A Fabric-Based Approach for Wearable Haptics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Wearable Haptic Systems: Technologies and Main Characteristics
1.2. Wearable Haptic Systems: Open Issues and Fabric-Based Approaches
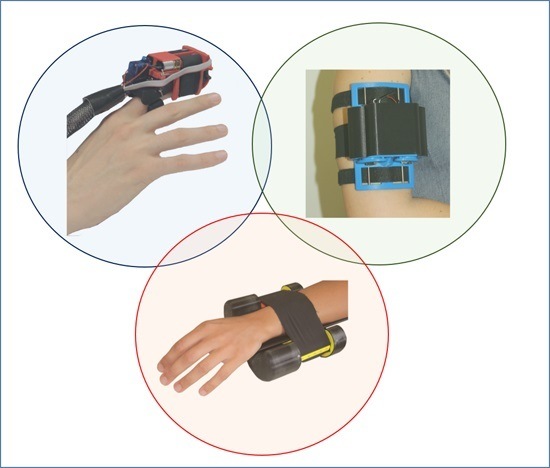
2. W-FYD
3. CUFF
4. Caress-Like Haptic Stimulation
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aristotle. A New Aristotle Reader; Ackrill, J.L., Ed.; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1987; pp. 161–205. [Google Scholar]
- Hannaford, B.; Okamura, A.M. Haptics. In Handbook on Robotics; Siciliano, B., Kathib, O., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 719–739. [Google Scholar]
- Chinello, F.; Malvezzi, M.; Pacchierotti, C.; Prattichizzo, D. A three DoFs wearable tactile display for exploration and manipulation of virtual objects. In Proceedings of the Haptics Symposium 2012, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 March 2012; pp. 71–76.
- Traylor, R.; Tan, H.Z. Development of a wearable haptic display for situation awareness in altered-gravity environment: Some initial findings. In Proceedings of the 10th Symposium on Haptic Interfaces Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 24–25 March 2002; pp. 159–164.
- Leonardis, D.; Solazzi, M.; Bortone, I.; Frisoli, A. A wearable fingertip haptic device with 3 dof asymmetric 3-rsr kinematics. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE World Haptics Conference (WHC), Evanston, IL, USA, 22–26 June 2015; pp. 388–393.
- Pacchierotti, C.; Chinello, F.; Malvezzi, M.; Meli, L.; Prattichizzo, D. Two finger grasping simulation with cutaneous and kinesthetic force feedback. In Proceedings of the International Conference, EuroHaptics 2012, Tampere, Finland, 13–15 June 2012; pp. 373–382.
- Lieberman, J.; Breazeal, C. TIKL: Development of a wearable vibrotactile feedback suit for improved human motor learning. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2007, 23, 919–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prattichizzo, D.; Pacchierotti, C.; Rosati, G. Cutaneous force feedback as a sensory subtraction technique in haptics. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2012, 5, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacchierotti, C.; Tirmizi, A.; Bianchini, G.; Prattichizzo, D. Enhancing the performance of passive teleoperation systems via cutaneous feedback. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2015, 8, 379–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasello, M.; Carpenter, M.; Call, J.; Behne, T.; Moll, H. Understanding and sharing intentions: The origins of cultural cognition. Behav. Brain Sci. 2005, 28, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuchenbecker, K.J.; Ferguson, D.; Kutzer, M.; Moses, M.; Okamura, A.M. The touch thimble: Providing fingertip contact feedback during point-force haptic interaction. In Proceedings of the 2008 Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Reno, NE, USA, 13–14 March 2008; pp. 239–246.
- Yang, G.H.; Kyung, K.U.; Srinivasan, M.A.; Kwon, D.S. Quantitative tactile display device with pin-array type tactile feedback and thermal feedback. Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Robot. Autom. 2006, 2006, 3917–3922. [Google Scholar]
- Buma, D.G.; Buitenweg, J.R.; Veltink, P.H. Intermittent stimulation delays adaptation to electrocutaneous sensory feedback. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casini, S.; Morvidoni, M.; Bianchi, M.; Catalano, M.G.; Grioli, G.; Bicchi, A. Design and realization of the CUFF—Clenching upper-limb force feedback wearable device for distributed mechano-tactile stimulation of normal and tangential skin forces. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Hamburg, Germany, 28 September–2 October 2015; pp. 1186–1193.
