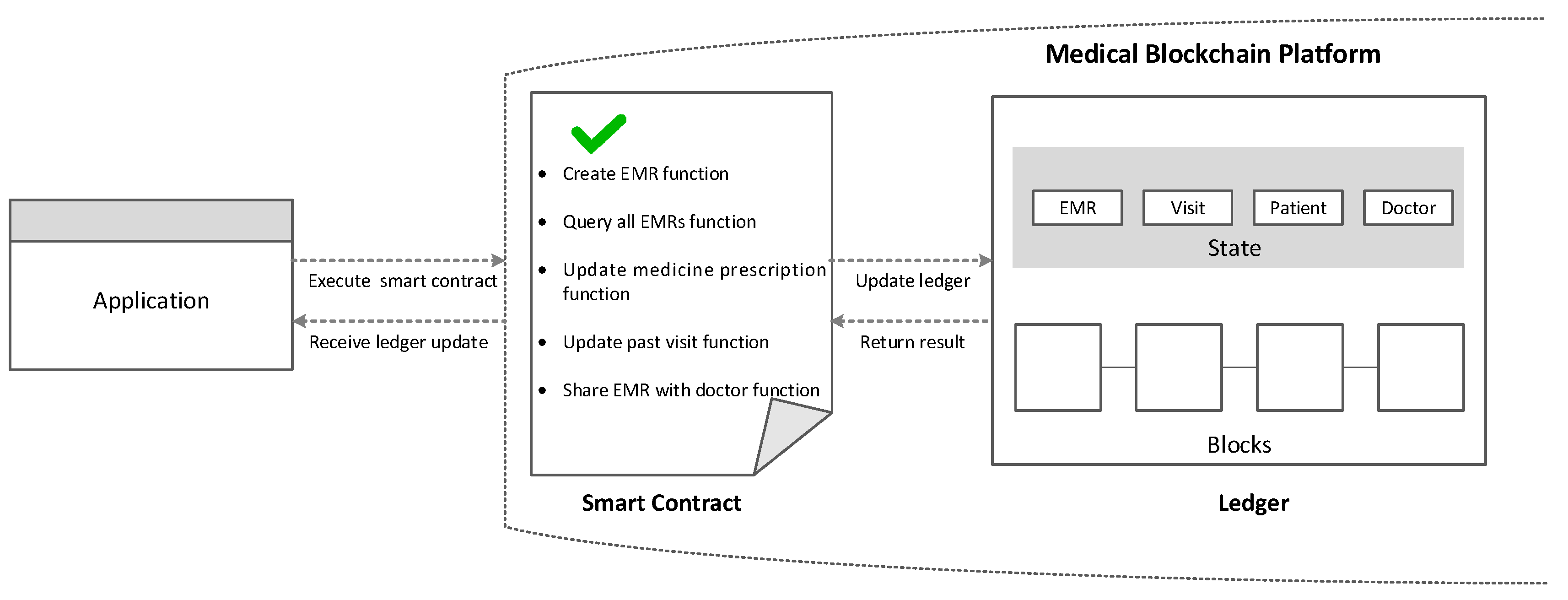
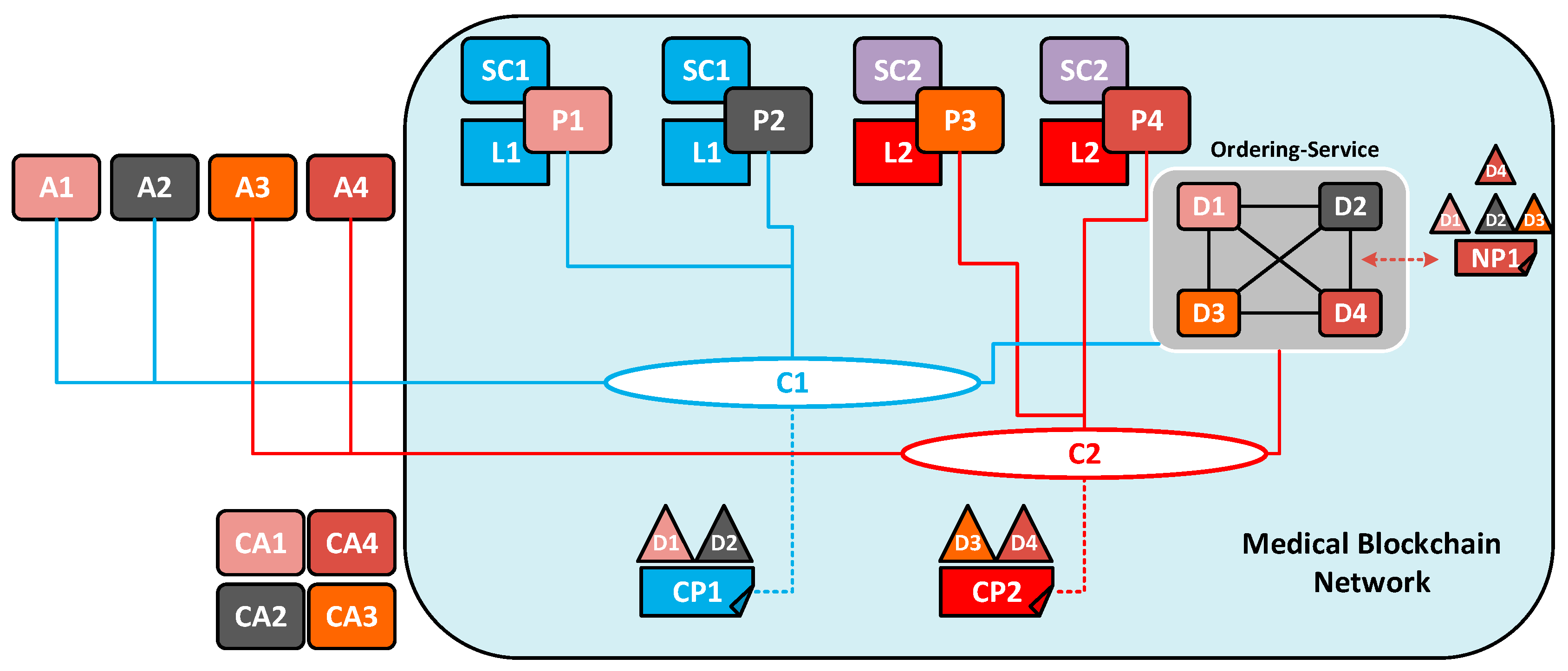
Nowadays, healthcare is witnessing an innovative approach to disease prevention and treatment that incorporates an individual patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle and environment. IT advancement has produced large data storage of health information and provided mechanisms to track engaged individuals more with their own healthcare. It can be speculated that by combining healthcare with information technology, it would bring a structural shift in the field of health IT. The blockchain is both a data structure and a timekeeping mechanism for that data structure. As a proof of the history of data, it is also easily reportable [
26]. Blockchain technology shows the great potential to address interoperability challenges in current health IT systems and is hoped to become a part of the core technical standard, enabling individual users, healthcare providers, and medical research centers to share electronic health data in a more secure way [
27].
