High-Linearity Self-Biased CMOS Current Buffer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
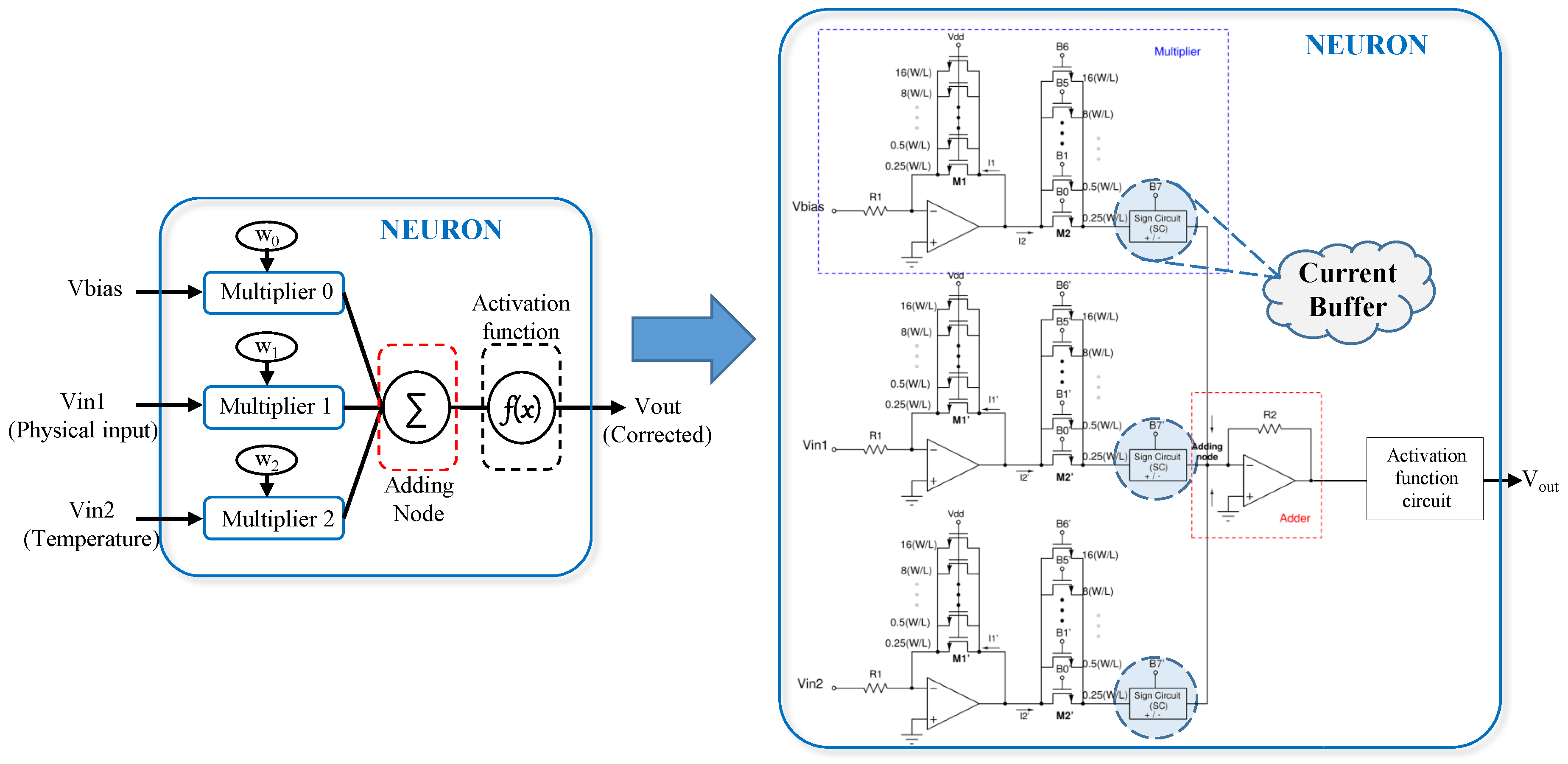
2. Proposed Self-Biased Current-Buffer
3. Performance Characterization
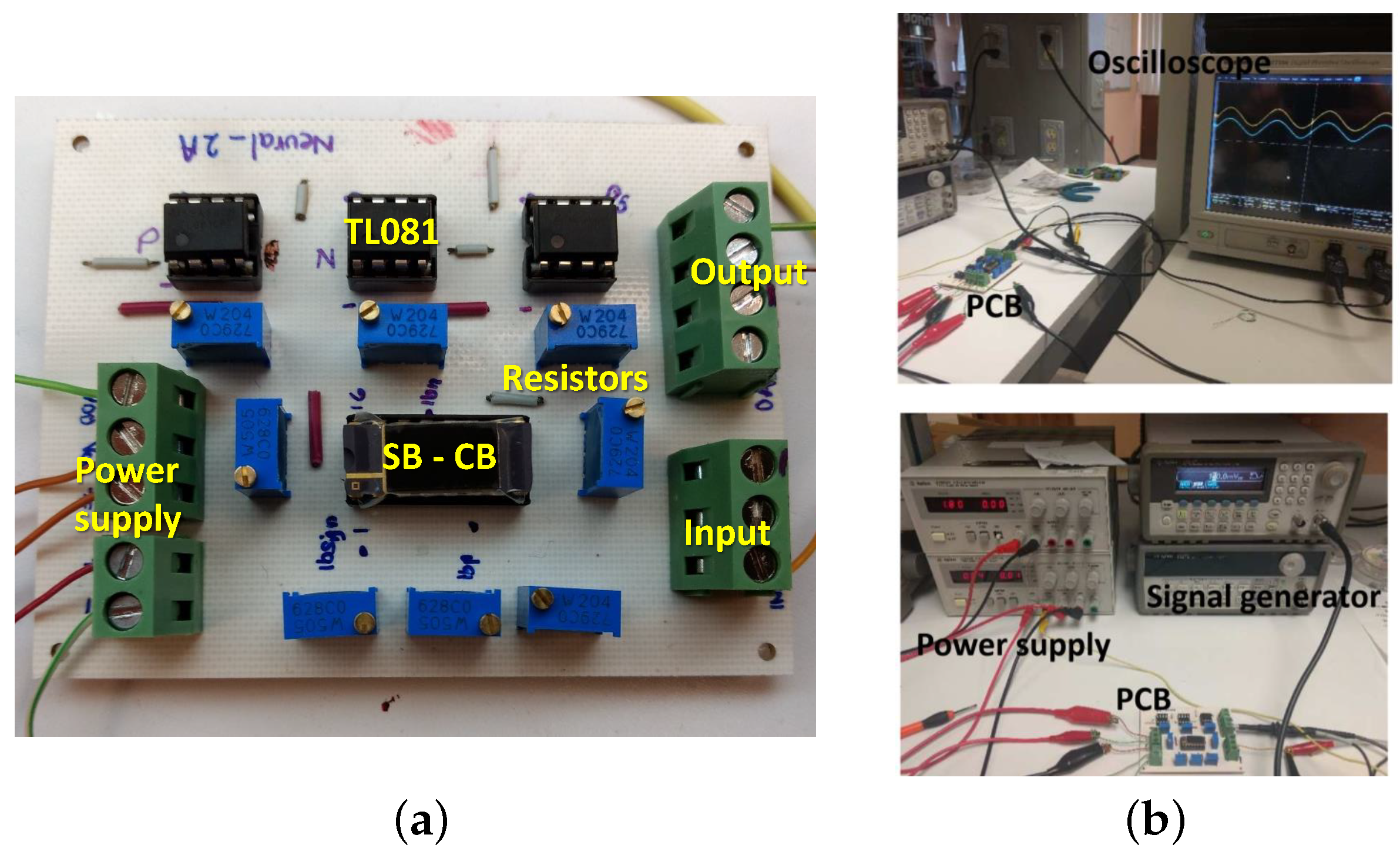
4. Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumgern, M.; Wareechol, E.; Phasukkit, P. Quadrature oscillator and universal filter based on translinear current conveyors. AEU Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 94, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cini, U. A low-offset high CMRR current-mode instrumentation amplifier using differential difference current conveyor. In Proceedings of the 2014 21st IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), Marseille, France, 7–10 December 2014; pp. 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza-Alfaro, F.; Pennisi, S.; Palumbo, G.; Lopez-Martin, A. Low-power class-AB CMOS voltage feedback current operational amplifier with tunable gain and bandwidth. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2014, 61, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, M.N.S. Modified CFOA, its transpose, and applications. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2016, 44, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshma, P.G.; Gopi, V.P.; Babu, V.S.; Wahid, K.A. Analog CMOS implementation of FFT using cascode current mirror. Microelectron. J. 2017, 60, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsirimokou, G.; Psychalinos, C. Ultra-low voltage fractional-order circuits using current mirrors. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2016, 44, 109–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotner, R.; Jerabek, J.; Langhammer, L.; Dvorak, J. Design and Analysis of CCII-Based Oscillator with Amplitude Stabilization Employing Optocouplers for Linear Voltage Control of the Output Frequency. Electronics 2018, 7, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowlavi, S.; Baharmast, A.; Sobhi, J.; Koozehkanani, Z. A novel current-mode low-power adjustable wide input range four-quadrant analog multiplier. Integration 2018, 63, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martin, A.; Garde, M.P.; Carvajal, R.G.; Ramírez-Angulo, J. On the Optimal Current Followers for Wide-Swing Current-Efficient Amplifiers. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Florence, Italy, 27–30 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martin, A.J.; Acosta, L.; Garcia-Alberdi, C.; Carvajal, R.G.; Ramirez-Angulo, J. Power-efficient analog design based on the class AB super source follower. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2012, 40, 1143–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourashraf, S.; Ramírez-Angulo, J.; Lopez-Martin, A.J.; González-Carvajal, R. A super class-AB OTA with high output current and no open loop gain degradation. In Proceedings of the IEEE 60th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems (MWSCAS), Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 August 2017; pp. 815–818. [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi, P.; Navarrini, D.; Piotto, M. A class-AB CMOS operational amplifier for application as rail-to-rail high current drive output buffer. In Proceedings of the 28th European Solid-State Circuits Conference (ESSCIRC), Florence, Italy, 24–26 September 2002; pp. 731–734. [Google Scholar]
- Kawahito, S.; Tadokoro, Y. CMOS class-AB current mirrors for precision current-mode analog-signal-processing elements. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 1996, 43, 843–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, Y.; Jia, D.; Dong, L. Ultra-high current efficiency single-stage class-AB OTA with completely symmetric slew rate. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2018, 87, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, A.D.; Marano, D.; Esparza-Alfaro, F.; Lopez-Martin, A.J.; Palumbo, G.; Pennisi, S. Self-biased dual-path push-pull output buffer amplifier for LCD column drivers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2014, 61, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Nieto, J.A.; Sanz-Pascual, M.T.; Medrano-Marques, N.J.; Calvo-Lopez, B. Self-biased class-AB CMOS current buffer. In Proceedings of the IEEE 7th Latin American Symposium on Circuits Systems (LASCAS), Florianopolis, Brazil, 28 February–2 March 2016; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Bult, K.; Geelen, G. An inherently linear and compact most-only current-division technique. In Proceedings of the Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–21 February 1992; pp. 198–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pun, K.P.; Choy, C.S.; Chan, C.F.; da Franca, J. Digital frequency tuning technique based on current division for integrated active RC filters. Electron. Lett. 2003, 39, 1366–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jia, S.; Pan, T.; Wang, Y. Design of low-power high-speed dual-modulus frequency divider with improved MOS current mode logic. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid State Circuits (EDSSC), Shenzhen, China, 6–8 June 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Nieto, J.A.; Sanz-Pascual, M.T.; Medrano-Marqués, N.J. Integrated mixed mode neural network implementation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Circuit Theory and Design (ECCTD), Catania, Italy, 4–6 September 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Nieto, A.; Medrano, N.; Sanz-Pascual, M.T.; Calvo, B. An accurate analysis method for complex IC analog neural network-based systems using high-level software tools. In Proceedings of the IEEE 9th Latin American Symposium on Circuits & Systems (LASCAS), Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 25–28 February 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Nieto, A.; Sanz-Pascual, M.T.; Marquez, A.; Perez-Bailon, J.; Calvo, B.; Medrano, N. A CMOS Mixed Mode Non-Linear Processing Unit for Adaptive Sensor Conditioning in Portable Smart Systems. Procedia Eng. 2016, 168, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, N.; Singh, A.K.; Gupta, A.K. High performance current mirrors using quasi-floating bulk. Microelectron. J. 2016, 52, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Lopez-Martin, A.; Carvajal, R.; Chavero, F. Very low-voltage analog signal processing based on quasi-floating gate transistors. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2004, 39, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Lopez-Martin, A.J.; Carvajal, R.G.; Calvo, B. Class-AB Fully Differential Voltage Followers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2008, 55, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Martin, A.; Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Carvajal, R.; Algueta, J. Compact class AB CMOS current mirror. Electron. Lett. 2008, 44, 1335–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garde, M.P.; Lopez-Martin, A.J.; Carvajal, R.G.; Ramirez-Angulo, J. Super class AB RFC OTA with adaptive local common-mode feedback. Electron. Lett. 2018, 54, 1272–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suadet, A.; Kasemsuwan, V. A compact class-AB bulk-driven quasi-floating gate current mirror for low voltage applications. In Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), Surat Thani, Thailand, 4–6 September 2013; pp. 298–302. [Google Scholar]
- Esparza-Alfaro, F.; Lopez-Martin, A.; Carvajal, R.G.; Ramirez-Angulo, J. Highly linear micropower class AB current mirrors using Quasi-Floating Gate transistors. Microelectron. J. 2014, 45, 1261–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, C.; Afzal, N.; Prasad, D. A High Performance Bulk Driven Quasi Floating Gate MOSEFT Based Current Mirror. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2016, 79, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Angulo, J.; Lopez-Martin, A.; Carvajal, R.; Torralba, A.; Jimenez, M. Simple class-AB voltage follower with slew rate and bandwidth enhancement and no extra static power or supply requirements. Electron. Lett. 2006, 42, 784–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Gonzalez, L.; Ducoudray-Acevedo, G. High accuracy self-biasing cascode current mirror. In Proceedings of the 49th IEEE International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, San Juan, Puerto Rico, 6–9 August 2006; Volume 1, pp. 465–468. [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro, S.O.; Grasso, A.D.; Mita, R.; Palumbo, G.; Pennisi, S. Design procedures for three-stage CMOS OTAs with nested-miller compensation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2007, 54, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, A.D.; Palumbo, G.; Pennisi, S. Three-stage CMOS OTA for large capacitive loads with efficient frequency compensation scheme. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2006, 53, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Mishra, C.; Sanchez-Sinencio, E. Single miller capacitor frequency compensation technique for low-power multistage amplifiers. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2005, 40, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parnklang, J.; Nanthanawanitch, W.; Titiroongruang, W. CMOS current follower circuits. In Proceedings of the IEEE Region 10 Conference TENCON 99, Cheju Island, Korea, 15–17 September 1999; Volume 2, pp. 1030–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Kurashina, T.; Ogawa, S.; Watanabe, K. A high performance class-AB current conveyor. In Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems, Lisboa, Portugal, 7–10 September 1998; Volume 3, pp. 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatorre, G.; Medrano, N.; Sanz, M.T.; Calvo, B.; Martinez, P.; Celma, S. Designing adaptive conditioning electronics for smart sensing. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinar-Solís, J.E.; García-Lozano, R.Z.; Hidalgo-Cortes, C.; Rocha-Perez, J.M.; Díaz-Sánchez, A. A very compact CMOS class AB current mirror for low voltage applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th Colombian Workshop on Circuits and Systems (CWCAS), Barranquilla, Colombia, 1–2 November 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Palmisano, G.; Pennisi, S. Dynamic biasing for true low-voltage CMOS class AB current-mode circuits. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Analog Digit. Signal Process. 2000, 47, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julien, M.; Bernard, S.; Soulier, F.; Kerzerho, V.; Cathebras, G. Breaking the speed-power-accuracy trade-off in current mirror with non-linear CCII feedback. Microelectron. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Texas Instruments. TL08xx JFET-Input Operational Amplifiers; Rev.3; Dallas, TX, USA, May 2015; Available online: http://www.ti.com/lit/ds/slos081i/slos081i.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- ROHDE & SCHWARZ. R&S FSV Signal and Spectrum Analyzer Operating Manual; Test and Measurements: Munich, Germany, 2011; Available online: http://www.eava.ee/$\sim$laborid/side/Spektri_A/FSV13/FSV_Operating.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2018).
- Keysight Technologies. Keysight E5061B ENA Vector Network Analyzer, 100 kHz to 1.5/3 GHz, 5 Hz to 500 M/1.5 G/3 GHz; Keysight Technologies: Santa Rosa, CA, USA, 2018; Available online: https://literature.cdn.keysight.com/litweb/pdf/5990-4392EN.pdf (accessed on 7 November 2018).

















