Immunomodulatory Activity of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Dasatinib to Elicit NK Cytotoxicity against Cancer, HIV Infection and Aging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Dasatinib
1.2. Natural Killer Cell Biology
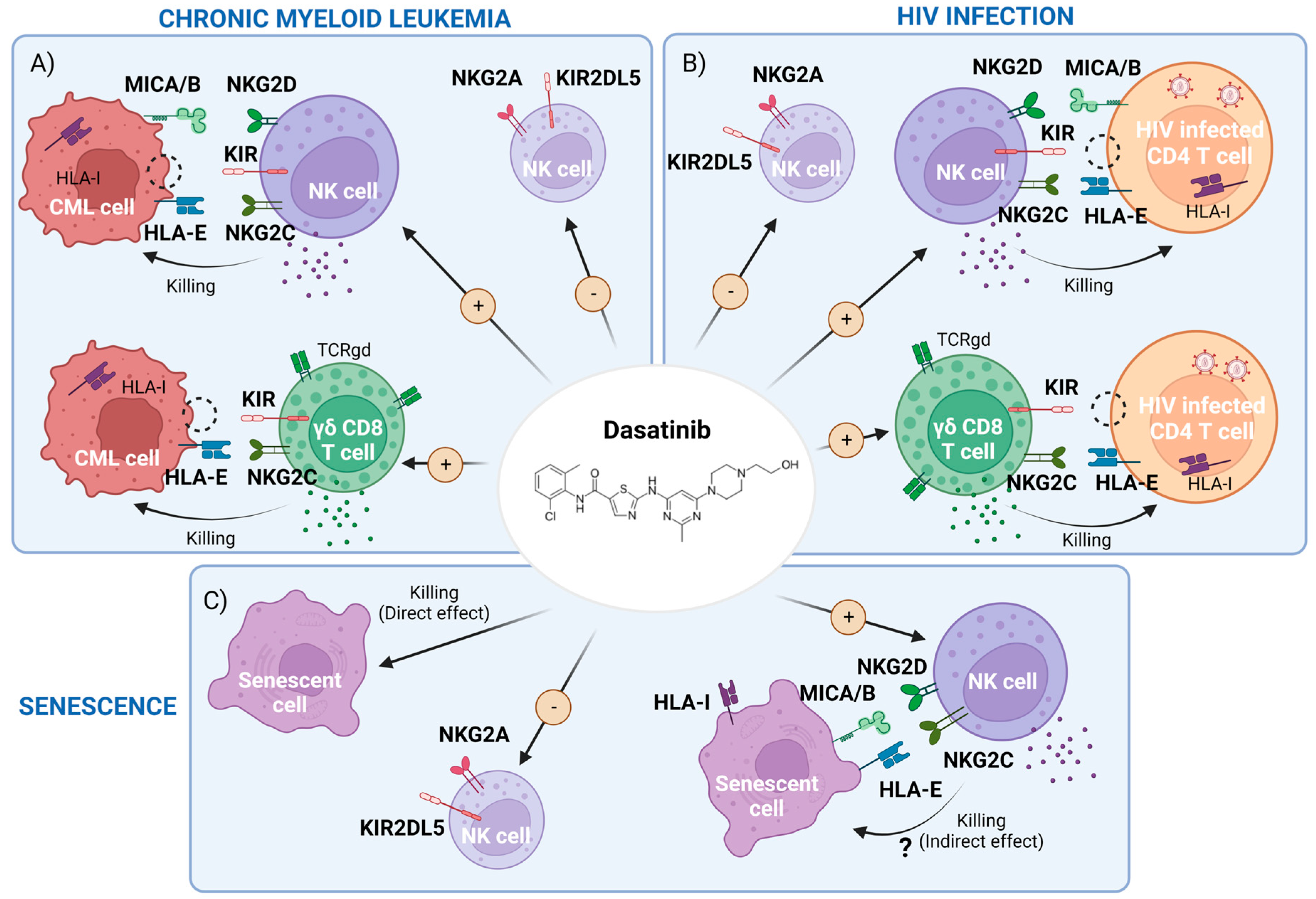
2. Dasatinib-Mediated Immunomodulatory Effects in CML
2.1. Dasatinib Effect on NK Cells and Innate T Cells
2.2. Dasatinib Increases Memory-like Natural Killer (NK) Subsets Displaying Activity against Both Leukemic and Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Infected Cells
2.3. CML Control and Therapeutic Treatment Interruption: Immunological Factors Involved in a Successful Treatment-Free Remission (TFR)
2.4. NK Immunogenetics Associated with CML Control or TFR
2.5. Dasatinib as an Immunomodulator in Other Therapeutic Strategies against Cancer
2.6. Summary of the CML Section
3. Potential Use of Dasatinib in the Setting of HIV-1 Infection
3.1. Effect of Dasatinib on HIV Infection and Reservoir: Direct Effect
3.2. Dasatinib’s Indirect Effect in HIV-1 Infection: Potentiation of NK and γδ CD8+T Cell Responses
3.3. NK Cells’ Role in HIV-Mediated Control and Functional Cure
3.4. Immunogenetic Factors of HIV Control and Functional Cure
3.5. Summary of the HIV Section
4. Dasatinib as a Senolytic Drug
4.1. Cellular Senescence Results in Increased Immune Surveillance
4.2. NK Cells Can Remove Senescent Tumor Cells
4.3. Senescent Cells Can Avoid NK-Cell Recognition, Thwarting Immune Clearance
4.4. Dasatinib as a Senolytic Therapy in Animal Models and Human Models
4.5. Summary of the Senescence Section
5. Concluding Remarks and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simoneau, C.-A. Treating Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Improving Management through Understanding of the Patient Experience. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2013, 17, E13–E20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Antonio, J. Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2007, 9, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Kantarjian, H.; Cortes, J. Imatinib and Beyond--Exploring the Full Potential of Targeted Therapy for CML. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, P.A.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Cortes, J.E. Diagnosis and Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in 2015. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2015, 90, 1440–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araujo, J.; Logothetis, C. Dasatinib: A Potent SRC Inhibitor in Clinical Development for the Treatment of Solid Tumors. Cancer Treat Rev 2010, 36, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, F.; Xu, Q.; Li, Q.; Cui, Z.; Li, W.; Zeng, F. Adverse Reactions after Treatment with Dasatinib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Characteristics, Potential Mechanisms, and Clinical Management Strategies. Front Oncol 2023, 13, 1113462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, K.; Kitawaki, T.; Sugimoto, N.; Sozu, T.; Anzai, N.; Okada, M.; Nohgawa, M.; Hatanaka, K.; Arima, N.; Ishikawa, T.; et al. Principal Component Analysis Uncovers Cytomegalovirus-Associated NK Cell Activation in Ph+ Leukemia Patients Treated with Dasatinib. Leukemia 2017, 31, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsieh, Y.-C.; Kirschner, K.; Copland, M. Improving Outcomes in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia through Harnessing the Immunological Landscape. Leukemia 2021, 35, 1229–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, N.F.; Kant, S.; Kiani, Z.; Tremblay, C.; Dupuy, F.P. Natural Killer Cells in Antibody Independent and Antibody Dependent HIV Control. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 879124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.; Xin, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, C.; Zhang, Z. Role of NKG2D and Its Ligands in Cancer Immunotherapy. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2064–2078. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Yin, J.; Sun, Q.; Hu, J.; Hong, M.; Qian, S.; Liu, W. The Prognostic Role of NKG2A Expression for Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after Treatment Discontinuation. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 2616–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindo, T.; Ureshino, H.; Kojima, H.; Tanaka, H.; Kimura, S. Allelic Polymorphisms of KIRs and Antitumor Immunity against Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Immunol. Med. 2021, 44, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Poursine-Laurent, J.; Truscott, S.M.; Lybarger, L.; Song, Y.-J.; Yang, L.; French, A.R.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Lemieux, S.; Hansen, T.H.; et al. Licensing of Natural Killer Cells by Host Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Molecules. Nature 2005, 436, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, J.E.; Hsu, K.C. Natural Killer Cell Education and the Response to Infection and Cancer Therapy: Stay Tuned. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 222–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, E.O.; Kim, H.S.; Liu, D.; Peterson, M.E.; Rajagopalan, S. Controlling Natural Killer Cell Responses: Integration of Signals for Activation and Inhibition. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 227–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fauriat, C.; Ivarsson, M.A.; Ljunggren, H.-G.; Malmberg, K.-J.; Michaëlsson, J. Education of Human Natural Killer Cells by Activating Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-like Receptors. Blood 2010, 115, 1166–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardiner, C.M.; Guethlein, L.A.; Shilling, H.G.; Pando, M.; Carr, W.H.; Rajalingam, R.; Vilches, C.; Parham, P. Different NK Cell Surface Phenotypes Defined by the DX9 Antibody Are Due to KIR3DL1 Gene Polymorphism. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 2992–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Izumi, K.; Shindo, T.; Ngo, H.T.; Nakayama-Hosoya, K.; Akahane, K.; Tamai, M.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Kawana-Tachikawa, A.; Inukai, T.; Takaori-Kondo, A. KIR3DL1 Allotype-Dependent Modulation of NK Cell Immunity against Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Immunohorizons 2021, 5, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Goodlett, D.R.; Ishitani, A.; Marquardt, H.; Geraghty, D.E. HLA-E Surface Expression Depends on Binding of TAP-Dependent Peptides Derived from Certain HLA Class I Signal Sequences. J. Immunol. 