Dual-Layer Path Planning Model for Autonomous Vehicles in Urban Road Networks Using an Improved Deep Q-Network Algorithm with Proportional–Integral–Derivative Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Urban Road Double-Layer Planning Model
2.1. Urban Network Environment Modeling
2.2. Double-Layer Planning Model
3. Urban Path Planning
3.1. Road Level Planning
| Algorithm 1 A* algorithm |
Initialize: the open list with start road node and closed list as empty
|
3.2. Lane-Level Planning
| Algorithm 2 PIDQN algorithm |
|
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
4.2. Experiment on Urban Roads
5. Conclusions and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostermeijer, F.; Koster, H.R.A.; van Ommeren, J.; Nielsen, V.M. Automobiles and Urban Density. J. Econ. Geogr. 2022, 22, 1073–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.U.; Huang, Y.; Lu, P.; Bridgelall, R. Technology Developments and Impacts of Connected and Autonomous Vehicles: An Overview. Smart Cities 2022, 5, 382–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frana, P.L.; Misa, T.J. An Interview with Edsger W. Dijkstra. Commun. ACM 2010, 53, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floyd, R.W. Algorithm 97: Shortest Path. Commun. ACM 1962, 5, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.E.; Nilsson, N.J.; Raphael, B. A Formal Basis for the Heuristic Determination of Minimum Cost Paths. IEEE Trans. Syst. Sci. Cybern. 1968, 4, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stentz, A. Optimal and Efficient Path Planning for Partially-Known Environments. In Proceedings of the 1994 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, San Diego, CA, USA, 8–13 May 1994; Volume 4, pp. 3310–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Qiang, J.; Yang, H. Research and Optimization of D-Start Lite Algorithm in Track Planning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 161920–161928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, I.I.; Hasan, M.S. A