A Survey on LiDAR Scanning Mechanisms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LiDAR Architecture Overview
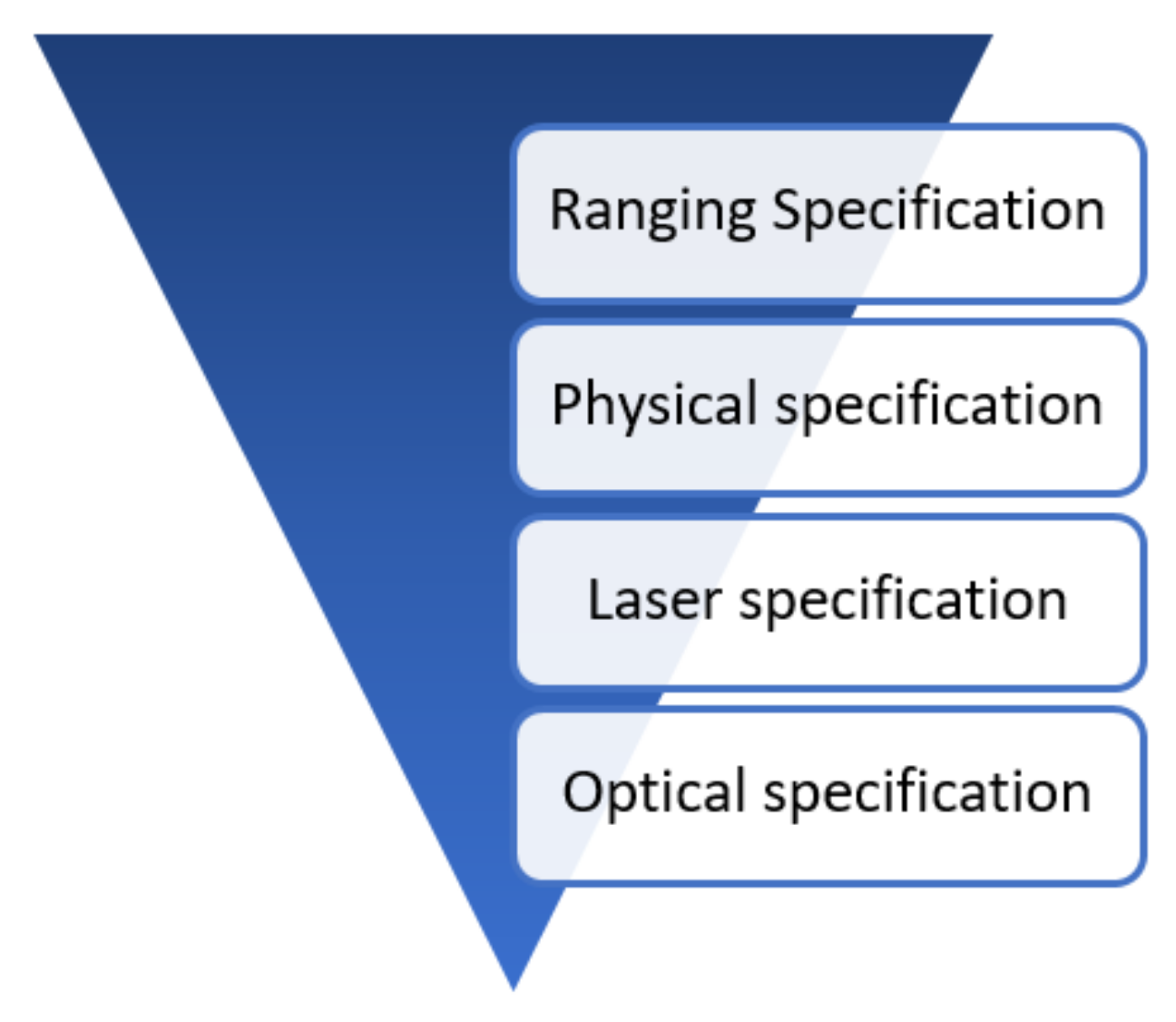
2.1. LiDAR Specifications
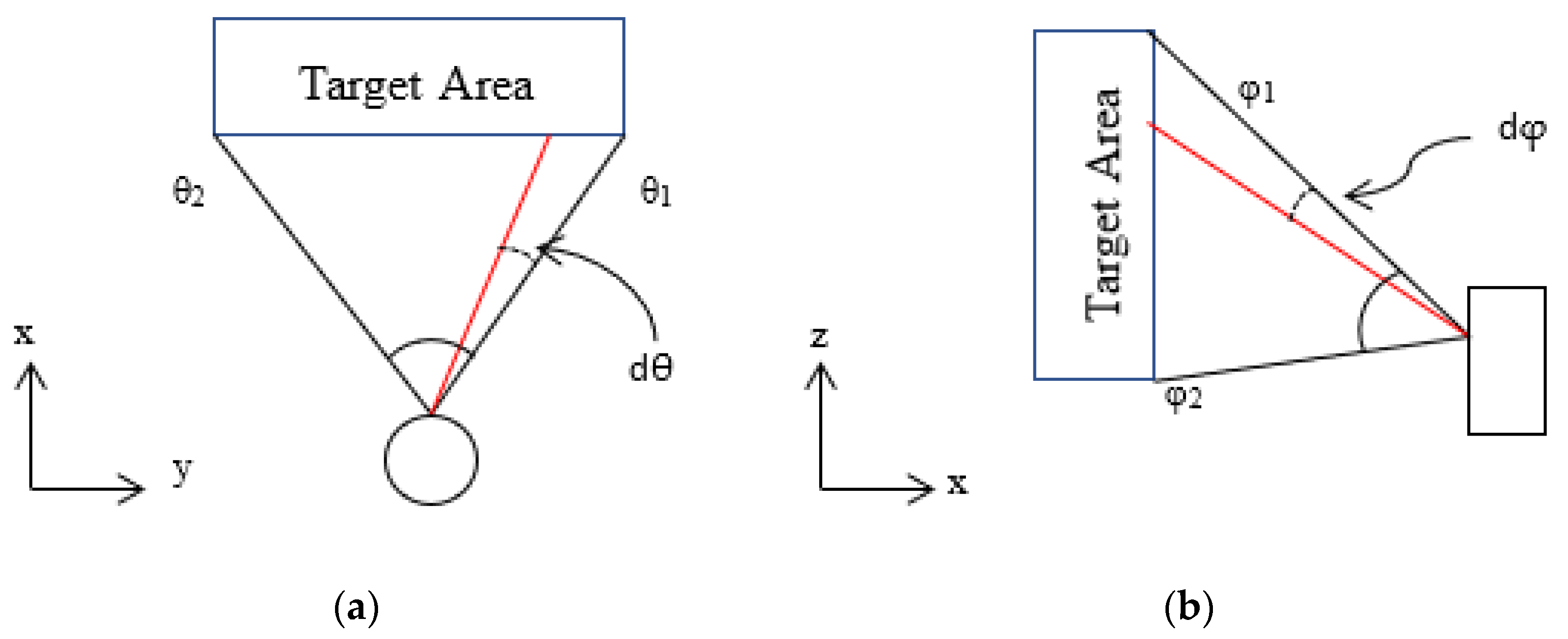
2.2. Beam Scanner Specifications
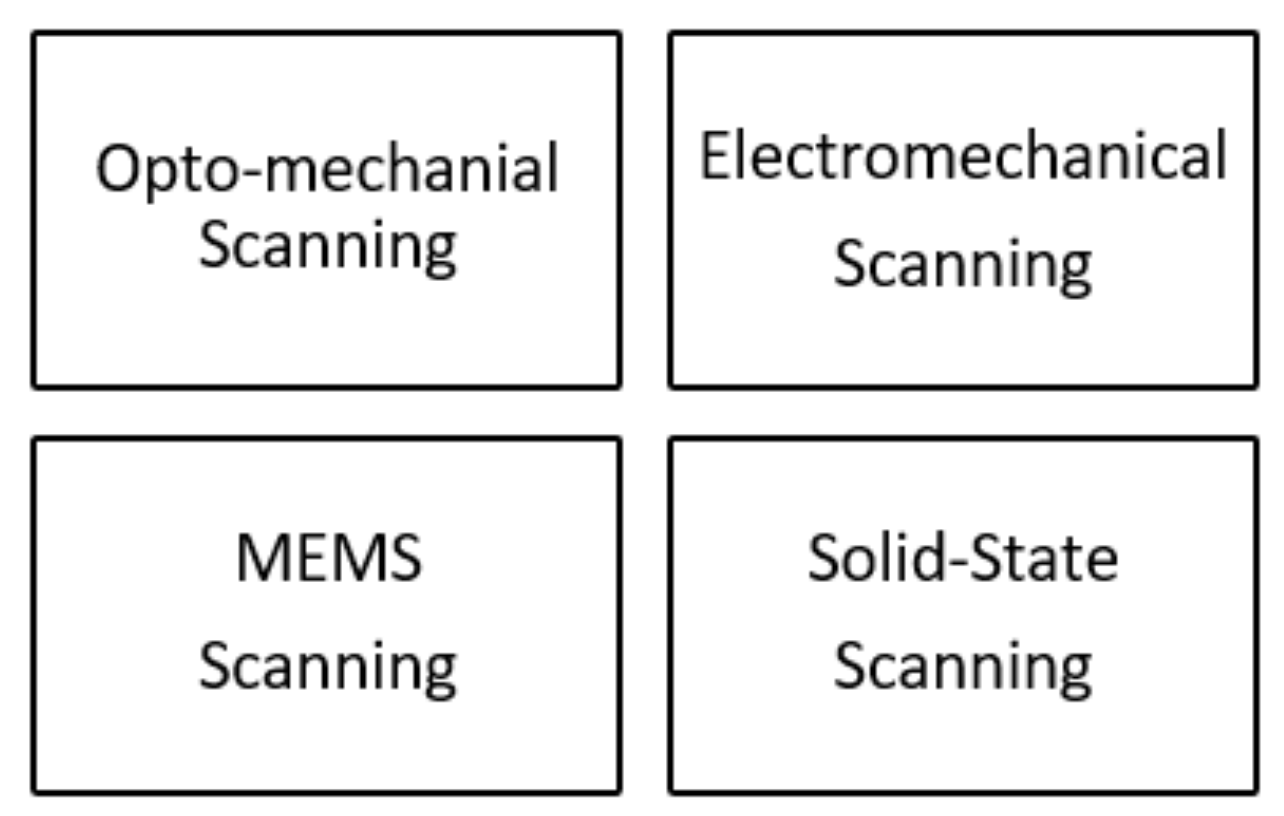
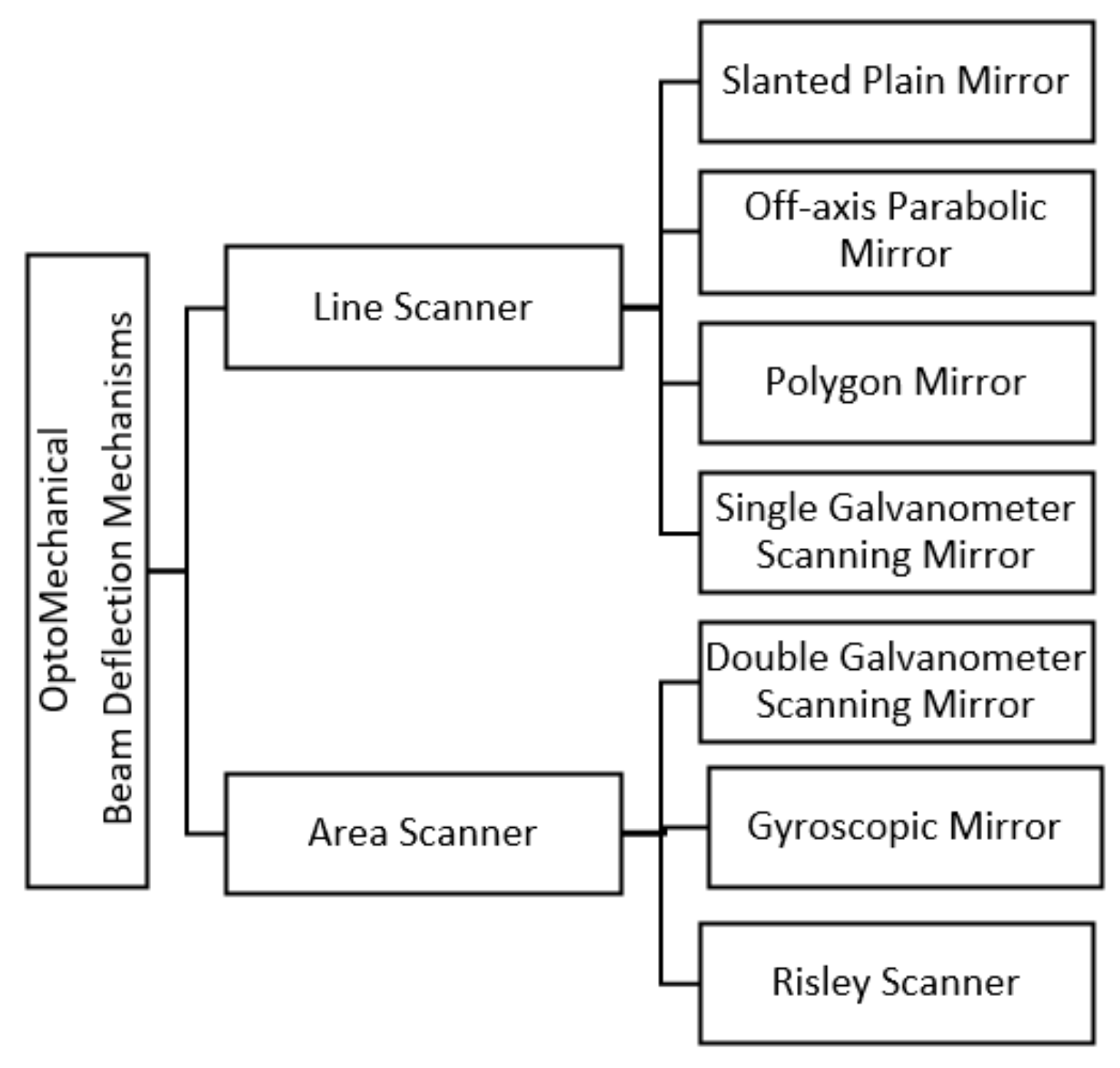
3. Beam Deflection Mechanisms
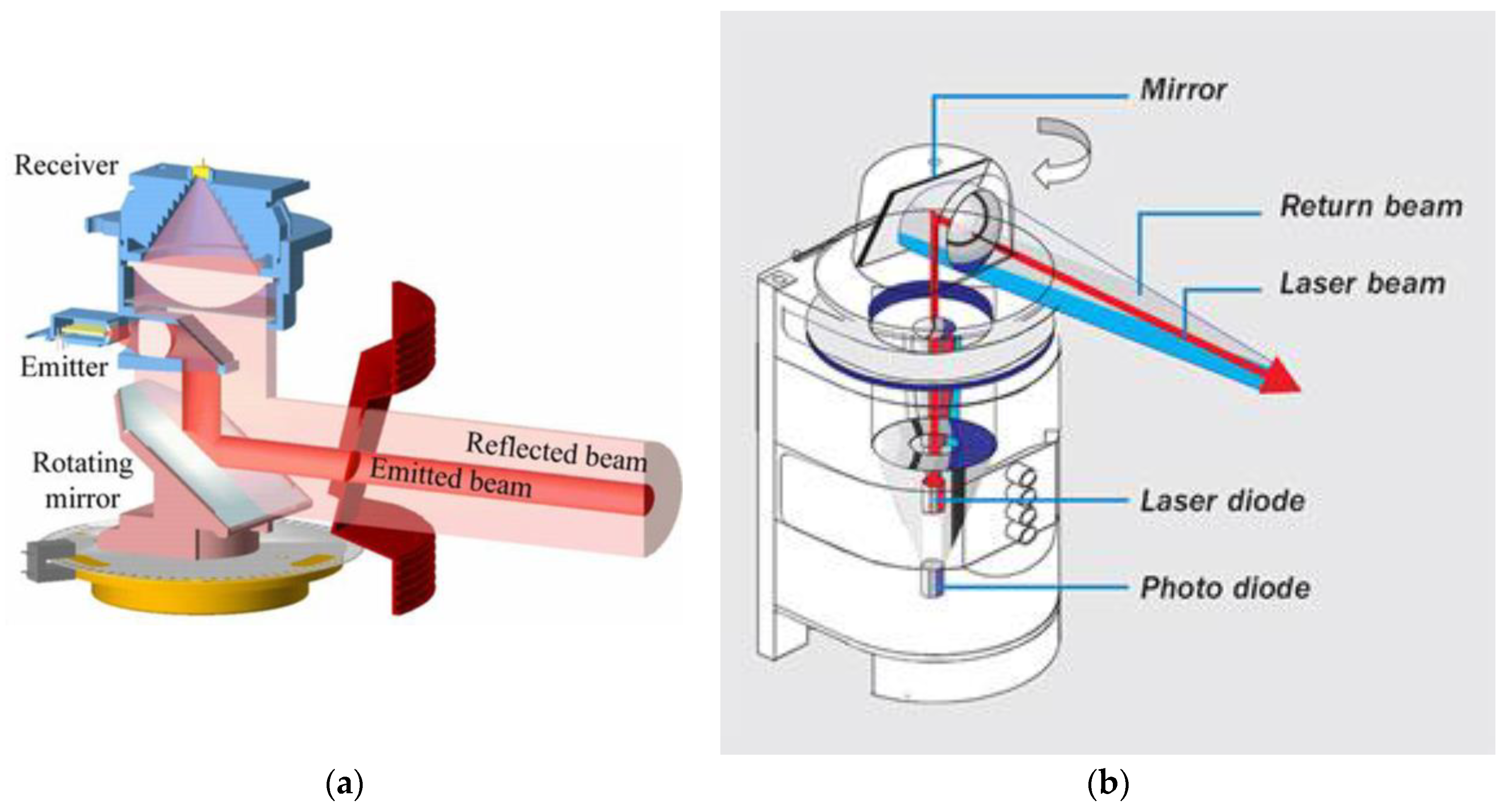
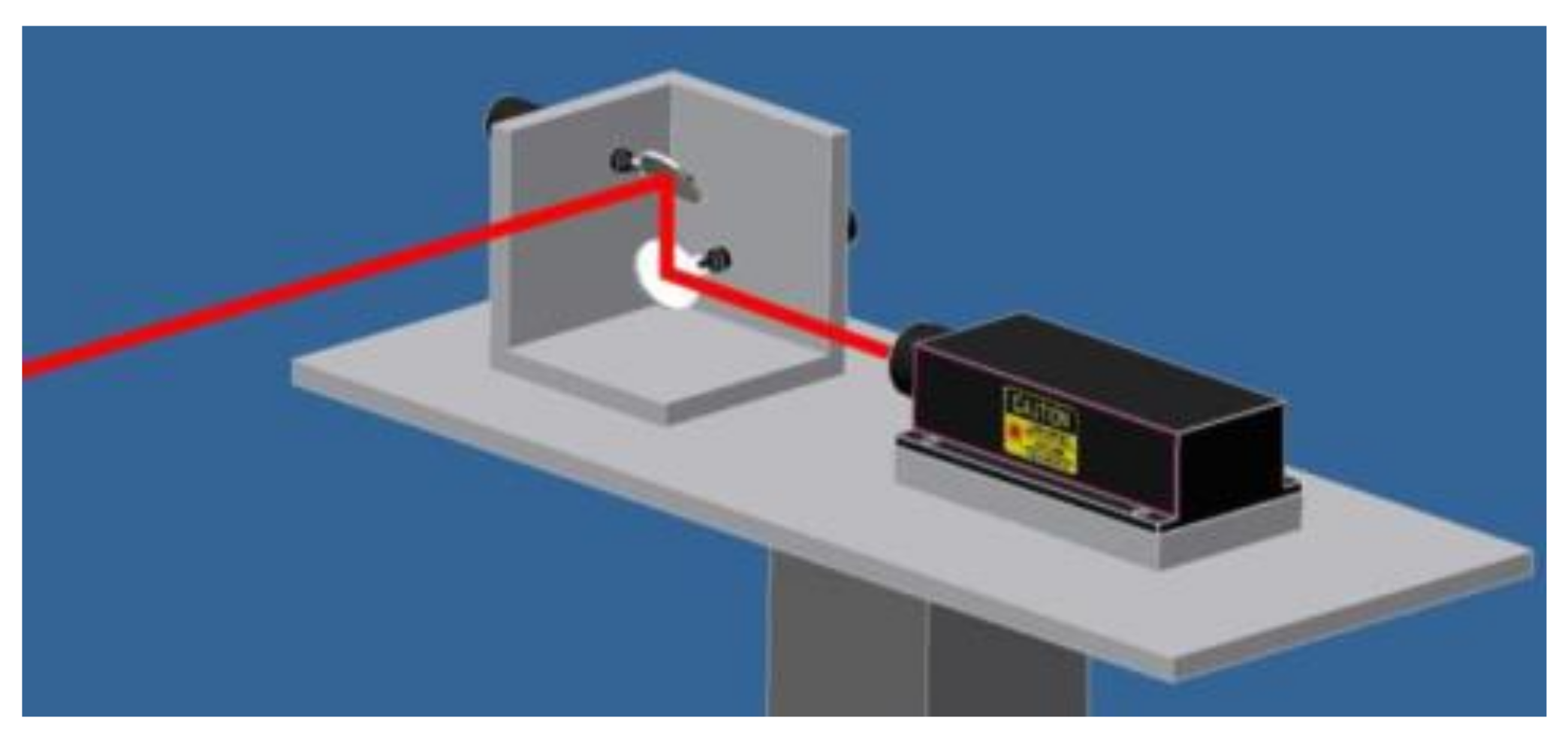
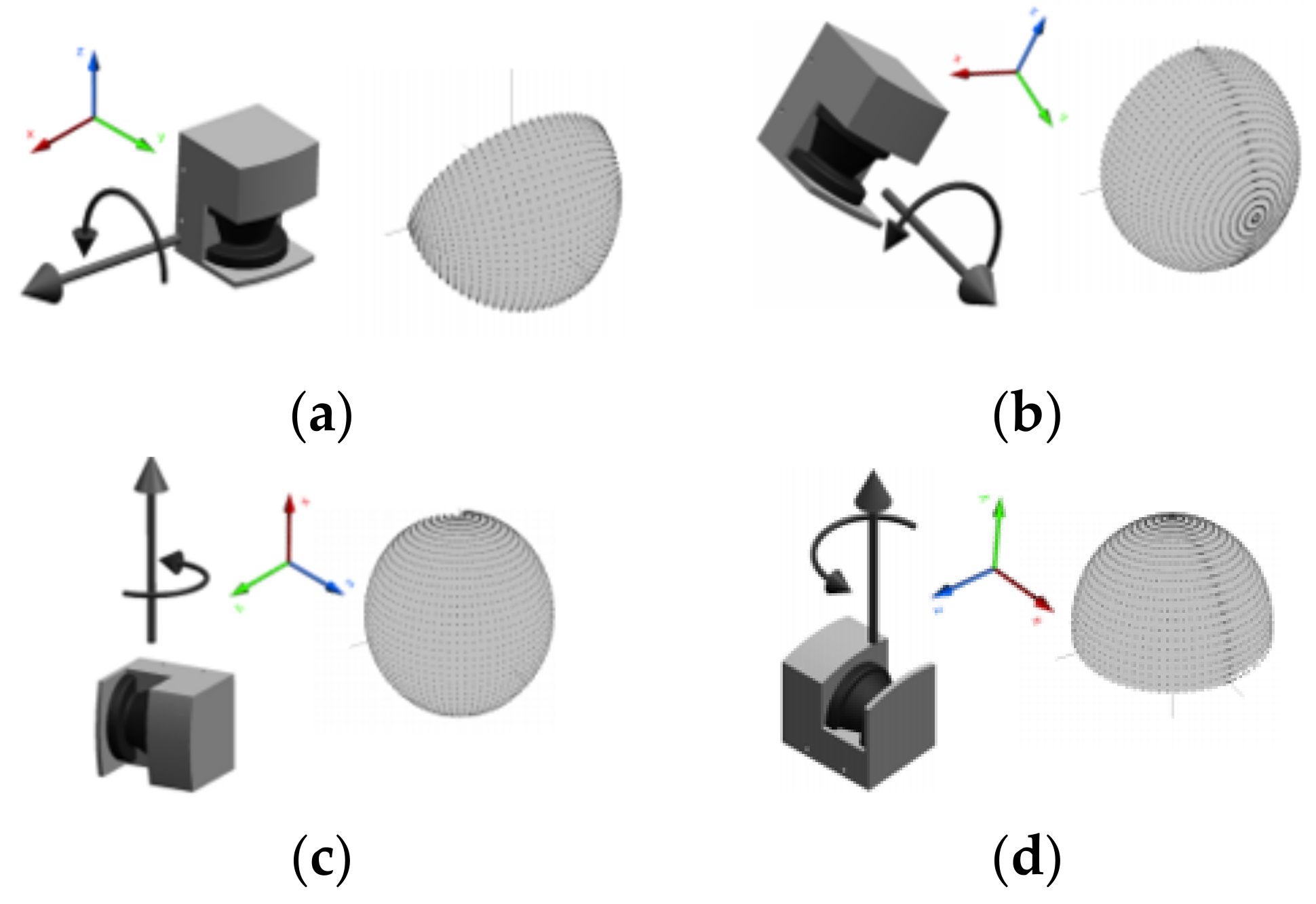
3.1. Optomechanical Scanning
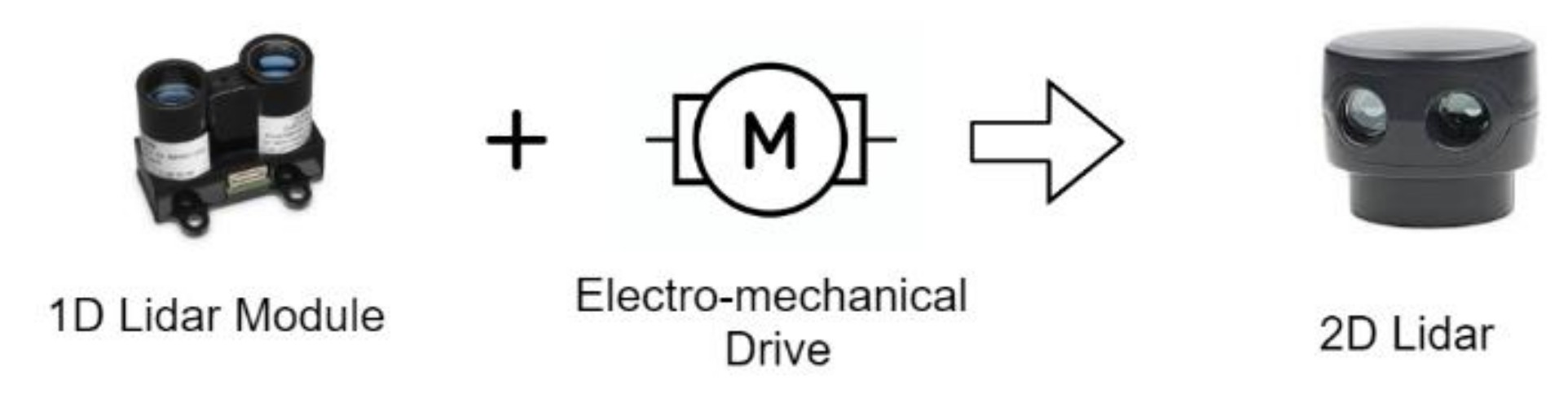
3.2. Electromechanical Scanning
3.3. MEMS Scanning
3.4. Solid-State Scanning
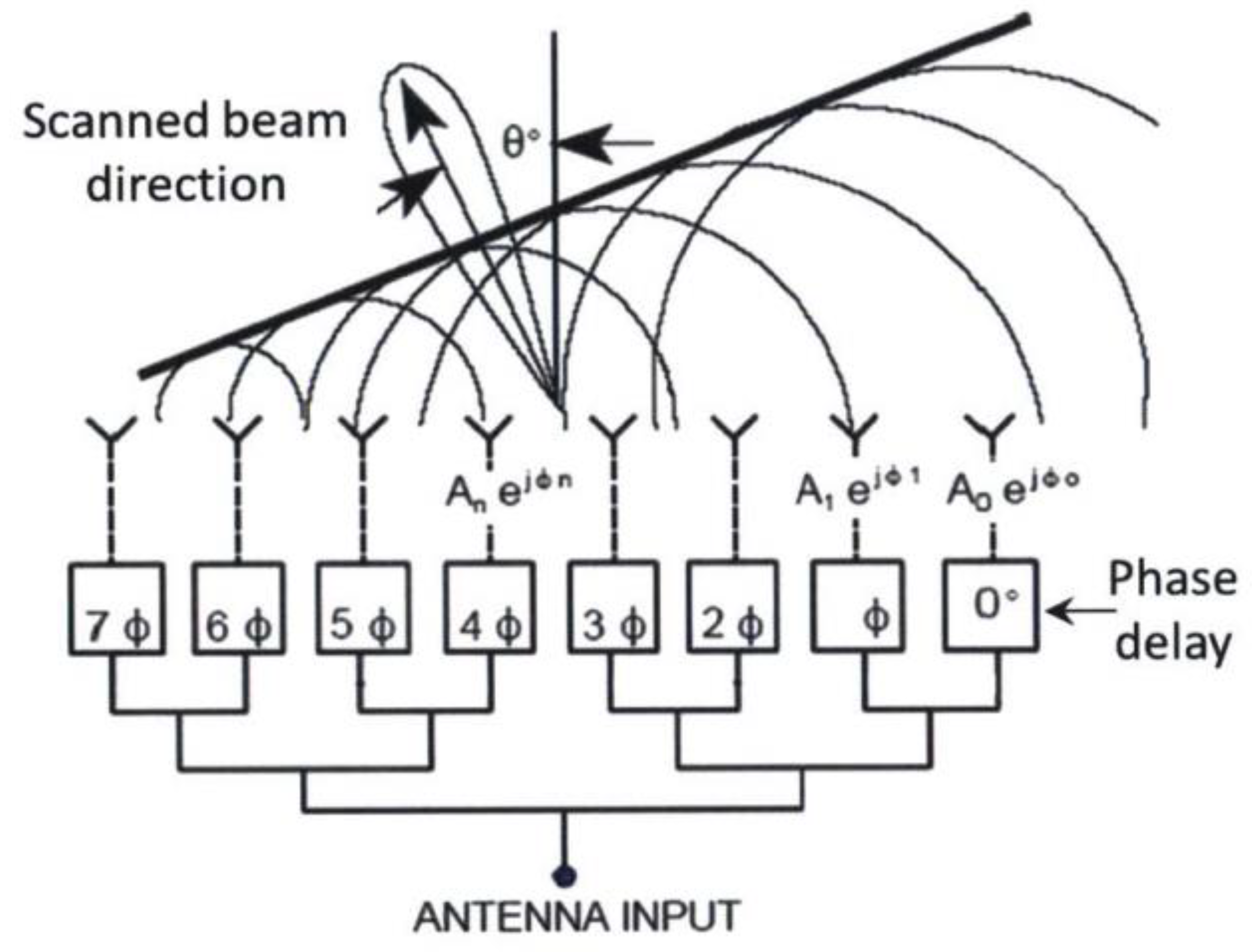
3.4.1. Optical Phased Array (OPA) Beam Scanning
3.4.2. Photonic Crystal Waveguide (PCW) Beam Scanning
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Liner, J. SWaP: The RF Solution that Can Mean the Difference between Flying High and Being Grounded; Analog Devices: Norwood, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Robin, G.J.; Jacky, C. Making a difference: Examples of the use of repeat LiDAR datasets to guide river management decisions following extreme floods. In Proceedings of the 7th Australian Stream Management Conference, Townsville, Australia, 27–30 July 2014; pp. 232–239. [Google Scholar]
