Tea Harvest Robot Navigation Path Generation Algorithm Based on Semantic Segmentation Using a Visual Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection and Labeling of Tea Canopy Data
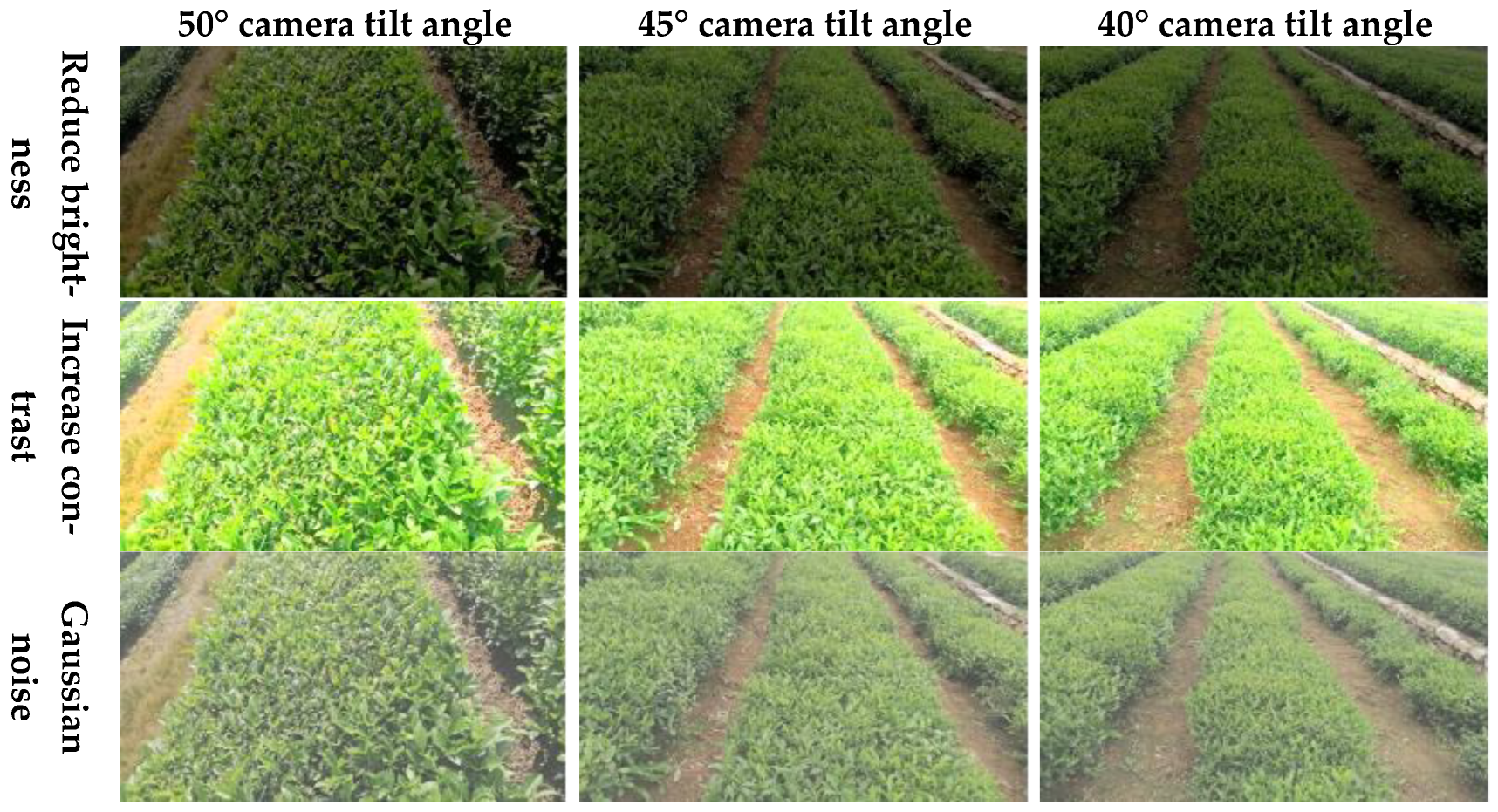
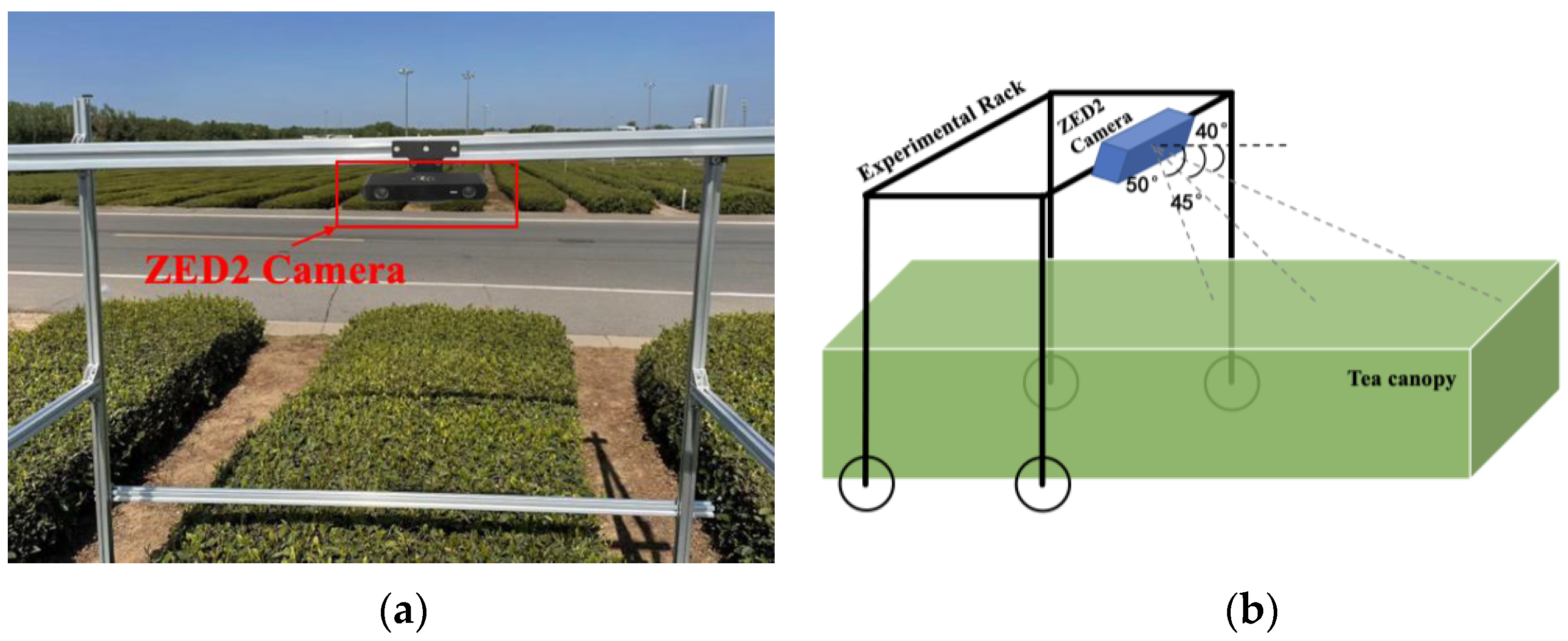
2.1.1. Data Acquisition
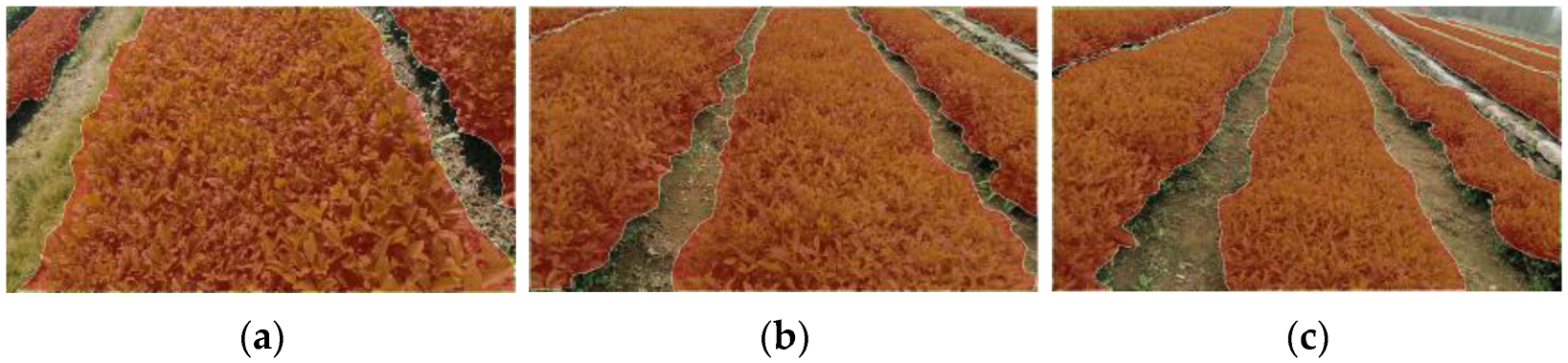
2.1.2. Dataset Production
2.2. Establishment of Tea Canopy Segmentation Model
2.2.1. Deeplabv3+ Model
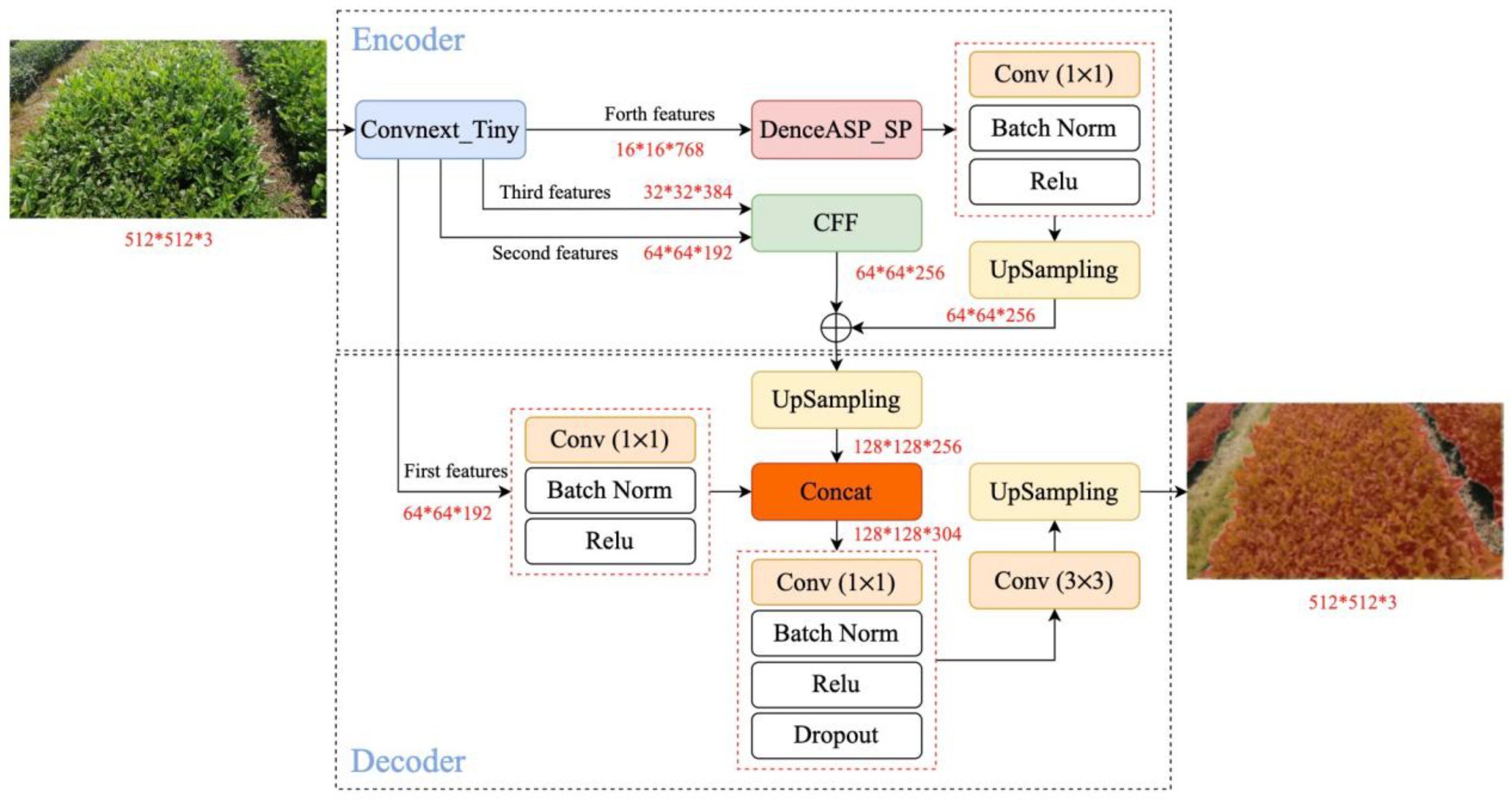
2.2.2. CDSC-Deeplabv3+ Model
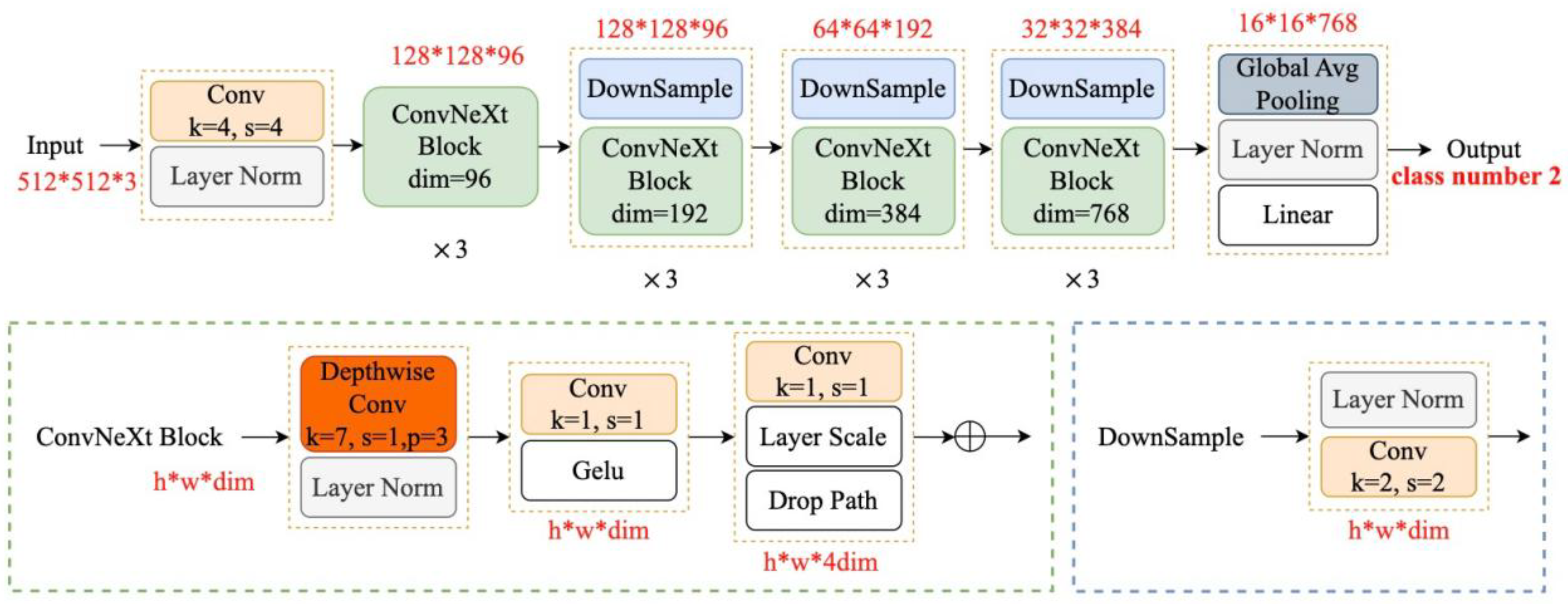
2.2.3. Convnext Backbone Network
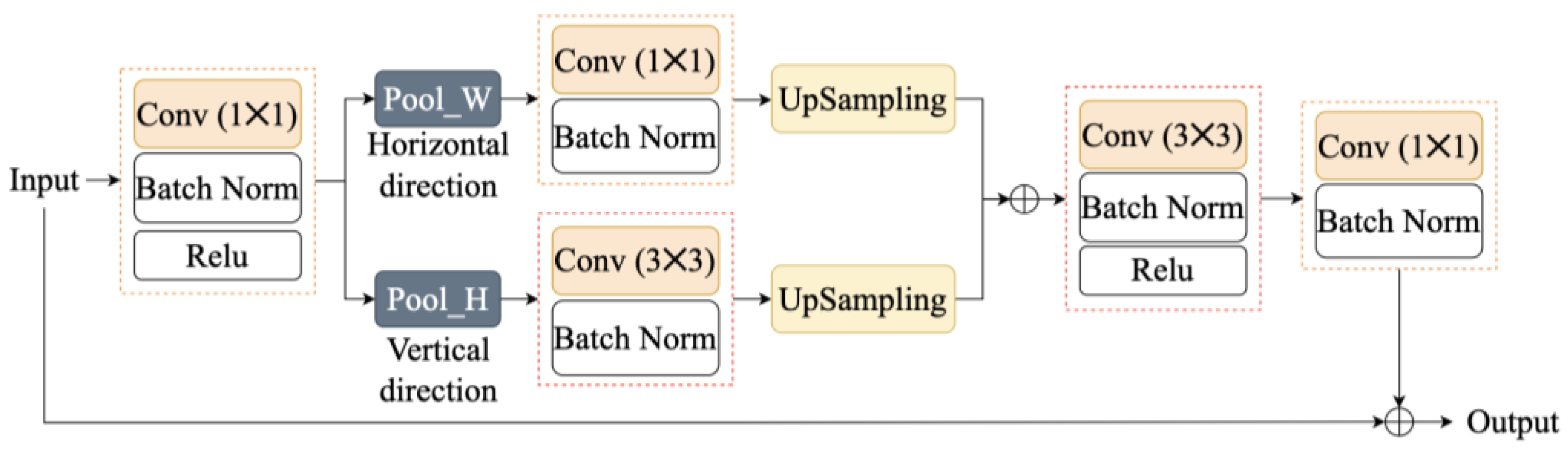
2.2.4. DenceASP_SP Module
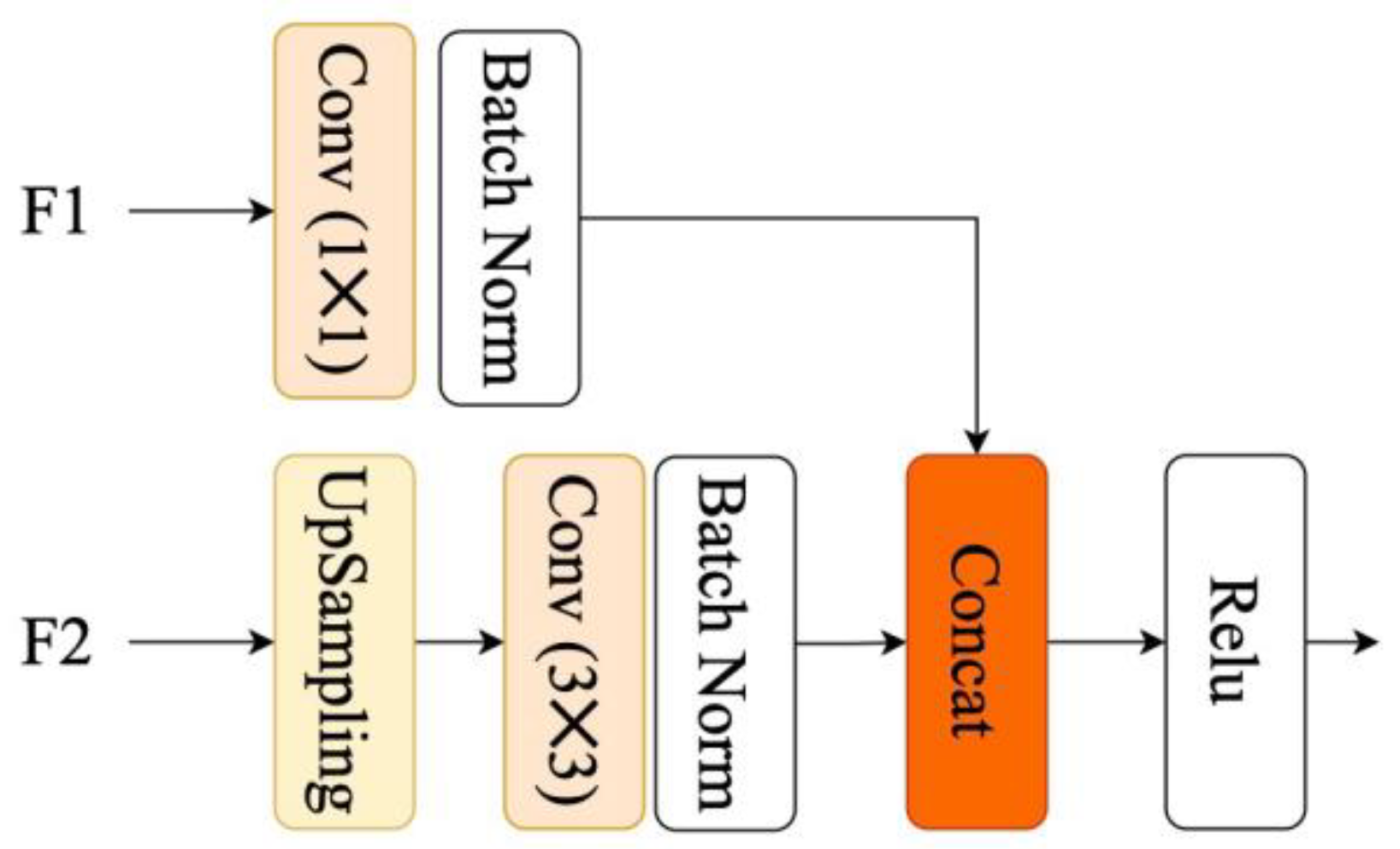
2.2.5. CFF Module
2.2.6. Indicators for Model Evaluation
2.3. Tea Canopy Navigation Central Line Extraction
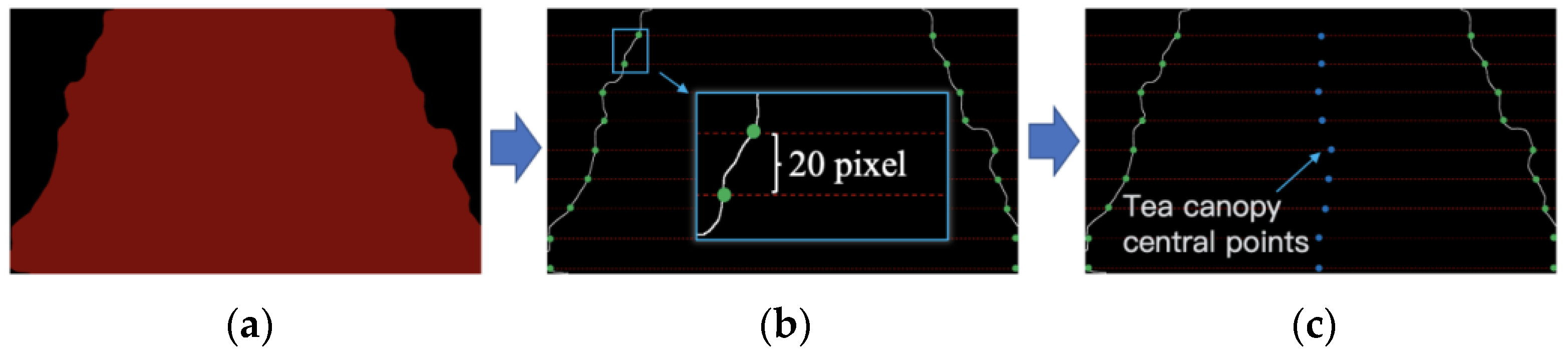
2.3.1. Sequence Extraction of Tea Canopy Central Points
2.3.2. Fitting of Tea Canopy Navigation Central Lines
2.3.3. Evaluation Indicators for Tea Canopy Navigation Central Line Fitting Performance
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Parameter Setting
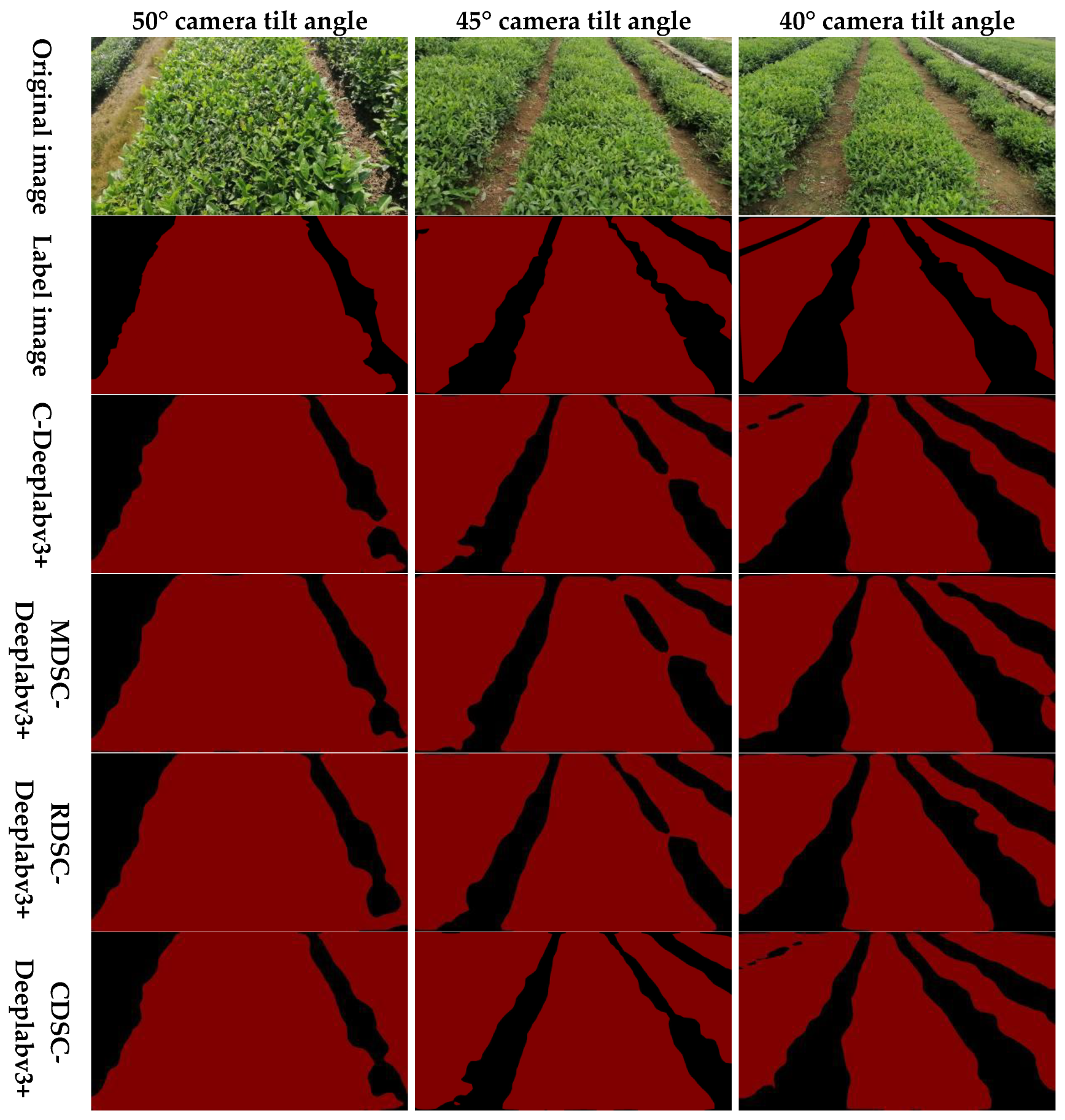
3.2. Experiment on Semantic Segmentation of Tea Canopy
3.2.1. Comparative Experiments with Multiple Framework Models
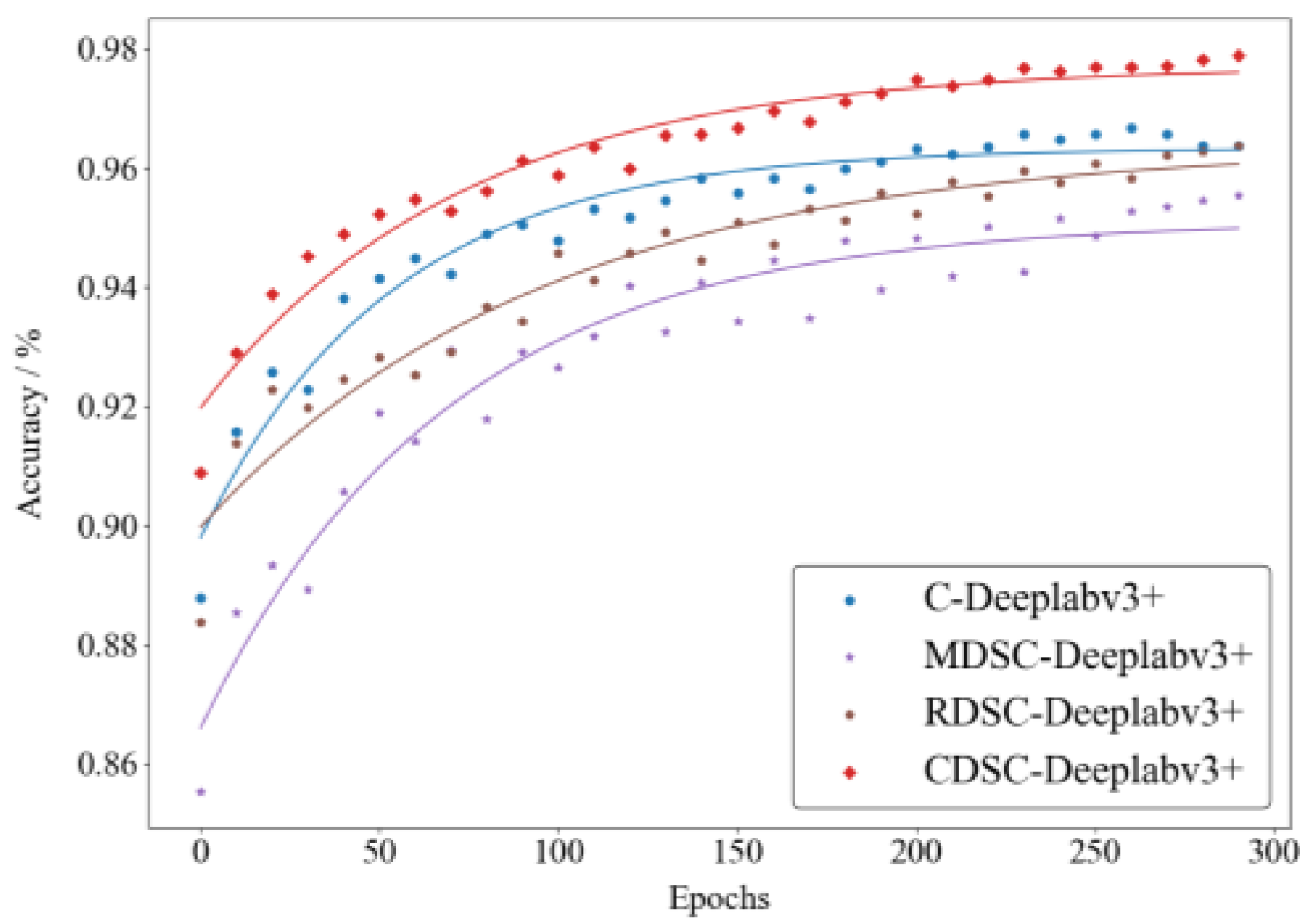
3.2.2. Basic Comparison Experiment
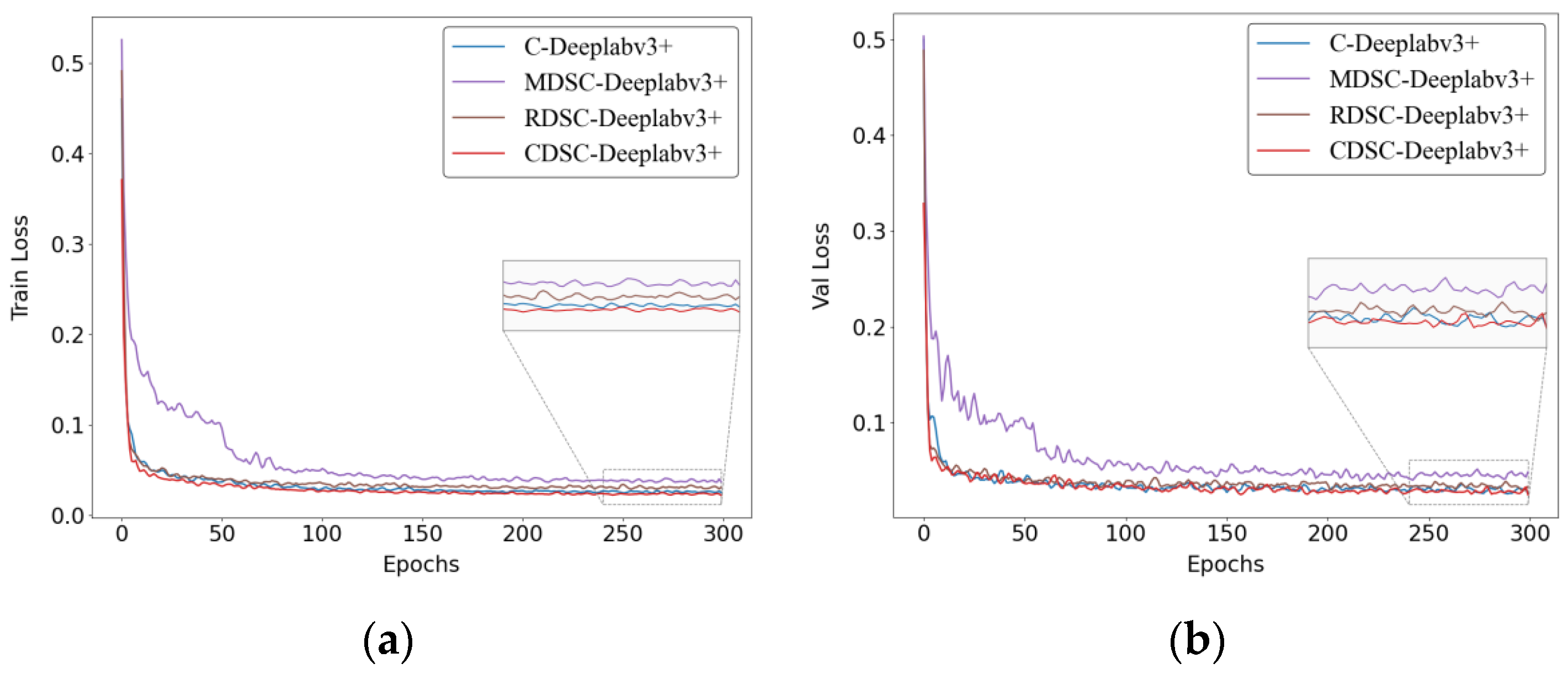
3.2.3. Ablation Experiments
3.3. Navigation Central Line Fitting Experiments
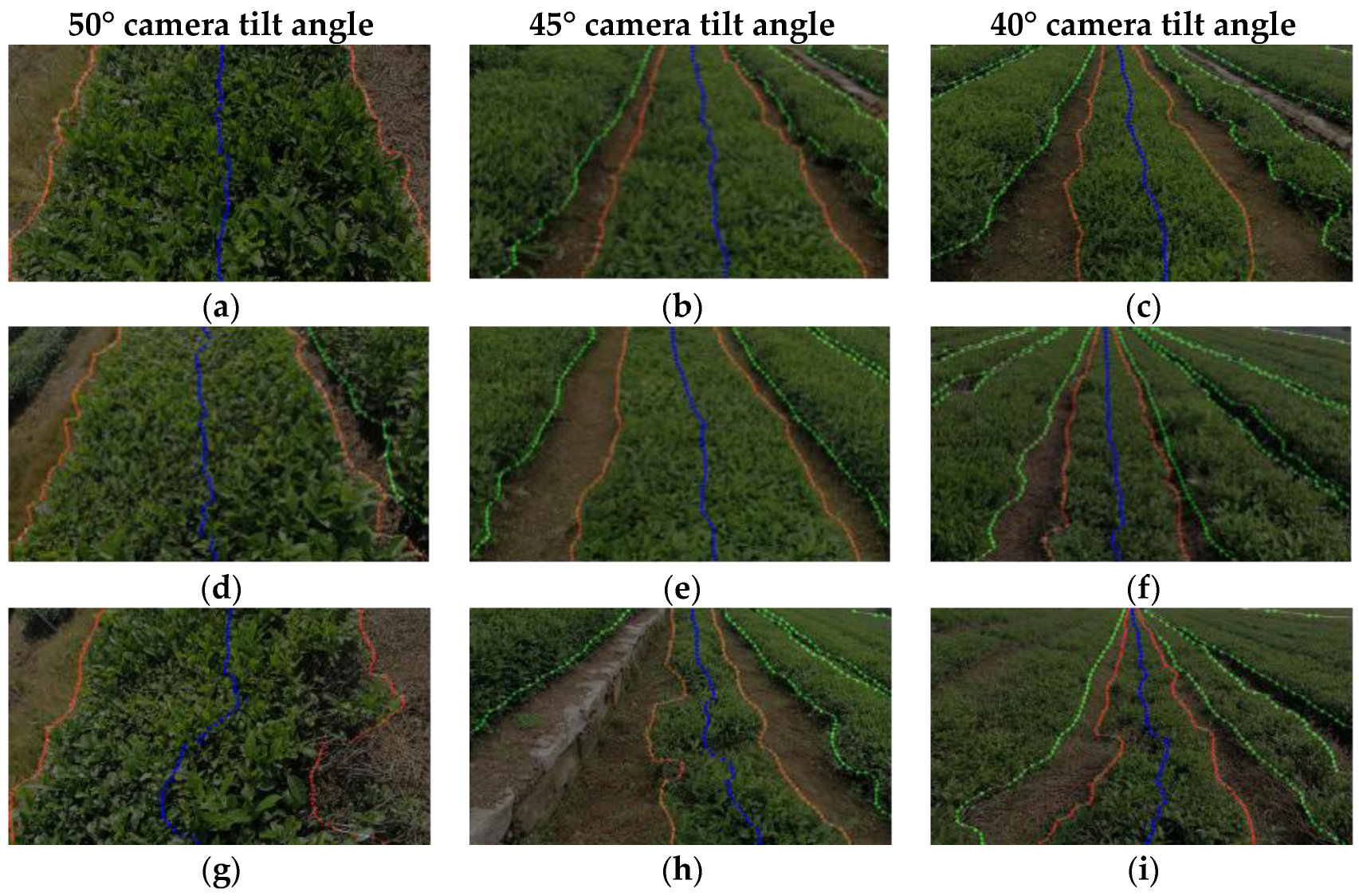
3.3.1. Experiment on the Extraction of Edge Lines and Central Point Sequences of Tea Canopy