Review: On Using ACO Based Hybrid Algorithms for Path Planning of Multi-Mobile Robotics. Int. J. Interact. Mob. Technol. (iJIM) 2020, 14, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, A.; Nguyen, N.G.; Kumari, R.; Kumar, S. Robot Path Planning Using Modified Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm. In Frontiers in Intelligent Computing: Theory and Applications; Satapathy, S.C., Bhateja, V., Nguyen, B.L., Nguyen, N.G., Le, D.N., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, L.; Lou, Y. Path Planning with Q-Learning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1948, 012038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wei, W.; Gao, Y.; Wang, D.; Fan, Z. PQ-RRT*: An Improved Path Planning Algorithm for Mobile Robots. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 152, 113425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Graves, A.; Antonoglou, I.; Wierstra, D.; Riedmiller, M. Playing Atari with Deep Reinforcement Learning. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.5602. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Tong, W.; Zhao, J.; Gu, Y. Path Planning for Autonomous Vehicles in Unknown Dynamic Environment Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Isler, V. Visual Coverage Path Planning for Urban Environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 5961–5968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, N.; Xi, Y.; Rao, J.; Ma, X.; Ren, F. Urban Multiple Route Planning Model Using Dynamic Programming in Reinforcement Learning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 8037–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, P.; Xu, K.; Jiang, X.; Xiao, Z.; Yan, J. Path Planning in an Unknown Environment Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning with Prior Knowledge. J. Intell. Fuzzy Syst. 2021, 41, 5773–5789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kori, N.; Chaurasiya, V.K. Real-Time Data Sharing, Path Planning and Route Optimization in Urban Traffic Management. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 82, 36343–36361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; He, F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, G. A Route Network Planning Method for Urban Air Delivery. Transp. Res. Part Logist. Transp. Rev. 2022, 166, 102872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vamsi, D.S.; Tanoj, T.V.S.; Krishna, U.M.; Nithya, M. Performance Analysis of PID Controller for Path Planning of a Quadcopter. In Proceedings of the 2019 2nd International Conference on Power and Embedded Drive Control (ICPEDC), Chennai, India, 21–23 August 2019; pp. 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Qi, L.; Yuan, H.; Guo, X.; Zhao, M.; Liu, Z.; Yang, T. Path Planning Method With Improved Artificial Potential Field—A Reinforcement Learning Perspective. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 135513–135523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Gong, D.; Wang, M.; Dai, X. Path Planning of Mobile Robot With Improved Ant Colony Algorithm and MDP to Produce Smooth Trajectory in Grid-Based Environment. Front. Neurorobotics 2020, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zou, X. Mobile Robot Path Planning Based on Improved DDPG Reinforcement Learning Algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 11th International Conference on Software Engineering and Service Science (ICSESS), Beijing, China, 16–18 October 2020; pp. 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
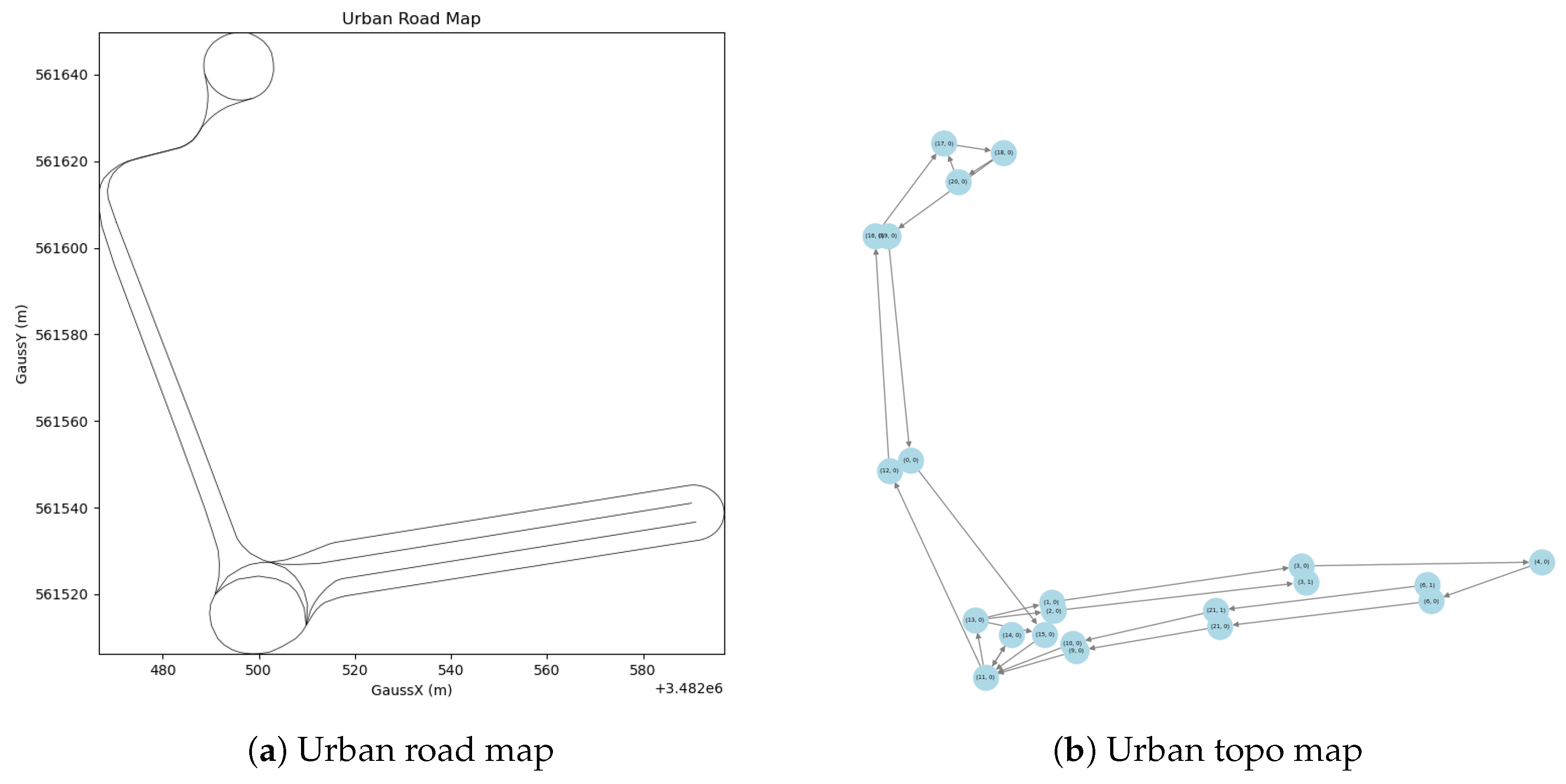

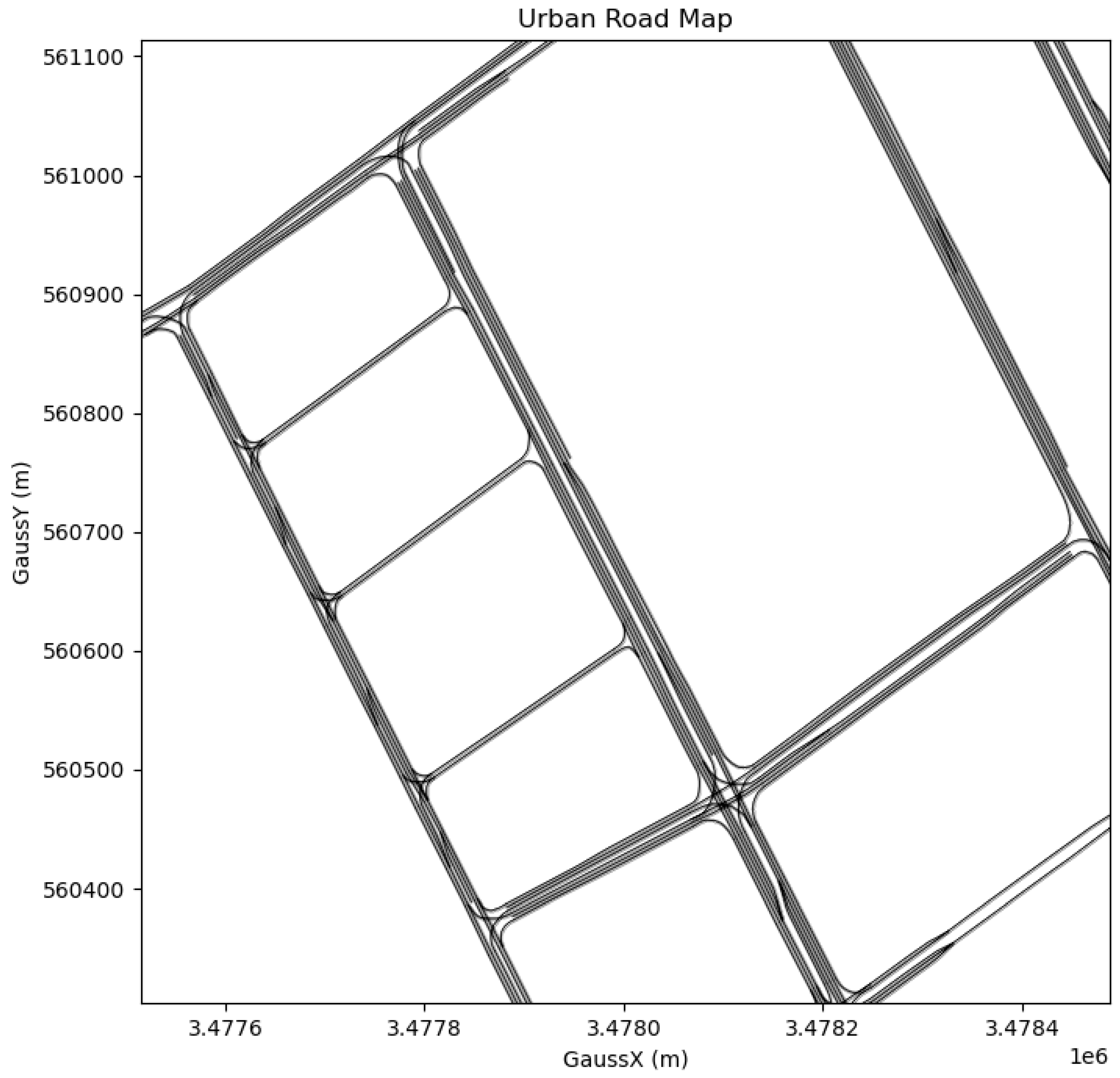
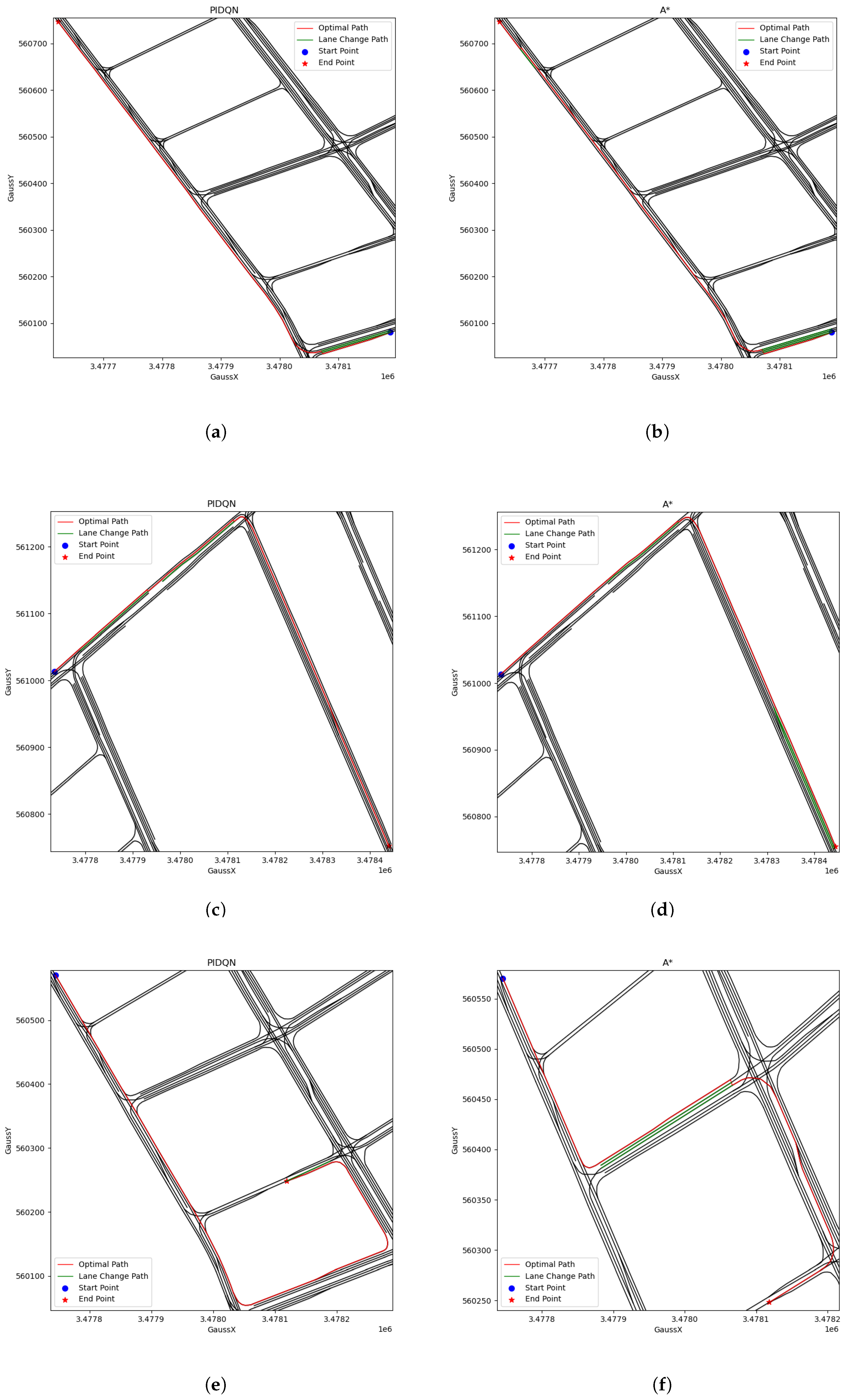




| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 0.0001 | |
| 0.001 | |
| 1 | |
| 0.25 | |
| 1 | |
| 0.2 | |
| 1 | |
| 0.008 | |
| 0.002 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| 0.99 | |
| 0.1 | |
| 0.002 | |
| 0.5 | |
| 0.01 | |
| 0.99 |
| Start Position | End Position |
|---|---|
| N, 120.633 E) | N, 120.638 E) |
