Abstract
Recent advances in information and communication technology (ICT) have enabled interaction and cooperation between components of the transportation system, and cooperative eco-driving systems that apply ICT to eco-driving systems are receiving significant attention. A cooperative eco-driving system is a complex system that requires consideration of the electronic control unit (ECU) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. To evaluate these complex systems, it is needed to integrate simulators with expertise. Therefore, this study presents an integrated driving hardware-in-the-loop (IDHIL) simulator for the testing and evaluation of cooperative eco-driving systems. The IDHIL simulator is implemented by integrating the driving hardware-in-the-loop simulator and a vehicular ad hoc network simulator to develop and evaluate a hybrid control unit and cooperative eco-driving application for the connected hybrid electric vehicle (CHEV). A cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application is utilized to demonstrate the use of our simulator. The results of the evaluation show the improved fuel efficiency of the CHEV through a calculation of the optimal speed profile and the optimal distribution of power based on V2X communication. Finally, this paper concludes with a description of future directions for the testing and evaluation of cooperative eco-driving systems.
1. Introduction
Methods for solving environmental problems caused by vehicles have received significant attention in recent years, and one typical approach is eco-driving. Eco-driving is an economic, environmentally friendly method that reduces air pollution and saves fuel consumption. It is a driving strategy that aims to reduce unnecessary acceleration and deceleration, thereby spending less time and fuel to travel the same distance. Eco-driving is one of the main goals of the intelligent transport systems (ITSs) along with road safety, comfort, and efficiency [1].
Recent advances in information and communication technology (ICT) have enabled high-speed communication between components of the transportation system, and research on a cooperative intelligent transport system (C-ITS) based on the connectivity between the components has received significant attention. A cooperative eco-diving system is one of the representative systems of a C-ITS that has improved the performance of eco-driving systems by utilizing connectivity technology. Many engineers have been developing cooperative eco-driving algorithms, and verification of such algorithms is needed before deploying cooperative eco-driving applications. Hu et al. [2] proposed an optimal controller for eco-driving of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) by using present and future information obtained through ITS, such as road topography and dynamic speed limit on a rolling terrain. Zambrano-Martinez et al. [3] proposed a centralized traffic management solution that predicts future traffic flows and balances the traffic flows using all the traffic data in a city, obtained through connectivity technology. The solution was validated in large-scale scenarios and the experimental results showed that the solution improved the travel times and average travel speed of vehicles.
Simulations have been used as a technique to develop and evaluate systems and offer a cost-efficient and safe environment for development and evaluation. In the context of C-ITS testing, typically used simulation tools include network simulators, traffic simulators, and driving simulators. Hallerbach et al. [4] proposed a simulation-based toolchain to identify and verify critical scenarios for connected and automated vehicles by integrating traffic, vehicle dynamics, and network simulation. They identified the critical scenarios to be tested before market penetration of the connected and automated vehicle (CAV) system by considering both functional and nonfunctional requirements, and verified the concrete scenarios using the simulation tool. Likewise, integrations of different simulators are commonly used in the C-ITS industry; the typical approach is the use of integration of traffic networks and network simulators, i.e., a so-called vehicular ad hoc network (VANET) simulator [5,6,7,8,9]. Although human factors are important to evaluate the performance of C-ITS, only a few studies have utilized a driving simulator involving human drivers [10,11,12,13]. Driving simulators are effective tools for developing vehicle systems and studying human factors, which are normally missing when using VANET simulators. In addition, driving simulators support the development of specialized electronic control units (ECUs) under realistic conditions using a hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) simulation. HIL simulation enables the specialized ECUs to be tested by providing interaction with all the rest of components of a vehicle system [14]. However, with respect to C-ITS testing and evaluation, driving simulators usually do not support realistic modeling of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, which is easily handled by the VANET simulator. Thus, an integration of all three types of simulators is needed to develop and evaluate a service of C-ITS precisely.
Therefore, this study presents an integrated driving HIL (IDHIL) simulator consisting of driving, traffic, HIL, and a network simulator for testing and evaluating a C-ITS, particularly a cooperative eco-driving system. The IDHIL simulator consists of the dSPACE Automotive Simulation Models (ASM), which run on a dSPACE HIL simulator Mid-Size [15], for the vehicle models, dSPACE ASM MotionDesk, ModelDesk, and ControlDesk for the driving and traffic simulators [16], and QualNet for the network simulator [17]. To develop an ECU for the cooperative eco-driving function of a connected hybrid electric vehicle (CHEV), a dSPACE MicroAutoBox is attached to the integrated simulator [18]. Furthermore, Cohda Wireless MK5 devices are attached to the integrated simulator for HIL testing of the V2X communication device by utilizing a network emulation function of the V2X communication packet [19]. In the evaluation, the hybrid control algorithms based on V2X communication and cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application are used to demonstrate the use of proposed IDHIL simulator for developing and testing a cooperative eco-driving system.
The remainder of this paper is organized as follows. The background of the integrated HIL simulator is described in Section 2. The architecture of the proposed integrated simulator is presented in Section 3. Section 4 describes the simulation environment and evaluation results of the application of the cooperative eco-driving system. Finally, some concluding remarks are given in Section 5.
2. Background
2.1. Integrated Simulator for Evaluation of C-ITS
Simulators have been used by researchers in the field of transportation to evaluate vehicle systems. Traffic simulators model large-scale transportation scenarios that are difficult to implement in real environments along with the movement of the vehicles, and thus it is possible to evaluate various scenarios involving transportation systems. Driving simulators model parameters such as the vehicle dynamics, driver model, and ECUs to evaluate the performance of vehicle control systems. Studies on VANETs have recently attracted considerable attention, and thus an evaluation of V2X communication systems using network simulators has been carried out. However, the use of a single simulator does not allow the evaluation of a sophisticated vehicle system when considering both the vehicle control system and the V2X communication system. Therefore, numerous studies have evaluated sophisticated vehicle systems, particularly C-ITS, through the integration of different simulators. There is commercial equipment that provides a simulation environment to develop and evaluate C-ITS considering both the vehicle control system and the V2X communication system; this is a dSPACE solution of closed-loop HIL testing of V2X-based applications [20]. It provides a real-time HIL simulation environment to test V2X applications utilizing HIL simulator and V2X communication devices. However, without the combination of a network simulator, there are limitations to the hierarchical behavior of VANET protocols and VANET algorithm studies such as routing and scheduling algorithms.
Of the many C-ITSs, we evaluated the cooperative eco-driving systems of CHEVs by developing an integrated simulator. The eco-driving system of the HEV calculates a situation-appropriate speed profile to reduce the acceleration and deceleration as much as possible while driving, which enables the motor and engine to efficiently consume energy through ECU functions such as the optimal power distribution and regenerative braking. To improve the fuel efficiency of HEVs, it is therefore important to design ECU functions properly. Many existing cooperative eco-driving systems have been evaluated using a driving simulator or vehicle simulator, assuming successful V2X communication [21,22,23]. However, V2X communication characteristics vary depending on the driving environment and service type, and thus consideration of V2X communication characteristics is essential to evaluate the performance of a cooperative eco-driving system. Herein, a simulation testbed for a CHEV is proposed by integrating a driving simulator with a VANET simulator, which allowed us to design and evaluate a cooperative eco-driving system in an environment similar to that of a real C-ITS.
2.2. Hardware-in-the-Loop Simulation
A HIL simulation is a technology used to develop and evaluate complex real-time systems, particularly in the automotive industry, enabling specialized ECU or ECU networks to be developed and evaluated under realistic conditions. A HIL simulator is a tool that provides the functionality of the rest of the vehicle systems such that a specialized ECU can be tested under realistic conditions. Since a HIL simulator runs in real-time and has variable in-vehicle network interfaces, actual hardware and software ECUs can be closed-loop tested for the entire vehicle systems through interaction with dynamic models implemented in a virtual environment. Furthermore, the hardware and software ECUs can be used for field tests after successful HIL test. A well-developed simulation testbed using an HIL simulator provides a cost-effective and safer environment for developing and evaluating vehicle systems.
Previous studies have tested ECUs by integrating a HIL simulator with a driving simulator. Patil et al. [24] designed the HEV model and ECUs to evaluate the performance of the HEV system using a driving simulator and a HIL simulator. V2X communication is required in the connected vehicle (CV) system, and the V2X communication device can be used to implement the HIL simulation testbed of the CV system. Cantas et el. [25] integrated a HIL simulator and a vehicle dynamics simulator with a V2X communication device to implement a HIL simulation testbed to develop a connected and automated vehicle (CAV) application, and proposed a green-wave algorithm for eco-driving, which improves the fuel efficiency of the CAV by using V2X communication. However, they did not consider the V2X communication channel characteristics, and thus they operated the algorithm by assuming the successful reception of V2X messages. V2X communication channel characteristics such as the communication delay and error rate depending on the driving environment must be considered to accurately evaluate the CV system, which is possible by integrating it with the network simulator. Therefore, in the proposed IDHIL simulator, a V2X communication device combined with a network simulator through a packet emulation function was integrated with the driving and HIL simulator for HIL testing of the V2X communication device in a realistic environment.