- Kim, H.; Seo, C.; Lee, J.; Ryu, J.; Yu, S.; Lee, S. Vibrotactile display for driving safety information. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference, Toronto, Canada, 17–20 September 2006; pp. 573–577.
- Prattichizzo, D.; Chinello, F.; Pacchierotti, C.; Malvezzi, M. Towards wearability in fingertip haptics: A 3-DoF wearable device for cutaneous force feedback. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2013, 6, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shull, P.B.; Damian, D.D. Haptic wearables as sensory replacement, sensory augmentation and trainer—A review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2015, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, M.; Battaglia, E.; Poggiani, M.; Ciotti, S.; Bicchi, A. A Wearable Fabric-based Display for Haptic Multi-Cue Delivery. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Haptics Symposium (HAPTICS), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 8–11 April 2016; pp. 277–283. [CrossRef]
- Scheggi, S.; Aggravi, M.; Morbidi, F.; Prattichizzo, D. Cooperative human-robot haptic navigation. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014. [CrossRef]
- Sergi, F.; Accoto, D.; Campolo, D.; Guglielmelli, E. Forearm orientation guidance with a vibrotactile feedback bracelet: On the directionality of tactile motor communication. In Proceedings of the 2008 2nd IEEE RAS & EMBS International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, 19–22 October 2008; pp. 433–438.
- Van Wegen, E.; De Goede, C.; Lim, I.; Rietberg, M.; Nieuwboer, A.; Willems, A.; Jones, D.; Rochester, L.; Hetherington, V.; Berendse, H.; et al. The effect of rhythmic somatosensory cueing on gait in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2006, 248, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witteveen, H.J.B.; Droog, E.A.; Rietman, J.S.; Veltink, P.H. Vibro- and electrotactile user feedback on hand opening for myoelectric forearm prostheses. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 2219–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bark, K.; Wheeler, J.; Shull, P.; Savall, J.; Cutkosky, M. Rotational skin stretch feedback: A wearable haptic display for motion. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2010, 3, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuillerme, N.; Chenu, O.; Demongeot, J.; Payan, Y. Controlling posture using a plantar pressure-based, tongue-placed tactile biofeedback system. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 179, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuillerme, N.; Pinsault, N.; Chenu, O.; Fleury, A.; Payan, Y.; Demongeot, J. A wireless embedded tongue tactile biofeedback system for balance control. Pervasive Mob. Comput. 2009, 5, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, T.; Beebe, D.J. An oral tactile interface for blind navigation. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. IEEE Trans. 2006, 14, 116–123. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, S.; Huang, J.; Janzen, R.; Lo, R.; Rampersad, V.; Chen, A.; Doha, T. Blind navigation with a wearable range camera and vibrotactile helmet. In Proceedings of the 19th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, New York, NY, USA, November 2011; pp. 1325–1328.
- Wall, C.; Weinberg, M.S.; Schmidt, P.B.; Krebs, D.E. Balance prosthesis based on micromechanical sensors using vibrotactile feedback of tilt. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 48, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanhoe-Mahabier, W.; Allum, J.H.; Pasman, E.P.; Overeem, S.; Bloem, B.R. The effects of vibrotactile biofeedback training on trunk sway in Parkinson’s disease patients. Park. Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Erp, J. Presenting directions with a vibrotactile torso display. Ergonomics 2005, 48, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKinney, Z.; Heberer, K.; Fowler, E.; Greenberg, M.; Nowroozi, B.; Grundfest, W. Initial biomechanical evaluation of wearable tactile feedback system for gait rehabilitation in peripheral neuropathy. Stud. Health Technol. Inform. 2014, 196, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McKinney, Z.; Heberer, K.; Nowroozi, B.N.; Greenberg, M.; Fowler, E.; Grundfest, W. Pilot evaluation of wearable tactile biofeedback system for gait rehabilitation in peripheral neuropathy. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Haptics Symposium (HAPTICS), Houston, TX, USA, 23–26 February 2014; pp. 135–140.
