A Reconfigurable CMOS Inverter-based Stacked Power Amplifier with Antenna Impedance Mismatch Compensation for Low Power Short-Range Wireless Communications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Circuit Design
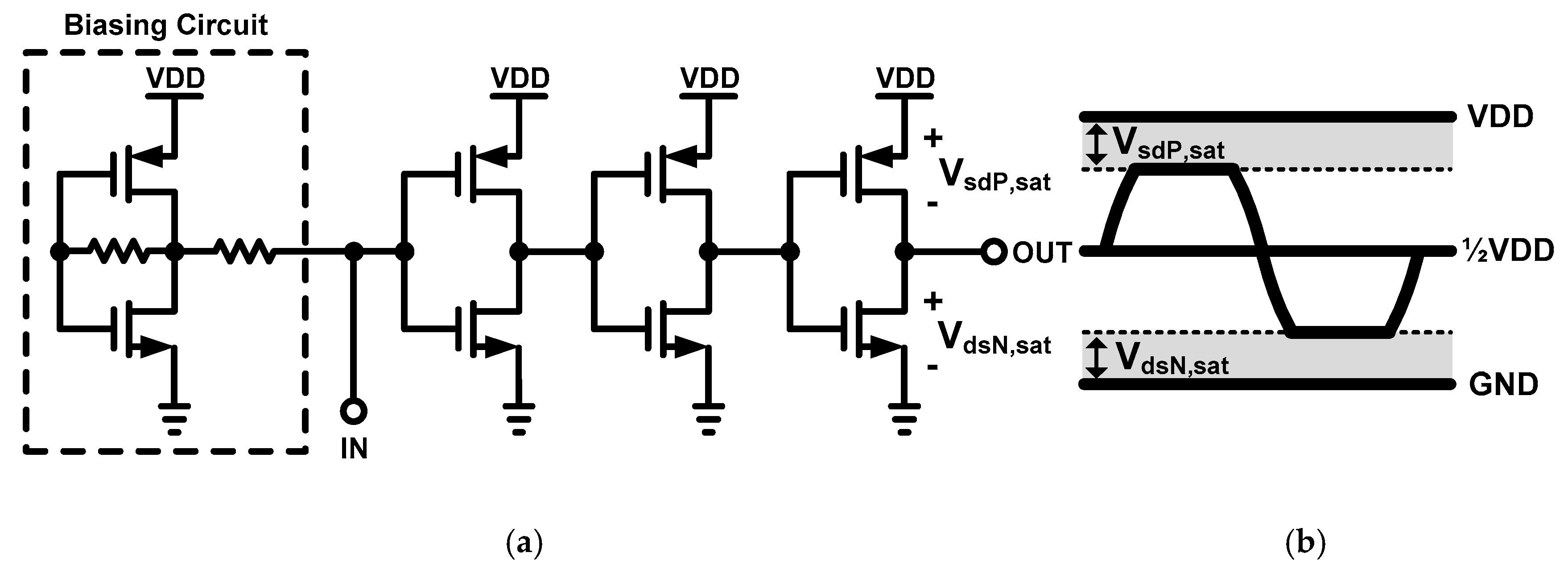
2.1. Conventional Inverter-based PA
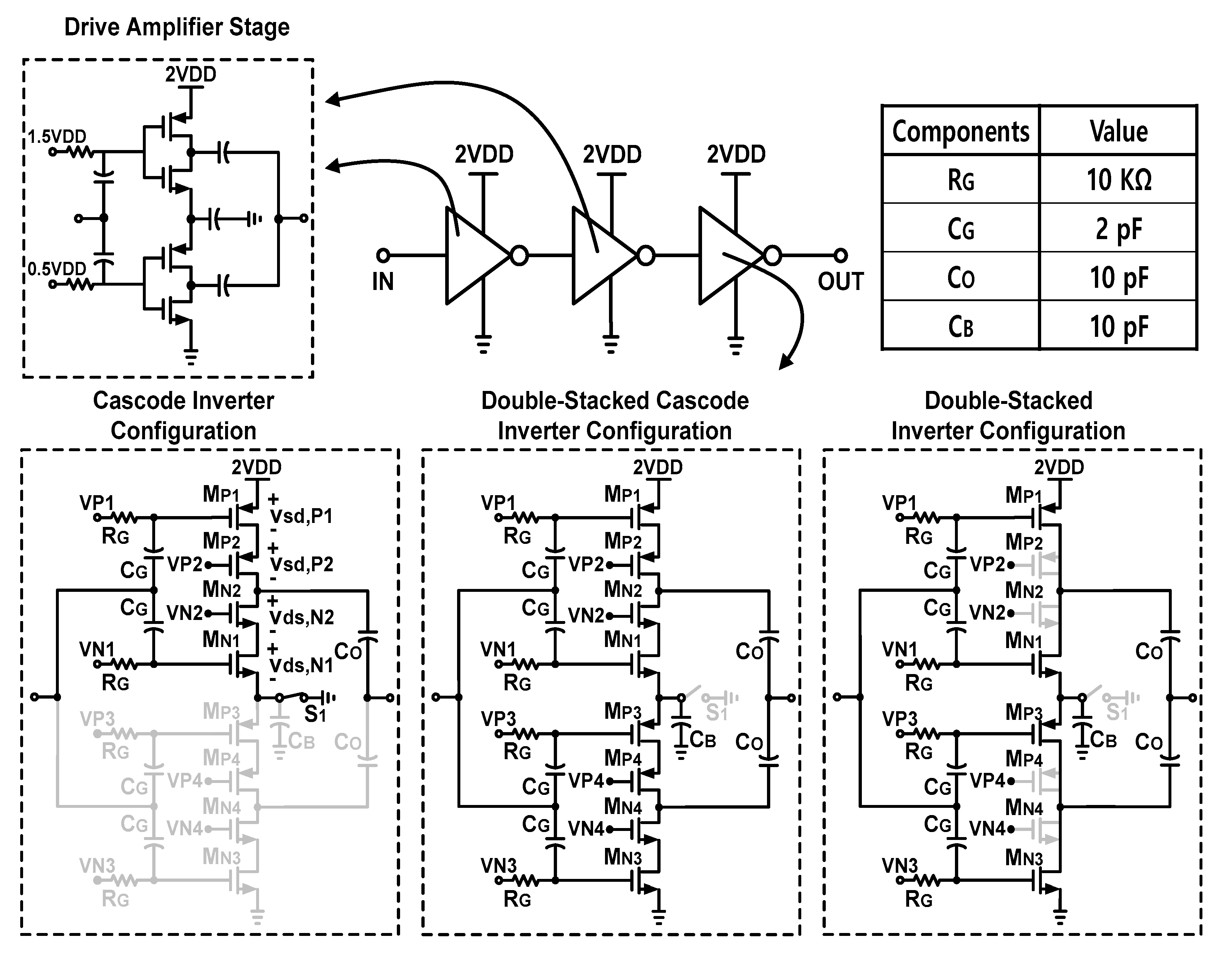
2.2. Proposed Reconfigurable Cascode Inverter-based Stacked PA
3. Simulation Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Keerti, A.; Pham, A.-V.H. RF characterization of SiGe HBT power amplifiers under load mismatch. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2007, 55, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Kim, H.; Kim, H.; Lee, K.; Lee, C.; Kenney, J.S. A 2.4-GHz CMOS power amplifier with an integrated antenna impedance mismatch correction system. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2014, 49, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Bakkaloglu, B.; Aberle, J.T. A CMOS adaptive antenna-impedance-tuning IC operating in the 850MHz-to-2GHz band. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 February 2009; pp. 384–385. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, J.; Kang, M. A ruggedness improved mobile radio frequency power amplifier module with Dynamic impedance correction by software defined atomization. Electronics 2019, 8, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sjöblom, P.; Sjöland, H. An adaptive impedance tuning CMOS circuit for ISM 2.4-GHz band. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2005, 52, 1115–1124. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Q.; Barker, S. Distributed MEMS tunable matching network using minimal-contact RF-MEMS varactors. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2006, 54, 2646–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Lourandakis, E.; Leidl, A.; Seitz, S.; Weigel, R. A comparison of tunable ferroelectric Π- and T-matching networks. In Proceedings of the European Microwave Conference, Munich, Germany, 9–12 October 2007; pp. 98–101. [Google Scholar]
- Retz, G.; Shanan, H.; Mulvaney, K.; O’Mahony, S.; Chanca, M.; Corwley, P.; Billon, C.; Khan, K.; Quinlan, P. A Highly Integrated Low-Power 2.4GHz Transceiver Using a Direct-Conversion Diversity Receiver in 0.18 μm CMOS for IEEE 802.15.4 WPAN. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 February 2009; pp. 414–415. [Google Scholar]