3. Integrated Driving HIL Simulator for Evaluation of Cooperative Eco-Driving System
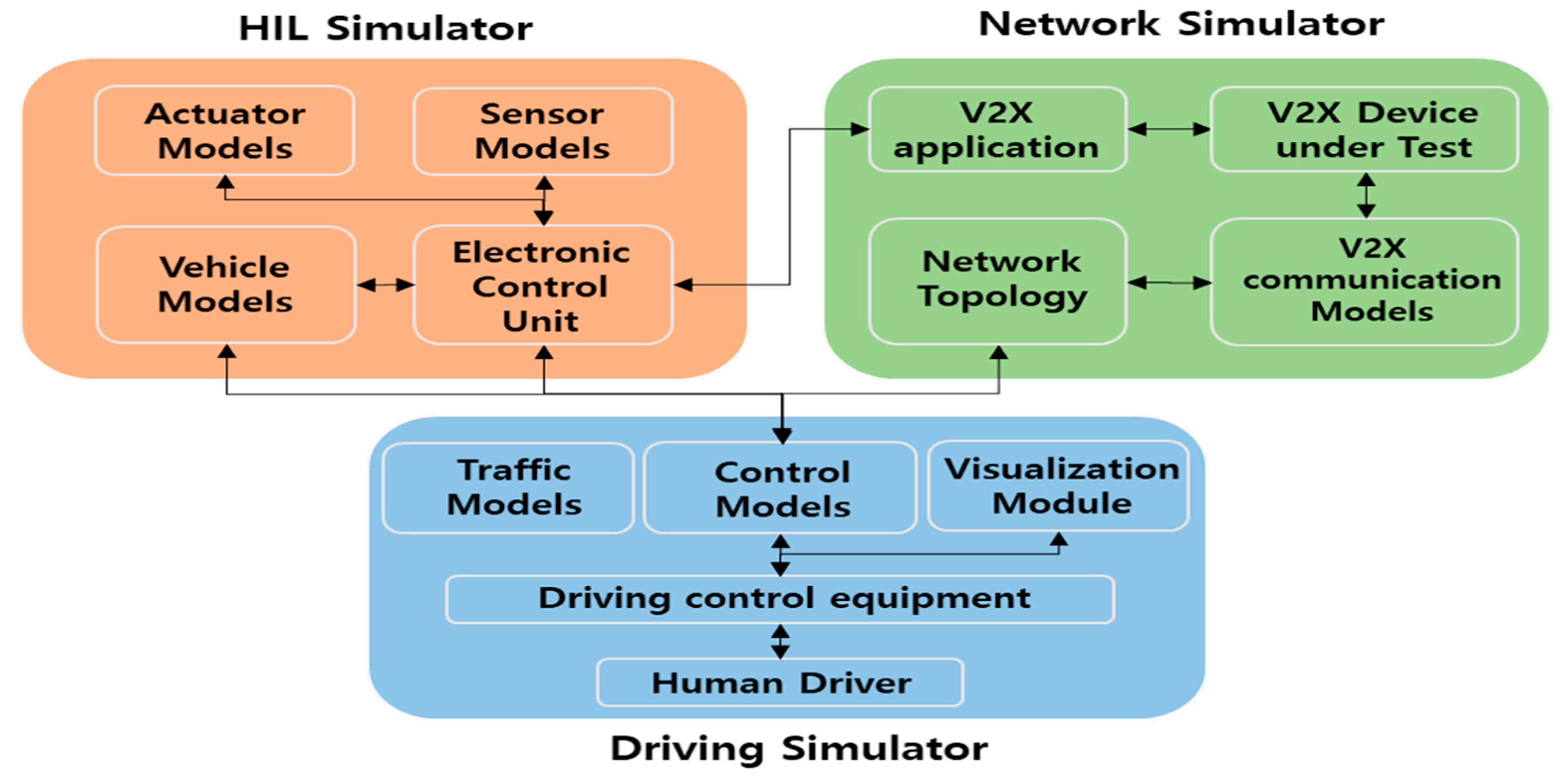
Figure 1 shows the architecture of the proposed IDHIL simulator for the evaluation of cooperative eco-driving systems. The development and evaluation of a cooperative eco-driving system considering both the V2X communication system and the vehicle control system requires an IDHIL simulator consisting of (1) dSPACE ASM running on a dSPACE Simulator Mid-Size as the driving and traffic simulator, (2) QualNet as the network simulator, (3) dSPACE MicroAutoBox controller to develop the ECU of a CHEV, and (4) Cohda Wireless MK5 for V2X communication between nodes. First, the behavior of each component of the IDHIL simulator is described, and the interface, interaction procedure, and data flow between the components are then described.
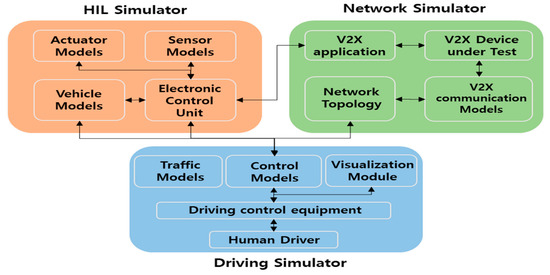
Figure 1.
Architecture of IDHIL simulator.
3.1. dSPACE Simulator Mid-Size
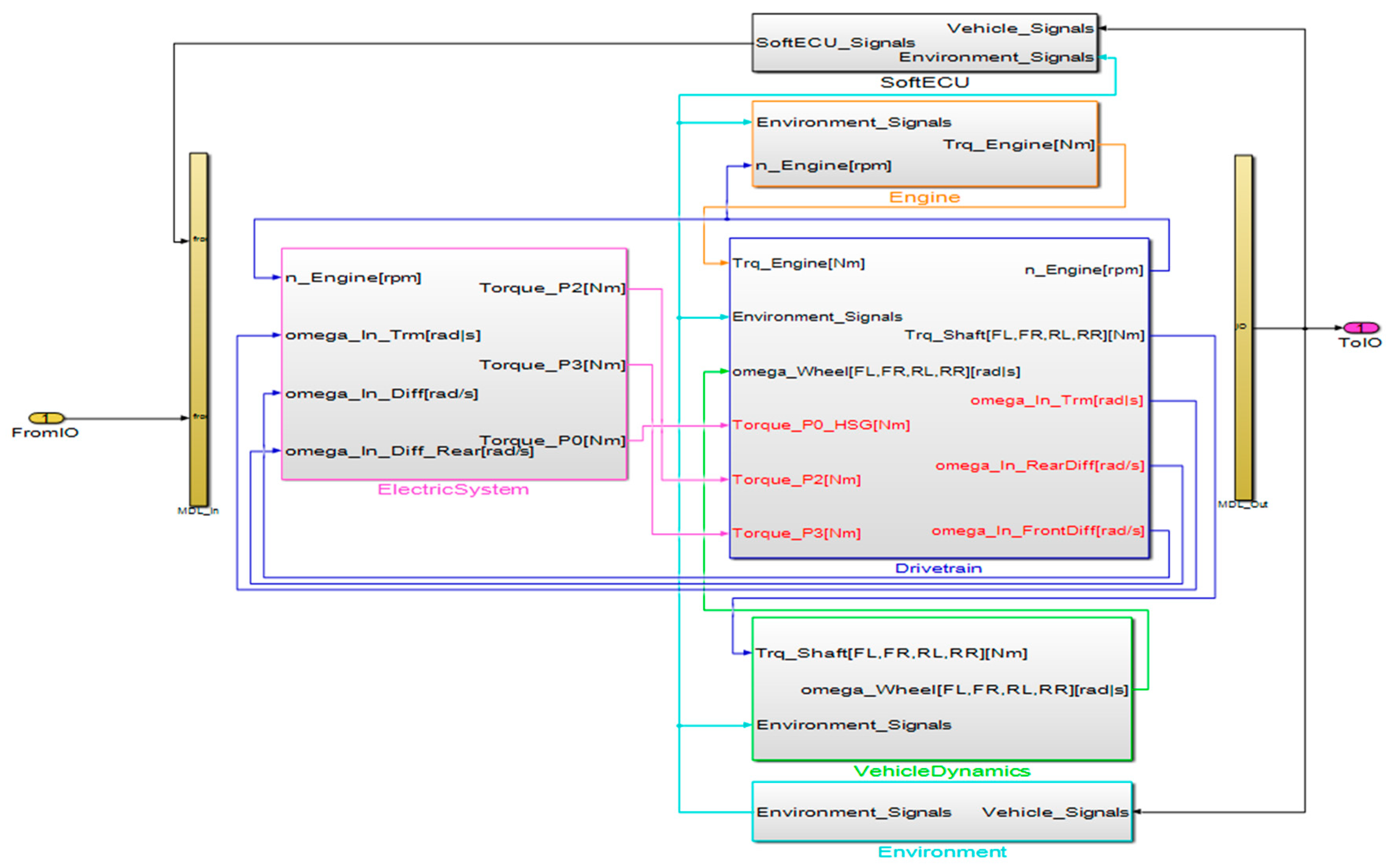
dSPACE Simulator Mid-Size is the compact HIL simulator ideally tailored for testing powertrain, vehicle dynamics, and body ECUs. It typically provides a function for testing ECU such as open-loop or closed-loop tests, function integration tests, and real-time simulation. ASM is used to model the automotive systems such as powertrain, vehicle dynamics, vehicular networks, and automotive ECUs on the Simulator Mid-Size. In the proposed study, a transmission-mounted electric device (TMED)-type hybrid vehicle system is modeled by adding an electric system model to the ASM basic model as shown in Figure 2.
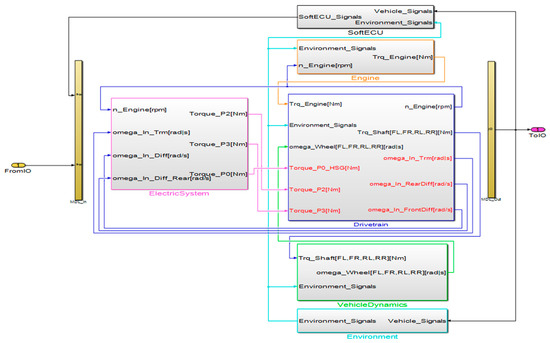
Figure 2.
TMED-type HEV simulation model.
In addition, a manual-driving HIL simulation environment was implemented by attaching a driving controller—such as a racing wheel and pedals—to the HIL simulator, which allows the simulation to handle the human factor. There are three types of software that support driving HIL simulation: dSPACE ModelDesk, ControlDesk, MotionDesk. ModelDesk is a tool for parameterizing ASM models and traffic scenario models. ControlDesk is a software for virtual testing, rapid control prototyping, HIL simulation, and ECU development. It is used to monitor and record HIL simulation data in real-time. MotionDesk is a tool for providing a driving feedback to driver through visualizing the movement of a vehicle in the 3D animation. A driver easily notices not only movement of the host vehicle (HV) but surrounding road environment. Driving environment such as vehicle, road, and traffic lights are constructed by using ModelDesk, and they are visualized by using MotionDesk so that the driver can identify them during simulation.
3.2. dSPACE MicroAutoBox
The dSPACE MicroAutoBox is used as a prototyping environment for development and testing ECU on the vehicle. The MicroAutoBox has all the network interfaces used in an actual vehicle, which enables development and testing of ECUs through interactions with other simulators.
Of the many ECUs in the HEV, one of the key ECUs is the hybrid control unit (HCU), which operates control algorithms for HEV. In the proposed simulation environment, MicroAutoBox was configured as the HCU for the CHEV; it has two hybrid control algorithms—driving mode decision algorithm, and power distribution control algorithm. The algorithms were implemented in a previous study and were modified for the TMED-type CHEV in this study [26]. The driving mode decision algorithm selects driving mode based on vehicle status such as state of charge of battery, engine speed, and pedal pressure. The power distribution control algorithm calculates an engine and motor torque in accordance with a driving mode. HCU control algorithms were modeled using Matlab/Simulink, and ControlDesk was used for measurement and monitoring of simulation data.