- Eitel, J.U.H.; Hö, B.; Vierling, L.A.; Abellán, A.; Asner, G.P.; Deems, J.S.; Glennie, C.L.; Joerg, P.C.; Lewinter, A.L.; Magney, T.S.; et al. Beyond 3-D: The new spectrum of lidar applications for earth and ecological sciences. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 372–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bosch, T. Laser ranging: A critical review of usual techniques for distance measurement. Opt. Eng. 2001, 40, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahim, M.A.-B. 3D Laser Scanners’ Techniques Overview. Int. J. Sci. Res. 2015, 4, 5–611. [Google Scholar]
- Berkovic, G.; Shafir, E. Optical methods for distance and displacement measurements. Adv. Opt. Photonics 2012, 4, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuchter, A. 3D Robotic Mapping. In Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; Volume 52. [Google Scholar]
- NASA. 2016 Lidar Technologies Review and Strategy; NASA Earth Science Technology Office: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 2016; p. 80. [Google Scholar]
- Toth, C.; Józ, G. Remote sensing platforms and sensors: A survey. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 115, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oludare, I.M.; Pradhan, B. A decade of modern cave surveying with terrestrial laser scanning: A review of sensors, method and application development. Int. J. Speleol. 2016, 45, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molebny, V.; Mcmanamon, P.; Chen, W. Laser radar: Historical prospective—From the East to the West. Opt. Eng. 2017, 56, 031220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomina, I.; Molina, P. Unmanned aerial systems for photogrammetry and remote sensing: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote. Sens. 2014, 92, 79–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xinzhao, C. Lecture 07, Fundamentals of Lidar remote sensing. 2012. Available online: http://superlidar.colorado.edu/Classes/Lidar2012/LidarLecture07_Architecture.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Xinzhao, C. Lecture 08, Fundamentals of Lidar remote sensing. 2016. Available online: http://superlidar.colorado.edu/Classes/Lidar2016/Lidar2016_Lecture08_Architecture.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Xinzhao, C. Lecture 36, Lidar Architecture and Lidar Design. 2016. Available online: http://superlidar.colorado.edu/Classes/Lidar2016/Lidar2016_Lecture36_LidarDesignArchitecture.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Xinzhao, C. Lecture 41, Lidar Architecture and Lidar Design. 2012. Available online: http://superlidar.colorado.edu/Classes/Lidar2012/LidarLecture41_LidarDesign1.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Baltsavias, E. Advances in Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences: 2008 ISPRS Congress Book, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0-415-47805-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hegna, T.A.; Pettersson, H.; Teknova, K.G.; Laundal, K.M. Inexpensive 3-D Laser Scanner System Based on A Galvanometer Scan Head. In Proceedings of the Optical Measurement Systems for Industrial Inspection VII, Munich, Germany, 23–26 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, D.; Bishop, M. A Novel Approach to 3D Laser Scanning. In Proceedings of the Australasian Conference on Robotics and Automation, Victoria University of Wellington, Wellington, New Zealand, 3–5 December 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Niewola, A.; Podsedkowski, L. A novel 3D laser scanner design for variable density scanning. In Proceedings of the 12th International Workshop on Robot Motion and Control (RoMoCo), Poznań, Poland, 8–10 July 2019; pp. 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuthea, V.; Toshiyoshi, H. A Design of Risley Scanner for LiDAR Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Optical MEMS and Nanophotonics (OMN), Lausanne, Switzerland, 29 July–2 August 2018; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Sick LMS200/211/221/291 Laser Measurement Systems Technical Description; SICK AG: Waldkirch, Germany, 2006.
