Dynamic Rotated Angular Beamforming Using Frequency Diverse Phased-Array for Secure MmWave Wireless Communications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
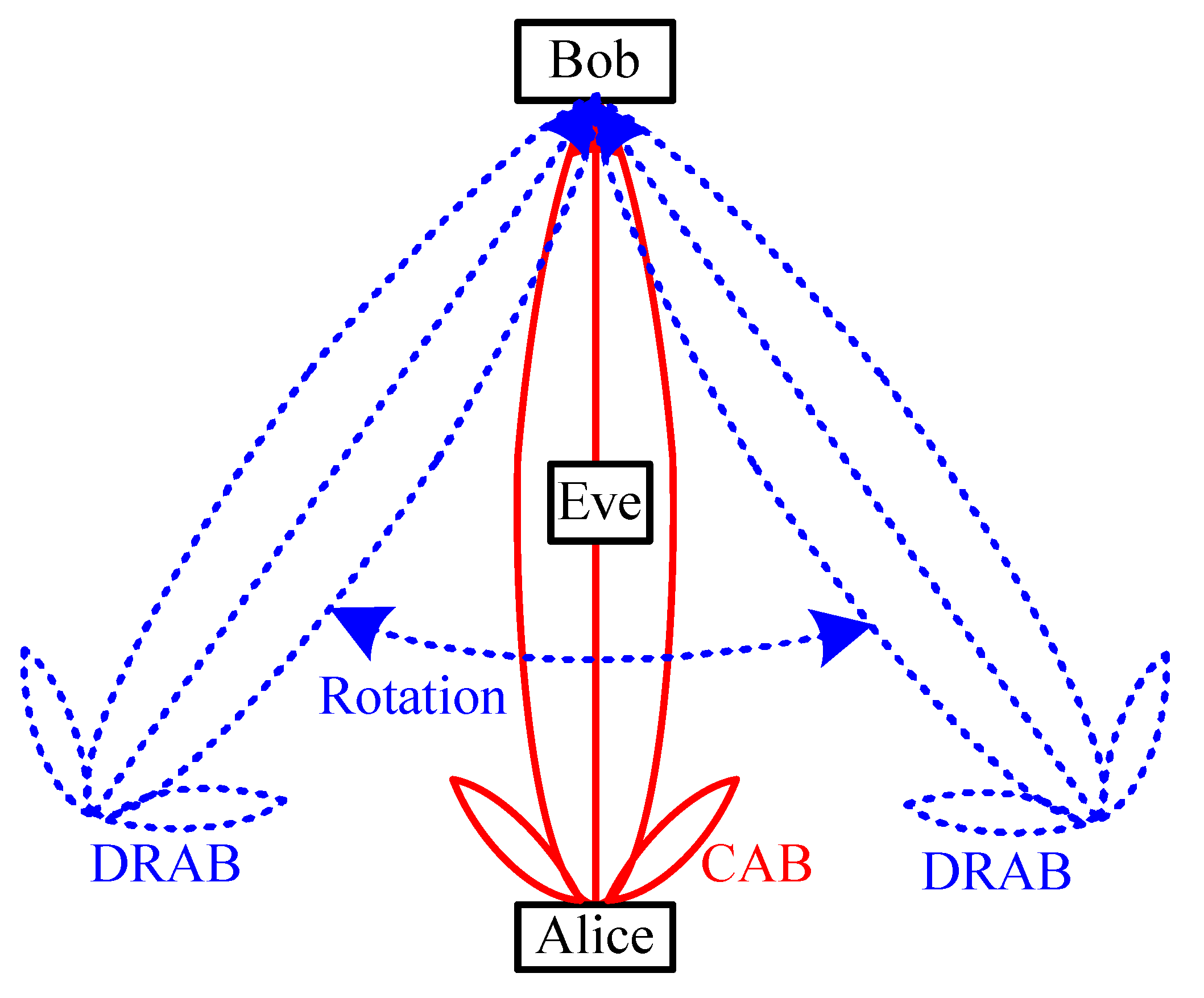
- We propose a novel FDPA-based DRAB transmission scheme to address the secure problem of mainlobe path. Compared with the existing CAB that can not discriminate, the eavesdropper in the target direction, our proposed DRAB is an angle-and-range double confined beam, which can circumvent the eavesdropper to steer the mainlobe by exploiting the DoF of frequency. Especially, the well-localization eavesdropper can be pointed by the zero gain sidelobe through an elaborate FOI across the FDPA.
