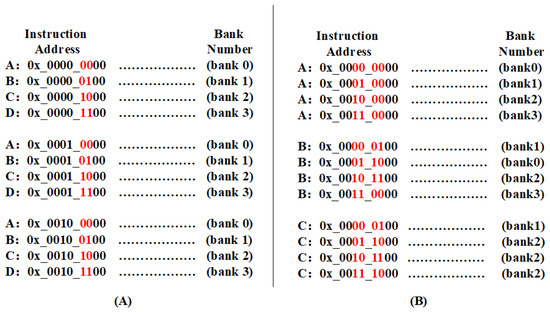
Figure 3.
Instruction address mapping to banks. (A) Direct bank mapping using two-bit addresses. The red bits are used for input to the decoder. (B) Bank mapping employing a novel hash function. The red bits are used for input to the hash function.
3.1.2. The V-BTB Module
The V-BTB comprises two elements: the way prediction mechanism and a 4 × 512 set-associated BTB. For the second-level structure, our paper proposes a strategy prioritizing filtering nonhit addresses. In the case of an input address, multiple ways are required to access and match the tag in parallel to obtain the result. Nevertheless, the number of sequential and nonbranch instruction addresses in a program significantly outweighs the number of branch instructions. Historical statistics showed that branch instructions account for no more than 17% of all instructions, meaning that over 83% of instruction addresses do not hit the BTB [21]. Accessing all ways for nonhit entries results in wasteful power loss.
Previous schemes aimed at reducing BTB accesses by increasing the instruction interval [21] or by introducing shifting and adding buffer operations [22]. While not requiring additional cycles, these schemes suffer from inaccurate predictions, leading to frequent entry replacements and performance loss. The approach in this paper uses a partial tag prediction mechanism to filter nonhit command addresses. If the partial tag match succeeds, a potential hit way is determined. The structural details are as follows:
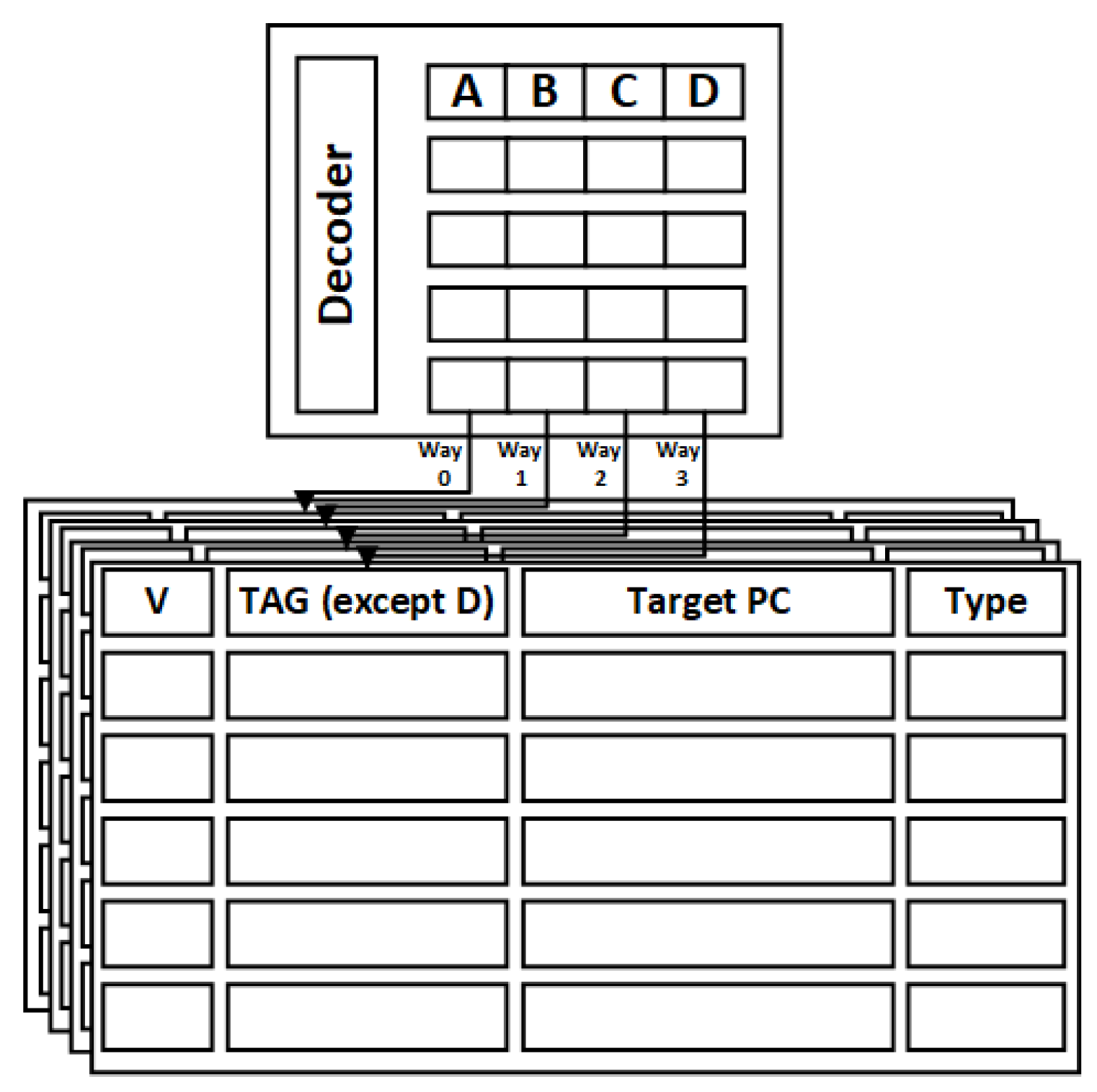
The Way Prediction Mechanism: As illustrated in Figure 4, the BTB structure is divided into two levels, comprising a look-up table and the BTB itself. In a BTB structure with 4 ways, the entries can be effectively distinguished using a 6-bit partial tag. Hence, the length of the look-up table item, defined as , accounts for this.
where , , , and represent partial tag for the 4 ways, forming a 512 × 24 look-up table. The notation (i-j)denotes the ith to jth bits of tag, which are used to filter nonhit addresses.