| N, 120.639 E) | N, 120.637 E) |
| N, 120.633 E) | N, 120.634 E) |
| N, 120.641 E) | N, 120.643 E) |
| Algorithm | Length | Curvature | Lane-Changing Frequency | Extended Entropy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2526.45 | 8.556 | 4 | 9.667 | |
| 2411.24 | 10.432 | 3 | 10.812 | |
| 3411.25 | 16.215 | 2 | 8.117 | |
| 2251.64 | 9.826 | 4 | 11.102 | |
| 2397.64 | 7.981 | 2 | 11.208 | |
| 2378.14 | 8.656 | 2 | 13.208 | |
| 3407.75 | 15.565 | 1 | 12.117 | |
| 2251.64 | 7.216 | 3 | 13.012 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, G.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, W.; Yu, Y.; Huang, F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y. Dual-Layer Path Planning Model for Autonomous Vehicles in Urban Road Networks Using an Improved Deep Q-Network Algorithm with Proportional–Integral–Derivative Control. Electronics 2025, 14, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14010116
Xu G, Chen L, Zhao X, Liu W, Yu Y, Huang F, Wang Y, Chen Y. Dual-Layer Path Planning Model for Autonomous Vehicles in Urban Road Networks Using an Improved Deep Q-Network Algorithm with Proportional–Integral–Derivative Control. Electronics. 2025; 14(1):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14010116
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Guoji, Lingling Chen, Xiaohui Zhao, Wengang Liu, Yue Yu, Fusen Huang, Yifan Wang, and Yifan Chen. 2025. "Dual-Layer Path Planning Model for Autonomous Vehicles in Urban Road Networks Using an Improved Deep Q-Network Algorithm with Proportional–Integral–Derivative Control" Electronics 14, no. 1: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14010116
APA StyleXu, G., Chen, L., Zhao, X., Liu, W., Yu, Y., Huang, F., Wang, Y., & Chen, Y. (2025). Dual-Layer Path Planning Model for Autonomous Vehicles in Urban Road Networks Using an Improved Deep Q-Network Algorithm with Proportional–Integral–Derivative Control. Electronics, 14(1), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14010116