1998, 160, 4951–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horowitz, A.; Djaoud, Z.; Nemat-Gorgani, N.; Blokhuis, J.; Hilton, H.G.; Béziat, V.; Malmberg, K.-J.; Norman, P.J.; Guethlein, L.A.; Parham, P. Class I HLA Haplotypes Form Two Schools That Educate NK Cells in Different Ways. Sci. Immunol. 2016, 1, eaag1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marinelli Busilacchi, E.; Costantini, A.; Viola, N.; Costantini, B.; Olivieri, J.; Butini, L.; Mancini, G.; Scortechini, I.; Chiarucci, M.; Poiani, M.; et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor In Vitro and In Vivo Study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Damele, L.; Montaldo, E.; Moretta, L.; Vitale, C.; Mingari, M.C. Effect of Tyrosin Kinase Inhibitors on NK Cell and ILC3 Development and Function. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giansanti, P.; Preisinger, C.; Huber, K.V.M.; Gridling, M.; Superti-Furga, G.; Bennett, K.L.; Heck, A.J.R. Evaluating the Promiscuous Nature of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Assessed in A431 Epidermoid Carcinoma Cells by Both Chemical- and Phosphoproteomics. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.; Clarson, J.; Tang, C.; Vidovic, L.; White, D.L.; Hughes, T.P.; Yong, A.S.M. CML Patients with Deep Molecular Responses to TKI Have Restored Immune Effectors and Decreased PD-1 and Immune Suppressors. Blood 2017, 129, 1166–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hughes, A.; Yong, A.S.M. Immune Effector Recovery in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia and Treatment-Free Remission. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nomura, S.; Ito, T.; Satake, A.; Ishii, K. Assessment of Soluble Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte-Associated Antigen-4, Transforming Growth Factor Β1, and Platelet-Derived Microparticles during Dasatinib Therapy for Patients with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. J. Blood Med. 2019, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Najima, Y.; Yoshida, C.; Iriyama, N.; Fujisawa, S.; Wakita, H.; Chiba, S.; Okamoto, S.; Kawakami, K.; Takezako, N.; Kumagai, T.; et al. Regulatory T Cell Inhibition by Dasatinib Is Associated with Natural Killer Cell Differentiation and a Favorable Molecular Response—The Final Results of the D-First Study. Leuk. Res. 2018, 66, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiansson, L.; Söderlund, S.; Mangsbo, S.; Hjorth-Hansen, H.; Höglund, M.; Markevärn, B.; Richter, J.; Stenke, L.; Mustjoki, S.; Loskog, A.; et al. The Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Imatinib and Dasatinib Reduce Myeloid Suppressor Cells and Release Effector Lymphocyte Responses. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mustjoki, S.; Ekblom, M.; Arstila, T.P.; Dybedal, I.; Epling-Burnette, P.K.; Guilhot, F.; Hjorth-Hansen, H.; Höglund, M.; Kovanen, P.; Laurinolli, T.; et al. Clonal Expansion of T/NK-Cells during Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Dasatinib Therapy. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Z.-Y.; Xu, W.; Li, J.-Y. Large Granular Lymphocytosis during Dasatinib Therapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Takaku, T.; Takeda, K.; Shirane, S.; Toyota, T.; Koike, M.; Noguchi, M.; Hirano, T.; Fujiwara, H.; Komatsu, N. Dasatinib-Induced Anti-Leukemia Cellular Immunity through a Novel Subset of CD57 Positive Helper/Cytotoxic CD4 T Cells in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Patients. Int. J. Hematol. 2018, 108, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzman, A.; Juvonen, V.; Kairisto, V.; Ekblom, M.; Stenke, L.; Seggewiss, R.; Porkka, K.; Mustjoki, S. Mono/Oligoclonal T and NK Cells Are Common in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients at Diagnosis and Expand during Dasatinib Therapy. Blood 2010, 116, 772–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mustjoki, S.; Auvinen, K.; Kreutzman, A.; Rousselot, P.; Hernesniemi, S.; Melo, T.; Lahesmaa-Korpinen, A.-M.; Hautaniemi, S.; Bouchet, S.; Molimard, M.; et al. Rapid Mobilization of Cytotoxic Lymphocytes Induced by Dasatinib Therapy. Leukemia 2013, 27, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schiffer, C.A.; Cortes, J.E.; Hochhaus, A.; Saglio, G.; le Coutre, P.; Porkka, K.; Mustjoki, S.; Mohamed, H.; Shah, N.P. Lymphocytosis after Treatment with Dasatinib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Effects on Response and Toxicity. Cancer 2016, 122, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kamel-Reid, S.; Chang, H.; Sutherland, R.; Jung, C.W.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, J.-J.; Lipton, J.H. Natural Killer or Natural Killer/T Cell Lineage Large Granular Lymphocytosis Associated with Dasatinib Therapy for Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Leukemia. Haematologica 2009, 94, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lissina, A.; McLaren, J.E.; Ilander, M.; Andersson, E.I.; Lewis, C.S.; Clement, M.; Herman, A.; Ladell, K.; Llewellyn-Lacey, S.; Miners, K.L.; et al. Divergent Roles for Antigenic Drive in the Aetiology of Primary versus Dasatinib-Associated CD8+ TCR-Vβ+ Expansions. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barbarin, A.; Abdallah, M.; Lefèvre, L.; Piccirilli, N.; Cayssials, E.; Roy, L.; Gombert, J.-M.; Herbelin, A. Innate T-Aβ Lymphocytes as New Immunological Components of Anti-Tumoral “off-Target” Effects of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Dasatinib. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, Y.; Nakamae, H.; Katayama, T.; Nakane, T.; Koh, H.; Nakamae, M.; Hirose, A.; Hagihara, K.; Terada, Y.; Nakao, Y.; et al. Different Immunoprofiles in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Imatinib, Nilotinib or Dasatinib. Leuk. Lymphoma 2012, 53, 1084–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreutzman, A.; Jaatinen, T.; Greco, D.; Vakkila, E.; Richter, J.; Ekblom, M.; Hjorth-Hansen, H.; Stenke, L.; Melo, T.; Paquette, R.; et al. Killer-Cell Immunoglobulin-like Receptor Gene Profile Predicts Good Molecular Response to Dasatinib Therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Exp. Hematol. 2012, 40, 906–913.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassold, N.; Seystahl, K.; Kempf, K.; Urlaub, D.; Zekl, M.; Einsele, H.; Watzl, C.; Wischhusen, J.; Seggewiss-Bernhardt, R. Enhancement of Natural Killer Cell Effector Functions against Selected Lymphoma and Leukemia Cell Lines by Dasatinib. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, E916–E927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.-X.; Wang, J.-P.; Lai, Y.-L.; Wu, H.; Sun, Y.-C.; Zhou, M.; Ouyang, G.-F.; Huang, H. Effects of Dasatinib on the Expansion, Subsets, Receptor Expression and Cytotoxic Function of NK Cells in Vitro. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2020, 28, 1762–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.-C.; Cheng, H.-I.; Hsu, K.; Hsu, Y.-N.; Kao, C.-W.; Chang, Y.-F.; Lim, K.-H.; Chen, C.G. NKG2A Down-Regulation by Dasatinib Enhances Natural Killer Cytotoxicity and Accelerates Effective Treatment Responses in Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kreutzman, A.; Ladell, K.; Koechel, C.; Gostick, E.; Ekblom, M.; Stenke, L.; Melo, T.; Einsele, H.; Porkka, K.; Price, D.A.; et al. Expansion of Highly Differentiated CD8+ T-Cells or NK-Cells in Patients Treated with Dasatinib Is Associated with Cytomegalovirus Reactivation. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rölle, A.; Brodin, P. Immune Adaptation to Environmental Influence: The Case of NK Cells and HCMV. Trends Immunol. 2016, 37, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, N.; Ishiyama, K.; Kitawaki, T. Cytomegalovirus Pulls Strings behind NK Cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93297–93298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Climent, N.; Plana, M. Immunomodulatory Activity of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Elicit Cytotoxicity Against Cancer and Viral Infection. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, K.-I.; Kitawaki, T.; Otsuka, Y.; Takaori-Kondo, A.; Kadowaki, N. Programmed Cell Death 1-Expressing CD56-Negative Natural Killer (NK) Cell Expansion Is a Hallmark of Chronic NK Cell Activation during Dasatinib Treatment. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duerkop, B.A.; Hooper, L.V. Resident Viruses and Their Interactions with the Immune System. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Saglio, G.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Baccarani, M.; Mayer, J.; Boqué, C.; Shah, N.P.; Chuah, C.; Casanova, L.; Bradley-Garelik, B.; et al. Final 5-Year Study Results of DASISION: The Dasatinib Versus Imatinib Study in Treatment-Naïve Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2333–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saußele, S.; Richter, J.; Hochhaus, A.; Mahon, F.-X. The Concept of Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2016, 30, 1638–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.; Rea, D.; Lipton, J.H. Treatment-Free Remission with First- and Second-Generation Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guru Murthy, G.S.; Atallah, E. Treatment-Free Remission in CML: The US Perspective. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2019, 14, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imagawa, J.; Tanaka, H.; Okada, M.; Nakamae, H.; Hino, M.; Murai, K.; Ishida, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Sato, S.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Discontinuation of Dasatinib in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Who Have Maintained Deep Molecular Response for Longer than 1 Year (DADI Trial): A Multicentre Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2015, 2, e528–e535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoguchi, I.; Yoshimoto, T.; Katagiri, S.; Mizuguchi, J.; Tauchi, T.; Kimura, Y.; Inokuchi, K.; Ohyashiki, J.H.; Ohyashiki, K. Sustained Upregulation of Effector Natural Killer Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia after Discontinuation of Imatinib. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, D.; Henry, G.; Khaznadar, Z.; Etienne, G.; Guilhot, F.; Nicolini, F.; Guilhot, J.; Rousselot, P.; Huguet, F.; Legros, L.; et al. Natural Killer-Cell Counts Are Associated with Molecular Relapse-Free Survival after Imatinib Discontinuation in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: The IMMUNOSTIM Study. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1368–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ureshino, H.; Kamachi, K.; Sano, H.; Okamoto, S.; Itamura, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Katsuya, H.; Ando, T.; Kimura, S. Higher Neutrophil Counts Are Associated with Successful Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Discontinuation in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Hematology 2022, 27, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilander, M.; Olsson-Strömberg, U.; Schlums, H.; Guilhot, J.; Brück, O.; Lähteenmäki, H.; Kasanen, T.; Koskenvesa, P.; Söderlund, S.; Höglund, M.; et al. Increased Proportion of Mature NK Cells Is Associated with Successful Imatinib Discontinuation in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, R.; Onizuka, M.; Matsusita, E.; Kikkawa, E.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsushita, H.; Ohgiya, D.; Murayama, H.; Machida, S.; Ohmachi, K.; et al. NKG2D Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated with Disease Control of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia by Dasatinib. Int. J. Hematol. 2017, 106, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.; Clarson, J.; White, D.L.; Ross, D.M.; Hughes, T.P.; Yong, A.S. Enhanced Natural Killer and Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Responses, with Decreased Monocytic Myeloid Derived Suppressor Cells May Promote Treatment Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Patients Following Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Cessation. Blood 2016, 128, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchert, A.; Saussele, S.; Eigendorff, E.; Müller, M.C.; Sohlbach, K.; Inselmann, S.; Schütz, C.; Metzelder, S.K.; Ziermann, J.; Kostrewa, P.; et al. Interferon Alpha 2 Maintenance Therapy May Enable High Rates of Treatment Discontinuation in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puzzolo, M.C.; Breccia, M.; Mariglia, P.; Colafigli, G.; Pepe, S.; Scalzulli, E.; Mariggiò, E.; Latagliata, R.; Guarini, A.; Foà, R. Immunomodulatory Effects of IFNα on T and NK Cells in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients in Deep Molecular Response Preparing for Treatment Discontinuation. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rea, D.; Nicolini, F.E.; Tulliez, M.; Guilhot, F.; Guilhot, J.; Guerci-Bresler, A.; Gardembas, M.; Coiteux, V.; Guillerm, G.; Legros, L.; et al. Discontinuation of Dasatinib or Nilotinib in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Interim Analysis of the STOP 2G-TKI Study. Blood 2017, 129, 846–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okada, M.; Imagawa, J.; Tanaka, H.; Nakamae, H.; Hino, M.; Murai, K.; Ishida, Y.; Kumagai, T.; Sato, S.; Ohashi, K.; et al. Final 3-Year Results of the Dasatinib Discontinuation Trial in Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Who Received Dasatinib as a Second-Line Treatment. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018, 18, 353–360.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, C.; Iriyama, N.; Najima, Y.; Fujisawa, S.; Wakita, H.; Chiba, S.; Okamoto, S.; Kawakami, K.; Takezako, N.; Kumagai, T.; et al. Association of Peripheral Regulatory T Cells with Achievement of Deep Molecular Response in Newly Diagnosed Chronic Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Dasatinib - the Final Results of D-First Study. Blood 2016, 128, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takaku, T.; Iriyama, N.; Mitsumori, T.; Sato, E.; Gotoh, A.; Kirito, K.; Noguchi, M.; Koike, M.; Sakamoto, J.; Oba, K.; et al. Clinical Efficacy and Safety of First-Line Dasatinib Therapy and the Relevance of Velocity of BCR-ABL1 Transcript Decline for Achievement of Molecular Responses in Newly Diagnosed Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: Report from the Juntendo Yamanashi Cooperative Study Group. Oncology 2018, 94, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayssials, E.; Jacomet, F.; Piccirilli, N.; Lefèvre, L.; Roy, L.; Guilhot, F.; Chomel, J.-C.; Leleu, X.; Gombert, J.-M.; Herbelin, A.; et al. Sustained Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Is Associated with an Increased Frequency of Innate CD8(+) T-Cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigón, L.; Luna, A.; Galán, M.; Rodríguez-Mora, S.; Fuertes, D.; Mateos, E.; Piris-Villaespesa, M.; Bautista, G.; San José, E.; Rivera-Torres, J.; et al. Identification of Immunological Parameters as Predictive Biomarkers of Relapse in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia on Treatment-Free Remission. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, Y.D.; Hughes, A.; Clarson, J.; Kok, C.H.; Shanmuganathan, N.; White, D.L.; Yeung, D.T.; Ross, D.M.; Hughes, T.P.; Yong, A.S.M. Successful Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia and Its Association with Reduced Immune Suppressors and Increased Natural Killer Cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuckey, R.; López Rodríguez, J.F.; Gómez-Casares, M.T. Discontinuation of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Review of the Biological Factors Associated with Treatment-Free Remission. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2022, 24, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlums, H.; Cichocki, F.; Tesi, B.; Theorell, J.; Beziat, V.; Holmes, T.D.; Han, H.; Chiang, S.C.C.; Foley, B.; Mattsson, K.; et al. Cytomegalovirus Infection Drives Adaptive Epigenetic Diversification of NK Cells with Altered Signaling and Effector Function. Immunity 2015, 42, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Tian, Z. NK Cell Education via Nonclassical MHC and Non-MHC Ligands. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Melendez, E.; Chondronasiou, D.; Mosteiro, L.; Martínez de Villarreal, J.; Fernández-Alfara, M.; Lynch, C.J.; Grimm, D.; Real, F.X.; Alcamí, J.; Climent, N.; et al. Natural Killer Cells Act as an Extrinsic Barrier for in Vivo Reprogramming. Development 2022, 149, dev200361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yawata, M.; Yawata, N.; Draghi, M.; Little, A.-M.; Partheniou, F.; Parham, P. Roles for HLA and KIR Polymorphisms in Natural Killer Cell Repertoire Selection and Modulation of Effector Function. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, G.M.; Guinan, K.J.; Cunningham, R.T.; Middleton, D.; Parham, P.; Gardiner, C.M. Functional Polymorphism of the KIR3DL1/S1 Receptor on Human NK Cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caocci, G.; Martino, B.; Greco, M.; Abruzzese, E.; Trawinska, M.M.; Lai, S.; Ragatzu, P.; Galimberti, S.; Baratè, C.; Mulas, O.; et al. Killer Immunoglobulin-like Receptors Can Predict TKI Treatment-Free Remission in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Exp. Hematol. 2015, 43, 1015–1018.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ureshino, H.; Shindo, T.; Kojima, H.; Kusunoki, Y.; Miyazaki, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Saji, H.; Kawaguchi, A.; Kimura, S. Allelic Polymorphisms of KIRs and HLAs Predict Favorable Responses to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in CML. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- La Nasa, G.; Caocci, G.; Littera, R.; Atzeni, S.; Vacca, A.; Mulas, O.; Langiu, M.; Greco, M.; Orrù, S.; Orrù, N.; et al. Homozygosity for Killer Immunoglobin-like Receptor Haplotype A Predicts Complete Molecular Response to Treatment with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients. Exp. Hematol. 2013, 41, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, D.T.; Tang, C.; Vidovic, L.; White, D.L.; Branford, S.; Hughes, T.P.; Yong, A.S. KIR2DL5B Genotype Predicts Outcomes in CML Patients Treated with Response-Directed Sequential Imatinib/Nilotinib Strategy. Blood 2015, 126, 2720–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ureshino, H.; Shindo, T.; Tanaka, H.; Saji, H.; Kimura, S. HLA Polymorphisms Are Associated with Treatment-Free Remission Following Discontinuation of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Villanueva, P.O.; Yunis, E.J.; Delgado, J.C.; Vittinghoff, E.; Buchbinder, S.; Leung, J.Y.; Uglialoro, A.M.; Clavijo, O.P.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Kalams, S.A.; et al. Control of HIV-1 Viremia and Protection from AIDS Are Associated with HLA-Bw4 Homozygosity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 5140–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, G.-T.; Mao, L.; Wu, L.; Deng, W.-W.; Bu, L.-L.; Liu, J.-F.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.-L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, W.