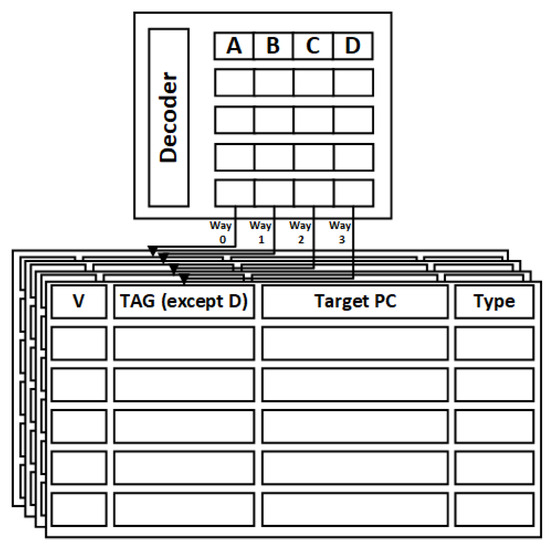
Figure 4.
Partial tag to V-BTB mapping.
For the second level of the BTB structure, partial tags are no longer stored in the lookup table. Taking way 0 as an example, the entry length is represented as :
represents the enable bits, (0-i) + (j-x) signifies the remaining tags, and and denote the lengths of the destination address and instruction type. In contrast to the conventional BTB structure, our approach avoids adding extra bits, and the look-up table directly corresponds to the BTB table entries, requiring only one decoder.
The way prediction algorithm, described in Algorithm 1, employs the input address () and determines which way needs to be accessed (). It begins by accessing the look-up table using the current to retrieve the partial tag, denoted as M (lines 3). M contains the (i-j) bits of , , , and , which correspond to the 4-way structure. We simultaneously match A, B, C, and D with , and if a match is successful, the corresponding way is assigned a value of 1; otherwise, it has assigned a value of 0. Ultimately, the results are tallied to determine the way to access. If equals 0, it signifies nonhit access or only the hit way needs to be accessed.
| Algorithm 1: Way prediction algorithm. |
 |
3.2. Experiment Settings
This experiment utilized the SimpleScalar simulator to emulate a classical multi-aunch sequential instruction pipeline processor [28]. The key processor parameters are presented in Table 1. The benchmarking involved a two-stage typical BTB structure using the two-stage prediction mechanism scheme. The SimpleScalar simulator emulated microprocessors with an MIPS/PISA-like instruction set structure for simulation [29]. The benchmarking program employed integer test vectors from SPEC 2000, and each test vector had a corresponding test input (TEST INPUT).

Table 1.
Processor simulation parameters.
For processor cores, the datapath width accommodated 4 instructions per cycle, while the load/store queue could hold 8 entries. The branch predictor employed was a Bimodal Predictor. In a two-level BTB structure, the first level consisted of a fully associative BTB with 64 entries, followed by a 4-way set associative BTB with 512 sets in the second level. The L1 cache and L2 cache possessed capacities of 32 kb and 2 MB, respectively.
For the power consumption evaluation, CACTI 6.5, with 32 nm technology, was employed to simulate the power consumption per query of the BTB structure, and the query power consumption was subsequently calculated based on the access count derived from the SimpleScalar simulation.
4. Experiment Evaluation
To demonstrate the advantages of our proposed two-level BTB structure, we analyzed the experimental results from multiple dimensions, including accesses, power consumption, area, performance, and way selection mechanism.
4.1. Analysis of Accesses
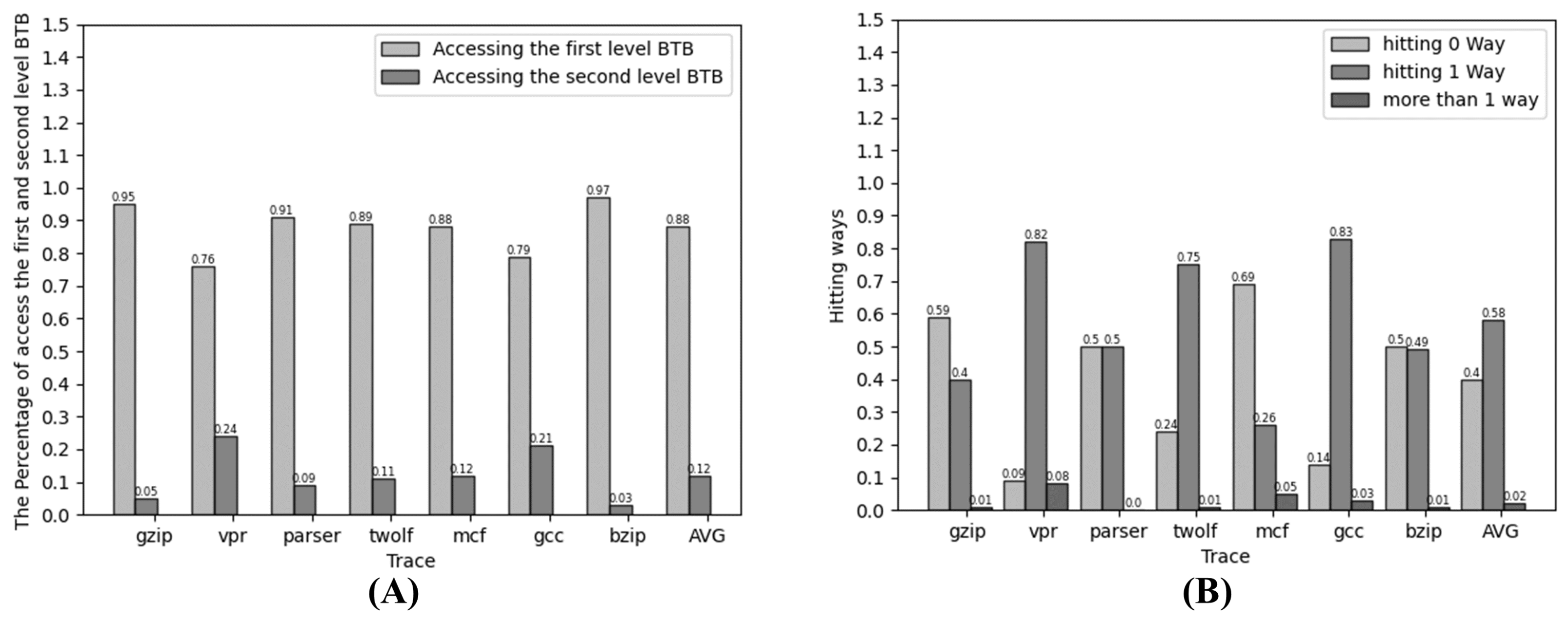
We conducted the experimental analysis to showcase the proposed two-level prediction mechanism’s effectiveness in reducing access numbers. Seven SPEC2000 traces were used to analyze the access patterns in the two-level BTB structure. Figure 5 depicts the proportion of Level 1 and Level 2 BTB hits in different trace scenarios, along with the count of hit ways. Specifically, Figure 5A illustrates the percentage of accesses to the M-BTB and V-BTB structures for a typical two-level BTB structure compared to the BTB structure with our proposed scheme. The results demonstrate that the accesses are concentrated in the first-level BTB structure, with the second-level BTB accesses representing a smaller fraction. Compared to the parallel two-level structure, the serial structure effectively reduces second-level BTB accesses and lowers the overall power consumption. The two-stage prediction mechanism introduced in our approach does not alter the access patterns of the original structure but instead reduces accesses to bank/way.
