Polyphenol Profile and In Vitro Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Different Solvent Extracts of Highland Barley Bran
Abstract
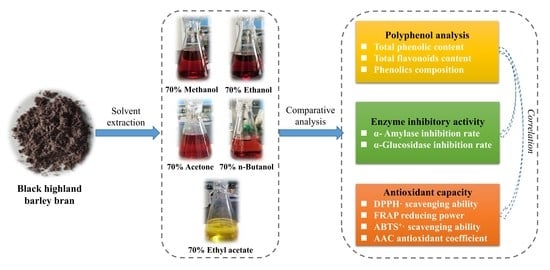
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Phenolic Content Analysis
2.2. Composition Analysis of Phenolic Compounds
2.3. Antioxidant Capacity of the Extracts
2.4. Enzyme Inhibitory Activity of the Extracts
2.5. Correlations between Antioxidant Capacity, Enzymatic Inhibitory, and Phenolics
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Materials
3.2. Preparation of Extracts of Black Highland Barley Bran
3.3. Assay of Total Phenolic Content
3.4. Assay of Total Flavonoids Content
3.5. Composition Analysis of Phenolics in Extracts
3.6. Determination of DPPH· Free Radical Scavenging Capacity
3.7. Determination of ABTS+· Free Radical Scavenging Capacity
3.8. Determination of Ferric Reducing Antioxidant Power
3.9. Assay of Antioxidant Capacity in β-Carotene-Linoleic Acid System
3.10. Inhibitory Activity of α-Amylase
3.11. Inhibitory Activity of α-Glucosidase
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Yang, X.-J.; Dang, B.; Fan, M.-T. Free and bound phenolic compound content and antioxidant activity of different cultivated blue highland barley varieties from the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Molecules 2018, 23, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Horvath, C.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Zheng, B. Understanding the nutrient composition and nutritional functions of highland barley (Qingke): A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 103, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Q.; Mascher, M.; Guo, G.; Li, S.; Mao, L.; Liu, Q.; Xia, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. Origin and evolution of qingke barley in Tibet. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Guo, H.; Gong, J.D.B.; Lu, M.; Lu, M.-Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, W.; Wu, D.-T. Phenolic profiles, β-glucan contents, and antioxidant capacities of colored Qingke (Tibetan hulless barley) cultivars. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 81, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, B.; Zhang, W.-G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.-J.; Xu, H.-D. Evaluation of nutritional components, phenolic composition, and antioxidant capacity of highland barley with different grain colors on the Qinghai Tibet Plateau. Foods 2022, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obadi, M.; Sun, J.; Xu, B. Highland barley: Chemical composition, bioactive compounds, health effects, and applications. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 110065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Liu, J.; Tsao, R.; Wang, Z.; Sun, B.; Wang, J. Whole grain consumption for the prevention and treatment of breast cancer. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zduńczyk, Z.; Flis, M.; Zieliński, H.; Wróblewska, M.; Antoszkiewicz, Z.; Juśkiewicz, J. In vitro antioxidant activities of barley, husked oat, naked oat, triticale, and buckwheat wastes and their influence on the growth and biomarkers of antioxidant status in rats. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 4168–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarikurkcu, C.; Ozer, M.S.; Tlili, N. LC–ESI–MS/MS characterization of phytochemical and enzyme inhibitory effects of different solvent extract of Symphytum anatolicum. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2019, 140, 111666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gevrenova, R.; Zengin, G.; Sinan, K.I.; Yildiztugay, E.; Zheleva-Dimitrova, D.; Picot-Allain, C.; Mahomoodally, M.F.; Imran, M.; Dall’Acqua, S. UHPLC-MS characterization and biologicalinsights of different solvent extracts of two Achillea species (A. aleppica and A. santolinoides) from Turkey. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maliar, T.; Slaba, G.; Nemeček, P.; Maliarová, M.; Benková, M.; Havrlentová, M.; Ondrejovič, M.; Kraic, J. Antioxidants, enzyme inhibitors, and biogenic compounds in grain extracts of barleys. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 1678–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.M.; Dang, B.; Zhang, W.G.; Zheng, W.C.; Yang, X.J. Polyphenol and anthocyanin composition and activity of highland barley with different colors. Molecules 2022, 27, 3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Qi, Y.; Zheng, H. Dietary polyphenol, gut microbiota, and health benefits. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irakli, M.; Lazaridou, A.; Mylonas, I.; Biliaderis, C.G. Bioactive components and antioxidant activity distribution in pearling fractions of different greek barley cultivars. Foods 2020, 9, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idehen, E.; Tang, Y.; Sang, S. Bioactive phytochemicals in barley. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Pasha, I.; Saeed, M.; Asgher, M. Antioxidant profiling of native and modified cereal brans. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 54, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Kim, R.-Y.; Park, E. Antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of different solvent extracts of skullcap (Scutellaria baicalensis). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Praveen, N.; Yu, B.R.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, I.M. Polyphenol composition and antioxidant capacity from different extracts of Aster scaber. Acta Biol. Hung. 2014, 65, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Han, D.; Kim, B.; Baek, N.; Baik, B.-K. Antioxidant and anti-hypertensive activity of anthocyanin-rich extracts from hulless pigmented barley cultivars. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 48, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuarab, S.F.; Talib, W.H. Immunomodulatory and anticancer activities of barley bran grown in Jordan: An in vitro and in vivo study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 838373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishna, R.; Sarkar, D.; Schwarz, P.; Shetty, K. Phenolic linked anti-hyperglycemic bioactives of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) cultivars as nutraceuticals targeting type 2 diabetes. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 107, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, T.; Fu, X.; Abbasi, A.M.; Zheng, B.; Liu, R.H. Phenolics content, antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of dehulled highland barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 439–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Zheng, B.; Li, T.; Liu, R.H. Assessment of the phenolic profiles, hypoglycemic activity, and molecular mechanism of different highland barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) varieties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, B. Effects of highland barley bran extract rich in phenolic acids on the formation of Nε-carboxymethyllysine in a biscuit model. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povilaitis, D.; Šulniūtė, V.; Venskutonis, P.R.; Kraujalienė, V. Antioxidant properties of wheat and rye bran extracts obtained by pressurized liquid extraction with different solvents. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 62, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, V.; Bucur, L.; Popescu, A.; Schroder, V.; Costache, T.; Rambu, D.; Cucolea, I.E.; Gird, C.E.; Caraiane, A.; Gherghel, D.; et al. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of Usnea barbata (L.) F.H. Wigg. dry extracts in different solvents. Plants 2021, 10, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, C.; Dai, F.; Xiao, G.; Luo, G. HPLC determination of phenolic compounds in different solvent extracts of mulberry leaves and antioxidant capacity of extracts. Int. J. Food Prop. 2021, 24, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, E.-S.M.; Choo, T.-M.; Dhillon, S.; Rabalski, I. Free and bound phenolic acids and total phenolics in black, blue, and yellow barley and their contribution to free radical scavenging capacity. Cereal Chem. 2012, 89, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, R.-Y.; Lui, W.-Y.; Wu, K.; Chan, C.-L.; Dai, S.-H.; Sui, Z.-Q.; Corke, H. Bioactive compounds and bioactivities of germinated edible seeds and sprouts: An updated review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 59, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Perea, P.; Guzmán-Ortiz, F.A.; Román-Gutiérrez, A.D.; Castro-Rosas, J.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; Rodríguez-Marín, M.L.; Falfán-Cortés, R.N.; González-Olivares, L.G.; Torruco-Uco, J.G. Bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of wheat bran and barley husk in the extracts with different polarity. Int. J. Food Prop. 2019, 22, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, T.; Mansouri, S.; Vecino-Bello, X.; Cruz-Freire, J.M.; Rezgui, S.; Ferchichi, A. Identification and characterization of phenolic compounds extracted from barley husks by LC-MS and antioxidant activity in vitro. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 81, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xiang, Z.; Lin, C.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, K.; Liu, T.; Xia, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Identification and quantification of free, esteri fied, and insoluble-bound phenolics in grains of hulless barley varieties and their antioxidant activities. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 151, 112001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agada, R.; Thagriki, D.; Esther Lydia, D.; Khusro, A.; Alkahtani, J.; Al Shaqha, M.M.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Soliman Elshikh, M. Antioxidant and anti-diabetic activities of bioactive fractions of Carica papaya seeds extract. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2021, 33, 101342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneria, M.; Chanda, S. Evaluation of antioxidant and antimicrobial capacity of Syzygium cumini L. leaves extracted sequentially in different solvents. J. Food Biochem. 2013, 37, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yao, H. Antioxidant activities of barley seeds extracts. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulut, O.; Akın, D.; Sönmez, Ç.; Öktem, A.; Yücel, M.; Öktem, H.A. Phenolic compounds, carotenoids, and antioxidant capacities of a thermo-tolerant Scenedesmus sp. (Chlorophyta) extracted with different solvents. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 1675–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.-Y.; Song, Y.