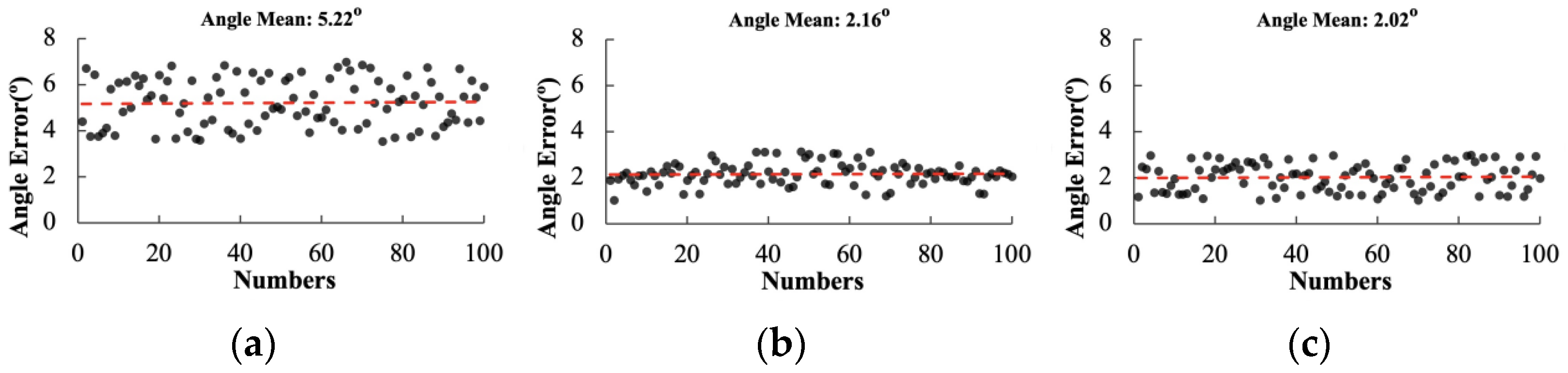
3.3.2. Comparison Experiment of Different Navigation Central Line Fitting Algorithms
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hang, Z.; Tong, F.; Xianglei, X.; Yunxiang, Y.; Guohong, Y. Research Status and Prospect of Tea Mechanized Picking Technology. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2023, 44, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Minglong, W.; Yao, X.; Zhihao, Z.; Lixue, Z.; Guichao, L. Research Progress of Intelligent Mechanized Tea Picking Technology and Equipment. J. Chin. Agric. Mech. 2024, 45, 305. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.; Xie, Y.; Li, Q.; Guo, Z.; Dai, Y.; Fang, Z.; Li, J. Development and Experiment of Adaptive Oolong Tea Harvesting Robot Based on Visual Localization. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Wan, S.; Rao, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Gu, L. Tea Picking Point Detection and Location Based on Mask-RCNN. Inf. Process. Agric. 2023, 10, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, L.; Li, J.; Shang, S.; Ding, X.; Wang, T. Detection and Classification of Tea Buds Based on Deep Learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 192, 106547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Xiao, H.; Lu, P.; Xie, B. Tea Sprout Picking Point Identification Based on Improved DeepLabV3+. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeller, R.; Deemyad, T.; Sebastian, A. Autonomous Navigation of an Agricultural Robot Using RTK GPS and Pixhawk. In Proceedings of the 2020 Intermountain Engineering, Technology and Computing (IETC), Orem, UT, USA, 2–3 October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, T.; Backman, J. Guidance System for Agricultural Tractor with Four Wheel Steering. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2013, 46, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Hu, X.; Xu, L.; Wu, Y. Construction and Accuracy Analysis of a BDS/GPS-Integrated Positioning Algorithm for Forests. Croat. J. For. Eng. J. Theory Appl. For. Eng. 2021, 42, 321–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Lee, H.; Jeon, C.-W.; Yun, C.; Kim, H.-J.; Wang, W.; Liang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Han, X. Improved Position Estimation Algorithm of Agricultural Mobile Robots Based on Multisensor Fusion and Autoencoder Neural Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corno, M.; Furioli, S.; Cesana, P.; Savaresi, S.M. Adaptive Ultrasound-Based Tractor Localization for Semi-Autonomous Vineyard Operations. Agronomy 2021, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Wang, S.; Xue, J.; Chen, Z.; Si, J. Obstacle Detection and Obstacle-Surmounting Planning for a Wheel-Legged Robot Based on Lidar. Robot. Intell. Autom. 2024, 44, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, R.; Cielniak, G.; Wang, G.; Gao, J. Deep Learning-Based Crop Row Detection for Infield Navigation of Agri-Robots. J. Field Robot. 