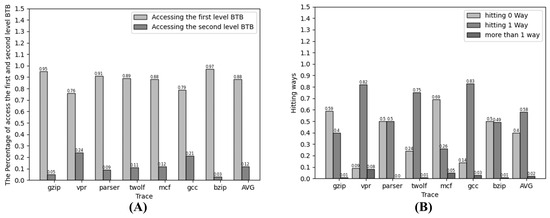
Figure 5.
(A) Distribution of BTB accesses; (B) comparison of hit ways in V-BTB.
Table 2 showcases a comparison of the accessed banks/ways. In the baseline BTB scheme, all banks need to be accessed. However, with the M-BTB, adding a bank prediction mechanism and the hashing of table entries via a hash function results in access to only one bank instead of all banks. The approach proposed in this paper reduces the access count by an average of 75%.

Table 2.
Processor simulation parameters.
Figure 5B illustrates the comparison of hit ways in V-BTB. By accessing the partial tag, our prediction mechanism achieves 40% filtering of nonhit instructions, eliminating the need for additional BTB structure access. For over 58% of instruction addresses, only one-way access to the BTB structure is required to access potential targets. More than 98% of instruction addresses achieve access with only no or one way, validating the effectiveness and practicality of the prediction mechanism.
4.2. Analysis of Power
We conducted comparative experiments to demonstrate the prediction mechanism’s advantages in reducing power consumption. CACTI 6.5 was used for power simulation of different BTB structures, and the power consumption for various traces was averaged to calculate the query power consumption.
The M-BTB structure comprises a decoder and a fully associated BTB with 64 entries. The M-BTB structure’s power consumption mainly consists of decoder power and register access power. The query power consumption for M-BTB is calculated as shown in Equation (4):
where represents decoder power consumption, is the number of predicted results accessed in bank i, and is the query power consumption for simultaneous access to bank i in the fully associative BTB.
The V-BTB architecture power consumption has two primary components: the look-up table and the set-associated BTB access power consumption. The query power consumption for V-BTB is calculated as shown in Equation (5):
where denotes the power consumption for a single access to V-BTB, represents the likelihood that the predicted result accesses the ith way, and signifies the power consumption associated with simultaneous access to the ith way in V-BTB.
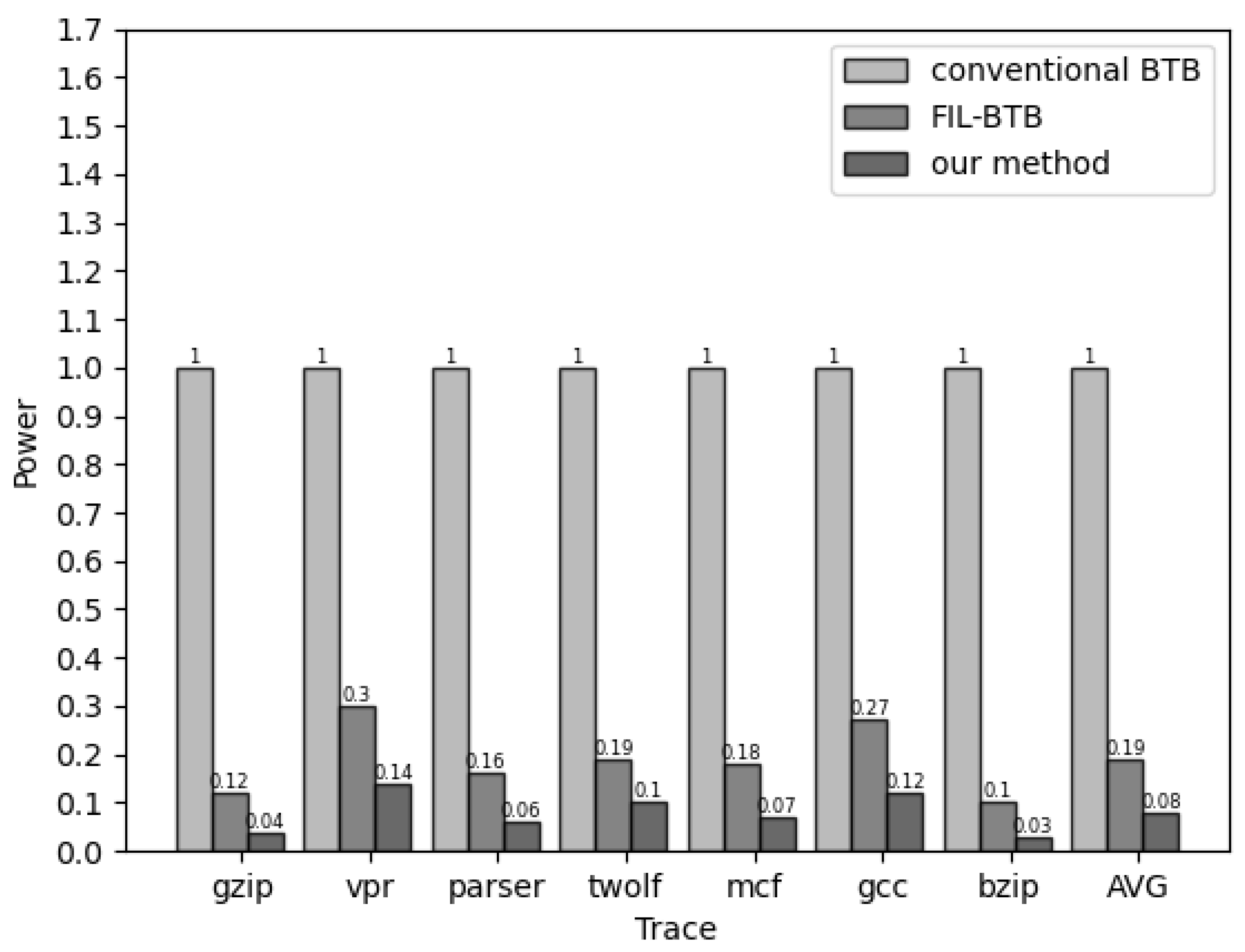
Figure 6 illustrates the power consumption associated with accessing the BTB structure, comparing a one-level architecture, a two-level architecture, and our proposed scheme across diverse traces. The power consumption values were normalized to one for the one-level BTB architecture. In the case of the two-level BTB structure, power consumption is 19% for the one-level structure, while our proposed scheme reduces power consumption to 8%. Notably, vpr and gcc exhibit higher power consumption due to a higher percentage of branches included in those traces.