3.3. QualNet
In the proposed study, a QualNet 4.5 was utilized as the network simulator. QualNet was used to model and simulate vehicular networks, including various protocols at different layers of the protocol stack, and the wireless communication channel. QualNet provides a comprehensive set of network models for the entire protocol stack from the application to the physical layer and includes a variety of ad hoc routing protocols. It also includes high-fidelity wireless models that incorporate physical environmental effects (e.g., fading, path loss, and shadowing). Extensive performance metrics for a complete understanding of network behavior can be collected, including the throughput, latency, and dropped packets. However, QualNet does not contain an IEEE 802.11p/wireless access in vehicular environment (WAVE) protocol, which is standard for vehicular communication systems, and thus we implemented IEEE 802.11p PHY/MAC by enhancing the IEEE 802.11a module included in the QualNet library, after which we implemented the WAVE/1609 communication stack to simulate the VANET environment. In addition, suitable channel models for V2X communication were implemented within QualNet, such as the Nakagami fading model, two-ray path loss model, and corner path loss model, based on the results of the V2X communication performance test using the actual device on various road environments. With these protocol stacks and channel models, V2X communication can be accurately simulated.
To interact with external entities such as other simulators and programs, two external interfaces were implemented within QualNet. One of the external interfaces is the location synchronization interface (LocaI) which allows QualNet to update the movement information of nodes with the movement information provided by other simulators. In the proposed simulation environment, the LocaI server was implemented within QualNet and the LocaI client was implemented within ASM ControlDesk; in addition, the server–client communicated using user datagram protocol (UDP)/IP to synchronize traffic scenarios between two simulators. Another external interface is an IP network emulation (IPNE), which allows virtual communication packets generated within QualNet to be sent to external programs or hardware on a real network. Further, it allows QualNet to receive real communication packets generated within external programs or hardware on a real network. In the proposed simulation environment, QualNet sent virtual V2X messages collected by the HV in QualNet to the V2X communication device through the IPNE.
3.4. Cohda Wireless MK5
In the proposed study, the Cohda Wireless MK5 device was used to transmit and receive real V2X communication messages in the CHEV, and to develop V2X applications. Two models of MK5 were used—on board unit (OBU) for vehicles and roadside unit (RSU) for infrastructures, each generating and transmitting V2V communication messages and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication messages.
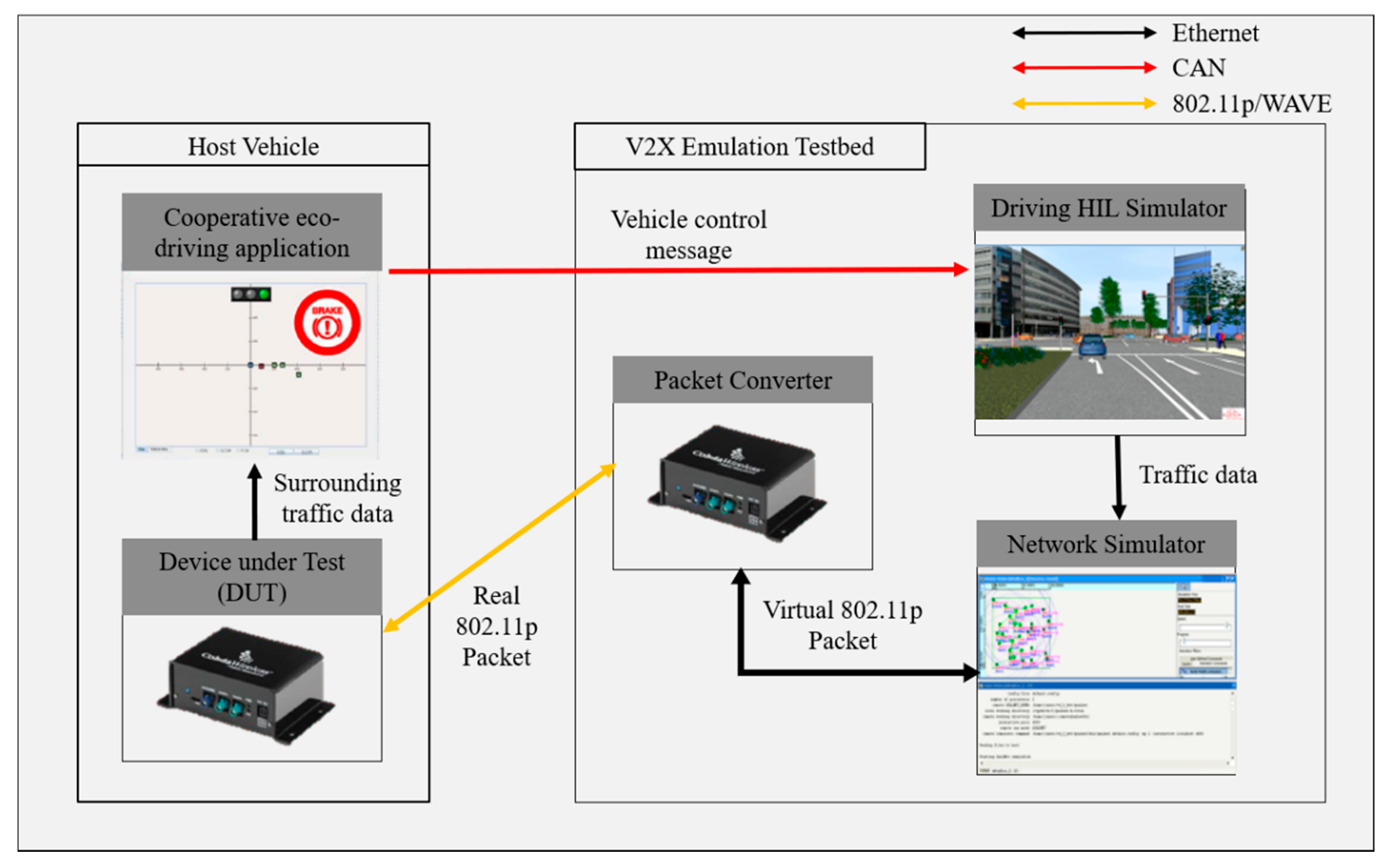
The MK5 device used in the proposed test bed has two roles. The first role is a packet converter for packet emulation. Packet emulation is a means of converting virtual network packets generated by a network simulator into real network packets and vice versa, such that real network devices can receive virtual V2X communication messages through a real V2X communication channel, which is often used for lab testing. The packet converter converts a virtual V2X message into a real V2X message whenever the node mapped to the HV receives the V2X message from a surrounding virtual node in QualNet and transmits the message through a real V2X communication channel. By contrast, it also converts a real V2X message into a virtual V2X message whenever it receives the real V2X message from the device under test (DUT) and transfers the message to the virtual node of the HV in QualNet. The second role is the DUT for developing and operating cooperative eco-driving applications. DUT is one of the ECUs composing the CHEVs, enabling HIL testing of V2X communication protocols and V2X applications. DUT receives the V2X messages generated by the surrounding virtual nodes during the simulation, and then operates a cooperative eco-driving application and transfers the results of the application to driving HIL simulator. Figure 3 shows the V2X network emulation architecture using the V2X device and network simulator.
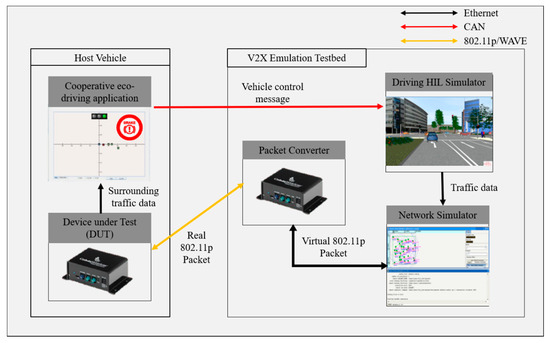
Figure 3.
V2X network emulation using V2X communication devices.
3.5. Interaction between Simulators
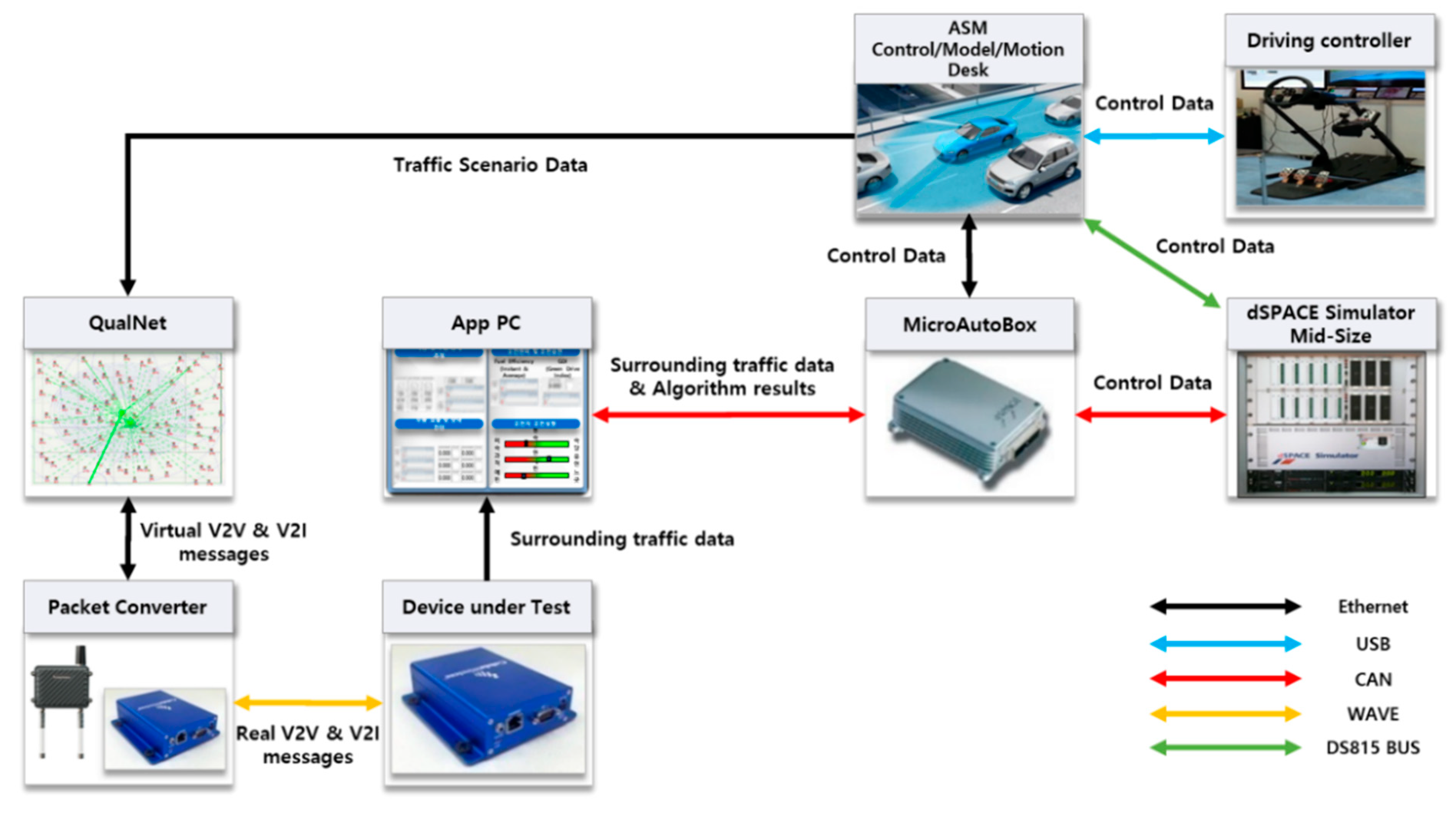
Figure 4 shows the interface and data flow for the interaction between each component composing the IDHIL simulator. First, to synchronize traffic scenario data between the ASM ModelDesk and QualNet, QualNet receives traffic scenario data periodically from the ethernet-connected ASM PC through LocaI. QualNet immediately updates the traffic data of virtual nodes which broadcast V2X messages based on the current state every 100 ms. Whenever a virtual HV node receives virtual V2X messages from the surrounding virtual node, QualNet passes the messages to the packet converter through ethernet. The packet converter converts virtual V2X messages into real V2X messages and transmits them to the DUT through the 802.11p wireless channel. DUT passes traffic data received from the surrounding nodes to the attached application PC through ethernet. The application PC operates the cooperative eco-driving application and informs a driver of the application results by visual, audible, and tactual methods, which helps a driver drive more fuel-efficiently. In addition, the application results and the surrounding traffic data are used to operate hybrid control algorithms running on HCU, and thus the application PC passes the results and data to the HCU running on MicroAutoBox through the controller area network (CAN). In the MicroAutoBox, the HCU operates a hybrid control algorithm, e.g., a driving mode decision algorithm, by using the current vehicle state data of the HV from the HIL simulator and surrounding traffic data from the application PC. During the simulation, the driving controller transmits a control data of the driver through the USB to the ASM PC, which leads to the operation of ECUs within MicroAutoBox and Simulator Mid-Size.