- Schmersal Schmersal Newsletter 02 Automotive; Schmersal: Wuppertal, Germany, 2003.
- Surmann, H.; Nuchter, A.; Hertzberg, J. An autonomous mobile robot with a 3D laser range finder for 3D exploration and digitalization of indoor environments. Robot. Auton. Syst. 2003, 45, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohanbash, D. SICK LMS Full LIDAR Teardown. Available online: http://robotsforroboticists.com/sick-lms-lidar-teardown/ (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Wulf, O.; Wagner, B. Fast 3D Scanning Methods for Laser Measurement Systems, 2003; pp. 312–317. Available online: https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/633d/42113180b581e64ac04b846cb55c6b9bffd2.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Surmann, H.; Worst, R. New Applications with Lightweight 3D Sensors. In Proceedings of the Joint Conference on Robotics. ISR 2006, 37th International Symposium on Robotics, and ROBOTIK 2006, 4th German Conference on Robotics, München, Germany, 15–17 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Surmann, H.; Lingemann, K.; Nuchter, A.; Hertzberg, J. Fast acquiring and analysis of three dimensional laser range data. In Proceedings of the 6th International Fall Workshop Vision, Modeling and Visualization, Stuttgart, Germany, 21–23 November 2001; pp. 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, Z.; Wu, E. Design and calibration of a fast 3D scanning LADAR. In Proceedings of the Design and Calibration of a Fast 3D Scanning LADAR, Luoyang, Henan, China, 25–28 June 2006; pp. 211–215. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, A.; Newman, P. High quality 3D laser ranging under general vehicle motion. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Pasadena, CA, USA, 19–23 May 2008; pp. 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, Z.J.; Qin, B.; Bandyopadhyay, T.; Ang, M.; Frazzoli, E.; Rus, D. Synthetic 2D LIDAR for precise vehicle localization in 3D urban environment. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Karlsruhe, Germany, 6–10 May 2013; pp. 1554–1559. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, M.; Chen, W.; Li, B.; Lv, T. Construction and realization of a 3D perceptual system based on 2D laser radar. In Proceedings of the 2008 3rd IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Singapore, 3–5 June 2008; pp. 680–684. [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli, F.; Droeschel, D.; Wisspeintner, T.; May, S.; Surmann, H. A 3D laser scanner system for autonomous vehicle navigation. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Advanced Robotics, Munich, Germany, 22–26 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Segovia, A.; Contreras, A.; Garduno, M.P. Mechanical Analysis of a Vertical Scanning System for 3D Images Acquisition with Microcontroller-Based Electronic Design; World Scientific and Engineering Academy and Society (WSEAS): Stevens Point, WI, USA, 2010; Volume 9, pp. 180–191. [Google Scholar]
- Segovia, A.; Contreras, A.; Garduno, M.P. Design and Development of a Vertical Scanning System for 3D Images Acquisition. In Proceedings of the 2nd WSEAS International Conference on Sensors, and Signals and Visualization, Imaging and Simulation and Materials Science (SENSIG’09/VIS’09/MATERIALS’09), Stevens Point, WI, USA, November 2009; pp. 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Reina, G.; Giannoccaro, N.I.; Messina, A.; Gentile, A. Mobile robot perception using an inexpensive 3-D laser rangefinder. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, Bari, Italy, 4–7 July 2010; pp. 2809–2814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.A.; Martinena, E.; Sanchez, A.; Rodriguez, R.G.; Nunez, P. A Cost-Efficient 3D Sensing System for Autonomous Mobile Robots. In Proceedings of the XII Workshop of Physical Agents (WAF 2011), Albacete, Spain, 5–6 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yong-kun, W.; Ju, H.; Xing-shun, W. A real-time robotic indoor 3D mapping system using duel 2D laser range finders. In Proceedings of the 33rd Chinese Control Conference, Nanjing, China, 28–30 July 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chou, Y.-S.; Liu, J.-S. A Robotic Indoor 3D Mapping System Using a 2D Laser Range Finder Mounted on a Rotating Four-Bar Linkage of a Mobile Platform. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, E. LiDAR Based Home Mapping: Using the OSLRF-01 and Arduino to Generate Floor Plans. Available online: https://soe.rutgers.edu/sites/default/files/imce/pdfs/gset-2014/GSET2015-LIDAR.pdf (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Reyes, A.L.; Cervantes, J.M.; Gutiérrez, N.C. Low Cost 3D Scanner by Means of a 1D Optical Distance Sensor. Procedia Technol. 2013, 7, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- RoboPeak Team RPLIDAR Low Cost 360 degree 2D Laser Scanner (LIDAR) System Introduction and Datasheet. 2014. Available online: https://www.robotshop.com/media/files/pdf/rplidar-a1m8-360-degree-laser-scanner-development-kit-datasheet-1.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Terabee. Teraranger One; Terabee: Saint-Genis-Pouilly, France, 2016; Volume 53, pp. 1689–1699. [Google Scholar]
- Scanse, Sweep v1.0 User Manual and Technical Specification; Scanse. 2017. Available online: https://s3.amazonaws.com/scanse/Sweep_user_manual.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
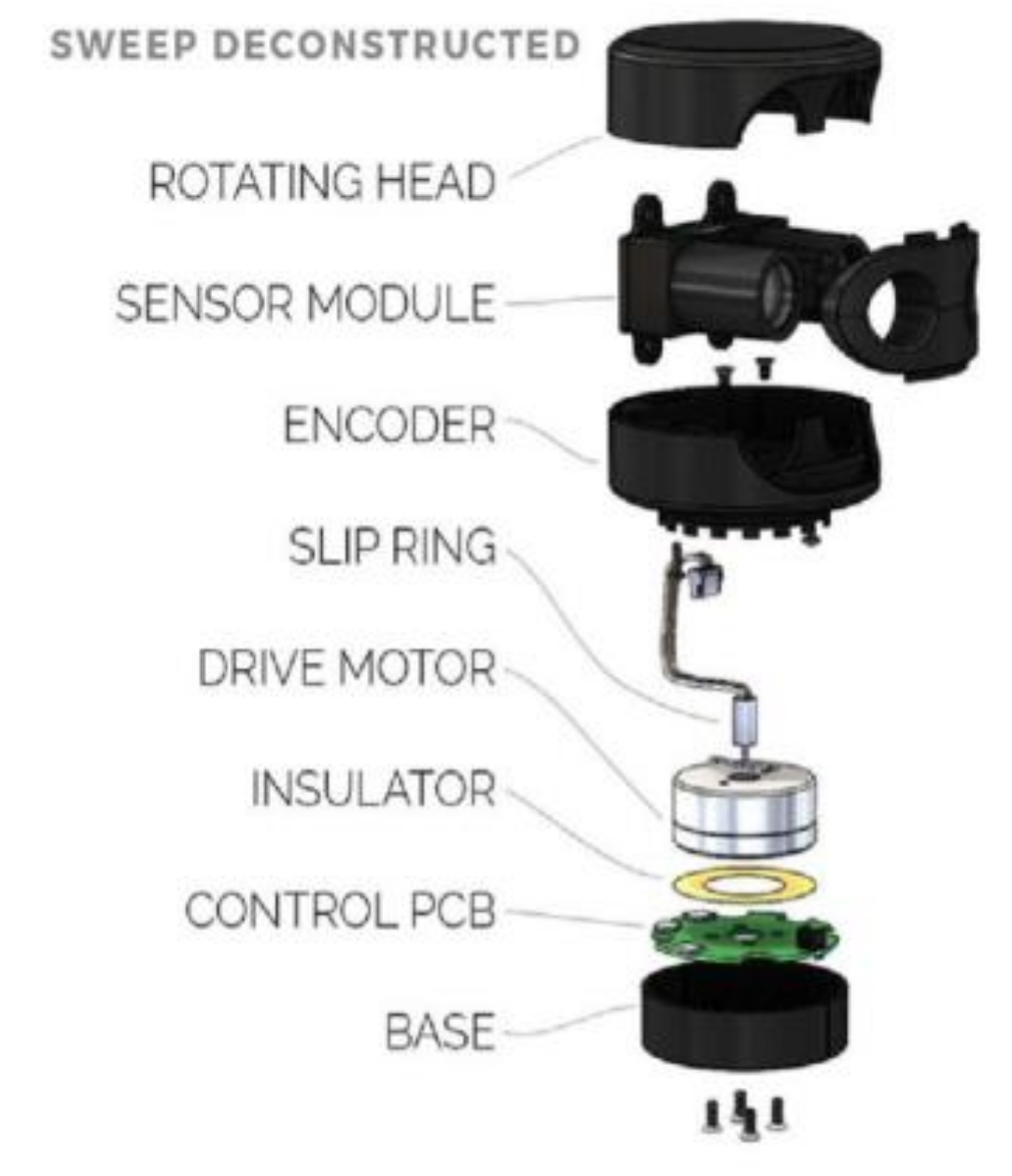
- Leeman, J. Scanse Sweep 3D Scanner Review, Servo Magazine. September 2017. Available online: https://www.servomagazine.com/magazine/article/the-multi-rotor-hobbyist-scanse-sweep-3d-scanner-review? (accessed on 4 December 2019).