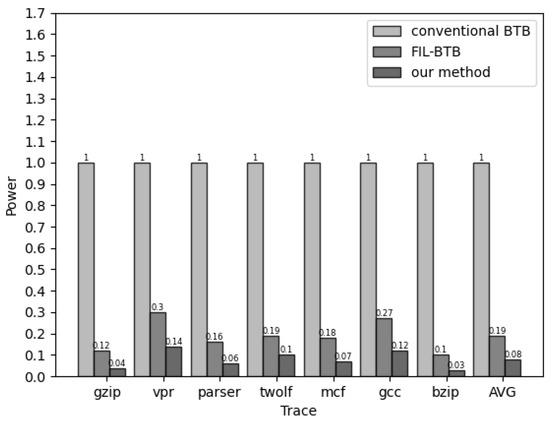
Figure 6.
Power consumption comparison among different schemes.
Table 3 presents a power comparison of the different BTB architectures. The AirBTB scheme primarily focuses on performance improvement with limited power optimization. The TG-BTB scheme decreases the number of accesses by increasing the instruction interval and demonstrates good power reduction for the SPEC2000 trace. The FIL-BTB, a typical two-level BTB structure, is partially optimized to balance performance and power consumption, resulting in an average power reduction of 70–90%. Our proposed scheme utilizes the improved two-level BTB as a benchmark and further reduces power consumption by adding a two-level prediction mechanism to the BTB structure, achieving an average reduction in access power consumption of 86–97%.

Table 3.
Processor simulation parameters.
4.3. Analysis of Area
To compare the area of the proposed schemes, we analyzed the area of the BTB schemes. In the conventional BTB structure [30,31], each table entry is approximately 56 bits, including the target index, target instruction address, and instruction type. The first level incorporates a fully associative register with 64 table entries in the two-level structure, and the second follows the conventional BTB structure. Our proposed scheme does not introduce additional area overhead. The first-level prediction mechanism utilizes a 2–4 decoder and a hash function for table entry dispersion. The second-level BTB structure splits the target indexes to form a 1-way look-up table and a 4-way BTB structure.
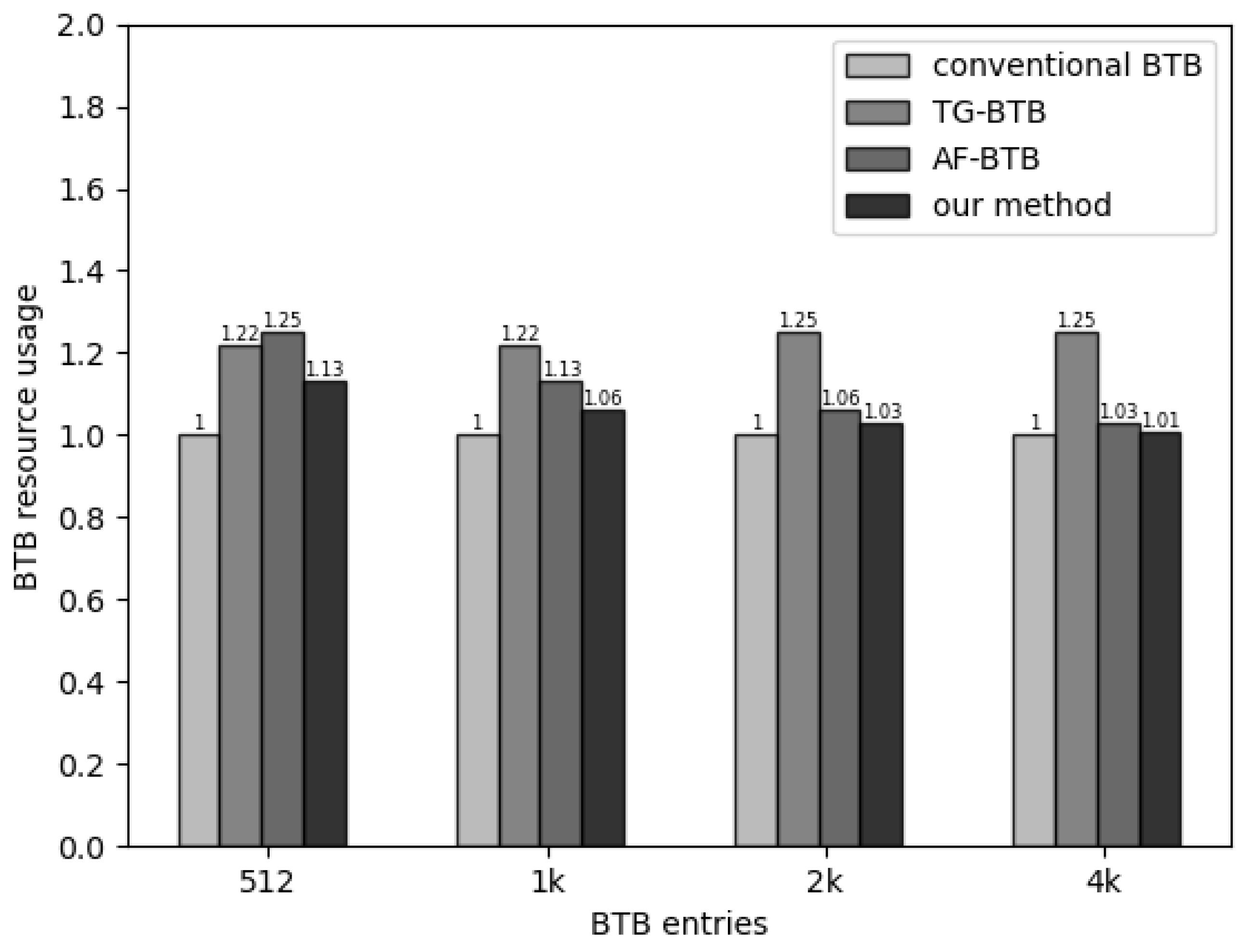
Figure 7 presents the area obtained through CACTI simulation, normalized to the conventional BTB structure. Among the compared schemes, the TG-BTB design exhibits the highest area increase, with a 25% rise. This increase is attributed to adding three extra registers expanding each table entry to 75 bits to record instruction intervals. The FIL-BTB scheme introduces a two-level filtering structure to filter non-branch instruction addresses, resulting in a larger area than the traditional BTB structure.
