Abstract
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) protocol plays a crucial role in wearable and IoT devices, enabling high-speed communication between microcontrollers and peripherals such as sensors, displays, and connectivity modules. With the increasing complexity of modern devices and system-on-chip (SoC) designs, robust verification methods are essential to ensure functionality and reliability. This paper utilizes the Universal Verification Methodology (UVM) to develop a scalable and reusable testbench for SPI verification. The process encompasses test planning, simulation, emulation, and top-level verification to validate multi-slave coordination and error-handling scenarios. The results demonstrate the critical importance of UVM in ensuring the performance and dependability of SPI in advanced electronics, contributing to the reliable integration of the protocol in future devices. The verification results demonstrated a functional coverage of 83.33% and 100% assertion coverage, confirming our approach’s robustness. Analysis of the uncovered functional bins revealed that specific edge cases, such as timing violations and multi-slave arbitration conflicts, require additional test scenarios for full verification. Furthermore, our testbench successfully identified and handled critical fault conditions, such as clock jitter, bus contention, and framing errors, ensuring reliable SPI operation in real-world deployments. These findings highlight the effectiveness of UVM-based verification in improving the reliability and robustness of SPI communication in modern low-power, resource-constrained embedded systems.
1. Introduction
The Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) protocol is a cornerstone of modern electronic systems, widely used in wearable devices and IoT applications [1] due to its high-speed, full-duplex communication capabilities [2]. Its architecture offers simplicity and flexibility, enabling seamless data exchange between microcontrollers and peripherals such as sensors, displays, and memory modules. In wearable gadgets like smartwatches and fitness trackers, SPI facilitates integration with heart rate sensors, accelerometers, and gyroscopes, allowing real-time data acquisition and graphical user interface (GUI) interactions [3]. The protocol’s configurability, combined with its ability to support multiple slave devices, makes it indispensable in IoT applications, including home automation systems [4], where it manages communication between microcontrollers, environmental sensors, and connectivity modules such as Zigbee and Wi-Fi [5,6].
As electronic products become increasingly complex, the SPI protocol’s role extends beyond simple device interconnectivity. It is now integral to highly sophisticated systems on chips (SoCs) [7] that power advanced wearable and IoT devices. The SPI protocol is a widely adopted synchronous communication standard, particularly in embedded systems, wearables, and IoT devices. It offers several advantages, such as full-duplex communication, a flexible data transfer width (up to 128 bits), and configurable clock edge timing for data transfer, making it well suited for low-to-medium-throughput applications [8].
While SPI, UART, and I2C are commonly used serial communication protocols in embedded systems, they differ in key aspects. UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver–Transmitter) is an asynchronous protocol, meaning it does not require a clock signal, making it more straightforward but potentially less reliable for high-speed data transfer. On the other hand, I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) is a multi-master, multi-slave protocol that uses only two wires (SDA and SCL) but operates at lower speeds than SPI. SPI provides higher data transfer rates than I2C, supports multiple slaves through chip select (CS) lines, and enables full-duplex communication, making it the preferred choice for applications requiring fast and efficient data exchange in IoT sensors, memory modules, and display controllers [9].
SPI’s strengths lie in its ability to efficiently handle communication between a master device and multiple slave devices, making it ideal for simpler systems where high-speed video or audio transfer is not required. It can interface with storage devices (e.g., flash memory) and sensors, providing a reliable link for low-bandwidth data exchange. In wearable devices and IoT systems, SPI facilitates communication between microcontrollers and peripherals, including sensors, displays, and wireless modules. While SPI is unsuitable for high-throughput video transmission, it is commonly used for smaller displays in wearables and for transferring data to and from memory modules that may handle internal encryption. Thus, SPI remains a fundamental protocol for low-power, cost-effective systems in various consumer electronics [10,11,12].
Universal Verification Methodology (UVM) plays a pivotal role in simplifying verification complexity, providing a robust framework for verifying the functionality of SPI-based systems. UVM enhances the confidence in design correctness and ensures scalability and reusability in verification environments [13,14]. By adopting UVM, engineers can construct modular testbenches that simulate a wide range of operational scenarios, effectively uncovering potential issues in SPI communication at an early stage. This becomes increasingly critical as wearable devices and IoT systems integrate more sensors, connectivity options, and processing capabilities.
In this study, the functional verification of an SPI protocol is approached through a systematic design verification process under UVM. The methodology starts with test planning, where scenarios are outlined to cover all functional aspects, including error handling, multi-slave coordination, and edge-case performance. These scenarios are then implemented in a UVM testbench [15] and validated through simulation and emulation stages before progressing to top-level verification. This rigorous process ensures that the SPI implementation is robust and can perform reliably under real-world conditions.
The importance of this approach lies in its ability to address the increasing complexity of modern electronic designs. As wearable and IoT devices evolve, the demands on communication protocols like SPI escalate, necessitating a verification methodology that is both thorough and scalable [16]. By leveraging UVM, this research demonstrates a structured approach to verifying SPI functionalities, contributing to the development of reliable and efficient electronic systems.
2. Literature Review
2.1. UVM on System-on-Chip
The adoption of UVM has become a cornerstone in hardware verification, particularly for modern, complex system-on-chip (SoC) designs. UVM enables reusable and scalable verification frameworks, which are crucial for systems with intricate interactions and high-performance demands. For instance, the use of UVM in designing FPGA-based task schedulers optimized for real-time systems illustrates the methodology’s capacity to address latency and predictability issues in hardware systems [17]. By leveraging hardware-accelerated scheduling algorithms like Earliest Deadline First (EDF), researchers demonstrated significant reductions in task scheduling time, achieving better system reliability and resource utilization.
2.2. Coverage of the Verification
Functional verification continues to be a bottleneck in the semiconductor industry, consuming over 60% of the development time for ASIC and SoC designs. Existing UVM-based testbenches streamline this process by integrating coverage-driven functional verification, as showcased in verification environments for instruction cache controllers. These frameworks utilize agents, reference models, and scoreboards to ensure high coverage metrics, including code coverage above 99% [18]. Moreover, directed and random tests enhance the reliability of the verification process by uncovering edge-case scenarios. Advanced tools like SystemVerilog Assertions (SVA) have been pivotal in embedding temporal logic checks into these environments, further improving fault detection capabilities [19,20].
2.3. Verification with Artificial Intelligence
Recent advancements emphasize integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into UVM workflows to address verification scalability challenges. AI-driven methods, such as convolutional neural networks (CNNs), have been shown to optimize documentation parsing and test scenario generation, significantly reducing human intervention in repetitive tasks like test planning, debugging, and regression analysis. In the context of SPI verification, AI-enhanced verification strategies could provide multiple benefits:
- Automated Test Scenario Generation:
- AI models trained on datasets derived from AMBA APB/AXI specifications have demonstrated high classification accuracy (98%) [21], outperforming traditional approaches such as **BERT [22,23,24] and TextConvoNet [25].
- Similar AI models could be extended to SPI verification, learning from previous test cases and protocol specifications, to automatically generate functional test scenarios and edge-case conditions [26].
- AI-Driven Coverage Optimization:
- Functional coverage in UVM-based verification often requires significant manual effort to define coverage points and bins.
- AI techniques, such as reinforcement learning, could dynamically adjust constrained-random-stimulus generation based on coverage gaps, ensuring more efficient coverage closure [27].
- Protocol Adaptation and Self-Learning Verification
- As IoT and wearable devices evolve, new variants of SPI controllers with modified protocols may emerge.
- AI models could be trained to recognize variations in SPI implementations and adapt verification environments automatically based on learned patterns [28].
- Intelligent Debugging and Root-Cause Analysis
- AI-based models could analyze simulation logs and waveforms to automatically detect patterns of failures and suggest probable root causes.
- By integrating natural language processing (NLP) models, the debugging process could be streamlined by cross-referencing failure scenarios with historical bug reports [29].
2.4. SPI Under Wearable and IoT Devices
The SPI protocol is a pivotal communication standard widely used in wearable and Internet of Things (IoT) devices because it handles high-speed, low-latency data transfers efficiently. In wearable technologies like smartwatches and fitness trackers, SPI enables seamless integration with sensors such as heart rate monitors, accelerometers, and gyroscopes, allowing real-time data acquisition and interaction with GUIs. Its lightweight protocol and configurability are advantageous in resource-constrained environments, ensuring minimal power consumption and efficient data handling. Similarly, home automation systems rely on SPI to connect microcontrollers with environmental sensors, connectivity modules like Zigbee and Wi-Fi, and actuators. SPI’s high data rates and ability to handle multiple slave devices make it ideal for centralized control in smart home architectures. Furthermore, SPI facilitates rapid and secure memory access for logging and encryption in applications like smart locks and security cameras. These versatile applications underscore SPI’s importance in creating robust, scalable, and responsive systems, solidifying its role in advancing the IoT and wearable sectors [5,6].
2.5. Comparison of UVM, Directed Testing, and ABV
Verification methodologies are critical in ensuring the functional correctness of hardware designs. Among them, UVM, directed testing, and ABV are widely used approaches, each with its strengths and limitations. This section compares these methodologies and highlights why UVM is preferred for verifying complex designs like SPI protocols in modern IoT and wearable devices.
2.5.1. Directed Testing
Directed testing is one of the most traditional verification methods, where test cases are manually written to exercise specific scenarios in the design. Engineers define explicit input sequences and expected outputs to validate functionality. While directed testing is straightforward and effective for small, well-defined modules, it becomes inefficient for large-scale and complex designs like SPI controllers. Since it relies on manually crafted tests, directed testing often lacks scalability, requiring significant engineering effort to cover corner cases and unexpected conditions [30]. Additionally, directed tests are typically not reusable across different projects, as each design requires a unique set of test cases tailored to its specifications [31].
2.5.2. Assertion-Based Verification (ABV)
ABV introduces formal verification techniques by embedding assertions—predefined properties—within the design to monitor expected behaviors. Assertions, written in SVA or Property Specification Language (PSL), automatically flag violations during simulations, enabling faster debugging [32]. ABV is beneficial for checking protocol compliance and identifying low-level design errors, such as signal timing violations and state machine inconsistencies [33]. However, ABV alone is not a comprehensive verification strategy, as it does not generate stimuli for testing multiple operational scenarios. Instead, it is complementary to other verification methods like UVM [34].