- In order to avoid the rotatable mainlobe path being captured by the unlocalization eavesdropper, we propose a random dynamic rotation method of beampattern. The average beampattern of DRAB is derived as a function of FOI. The average mainlobe is only focused on the target region and the average sidelobes outside the target region are suppressed remarkably. As a beneficial result, the security threat in the mainlobe path of CAB can be alleviated.
- We also propose a DRAB-based IAS scheme to further randomize the sidelobe against sensitive eavesdropper by exploiting the DoF of digital phase shifter in FDPA, where some elements of beam steering weight vector are randomly selected with same probability to shift an extra phase . Thus, in the sidelobe region, the AN is produced to interfere with the sensitive eavesdropper and the PLS performance is improved.
2. DRAB Transmission Technique
2.1. System Model
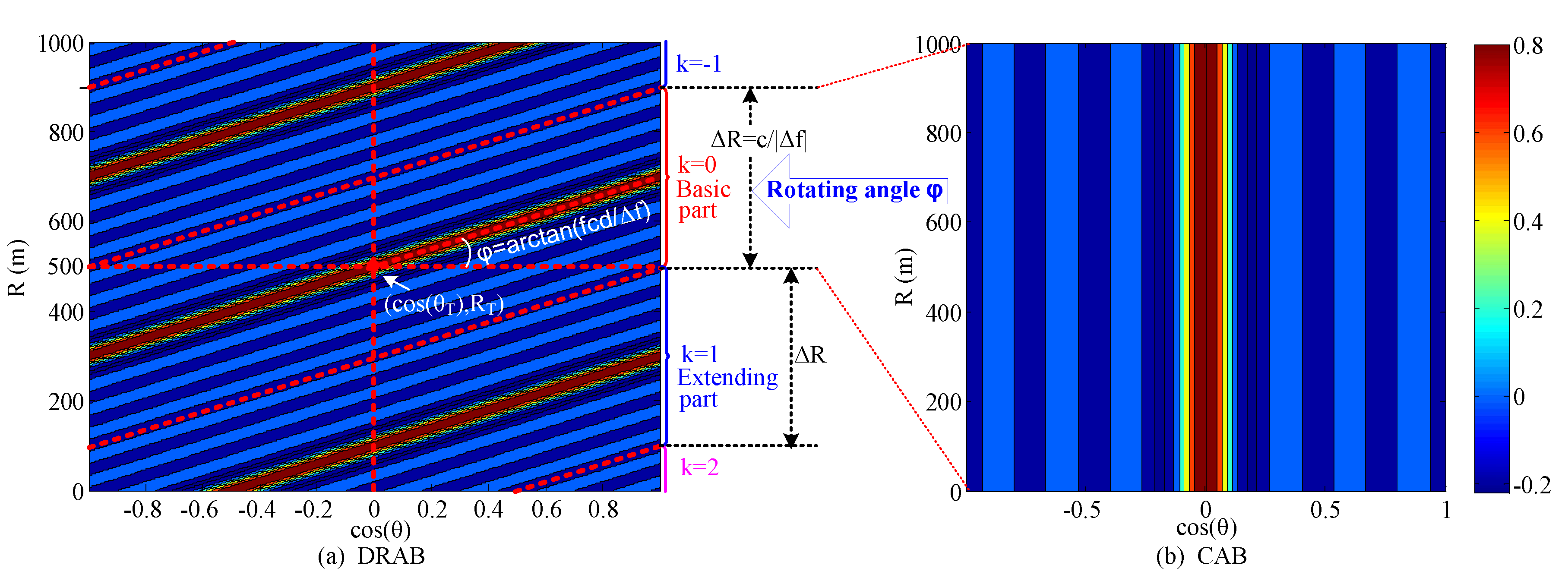
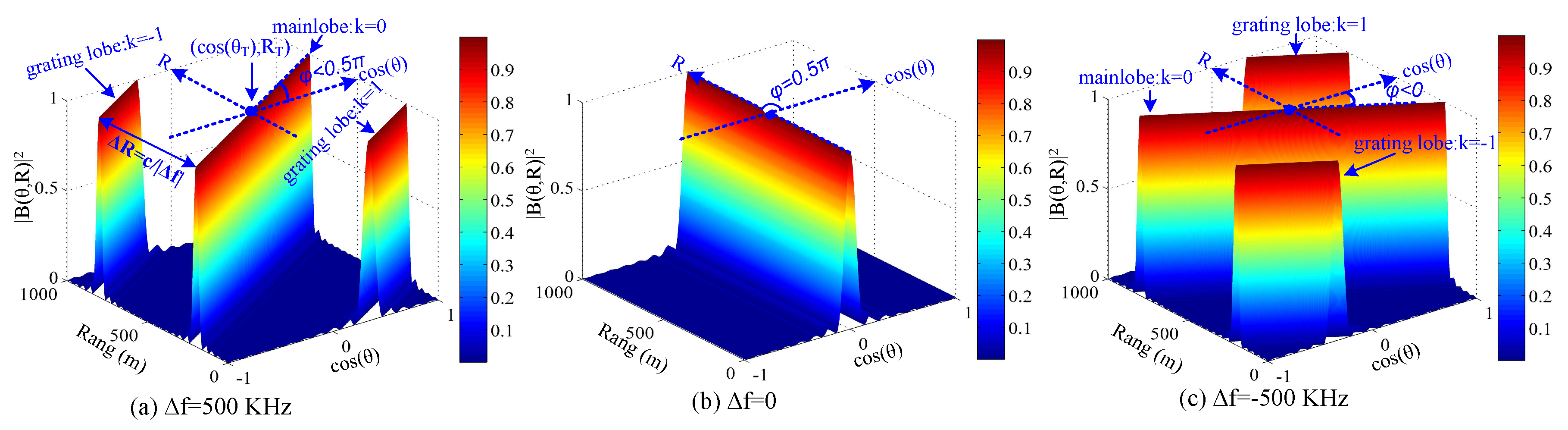
2.2. Dynamic Rotated Angular Beamforming
2.3. Average Beampattern of DRAB
2.4. IAS-Based Sidelobe Randomization
3. PLS Performance Analysis
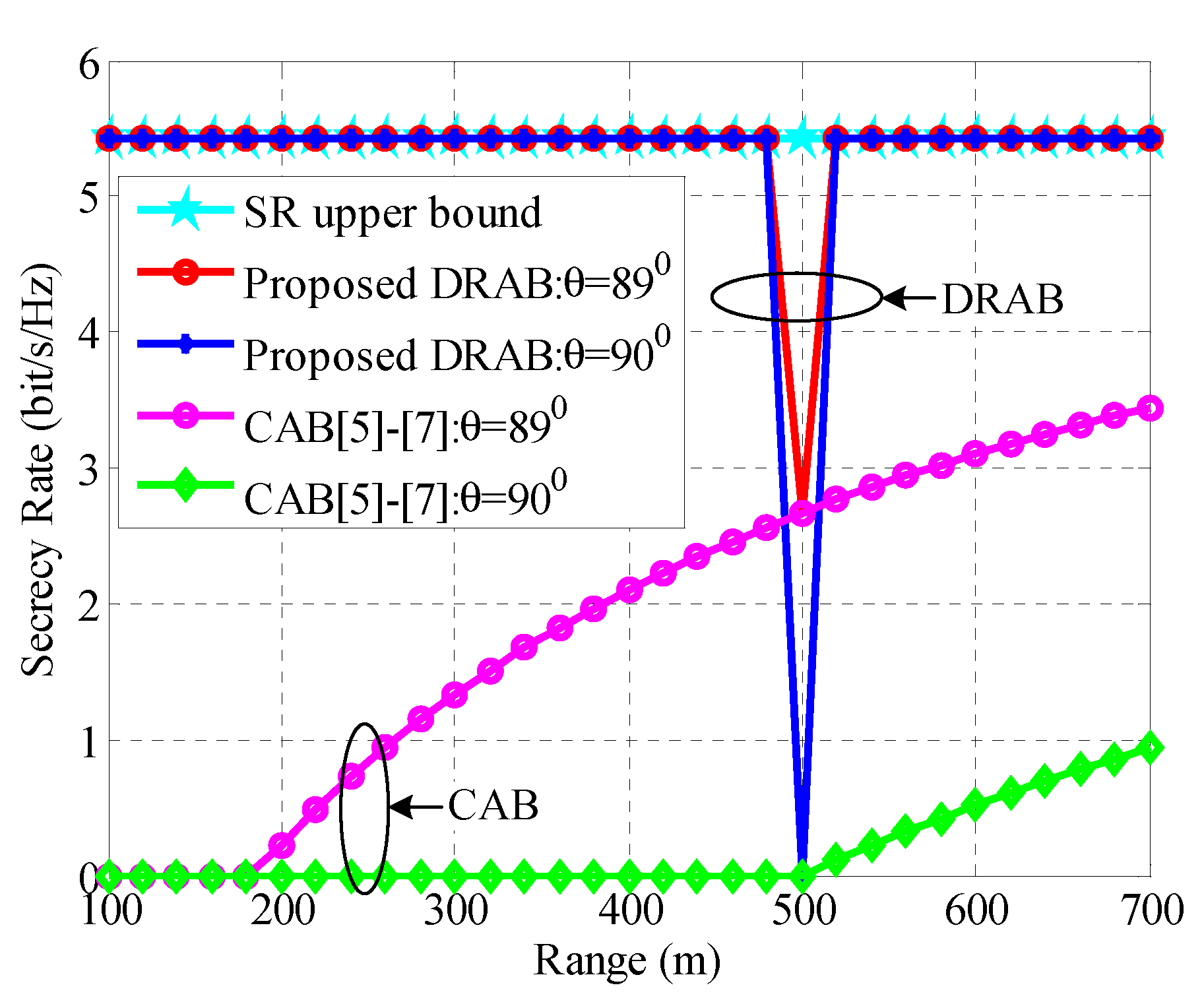
3.1. Secrecy Rate
3.2. Case 1: With Eavesdropping Location Information
3.3. Case 2: Without Eavesdropping Location Information
4. Simulation Results