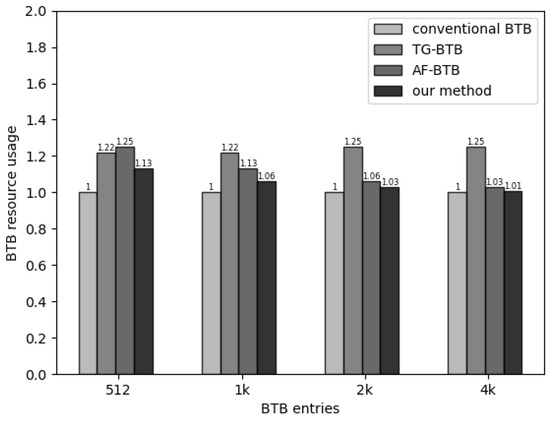
Figure 7.
Area comparison of different BTB architectures.
In contrast, the proposed scheme occupies the least area among the various schemes. Compared to the TG-BTB structure, our scheme does not increase the length of table entries. We simply split and reorganize the tag bits within the table entries to achieve partial matching. Compared to the FIL-BTB, our approach employs a fully associative BTB with 64 entries to achieve higher prediction performance with a smaller area footprint. Adding our two-level prediction mechanism only increases the area by for a BTB structure containing 2 k table entries, demonstrating a balanced trade-off between area and power consumption.
4.4. The Analysis of Performance
To analyze the impact of the proposed scheme on performance, we evaluated it using instructions per cycle (IPC). A higher IPC value indicates that more instructions are executed per unit cycle, signifying improved performance. For the proposed two-level prediction mechanism, the first stage, involving hashing and decoding, presents a minimal delay and can be accommodated in the previous cycle. Thus, there are no additional cycle constraints. For the second-level prediction mechanism, a cycle penalty is added for partial tag access and matching.
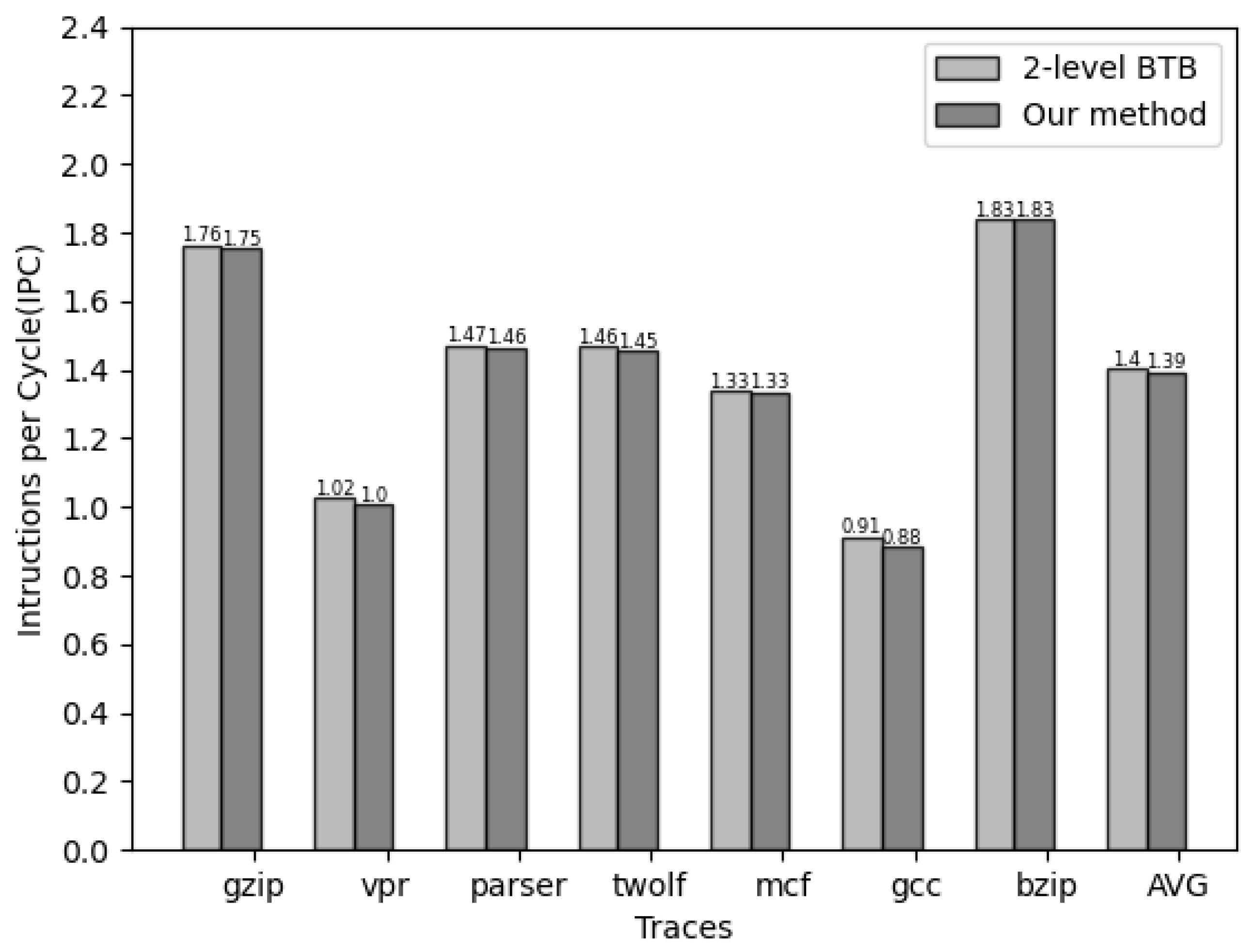
Figure 8 illustrates the performance comparison between the original two-level BTB structure and the BTB structure with the two-level prediction mechanism. Across seven different traces, the addition of the proposed two-level prediction mechanism results in only a slight reduction in the IPC to 1.39.