2.5.3. Advantages of UVM over Directed Testing and ABV
UVM, compared to directed testing and ABV, provides significant advantages in terms of scalability, reusability, and automation, making it the preferred methodology for verifying complex SoC components like SPI controllers:
- Scalability: UVM supports constrained-random-stimulus generation, allowing verification environments to cover many test scenarios without requiring individual test cases for each condition. Unlike directed testing, which necessitates manually crafted input sequences, UVM dynamically generates a diverse set of transactions, improving overall test coverage [26].
- Reusability: The modular architecture of UVM, with agents, drivers, monitors, and scoreboards, enables component reusability across different projects. Unlike directed testing, where each test environment is tailored to a specific design, UVM allows verification IPs to be repurposed with minimal modifications, significantly reducing development effort [35].
- Automation and debugging efficiency: Unlike ABV, which primarily flags errors based on predefined properties, UVM automates the verification flow by integrating test generation, execution, and analysis into a structured environment. This results in more comprehensive debugging, as UVM logs transactions, coverage metrics, and assertion failures in a well-organized report [36].
2.5.4. Justification for UVM in SPI Protocol Verification
Given the complex nature of SPI protocol verification, which involves multi-slave coordination, timing constraints, and data integrity validation, UVM is the most effective methodology. It combines the direct control of directed testing, the formal property checking of ABV, and the scalability and automation required for modern hardware verification. The use of functional coverage and assertion-based validation within the UVM testbench ensures that all critical protocol features are exercised, making UVM the optimal choice for verifying SPI-based IoT and wearable devices [14].
2.6. Comparative Analysis of SPI Verification Approaches
Verification of SPI has been explored using various methodologies, including UVM, formal verification, and machine learning-based approaches. Traditional UVM-based verification provides structured testbenches and reusable verification components but is often criticized for its complexity and resource-intensive nature. Studies such as [37,38] demonstrate UVM’s robustness in functional verification but highlight its inefficiency in handling large-scale protocol verification in Table 1 of the comparison of each approach.

Table 1.
Comparative analysis of SPI verification approaches.
Recent works have proposed AI-driven verification methods, leveraging large language models (LLMs) to automate test generation and bug detection. For instance, ref. [40] explored LLM-assisted test case generation, showing that AI can reduce human effort in crafting directed tests. However, LLM-based approaches still require extensive fine-tuning to align with hardware verification constraints.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials: What Should Be Tested in SPI
The SPI protocol is a highly versatile and efficient synchronous communication standard. It is well suited for testing due to its full-duplex capabilities, which allow simultaneous data transmission and reception, enabling real-time monitoring of both MOSI and MISO lines. It facilitates efficient verification of synchronization, data integrity, and error handling within a single test cycle, reducing the need for separate test iterations and support for flexible configurations. Its unique features, such as variable word lengths of up to 128 bits, MSB-/LSB-first data transmission, and edge-selectable data transfer, distinguish it from other protocols like I2C and UART. Unlike these protocols, SPI operates without addressing overhead, allowing for high-speed, low-latency communication. Additionally, the support for up to eight slave select lines makes it ideal for multi-device setups in modern embedded systems.
Software and hardware resources are used to test the SPI protocol. This includes the development of a UVM-based testbench to simulate real-world operational scenarios. The testbench interacts with an SPI master implemented in Verilog, which is synthesized and run on FPGA hardware to validate performance under actual conditions. The specification highlights that testing involves verification of fundamental operations, such as full-duplex data transmission and configurable clock edge timing, alongside advanced configurations like multi-slave setups and variable character lengths.
3.2. Goal of SPI Verification
Verifying the SPI protocol ensures reliability, robustness, and correctness in modern embedded systems, particularly for IoT and wearable devices. A structured verification approach must comprehensively evaluate the SPI protocol’s behavior under various conditions to confirm its adherence to industry standards. One of the primary goals of SPI verification is ensuring protocol compliance. This involves validating the correct operation of SPI modes, including proper clock polarity and phase settings, and confirming that the chip select signal behaves as expected to prevent unintended slave activation. Additionally, adherence to standard timing requirements, such as setup and hold times for data transmission, must be verified. Full-duplex communication must also be tested to maintain data integrity between the master and slave devices. Another crucial verification aspect is error handling and fault detection, which ensures that SPI communication remains reliable under various fault conditions. This includes detecting and addressing clock jitter, bus contention, and framing errors that may result from incorrect bit alignment or premature termination of communication. The system’s response to unexpected events, such as simultaneous multiple slave selection or out-of-range clock frequency settings, must also be assessed. Furthermore, verification must confirm that the protocol can handle transmission interruptions and implement retry or recovery mechanisms when necessary. Functional correctness is vital in SPI verification, as the interface must operate reliably across different scenarios. This includes verifying data transmission integrity for various word lengths, ensuring that MSB-first and LSB-first transmission formats are correctly implemented, and validating the execution of register configurations that control SPI operations. Additionally, as the system’s complexity increases, the verification process must confirm that SPI performs correctly in both austere and multi-slave environments. This study establishes a structured and rigorous verification framework for SPI communication by addressing these key aspects. Using UVM, the proposed approach ensures scalability and reusability, providing a comprehensive validation strategy for SPI in modern embedded applications.
3.3. Methods: Test Plan
A well-structured test plan is essential for verifying the functionality of the SPI protocol, especially when integrated into complex designs like wearable and IoT devices. The test plan ensures that all functional aspects of the protocol based on the specifications of the protocol, including communication integrity, edge cases, and control mechanisms, are systematically validated. Without a rigorous plan, ensuring that SPI-based systems meet design specifications becomes challenging, particularly given the diverse configurations and applications highlighted in the SPI Master core specification.
3.4. Methods: Designing the Test Plan
The testing process begins with setting up the SPI Master core using the specifications defined in the attached document. The system’s primary features, such as control registers and slave select lines, are configured to match expected operational modes. A suite of targeted test cases are executed, starting with basic functional tests, such as verifying the correct initialization and default behavior of the SPI core. More advanced scenarios are then conducted, including multi-bit word transmission (8–128 bits) and edge-sensitive data transfer tests. Timing analyses also confirm the clock divider’s accuracy under varying frequencies.
Additionally, error conditions, such as simultaneous multiple slave selection and misaligned clock settings, are intentionally introduced to evaluate fault tolerance and error reporting capabilities. Hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) emulation using an FPGA validates the protocol’s behavior under physical constraints. By progressively increasing the test complexity, the process ensures robust verification of SPI’s design while leveraging its unique characteristics for diverse embedded system applications in Table 2.

Table 2.
Test plan design.
The selected test cases comprehensively evaluate the SPI protocol’s functionality by covering key aspects such as data transmission formats (MSB-first and LSB-first), clock divider configurations, and full-duplex communication. They ensure robustness across different word lengths and verify control register operations critical for proper SPI configuration. The edge sensitivity tests assess timing dependencies, while the extended character length validation confirms compatibility with high-data-volume applications like IoT and wearable devices. Implemented using SystemVerilog/UVM, this verification approach enhances scalability, automation, and adaptability, making it applicable to many SPI-based systems.
- Test item definition: Test items are defined to cover all possible scenarios, from basic data transmission to advanced functionalities. The provided test items, such as verifying MSB-/LSB-first transmission, edge-based communication, and variable word lengths, ensure that all critical aspects of the protocol are tested. These test cases align with the SPI Master core specification, which allows flexible configurations like up to 128-bit data transfers, MSB- or LSB-first settings, and edge-specific transmission.
- Test case prioritization: High-priority cases like basic transmission are a foundation for testing more complex scenarios like variable word lengths and multi-character transmissions. This incremental approach minimizes the risk of overlooking fundamental issues.
- Simulation and emulation: The testing methodology transitions from simulation to emulation for validating SPI under real-world conditions. Simulations are conducted at the register-transfer level (RTL) using models like UVM to verify logical functionality, while emulation replicates the behavior on physical hardware. This dual-layer approach ensures comprehensive coverage and identifies design flaws early.
- Top-level verification: Finally, the entire SPI system is tested as part of a fully integrated design to validate subsystem interactions. This phase confirms the protocol’s reliability under operational constraints typical of wearable and IoT environments.
3.5. Example Test Cases and Their Significance
3.5.1. Fundamental Operation: Ensuring That the Core Settings Perform as Expected
This step involves testing the basic functionality of the SPI controller core. The core should be able to transmit and receive data correctly under typical conditions, with the expected behavior when initialized. This validation checks whether the SPI controller operates as designed, without any errors or unexpected behavior, and that the settings, such as baud rate, data format, and polarity, are correctly configured and functioning.
3.5.2. Checks the Clock Divider’s Accuracy: SPI and External Peripherals’ Synchronization
The clock divider is a crucial component of the SPI system, as it divides the system clock to generate the SPI clock (SCK), which is used for data transmission. If the clock divider is not accurate, the timing between the SPI controller and the connected peripheral devices could be mismatched. This can result in communication errors or data corruption. Verifying the clock divider ensures that the SPI controller generates the correct clock speed that matches the timing requirements of the external device it is communicating with.
3.5.3. Behavior of Control Registers: Advanced Features
SPI communication often requires control over advanced features such as enabling interrupts (IE) or selecting specific slave devices (ASS, or Slave Select). The control registers configure the SPI controller’s operation for such features. Verifying these control registers ensures the following:
- The interrupt functionality behaves as expected (triggering appropriate actions when specific conditions, like data ready or transmission complete, occur).
- The slave selection works appropriately, ensuring that the correct device (in a multi-slave configuration) is addressed when the SPI bus is used. This step is important for confirming that the SPI controller’s more complex, advanced features are operational and that the device interacts correctly with various external components or peripherals.
By following this structured methodology and referencing the SPI Master core specification, the test plan ensures robust verification of the SPI protocol, facilitating its reliable integration into sophisticated applications.