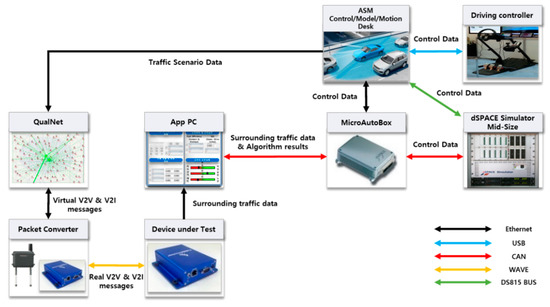
Figure 4.
Data flow of IDHIL simulator.
Components with ethernet connection exchanged packets through the UDP within the private local network formed using only a network switch to avoid unwanted connections, and thus they had a low delay of within 1 ms. Wireless communication between the packet converter and DUT had an extremely low communication delay within 0.1 ms because they were in a lab testing environment having a line-of-sight (LOS) and very short distance between them. Therefore, it was assumed that the communication delay between the packet converter and the DUT was included in the communication delay of the virtual V2X message received by the virtual node mapped to the HV within QualNet.
4. Evaluation
4.1. Cooperative Eco-Driving Speed Guidance Application
A representative application of a cooperative eco-driving system is a cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application. The cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application provides the driver with an eco-speed that improves the fuel efficiency by utilizing the dynamic information contained in the V2X messages. A CHEV can perceive objects within a distance of up to 1 km using V2X communication [27]. Therefore, a CHEV recognizes upcoming events by receiving V2X messages from surrounding nodes within the communication range, while the cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application provides an eco-speed for driver to drive economically in response to the events.
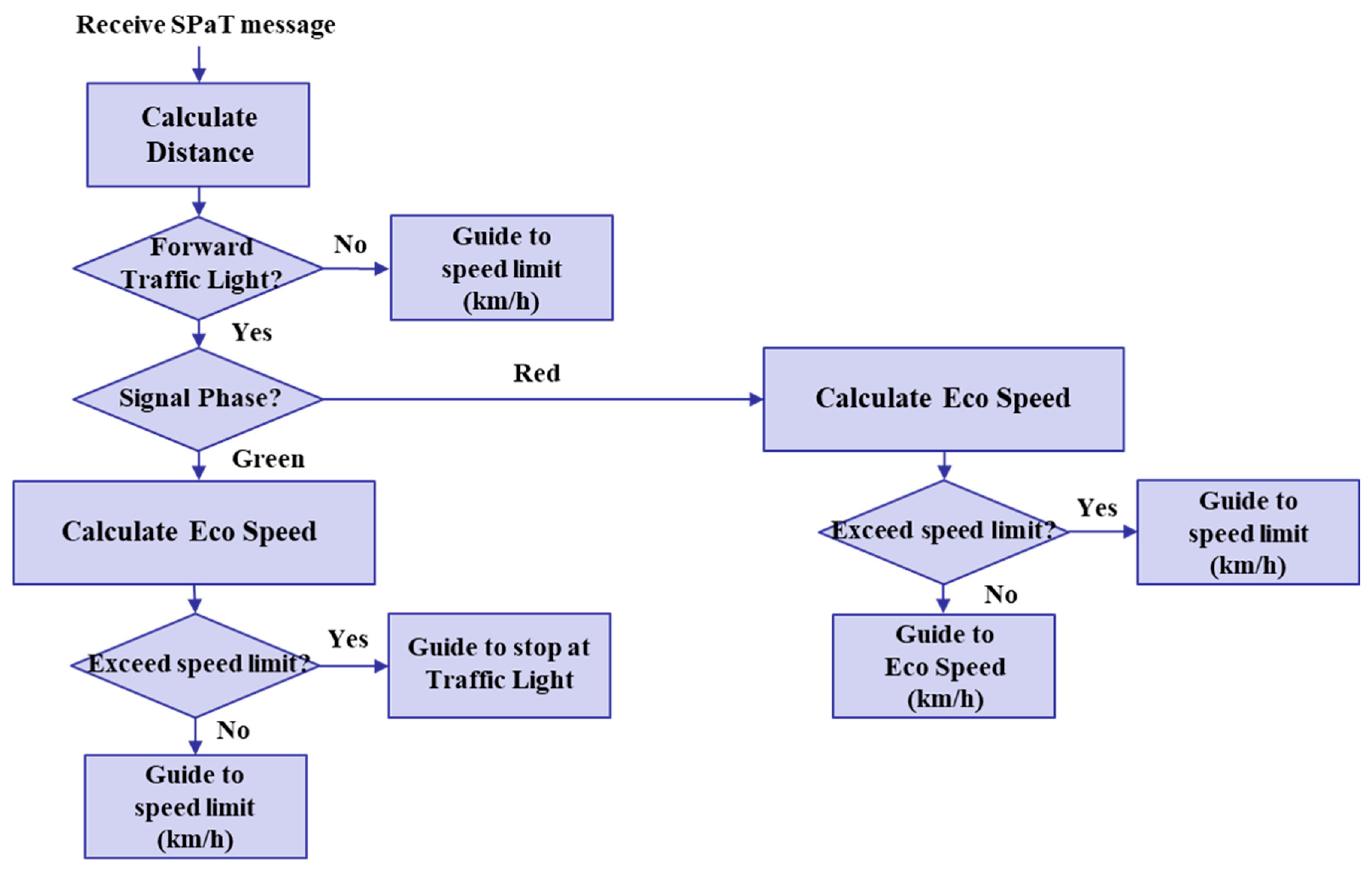
To demonstrate the performance of the proposed IDHIL simulator, we considered a scenario of exchanging traffic light signal information through V2I communication between a HV and traffic lights in an urban intersection driving environment. The cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application in DUT is operated to calculate and provide the driver with the eco-speed using the received V2I messages from the traffic lights, which are the signal phase and timing (SPaT) messages. A flowchart of the implemented cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application is shown in Figure 5. The application operates whenever the HV receives a SPaT message. The performance of the cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application is evaluated by comparing the total fuel consumption between driving with eco-speed and when driving without it. Consequently, the comparison results prove the effectiveness of the IDHIL simulator.
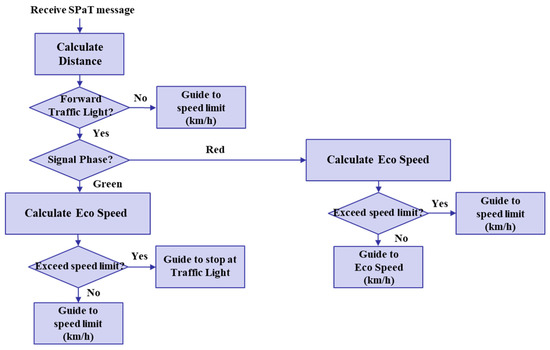
Figure 5.
Flowchart of cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application.
4.2. Setup
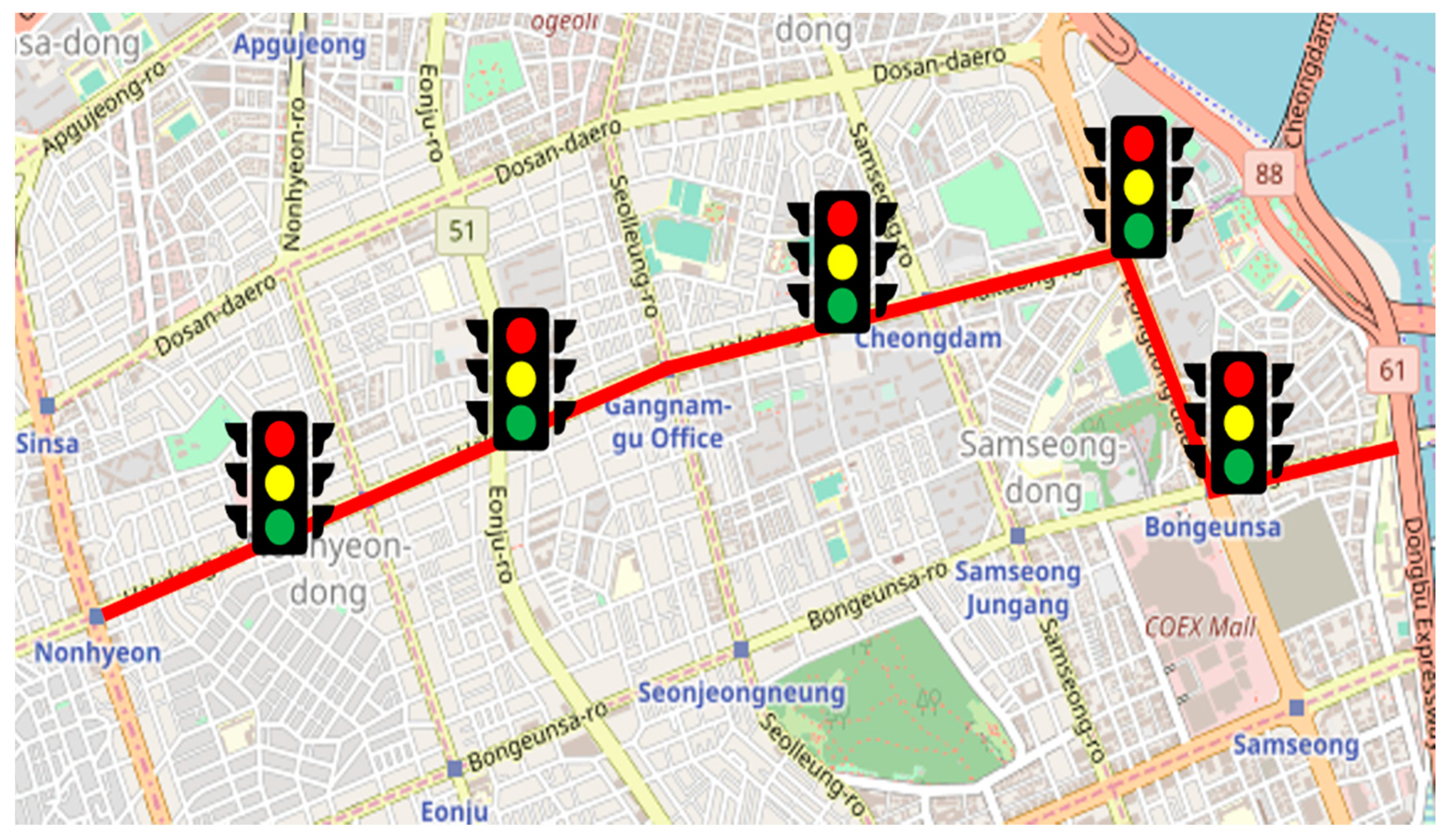
To simulate the behavior of the vehicles in a simulation environment as accurately as possible, the actual road information should be reflected in the simulation environment. In particular, the slope of the road has to be considered because it significantly affects the fuel consumption of the vehicle. Therefore, we used survey equipment to survey the map data used for the simulation, including the altitude. The driving route (marked with the red line) along with the traffic lights are shown in Figure 6. Based on the map data surveyed, an urban intersection driving environment was implemented within the ASM ModelDesk.
