Event-Triggered and Memory-Based Sliding Mode Variable Structure Control for Memristive Systems
Abstract
:1. Introduction
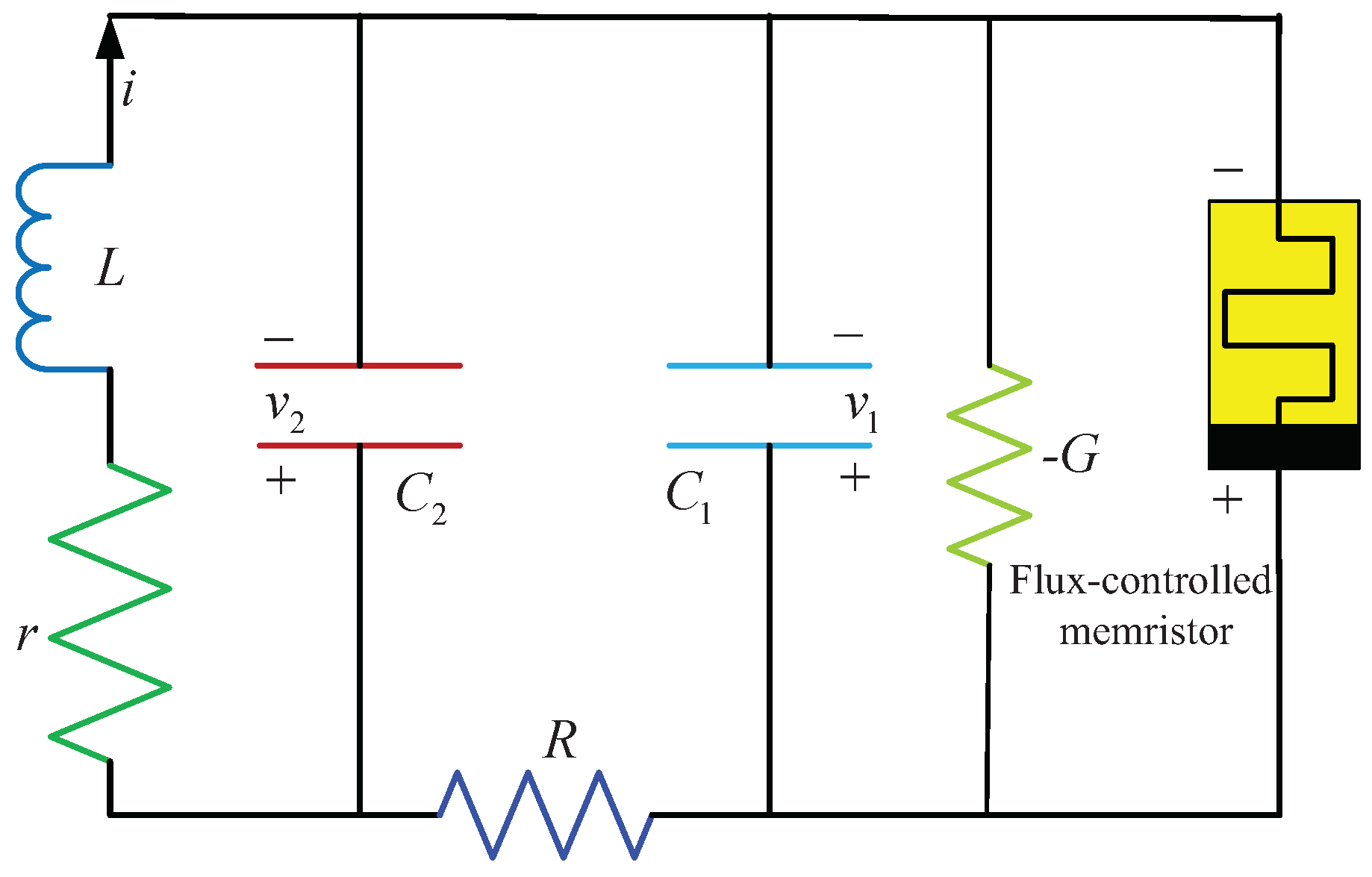
2. Description of Chua’s Circuits with Memristors
3. Main Results
3.1. Switching Hyperplane Design
3.2. The Design of Event-Based Sliding-Mode Reaching Controller
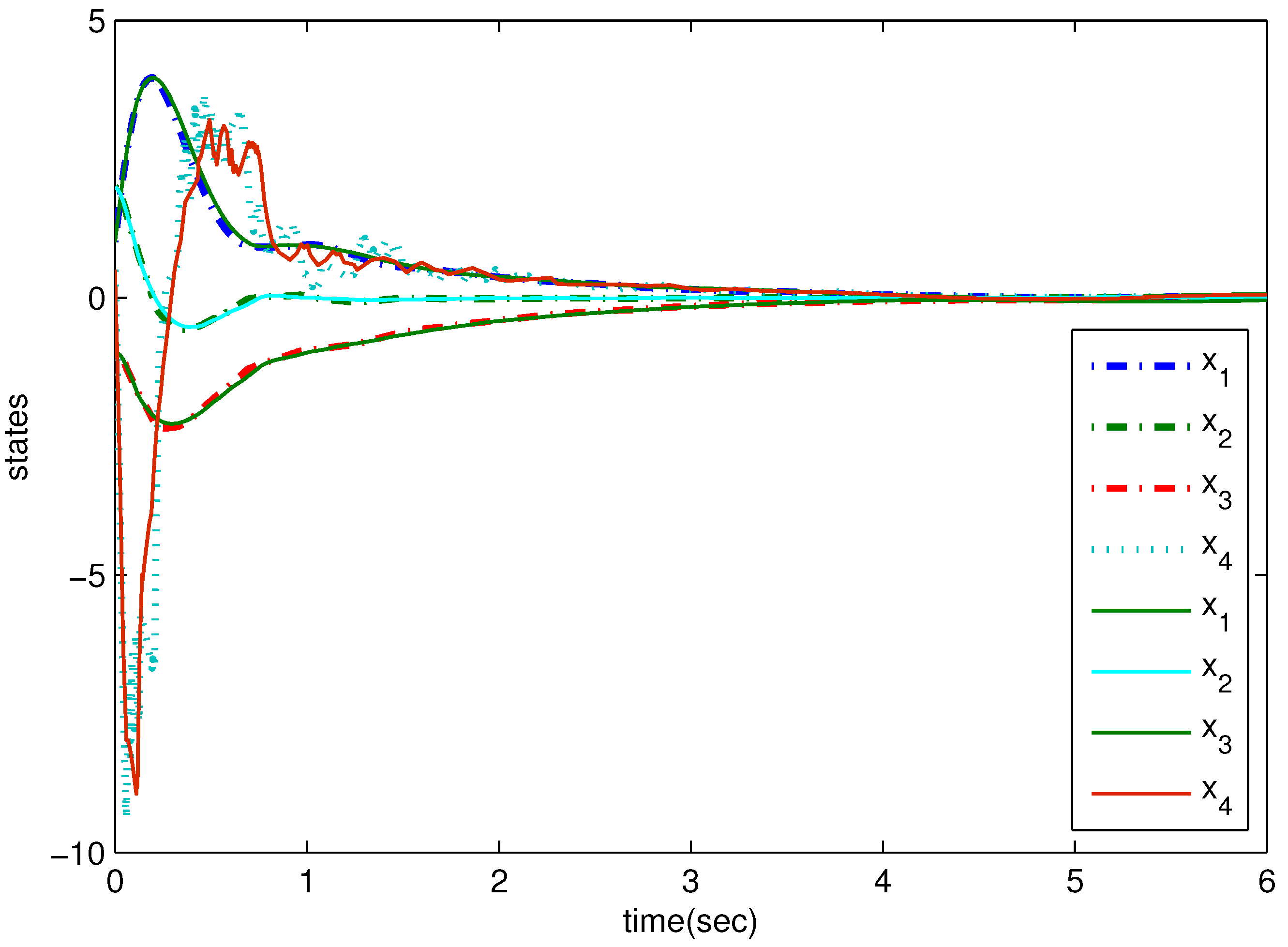
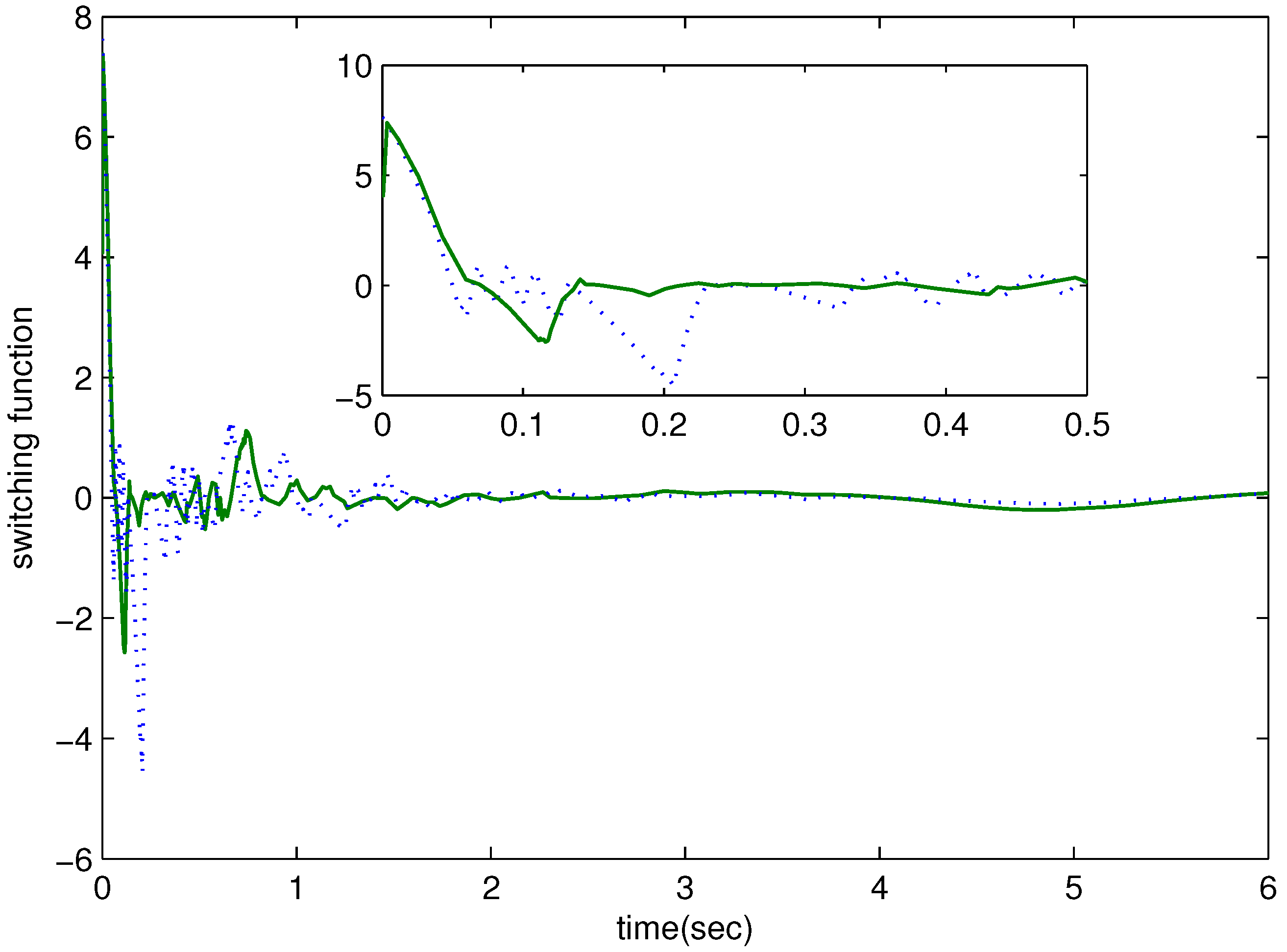
4. Example
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ESMC | Event-triggered sliding mode variable structure control |
| SMC | Sliding mode variable structure control |
| MS(s) | Memristive system(s) |
| LMI | Linear matrix inequality |
References
- Chua, L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuits Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, M.; Chua, L. Memristor oscillators. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2008, 18, 3183–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, A.; Elsaid, A.; Nour, H.; Elsonbaty, A. Dynamical behavior, chaos control and synchronization of a memristive ADVP circuit. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2013, 18, 148–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joglekar, Y.N.; Wolf, S.J. The elusive memristor: Properties of basic electrical circuits. Eur. J. Phys. 2009, 30, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iu, H.; Yu, D.; Fitch, A.; Sreeram, V.; Chen, H. Controlling chaos in a memristor based circuit using a Twin-T notch filter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2011, 58, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, Q.; Zeng, Z. Hierarchical type stability criteria for delayed neural networks via canonical Bessel-Legendre inequalities. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 1660–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Cui, M.; Cai, B.; Wang, X.; Hu, T. A chaotic oscillator based on HP memristor model. Math. Probl. Eng. 2015, 2015, 561901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, C.; He, X. Stabilization of a memristor-based chaotic system by intermittent control and fuzzy processing, Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2013, 11, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.; Spurgeon, C. Sliding Mode Control: Theory and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, X.; Wang, B.; Li, X. Computer-controlled variable structure systems: The state-of-the-art. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2012, 8, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, S.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, B.; Wang, Z. Quantized feedback fuzzy sliding mode control design via memory-based strategy. Appl. Math. Comput. 