- Stann, B.L.; Dammann, J.F.; Giza, M.M.; Jian, P.-S.; Lawler, W.B.; Nguyen, H.M.; Sadler, L.C. MEMS-scanned ladar sensor for small ground robots. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security and Sensing, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–9 April 2010; Volume 7684. [Google Scholar]
- Moss, R.; Yuan, P.; Bai, X.; Quesada, E.; Sudharsanan, R.; Stann, B.L.; Dammann, J.F.; Giza, M.M.; Lawler, W.B. Low-cost compact MEMS scanning ladar system for robotic applications. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security and Sensing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 24–26 April 2012; Volume 8379. [Google Scholar]
- Kasturi, A.; Milanovic, V.; Atwood, B.H.; Yang, J. UAV-borne lidar with MEMS mirror-based scanning capability. In Proceedings of the SPIE Defense, Security and Sensing, Baltimore, MD, USA, 20 April 2016; Volume 9832. [Google Scholar]
- Adamo, G.; Mistretta, L.; Livreri, P.; Busacca, A. A LiDAR Prototype with Silicon Photomultiplier and MEMS Mirrors. In Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Forum on Research and Technologies for Society and Industry, Palermo, Italy, 10–13 September 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Strasser, A.; Stelzer, P.; Steger, C.; Druml, N. Speed-Up of MEMS Mirror’s Transient Start-Up Procedure. In Proceedings of the SAS 2019—2019 IEEE Sensors Applications Symposium, Sophia Antipolis, France, 11–13 March 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.-Y.; Lu, C.-E.; Huang, Z.-R.; Lin, S.; Lo, S.-C.; Chen, R.; Fang, W. Fabrication and Integration of Binary Phased Fresnel Lens and Micro Linear Actuator for IR Laser Beam Scanning Application. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems & Eurosensors XXXIII, Berlin, Germany, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1584–1587. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Watkins, C.; Koppal, S.; Li, M.; Ding, Y.; Xie, H. A Compact Omnidirectional Laser Scanner Based on an Electrothermal Tripod Mems Mirror for Lidar Please Leave. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems & Eurosensors XXXIII, Berlin, Germany, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1526–1529. [Google Scholar]
- Niclass, C.; Ito, K.; Sago, M.; Matsubara, H.; Kato, S.; Kagami, M. Design and characterization of a 256 × 64-pixel single-photon imager in CMOS for a MEMS-based laser scanning time-of-flight sensor. Opt. Express 2012, 20, 11863–11881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, F.; Qiao, D.; Song, X.; Zheng, W.; He, Y.; Fan, Q. A Semi-coaxial MEMS-based LiDAR. In Proceedings of the IECON 2019—45th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, Lisbon, Portugal, 14–17 October 2019; Volume 1, pp. 6726–6731. [Google Scholar]
- Takeaki, K.; Takashi, S.; Kazuhiro, H. Cycloidal scanning with MEMS micro mirror for an omnidirectional long range LiDAR. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Optical MEMS and Nanophotonics, Daejeon, Korea, 28 July–1 August 2019; pp. 142–143. [Google Scholar]
- Pensala, T.; Kiihamaki, J.; Kyynarainen, J.; Dekker, J.; Gorelick, S.; Pekko, P.; Pernu, T.; Ylivaara, O.; Gao, F.; Morits, D. Wobbling Mode AlN-Piezo-MEMS Mirror Enabling 360-Degree Field of View LIDAR for Automotive Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS), Glasgow, UK, 6–9 October 2019; pp. 1977–1980. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Rojas, S.S.; Shuping, A.; Tasneem, Z.; Koppal, S.; Xie, H. An Integrated Forward-View 2-Axis Mems Scanner for Compact 3D Lidar. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 13th Annual International Conference on Nano/Micro Engineered and Molecular Systems (NEMS), Singapore, 22–26 April 2018; pp. 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, X.; Koppal, S.; Xie, H. A compact MEMS-based wide-angle optical scanner. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Optical MEMS and Nanophotonics (OMN), Santa Fe, NM, USA, 13–17 August 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Hui, Z.; Siyuan, H. 1D LiDAR Based on Large Apeture FPCB Mirror. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Optical MEMS and Nanophotonics, Daejeon, Korea, 28 July–1 August 2019; pp. 150–151. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, G.; You, Z.; Zhang, C. A 2D resonant MEMS scanner with an ultra-compact wedge-like multiplied angle amplification for miniature LIDAR application. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Sensors, Orlando, FL, USA, 30 October–3 November 2016; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-J.; Lim, J.; Moon, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, K.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.-H. MEMS Scanner-Based Biaxial LiDAR System for Direct Detection of Three-Dimensional Images. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Optical MEMS and Nanophotonics (OMN), Lausanne, Switzerland, 29 July–2 August 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbach, J.; Kästner, F.; Has, R.; Bogatscher, S.; Rembe, C. Demonstration of a Mems-Mirror, 3d-Lidar System with Large Aperture and Scanning Angle Robert Bosch Gmbh, Chassis Systems Control, Germany and Clausthal University of Technology, Institute of Electrical Information Technology, Germany. In Proceedings of the 2019 20th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems and Eurosensors XXXIII, Berlin, Germany, 23–27 June 2019; pp. 1499–1502. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchiya, T. MEMS mirrors for automotive applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Meeting for Future of Electron Devices, Kansai (IMFEDK), Kyoto, Japan, 29–30 June 2017; pp. 82–83. [Google Scholar]