3.6. Importance of Sanity Testing in Verification
Sanity testing is indispensable in complex verification environments like SPI. Validating essential configurations and operational correctness in a controlled setup ensures that subsequent tests operate on a verified foundation. This reduces the time spent debugging and enhances overall productivity. The spi_sanity_test.sv serves this purpose by configuring and validating key SPI control registers, checking for protocol adherence, and confirming the proper functioning of the environment. Each register setting and phase of the code plays a crucial role in ensuring reliability and correctness during this process.
Using a sanity test in SystemVerilog, particularly within a UVM framework, is critical in ensuring that the design under test (DUT) and the testbench environment are configured correctly before moving to more comprehensive testing. A sanity test validates the basic functionalities and confirms the correctness of the setup. In an SPI environment, this means ensuring that communication protocols, registers, and initial configurations behave as expected before progressing to more advanced and resource-intensive tests. The spi_sanity_test class in the code is designed as a foundational test, verifying the correctness of the basic SPI settings and sequences, ensuring subsequent tests have a reliable starting point.
The top-level idea is illustrated in the pseudo-code. Please refer to Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Abstract Representation of spi_sanity_test in UVM |
|
3.7. Breakdown of the Code: spi_sanity_test Class
3.7.1. Detailed Explanation of UVM Testbench Structure
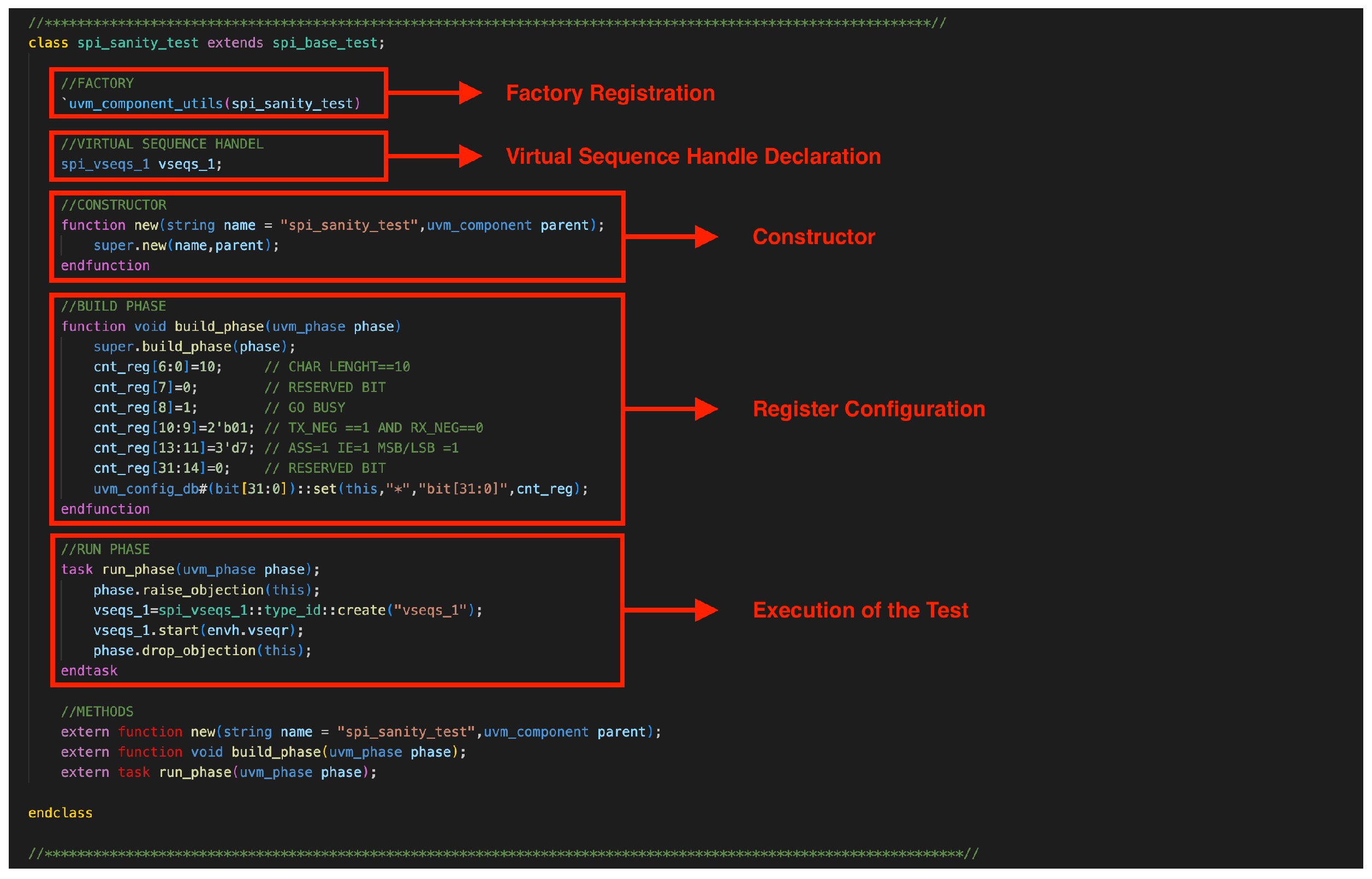
The SPI verification environment follows the UVM framework in Figure 1, incorporating a structured hierarchy to ensure modularity, reusability, and scalability. The directory structure consists of multiple components, each fulfilling specific roles within the verification process.
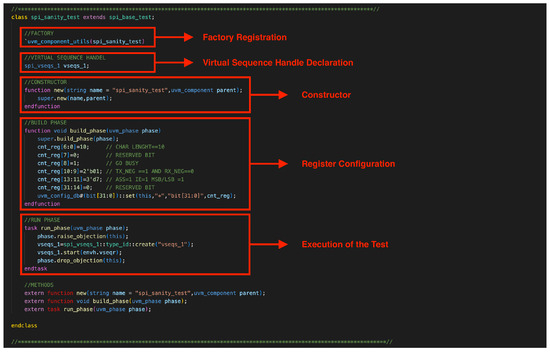
Figure 1.
Class spi_sanity_test in UVM, showcasing factory registration, virtual sequence handle declaration, constructor, register configuration in the build phase, and test execution in the run phase.
3.7.2. Testbench (tb) Overview
The tb directory encapsulates the top-level testbench components essential for executing UVM-based verification. These include the following:
- spi_env_config.sv: Configuration class responsible for global test parameters.
- spi_env.sv: The UVM environment that instantiates and connects various verification components.
- spi_scoreboard.sv: A reference model that compares expected and actual results, ensuring data integrity.
- spi_top.sv: The top module that integrates different agents and the DUT.
- spi_vseqr.sv and spi_vseqs.sv: Virtual sequencers and sequences coordinating transaction execution across multiple agents.
3.7.3. Master and Slave Agents
The environment consists of two key agents: master_agent and slave_agent, both following the UVM agent structure.
Master Agent (master_agent/)
- master_agent.sv: The UVM agent encapsulating the driver, monitor, and sequencer.
- master_driver.sv: Drives SPI transactions to the DUT based on generated sequences.
- master_monitor.sv: Captures SPI transactions from the DUT for analysis.
- master_seqs.sv and master_read_seqs.sv: Defines sequences generating SPI transactions.
- master_sequencer.sv: Orchestrates sequences and drives transactions.
Slave Agent (slave_agent/)
Similar to the master agent, it consists of the following:
- slave_agent.sv, slave_driver.sv, slave_monitor.sv, and slave_sequencer.sv, mirroring the structure of the SPI slave interactions.
3.7.4. Design Under Test
The rtl directory contains the SystemVerilog modules defining the SPI functionality, including the following:
- spi_top.v: The top-level SPI RTL module.
- spi_slave.v and spi_shift.v: Components handling SPI data processing.
- spi_defines.v: Macros and constant definitions used across the design.
3.7.5. Test Directory (test/)
The test directory hosts the test cases extending UVM test classes:
- spi_base_test.sv: Base test class configuring the environment and test sequences.
- spi_pkg.sv: Contains UVM package and testbench configurations.
3.7.6. Role in Sanity Testing
The structured testbench ensures a controlled and modular verification approach. The spi_sanity_test leverages the tb components to validate fundamental SPI operations, ensuring configuration correctness before proceeding with more complex tests. The master and slave agents interact with the DUT to verify protocol adherence, and the scoreboard checks for discrepancies.
By organizing the verification environment into modular components, the UVM testbench ensures reliability, efficiency, and comprehensive SPI validation.
