Single Phase Induction Motor Driver for Water Pumping Powered by Photovoltaic System
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Available solar energy for the given site.
- The volume of water needed for the irrigation process.
- The given period depends upon the climate changes.
- The quality and quantity of the water.
- The reliability of the proposed topology and the system dynamics.
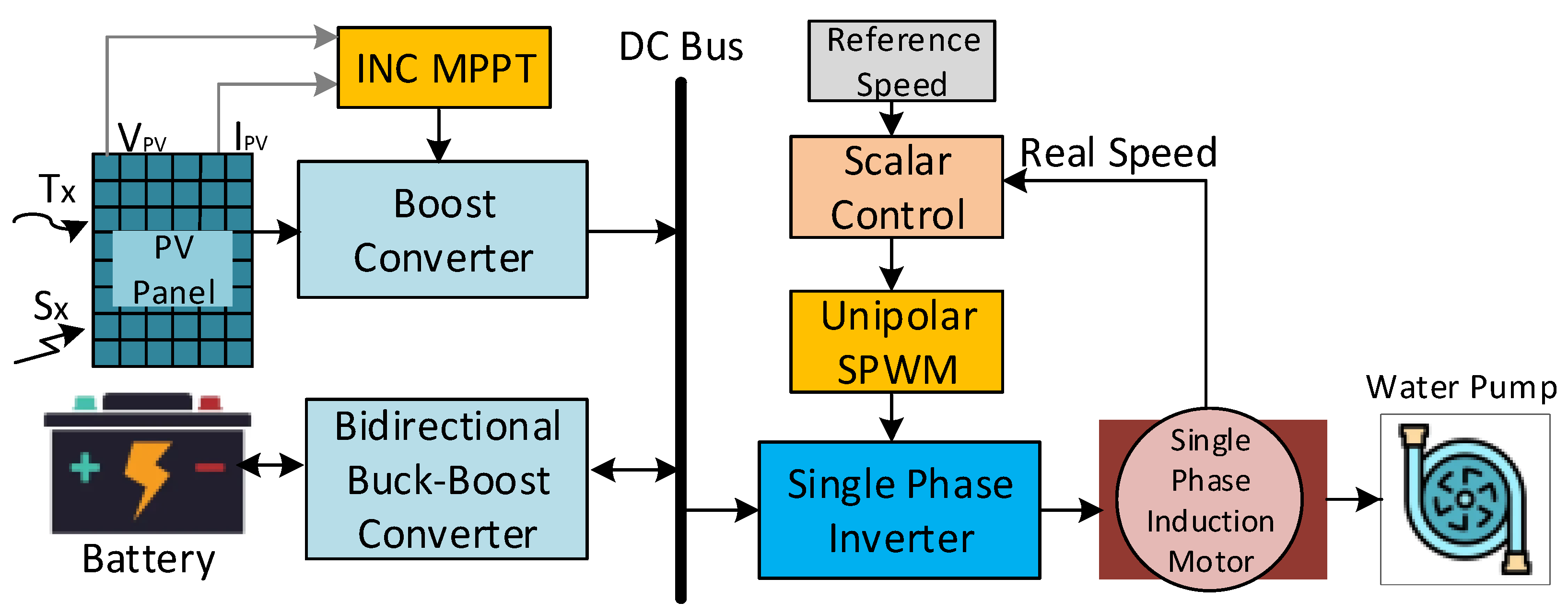
2. The Components of the Designed System
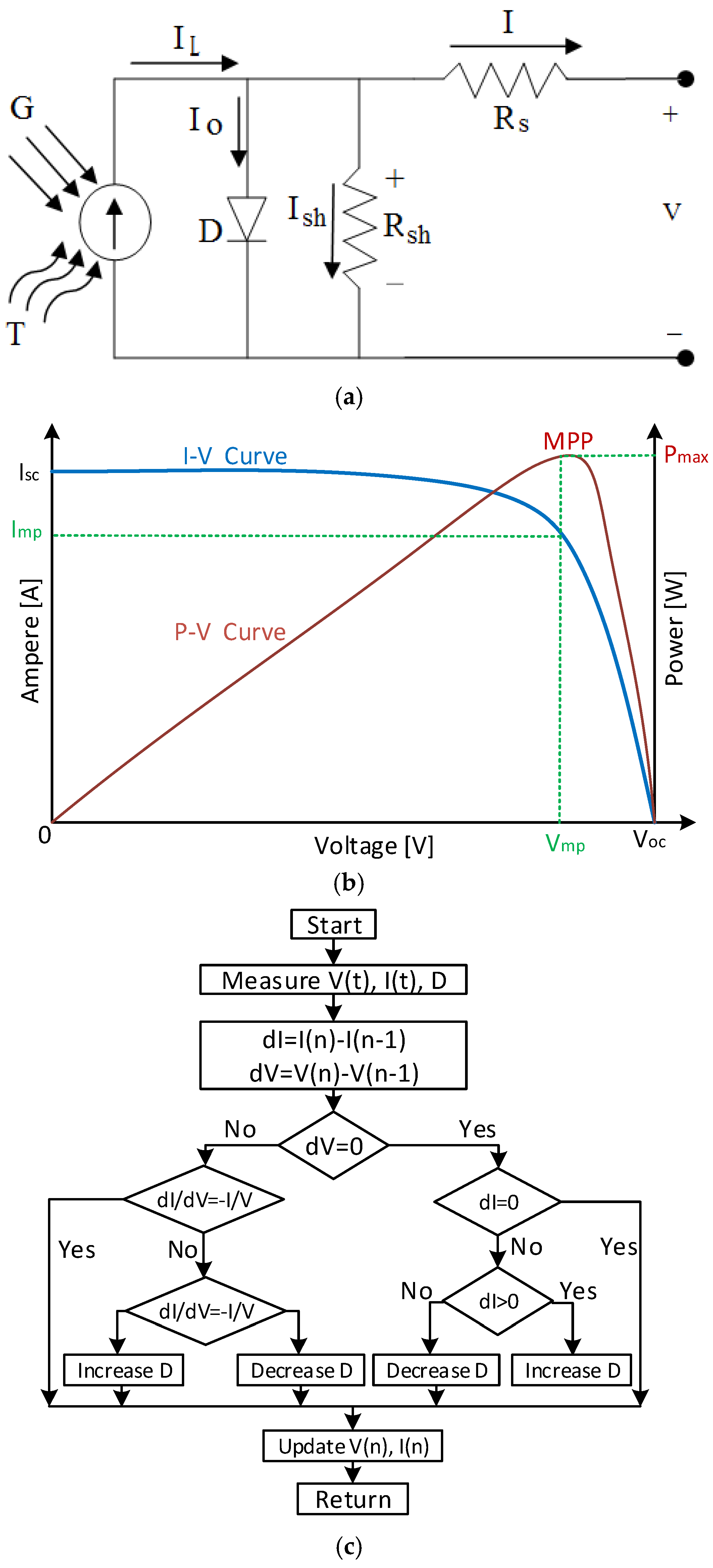
2.1. Photovoltaic Arrays
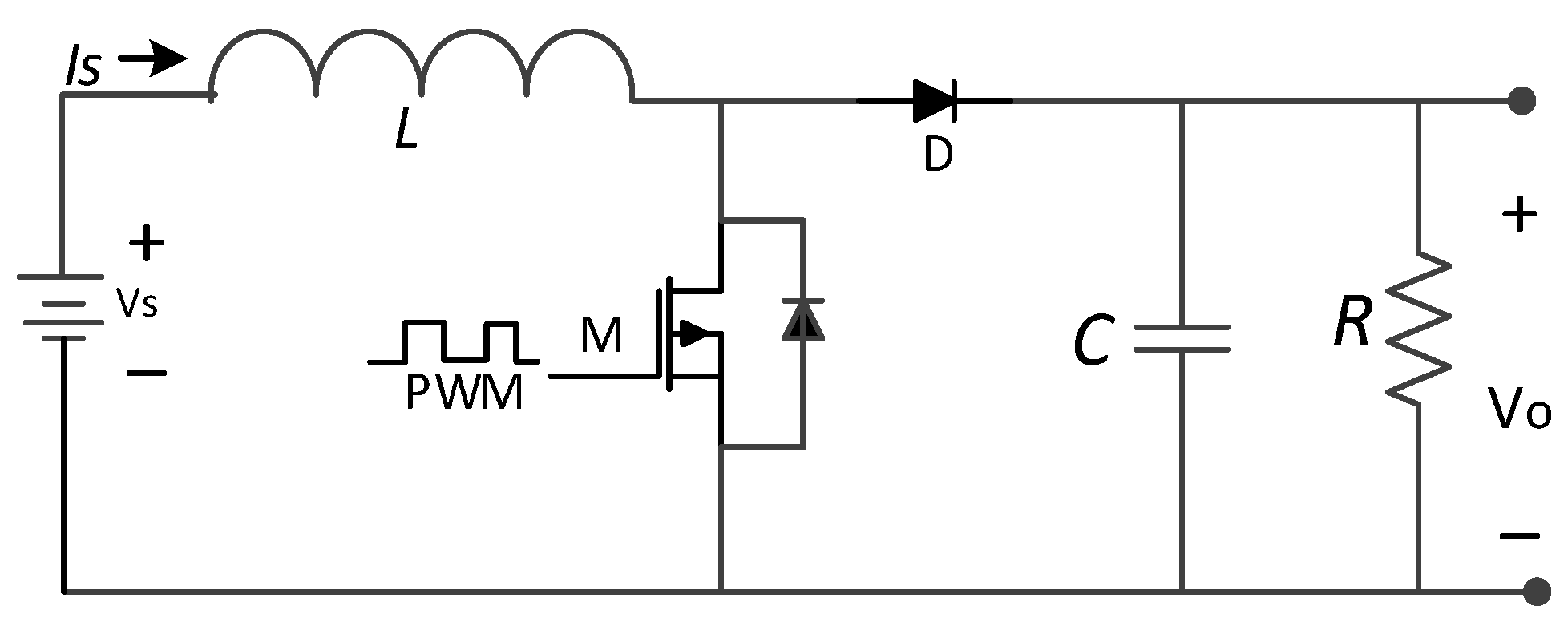
2.2. Boost Converter
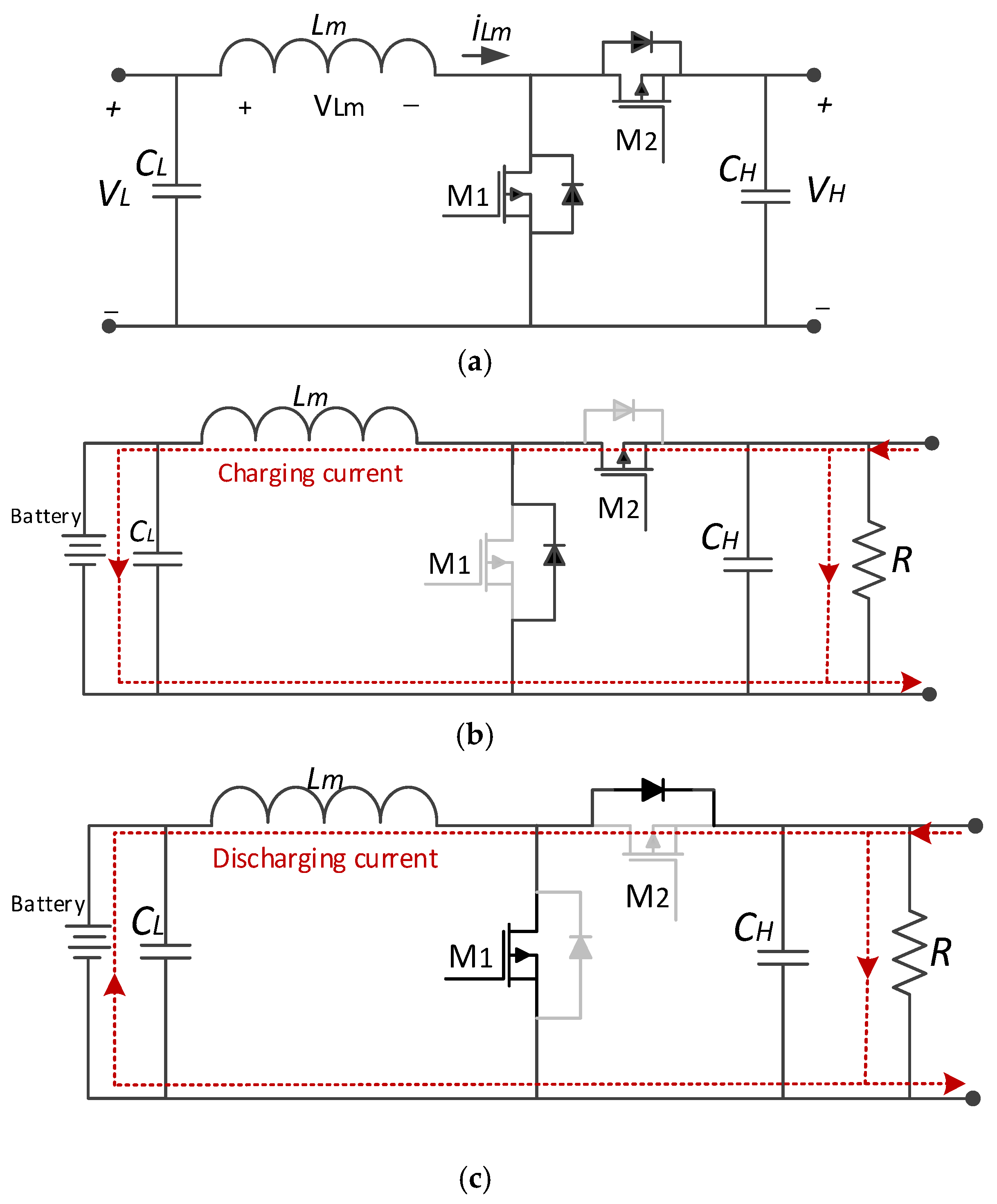
2.3. Bidirectional Buck-Boost Converter
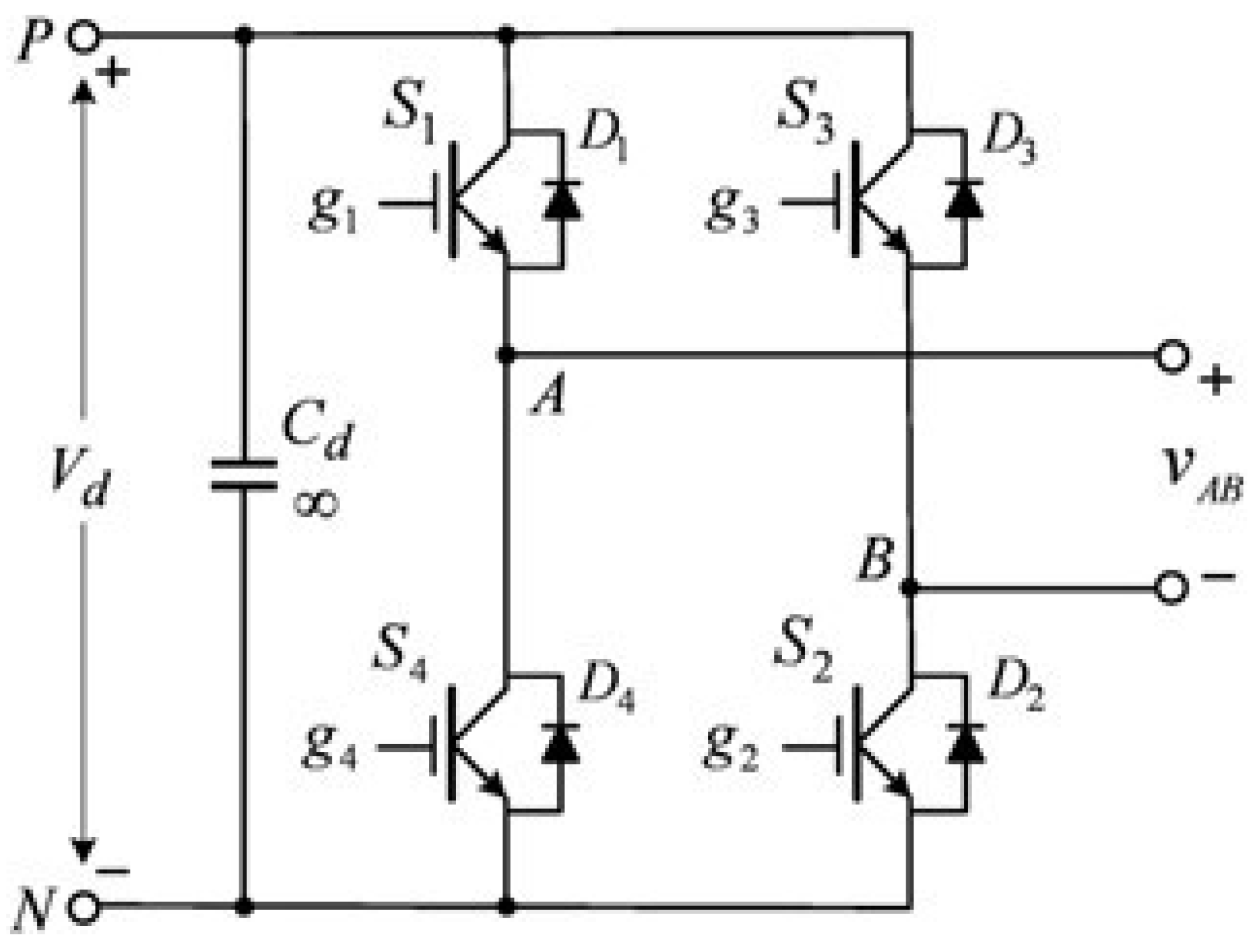
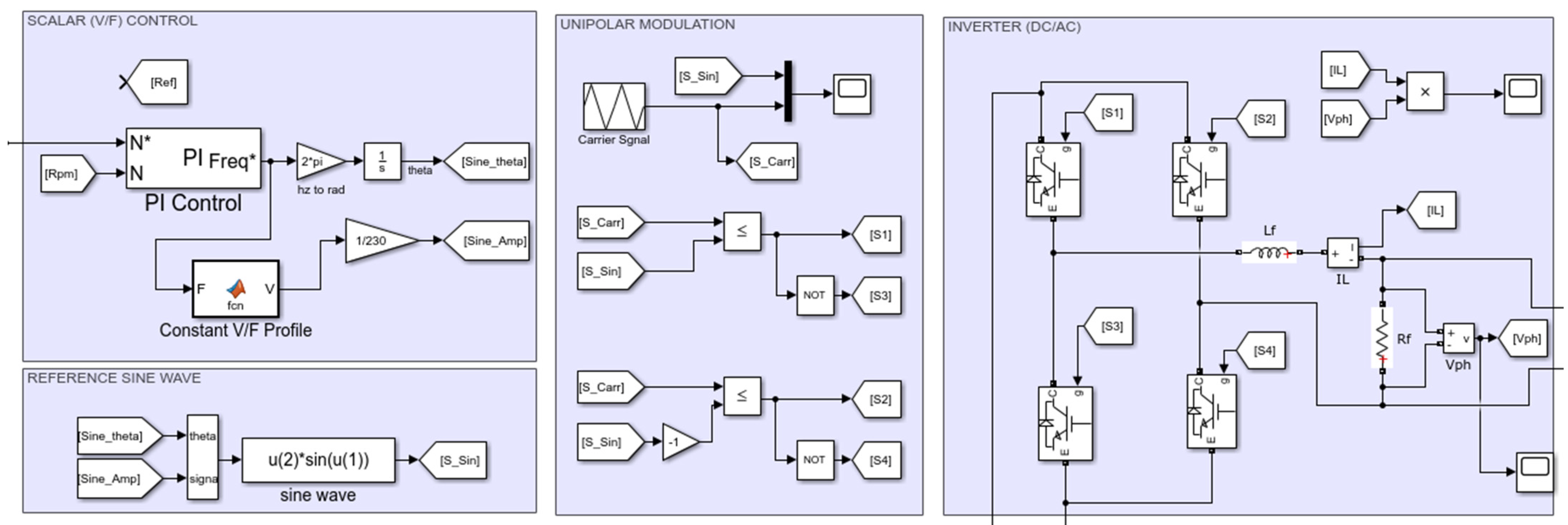
2.4. Inverter and Unipolar Modulation Control
2.5. V/f Scaler Control of Single-Phase Induction Motor
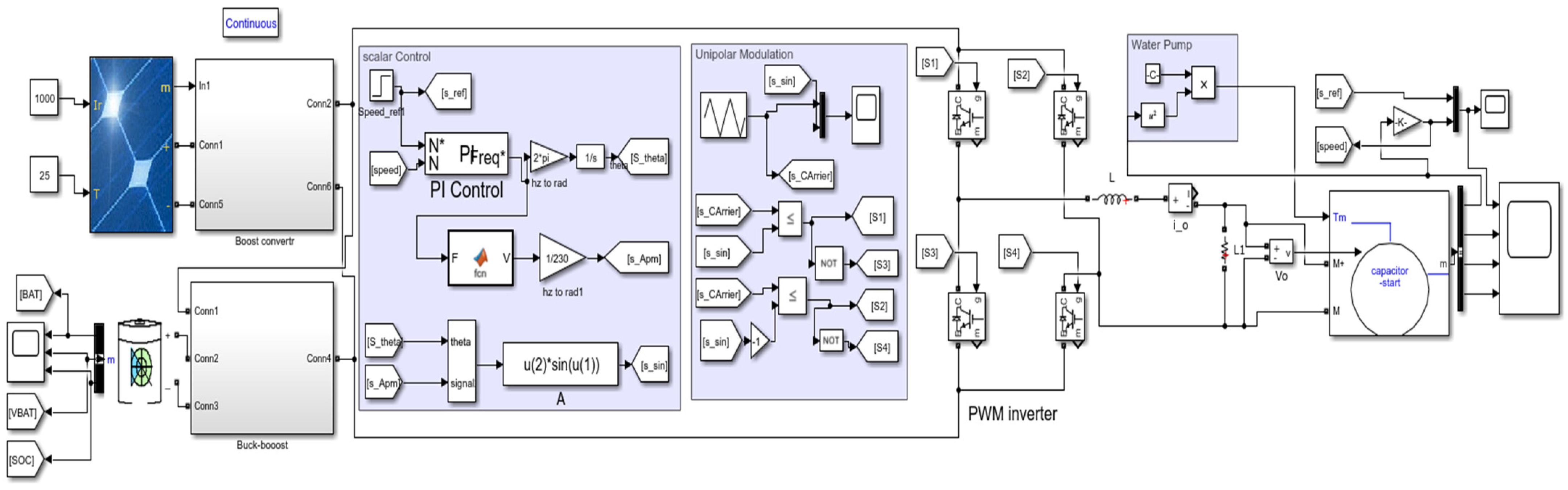
3. The Simulation of the Designed System
4. Simulation Results
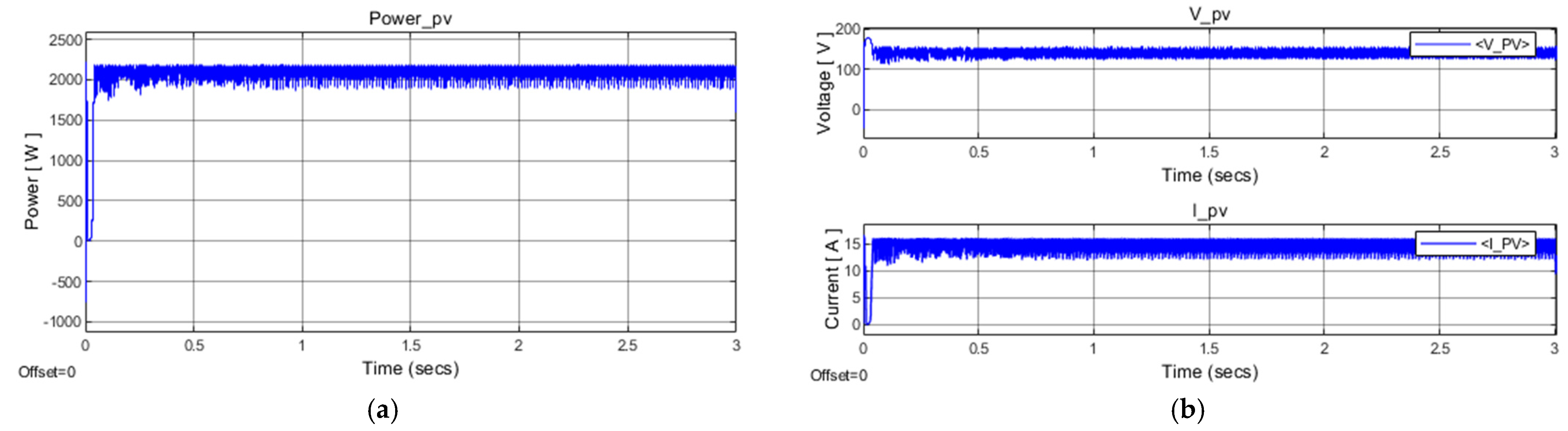
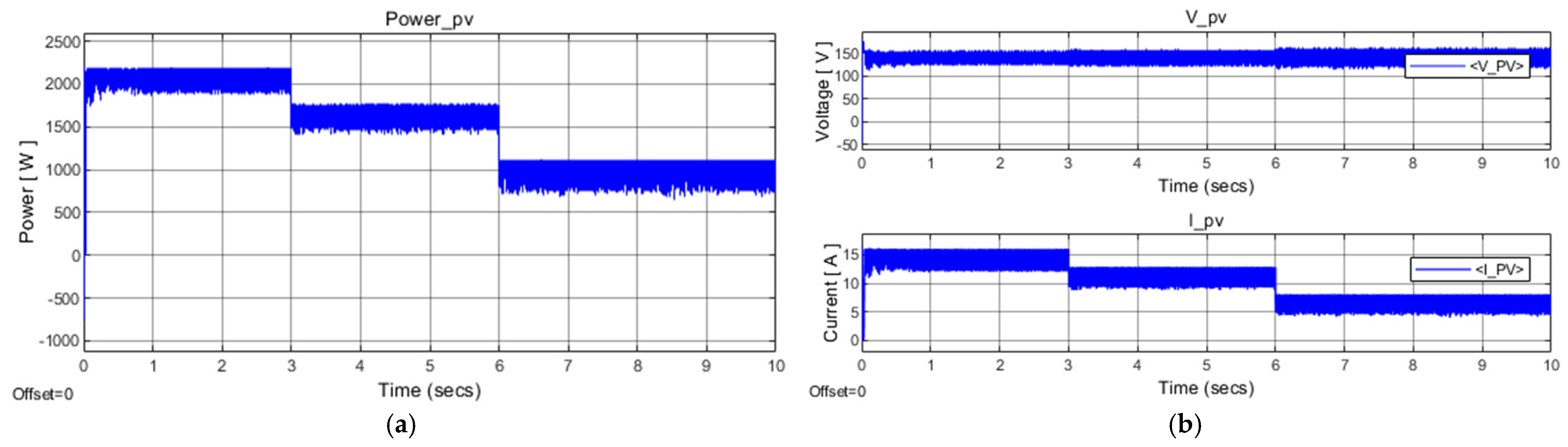
4.1. Simulation Results of PV Array
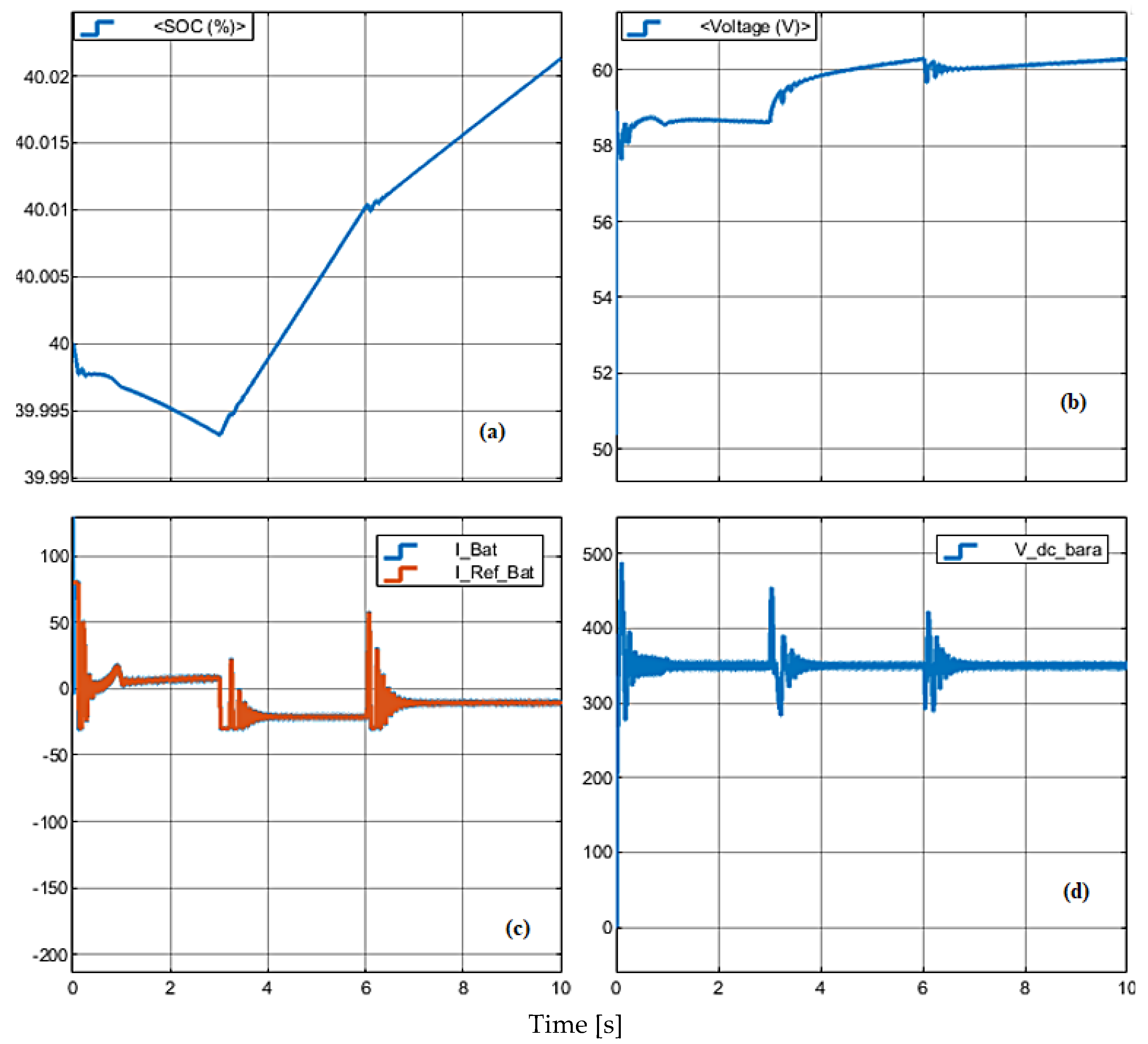
4.2. Simulation Results of Battery Output
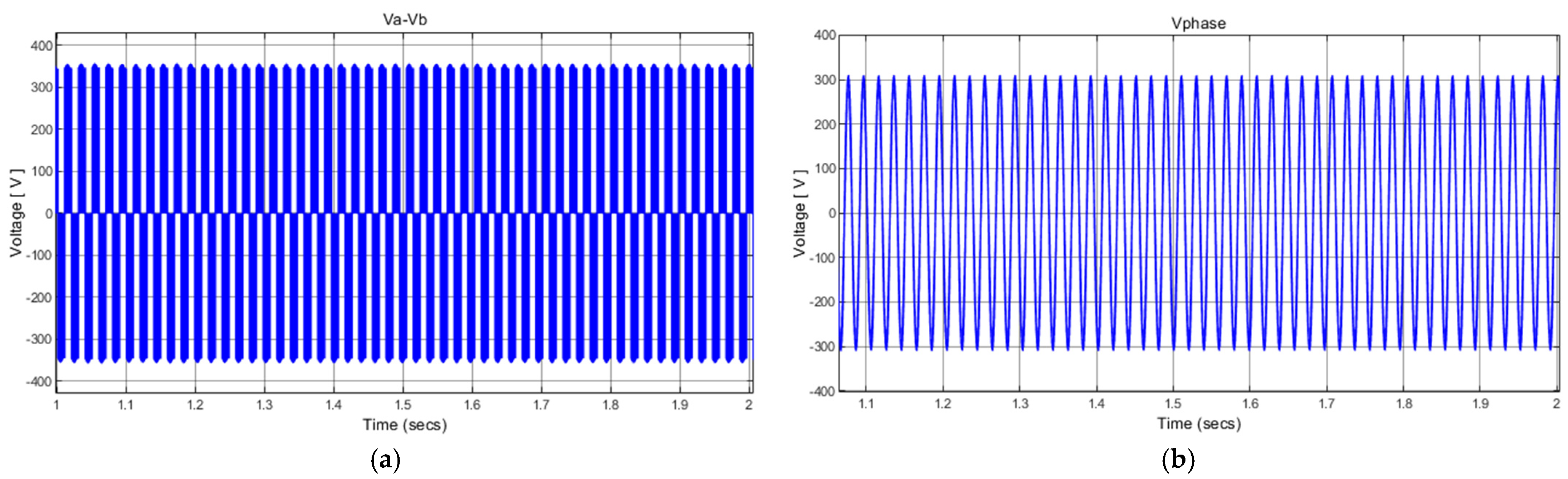
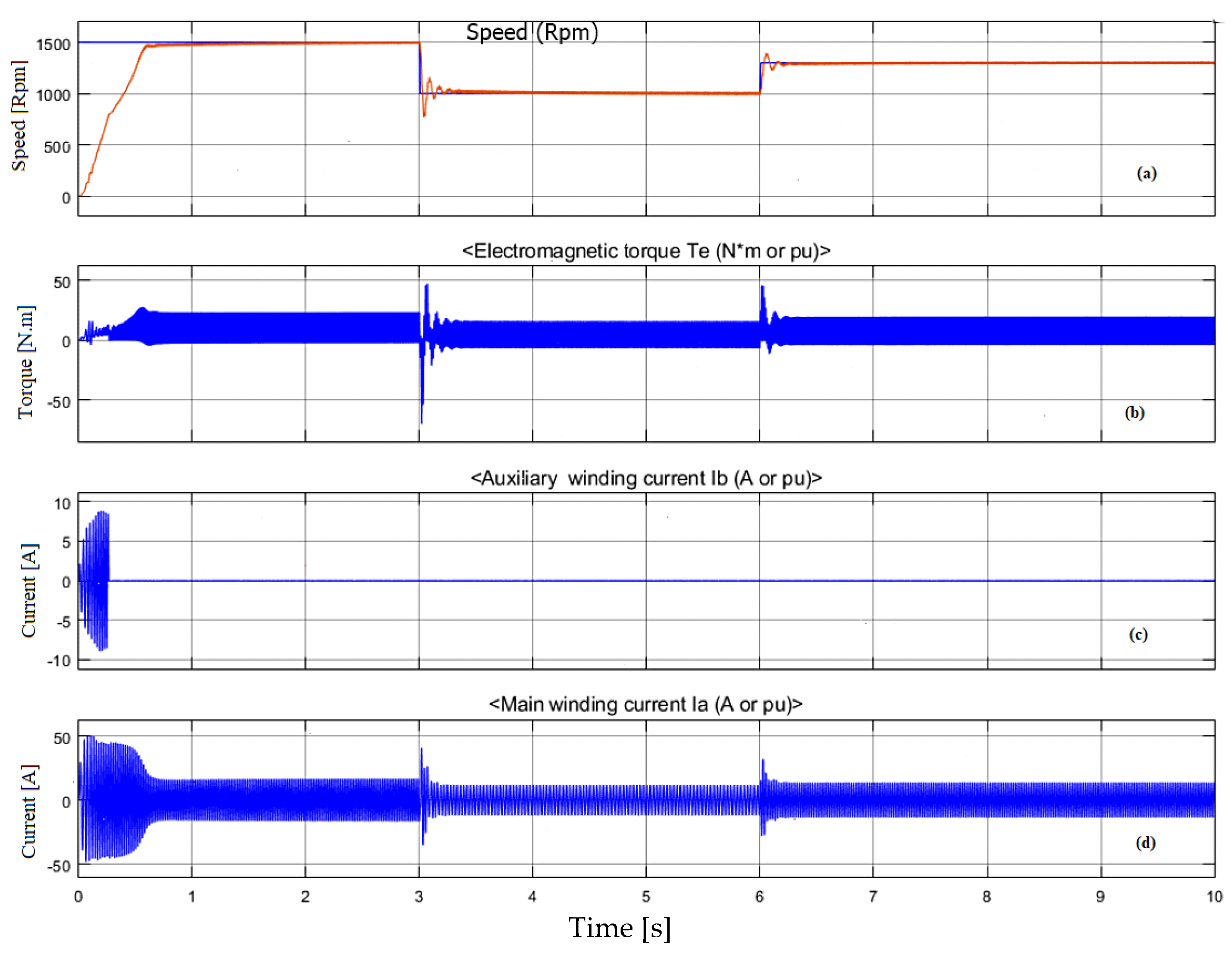
4.3. Simulation Results of SPIM
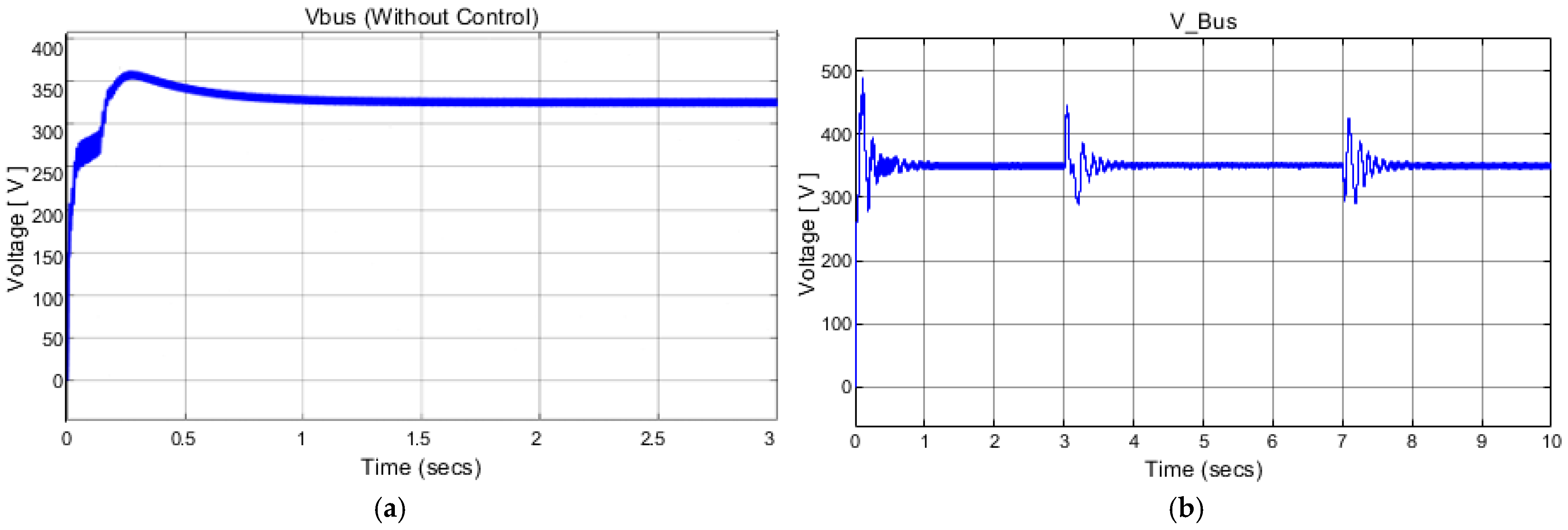
4.4. Comparison of Simulation Numerical Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPPT | Maximum power point tracking |
| IMD | Induction motor driver |
| SVPWM | Space vector pulse width modulation |
| VSI | Voltage source inverter |
| SPIM | Single-phase induction motors |
| SPVWP | Solar photovoltaic water pumping |
| PVWP | Photovoltaic water pumping |
| SNL | Sandia National Laboratories |
| V/f | Voltage/frequency |