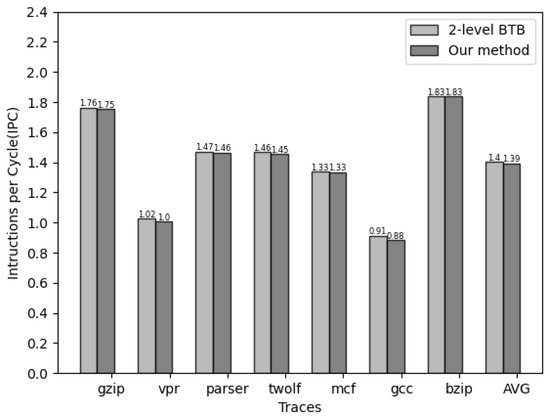
Figure 8.
Performance comparison between two-level BTB and our approach.
Compared to the original structure, the reduction is minimal () because most accesses are concentrated in the first-level BTB. The second-level BTB access is only performed when the branch predictor hits and the first-level BTB fails to match the instruction address. In the case of a hit on the second-level access, an additional cycle of delay is introduced as a penalty for the prediction mechanism. However, when the second-level BTB fails to hit, no extra cycle penalty is imposed since it does not affect the normal execution of the program. Consequently, our proposed mechanism is an energy-efficient power optimization scheme for the original BTB structure.
4.5. Way Selection Mechanism
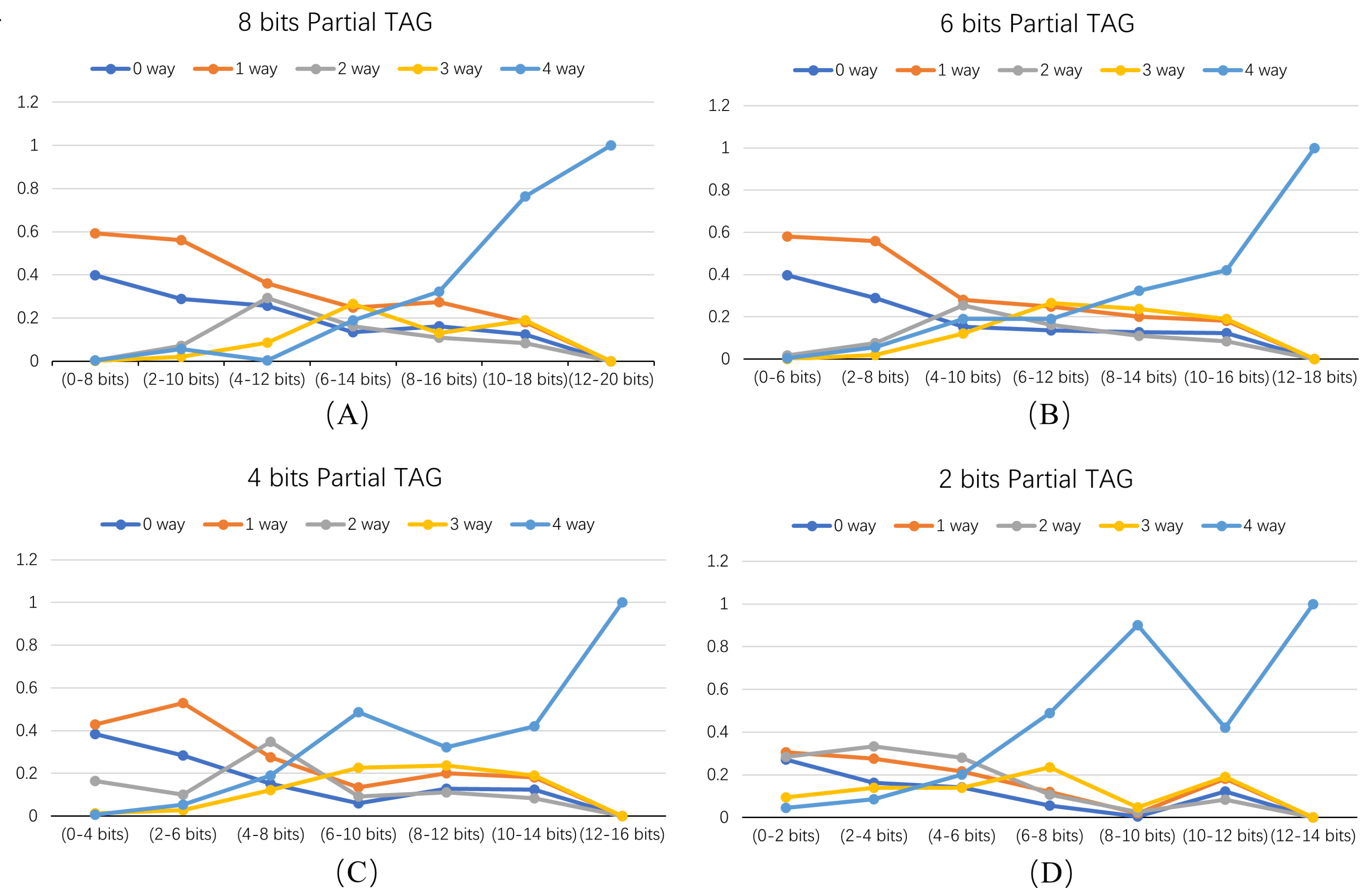
In theory, using more bits of the current address as a partial tag can lead to better prediction performance but at the cost of additional area and power consumption. To strike a balance between efficiency and accuracy, a series of experiments were conducted using 4, 6, 8, and 10 bits of the PC address as a partial tag. Multiple traces from SPEC 2000 were used including gzip, vpr, parser, twolf, mcf, gcc, and bzip, and each trace was simulated once. The results were averaged for analysis.