- Milanovic, V.; Castelino, K.; McCormick, D.T. Highly adaptable MEMS-based display with wide projection angle. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 20th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), Hyogo, Japan, 21–25 January 2007; pp. 143–146. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, X.; Wang, C. Optical design for uniform scanning in MEMS-based 3D imaging lidar. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 2219–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmstrom, S.T.S.; Baran, U.; Urey, H. MEMS Laser Scanners: A Review. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2014, 23, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- It Began with a Race…16 Years of Velodyne LiDAR. 2017. Available online: https://velodynelidar.com/blog/it-began-with-a-race16-years-of-velodyne-lidar/ (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Velodyne Lidar-64E High Definition Real-Time 3D LiDAR Sensor. 2018. Available online: https://velodynelidar.com/products/hdl-64e/ (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Poulton, C.V.; Watts, M.R. IEEE SPECTRUM; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Ngai, T.; Timalsina, Y.; Watts, M.R.; Stojanovic, V.; Bhargava, P.; Poulton, C.V.; Notaros, J.; Yaacobi, A.; Timurdogan, E.; et al. A Single-Chip Optical Phased Array in a Wafer-Scale Silicon Photonics/CMOS 3D-Integration Platform. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 3061–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Bhargava, P.; Poulton, C.V.; Notaros, J.; Yaacobi, A.; Timurdogan, E.; Baiocco, C.; Fahrenkopf, N.; Kruger, S.; Ngai, T.; et al. 29.5 A Single-Chip Optical Phased Array in a 3D-Integrated Silicon Photonics/65nm CMOS Technology. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–21 February 2019; pp. 464–466. [Google Scholar]
- Van Acoleyen, K.; Komorowska, K.; Bogaerts, W.; Baets, R. Integrated Optical Beam Steerers. In Proceedings of the 2013 Optical Fiber Communication Conference and Exposition and the National Fiber Optic Engineers Conference (OFC/NFOEC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2013; pp. 6–8. [Google Scholar]
- Yaacobi, A. Integrated Optical Phased Arrays for Lidar Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, S.; Abediasl, H.; Hashemi, H. A Monolithically Integrated Large-Scale Optical Phased Array in Silicon-on-Insulator CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, E. IEEE SPECTRUM. December 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman, E. IEEE SPECTRUM. September 2016; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Furukado, Y.; Abe, H.; Hinakura, Y.; Baba, T. Experimental simulation of ranging action using Si photonic crystal modulator and optical antenna. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 18222–18229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, K.; Tatebe, T.; Hachuda, S.; Abe, H.; Koyama, F.; Baba, T. Fan-beam steering device using a photonic crystal slow-light waveguide with surface diffraction grating. Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 4990–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, G.; Terada, Y.; Takeuchi, M.; Abe, H.; Ito, H.; Baba, T. Thermally controlled Si photonic crystal slow light waveguide beam steering device. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 3338–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abe, H.; Takeuchi, M.; Takeuchi, G.; Ito, H.; Yokokawa, T.; Kondo, K.; Furukado, Y.; Baba, T. Two-dimensional beam-steering device using a doubly periodic Si photonic-crystal waveguide. Opt. Express 2018, 26, 9389–9397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baba, T. Development of Non-Mechanical Beam Steering and LiDAR Based on Photonic Crystal and Si Photonics. In Proceedings of the 2019 21st International Conference on Transparent Optical Networks (ICTON), Angers, France, 9–13 July 2019; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Optoelectronics, L. OSLRF-01 Product Manual. 2014. Available online: http://www.mantech.co.za/Datasheets/Products/OSLRF-01_LIGHTWARE.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Optoelectronics, L. SF02 Product Manual, Revision 12. 2017. Available online: https://www.parallax.com/sites/default/files/downloads/28043-SF02-Laser-Rangefinder-Manual-Rev-12.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Optoelectronics, L. Sf30 Datasheet. 2016; pp. 1–16. Available online: http://documents.lightware.co.za/SF30%20-%20Laser%20Altimeter%20Manual%20-%20Rev%209.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Garmin Lidar Lite v3 Operation Manual and Technical Specifications; Garmin: Olathe, KS, USA, 2016; pp. 1–14.
- PulsedLight LLC Technology and System Hardware Overview LIDAR-Lite Block Diagram; Garmin: Olathe, KS, USA, 2016.
- SLAMTEC Rplidar A2 Instruction and Datasheet. 2016. Available online: https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/e/a/f/9/8/LD208_SLAMTEC_rplidar_datasheet_A2M8_v1.0_en.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Benewake Co. Ltd. (Beijing). TFmini LiDAR Module; Benewake: Beijing, China, 2017; pp. 1–4. Available online: https://cdn.sparkfun.com/assets/5/e/4/7/b/benewake-tfmini-datasheet.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Palojärvi, P. Integrated Electronic and Optoelectronic Circuits and Devices for Pulsed Time-of-Flight Laser Rangefinding. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Olulu, Olulu, Finland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtti, S. Integrated Receiver Channel and Timing Discrimination Circuits for a Pulsed Time-of-Flight Laser Rangefinder. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Olulu, Olulu, Finland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
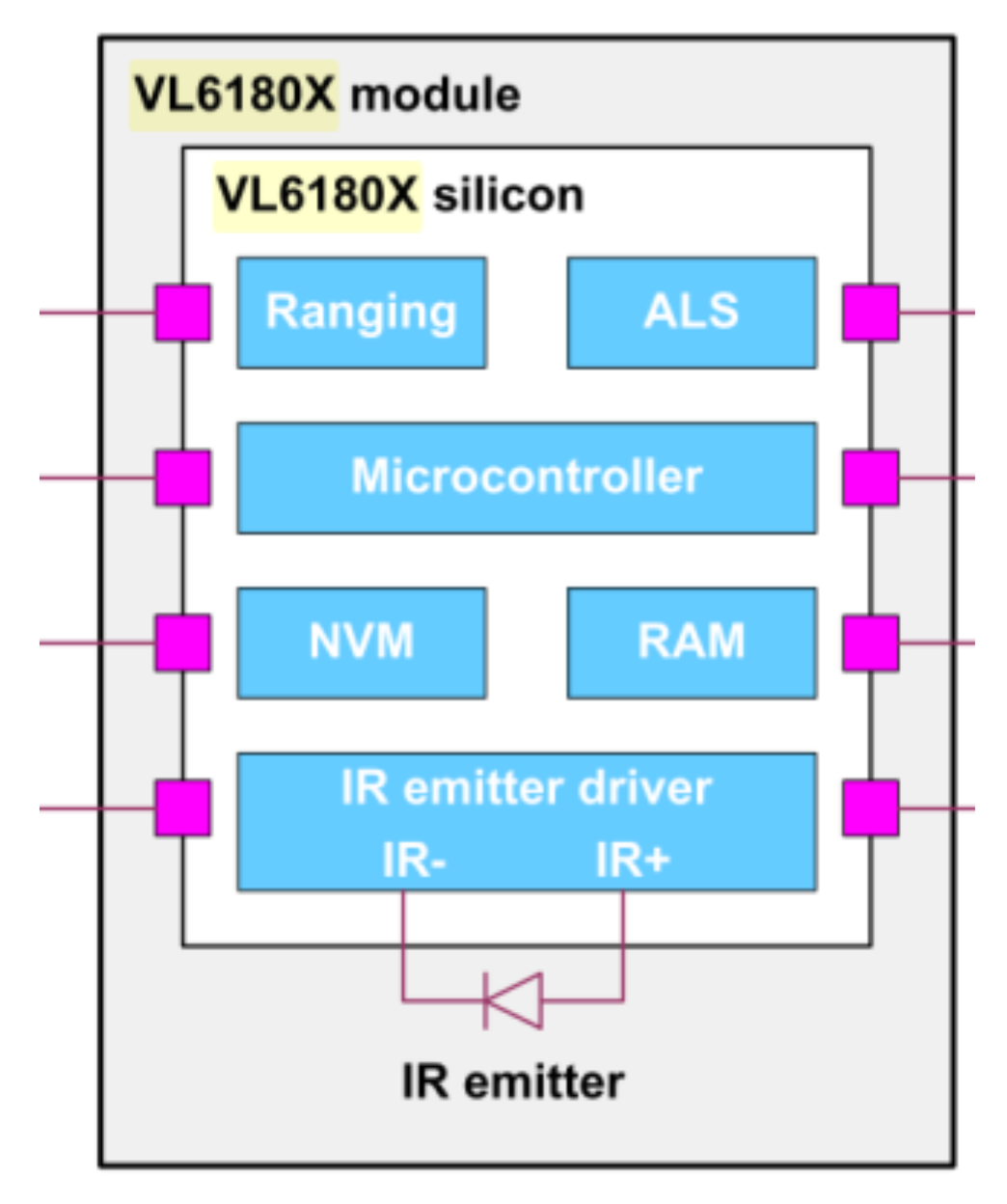