- Velázquez, R.; Bazán, O. Preliminary evaluation of podotactile feedback in sighted and blind users. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2010, 2010, 2103–2106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Kwon, D.S.; Book, W.J. Development of a miniature pin-array tactile module using elastic and electromagnetic force for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the Third Joint EuroHaptics conference, 2009 and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–20 March 2009; pp. 13–17.
- Wentink, E.C.; Talsma-Kerkdijk, E.J.; Rietman, H.S.; Veltink, P. Feasibility of error-based electrotactile and auditive feedback in prosthetic walking. Prosthet. Orthot. Int. 2015, 39, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minamizawa, K.; Fukamachi, S. Gravity grabber: Wearable haptic display to present virtual mass sensation. ACM Emerg. Technol. 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, R.S.; Westling, G. Signals in tactile afferents from the fingers eliciting adaptive motor responses during precision grip. Exp. Brain Res. 1987, 66, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westling, G.; Johansson, R.S. Responses in glabrous skin mechanoreceptors during precision grip in humans. Exp. Brain Res. 1987, 66, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederman, S.J.; Klatzky, R.L. Haptic perception: A tutorial. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2009, 71, 1439–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, R.S.; Westling, G. Roles of glabrous skin receptors and sensorimotor memory in automatic control of precision grip when lifting rougher or more slippery objects. Exp. Brain Res. 1984, 56, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, J.M.; Kluender, K.R.; Levi, D.M.; Bartoshuk, L.M.; Herz, R.S.; Klatzky, R.L.; Lederman, S.J.; Merfeld, D.M. Sensation and Perception; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- McGlone, F.; Wessberg, J.; Olausson, H. Discriminative and Affective Touch: Sensing and Feeling. Neuron 2008, 82, 737–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbonaro, N.; Mura, G.D.; Lorussi, F.; Paradiso, R.; De Rossi, D.; Tognetti, A. Exploiting wearable goniometer technology for motion sensing gloves. IEEE J. Biomed. Heal. Informatics 2014, 18, 1788–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windmiller, J.R.; Wang, J. Wearable Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors: A Review. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Wearable sensors for human activity monitoring: A review. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Shu, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, S.; Wang, F.; Tao, X.-M. Fiber-based wearable electronics: A review of materials, fabrication, devices, and applications. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5310–5336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darden, M.A.; Schwartz, C.J. Investigation of skin tribology and its effects on the tactile attributes of polymer fabrics. Wear 2009, 267, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volino, P.; Davy, P.; Bonanni, U.; Luible, C.; Magnenat-Thalmann, N.; Mäkinen, M.; Meinander, H. From measured physical parameters to the haptic feeling of fabric. Vis. Comput. 2007, 23, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäkinen, M.; Meinander, H.; Luible, C.; Magnenat-thalmann, N. Influence of Physical Parameters on Fabric Hand. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Haptic and Tactile Perception of Deformable Objects, Leibniz Haus, Hanover, Germany, 1–2 December 2005; pp. 8–16.