2024, 41, 2299–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Le, F.; Si, S.; Cui, L.; Xue, X. Image Segmentation-Based Oilseed Rape Row Detection for Infield Navigation of Agri-Robot. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, S.P.; Kim, G.; Kim, H. Deep Neural Network-Based System for Autonomous Navigation in Paddy Field. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 71272–71278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. In Computer Vision—ECCV 2018, 15th European Conference, Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Shi, J.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, J. Pyramid Scene Parsing Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2015, 18th International Conference, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning with Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1800–1807. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. Convnext v2: Co-designing and scaling convnets with masked autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 16133–16142. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer Using Shifted Windows. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.-Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T.; Xie, S. A ConvNet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial Pyramid Pooling in Deep Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2014, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, M.-M.; Feng, J. Strip Pooling: Rethinking Spatial Pooling for Scene Parsing. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H. Cascaded Feature Fusion with Multi-Level Self-Attention Mechanism for Object Detection. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 138, 109377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canny, J. A Computational Approach to Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1986, PAMI–8, 679–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Diao, Z.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, R.; Yang, R.; Ma, S.; He, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, B. Navigation line extraction algorithm for corn spraying robot based on YOLOv8s-CornNet. J. Field Robot. 2024, 41, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winterhalter, W.; Fleckenstein, F.; Dornhege, C.; Burgard, W. Localization for Precision Navigation in Agricultural Fields—Beyond Crop Row Following. J. Field Robot. 2021, 38, 429–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.; Mithal, V.; Polatkan, G.; Ramanath, R. An Attentive Survey of Attention Models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2021, 12, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Carey, M.J. LSM-Based Storage Techniques: A Survey. VLDB J. 2020, 29, 393–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhai, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Tian, G.; Zhang, J.; Huang, P.; Li, L. Potato Visual Navigation Line Detection Based on Deep Learning and Feature Midpoint Adaptation. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Hong, F.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, L.; Zhuang, Q.; Jia, J.; Chen, J.; Wu, C. CYVIO: A visual inertial odometry to acquire real-time motion information of profiling tea harvester along the planting ridge. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Jin, C.; Chen, M. DeeplabV3+-Based Navigation Line Extraction for the Sunlight Robust Combine Harvester. Sci. Prog. 2024, 107, 00368504231218607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, J. MA-Res U-Net: Design of Soybean Navigation System with Improved U-Net Model. PHYTON 2024, 93, 2663–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Guo, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Hong, Z.; Xue, W. A Method for Recognizing Inter-Row Navigation Lines of Rice Heading Stage Based on Improved ENet Network. Measurement 2025, 241, 115677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Model | mAP % | mIoU % | F1-Score % | Parameter (MB) | FPS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PspNet | Convnext | 94.36 | 91.65 | 96.02 | 31.06 | 25.4 |
| MobileNetV2 | 94.89 | 92.23 | 96.75 | 2.38 | 30.2 | |
| ResNet50 | 94.81 | 91.05 | 97.24 | 46.71 | 22.3 | |
| U-Net | Convnext | 87.82 | 84.21 | 95.01 | 43.1 | 23.9 |
| MobileNetV2 | 95.34 | 92.01 | 96.31 | 10.64 | 28.4 | |
| ResNet50 | 94.86 | 92.84 | 96.03 | 43.93 | 23.6 | |
| Deeplabv3 | Convnext | 96.57 | 93.75 | 98.21 | 118.57 | 6.4 |
| MobileNetV2 | 94.37 | 89.45 | 95.76 | 12.43 | 27.1 | |
| ResNet50 | 95.02 | 91.31 | 96.51 | 110.87 | 9.5 | |
| Model | R2 | Accuracy % | mAP % | mIoU % | F1-Score % | Parameter (MB) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Deeplabv3+ | 0.86 | 96.34 | 96.57 | 93.75 | 98.21 | 118.57 | 6.4 |