| SPWM | Sine pulse width modulation |
| P–O | Perturb and observe |
| INC | Incremental conductance |
| SOC | State of charge |
| CCM | Continuous current mode |
References
- Bukhari, S.F.A. Transformerless Photovoltaic System Fed Single Phase Induction Motor Driver for Water Pumping. Master’s Thesis, Karadeniz Technical University, Trabzon, Turkiye, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Mei, S.; Jian, Y.; Dongran, S.; Deqiang, H.; Shaojian, S. Combined reactive power injection modulation and grid current distortion improvement approach for H6 transformer-less photovoltaic inverter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2017, 32, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpathy, S. Photovoltaic Power Control Using MPPT and Boost Converter. Ph.D. Thesis, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yağcı, B.E.; Demirsoy, G.; Akpolat, A.N. General overview of artificial neural network applications in renewable energy systems. Turk. J. Electromechanics Energy 2024, 9, 95–107. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Y.; Wenli, Y.; Poh, C.; Frede, B. Highly reliable transformerless photovoltaic inverters with leakage current and pulsating power elimination. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1016–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Kalyan, R.; Hemanth, K. Implementation of MPPT algorithm for solar photovoltaic cell by comparing short-circuit method and incremental conductance method. Procedia Technol. 2014, 12, 705–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akın, E.; Şahin, M.E. Investigation of Incremental Conductance MPPT Algorithm in MATLAB/Simulink Using Photovoltaic Powered DC-DC Boost Converter. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Symposium on Power Electronics, Novi Sad, Serbia, 25–28 October 2023; Volume 1, pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Freris, L.; David, I. Renewable Energy in Power Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.; Singh, B. Solar PV powered BLDC motor drive for water pumping using Cuk converter. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2017, 11, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjai, A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Sandhibigraha, M. Study of Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) Techniques in a Solar Photovoltaic Array. Ph.D. Thesis, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm, F.A.; Fossum, J.G.; Burgess, E.L. Application of the superposition principle to solar-cell analysis. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1979, 26, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekioua, D.; Matagne, E. Optimization of Photovoltaic Power Systems: Modelization, Simulation and Control; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Meah, K.; Ula, S.; Barrett, S. Solar photovoltaic water pumping-opportunities and challenges. Renew Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 1162–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, T.D.; Thompson, P. Breaking the mould: Solar water pumping-the challenges and the reality. Sol. Energy 2003, 75, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, R.; Cota, A. Solar water pumping advances and comparative economics. Energy Procedia 2014, 57, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullenkav, T. Solar Water Pumping for Irrigation: Opportunities in Bihar, Deutche Gesellschaft fur Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) GmbH, Indo-German Energy Programme. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, R.; Hanley, C. Life cycle cost analysis for photovoltaic water pumping systems in Mexico. In Proceedings of the 2nd World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, Vienna, Austria, 6–10 July 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Reca-Cardeña, J.; López-Luque, R. Design principles of photovoltaic irrigation systems. In Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 295–333. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, M.E.; Blaabjerg, F. A hybrid PV-battery/supercapacitor system and a basic active power control proposal in MATLAB/Simulink. Electronics 2020, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Željko, V. Despotović, Hybrid “Off-Grid” Power Supply Systems and Their Applications in Agriculture: Practical Realizations. In Proceedings of the 10th ICREPS Conference (MKOIEE 10.1), Belgrade, Serbia, 17–18 October 2022; pp. 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Chandel, S.; Naik, M.N.; Chandel, R. Review of solar photovoltaic water pumping system technology for irrigation and community drinking water supplies. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 49, 1084–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldu, İ.; Şahin, M.E. A MATLAB/GUI Based Photovoltaic System Simulator for Estimation of PV Parameter using Newton-Raphson Method. Gazi J. Eng. Sci. 2021, 7, 196–212. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.H. Power Electronics, Circuits, Devices, and Applications, 3rd ed.; Pearson Education, Inc.: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, K.H.; Tseng, C.; Huang, H.; Liu, G. Design and Implementation of a Bidirectional DC-DC Converter for Stand-Alone Photovoltaic Systems. Int. J. Comput. Consum. Control 2013, 2, 44–45. [Google Scholar]