-F.; et al. Inhibition of SRC Family Kinases Facilitates Anti-CTLA4 Immunotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4223–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, M.M.; Lee, F.Y.F.; Jones, R.T.; Kimball, A.K.; Saravia, E.; Graziano, R.F.; Coleman, B.; Menard, K.; Yan, J.; Michaud, E.; et al. Targeting DDR2 Enhances Tumor Response to Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaav2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mestermann, K.; Giavridis, T.; Weber, J.; Rydzek, J.; Frenz, S.; Nerreter, T.; Mades, A.; Sadelain, M.; Einsele, H.; Hudecek, M. The Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Dasatinib Acts as a Pharmacologic on/off Switch for CAR T Cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau5907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, Y.; Shao, M.; Teng, X.; Jiang, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Cui, J.; Yu, J.; Liang, Z.; et al. Dasatinib Enhances Anti-Leukemia Efficacy of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells by Inhibiting Cell Differentiation and Exhaustion. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Board, N.L.; Moskovljevic, M.; Wu, F.; Siliciano, R.F.; Siliciano, J.D. Engaging Innate Immunity in HIV-1 Cure Strategies. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2022, 22, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmussen, T.A.; Tolstrup, M.; Søgaard, O.S. Reversal of Latency as Part of a Cure for HIV-1. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiras, M.; Ambrosioni, J.; Cervantes, F.; Miró, J.M.; Alcamí, J. Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Potential Use and Safety Considerations in HIV-1 Infection. Expert. Opin. Drug Saf. 2017, 16, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermejo, M.; López-Huertas, M.R.; García-Pérez, J.; Climent, N.; Descours, B.; Ambrosioni, J.; Mateos, E.; Rodríguez-Mora, S.; Rus-Bercial, L.; Benkirane, M.; et al. Dasatinib Inhibits HIV-1 Replication through the Interference of SAMHD1 Phosphorylation in CD4+ T Cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 106, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coiras, M.; Bermejo, M.; Descours, B.; Mateos, E.; García-Pérez, J.; López-Huertas, M.-R.; Lederman, M.M.; Benkirane, M.; Alcamí, J. IL-7 Induces SAMHD1 Phosphorylation in CD4+ T Lymphocytes, Improving Early Steps of HIV-1 Life Cycle. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bermejo, M.; Ambrosioni, J.; Bautista, G.; Climent, N.; Mateos, E.; Rovira, C.; Rodríguez-Mora, S.; López-Huertas, M.R.; García-Gutiérrez, V.; Steegmann, J.L.; et al. Evaluation of Resistance to HIV-1 Infection Ex Vivo of PBMCs Isolated from Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treated with Different Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 156, 248–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.S.C.P.; Szaniawski, M.A.; Martins, L.J.; Innis, E.A.; Alcamí, J.; Hanley, T.M.; Spivak, A.M.; Coiras, M.; Planelles, V. Dasatinib: Effects on the Macrophage Phospho Proteome with a Focus on SAMHD1 and HIV-1 Infection. Clin. Res. HIV AIDS 2022, 8, 1053. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, S.D.S.; Leontyev, D.; Nicoletti, P.; Binnington, B.; Kozlowski, H.N.; Ostrowski, M.; Cochrane, A.; Branch, D.R.; Wong, R.W. Targeting ABL1 or ARG Tyrosine Kinases to Restrict HIV-1 Infection in Primary CD4+ T-Cells or in Humanized NSG Mice. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2019, 82, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigón, L.; Rodríguez-Mora, S.; Luna, A.; Sandonís, V.; Mateos, E.; Bautista, G.; Steegmann, J.L.; Climent, N.; Plana, M.; Pérez-Romero, P.; et al. Cytotoxic Cell Populations Developed during Treatment with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Protect Autologous CD4+ T Cells from HIV-1 Infection. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 182, 114203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigón, L.; Martínez-Román, P.; Rodríguez-Mora, S.; Torres, M.; Puertas, M.C.; Mateos, E.; Salgado, M.; Navarro, A.; Sánchez-Conde, M.; Ambrosioni, J.; et al. Provirus Reactivation Is Impaired in HIV-1 Infected Individuals on Treatment with Dasatinib and Antiretroviral Therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 192, 114666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innis, E.A.; Levinger, C.; Szaniawski, M.A.; Williams, E.S.C.P.; Alcamí, J.; Bosque, A.; Schiffer, J.T.; Coiras, M.; Spivak, A.M.; Planelles, V. Pharmacologic Control of Homeostatic and Antigen-Driven Proliferation to Target HIV-1 Persistence. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 194, 114816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, N.; Ambrosioni, J.; González, T.; Xufré, C.; Casadellà, M.; Noguera-Julian, M.; Paredes, R.; Plana, M.; Grau-Expósito, J.; Mallolas, J.; et al. Immunological and Virological Findings in a Patient with Exceptional Post-Treatment Control: A Case Report. Lancet HIV 2023, 10, e42–e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Gaona, N.; Gallego, A.; Astorga, A.; Rallón, N.; Benito, J.M.; Falcó, V.; Genescà, M.; Buzón, M.J. Characterization of NK Cells in Elite Controllers Losig HIV Control. [CROI Abstract 307]. In Proceedings of the CROI 2022 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, Virtual, 12–16 February 2022; p. 118. [Google Scholar]
- Gondois-Rey, F.; Chéret, A.; Granjeaud, S.; Mallet, F.; Bidaut, G.; Lécuroux, C.; Ploquin, M.; Müller-Trutwin, M.; Rouzioux, C.; Avettand-Fenoël, V.; et al. NKG2C+ Memory-like NK Cells Contribute to the Control of HIV Viremia during Primary Infection: Optiprim-ANRS 147. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2017, 6, e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flórez-Álvarez, L.; Hernandez, J.C.; Zapata, W. NK Cells in HIV-1 Infection: From Basic Science to Vaccine Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peppa, D.; Pedroza-Pacheco, I.; Pellegrino, P.; Williams, I.; Maini, M.K.; Borrow, P. Adaptive Reconfiguration of Natural Killer Cells in HIV-1 Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sáez-Cirión, A.; Bacchus, C.; Hocqueloux, L.; Avettand-Fenoel, V.; Girault, I.; Lecuroux, C.; Potard, V.; Versmisse, P.; Melard, A.; Prazuck, T.; et al. Post-Treatment HIV-1 Controllers with a Long-Term Virological Remission after the Interruption of Early Initiated Antiretroviral Therapy ANRS VISCONTI Study. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namazi, G.; Fajnzylber, J.M.; Aga, E.; Bosch, R.J.; Acosta, E.P.; Sharaf, R.; Hartogensis, W.; Jacobson, J.M.; Connick, E.; Volberding, P.; et al. The Control of HIV After Antiretroviral Medication Pause (CHAMP) Study: Posttreatment Controllers Identified From 14 Clinical Studies. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1954–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, J.M.; Listgarten, J.; Pfeifer, N.; Tan, V.; Kadie, C.; Walker, B.D.; Ndung’u, T.; Shapiro, R.; Frater, J.; Brumme, Z.L.; et al. Widespread Impact of HLA Restriction on Immune Control and Escape Pathways of HIV-1. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5230–5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, X.; Xia, W.; Li, W.; Zhang, T.; Wu, H.; Xu, X.; Yan, H. HLA-B*44 Is Associated with a Lower Viral Set Point and Slow CD4 Decline in a Cohort of Chinese Homosexual Men Acutely Infected with HIV-1. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, K.K.; Qin, M.; Brummel, S.S.; Angelidou, K.; Trout, R.N.; Fenton, T.; Spector, S.A. Killer Cell Immunoglobulin-Like Receptor Alleles Alter HIV Disease in Children. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruthamuthu, S.; Rajalingam, R.; Pandian, K.; Madasamy, S.; Manoharan, M.; Pitchai, L.; Murugesan, A.; Mariakuttikan, J. Inhibitory Natural Killer Cell Receptor KIR3DL1 with Its Ligand Bw4 Constraints HIV-1 Disease among South Indians. AIDS 2018, 32, 2679–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsuran, V.; Naranbhai, V.; Horowitz, A.; Qi, Y.; Martin, M.P.; Yuki, Y.; Gao, X.; Walker-Sperling, V.; Del Prete, G.Q.; Schneider, D.K.; et al. Elevated HLA-A Expression Impairs HIV Control through Inhibition of NKG2A-Expressing Cells. Science 2018, 359, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boulet, S.; Song, R.; Kamya, P.; Bruneau, J.; Shoukry, N.H.; Tsoukas, C.M.; Bernard, N.F. HIV Protective KIR3DL1 and HLA-B Genotypes Influence NK Cell Function Following Stimulation with HLA-Devoid Cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parsons, M.S.; Boulet, S.; Song, R.; Bruneau, J.; Shoukry, N.H.; Routy, J.-P.; Tsoukas, C.M.; Bernard, N.F. Mind the Gap: Lack of Association between KIR3DL1*004/HLA-Bw4-Induced Natural Killer Cell Function and Protection from HIV Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202 (Suppl. S3), S356–S360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kamya, P.; Boulet, S.; Tsoukas, C.M.; Routy, J.-P.; Thomas, R.; Côté, P.; Boulassel, M.-R.; Baril, J.-G.; Kovacs, C.; Migueles, S.A.; et al. Receptor-Ligand Requirements for Increased NK Cell Polyfunctional Potential in Slow Progressors Infected with HIV-1 Coexpressing KIR3DL1*h/*y and HLA-B*57. J. Virol. 2011, 85, 5949–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, O.; Maréchal, V.; Le Gall, S.; Lemonnier, F.; Heard, J.M. Endocytosis of Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Molecules Is Induced by the HIV-1 Nef Protein. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, G.B.; Gandhi, R.T.; Davis, D.M.; Mandelboim, O.; Chen, B.K.; Strominger, J.L.; Baltimore, D. The Selective Downregulation of Class I Major Histocompatibility Complex Proteins by HIV-1 Protects HIV-Infected Cells from NK Cells. Immunity 1999, 10, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaparte, M.I.; Barker, E. Killing of Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Primary T-Cell Blasts by Autologous Natural Killer Cells Is Dependent on the Ability of the Virus to Alter the Expression of Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Molecules. Blood 2004, 104, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apps, R.; Del Prete, G.Q.; Chatterjee, P.; Lara, A.; Brumme, Z.L.; Brockman, M.A.; Neil, S.; Pickering, S.; Schneider, D.K.; Piechocka-Trocha, A.; et al. HIV-1 Vpu Mediates HLA-C Downregulation. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, R.; Lisovsky, I.; Lebouché, B.; Routy, J.-P.; Bruneau, J.; Bernard, N.F. HIV Protective KIR3DL1/S1-HLA-B Genotypes Influence NK Cell-Mediated Inhibition of HIV Replication in Autologous CD4 Targets. PLoS Pathog 2014, 10, e1003867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, Z.; Dupuy, F.P.; Bruneau, J.; Lebouché, B.; Retière, C.; Geraghty, D.E.; Bernard, N.F. The Education of NK Cells Determines Their Responsiveness to Autologous HIV-Infected CD4 T Cells. J. Virol. 2019, 93, e01185-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Körner, C.; Simoneau, C.R.; Schommers, P.; Granoff, M.; Ziegler, M.; Hölzemer, A.; Lunemann, S.; Chukwukelu, J.; Corleis, B.; Naranbhai, V.; et al. HIV-1-Mediated Downmodulation of HLA-C Impacts Target Cell Recognition and Antiviral Activity of NK Cells. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 111–119.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vieira, V.A.; Adland, E.; Malone, D.F.G.; Martin, M.P.; Groll, A.; Ansari, M.A.; Garcia-Guerrero, M.C.; Puertas, M.C.; Muenchhoff, M.; Guash, C.F.; et al. An HLA-I Signature Favouring KIR-Educated Natural Killer Cells Mediates Immune Control of HIV in Children and Contrasts with the HLA-B-Restricted CD8+ T-Cell-Mediated Immune Control in Adults. PLoS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1010090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.; Low, H.Z.; Kniesch, K.; Jacobs, R.; Schmidt, R.E.; Witte, T. NKG2C Deletion Is a Risk Factor of HIV Infection. AIDS Res. Hum. Retrovir. 2012, 28, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Essat, A.; Scott-Algara, D.; Monceaux, V.; Avettand-Fenoel, V.; Didier, C.; Caillat-Zucman, S.; Orr, S.; Theodorou, I.; Goujard, C.; Boufassa, F.; et al. Association between Immunogenetic Factors and Post-Treatment Control of HIV-1 Infection. ANRS VISCONTI and PRIMO Studies. In Proceedings of the 22nd International AIDS Conference (AIDS 2018), Amsterdam, Netherlands, 23–27 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sáez-Cirión, A. Mechanisms of Post-Treatment HIV Control: ANRS VISCONTI Study. In Proceedings of the IAS 2019, 10th International Conference on HIV Science, Mexico City, Mexico, 21 July 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juno, J.A.; Kent, S.J. What Can Gamma Delta T Cells Contribute to an HIV Cure? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambotte, O.; Boufassa, F.; Madec, Y.; Nguyen, A.; Goujard, C.; Meyer, L.; Rouzioux, C.; Venet, A.; Delfraissy, J.-F. SEROCO-HEMOCO Study Group HIV Controllers: A Homogeneous Group of HIV-1-Infected Patients with Spontaneous Control of Viral Replication. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 1053–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLaren, P.J.; Ripke, S.; Pelak, K.; Weintrob, A.C.; Patsopoulos, N.A.; Jia, X.; Erlich, R.L.; Lennon, N.J.; Kadie, C.M.; Heckerman, D.; et al. Fine-Mapping Classical HLA Variation Associated with Durable Host Control of HIV-1 Infection in African Americans. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 4334–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, D.; Johnson, S.A.; Peterson, B.A.; Natarajan, V.; Salgado, M.; Dewar, R.L.; Burbelo, P.D.; Doria-Rose, N.A.; Graf, E.H.; Greenwald, J.H.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Unique Cases with Extraordinary Control over HIV Replication. Blood 2012, 119, 4645–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casado, C.; Galvez, C.; Pernas, M.; Tarancon-Diez, L.; Rodriguez, C.; Sanchez-Merino, V.; Vera, M.; Olivares, I.; De Pablo-Bernal, R.; Merino-Mansilla, A.; et al. Permanent Control of HIV-1 Pathogenesis in Exceptional Elite Controllers: A Model of Spontaneous Cure. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, C.; Lian, X.; Gao, C.; Sun, X.; Einkauf, K.B.; Chevalier, J.M.; Chen, S.M.Y.; Hua, S.; Rhee, B.; Chang, K.; et al. Distinct Viral Reservoirs in Individuals with Spontaneous Control of HIV-1. Nature 2020, 585, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Picado, J. Exceptional HIV Elite Controllers. Towards an HIV Cure. In Proceedings of the AIDS 2022 Congress, Montreal, Canada, 28 July 2022; Abstract Supplement Abstracts from AIDS 2022—the 24th International AIDS Conference, Virtual, 29 July–2 August 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, G.; Seiger, K.; Lian, X.; Sun, W.; Parsons, E.M.; Gao, C.; Rassadkina, Y.; Polo, M.L.; Czernikier, A.; Ghiglione, Y.; et al. A Possible Sterilizing Cure of HIV-1 Infection Without Stem Cell Transplantation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2022, 175, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campisi, J. Aging, Cellular Senescence, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demaria, M.; Ohtani, N.; Youssef, S.A.; Rodier, F.; Toussaint, W.; Mitchell, J.R.; Laberge, R.-M.; Vijg, J.; Van Steeg, H.; Dollé, M.E.T.; et al. An Essential Role for Senescent Cells in Optimal Wound Healing through Secretion of PDGF-AA. Dev. Cell 2014, 31, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritschka, B.; Storer, M.; Mas, A.; Heinzmann, F.; Ortells, M.C.; Morton, J.P.; Sansom, O.J.; Zender, L.; Keyes, W.M. The Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype Induces Cellular Plasticity and Tissue Regeneration. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 172–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paramos-de-Carvalho, D.; Martins, I.; Cristóvão, A.M.; Dias, A.F.; Neves-Silva, D.; Pereira, T.; Chapela, D.; Farinho, A.; Jacinto, A.; Saúde, L. Targeting Senescent Cells Improves Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calcinotto, A.; Kohli, J.; Zagato, E.; Pellegrini, L.; Demaria, M.; Alimonti, A. Cellular Senescence: Aging, Cancer, and Injury. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1047–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasser, S.; Orsulic, S.; Brown, E.J.; Raulet, D.H. The DNA Damage Pathway Regulates Innate Immune System Ligands of the NKG2D Receptor. Nature 2005, 436, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krizhanovsky, V.; Yon, M.; Dickins, R.A.; Hearn, S.; Simon, J.; Miething, C.; Yee, H.; Zender, L.; Lowe, S.W. Senescence of Activated Stellate Cells Limits Liver Fibrosis. Cell 2008, 134, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sagiv, A.; Burton, D.G.A.; Moshayev, Z.; Vadai, E.; Wensveen, F.; Ben-Dor, S.; Golani, O.; Polic, B.; Krizhanovsky, V. NKG2D Ligands Mediate Immunosurveillance of Senescent Cells. Aging 2016, 8, 328–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arora, S.; Thompson, P.J.; Wang, Y.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Apostolopoulou, H.; Hatano, R.; Naikawadi, R.P.; Shah, A.; Wolters, P.J.; Koliwad, S.; et al. Invariant Natural Killer T Cells Coordinate Removal of Senescent Cells. Med 2021, 2, 938–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazeldine, J.; Hampson, P.; Lord, J.M. Reduced Release and Binding of Perforin at the Immunological Synapse Underlies the Age-Related Decline in Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelyapov, N.; Nguyen, T.T.; Gonzalez, R. Autologous NK Cells Propagated and Activated Ex Vivo Decrease Senescence Markers in Human PBMCs. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 32, 101380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Zender, L.; Miething, C.; Dickins, R.A.; Hernando, E.; Krizhanovsky, V.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Lowe, S.W. Senescence and Tumour Clearance Is Triggered by P53 Restoration in Murine Liver Carcinomas. Nature 2007, 445, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iannello, A.; Raulet, D.H. Immune Surveillance of Unhealthy Cells by Natural Killer Cells. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2013, 78, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruscetti, M.; Leibold, J.; Bott, M.J.; Fennell, M.; Kulick, A.; Salgado, N.R.; Chen, C.-C.; Ho, Y.-J.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; Feucht, J.; et al. NK Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity Contributes to Tumor Control by a Cytostatic Drug Combination. Science 2018, 362, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sawasdee, N.; Wattanapanitch, M.; Thongsin, N.; Phanthaphol, N.; Chiawpanit, C.; Thuwajit, C.; Yenchitsomanus, P.-T.; Panya, A. Doxorubicin Sensitizes Breast Cancer Cells to Natural Killer Cells in Connection with Increased Fas Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, B.I.; Devine, O.P.; Vukmanovic-Stejic, M.; Chambers, E.S.; Subramanian, P.; Patel, N.; Virasami, A.; Sebire, N.J.; Kinsler, V.; Valdovinos, A.; et al. Senescent Cells Evade Immune Clearance via HLA-E-Mediated NK and CD8+ T Cell Inhibition. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Rei, M.; Brackenridge, S.; Brenna, E.; Sun, H.; Abdulhaqq, S.; Liu, M.K.P.; Ma, W.; Kurupati, P.; Xu, X.; et al. HLA-E-Restricted, Gag-Specific CD8+ T Cells Can Suppress HIV-1 Infection, Offering Vaccine Opportunities. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabg1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Mitri, D.; Toso, A.; Chen, J.J.; Sarti, M.; Pinton, S.; Jost, T.R.; D’Antuono, R.; Montani, E.; Garcia-Escudero, R.; Guccini, I.; et al. Tumour-Infiltrating Gr-1+ Myeloid Cells Antagonize Senescence in Cancer. Nature 2014, 515, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, T.; Wolter, K.; Ji, J.; Ma, C.; Yevsa, T.; Klotz, S.; Medina-Echeverz, J.; Longerich, T.; Forgues, M.; Reisinger, F.; et al. Distinct Functions of Senescence-Associated Immune Responses in Liver Tumor Surveillance and Tumor Progression. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 533–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Tchkonia, T.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Gower, A.C.; Ding, H.; Giorgadze, N.; Palmer, A.K.; Ikeno, Y.; Hubbard, G.B.; Lenburg, M.; et al. The Achilles’ Heel of Senescent Cells: From Transcriptome to Senolytic Drugs. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, M.J.; White, T.A.; Iijima, K.; Haak, A.J.; Ligresti, G.; Atkinson, E.J.; Oberg, A.L.; Birch, J.; Salmonowicz, H.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Cellular Senescence Mediates Fibrotic Pulmonary Disease. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Shen, Y.; Huang, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, J. Senolytic Therapy Ameliorates Renal Fibrosis Postacute Kidney Injury by Alleviating Renal Senescence. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguayo-Mazzucato, C.; Andle, J.; Lee, T.B.; Midha, A.; Talemal, L.; Chipashvili, V.; Hollister-Lock, J.; van Deursen, J.; Weir, G.; Bonner-Weir, S. Acceleration of β Cell Aging Determines Diabetes and Senolysis Improves Disease Outcomes. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 129–142.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, C.M.; Zhang, B.; Palmer, A.K.; Ogrodnik, M.B.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Thalji, N.M.; Hagler, M.; Jurk, D.; Smith, L.A.; Casaclang-Verzosa, G.; et al. Chronic Senolytic Treatment Alleviates Established Vasomotor Dysfunction in Aged or Atherosclerotic Mice. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 973–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saccon, T.D.; Nagpal, R.; Yadav, H.; Cavalcante, M.B.; Nunes, A.D.d.C.; Schneider, A.; Gesing, A.; Hughes, B.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Tchkonia, T.; et al. Senolytic Combination of Dasatinib and Quercetin Alleviates Intestinal Senescence and Inflammation and Modulates the Gut Microbiome in Aged Mice. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Silva, D.; Cantón-Sandoval, J.; Martínez-Navarro, F.J.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; de Oliveira, S.; Mulero, V.; Alcaraz-Pérez, F.; Cayuela, M.L. Senescence-Independent Anti-Inflammatory Activity of the Senolytic Drugs Dasatinib, Navitoclax, and Venetoclax in Zebrafish Models of Chronic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Justice, J.N.; Nambiar, A.M.; Tchkonia, T.; LeBrasseur, N.K.; Pascual, R.; Hashmi, S.K.; Prata, L.; Masternak, M.M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Musi, N.; et al. Senolytics in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Results from a First-in-Human, Open-Label, Pilot Study. EBioMedicine 2019, 40, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hickson, L.J.; Langhi Prata, L.G.P.; Bobart, S.A.; Evans, T.K.; Giorgadze, N.; Hashmi, S.K.; Herrmann, S.M.; Jensen, M.D.; Jia, Q.; Jordan, K.L.; et al. Senolytics Decrease Senescent Cells in Humans: Preliminary Report from a Clinical Trial of Dasatinib plus Quercetin in Individuals with Diabetic Kidney Disease. EBioMedicine 2019, 47, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaib, S.; Tchkonia, T.; Kirkland, J.L. Cellular Senescence and Senolytics: The Path to the Clinic. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1556–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, N.; Casanova, V.; Maleno, M.J.; Rodríguez-Agustín, A.; Sánche-Palomino, S.; González, T.; Hurtado, C.; Martínez, E.; Mallolas, J.; Ambrosioni, J.; et al. HIV-Induced Cellular Senescence in PLWH Is Decreased by D+Q Senolytic Drugs. [CROI Abstract 223]. In Proceedings of the CROI 2022 Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections, Virtual, 12–16 February 2022; p. 222. [Google Scholar]
- Baar, M.P.; Brandt, R.M.C.; Putavet, D.A.; Klein, J.D.D.; Derks, K.W.J.; Bourgeois, B.R.M.; Stryeck, S.; Rijksen, Y.; van Willigenburg, H.; Feijtel, D.A.; et al. Targeted Apoptosis of Senescent Cells Restores Tissue Homeostasis in Response to Chemotoxicity and Aging. Cell 2017, 169, 132–147.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kovacovicova, K.; Skolnaja, M.; Heinmaa, M.; Mistrik, M.; Pata, P.; Pata, I.; Bartek, J.; Vinciguerra, M. Senolytic Cocktail Dasatinib+Quercetin (D+Q) Does Not Enhance the Efficacy of Senescence-Inducing Chemotherapy in Liver Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Tyrosine Kinase Target (s) | Pathways and Processes |
|---|---|
| SRC family (SRC, LCK, YES, FYN) | Oncogenic, invasive and bone-metastatic processes |
| BCR-ABL | Promotion of growth advantage of leukemic cells |
| c-KIT | Cell growth |
| PDGFRβ | Tumor growth capacity and cell survival |
| c-FMS | Macrophage behavior regulation by M-CSF |
| EPHA2 receptor | Interference with EFNB-dependent suppression of apoptosis/Cell behavior |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Agustín, A.; Casanova, V.; Grau-Expósito, J.; Sánchez-Palomino, S.; Alcamí, J.; Climent, N. Immunomodulatory Activity of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Dasatinib to Elicit NK Cytotoxicity against Cancer, HIV Infection and Aging. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030917
Rodríguez-Agustín A, Casanova V, Grau-Expósito J, Sánchez-Palomino S, Alcamí J, Climent N. Immunomodulatory Activity of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Dasatinib to Elicit NK Cytotoxicity against Cancer, HIV Infection and Aging. Pharmaceutics. 2023; 15(3):917. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030917
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Agustín, Andrea, Víctor Casanova, Judith Grau-Expósito, Sonsoles Sánchez-Palomino, José Alcamí, and Núria Climent. 2023. "Immunomodulatory Activity of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Dasatinib to Elicit NK Cytotoxicity against Cancer, HIV Infection and Aging" Pharmaceutics 15, no. 3: 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030917
APA StyleRodríguez-Agustín, A., Casanova, V., Grau-Expósito, J., Sánchez-Palomino, S., Alcamí, J., & Climent, N. (2023). Immunomodulatory Activity of the Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Dasatinib to Elicit NK Cytotoxicity against Cancer, HIV Infection and Aging. Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 917. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics15030917