| MDSC-Deeplabv3+ | 0.82 | 95.31 | 94.04 | 90.35 | 95.97 | 18.44 | 29.7 |
| RDSC-Deeplabv3+ | 0.84 | 95.87 | 95.07 | 92.64 | 96.98 | 116.46 | 8.02 |
| CDSC-Deeplabv3+ | 0.88 | 97.32 | 96.99 | 94.71 | 98.66 | 123.56 | 5.0 |
| Model | Convnext | DenceASPP | CFF | SP | mAP % | mIoU % | F1-Score % | Parameter (MB) | FPS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-Deeplabv3+ | √ | 96.57 | 93.75 | 98.21 | 118.57 | 6.4 | |||
| CD-Deeplabv3+ | √ | √ | 96.45 | 93.61 | 98.06 | 125.86 | 4.5 | ||
| CF-Deeplabv3+ | √ | √ | 96.65 | 93.81 | 98.25 | 118.84 | 6.4 | ||
| CS-Deeplabv3+ | √ | √ | 96.58 | 93.80 | 98.27 | 119.62 | 6.1 | ||
| CDC-Deeplabv3+ | √ | √ | √ | 96.60 | 94.75 | 98.22 | 122.51 | 5.5 | |
| CDS-Deeplabv3+ | √ | √ | √ | 96.63 | 94.81 | 98.3 | 128.48 | 4.1 | |
| CSC-Deeplabv3+ | √ | √ | √ | 96.64 | 93.83 | 98.32 | 119.88 | 6.0 | |
| CDSC-Deeplabv3+ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 96.99 | 94.71 | 98.66 | 123.56 | 5.0 |
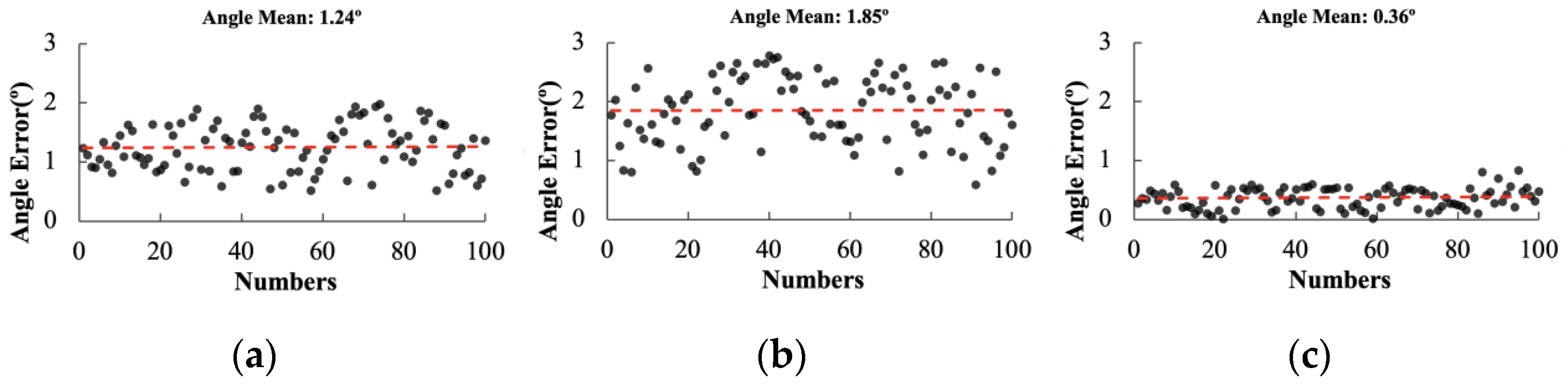
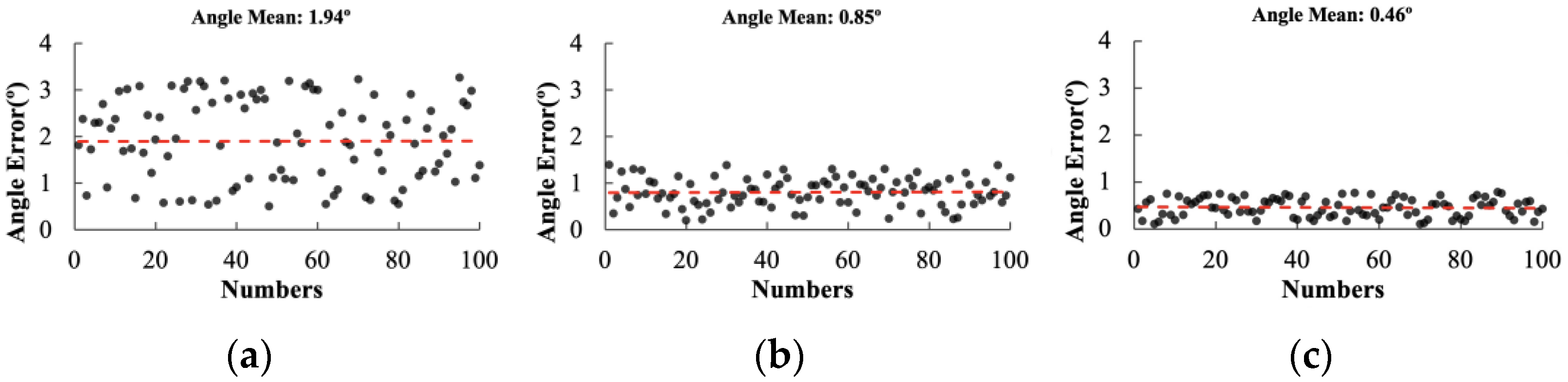
| Performance Indicators | LSM | Hough | RANSAC | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50° | 45° | 40° | 50° | 45° | 40° | 50° | 45° | 40° | |
| Average angular deviation (n/°) | 5.22 | 1.24 | 1.94 | 2.16 | 1.85 | 0.80 | 2.02 | 0.36 | 0.46 |
| Average fitting time (t/ms) | 6.8 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 8320.0 | 7420.0 | 7380.0 | 56.4 | 44.7 | 48.3 |
| Model | Target | mAP % | mIoU % | Algorithms | Average Angle Error/° | Average Fitting Time/ms |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VC-UNet [14] | Rape Crop Rows | 90.15 | 87.3 | LSM | 3.76 | 9 |