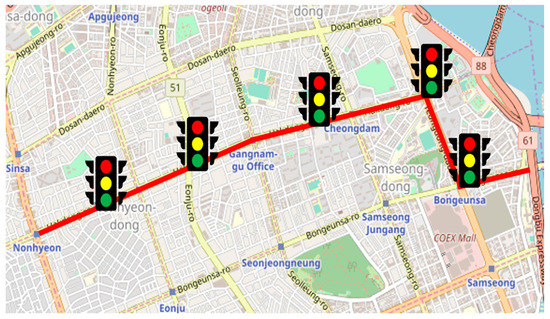
Figure 6.
Driving route on map with traffic lights.
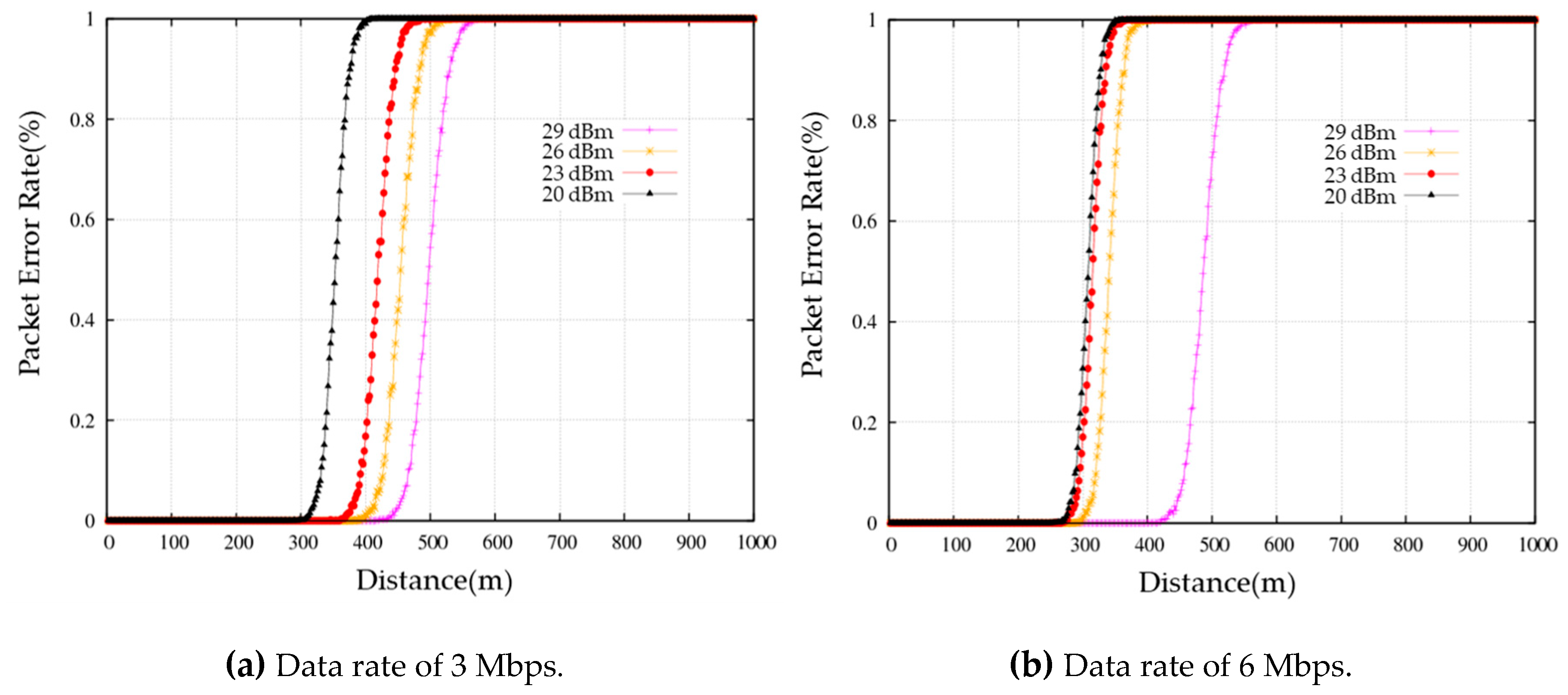
To simulate the behavior of realistic V2X communication in a simulation environment, the channel in which the actual DUTs are tested should be applied to the simulation environment. We analyzed the performance of the V2X communication in an urban intersection driving environment through field tests using V2X communication devices. Based on the results of the analysis, the characteristics of the V2X communication channel were configured within QualNet. Figure 7 shows the packet error rate of the IEEE 802.11p channel configured within QualNet based on field test results. To model the IEEE 802.11p channel in the urban LOS environment, the reliable path loss and fading models are chosen. For the path loss model, the CORNER model is used as follows:
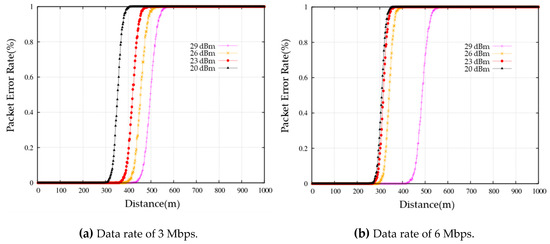
Figure 7.
Packet error rate of V2X communication channel in the urban LOS environment.
Where λ is the wavelength of the propagating signal, and d is the distance between the HV and traffic light [28]. For the fading model, the Nakagami-m model is used. The received fading signal envelope probability density function of the Nakagami-m distribution is given as follows:
where is the gamma function,
which is the average signal power, and
which is the Nakagami distribution shape factor that controls the severity or depth of the fading [29].
The parameters related to the simulation, including the specifications of the HEV model to be used in the simulation, modeled using the ASM, are defined in Table 1.

Table 1.
Parameters in cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application simulation.
4.3. Results
Finally, the effectiveness of the IDHIL simulator is demonstrated by comparing the evaluated results for two cases: (1) normal HEV, and (2) CHEV.
Commonly, most of the fuel consumption of the vehicle occurs when the engine is running due to acceleration. To compare the fuel consumption according to frequency and extent of acceleration and deceleration of a vehicle between the two cases, we set up a scenario to have several conditions. (1) There was one vehicle, i.e., the HV, and five traffic lights. (2) To highlight the effect of V2I communication on the fuel consumption, there should be an obvious difference in the extent of acceleration and deceleration of a vehicle between the two cases. Therefore, the signal timings of the each traffic light were set to prevent the CHEV from stopping at the traffic lights and to let the normal HEV stopping at the traffic lights, and thus the driver always perceived the red signal phase, which was going to turn green signal phase soon, when entering each intersection. (3) The driver tried to drive at the speed limit or eco-speed. (4) In general, an eco-driving system is evaluated by considering the combination of travel time, travel distance, and fuel consumption. In this experiment, to evaluate the proposed cooperative eco-driving system by comparing only the fuel consumption, the travel time and distance in both cases were same, respectively.