2017, 298, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Han, Q.; Zhang, X. Recent advances in vibration control of offshore platforms. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 89, 755–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.-C.; Yu, X.; Xue, Y. Quantized feedback sliding-mode control: An event-triiggered approached. Automatica 2018, 91, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zheng, B.-C.; Yu, X. Robust sliding mode control for T-S fuzzy systems via quantized state feedback IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2018, 26, 2261–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.-C.; Park, J.H. Sliding mode control design for linear systems subject to quantization parameter mismatch J. Frankl. Inst. 2016, 353, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C. A practical method for the design of sliding mode controllers using linear matrix inequalitie. Automatica 2004, 40, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-G.; Edwards, C. Nonlinear robust fault reconstruction and estimation using a sliding mode observer. Automatica 2007, 43, 1605–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, C.; Akoachere, A. Sliding-mode output feedback controller design using linear matrix inequalities. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2001, 46, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.P.; Edwards, C. An LMI approach for designing sliding mode observers. Int. J. Control 2001, 74, 1559–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.H. Variable structure output feedback control design for a class of uncertain dynamic systems. Automatica 2002, 38, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.H. An explict formula of linear sliding surfaces for a class of uncertain dynamic systems with mismatched uncertainties. Automatica 1998, 34, 1015–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.H. Output feedback variable structure control design with an H∞ performance bound constraint. Automatica 2008, 44, 2403–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Han, Q.; Zhang, X. Sliding mode control with mixed current and delayed states for offshore steel jacket platform. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 22, 1769–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Huang, T.; Yu, X.; Chen, M.Z.; Zeng, Z. Sliding-mode control of memristive Chua’s systems via the event-based method. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 64, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abolmasoumi, A.H.; Khosravinejad, S. Chaos Control in Memristor-Based Oscillators Using Intelligent Terminal Sliding Mode Controller. Int. J. Comput. Theory Eng. 2016, 8, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Bayani, A.; Khalaf, A.J.M.; Namazi, H.; Jafari, S.; Pham, V.T. A no-equilibrium memristive system with four-wing hyperchaotic atracto. Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 95, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, K.; Guessas, L.; Karthikeyan, A.; Srinivasan, A.; Adam, G. Fractional order memristor no equilibrium chaotic system with its adaptive sliding mode synchronization and genetically optimized fractional order PID synchronization. Complexity 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, Q. Network-based H∞ filtering using a logic jumping-like trigger. Automatica 2013, 49, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Han, Q.-L.; Fei, M.; Peng, C. Network-based T-S fuzzy dynamic positioning controller design for unmanned marine vehicles. IEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 48, 2750–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Han, Q.-L. Network-based modelling and dynamic output feedback control for unmanned marine vehicles. Automatica 2018, 91, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zha, L.; Xie, X.; Tian, E. Resilient observer-based control for networked nonlinear T-S fuzzy systems with hybrid-triggered scheme. Nonlinear Dyn. 2018, 91, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xia, J.; Tian, E.; Fei, S. Hybrid-driven-based H-infinity filter design for neural networks subject to deception attacks. Appl. Math. Comput. 2018, 320, 158–174. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Liao, X.; Huang, T.; Zhu, W. Event-triggering sampling based leader-following consensus in second-order multi-agent systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2015, 60, 1998–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Han, Q.-L. Event-triggered H∞ control for a class of nonlinear networked control systems using novel integral inequalities. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2017, 27, 679–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-M.; Han, Q.-L. A decentralized event-triggered dissipative control scheme for systems with multiple sensors to sample the system outputs. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2016, 46, 2745–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Liao, X.; Huang, T.; Chen, G. Leader-following exponential consensus of general linear multi-agent systems via event-triggered control with combinational measurements. Appl. Math. Lett. 2015, 40, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Huang, T.; Yu, X.; Chen, M.Z.; Zeng, Z. Aperiodic sampled-data sliding-mode control of fuzzy systems with communication delays via the event-triggered method. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 2016, 24, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Han, Q.; Zhang, X. Event-triggered H∞ control for offshore structures in network environments. J. Sound Vib. 2016, 368, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, Q. Event-triggered generalized dissipativity filtering for neural networks with time-varying delays. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2016, 27, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, A.; Bandyopadhyay, B. Robust sliding mode control: An event-triggering approach. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 64, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, I. Fractional-order memristor-based Chua’s circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2010, 57, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, T. Event-based control for memristive systems. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2014, 19, 3431–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocamaz, U.E.; Cevher, B.; Uyaroǧlu, Y. Control and synchronization of chaos with sliding mode control based on cubic reaching rule. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2017, 105, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablay, G. Sliding mode control of uncertain unified chaotic systems. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 2009, 3, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, B.-C.; Fei, S.; Liu, X. Event-Triggered and Memory-Based Sliding Mode Variable Structure Control for Memristive Systems. Electronics 2018, 7, 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100253
Zheng B-C, Fei S, Liu X. Event-Triggered and Memory-Based Sliding Mode Variable Structure Control for Memristive Systems. Electronics. 2018; 7(10):253. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100253
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Bo-Chao, Shumin Fei, and Xiaoguang Liu. 2018. "Event-Triggered and Memory-Based Sliding Mode Variable Structure Control for Memristive Systems" Electronics 7, no. 10: 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100253
APA StyleZheng, B.-C., Fei, S., & Liu, X. (2018). Event-Triggered and Memory-Based Sliding Mode Variable Structure Control for Memristive Systems. Electronics, 7(10), 253. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100253