3.7.7. Testbench Environment for Verifying the SPI Protocol
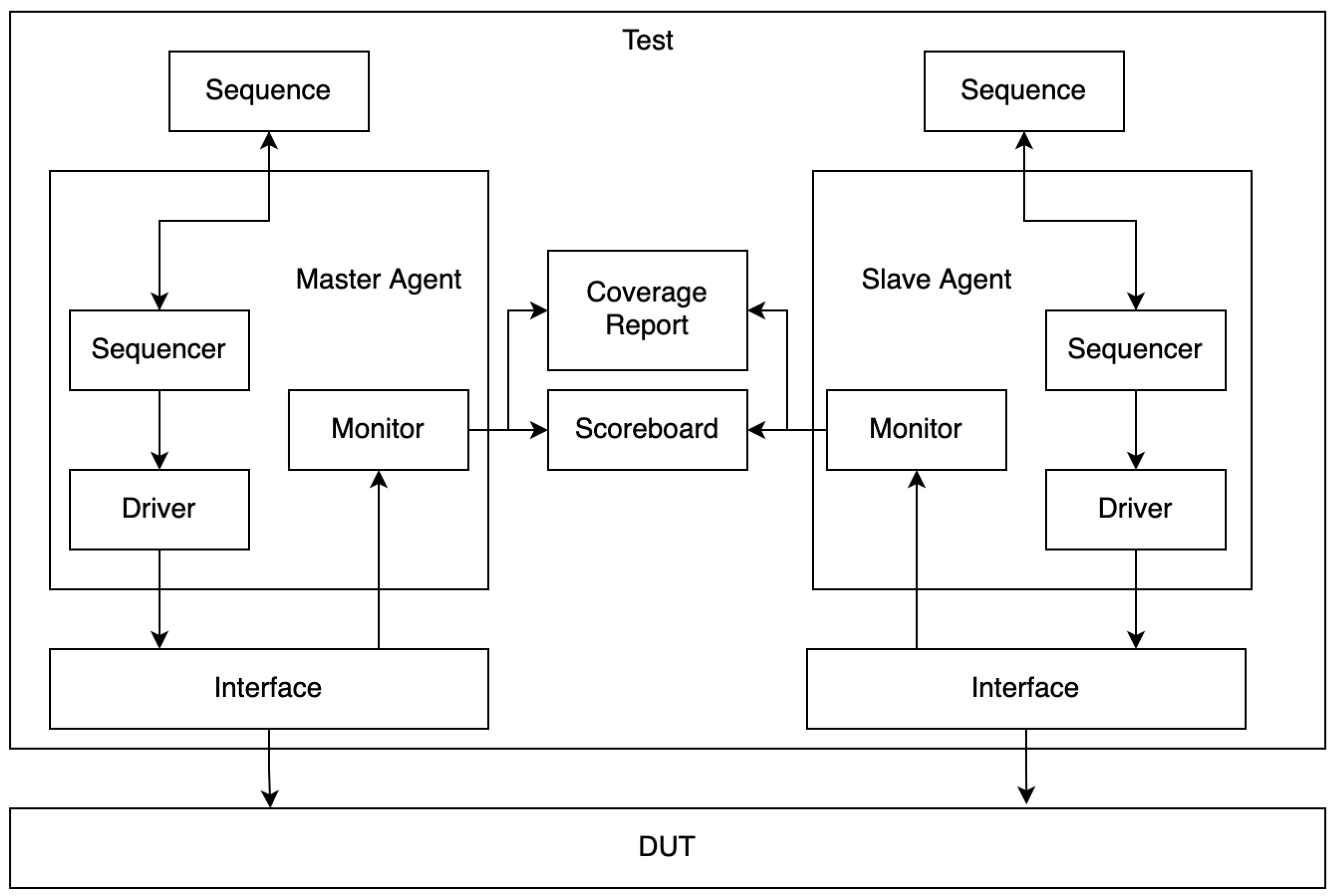
Figure 2 represents a UVM testbench environment for verifying the SPI protocol. The testbench consists of a master agent and a slave agent, each comprising a sequencer, driver, and monitor. The sequence generates a stimulus, which the sequencer processes and sends to the driver. The driver interacts with the interface, which communicates with the device under test (DUT). The monitor captures transactions from the interface and sends them to the scoreboard for comparison with expected results. The scoreboard helps check data integrity and a coverage report is generated to assess test coverage. This structured approach ensures a comprehensive verification of the SPI protocol, checking data transmission between the master and slave while monitoring functionality and performance.
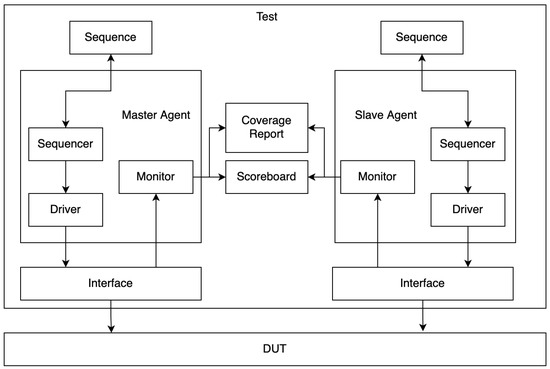
Figure 2.
Testbench environment for SPI protocol on UVM.
3.7.8. Factory Registration
The uvm_component_utils macro registers the spi_sanity_test class with the UVM factory. This enables dynamic object creation and type-specific customization during runtime, a feature integral to UVM for scalability and reusability. Factory registration ensures that this test can be instantiated using the UVM type system, allowing configurations to be swapped dynamically without modifying the base testbench structure.
3.7.9. Virtual Sequence Handle Declaration
The vseqs_1 handle represents a virtual sequence (sequence driver for the testbench). It is an entry point to drive sequences that generate transactions on the DUT interface, ensuring the test’s and the stimulus’s abstraction.
3.7.10. Constructor
The constructor initializes the class by invoking the base class’s new method with a default name (spi_sanity_test) and its parent. It adheres to UVM’s hierarchical component structure, ensuring modularity and consistency.
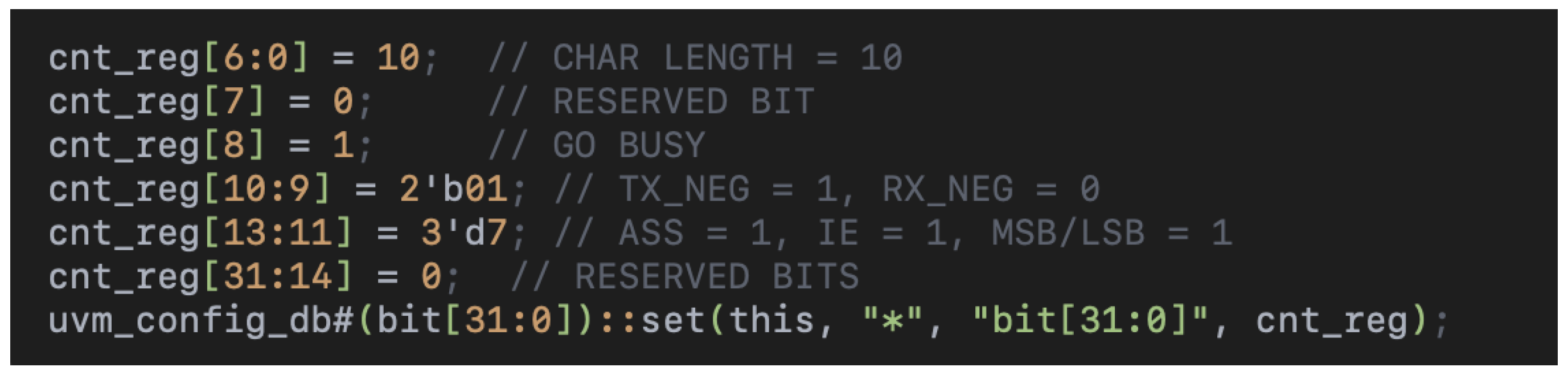
3.8. Build Phase: Register Configuration
The build_phase is a critical part of UVM where the testbench’s topology and default configurations are set up. For SPI, this involves defining specific control register (cnt_reg) values to initialize the SPI protocol (Figure 3).
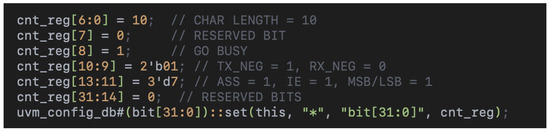
Figure 3.
Detailed register configuration in the build_phase method, setting up the control register (cnt_reg) with specific bit-field values for SPI testing.
- CHAR LENGTH (cnt_reg[6:0] = 10): This specifies the number of bits per transaction. A value of 10 indicates that each SPI transfer consists of 10 bits, a standard configuration for validating medium-length transfers during a sanity test.
- RESERVED BIT (cnt_reg[7] = 0): Reserved bits are set to 0 for consistency and to ensure no undefined behaviors in register configurations.
- GO BUSY (cnt_reg[8] = 1): The GO or BUSY flag signals to the SPI interface to initiate a transfer. Setting this bit ensures that the SPI controller begins a transaction during the test.
- TX_NEG and RX_NEG (cnt_reg[10:9] = 2’b01): These bits control the data capture and transmission phase. Setting TX_NEG = 1 and RX_NEG = 0 configures the transmitter to change data on the falling edge and the receiver to sample data on the rising edge, a common configuration for SPI protocols.
- ASS, IE, MSB/LSB (cnt_reg[13:11] = 3’d7):
- –
- ASS (Automatic Slave Select): A value of 1 ensures the chip select (CS) signal is managed automatically.
- –
- IE (Interrupt Enable): Enabling interrupts (IE = 1) ensures that any irregularities during communication are flagged immediately.
- –
- MSB/LSB: Setting this to 1 configures the SPI to transmit the most significant bit (MSB) first, which is standard for many SPI devices.
- RESERVED BITS (cnt_reg[31:14] = 0): Setting all unused bits to 0 prevents unintentional interference.
Finally, the uvm_config_db API makes this configuration accessible throughout the testbench.
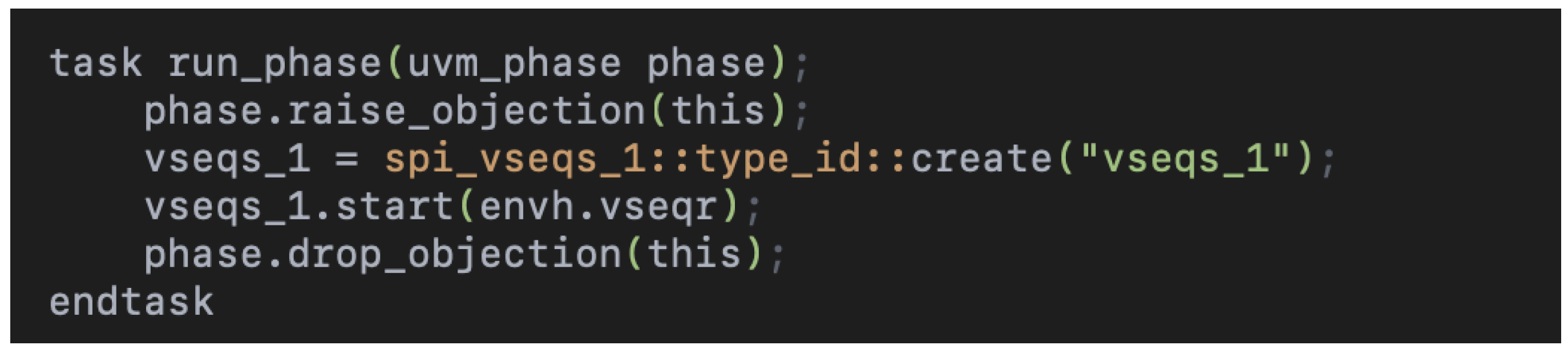
3.9. Run Phase: Execution of the Test
The run_phase in Figure 4 drives the test logic after the environment is constructed and configured:
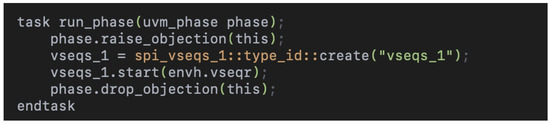
Figure 4.