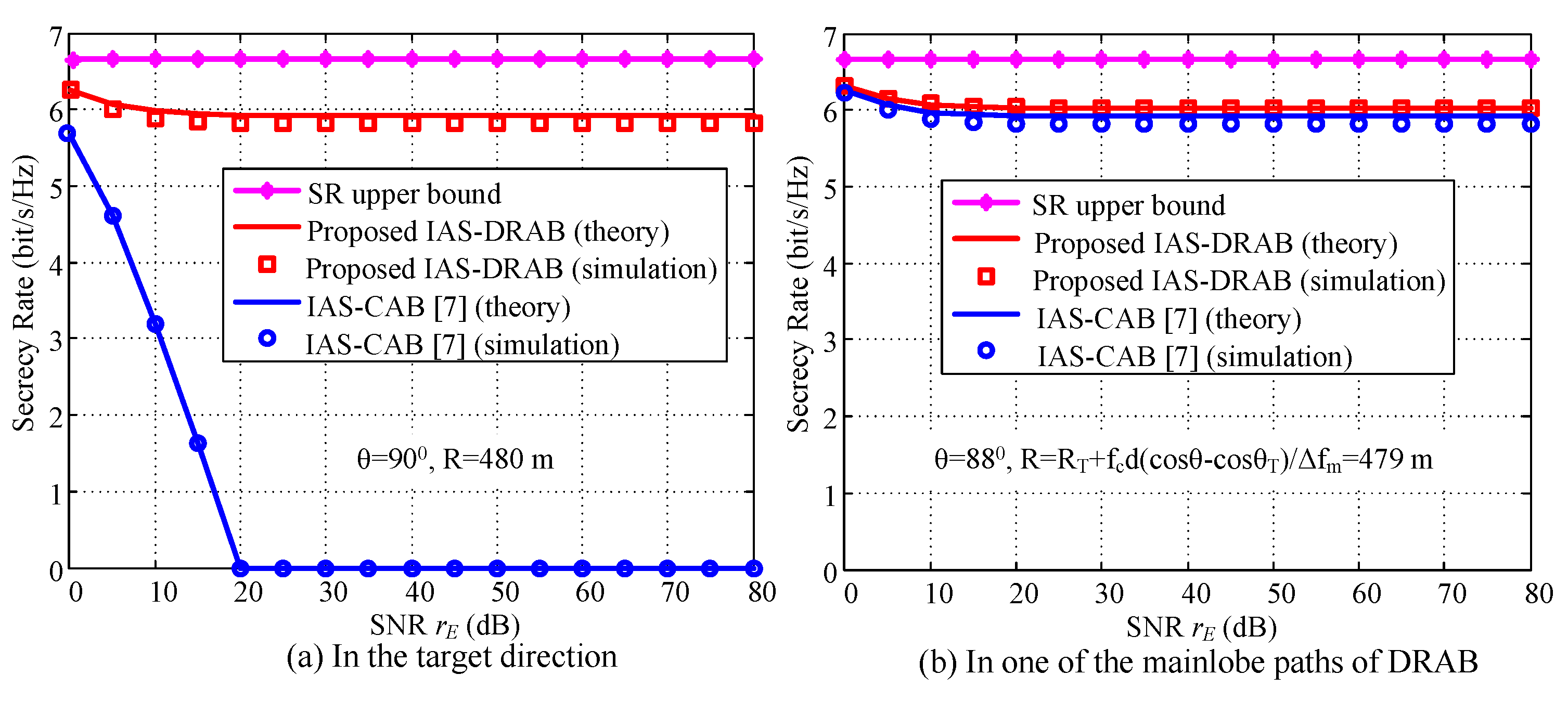
4.1. DRAB with Eavesdropping Location
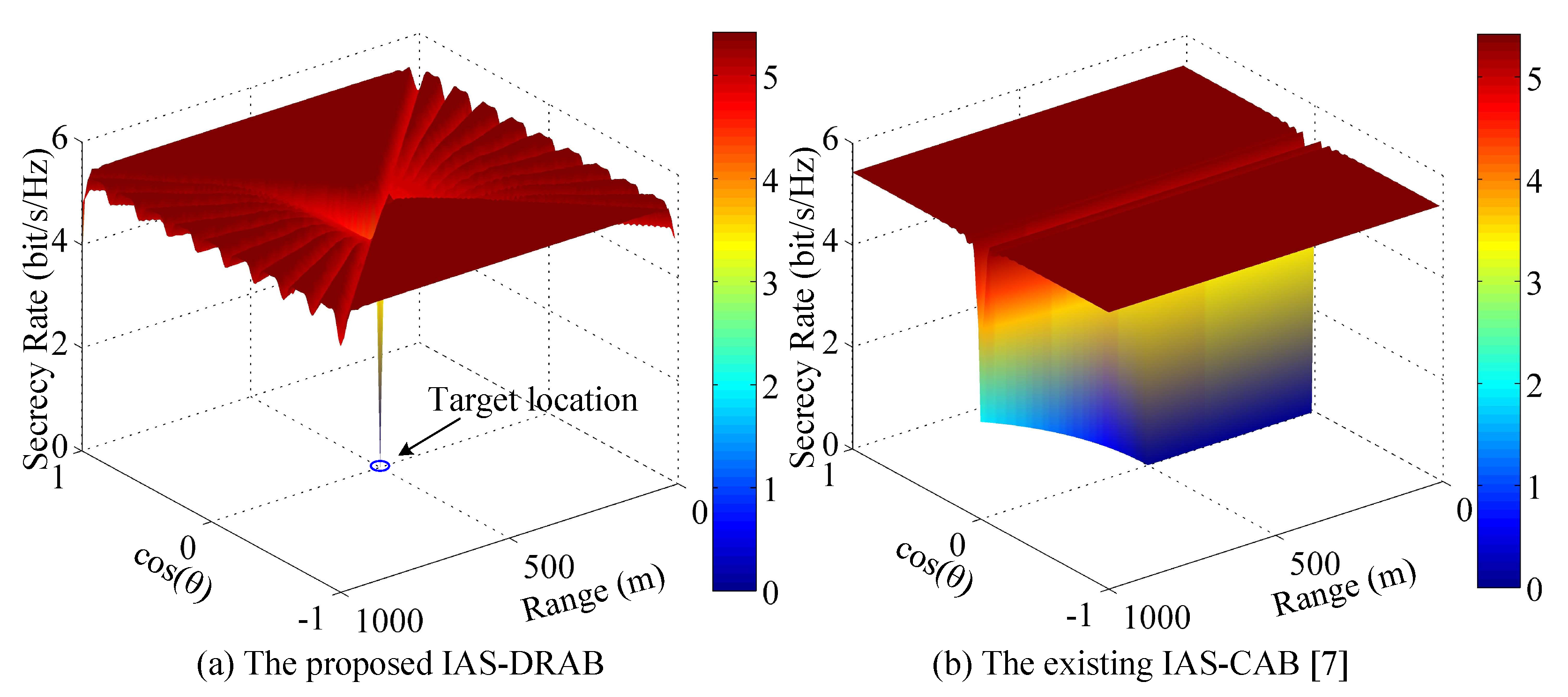
4.2. IAS-DRAB without Eavesdropping Location
4.3. Robust SR Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
Appendix C
Appendix D
Appendix E
References
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.H.; Wang, L. Physical Layer Security for Next Generation Wireless Networks: Theories, Technologies, and Challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tut. 2017, 19, 347–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Khisti, A.; Xiao, C.; Caire, G.; Wong, K.; Gao, X. A Survey of Physical Layer Security Techniques for 5G Wireless Networks and Challenges Ahead. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2018, 36, 679–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Althunibat, S.; Sucasas, V.; Rodriguez, J. A Physical-Layer Security Scheme by Phase-Based Adaptive Modulation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 9931–9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ng, D.W.K.; Gerstacker, W.H.; Chen, H. A Survey on Multiple-Antenna Techniques for Physical Layer Security. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tuts. 2017, 19, 1027–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valliappan, N.; Lozano, A.; Heath, R.W. Antenna Subset Modulation for Secure Millimeter-Wave Wireless Communication. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2013, 61, 3231–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alotaibi, N.N.; Hamdi, K.A. Switched Phased-Array Transmission Architecture for Secure Millimeter-Wave Wireless Communication. IEEE Trans. Commun. 2016, 64, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Jing, X.; Gao, H. Programmable Weight Phased-Array Transmission for Secure Millimeter-Wave Wireless Communications. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2018, 12, 399–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Shrestha, R.; Adelberg, J.; Yeh, C.Y.; Hossain, Z.; Knightly, E.; Jornet, J.M.; Mittleman, D.M. Security and Eavesdropping in Terahertz Wireless Links. Nature 2018, 563, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, M.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, R. Secure Wireless Communication via Intelligent Reflecting Surface. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2019, 8, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eltayeb, M.E.; Heath, R.W. Securing mmWave Vehicular Communication Links with Multiple Transmit Antennas. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Communications Workshops (ICC Workshops), Kansas City, MO, USA, 20–24 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, J.; Shao, H.; Wang, W. Physical-Layer Security for Proximal Legitimate User and Eavesdropper: A Frequency Diverse Array Beamforming Approach. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forens. Secur. 2018, 13, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Li, Q.; Yang, J. Frequency diverse array beamforming for physical-layer security with directionally-aligned legitimate user and eavesdropper. In Proceedings of the 2017 25th European Signal Processing Conference (EUSIPCO), Kos, Greece, 28 August–2 September 2017; pp. 2166–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, B.; Xie, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y. Artificial-Noise-Aided Secure Transmission for Proximal Legitimate User and Eavesdropper Based on Frequency Diverse Arrays. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 52531–52543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smulders, P.F.M. Deterministic modelling of indoor radio propagation at 40–60 GHz. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 1994, 1, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, A.; Pudeyev, A.; Bolotin, I.; Morozov, G.; Karls, I.; Faerber, M.; Siaud, I.; Ulmer-Moll, A.M.; Conrat, J.M.; Weiler, R.J.; et al. Millimetre-Wave Evolution for Backhaul and Access; Tech. rep. fp7-ict 368721/d5.1; MiWEBA: Breitengüßbach, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Eltayeb, M.E.; Choi, J.