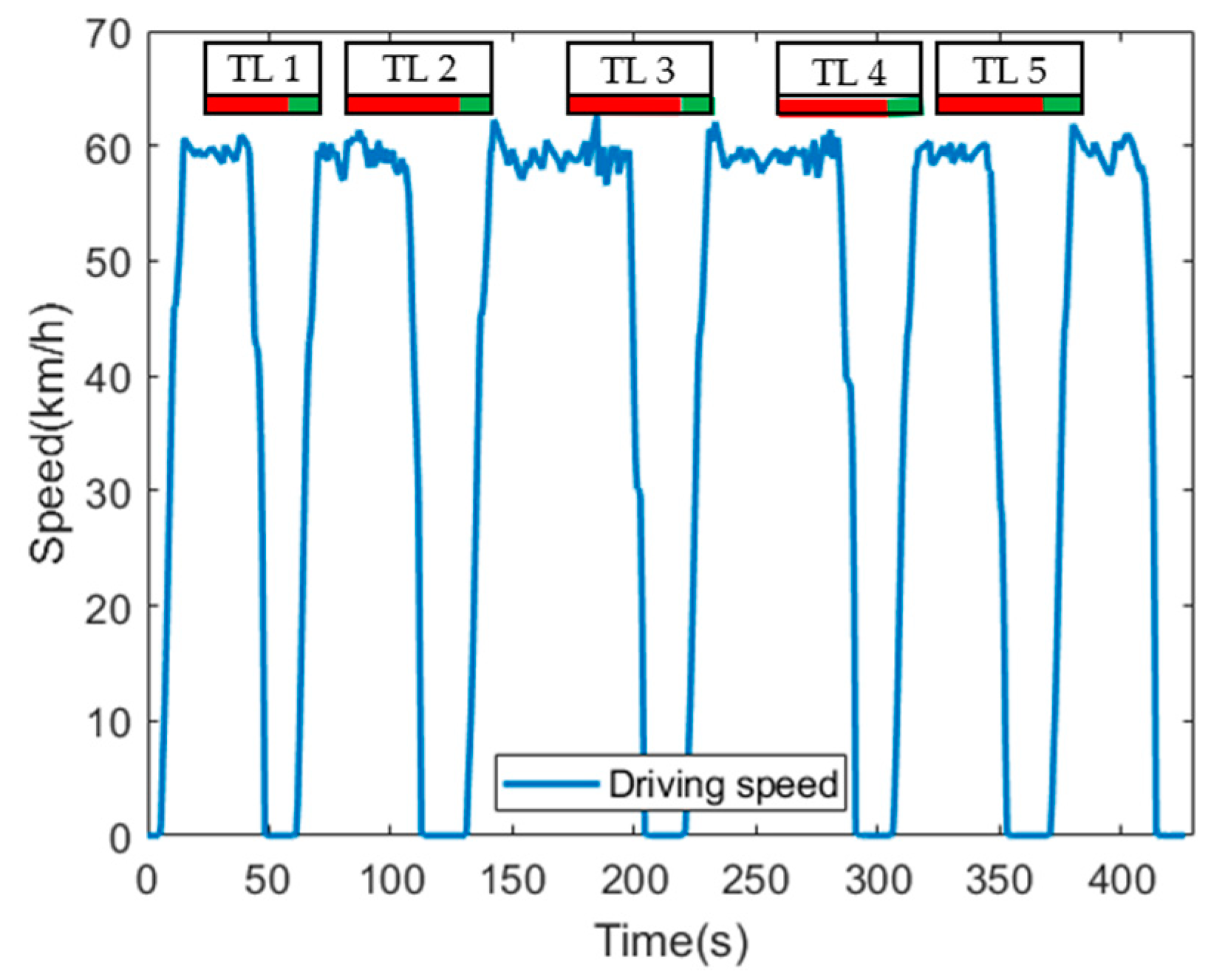
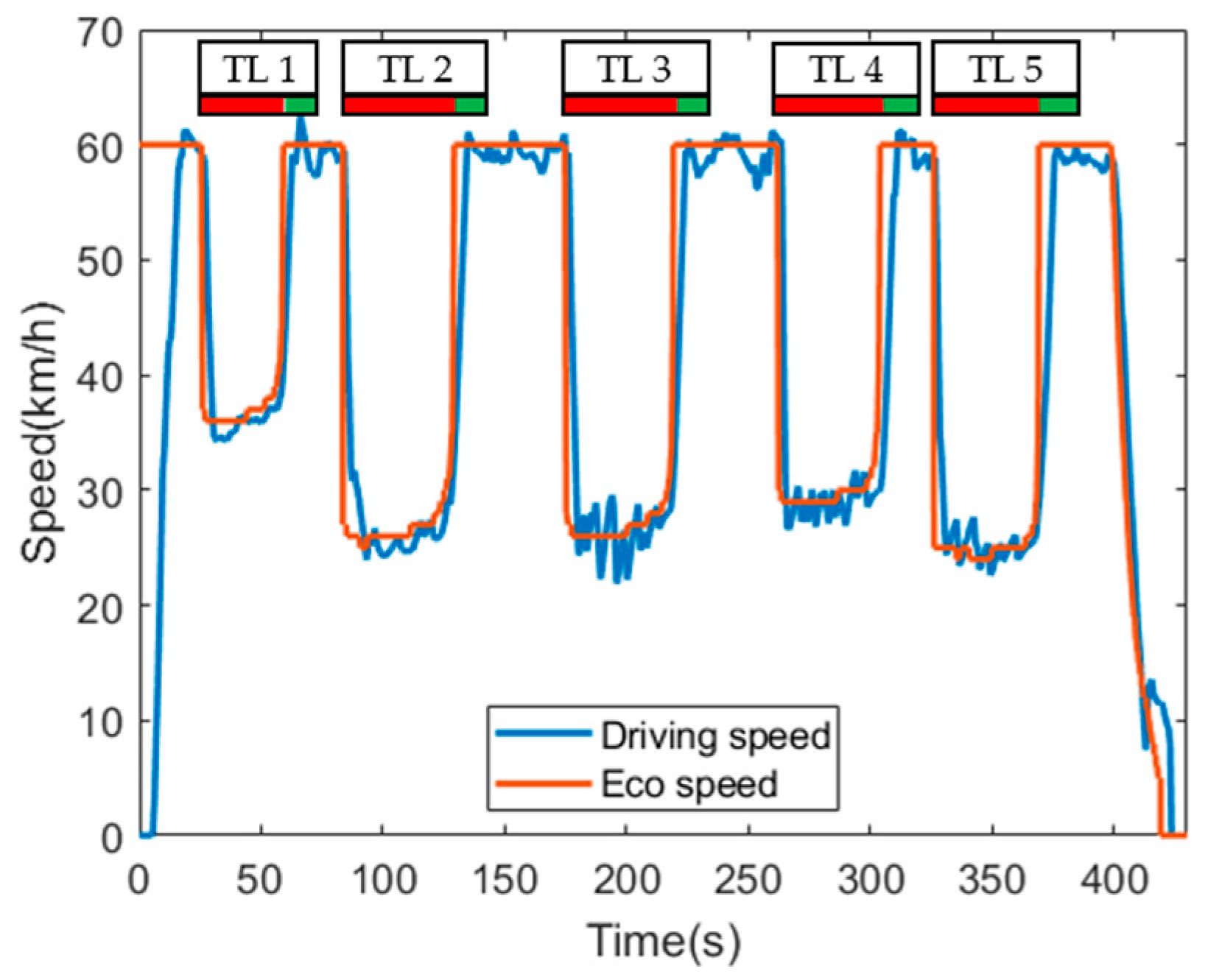
Figure 8 shows the driving speed of the normal HEV during simulation. The signal phase and timing information of each traffic light at the time of approaching the traffic light is also shown at the top of the graph. The time when the signal phase of the traffic light changes to green is 60 s, 130 s, 220 s, 305 s, 370 s, from the first to the fifth traffic light, respectively. The normal HEV was not provided with the eco-speed, so the driver drove at the speed limit until perceiving the traffic light. Since it was a manual driving, the acceleration and deceleration occurred frequently for maintaining the speed limit. The normal HEV perceived a red signal phase 50 m ahead of the traffic light, and then decelerated to stop at the stop line. It waits an average of 20 s at the stop line until the red signal phase changes to the green signal phase, and then accelerated rapidly to speed limit.
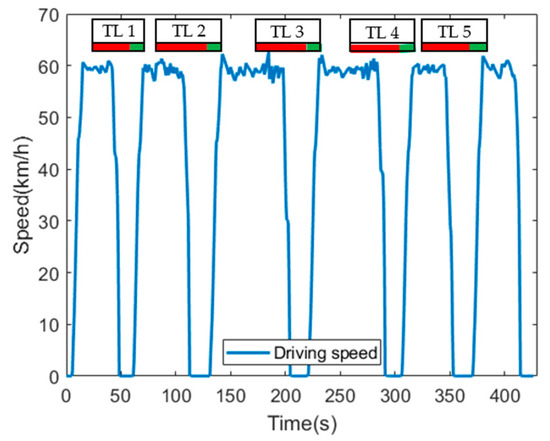
Figure 8.
Driving speed of normal HEV.
Figure 9 shows the driving speed of the CHEV at the eco-speed. In the case of CHEV, the driver was provided with the eco-speed, which is the result of the operation of the cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application, so the driver drove at the eco-speed. Whenever the CHEV entered the communication range of the traffic light, the application noticed that the signal phase was going to turn green signal phase soon after the red signal phase by using the received SPaT message, and the application provided the calculated eco-speed to the driver. When the CHEV received the SPaT message of the first traffic light, the remaining time of the red signal phase was 30 s and the distance was 300 m, so the application provided 36 km/h as the eco-speed that enabled the CHEV to pass through the intersection without stopping. The eco-speed was modified in real-time considering the current vehicle speed because the manual driving made it difficult to maintain the guided eco-speed accurately. After passing through an intersection, the application provided the 60 km/h, which was the speed limit, as the eco-speed until the CHEV received the SPaT message from the next traffic light.
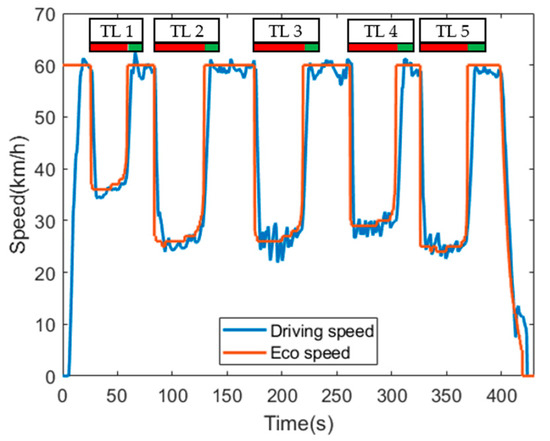
Figure 9.
Driving speed of CHEV.