Run phase implementation, including objection handling and virtual sequence instantiation and execution for the SPI test.
- Raise/drop objection: These methods synchronize the testbench phases. Objecting indicates that the test is still executing while dropping it signals completion.
- Sequence creation and execution: The spi_vseqs_1 sequence is dynamically created and started on the virtual sequencer (envh.vseqr). This abstraction ensures the generated transactions align with the defined protocol and environmental setup.
3.10. Verification Environment
We now specify the UVM version (1.2) and the SystemVerilog simulator (Synopsys VCS v2022.06-SP2, Sunnyvale, CA, USA) used in the verification setup. These tools ensure compatibility and efficient execution of the verification process.
4. Results
4.1. Master and Slave Devices Under the Testbench
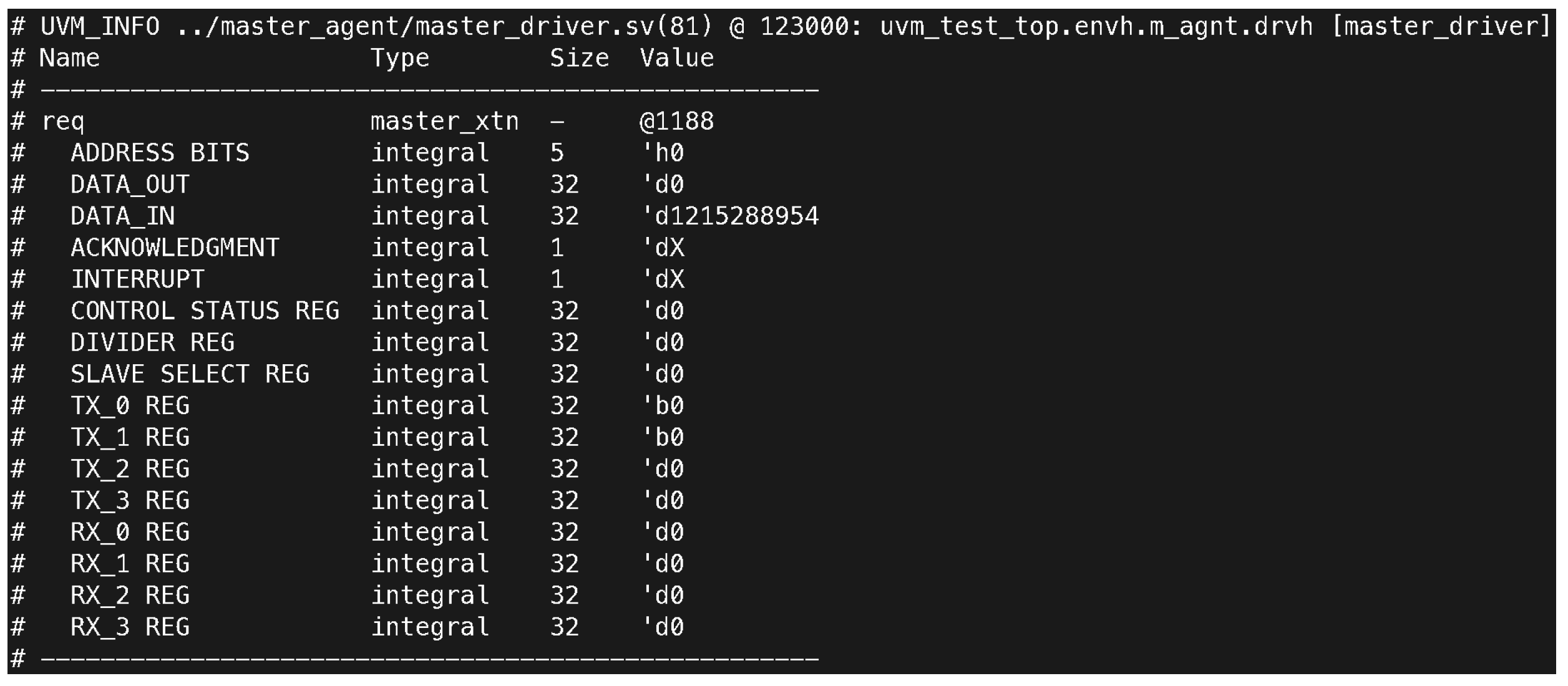
The results of the SPI protocol in Figure 5 testing demonstrated successful data transmission between the master and slave devices, verifying the functionality and reliability of the system. The master device issued multiple requests (master_xtn) at different timestamps (9000 ns, 15,000 ns, 21,000 ns, 27,000 ns, and 123,000 ns). Each request included key data elements such as address bits (ADDRESS BITS), output data (DATA_OUT), input data (DATA_IN), and control registers. The master driver’s log showed consistent updates to these fields, reflecting the correctness of data flow at each test phase. On the other hand, the slave device received and processed the transmitted data successfully. For instance, at 109,000 ns, the slave monitor captured the request (slave_xtn) with integral fields for MISO and MOSI. The transmission data integrity and timing accuracy observed in these exchanges validate the robust synchronization between master and slave devices.
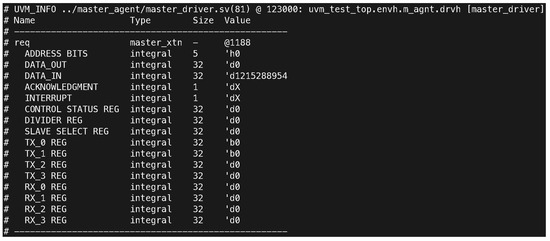
Figure 5.
Log of the master driver displaying register and transaction states at 123,000 ns. The DATA_IN value was recorded as 2456940507, while DATA_OUT, CONTROL STATUS REG, and TX registers remained consistent. These results validate the driver’s correct operation in managing SPI transactions.
4.2. Monitor and Driver Devices Under the Testbench
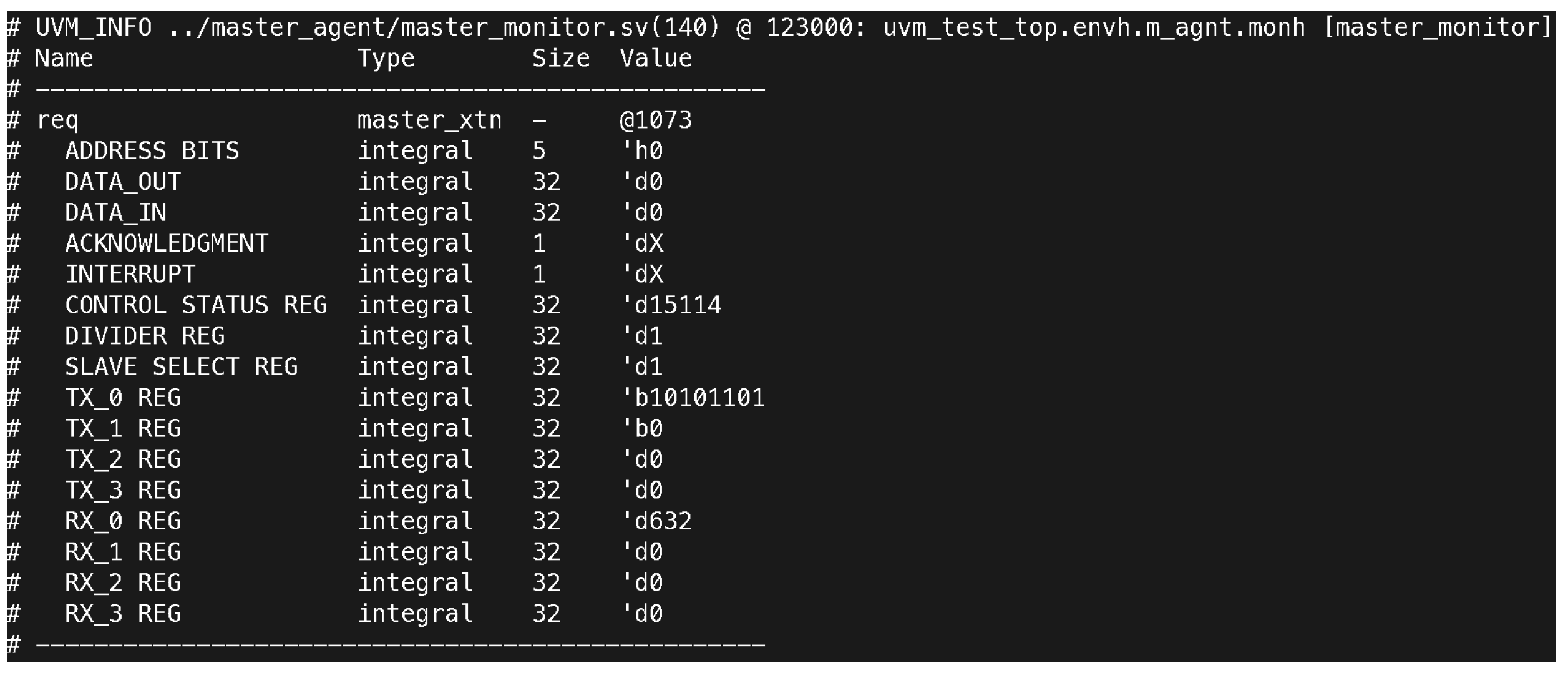
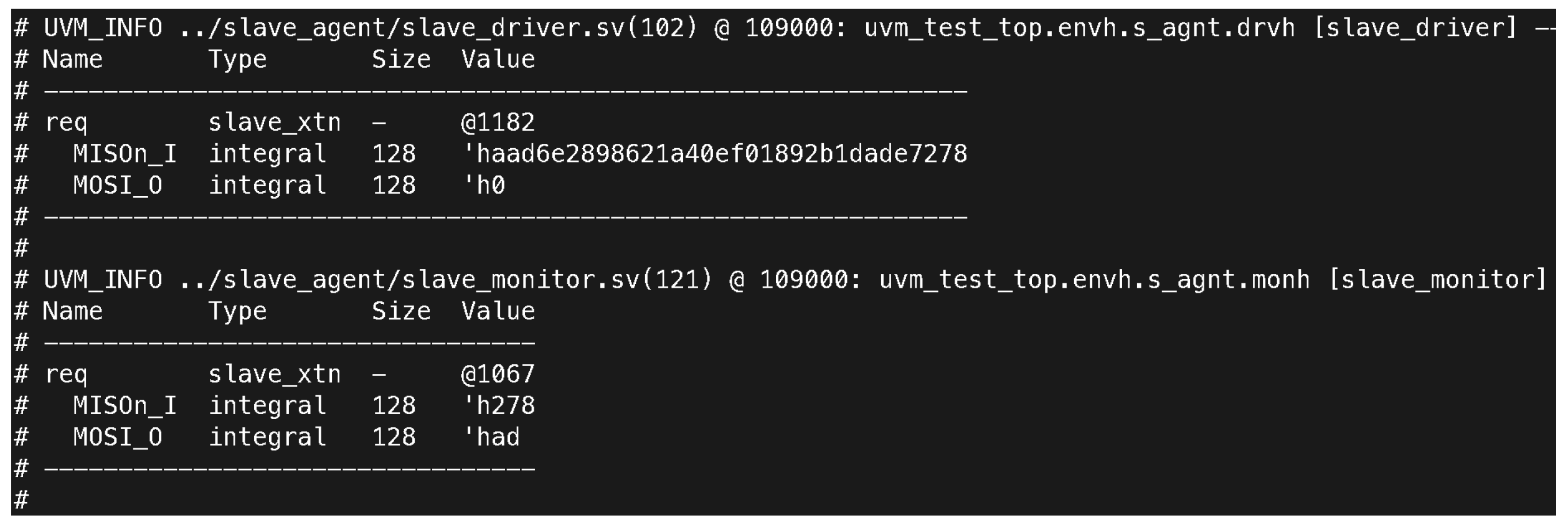
The monitoring components of the SPI system in Figure 6 and Figure 7, particularly the master and slave monitors, provided detailed insights into data transmission. They captured the exact values of the transmitted and received data, ensuring accuracy in reporting and verifying system behavior. For example, the master monitor at 123,000 ns reported a DATA_IN value of 2,456,940,507 and a CONTROL STATUS REG value of 15,114, indicating proper control and data signal processing. Additionally, the log files’ comparisons of received and transmitted data revealed consistent alignment between expected and actual values. The test outcomes highlight that the character length was correctly set to 10 bits, with MOSI (Master Out Slave In) data recorded as 123 and MISO (Master In Slave Out) data as 798, matching the expectations for successful SPI communication.
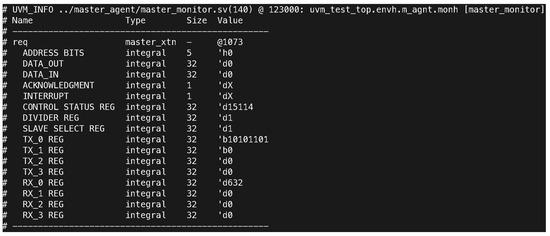
Figure 6.
Log output from the master monitor capturing detailed register states at 123,000 ns. Key data include DATA_IN set to d0, CONTROL STATUS REG set to d15114, and TX-0 REG represented as b1111011. These values confirm proper master-side data monitoring during SPI communication.