- Zolfaghari, A.; Said, M.E.; Youssef, M.; Zhang, G.; Liu, T.T.; Cattivelli, F.; Syllaios, Y.I.; Khan, F.; Fang, F.Q.; Wang, J.; et al. A Multi-Mode WPAN (Bluetooth, BLE, IEEE 802.15.4) SoC for Low-Power and IoT Applications. In Proceedings of the Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 5–8 June 2017; pp. 74–75. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Hu, D.Y.; Lam, C.K.; Cui, J.Q.; Soh, L.K.; Song, D.C.; Zhong, X.W.; Hor, H.C.; Heng, C.L. A +8 dBm BLE/BT Transceiver with Automatically Calibrated Integrated RF Bandpass Filter and −58 dBc TX HD2. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2017; pp. 136–137. [Google Scholar]
- Paidimarri, A.; Nadeau, P.; Mercier, P.; Chandrakasan, A. A 2.4 GHz Multi-Channel FBAR-based Transmitter with an Integrated Pulse-Shaping Power Amplifier. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2013, 48, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiumarsi, H.; Mizuochi, Y.; Ito, H.; Ishihara, N.; Masu, K. A Three-stage inverter-based stacked power amplifier in 65 nm complementary metal oxide semiconductor process. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 02BC01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Langevelde, R.; van Elzakker, M.; Van Goor, D.; Termeer, H.; Moss, J.; Davie, A.J. An ultra-low-power 868/915 MHz RF transceiver for wireless sensor network applications. Proceedings of IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Boston, MA, USA, 7–9 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, K.; Chen, S. An ultralow-power wake-up receiver based on direct active RF detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2017, 64, 1661–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, C.; Cheng, K. A 4.5 μW 2.4 GHz wake-up receiver based on complementary current-reuse RF detector. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Lisbon, Portugal, 24–27 May 2015; pp. 1214–1217. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Chia, M. A low-power ultra-wideband CMOS true RMS power detector. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2008, 56, 1052–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prummel, J.; Papamichail, M.; Ancis, M.; Willms, J.; Todi, R.; Aartsen, W.; Kruiskamp, W.; Haanstra, J.; Opbroek, E.; Rievers, S.; et al. A 10 mW bluetooth low-energy transceiver with on-chip matching. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2015, 50, 3077–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, T.; Mizokami, M.; Matsui, H.; Ueda, K.; Shibata, K.; Toyota, K.; Saitou, T.; Sato, H.; Yahagi, K.; Hayashi, Y. A 6.3mW BLE transceiver embedded RX image-rejection filter and TX harmonic-suppression filter reusing on-chip matching network. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC) Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015; pp. 240–241. [Google Scholar]