- STMicroelectronics VL6180 Datasheet. 2016. Available online: https://www.st.com/resource/en/datasheet/vl6180x.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- STMicroelectronics VL53L0X DATA SHEET. 2016, 1–26. Available online: https://www.st.com/resource/en/datasheet/vl53l0x.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- ISL29501 Time of Flight (TOF) Signal Processing IC. 2017. Available online: https://www.renesas.com/sg/en/doc/datasheet/isl29501.pdf (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Kelden, P. Development of a Low-Cost Laser Range-Finder (LIDAR). Master’s Thesis, Chalmers University of Technology, Goteborg, Sweden, 2015. [Google Scholar]








| Reference Type | FOV (H × V) | Resolution (H × V) | Axis Rate (H × V) | Scanning Area/Pattern | Cost Size Weight Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [18] Research | 40°-H | - | - | Bounded Area/Raster scan | - |
| 40°-V | |||||
| [22] Commercial | 180°-H | 0.25°/0.5°/1.0°-H | 19/38/75 Hz-H | Line scan | €3500 |
| 155 mm × 156 mm × | |||||
| 210 mm | |||||
| 4.5 kg | |||||
| 17 W | |||||
| [19] Commercial | 360°-H | 0.01°-H | 20 Hz-H | Bounded Area Scan/Full area scan | €12,775 |
| 300 mm × 150 mm × | |||||
| 150 mm | |||||
| 70°-V | 0.01°-V | 3 Hz-V | 2.5 kg | ||
| 50 W |
| Reference/Type | FOV (H × V) | Resolution (H × V) | Axis Rate (H × V) | Scanning Area/Pattern | Cost Size (mm) Weight(g) Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] Research | 100°-H | 1.0°-H | 75 Hz-H | Bounded Area/Raster scan | €6501 |
| 166 × 286 x 166 | |||||
| 124°-V | 1.0°-V | 0.3 Hz-H | 7400 g | ||
| 17.85 W | |||||
| [33] Research | 360°-H | 4.0°-H | 1.67 Hz-H | Full Area | €11,613 |
| 320 × 500 × 500 | |||||
| 13.0 kg | |||||
| 360°-V | 1.0°-V | 75 Hz-V | 34.85 W | ||
| [36] Research | 240°-H | 0.36°-H | - | Bounded Area/Raster scan | 17W |
| 270°-V | 0.36°-V | ||||
| [26] Research | 180°-H | 0.5°–H | - | - | |
| 180°-V | 0.5°-V | ||||
| [29] Research | 180°-H | 0.5°-H | 38 Hz-H | - | |
| 90°-V | 0.45°-V | 0.19 Hz-V | |||
| [34,35] Research | 180°-H | 0.5°-H | 38 Hz-H | - | |
| 150°-V | 0.72°-V | 0.09 Hz-V | |||
| [37] Research | 270°-H | 0.36°-H | - | - | |
| 360°-V | 1.8°-H | ||||
| [42] Commercial | 360°-H | 0.9°-H | 10 Hz-H | Line scan | €350 |
| 75.7 × 75.7 × 40.8 | |||||
| 190 g | |||||
| 2W | |||||
| [43] Commercial | 360°-H | 0.36°-H | 11 Hz-H | 75 × 44 × 44 | |
| 125 g | |||||
| 2 W | |||||
| [44] Commercial | 360°-H | 0.7°-H | 10 Hz-H | €228 | |
| 65 × 61.9 | |||||
| 120 g | |||||
| 2.25 W | |||||
| [45] Commercial | 360°-H | 0.75°-H | 10 Hz-H | Bounded Area/Raster scan | €731 |
| 360°-V | 0.9°-V | 0.025 Hz-V | 500 g | ||
| 5 W |
| Reference/Type | FOV (H × V) | Resolution (H × V) | Axis Rate (H × V) | Scanning Mode | Cost Size Weight Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [48] Research | 20°-H | - | - | Quasi-static, Resonant mode | 90 mm × 60 mm × 40 mm |
| 40 g | |||||
| 20°-V | 750 mW | ||||
| [49] Research | 12°-H | - | 811 Hz-V | - | €1200 |
| 12°-V | |||||
| [51] Research | 13.68°-H | - | 2 KHz-V | Resonant mode | - |
| 13.68°-V | |||||
| [52] Research | 8°-H | - | - | Quasi-static | - |
| [53] Research | 45°-H | - | - | Quasi-static | - |
| 11°-V | |||||
| [54] Research | 60°-H | 0.05°-H | 20 Hz-V | Resonant mode | - |
| 20°-V | 0.1°-V | ||||
| [55] Research | 30°-H | - | 2281 Hz | Resonant mode | 6.75 mm × 6.75 mm × 2 mm |
| 30°—V | |||||
| [57] Research | 17°-H | - | 1.6 kHz | Resonant mode | 4 mm × 4.5 mm × 1.6 mm |
| 17°-V | 16 mg | ||||
| [58] Research | 90°-H | - | - | Quasi-static | - |
| [60] Research | 45.3°-H | - | - | Resonant mode | - |
| 42.6°-V | |||||
| [61] Research | 5.78°-H | 0.8 mrad-H | 100 Hz-H | - | - |
| 6.36°-V | 2.2 mrad-V | 1 Hz-V |
| Reference/Type | Steering Angle (H × V) | Beam Width (H × V) | Scan Rate (H × V) | Scanning Pattern | Cost Size Weight Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [69] | 51°-H | - | - | Line scan | €9 * |
| 0.5 mm × 6 mm | |||||
| [70,71] | 16°-H | 0.6°-H | - | Raster scan | - |
| 18.5°-V | 0.15°-V | ||||
| [72] | 15°-H | 2.8°-H | 0.148o/nm-H | - | |
| 50°-V | 8°-V | 6.5o/nm-V | |||
| [74] | 45°-H | 0.03°-V | - | 5.7 mm × 6.4 mm | |
| 45°-V | 55.296 W |
| Reference/Type | FOV (H × V) | Resolution (H × V) | Scan Rate (H × V) | Scanning Pattern | Cost Size Weight Power |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [78] Research | 23°-H | 0.23°-H | - | Fan beam | 600 um |
| [80] Research | 24°-H | 0.3°-H | - | Fan beam | - |
| 6°-V | 1.5°-V | ||||
| [79] Research | 21°-H | 0.175°-H | 100 kHz-H | Fan beam | 12 um × 90 um × 70 um |
| 1.3 W | |||||
| [81] Research | 48°-H | 0.12°-H | - | Fan beam | - |
| 30°-V | 0.9°-V |
| Specifications | Minimum Requirement |
|---|---|
| Range | 100–200 M |
| Resolution | <25 cm |
| Rate | >25 fps |
| FOV horizontal | >90° |
| Horizontal resolution | 5000 points |
| Vertical resolution | 400 points |
| Cost | $100–$200 |
| Safety | Safe to eyes |
| System Power budget | 10–30 W |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Raj, T.; Hashim, F.H.; Huddin, A.B.; Ibrahim, M.F.; Hussain, A. A Survey on LiDAR Scanning Mechanisms. Electronics 2020, 9, 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050741
Raj T, Hashim FH, Huddin AB, Ibrahim MF, Hussain A. A Survey on LiDAR Scanning Mechanisms. Electronics. 2020; 9(5):741. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050741
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaj, Thinal, Fazida Hanim Hashim, Aqilah Baseri Huddin, Mohd Faisal Ibrahim, and Aini Hussain. 2020. "A Survey on LiDAR Scanning Mechanisms" Electronics 9, no. 5: 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050741
APA StyleRaj, T., Hashim, F. H., Huddin, A. B., Ibrahim, M. F., & Hussain, A. (2020). A Survey on LiDAR Scanning Mechanisms. Electronics, 9(5), 741. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050741