- Edelmoser, K.H.; Himmelstoss, F.A. Bidirectional DC-to-DC Converter for Solar Battery Backup Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 35th Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Aachen, Germany, 20–25 June 2004; Volume 6, pp. 2070–2074. [Google Scholar]
- Şahin, M.E.; Blaabjerg, F. PV-powered hybrid energy storage system control using bidirectional and boost converters. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2022, 49, 1260–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, B.; Cheung, R. Advanced algorithm for MPPT control of photovoltaic systems. In Proceedings of the Canadian Solar Buildings Conference, Montreal, Canada, 20–24 August 2004; pp. 20–24. [Google Scholar]
- Jeevan, K.; Soumitra, K. Study of single-phase voltage source inverter with SPWM and PWM techniques. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Sci. Res. (IJCESR) 2018, 5, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Namboodiri, A.; Wani, H.S. Unipolar and bipolar PWM inverter. Int. J. Innov. Research Sci. Technol. 2014, 1, 237–243. [Google Scholar]
- Sultani, J.F. Modelling Design and Implementation of DQ Control in Single-Phase Grid-Connected Inverters for Photovoltaic Systems Used in Domestic Dwellings. Ph.D. Thesis, De Montfort University, Leicester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, B.; Taib, S.; Saad, A.M.; Isa, M.; Hadzer, C.M. Development of a single phase SPWM microcontroller-based inverter. Int. Power Energy Conf. 2006, 11, 437–440. [Google Scholar]