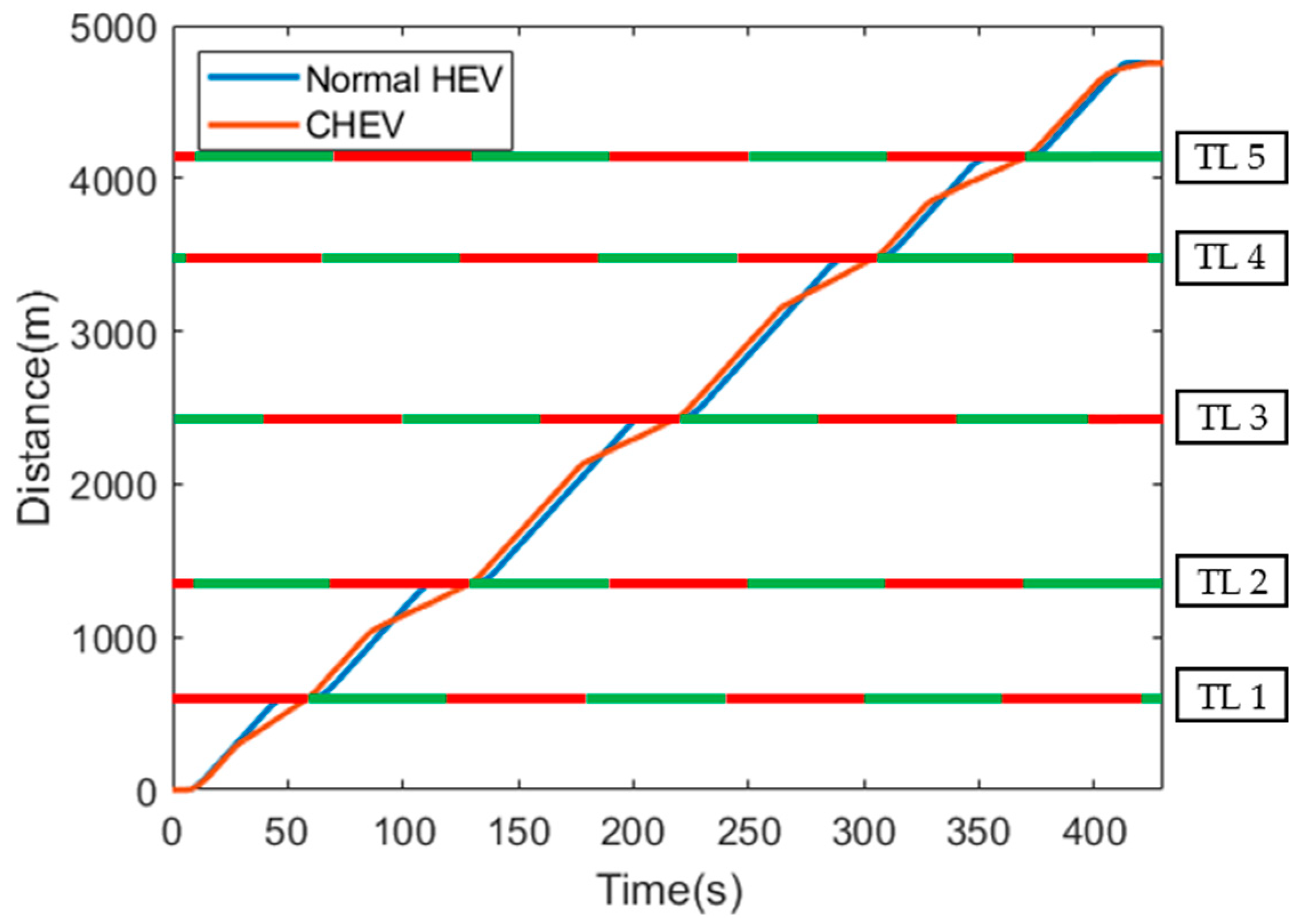
The travel distance of the normal HEV and the CHEV and the signal phase of each traffic light are shown in Figure 10. In both cases, the travel distance and the travel time were the same at 4750 m and 430 s, respectively. Each traffic light was located at 610 m, 1355 m, 2440 m, 3485 m, 4140 m of the travel distance, and the signal cycle of each traffic light was set to 60 s.
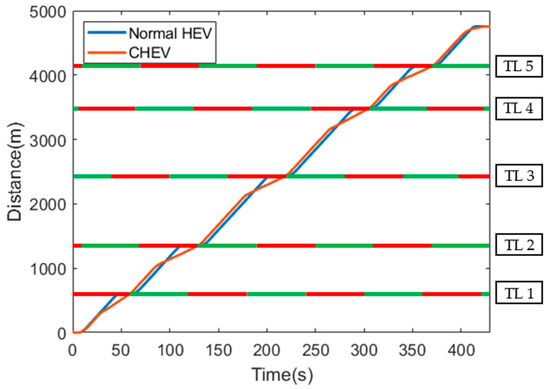
Figure 10.
Distance with traffic light information.
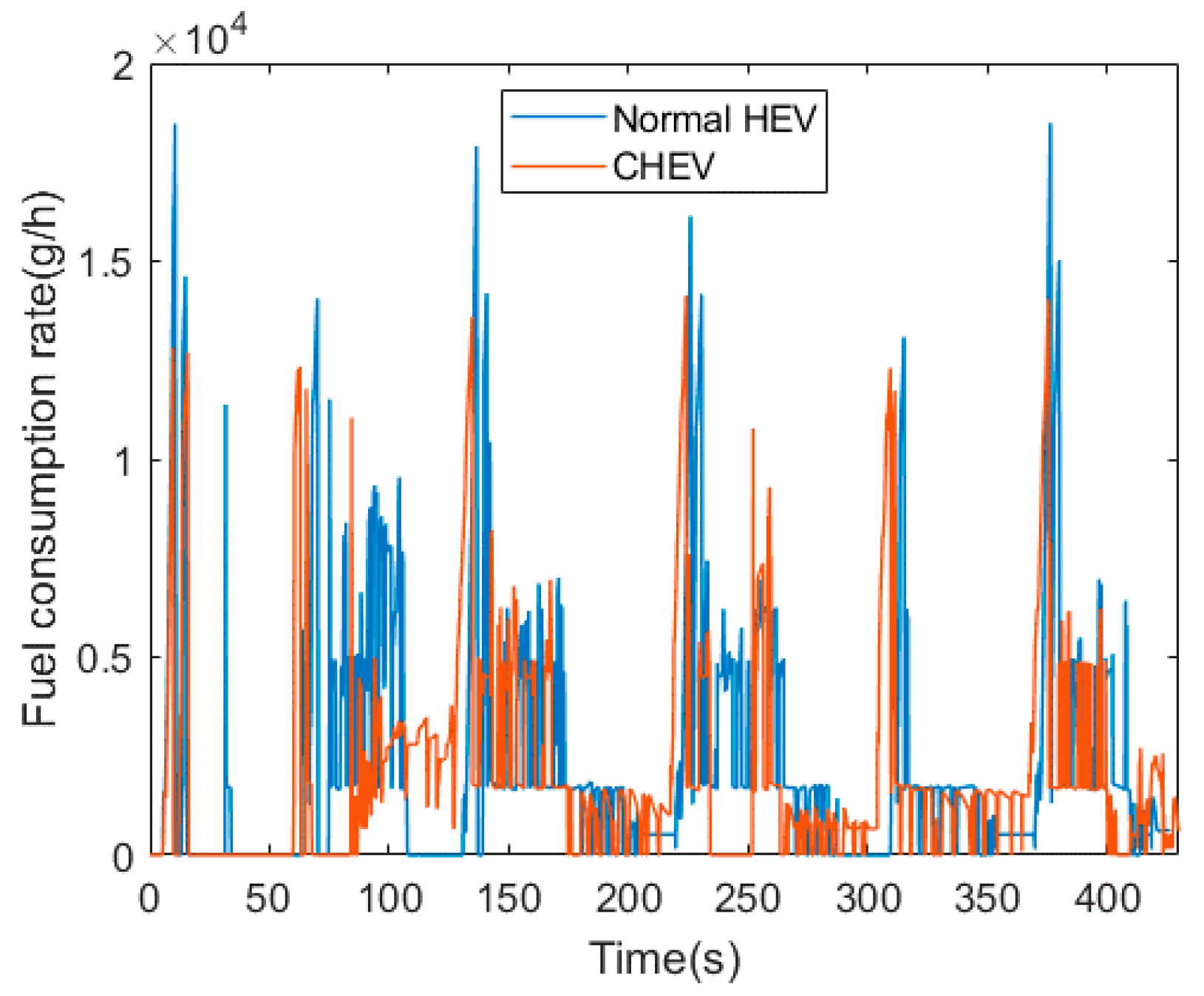
Figure 11 shows the fuel consumption rate of the normal HEV and the CHEV during simulation. The fuel consumption rate varies with the intensity of acceleration, and the fuel consumption rate graph is suitable to indicate the frequency and intensity of acceleration that occurred during the simulation. The normal HEV rapidly increased the speed from 0 km/h to 60 km/h when it passed through the intersection, resulting in significant fuel consumption. Whereas, the CHEV, on average, increased the speed from 25 km/h to 60 km/h in the same situation, so the fuel consumption was relatively low. These results lead to the difference in the total fuel consumption between the two cases.
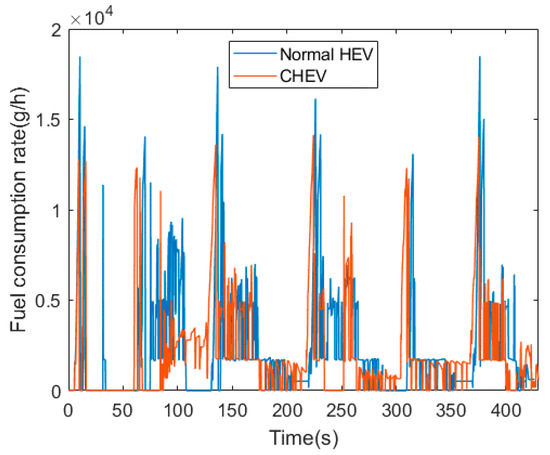
Figure 11.
Fuel consumption rate.
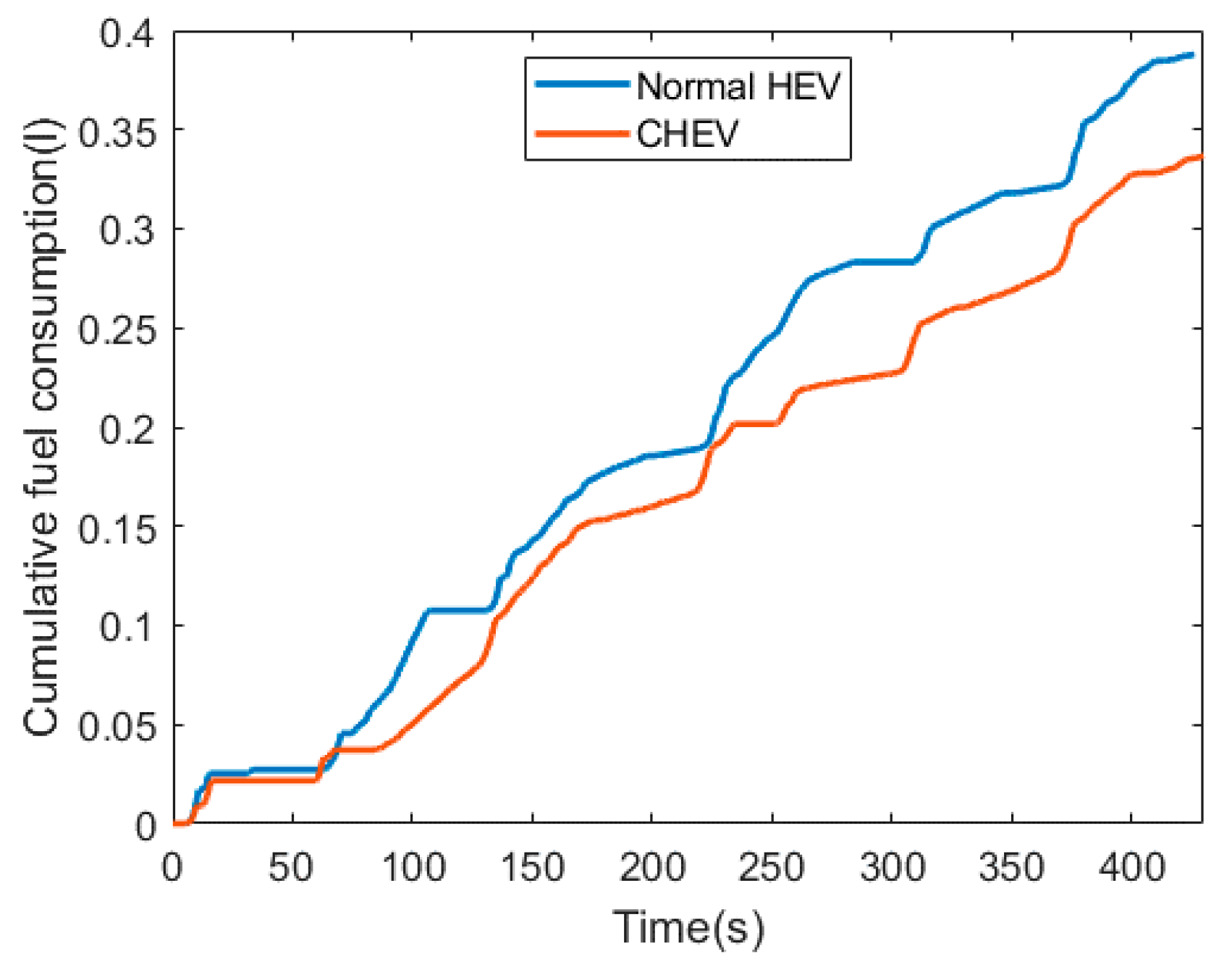
Figure 12 shows the cumulative fuel consumption of the normal HEV and the CHEV. The difference in fuel consumption between both cases increased distinctly when passing through an intersection, and the difference was accumulated during the simulation. As a result, the normal HEV and the CHEV consumed 0.3855 and 0.3368 kg of fuel, respectively. Table 2 shows a comparison of the fuel efficiencies of the normal HEV and the CHEV. The fuel efficiency of the HEV improved by 14.34% with the cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application. This result is reasonable and implies that the IDHIL simulator is useful for developing and evaluating cooperative eco-driving systems.