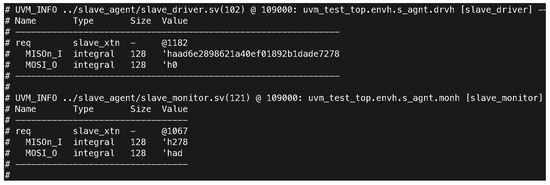
Figure 7.
Snapshot of the slave driver and monitor logs showing the captured MISO and MOSI data. The slave driver received a MISO value of he37e64871581d6a68e5df96946a26b1e and transmitted a MOSI value of h0. The slave monitor observed a MISO value of h31e and a MOSI value of h7b at 109,000 ns.
4.3. Waveform Demonstration on Results
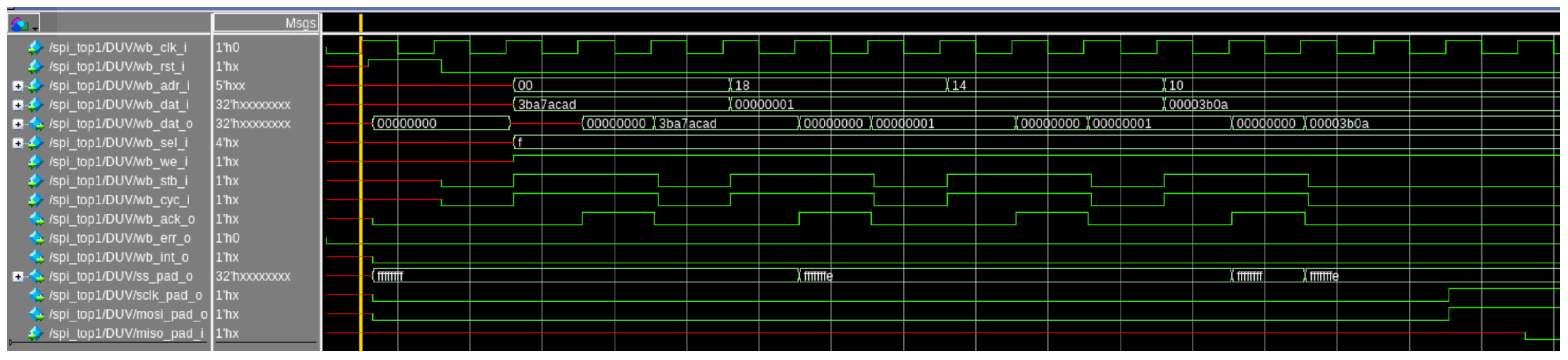
The waveform illustrates a detailed sequence of SPI transactions between the master and slave devices. Key signals such as wb_clk_i, wb_rst_i, mosi_pad_i, and miso_pad_i are well synchronized, indicating robust clock-domain crossing and data integrity throughout the communication. The address (wb_adr_i) and data (wb_dat_i) buses reflect precise transactions at designated clock cycles, ensuring accurate data handshaking between components. For example, the transitions in wb_ack_o and wb_err_o validate proper acknowledgment mechanisms and error-free communication. Furthermore, the sequence transitions in control signals such as wb_we_i, wb_stb_i, and wb_cyc_i demonstrate an effective write-and-read operation workflow. The miso_pad_i and mosi_pad_o signals exhibit consistent data flow following the SPI protocol, further validating the design’s adherence to specifications.
This waveform in Figure 8 underscores the importance of employing UVM and SystemVerilog for such complex verification tasks. UVM provides a scalable and reusable verification framework, allowing for structured testbench development that facilitates debugging and analysis, as evident from the precise signal monitoring in the simulation. SystemVerilog enhances the verification process by offering advanced constructs for modeling, constrained random testing, and functional coverage. Together, they empower engineers to identify intricate bugs and ensure protocol compliance effectively, reducing the risk of design flaws in real-world applications. This combination of tools is indispensable for modern hardware design and verification, providing high-quality, robust, and reliable system performance.
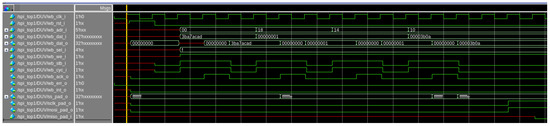
Figure 8.
Waveform depicting SPI transactions, showcasing synchronized clocking, data handshaking on wb_adr_i and wb_dat_i, and successful communication via mosi_pad_o and miso_pad_i signals, adhering to the SPI protocol specification.
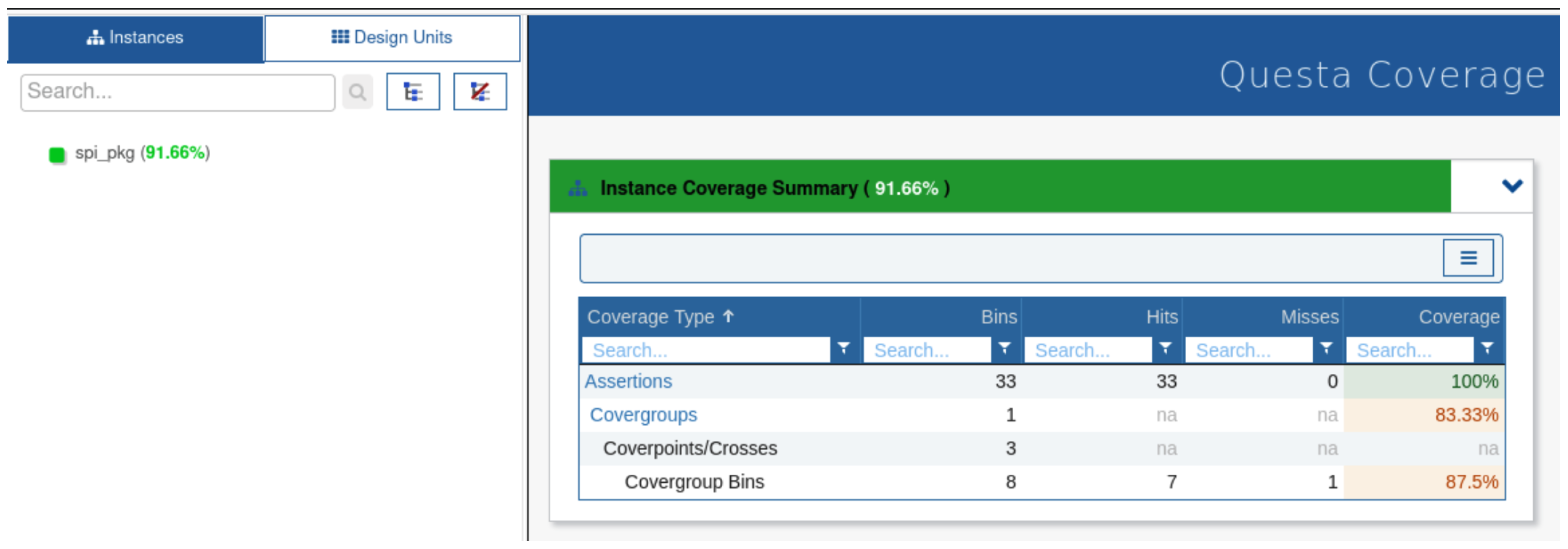
4.4. Coverage Analysis Summary
The coverage report in Figure 9 for the SPI package demonstrates a robust verification process, achieving an overall instance coverage of 91.66%. The assertion coverage reached 100%, indicating that all specified assertions were effectively hit during simulation, ensuring key functional checks were comprehensively validated. The covergroup coverage, however, stands at 83.33%, revealing some room for improvement in exercising specific functional scenarios or corner cases. Additionally, the coverage for bins within the covergroups shows a rate of 87.5%, with one bin remaining unhit. This suggests that while most of the design’s functionality was verified, additional test scenarios targeting unhit conditions could further enhance the thoroughness of the verification process. These results highlight the efficiency of the UVM-based verification environment while also emphasizing the need for refining test coverage to achieve complete verification.