Figure 9 shows the percentage of predicted ways using different bits for matching. Figure 9A–D represent the eight, six, four, and two bits used for indexing. Each figure’s horizontal axis indicates the bits selected for the query, while the vertical axis represents the percentage of queries resulting in zero-way, one-way, two-way, three-way, and four-way accesses. Partial tag prediction aims to maximize the ratio (P) of zero-way and one-way accesses to be as close to one as possible, indicating the efficiency of our prediction mechanism.
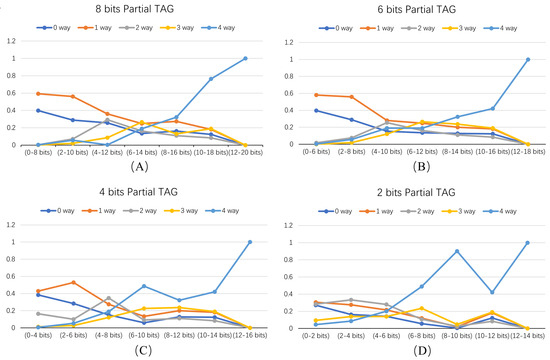
Figure 9.
Percentage of predicted ways using different partial tags. (A–D) represent experiments with 8-, 6-, 4-, and 2-bit partial tags, respectively. (Horizontal: partial tag selection; vertical: hit ratios for 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 ways).
Partial tag is defined as eight bits in Figure 9A. When bits 0–8 are used, p-value reaches 0.99. When 2–10 bits are used, P stands at 0.85, indicating that for more than 15% of the addresses, over two ways need to be accessed to obtain a hit. When the partial tag has 6 bits and bits 0–6 are employed, P is 0.98. Comparing these results, it becomes evident that a higher number of bits in the partial tag leads to a higher p-value. Starting from zero bits for an eight-bit partial tag provides a higher p-value.
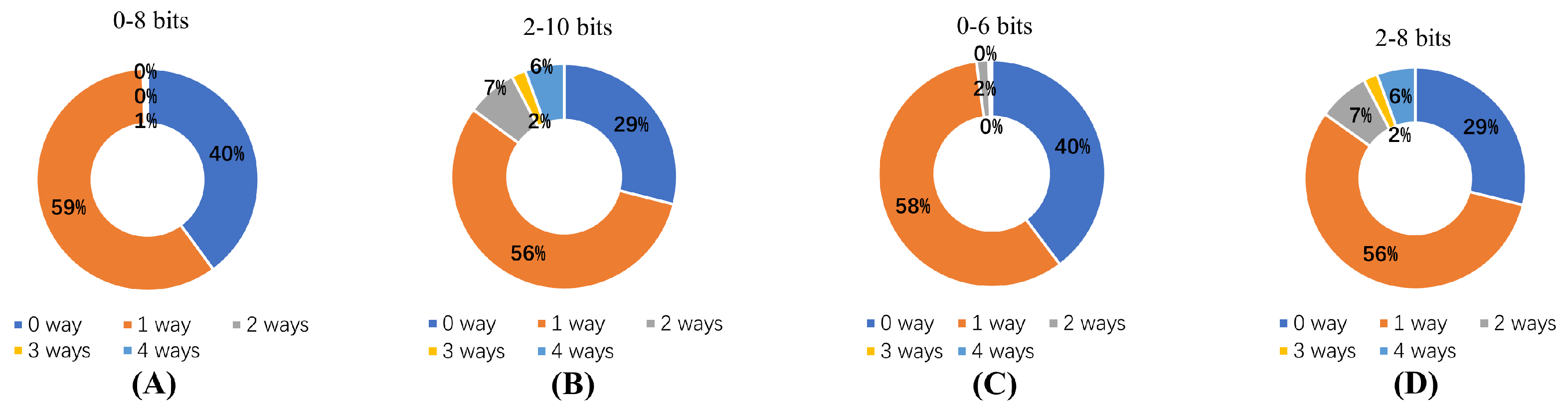
To further analyze the experimental results, four groups with high p-value combinations were selected for evaluation. Figure 10 illustrates the proportion of hit ways when different address bits are used as the partial tag. Figure 9A,B represent eight bits of the partial tag with a high p-value for bits 0–8, indicating more effective prediction. In Figure 9A,D, a six-bit partial tag with a high p-value for bits 0–6 is shown. For an eight-bit partial tag, the p-value is 0.99 when starting from 0 bits, whereas for a six-bit Partial tag, the p-value is 0.98 for bits 0–6. Balancing power consumption and prediction performance, a six-bit partial tag was chosen for tag segmentation in this experiment.
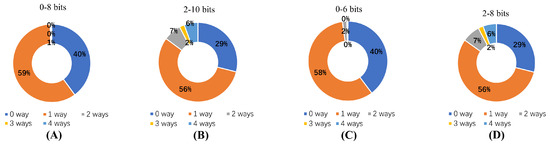
Figure 10.
Comparison of high p-value groups based on various partial tags. (A,B) represent experiments with 8-bits partial tag and (C,D) represent experiments with 6-bits partial tag.
5. Conclusions
This study introduced a straightforward yet practical low-power design approach for a two-level BTB structure. The proposed design incorporates a two-level prediction mechanism to anticipate the bank/way of potential accesses. Access to the two-level BTB occurs sequentially, with the second-level BTB accessed only when the first-level BTB fails to hit, effectively reducing the power consumption associated with BTB access. Within the M-BTB, a decoder is employed to interpret partial bits for bank selection while implementing a skew design to mitigate correlations among table entries within the bank. In the V-BTB, an address mapping method transforms the partial address into a partial tag. This approach reduces the power consumption related to parallel access to multiple ways by identifying potential hit ways through partial tag comparisons.