-L.; Zhang, L. α-Glucosidase inhibitory and antioxidant properties and antidiabetic activity of Hypericum ascyron L. Med. Chem. Res. 2010, 20, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradeep, P.M.; Sreerama, Y.N. Phenolic antioxidants of foxtail and little millet cultivars and their inhibitory effects on α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities. Food Chem. 2018, 247, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, H.; Hosseini-Ghazvini, S.M.; Adibi, H.; Khodarahmi, R. Different α-amylase/α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of plant-derived phenolic compounds: A virtual screening perspective for the treatment of obesity and diabetes. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1942–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, M.S.; Uren, M.C.; Calapoglu, M.; Tepe, A.S.; Mocan, A.; Rengasamy, K.R.R.; Sarikurkcu, C. Phenolic profile, antioxidant and enzyme inhibitory activities of Stachys annua subsp. annua var. annua. South Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 113, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, H.; Jdey, A.; Taamalli, A.; Taamalli, W.; Jebara, M.; Brini, F.; Riciputi, Y.; Pasini, F.; Christian, M.; Verardo, V. Phenolic composition as measured by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and biological properties of Tunisian barley. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adom, K.K.; Sorrells, M.E.; Liu, R.H. Phytochemical profiles and antioxidant activity of wheat varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7825–7834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu Bakar, M.F.; Mohamed, M.; Rahmat, A.; Fry, J. Phytochemicals and antioxidant activity of different parts of bambangan (Mangifera pajang) and tarap (Artocarpus odoratissimus). Food Chem. 2009, 113, 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.D.; Ma, Y.J.; Parry, J.; Gao, J.M.; Yu, L.L.; Wang, M. Phenolics content and antioxidant activity of tartary buckwheat from different locations. Molecules 2011, 16, 9850–9867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benzie, I.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Zhou, A.G. Evaluation of the antioxidant effects of polysaccharides extracted from Lycium barbarum. Med. Chem. Res. 2007, 15, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.L.; Si, X.; Wang, Y.H.; Gong, E.S.; Xie, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Shu, C. Bioactive flavonoids from Rubus corchorifolius inhibit α-glucosidase and α-amylase to improve postprandial hyperglycemia. Food Chem. 2021, 341, 128149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Phenolic Content (mg/100 g DW) | 70% Methanol | 70% Ethanol | 70% Acetone | 70% n-Butanol | 70% Ethyl Acetate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC | 253.48 ± 9.54 b | 256.86 ± 6.98 b | 281.98 ± 4.29 a | 206.35 ± 6.02 c | 197.93 ± 5.69 c |
| TFC | 9.85 ± 0.78 b | 10.00 ± 0.82 b | 12.22 ± 0.43 a | 8.00 ± 0.65 c | 2.52 ± 0.24 d |
| Phenolic Compounds (μg/g) | 70% Methanol | 70% Ethanol | 70% Acetone | 70% n-Butanol | 70% Ethyl Acetate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gallic acid | 0.29 ± 0.01 c | 0.25 ± 0.01 d | 0.34 ± 0.01 b | 0.54 ± 0.04 a | 0.15 ± 0.01 e |
| Homogentisic acid | 0.02 ± 0.00 c | 2.02 ± 0.51 a | 1.74 ± 0.17 b | 2.03 ± 0.04 a | 0.01 ± 0.01 d |
| Protocatechuic acid | 14.62 ± 0.33 c | 14.16 ± 0.23 c | 15.98 ± 0.25 ab | 16.93 ± 0.69 a | 15.34 ± 0.38 b |
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 2.79 ± 0.06 b | 2.65 ± 0.04 bc | 2.53 ± 0.03 c | 2.5 ± 0.23 c | 3.62 ± 0.04 a |
| Chlorgenic acid | 0.22 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.01 a | 0.23 ± 0.10 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | 0.02 ± 0.01 b |
| Vanillic acid | 10.7 ± 0.09 b | 10.06 ± 0.27 b | 9.13 ± 0.55 c | 7.5 ± 1.15 d | 13.17 ± 0.10 a |