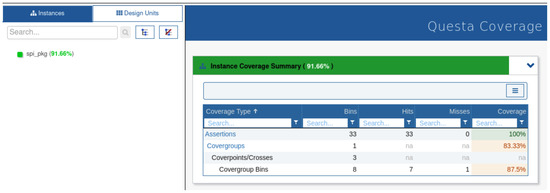
Figure 9.
Coverage analysis results for the SPI package, showing 91.66% overall instance coverage, 100% assertion coverage, 83.33% covergroup coverage, and 87.5% bin coverage, highlighting effective verification with opportunities for further improvement in specific scenarios.
5. Discussion
The nuances of functional and code coverage underscore the complexity of verification tasks. While achieving functional coverage was a primary objective in this project, previous experiences, such as with a 1x3 router design, highlighted the importance of reaching 100% code coverage by exercising all lines, branches, and conditions in the HDL code. Nevertheless, code coverage and assertion coverage are complementary metrics—neither can fully guarantee design quality in isolation. For example, the functional suite successfully validated RX scenarios, but issues with TX bins revealed a potential RTL bug. Despite sequences covering all TX scenarios, specific bins remained unhit, emphasizing the importance of both metrics in identifying corner cases. Addressing such coverage gaps ensures a robust verification process and paves the way for improved hardware reliability.
5.1. Research Contributions
This paper presents a comprehensive UVM-based verification methodology for the SPI protocol, specifically tailored for IoT and wearable devices. Our work systematically addresses key challenges in SPI verification, including multi-slave communication, signal integrity, and low-power constraints. It introduces a robust framework for verifying SPI implementations using functional, assertion-based, and coverage-driven verification techniques.
The key contributions of this research are as follows:
- Development of a scalable UVM-based testbench: We design a modular and reusable UVM test environment that enables constrained random testing, functional coverage tracking, and ABV for SPI protocol validation. This framework ensures compliance with SPI specifications while enabling efficient reuse across multiple verification projects.
- Evaluation of SPI in multi-slave and low-power scenarios: The study rigorously verifies multi-slave SPI communication, ensuring correct chip select (CS) toggling, data consistency, and timing integrity. Additionally, we validate SPI’s behavior in low-power operational modes, assessing wake-up latency, power state transitions, and energy-efficient data transfers.
- Comparison of UVM with alternative verification approaches: We provide a comparative analysis of UVM, directed testing, and ABV, demonstrating UVM’s superiority in scalability, reusability, and automation for complex SPI verification.
- Integration of formal and simulation-based verification: We incorporate SVA to complement constrained-random-test generation, ensuring that timing constraints, protocol compliance, and error-handling mechanisms are thoroughly validated.
These contributions establish a structured, automated, and reusable SPI verification framework, reinforcing UVM’s effectiveness in modern embedded system design and laying the foundation for future research in AI-driven verification automation.
5.2. Potential Areas for Improvement
- Additional assertions: While the test effectively validates initial configurations and essential operations, it could benefit from assertions to monitor specific runtime conditions. For example, verifying that the GO BUSY flag clears after a transaction or that the MSB/LSB configuration aligns with transmitted data would enhance the test’s robustness.
- Coverage metrics: The test does not explicitly mention functional coverage or code coverage metrics. Adding a coverage model that tracks key aspects, such as edge cases in character lengths or timing variations in TX/RX signals, would provide quantitative feedback on the test’s effectiveness.
- Error injection: The test could introduce scenarios with intentional misconfigurations to further validate the SPI design. For example, setting the reserved bits (cnt_reg[7] or cnt_reg[31:14]) to non-zero values could test the DUT’s resilience to unexpected inputs.
- Scalability to larger configurations: While the test focuses on a 10-bit character length, SPI designs often support configurable lengths (e.g., 8, 16, 32 bits). Expanding the test to handle multiple configurations dynamically would enhance its utility.
5.3. Educational Value and Industry Relevance
This implementation is highly relevant for students and professionals learning UVM and SPI protocols. It demonstrates practical applications of register configuration, virtual sequences, and phase synchronization. Moreover, SPI remains ubiquitous in applications ranging from embedded systems to high-speed communication interfaces. This test, therefore, provides a framework that is both educational and immediately applicable in industry settings.
5.4. Limitations of UVM and Lightweight Alternatives
While UVM is a robust and widely adopted verification methodology, its inherent limitations may make it less suitable for more straightforward verification tasks. One of the most cited drawbacks of UVM is its steep learning curve. UVM introduces a complex object-oriented architecture in SystemVerilog, requiring engineers to understand transaction-level modeling (TLM), factory patterns, and sequence-based stimulus generation. This makes UVM adoption challenging for small teams or projects with limited verification resources.
Another significant limitation is the potential overhead in simulation execution and debugging. Due to its layered architecture—including drivers, monitors, sequencers, and scoreboards—UVM testbenches can become computationally heavy, leading to longer simulation runtimes. In contrast, lightweight alternatives such as directed testing and Python3-based verification frameworks (e.g., Cocotb) offer faster setup and execution for simpler designs. While less scalable, directed testing requires minimal infrastructure and is often sufficient for verifying smaller modules or peripheral IPs like basic SPI controllers. Additionally, formal verification techniques, such as property checking with SVA, provide an alternative to dynamic simulations by mathematically proving design correctness without requiring extensive testbenches.
Despite these limitations, UVM remains the industry standard for large and complex verification environments, particularly for SoC and ASIC-level verification, where constrained random testing and coverage-driven verification provide significant benefits. However, for low-power microcontrollers, basic sensor interfaces, and FPGA-based projects, a hybrid approach—combining directed testing, ABV, and selective UVM—can optimize verification efforts while maintaining efficiency.
5.5. UVM-Based Verification for Real-World Reliability in SPI for IoT and Wearable Devices
UVM plays a crucial role in ensuring the robustness and reliability of SPI communication in real-world IoT and wearable applications. These devices often operate under strict power constraints and varying environmental conditions, so rigorous verification is necessary to prevent system failures.
- Ensuring reliable data transmission: IoT and wearable devices rely heavily on SPI for sensor interfacing, real-time data acquisition, and low-latency communication. UVM-based verification rigorously checks for timing violations, metastability issues, and protocol compliance, ensuring seamless data exchange between microcontrollers, sensors, and memory modules.
- Handling power and performance trade-offs: Low-power operation is a key requirement for IoT and wearable technology. UVM verification enables thorough testing of SPI power modes, clock gating strategies, and dynamic frequency scaling mechanisms, helping to optimize energy efficiency while maintaining high communication reliability.
- Robustness against environmental factors: Wearable and IoT devices often function in diverse conditions, from temperature fluctuations to electromagnetic interference. UVM-based testbenches incorporate randomized stimulus generation and stress testing scenarios, validating the SPI controller’s ability to handle noisy environments and signal integrity degradation.
- Fault detection and recovery mechanisms: In real-world scenarios, transient faults such as clock glitches, transmission errors, and bus contention are common. UVM verification frameworks integrate assertion-based checking and error injection mechanisms to assess the SPI system’s resilience, ensuring robust error handling and recovery strategies.
- Long-term reliability and compliance: Wearables and IoT devices require prolonged operational stability. UVM-based verification frameworks employ functional coverage-driven verification and regression testing to validate long-term SPI performance, ensuring compliance with industry standards such as IEEE 1666 (SystemC), AMBA, and ISO 26262 (for automotive IoT applications).
By integrating UVM-driven verification into the SPI design process, manufacturers can significantly reduce the risk of field failures, enhance product durability, and accelerate time to market for reliable IoT and wearable solutions.
5.6. Possible Reasons for 83.33% Functional Coverage:
- Uncovered edge cases: Some rare or extreme test scenarios, such as corner-case timing violations, simultaneous multi-slave access conflicts, or specific protocol error conditions, may not have been fully triggered in the constrained random stimulus generation.
- Coverage holes in test plan: The functional coverage model might have bins that were defined but not adequately exercised due to testbench constraints or limitations in stimulus variation.
- Limitations in constrained random testing: Despite using constrained-random-stimulus generation, some constraints prevented generating specific values or sequences. For example, if a constraint unintentionally limited the range of clock divider values, some SPI clock speeds may not have been tested.
- The SPI controller’s behavior in fault conditions, such as incorrect framing, unexpected clock stretching, or misaligned data transfers, may have been partially tested but not fully covered across all test scenarios.