- Manfo, T.A.; Şahin, M.E. Development of an Automatic Photovoltaic Cell-Battery Powered Water Irrigation System Incorporated with Arduino Software for Agricultural Activities. Gazi Mühendislik Bilim. Derg. 2024, 10, 314–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habbi, H.M.D.; Ajeel, H.J.; Ali, I.I. Speed control of induction motor using PI and V/F scalar vector controllers. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 151, 36–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannides, M.G. Design and implementation of PLC-based monitoring control system for induction motor. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2004, 19, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, G.I.; Papazis, S.A.; Ioannidou, F.G. Implementation of a scalar control scheme for variable frequency induction motor actuator system. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2003, 106, 306–309. [Google Scholar]
- Boldea, I.; Moldovan, A.; Tutelea, L. Scalar V/f and I-f control of AC motor drives: An overview. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Aegean Conference on Electrical Machines & Power Electronics (ACEMP), 2015 International Conference on Optimization of Electrical & Electronic Equipment (OPTIM) & 2015 International Symposium on Advanced Electromechanical Motion Systems (ELECTROMOTION), Side, Turkey, 2–4 September 2015; pp. 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Akin, B.; Garg, N. Scalar (V/f) Control of 3-Phase Induction Motors; Texas Instruments Incorporated: Dallas, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Peña, J.M.; Díaz, E.V. Implementation of V/f scalar control for speed regulation of a three-phase induction motor. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE ANDESCON, Arequipa, Peru, 19–21 October 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Waleed, U.; Waseem, M.; Shaukat, H.; Ijaz, A.; Almalaq, A.; Mohamed, M.A. An Efficient FPGA Based Scalar V/f Control Mechanism of Three Phase Induction Motor for Electric Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2021 31st Australasian Universities Power Engineering Conference (AUPEC), Perth, Australia, 26–30 September 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rekioua, D.; Zaouche, F.; Mokrani, Z.; Rekioua, T.; Logerais, P.O. Power management control for photovoltaic water pumping system in Agriculture. Turk. J. Electromechanics Energy 2023, 8, 109–117. [Google Scholar]
- Vostrov, K. Synchronous Machine Vector Control System Development and Implementation. Master’s Thesis, Lappeenranta University of Technology, Lappeenranta, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]




| PV Source Parameters and Values | |
| Parameters | Value |
| Open circuit voltage (Voc) | 44.3 V |
| Short circuit current (Isc) | 8.25 A |
| Voltage at maximum power (Vmp) | 35.5 V |
| Cells per module | 72 |
| Current at maximum power Imp (A) | 7.6 A |
| Maximum power (W) | 269.8 W |
| Converters Parameters and Values | |
| Parameters | Value |
| Input capacitor of boost converter | 100 µF |
| Inductor of the boost converter | 1.8 mH |
| Output capacitor of boost converter | 1500 µF |
| Input capacitor of buck-boost converter | 1000 µF |
| Inductor of the buck-boost converter | 1 mH |
| Output capacitor of buck-boost converter | 1000 µF |
| Motor Parameters and Values | |
| Parameters | Value |
| Motor power | 2000 W |
| Number of poles | 4-Pole |
| Motor speed | 1440 rpm |
| Main winding stator resistance | 0.602 Ω |
| Stator inductance | 7.4 mH |
| Rotor resistance | 1.012 Ω |
| Rotor inductance | 5.6 mH |
| Auxiliary winding resistance | 7.14 Ω |
