The Efficacy of Pilates on Urinary Incontinence in Korean Women: A Metabolomics Approach
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anthropometrical Data and PFM Function of Subjects
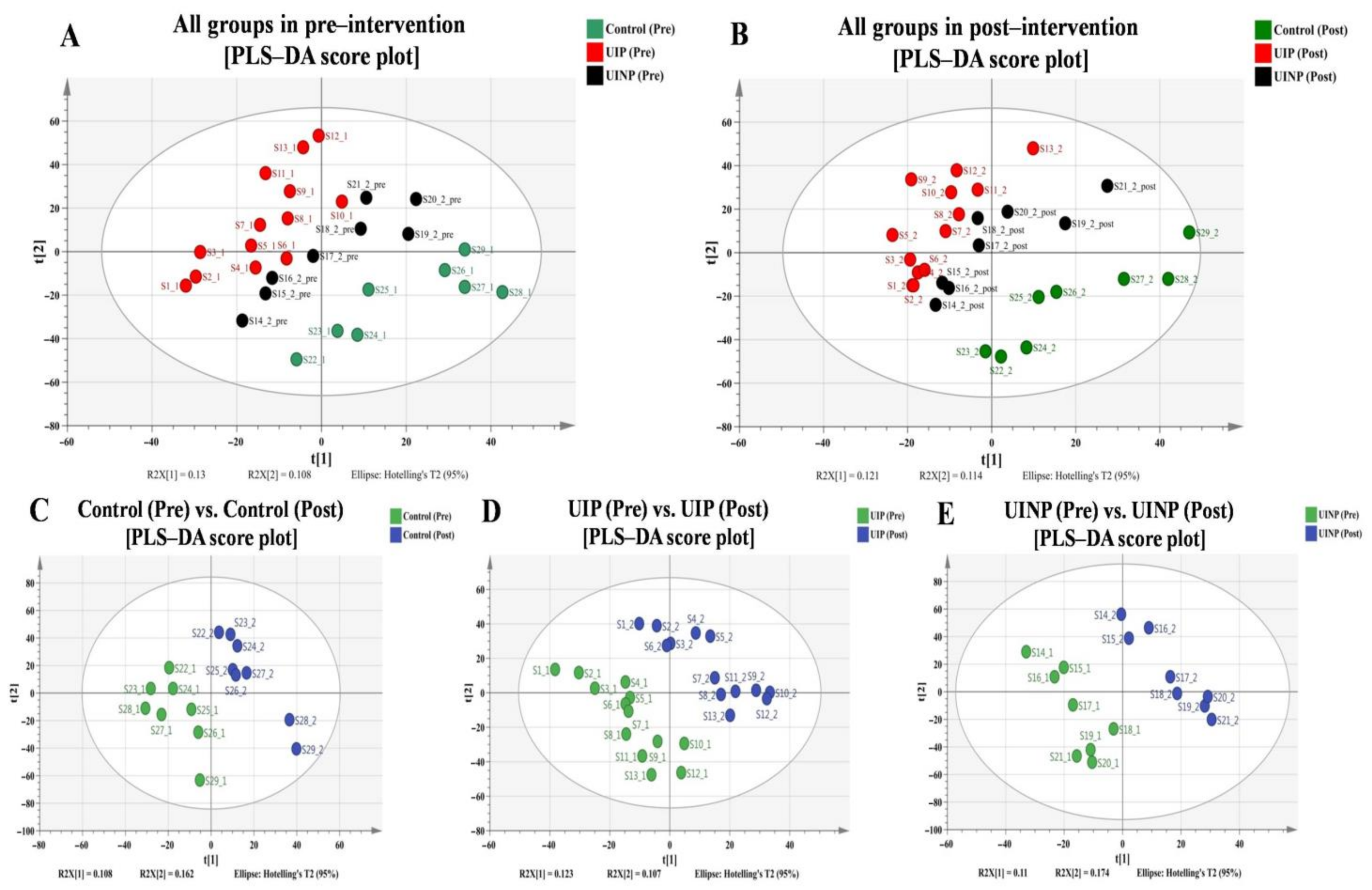
2.2. Discrimination of Metabolic Profiles in and between Pre- and Post-Intervention
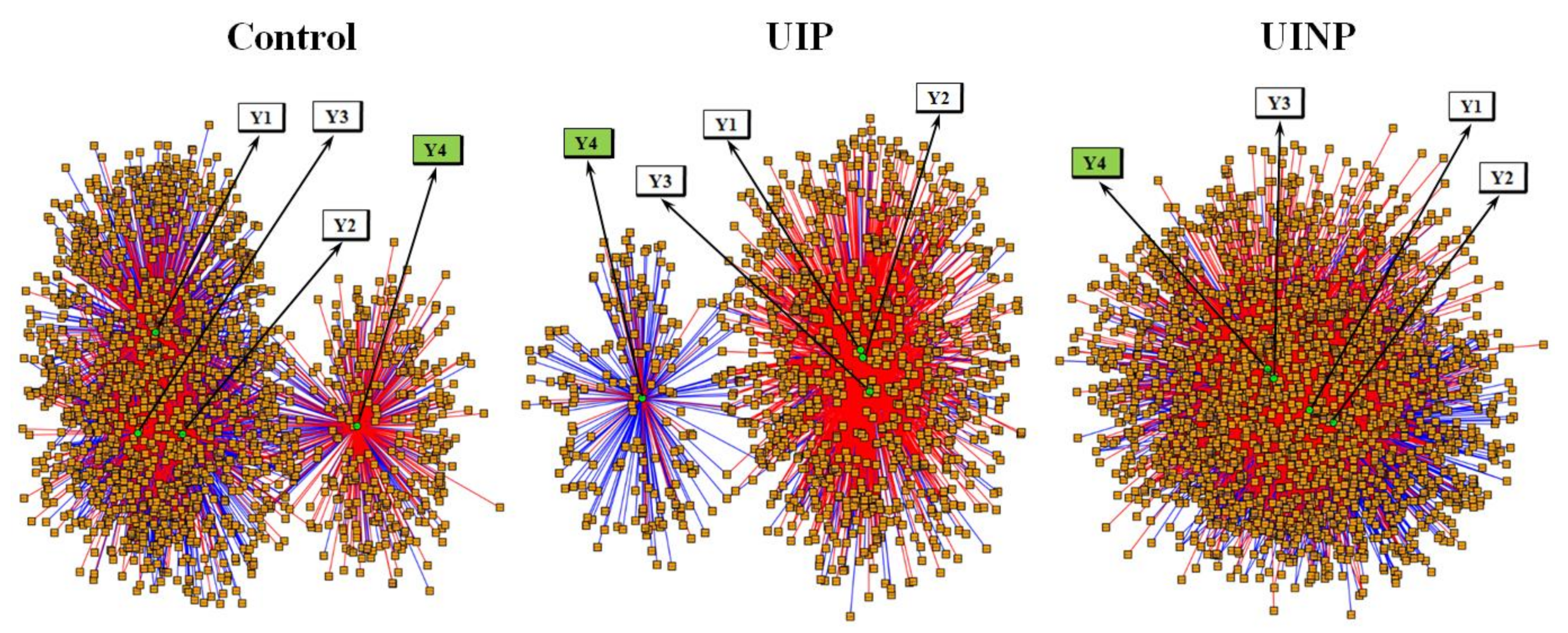
2.3. Integrative and Differential Network Analysis between Metabolic Features and FMP Ratio
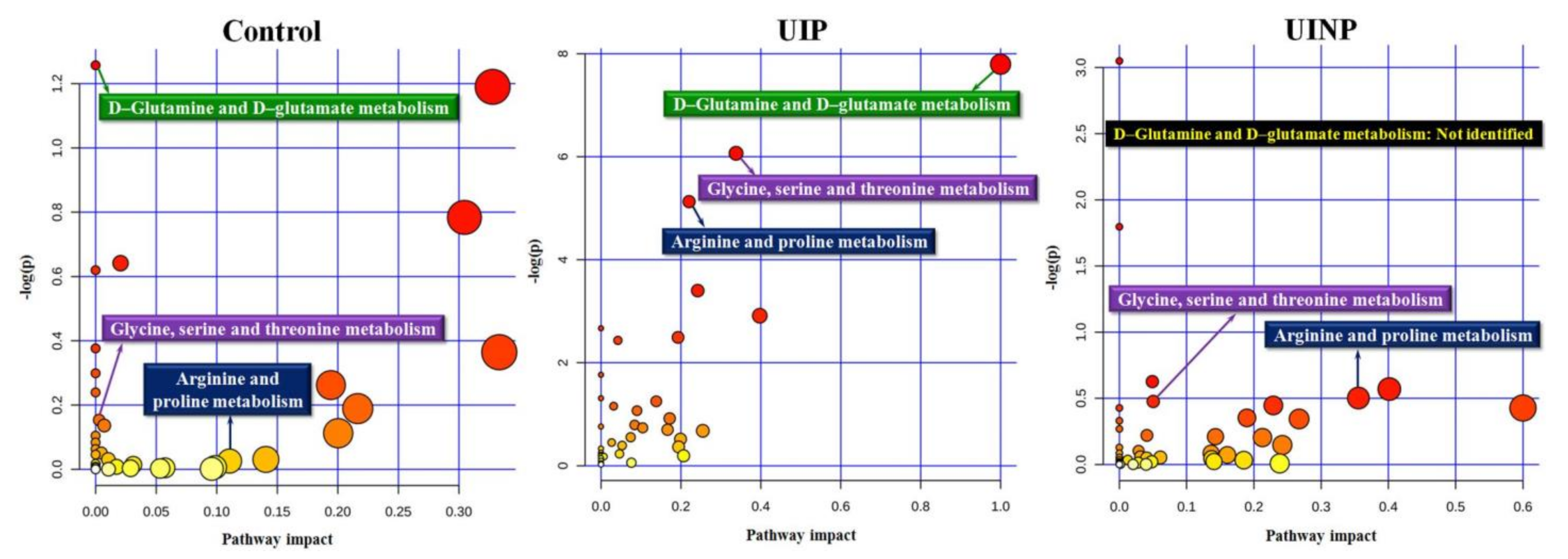
2.4. Identification of Metabolic Pathways Associated with FMP Ratio
2.5. Change in Identified Metabolic Features Associated with FMP Ratio
2.6. Change of Anthropometrical Data and FMP Ratio between Pre- and Post-Intervention
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Approval
4.2. Participants
4.3. Exercise Intervention—Pilates
4.4. Ultrasonography—Functional Movement of PFM
4.5. Hematology and Blood Sample Preparation
4.6. Untargeted Data Acquisition Using LC-MS Q-TOF
4.7. LC/MS Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
4.7.1. Data Extraction of LC/MS Raw Files
4.7.2. Discriminative Analysis between Pre and Post-Intervention in Control, UIP, and UINP