- Bau, O.; Petrevski, U.; Mackay, W. BubbleWrap: A Textile-Based Electromagnetic Haptic Display. In Proceedings of CHI ′09 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Boston, MA, USA, 4–9 April 2009; pp. 3607–3612. [CrossRef]
- De Rossi, D.; Carpi, F.; Lorussi, F.; Scilingo, E.P.; Tognetti, A. Wearable kinesthetic systems and emerging technologies in actuation for upperlimb neurorehabilitation. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2009, 2009, 6830–6833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Rossi, D.; Carpi, F.; Carbonaro, N.; Tognetti, A.; Scilingo, E.P. Electroactive polymer patches for wearable haptic interfaces. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2011, 2011, 8369–8372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mueller, F.F.; Vetere, F.; Gibbs, M.R.; Kjeldskov, J.; Pedell, S.; Howard, S. Hug over a distance. In Proceedings of CHI EA ′05 CHI ′05 Extended Abstracts on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Portland, OR, USA, 2–7 April 2005; pp. 1673–1676. [CrossRef]
- Rotella, M.F.; Guerin, K.; He, X.; Okamura, A.M. HAPI bands: A haptic augmented posture interface. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Haptics Symposium (HAPTICS), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 4–7 March 2012; pp. 163–170.
- Sahoo, D.R.; Hornbæk, K.; Subramanian, S. TableHop: An Actuated Fabric Display Using Transparent Electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, San Jose, CA, USA, 7–12 May 2016; pp. 3767–3780.
- Sadihov, D.; Migge, B.; Gassert, R.; Kim, Y. Prototype of a VR upper-limb rehabilitation system enhanced with motion-based tactile feedback. In Proceedings of the World Haptics Conference (WHC), Daejeon, Korea, 14–17 April 2013; pp. 449–454.
- Bianchi, M.; Valenza, G.; Serio, A.; Lanata, A.; Greco, A.; Nardelli, M.; Scilingo, E.P.; Bicchi, A. Design and preliminary affective characterization of a novel fabric-based tactile display. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Haptics Symposium (HAPTICS), Houston, TX, USA, 23–26 February 2014; pp. 591–596.
- Bergmann Tiest, W.M.; Kappers, A.M.L. Cues for haptic perception of compliance. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2009, 2, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Scilingo, E.P.; Serio, A.; Bicchi, A. A new softness display based on bi-elastic fabric. In Proceedings of the Third Joint EuroHaptics Conference, 2009 and Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–20 March 2009; pp. 382–383.
- Bianchi, M.; Serio, A.; Scilingo, E.P.; Bicchi, A. A new fabric-based softness display. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Haptics Symposium, Waltham, MA, USA, 25–26 March 2010; pp. 105–112.
- Serio, A.; Bianchi, M.; Bicchi, A. A device for mimicking the contact force/contact area relationship of different materials with applications to softness rendering. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 3–7 November 2013; pp. 484–490.
- Bianchi, M.; Serio, A. Design and Characterization of a Fabric-Based Softness Display. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2015, 8, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condino, S.; Viglialoro, R.; Fani, S.; Bianchi, M.; Morelli, L.; Ferrari, M.; Bicchi, A.; Ferrari, V. Tactile augmented reality for arteries palpation in open surgery training. Med. Imaging Augment. Real. 2016. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Catalano, M.G.; Grioli, G.; Farnioli, E.; Serio, A.; Piazza, C.; Bicchi, A. Adaptive synergies for the design and control of the Pisa/IIT SoftHand. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2014, 33, 768–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, S.; Bianchi, M.; Bicchi, A.; Santello, M. Influence of Force Feedback on Grasp Force Modulation in Prosthetic Applications: A Preliminary Study. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2016. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Ajoudani, A.; Godfrey, S.B.; Bianchi, M.; Catalano, M.G.; Grioli, G.; Tsagarakis, N.; Bicchi, A. Exploring teleimpedance and tactile feedback for intuitive control of the Pisa/IIT SoftHand. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2014, 7, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scilingo, E.P.; Bianchi, M.; Grioli, G.; Bicchi, A. Rendering softness: Integration of kinesthetic and cutaneous information in a haptic device. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2010, 3, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, T. Touch; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Huisman, G. A touch of affect: Mediated social touch and affect. In Proceedings of the the 14th ACM international conference on Multimodal interaction, Santa Monica, CA, USA, 22–26 October 2012; pp. 317–320. [CrossRef]
- Calvo, R.; D’Mello, S. Affect detection: An interdisciplinary review of models, methods, and their applications. Affect. Comput. IEEE Trans. 2010, 1, 18–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posner, J.; Russell, J.; Peterson, B. The circumplex model of affect: An integrative approach to affective neuroscience, cognitive development, and psychopathology. Dev. Psychopathol. 2005, 17, 715–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenza, G.; Greco, A.; Citi, L.; Bianchi, M.; Barbieri, R.; Scilingo, E.P. Inhomogeneous Point-Processes to Instantaneously Assess Affective Haptic Perception through Heartbeat Dynamics Information. Sci Rep. 2016, 6, 28567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardelli, M.; Valenza, G.; Bianchi, M.; Greco, A.; Lanata, A.; Bicchi, A.; Scilingo, E.P. Gender-specific velocity recognition of caress-like stimuli through nonlinear analysis of Heart Rate Variability. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 298–301.