| Deeplabv3+ [35] | Rice Crop Rows | \ | 79.22 | Canny | 3.33 | \ |
| MA-Res UNet [36] | Soybean Crop rows | 92.1 | 82.9 | RANSAC | 2.09 | \ |
| SEU-ENet [37] | Rice Crop Rows | 96.39 | 89.0 | LSM | 1.91 | 24.6 |
| CDSC-Deeplabv3+ | Tea Crop Rows | 97.04 | 94.96 | RANSAC | 0.95 | 49.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, H.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Yi, T.; Wu, M. Tea Harvest Robot Navigation Path Generation Algorithm Based on Semantic Segmentation Using a Visual Sensor. Electronics 2025, 14, 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050988
Tao H, Zhang R, Zhang L, Zhang D, Yi T, Wu M. Tea Harvest Robot Navigation Path Generation Algorithm Based on Semantic Segmentation Using a Visual Sensor. Electronics. 2025; 14(5):988. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050988
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Houqi, Ruirui Zhang, Linhuan Zhang, Danzhu Zhang, Tongchuan Yi, and Mingqi Wu. 2025. "Tea Harvest Robot Navigation Path Generation Algorithm Based on Semantic Segmentation Using a Visual Sensor" Electronics 14, no. 5: 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050988
APA StyleTao, H., Zhang, R., Zhang, L., Zhang, D., Yi, T., & Wu, M. (2025). Tea Harvest Robot Navigation Path Generation Algorithm Based on Semantic Segmentation Using a Visual Sensor. Electronics, 14(5), 988. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14050988