This study examined the bank/way structure’s performance on seven trace sets. For the M-BTB structure, our proposed scheme significantly reduces access counts by an impressive 75%. In the V-BTB, more than 98% of addresses necessitate just zero-way and one-way accesses to yield hits. The experimental results demonstrated that our scheme delivers a substantial power reduction, ranging from 86% to 97%, with minimal performance degradation and area expansion. This approach is an efficient power-saving strategy compatible with various BTB design schemes and is well suited for low-power applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.N. and X.G.; methodology, J.N., M.Y., S.Z. and H.L.; validation, J.N. and X.G.; formal analysis, J.N.; investigation, J.N. and X.G.; resources, J.N. and X.G.; data curation, J.N. and X.G.; writing—original draft preparation, J.N.; writing—review and editing, M.Y.; visualization, J.N.; supervision, X.G. and M.Y.; project administration, J.N.; funding acquisition, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data and the code will be available upon a reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the reviewers for their helpful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Jiawein Nian, Hongjin Kiu, Xin Gao and Shaolin Zhang were employed by the company Beijing SunWise Space Technology Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Vishal, G.; Panda, B. Micro btb: A high performance and storage efficient last-level branch target buffer for servers. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Computing Frontiers, Turin, Italy, 17–22 May 2022; pp. 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Jun, J.; Na, Y.; Kim, S.W. Design of a G-Share branch predictor for EISC processor. IEIE Trans. Smart Process. Comput. 2015, 4, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranganathan, N.; Nagarajan, R.; Jimenez, D.; Burger, D.; Keckler, S.W.; Lin, C. Combining Hyperblocks and Exit Prediction to Increase Front-End Bandwidth and Performance; The University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Seznec, A. A new case for the tage branch predictor. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Porto Alegre, Brazil, 3–7 December 2011; pp. 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartstein, A.; Puzak, T.R. The optimum pipeline depth for a microprocessor. ACM Sigarch Comput. Archit. News 2002, 30, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, A.; Stephens, N.; Bruce, M. The arm neoverse n1 platform: Building blocks for the next-gen cloud-to-edge infrastructure soc. IEEE Micro 2020, 40, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dvorkin, Y.; Fernández-Blanco, R.; Xu, B.; Qiu, T.; Kirschen, D.S. Look-ahead bidding strategy for energy storage. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2017, 8, 1106–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadooghi-Alvandi, M.; Aasaraai, K.; Moshovos, A. Toward virtualizing branch direction prediction. In Proceedings of the 2012 Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Dresden, Germany, 12–16 March 2012; pp. 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asheim, T.; Grot, B.; Kumar, R. Btb-x: A storage-effective btb organization. IEEE Comput. Archit. Lett. 2021, 20, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaynak, C.; Grot, B.; Falsafi, B. Confluence: Unified instruction supply for scale-out servers. In Proceedings of the 48th International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Waikiki, HI, USA, 5–9 December 2015; pp. 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burcea, I.; Moshovos, A. Phantom-btb: A virtualized branch target buffer design. ACM Sigplan Not. 2009, 44, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.Y.; Lin, Z.H.; Ren, H.Q. Efficient BTB Based on Taken Trace. Comput. Sci. 2017, 93, 104620. [Google Scholar]
- Grayson, B.; Rupley, J.; Zuraski, G.Z. Evolution of the samsung exynos cpu microarchitecture. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM/IEEE 47th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Virtual, 30 May–3 June 2020; pp. 40–51. [Google Scholar]
- Adiga, N.; Bonanno, J.; Collura, A.; Heizmann, M.; Prasky, B.R.; Saporito, A. The ibm z15 high frequency mainframe branch predictor industrial product. In Proceedings of the 2020 ACM/IEEE 47th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Virtual, 30 May–3 June 2020; pp. 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, A.; Jimborean, A. The entangling instruction prefetcher. IEEE Comput. Archit. Lett. 2020, 19, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perais, A.; Sheikh, R. Branch Target Buffer Organizations. In Proceedings of the 56th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Toronto, ON, Canada, 28 October–1 November 2023; pp. 240–253. [Google Scholar]
- Campanizzi, J.A. Effects of locus of control and provision of overviews in a computer-assisted instruction sequence. AEDS J. 1978, 12, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Lee, J.; Nathella, K.; Sunwoo, D. Rebasing instruction prefetching: An industry perspective. IEEE Comput. Archit. Lett. 2020, 19, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Grot, B.; Nagarajan, V. Blasting through the front-end bottleneck with shotgun. ACM Sigplan Not. 2018, 53, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asheim, T.; Kumar, R.; Grot, B. Fetch-Directed Instruction Prefetching Revisited. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.13547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.J. An energy-efficient BTB lookup scheme for embedded processors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2006, 53, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levison, N.; Weiss, S. Low power branch prediction for embedded application processors. In Proceedings of the 16th ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Low Power Electronics and Design, Austin, TX, USA, 118–20 August 2010; pp. 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.A.; Brown, N.; Sriraman, A. Twig: Profile-guided btb prefetching for data center applications. In Proceedings of the MICRO-54: 54th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Virtual Event, Greece, 18–22 October 2021; pp. 816–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levison, N.; Weiss, S. Branch target buffer design for embedded processors. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2010, 34, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asheim, T.; Grot, B.; Kumar, R. A specialized BTB organization for servers. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Parallel Architectures and Compilation Techniques, Chicago, IL, USA, 10–12 October 2022; pp. 548–549. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Hu, J.; Ziavras, S.G. BTB access filtering: A low energy and high performance design. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI, Montpellier, France, 7–9 April 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardashti, S.; Seznec, A.; Wood, D.A. Skewed compressed caches. In Proceedings of the 2014 47th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture, Cambridge, UK, 13–17 December 2014; pp. 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralimanohar, N.; Balasubramonian, R.; Jouppi, N.P. CACTI 6.0: A tool to model large caches. HP Lab. 2009, 27, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, T.; Larson, E.; Ernst, D. SimpleScalar: An infrastructure for computer system modeling. Computer 2002, 35, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perleberg, C.H.; Smith, A.J. Branch target buffer design and optimization. IEEE Trans. Comput. 1993, 42, 396–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pyne, S.; Pal, A. Branch Target Buffer Energy Reduction Through Efficient Multiway Branch Translation Techniques. J. Low Power Electron. 2012, 8, 604–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).