| 2-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid | 0.16 ± 0.06 a | 0.15 ± 0.04 a | 0.14 ± 0.03 b | 0.07 ± 0.02 d | 0.1 ± 0.01 c |
| 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| Caffeic acid | 1.95 ± 0.08 b | 1.92 ± 0.05 b | 1.98 ± 0.09 b | 2.84 ± 0.17 b | 6.16 ± 0.07 a |
| Syringic acid | 2.89 ± 0.10 b | 2.55 ± 0.02 c | 2.43 ± 0.04 c | 2.12 ± 0.28 d | 3.13 ± 0.04 a |
| p-Coumaric acid | 1.15 ± 0.03 b | 1.19 ± 0.02 b | 1.02 ± 0.01 c | 1.87 ± 0.01 a | 1.2 ± 0.00 b |
| o-Coumaric acid | 0.03 ± 0.01 c | 0.09 ± 0.05 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 e | 0.02 ± 0.01 d |
| Ferulic acid | 7.07 ± 0.15 b | 6.55 ± 0.06 c | 6.1 ± 0.14 c | 7.06 ± 0.61 b | 20.98 ± 0.24 a |
| Veratric acid | 0.41 ± 0.04 a | 0.07 ± 0.00 d | 0.11 ± 0.02 b | 0.09 ± 0.01 c | 0.11 ± 0.01 b |
| Benzoic acid | 0.96 ± 0.24 b | 0.78 ± 0.13 d | 0.82 ± 0.04 c | 0.67 ± 0.09 e | 1.47 ± 0.21 a |
| Salicylic acid | 0.08 ± 0.01 b | 0.07 ± 0.00 c | 0.08 ± 0.02 b | 0.07 ± 0.01 c | 0.13 ± 0.01 a |
| Procyanidin B2 | 1.43 ± 0.02 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 d | 0.01 ± 0.00 e | 0.07 ± 0.02 c | 0.31 ± 0.01 b |
| Phlorogucinol | 10.7 ± 0.24 b | 12.00 ± 1.52 a | 12.17 ± 1.14 a | 0.05 ± 0.00 c | 12.71 ± 0.95 a |
| Pyrogallol | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a |
| Maltol | 0.79 ± 0.23 b | 0.58 ± 0.18 d | 0.46 ± 0.11 e | 0.88 ± 0.23 a | 0.7 ± 0.05 c |
| Sesamol | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.01 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0.01 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 b |
| 6-Gingerol | 0.04 ± 0.02 a | 0.04 ± 0.02 a | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.04 ± 0.02 a | 0.03 ± 0.01 b |
| Taxifolin | 0.26 ± 0.00 c | 0.3 ± 0.00 b | 0.27 ± 0.00 c | 0.45 ± 0.02 a | 0.47 ± 0.01 a |
| 4-Hydrosxybenzaldehyde | 0.37 ± 0.02 a | 0.31 ± 0.01 c | 0.33 ± 0.02 bc | 0.35 ± 0.05 ab | 0.3 ± 0.01 c |
| Vanillin | 2.17 ± 0.05 a | 1.79 ± 0.05 c | 1.93 ± 0.17 b | 1.76 ± 0.16 c | 1.78 ± 0.09 c |
| Catechin | 8.81 ± 0.05 b | 9.23 ± 0.05 b | 9.01 ± 0.06 b | 10.40 ± 0.10 a | 6.83 ± 0.02 c |
| Epicatechin | 0.13 ± 0.01 b | 0.13 ± 0.00 b | 0.16 ± 0.01 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 bc | 0.11 ± 0.00 c |
| Naringin | 0.14 ± 0.01 a | 0.13 ± 0.00 a | 0.13 ± 0.01 a | 0.09 ± 0.01 b | 0.02 ± 0.00 c |
| Hesperidin | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.04 ± 0.00 b | 0.05 ± 0.01 a |
| Rutin | 0.74 ± 0.02 a | 0.72 ± 0.01 a | 0.67 ± 0.03 b | 0.47 ± 0.02 c | 0.25 ± 0.00 d |
| Myricetin | 0.00 ± 0.00 c | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.01 ± 0.00 b | 0.06 ± 0.01 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 c |
| Naringenin | 0.00 ± 0.00 e | 0.12 ± 0.01 c | 0.07 ± 0.01 d | 0.17 ± 0.01 a | 0.15 ± 0.00 b |
| Phloretin | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a | 0.00 ± 0.00 a |
| Quercetin | 1.14 ± 0.02 d | 1.7 ± 0.05 b | 1.25 ± 0.01 c | 6.2 ± 0.18 a | 0.34 ± 0.02 e |
| Isoquercitrin | 9.68 ± 0.15 a | 8.51 ± 0.10 b | 6.99 ± 0.07 c | 5.56 ± 0.06 d | 1.88 ± 0.01 e |
| Vitexin | 0.18 ± 0.00 a | 0.18 ± 0.01 a | 0.19 ± 0.02 a | 0.16 ± 0.00 b | 0.11 ± 0.00 c |
| Isovitexin | 7.51 ± 0.05 c | 7.35 ± 0.05 c | 6.99 ± 0.08 d | 10.05 ± 0.22 a | 8.08 ± 0.20 b |
| Kaempferol | 0.04 ± 0.01 b | 0.03 ± 0.01 c | 0.01 ± 0.01 e | 0.05 ± 0.02 a | 0.02 ± 0.00 d |
| Kaempferol-3-o-rutinoside | 1.21 ± 0.02 a | 1.17 ± 0.04 a | 1.05 ± 0.03 b | 0.16 ± 0.01 d | 0.35 ± 0.21 c |
| Diosmin | 12.76 ± 0.25 a | 12.41 ± 0.30 a | 11.72 ± 0.24 b | 12.79 ± 1.33 a | 0.91 ± 0.01 c |
| Homoorientin | 2.79 ± 0.09 b | 2.98 ± 0.06 b | 3.04 ± 0.02 b | 3.93 ± 0.22 a | 1.77 ± 0.01 c |