5.7. Next Steps for Full Functional Coverage (100%)
To improve functional coverage, we can perform the following:
- Analyze missing coverage bins to identify gaps in stimulus generation. Add directed test cases to cover missing corner cases explicitly.
- Refine constrained random constraints to allow greater variability in generated scenarios.
- Ensure cross-coverage combinations are sufficiently exercised in regression runs.
6. Conclusions
The verification of the SPI protocol using UVM has proven to be a robust approach to ensuring the functionality and reliability of this critical communication protocol in modern IoT and wearable devices. By methodically covering key features such as full-duplex transmission, variable word lengths, and edge-sensitive data handling, this study demonstrated that the SPI protocol can meet the stringent demands of real-world applications. The results highlight comprehensive functional coverage and assertion coverage, validating the correctness of the SPI Master core under diverse scenarios, including high-speed data exchange and fault handling. This thorough verification process ensures the readiness of SPI for integration into application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), which are essential for advanced wearable technology and IoT systems.
The spi_sanity_test is a well-crafted implementation that highlights the importance of early-stage validation in the verification process. Its detailed configuration and adherence to UVM principles make it a valuable resource for ensuring the reliability of SPI designs. While opportunities exist to expand its functionality, the test provides a solid foundation for learning and professional use. By emphasizing clarity, modularity, and adherence to standards, it is an exemplary model for UVM-based verification in SPI communication.
Wearable devices, in particular, demand precise, high-speed communication between microcontrollers and peripherals like sensors, displays, and connectivity modules. The application of UVM enables an efficient and scalable verification framework, reducing the time to market while maintaining the integrity of these intricate designs. This methodology ensures the quality of current ASIC implementations and sets a standard for emerging technologies in embedded systems. The insights gained from this work lay a foundation for future research, including optimizing verification workflows for energy-efficient designs and exploring the application of UVM in other communication protocols, cementing its importance in advancing modern electronics.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.-C.L.; Software, Y.-C.L.; Writing—original draft, H.-C.Y.; Writing—review & editing, Y.-C.L.; Supervision, C.-W.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Yu-Cheng Liao was employed by the company Cisco Systems, Inc. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SPI | Serial Peripheral Interface |
| UVM | Universal Verification Methodology |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| DUT | Design under test |
| GUI | Graphical user interface |
| ABV | Assertion-based verification |
| SVA | SystemVerilog Assertions |
| PSL | Property Specification Language |
References
- Dobrescu, C.C.; González, I.; Carneros-Prado, D.; Fontecha, J.; Nugent, C. Direct Memory Access-Based Data Storage for Long-Term Acquisition Using Wearables in an Energy-Efficient Manner. Sensors 2024, 24, 4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, S. Analysis and Comparison of UART, SPI and I2C. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Electrical Engineering, Big Data, and Algorithms (EEBDA), Changchun, China, 24–26 February 2023; pp. 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolagatla, V.R.; Raveendran, A.; Desalphine, V. A Novel and Efficient SPI enabled RSA Crypto Accelerator for Real-Time Applications. In Proceedings of the 2024 28th International Symposium on VLSI Design and Test (VDAT), Vellore, India, 1–3 September 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Ray, A.; Singh, M.; Venkatesan, S.; Anand, A.S. Automated Hardware Auditing Testbed for UART and SPI-based IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the 2023 10th International Conference on Internet of Things: Systems, Management, and Security (IOTSMS), San Antonio, TX, USA, 23–25 October 2023; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H. Research on Airborne Wireless Pressure Testing Network System Based on Zigbee. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 2nd International Conference on Image Processing and Computer Applications (ICIPCA), Shenyang, China, 28–30 June 2024; pp. 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yuan, K.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X. Design of Industrial Hot Air Furnace Monitoring System Based on ZigBee. In Proceedings of the 2023 5th International Academic Exchange Conference on Science and Technology Innovation (IAECST), Guangzhou, China, 8–10 December 2023; pp. 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, P.R.; Rao, S.P.V.M. Data Transactions from UART to SPI Slave Devices through UART-SPI Controller for a SOC. Adv. Electron. Electr. Eng. 2013, 3, 413–420. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhury, S.; Singh, G.K.; Mehra, R.M. Design and Verification Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Protocol for Low Power Applications. Int. J. Innov. Res. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2014, 3, 16750–16758. [Google Scholar]
- Subero, A. USART, SPI, I2C, and Communication Protocols. In Programming PIC Microcontrollers with XC8: Mastering Classical Embedded Design; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2024; pp. 297–366. [Google Scholar]
- Álvarez, J.L.; Mozo, J.D.; Durán, E. Analysis of Single Board Architectures Integrating Sensors Technologies. Sensors 2021, 21, 6303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheba, M.A.; Mansour, D.A.; Abbasy, N.H. A new low-cost and low-power industrial Internet of Things infrastructure for effective integration of distributed and isolated systems with smart grids. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 2023, 17, 4554–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W. Design of Supervisory Controllers and Ultra-Low Power Data Loggers for Hybrid Power Systems. Master’s Thesis, Memorial University of Newfoundland, St. John’s, NL, Canada, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kadambarajan, J.P.; Kadarkarai, P.; Kalyani, B.; Bathul, M.R.; Sandhya, T.; Greeshma, M. SPI Verification Monitor Module Using UVM. In Proceedings of the 2024 10th International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Systems (ICACCS), Coimbatore, India, 14–15 March 2024; pp. 1838–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaila, C.K.; Manoj, G.; Divya, P.S.; Vijila, M. Functional Verification of SPI Protocol using UVM based on AMBA Architecture for Flash Memory Applications. In Proceedings of the 2023 4th International Conference on Signal Processing and Communication (ICSPC), Coimbatore, India, 23–24 March 2023; pp. 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Bhargava, L.; Kumar, V. Hybrid learning scenario path selection and abstraction framework for smart verification of complex SoCs. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 6207–6233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Souza, K.J. Database-Driven FPGA Workflow for Digital System Verification. Master’s Thesis, Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Kohútka, L.; Mach, J. A new FPGA-based task scheduler for real-time systems. Electronics 2023, 12, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, B. A universal-verification-methodology-based testbench for the coverage-driven functional verification of an instruction cache controller. Electronics 2023, 12, 3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Mohanty, R.; Dasgupta, P.; Chakrabarti, P.P. Synthesis of system Verilog assertions. In Proceedings of the Design Automation & Test in Europe Conference, Munich, Germany, 6–10 March 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Das, S.; Mohanty, R.; Dasgupta, P.; Chakrabarti, P.P. Automatic generation of System Verilog assertions for verification of safety mechanisms. In Proceedings of the 2024 4th Interdisciplinary Conference on Electrics and Computer (INTCEC), Chicago, IL, USA, 11–13 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Dranga, D.; Dumitrescu, C. Artificial intelligence application in functional verification. Electronics 2024, 13, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroteev, M.V. BERT: A review of applications in natural language processing and understanding. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2103.11943. [Google Scholar]
- Jawahar, G.; Sagot, B.; Seddah, D. What does BERT learn about language structure? In Proceedings of the ACL 2019—57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 28 July–2 August 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; Yu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G.; Zhang, K.; Ji, C.; Yan, Q.; He, L.; et al. A comprehensive survey on pre-trained foundation models: A history from BERT to ChatGPT. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2024, 1–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, S.; Chouhan, S.S.; Rathore, S.S. TextConvoNet: A convolutional neural network-based architecture for text classification. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 14249–14268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, V.R. Optimizing Constraint Selection in a Design Verification Environment for Efficient Coverage Closure. Ph.D. Thesis, Nova Southeastern University, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannides, C.; Eder, K.I. Coverage-directed test generation automated by machine learning—A review. ACM Trans. Des. Autom. Electron. Syst. (TODAES) 2012, 17, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, H.; Gulzar, M.M.; Aziz, S.; Habib, S.; Ahmed, I. AI-based anomaly identification techniques for vehicles communication protocol systems: Comprehensive investigation, research opportunities and challenges. Internet Things 2024, 27, 101245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankar, V.; Parsana, S. An overview and empirical comparison of natural language processing (NLP) models and an introduction to and empirical application of autoencoder models in marketing. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 2022, 50, 1324–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wit, A. Comparison of Feature Verification and Directed Verification Coverage. Master’s Thesis, Aalto University School of Electrical Engineering, Espoo, Finland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasena, A.; Mishra, P. Directed test generation for hardware validation: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 2024, 56, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witharana, H.; Lyu, Y.; Charles, S.; Mishra, P. A survey on assertion-based hardware verification. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2022, 54, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knuutinen, A. Formal Connectivity Verification of Clock and Reset Signals in Ultra-Low-Power SoC Designs. Master’s Thesis, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, H.; Hosseini, M.; Azarpeyv, A.; Iman, M.R.H.; Ghasempouri, T. Automatic high functional coverage stimuli generation for assertion-based verification. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 30th International Symposium on On-Line Testing and Robust System Design (IOLTS), Rennes, France, 3–5 July 2024; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Bhuvaneswary, N.; Deny, J.; Lakshmi, A. Exploration on reusability of universal verification methodology. In Proceedings of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), Greater Noida, India, 28–29 April 2022; pp. 1865–1868. [Google Scholar]
- Sinervä, M. UVM Testbench in Python: Feature and Performance Comparison with SystemVerilog Implementation. Master’s Thesis, University of Oulu, Oulu, Finland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Salah, K. A UVM-based smart functional verification platform: Concepts, pros, cons, and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2014 9th International Design and Test Symposium (IDT), Algeries, Algeria, 16–18 December 2014; pp. 94–99. [Google Scholar]
- Sahay, N.; Gajjar, S. Design and UVM-based verification of UART, SPI, and I2C protocols. In Proceedings of the 2024 5th International Conference on Smart Electronics and Communication (ICOSEC), Trichy, India, 18–20 September 2024; pp. 330–335. [Google Scholar]
- Krichen, M. A survey on formal verification and validation techniques for Internet of Things. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, H.; Wen, X.; Xu, K.; Tan, H. Enhancing chip design verification through AI-powered bug detection in RTL code. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2024, 92, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).