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y.; Heath, R.W. Enhancing Secrecy with Multi-Antenna Transmission in Millimeter Wave Vehicular Communication Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2017, 66, 8139–8151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Shi, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, L.; Li, W. Range-angle-decoupled beampattern synthesis with subarray-based frequency diverse array. Digit. Signal Process. 2017, 64, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdeniz, M.R.; Liu, Y.; Sun, S.; Rangan, S.; Rappaport, T.S.; Erkip, E. Millimeter Wave Channel Modeling and Cellular Capacity Evaluation. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2014, 32, 1164–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Work | Target Receiver | Auxiliary Equipment | Scenario | PLS Countermeasure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [9] | Untransparent | Unneeded | Known eavesdropper | AN |
| [10] | Transparent | Needed | Known eavesdropper | AN |
| [11,12] | Transparent | Unneeded | Known eavesdropper | Beampattern Rotation |
| [13] | Transparent | Unneeded | Known eavesdropper | AN |
| Proposed | Transparent | Unneeded | Known Eavesdropper Unknown eavesdropper | Beampattern rotation AN |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R (m) | 500 | 1500 | 2500 | 3500 | 4500 | 5500 | 6500 | 7500 | 8500 | 9500 | 10,500 |
| (dB) | 123.8 | 133.3 | 137.8 | 140.7 | 142.9 | 144.6 | 146.1 | 147.3 | 148.4 | 149.4 | 150.2 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, Y.; Jing, X.; He, Y.; Mu, J. Dynamic Rotated Angular Beamforming Using Frequency Diverse Phased-Array for Secure MmWave Wireless Communications. Electronics 2020, 9, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010010
Hong Y, Jing X, He Y, Mu J. Dynamic Rotated Angular Beamforming Using Frequency Diverse Phased-Array for Secure MmWave Wireless Communications. Electronics. 2020; 9(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Yuanquan, Xiaojun Jing, Yuan He, and Junsheng Mu. 2020. "Dynamic Rotated Angular Beamforming Using Frequency Diverse Phased-Array for Secure MmWave Wireless Communications" Electronics 9, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010010
APA StyleHong, Y., Jing, X., He, Y., & Mu, J. (2020). Dynamic Rotated Angular Beamforming Using Frequency Diverse Phased-Array for Secure MmWave Wireless Communications. Electronics, 9(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010010