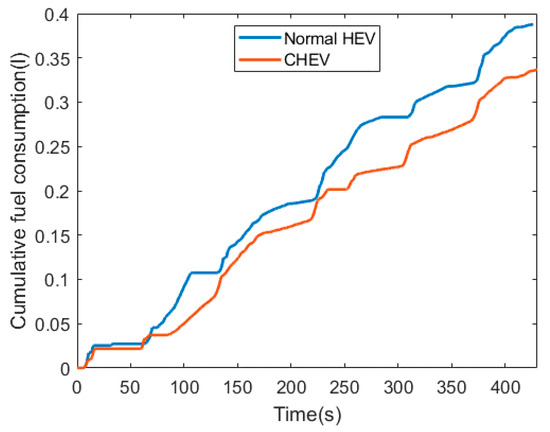
Figure 12.
Cumulative fuel consumption.

Table 2.
Fuel efficiency comparison of normal HEV and CHEV.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents an IDHIL simulator to develop and evaluate cooperative eco-driving systems of CHEV. Using the IDHIL simulator, the systems can be tested under realistic driving environments without huge costs and endangering human lives.
The IDHIL simulator consists of QualNet for V2X communication among nodes, dSPACE simulator Mid-Size for HIL simulation, dSPACE softwares for HEV models and simulation scenarios, dSPACE MicroAutoBox for HCU development, Cohda Wireless MK5 for cooperative eco-driving application development, and a driving controller for manual driving of a user. An example application to demonstrate the IDHIL simulator is cooperative eco-driving speed guidance application using V2I communication between traffic lights and HV. The application notifies the eco-speed calculated using received SPaT message to a driver. As a driver drives at the eco-speed, a CHEV operates driving mode decision and power distribution control algorithms, and thus a CHEV can reduce fuel consumption. In the results, the fuel efficiency has improved by 14.34% when driving with eco-speed. The results demonstrate that the developed algorithms of CHEV are effective, and furthermore, the IDHIL simulator is useful.
To further improve a fuel efficiency of CHEV, a high-level automation of vehicle systems is needed. Therefore, we suggest future research project of implementation of a simulator to develop and evaluate cooperative eco-driving systems for connected and automated vehicle by adding partially and fully automated driving functions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.-i.J.; methodology, J.-i.J., G.L., and S.H.; software, G.L. and S.H.; validation, J.-i.J., G.L., and S.H.; formal analysis, G.L. and S.H.; investigation, G.L. and S.H.; resources, J.-i.J.; data curation, G.L. and S.H.; writing—original draft preparation, G.L. and S.H.; writing—review and editing, J.-i.J.; visualization, G.L.; supervision, J.-i.J.; project administration, J.-i.J.; funding acquisition, J.-i.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology (KEIT) funded by the Republic of Korea (No. 20000578) and the Institute for Information & communication Technology Planning & evaluation (IITP) funded by the Republic of Korea (No. 2019-0-00148). The APC was funded by KEIT (No. 20000578).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Beloufa, S.; Cauchard, F.; Vedrenne, J.; Vailleau, B.; Kemeny, A.; Mérienne, F.; Boucheix, J.M. Learning eco-driving behaviour in a driving simulator: Contribution of instructional videos and interactive guidance system. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2019, 61, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, M.; Bared, J.; Huang, P. Integrated optimal eco-driving on rolling terrain for hybrid electric vehicle with vehicle-infrastructure communication. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2016, 68, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Martinez, J.L.; Calafate, C.T.; Soler, D.; Lemus-Zúñiga, L.-G.; Cano, J.-C.; Manzoni, P.; Gayraud, T. A centralized route-management solution for autonomous vehicles in urban areas. Electronics 2019, 8, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallerbach, S.; Xia, Y.; Eberle, U.; Koester, F. Simulation-based identification of critical scenarios for cooperative and automated vehicles. SAE Intl. J. CAV 2018, 1, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangharam, R.; Weller, D.; Rajkumar, R.; Mudalige, P.; Bai, F. Groovenet: A hybrid simulator for vehicle-to-vehicle networks. In Proceedings of the 2006 Third Annual International Conference on Mobile and Ubiquitous Systems: Networking & Services, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–21 July 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Balcioglu, B.X. Integrated V2V Wireless Network and Vehicular Traffic Simulator Design. Master’s Thesis, Science in the Graduate School of the Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rondinone, M.; Maneros, J.; Krajzewicz, D.; Bauza, R.; Cataldi, P.; Hrizi, F.; Goza-lvez, J.; Kumar, V.; Röckl, M.; Lin, L.; et al. iTETRIS: A modular simulation platform for the large scale evaluation of cooperative its applications. Simul. Model. Pract. Theory 2013, 34, 99–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schünemann, B. V2x simulation runtime infrastructure VSimRTI: An assessment tool to design smart traffic management systems. Comput. Netw. 2011, 55, 3189–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, C.; German, R.; Dressler, F. Bidirectionally coupled network and road traffic simulation for improved IVC analysis. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2011, 10, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajananan, K.; Sontisirikit, S.; Zhang, J.; Miska, M.; Chung, E.; Guha, S.; Prendinger, H. A cooperative ITS study on green light optimization using an integrated traffic, driving, and communication simulator. In Proceedings of the 36th-ATRF, Brisbane, Queensland, Australia, 2–4 October 2013; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Prendinger, H.; Miska, M.; Gajananan, K.; Nantes, A. A cyber-physical system simulator for risk-free transport studies. Comput. Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2014, 29, 480–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wagh, A.; Hou, Y.; Hulme, K.; Qiao, C. Integrated traffic driving- networking simulator for the design of connected vehicle applications: Eco-signal case study. J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2016, 20, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramrattana, M.; Larsson, T.; Jansson, J.; Nåbo, A. A simulation framework for cooperative intelligent transport systems testing and evaluation. Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav. 2019, 61, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibba, G.; Malz, C.; Stoermer, C.; Nagarajan, N.; Zhang, L.; Chakraborty, S. Testing automotive embedded systems under X-in-the-loop setups. In Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Computer-Aided Design ICCAD 2016, New York, NY, USA, 7–10 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- dSPACE, “dSPACE Simulator Mid-Size”. Available online: https://www.dspace.com/en/inc/home/products/hw/simulator_hardware/dspace_simulator_mid_size.cfm (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- dSPACE, “ModelDesk, MotionDesk, ControlDesk”. Available online: https://www.dspace.com/en/inc/home/products/products.cfm (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Scalable Network Technologies, “QualNet (Quality Networking)”. Available online: https://www.scalable-networks.com/products/qualnet-network-simulation-software-tool/ (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- dSPACE, “MicroAutobox II”. Available online: https://www.dspace.com/en/inc/home/products/hw/micautob/microautobox2.cfm (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Cohda Wireless, “MK5”. Available online: https://cohdawireless.com/solutions/hardware/mk5-obu/ (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- dSPACE, “Closed-Loop HIL Testing of V2X-Based Applications”. Available online: https://www.dspace.com/en/inc/home/applicationfields/our_solutions_for/driver_assistance_systems/hil_simulation/closed_loop_hil_system_v2x.cfm (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Kamal, M.A.S.; Mukai, M.; Murata, J.; Kawabe, T. Ecological driver assistance system using model based anticipation of vehicle-road-traffic information. IET J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2010, 4, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Muldoon, S.; Chang, C.F. ‘InfoRich’ eco-driving control strategy for connected and automated vehicles. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 10–12 July 2019; pp. 4621–4627. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, L.; Park, B. Assessing eco-driving behaviors using driving simulator. In Proceedings of the 96th Annual Meeting Transportation Research Board, Washington, DC, USA, 8–12 January 2017; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, K.; Molla, S.K.; Schulze, T. Hybrid vehicle model development using ASM-AMESim-Simscape co-simulation for real-time HIL applications. In Proceedings of the SAE 2012 World Congress & Exhibition, Detroit, MI, USA, 24–26 April 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cantas, M.R.; Kavas, O.; Tamilarasan, S.; Gelbal, S.Y.; Guvenc, L. Use of hardware in the loop (HIL) simulation for developing connected autonomous vehicle (CAV) applications. In Proceedings of the WCX SAE World Congress Experience, Detroit, MI, USA, 13–15 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, S.; Park, T.; Na, W.; Lee, H. Power distribution control algorithm for fuel economy optimization of 48V mild hybrid vehicle. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Modeling and Applied Simulation, Barcelona, Spain, 18–20 September 2017; pp. 185–190. [Google Scholar]
- De Ponte Muller, F. Survey on ranging sensors and cooperative techniques for relative positioning of vehicles. Sensors 2017, 17, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, E.; Frank, R.; Pau, G.; Gerla, M. CORNER: A radio propagation model for VANETs in urban scenarios. Proc. IEEE 2011, 99, 1280–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, N.C.; Cheng, C. Efficient Nakagami-m fading channel simulation. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2005, 54, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).