| Tectorigenin | 0.01 ± 0.01 c | 0.02 ± 0.01 b | 0 ± 0.00 d | 0.05 ± 0.01 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 b |
| Luteolin | 0 ± 0.00 e | 22.68 ± 0.08 b | 14.82 ± 0.23 d | 39.81 ± 0.97 a | 16.59 ± 0.41 c |
| Diosmetin | 0 ± 0.00 e | 131.37 ± 0.31 b | 95.18 ± 0.32 c | 185.39 ± 1.95 a | 83.1 ± 1.78 d |
| Psoralidin | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 a | 0 ± 0.00 a | nd |
| TPH | 104.31 ± 5.21 d | 256.55 ± 8.77 b | 209.24 ± 5.53 c | 323.44 ± 12.49 a | 202.50 ± 4.98 c |
| Groups | DPPH | ABTS | FRAP | AAC | α-Glucosidase | α-Amylase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPC | 0.881 * | 0.971 * | 0.970 * | |||
| TFC | 0.706 | 0.805 | 0.781 | |||
| α-Glucosidase | 0.346 | 0.186 | 0.028 | 0.934 * | ||
| α-Amylase | 0.191 | 0.011 | 0.869 | 0.982 * | ||
| p-hydroxybenzoic acid | 0.378 | 0.604 | 0.729 | |||
| Chlorgenic acid | 0.781 | 0.976 * | 0.984 * | 0.180 | 0.024 | |
| Vanillic acid | 0.417 | 0.608 | 0.684 | |||
| 2-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid | 0.612 | 0.874 | 0.931 * | 0.202 | 0.106 | |
| 2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | 0.642 | 0.693 | 0.746 | |||
| Caffeic acid | 0.259 | 0.515 | 0.668 | |||
| Syringic acid | 0.016 | 0.038 | 0.535 | 0.648 | 0.695 | |
| o-Coumaric Acid | 0.376 | 0.514 | 0.716 | |||
| Ferulic acid | 0.319 | 0.576 | 0.718 | |||
| Veratric acid | 0.054 | 0.386 | 0.280 | 0.569 | 0.300 | 0.211 |
| Benzoic acid | 0.525 | 0.730 | 0.828 | |||
| Salicylic acid | 0.457 | 0.679 | 0.798 | |||
| Procyanidin B2 | 0.252 | 0.171 | 0.533 | 0.302 | 0.244 | |
| Phlorogucinol | 0.502 | 0.555 | 0.626 | 0.368 | 0.506 | 0.469 |
| Pyrogallol | 0.805 | 0.483 | 0.433 | 0.064 | 0.141 | 0.054 |
| Sesamol | 0.173 | 0.403 | 0.322 | |||
| 4-Hydrosxybenzaldehyde | 0.018 | 0.238 | 0.089 | 0.227 | ||
| Vanillin | 0.392 | 0.669 | 0.550 | 0.627 | 0.355 | 0.217 |
| Epicatechin | 0.963 * | 0.866 | 0.807 | 0.187 | 0.102 | |
| Naringin | 0.574 | 0.791 | 0.784 | |||
| Hesperidin | 0.413 | 0.717 | 0.744 | 0.409 | 0.313 | 0.215 |
| Rutin | 0.545 | 0.813 | 0.846 | |||
| Isoquercitrin | 0.374 | 0.708 | 0.739 | |||
| Vitexin | 0.623 | 0.798 | 0.798 | |||
| Kaempferol-3-o-rutinoside | 0.638 | 0.902 * | 0.962 * | 0.093 | ||
| Diosmin | 0.291 | 0.481 | 0.474 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Lan, Y.; Dang, B.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; Du, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, Z. Polyphenol Profile and In Vitro Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Different Solvent Extracts of Highland Barley Bran. Molecules 2023, 28, 1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041665
Zhang W, Lan Y, Dang B, Zhang J, Zheng W, Du Y, Yang X, Li Z. Polyphenol Profile and In Vitro Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Different Solvent Extracts of Highland Barley Bran. Molecules. 2023; 28(4):1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041665
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wengang, Yongli Lan, Bin Dang, Jie Zhang, Wancai Zheng, Yan Du, Xijuan Yang, and Zhonghong Li. 2023. "Polyphenol Profile and In Vitro Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Different Solvent Extracts of Highland Barley Bran" Molecules 28, no. 4: 1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041665
APA StyleZhang, W., Lan, Y., Dang, B., Zhang, J., Zheng, W., Du, Y., Yang, X., & Li, Z. (2023). Polyphenol Profile and In Vitro Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibitory Activities of Different Solvent Extracts of Highland Barley Bran. Molecules, 28(4), 1665. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28041665