| Transistor | (m/m) |
|---|---|
| , | 2/1 |
| , , | 20/1 |
| 15/1 | |
| 0.72/3 | |
| , | 2/2 |
| 0.54/2 |
| Circuit | THD (dB) | Max. Power (W) | BW | Rin | Rout | (%) | Settling Time | Active * | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | @1 kHz | Static | Dynamic | (MHz) | () | (M) | at 0.1% (s) | Area () | ||
| Proposed | 8 | −85.6 | 30.9 | 49.1 | 3.8 | 483 | 0.24 | (MOS) 118 | ||
| SB-CB1 | (MIM) 1404 | |||||||||
| Proposed | 8 | −111.3 | 32.4 | 51.6 | 2.6 | 0.09 | (MOS) 118 | |||
| SB-CB2 | (MIM) 1404 | |||||||||
| QFG-CB | 3 | −103.8 | 14.6 | 33.4 | 2.2 | 0.08 | (MOS) 176 | |||
| (MIM) 1404 | ||||||||||
| CC-CB | 5 | −50.1 | 24.7 | 59.3 | 1.0 | 1.74 | (MOS) 630 | |||
| Process Corner | [A] | SB-CB1 | SB-CB2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Power [W] | THD [dB] * | Power [W] | THD [dB] * | ||
| typical | 8.0 | 30.9 | −85.6 | 32.4 | −111.3 |
| slow NMOS-slow PMOS | 6.5 | 24.8 | −85.0 | 26.7 | −108.3 |
| fast NMOS-fast PMOS | 10.0 | 38.7 | −87.1 | 41.6 | −115.5 |
| slow NMOS-fast PMOS | 9.0 | 35.3 | −86.5 | 38.2 | −113.7 |
| fast NMOS-slow PMOS | 7.3 | 28.4 | −84.7 | 30.4 | −109.3 |
| Monte Carlo Analysis | SB-CB1 | SB-CB2 | QFG-CB | CC-CB | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Mean | Mean | Mean | |||||
| (A) | 8.0 | 0.1 | 8.0 | 0.1 | — | — | — | — |
| Gain | 1.000 | 0.007 | 1.000 | 0.007 | 1.000 | 0.004 | 1.007 | 0.002 |
| Offset (nA) | −1.1 | 124.3 | −0.5 | 132.8 | −0.45 | 73.07 | −4.81 | 29.96 |
| THD (dB) | −66.4 | 6.1 | −67.0 | 6.7 | −56.1 | 5.4 | −49.1 | 1.2 |
| Parameter | This Work | Lopez-Martin’08 | Suadet’13 | Esparza’14 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [26] | [28] | [29] | ||
| CMOS Technology | m | m | m | m |
| Power Supply (V) | 1.8 | 3.3 | 0.5 | 1.2 |
| (A) | 12 | 10 | 6 | 10 |
| THD (dB) | <−61@@1 kHz | −59@@120 kHz | −40@@1 MHz | −41@ ** |
| <−53@@10 kHz | ||||
| Power Consumption (W) | 48 | 165 | 8.2 | 36 |
| BW (MHz) | 2.6 | 120 | 230 | 72.4 |
| Rin | 89 | 25 | 934 | 4.8k |
| Rout (M) | 2.4 | — | 1.13 | 7.2 |
| (%) | 1.35%@ | — | — | — |
| Settling Time (s) | 8.6 | — | — | — |
| Area () | 6149 | 18,200 | — | 25,020 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez-Nieto, J.A.; Sanz-Pascual, M.T.; Medrano-Marqués, N.; Calvo-López, B.; Sarmiento-Reyes, A. High-Linearity Self-Biased CMOS Current Buffer. Electronics 2018, 7, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120423
Martínez-Nieto JA, Sanz-Pascual MT, Medrano-Marqués N, Calvo-López B, Sarmiento-Reyes A. High-Linearity Self-Biased CMOS Current Buffer. Electronics. 2018; 7(12):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120423
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez-Nieto, Javier Alejandro, María Teresa Sanz-Pascual, Nicolás Medrano-Marqués, Belén Calvo-López, and Arturo Sarmiento-Reyes. 2018. "High-Linearity Self-Biased CMOS Current Buffer" Electronics 7, no. 12: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120423
APA StyleMartínez-Nieto, J. A., Sanz-Pascual, M. T., Medrano-Marqués, N., Calvo-López, B., & Sarmiento-Reyes, A. (2018). High-Linearity Self-Biased CMOS Current Buffer. Electronics, 7(12), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120423