- Valenza, G.; Greco, A.; Nardelli, M.; Bianchi, M.; Lanata, A.; Rossi, S.; Scilingo, E.P. Electroencephalographic spectral correlates of caress-like affective haptic stimuli. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 4733–4736.
- Bianchi, M.; Valenza, G.; Greco, A.; Nardelli, M.; Battaglia, E.; Bicchi, A.; Scilingo, E.P. Towards a Novel Generation of Haptic and Robotic Interfaces: Integrating Affective Physiology in Human-Robot Interaction. IEEE Int. Symp. Robot Hum. Interact. Commun. 2016. accepted. [Google Scholar]
- Bradley, M.; Lang, P.J. Measuring Emotion: The Self-Assessment Semantic Differential Manikin and the semantic differential. J. Behav. Ther. Exp. Psychiatry 1994, 25, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, M.; Valenza, G.; Lanata, A.; Greco, A.; Nardelli, M.; Bicchi, A.; Scilingo, E.P. On the role of affective properties in hedonic and discriminant haptic systems. Int. J. Soc. Robot. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Stimulus/Actuation Type | Devices |
|---|---|
| Pin-arrays | [12,34] |
| Electrocutaneous | [13,22,35] |
| Vibration | [4,7,30] |
| Deformation/Forces | [5,16,36] |
| Pneumatic | [31,32] |
| Mechanoreceptors | Primary Functions |
|---|---|
| Slowly Adapting type I (SAI) | Very-low-frequency vibration detection; coarse texture perception; pattern/form detection |
| Fast-adapting type I (FA I) | Low-frequency vibration detection |
| Fast-adapting type II (FA II) | High-frequency vibration detection; fine texture perception |
| Slowly Adapting type II (SAII) | Direction of object motion and force due to skin |
| Stretch; finger position |
| Name | Dimensions (mm) | Weight (g) | Stimuli | Body Location | Touch | Force Range | Measurements Provided | Stiffness Range | Control Cycle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-FYD | 100 × 60 × 36 | 100 | Active/passive softness; sliding | Finger | Discriminative | Up to 10 N | Force; motor position; indentation | Up to 0.8 N/mm | ≤1ms |
| CUFF | 145 × 97 × 116 | 494 | Normal-tangential force | Arm | Discriminative | Up to 21 N | Force; motor position | - | ≤1ms |
| Caress | 150 × 150 × 80 | 560 | Velocity; normal force (combination) | Forearm | Affective | Up to 20 N | Force; motor position | - | ≤1ms @7Hz |
© 2016 by the author; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianchi, M. A Fabric-Based Approach for Wearable Haptics. Electronics 2016, 5, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics5030044
Bianchi M. A Fabric-Based Approach for Wearable Haptics. Electronics. 2016; 5(3):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics5030044
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianchi, Matteo. 2016. "A Fabric-Based Approach for Wearable Haptics" Electronics 5, no. 3: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics5030044
APA StyleBianchi, M. (2016). A Fabric-Based Approach for Wearable Haptics. Electronics, 5(3), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics5030044