- Masuch, J.; Delgado-Restituto, M. A 1.1-mW-RX 81.4 dBm sensitivity CMOS transceiver for bluetooth low energy. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 1660–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| PA | 1 Proposed PA | 2 [17] | 2 [18] | 2 [19] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIC | DSCIC | DSIC | ||||
| CMOS Technology (nm) | 65 | 55 | 40 | 130 | ||
| Supply Voltage (V) | 2.4 | 0.9–3.3 | 1.1 | 1 | ||
| Output Matching Network | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Saturated Power (Psat) (dBm) | +6.1 | +4.5 | +5.2 | 0 | 0 | 1.6 |
| PA Efficiency @ Psat (%) | 41.1% | 44.3% | 37.1% | 30.0% | <30% | 26.8% |
| Strongest Harmonic Emission (dBm) | 3 HD3 −27 | 3 HD3 −20 | 3 HD3 −31 | 4 HD3 −52 | 4 HD3 −48 | 4 HD3 −32 |
| Power Consumption @ Psat (mW) | 9.8 | 6.2 | 8.8 | 5 10.1 | 5 7.7 | 5 5.9 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-M.; Kim, D.; Jeong, H.-G.; Im, D. A Reconfigurable CMOS Inverter-based Stacked Power Amplifier with Antenna Impedance Mismatch Compensation for Low Power Short-Range Wireless Communications. Electronics 2020, 9, 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040562
Kim D-M, Kim D, Jeong H-G, Im D. A Reconfigurable CMOS Inverter-based Stacked Power Amplifier with Antenna Impedance Mismatch Compensation for Low Power Short-Range Wireless Communications. Electronics. 2020; 9(4):562. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040562
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Dong-Myeong, Dongmin Kim, Hang-Geun Jeong, and Donggu Im. 2020. "A Reconfigurable CMOS Inverter-based Stacked Power Amplifier with Antenna Impedance Mismatch Compensation for Low Power Short-Range Wireless Communications" Electronics 9, no. 4: 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040562
APA StyleKim, D.-M., Kim, D., Jeong, H.-G., & Im, D. (2020). A Reconfigurable CMOS Inverter-based Stacked Power Amplifier with Antenna Impedance Mismatch Compensation for Low Power Short-Range Wireless Communications. Electronics, 9(4), 562. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040562