The following section discusses some of the notable projects and applications for medical- and health-care built on blockchain. MediBloc [
28] follows an open-source protocol and defines itself as a decentralized healthcare information ecosystem built on blockchain technology for patients, healthcare providers, and researchers. Its blockchain platform allows it to track and record everything revolving around your healthcare world such as doctors’ visits and record updates. The platform is a DApp formulated on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). It uses the Medi Point system (MP), a points-based system that measures user participation. This token can be used in medical transactions such as insurance payments. MedRec [
29] is a novel, decentralized record management system to handle EMRs, using blockchain technology. It leverages various blockchain properties to manage confidentiality, authentication, sharing and data accountability, which should be taken into account when processing sensitive medical information. This system is designed with a modular architecture that integrates with the existing data storage infrastructure and approaches, which makes the designed system more interoperable and adaptable. Furthermore, a unique incentive method is proposed to stimulate medical stakeholders (patient, health researchers, etc.) to act as miners in the blockchain network. Participants involved with the network can get access permission to aggregated and anonymized medical data as mining rewards, for contributing computing power to secure and sustain the network. MediLedger [
30] is an initiative to establish the first peer-to-peer network for the pharmaceutical industry. The MediLedger network establishes a number of standards, interoperable protocol primitives that allow the pharmaceutical industry to easily exchange data across organizations. The network is powered by the blockchain in order to implement and execute cross-industry business processes and validate messages that are exchanged amongst the participants. Permission-based private messaging is used to share only the data the user wants to share with the partners they wants to share it with. It connects with trading partners and trusted service providers at the vanguard of emerging solutions for the pharmaceutical industry. HealthCoin [
31] is a blockchain technology-based currency, the seemingly different aspects of preventive healthcare—hospitals, employers, health plans, insurers, governments, non-governmental organizations, wellness apps—are brought under a single roof. The medical data is verified without any loss in transactions by using massive database analytics and nationwide collaboration, and a targeted program is developed to prevent various disorders. It works by tokenizing measurable improvements in health. Information about health apps, doctors, health plans, and insurer biometric screening is recorded. For diabetes, in particular, A1c, high-density lipoprotein, blood pressure, even gene markers, and family history is noted down which can indicate the affinity to develop Type II Diabetes. Connecting Care [
32] is a digital care record sharing system used in several cities of England such as Bristol, North Somerset and South Gloucestershire. This system is made to provide secure access to import information held by hospitals and other health and social care organizations. It also allows clinical professionals involved in care to access users’ health and social care records and reduces the time cost by professionals checking details from different health and social care organizations. Furthermore, it can also reduce delays to the treatment due to the lack of information. Connecting Care is only accessible to authorized users who have been assigned with work roles, which define user levels to which information they can see. Robomed Network [
33] is another decentralized medical network intended to provide effective medical care services. As the value criteria of clinical pathways, a smart contract is utilized by this project to connect healthcare service providers and patients. This particular concept which focus on patient outcomes has driven the conventional healthcare market in to a new era, which creates a single point of care for patients. Robomed Network issues its own tokens to support a smart contract between healthcare providers and patients. A comprehensive review of potential application using blockchain technologies in terms of healthcare is discussed in [
34]. For example, the authors in [
35] propose a novel blockchain framework specified for resource-constraint medical devices. To eliminate the use of mining, a lightweight cryptographic approach based on key pairs are presented. This method ensures the patient-centric access control for medical data over the blockchain network. This work gives a good indication to make Internet of Things (IoT) data secure and transparent using the blockchain technologies. FHIRChain is another system utilizing the smart contract for exchanging health data in standard Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR) [
36], where clinical data is stored off chain while the blockchain itself stores encrypted metadata which act as references to the primary data source. The authors in [
37] propose a user-centric health data sharing solution on the basis of a permissioned blockchain network. A mobile application is implemented to collect health data from wearable health devices and synchronize data to the cloud for sharing with other partners. A similar mobile-based system proposed in [
38] uses smartphones to collect and send EMR data to a permissioned blockchain network. The authors in [
39] propose a secure and trustable EMR management system using permissioned blockchain. The designed system enables the EMR (specified for cancer patient care) data sharing between healthcare providers and research studies. The EMR data registered to the blockchain network is resistant to tampering and revision. A provenance system based on a distributed network and smart contracts is proposed [
40] to instrument some widely used international EMR standards such as Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE) and Health Level Seven International (HL7). A proof of concept implementation is built on a permissioned network to indicate the usability and efficiency of the proposed architecture.
Some of these existing systems are built on a permission-less blockchain network where anyone can participate. In order to mitigate the absence of trust, these existing systems usually employ the use of native cryptocurrency or transaction fees that can result in high computing power consumption. Although a few works are built on a permissioned network, these works only focus on the sharing of EMR data and is not suitable for a deployment in a practical product environment. This paper aims to solve all these issues and presents a flexible and easy-to-use blockchain platform that can be deployed in real hospitals.