| Auxiliary winding inductance | 8.5 mH |
| System Parameters | Steady State Conditions (25 °C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Irradiance (W/m2) | 1000 | 800 | 500 |
| Motor Speed (rpm) | 1500 | 1000 | 1300 |
| PV System Power (W) | 1997 | 1610.5 | 941 |
| Battery Power (W) | 29.5 | −876 | 385.5 |
| SPIM Power Output (W) | 1647 | 510.5 | 1108 |
| Efficiency (%) | 81.3 | 86.1 | 83.5 |
| System Parameters | Steady State Conditions (1000 W/m2) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar Temperature (°C) | 75 | 50 | 25 |
| Motor Speed (rpm) | 1500 | 1000 | 1300 |
| PV System Power (W) | 1594 | 1846 | 2058.5 |
| Battery Power (W) | 444.5 | −1080 | −630 |
| SPIM Power Output (W) | 1647 | 510.5 | 1108 |
| Efficiency (%) | 80.8 | 86.2 | 84.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bukhari, S.F.A.; Kahveci, H.; Şahin, M.E. Single Phase Induction Motor Driver for Water Pumping Powered by Photovoltaic System. Electronics 2025, 14, 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061189
Bukhari SFA, Kahveci H, Şahin ME. Single Phase Induction Motor Driver for Water Pumping Powered by Photovoltaic System. Electronics. 2025; 14(6):1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061189
Chicago/Turabian StyleBukhari, Syed Faizan Ali, Hakan Kahveci, and Mustafa Ergin Şahin. 2025. "Single Phase Induction Motor Driver for Water Pumping Powered by Photovoltaic System" Electronics 14, no. 6: 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061189
APA StyleBukhari, S. F. A., Kahveci, H., & Şahin, M. E. (2025). Single Phase Induction Motor Driver for Water Pumping Powered by Photovoltaic System. Electronics, 14(6), 1189. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14061189