4.7.3. Integrative and Differential Network Analysis Using xMWAS
4.7.4. Metabolomics Analysis for Metabolic Pathway
4.8. Statistical Analysis and Analytical Data Visualization
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Haylen, B.T.; de Ridder, D.; Freeman, R.M.; Swift, S.E.; Berghmans, B.; Lee, J.; Monga, A.; Petri, E.; Rizk, D.E.; Sand, P.K.; et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2010, 21, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Forum on Incontinence. About Incontinence. Available online: https://www.gfiforum.com/incontinence (accessed on 4 January 2021).
- Aoki, Y.; Brown, H.W.; Brubaker, L.; Cornu, J.N.; Daly, J.O.; Cartwright, R. Urinary incontinence in women. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitti, V.W. The prevalence of urinary incontinence. Rev. Urol. 2001, 3 (Suppl. 1), S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stav, K.; Alcalay, M.; Peleg, S.; Lindner, A.; Gayer, G.; Hershkovitz, I. Pelvis architecture and urinary incontinence in women. Eur. Urol. 2007, 52, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavkaytar, S.; Kokanali, M.K.; Topcu, H.O.; Aksakal, O.S.; Doganay, M. Effect of home-based Kegel exercises on quality of life in women with stress and mixed urinary incontinence. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. J. Inst. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2015, 35, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cheng, J.W.; Wagner, H. The effect of high impact crossfit exercises on stress urinary incontinence in physically active women. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2019, 38, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumoulin, C.; Cacciari, L.P.; Hay-Smith, E.J.C. Pelvic floor muscle training versus no treatment, or inactive control treatments, for urinary incontinence in women. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 10, Cd005654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, K.; Frawley, H.C.; Haylen, B.T.; Abramov, Y.; Almeida, F.G.; Berghmans, B.; Bortolini, M.; Dumoulin, C.; Gomes, M.; McClurg, D.; et al. An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for the conservative and nonpharmacological management of female pelvic floor dysfunction. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 221–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, C.S.; Pedriali, F.R.; Urbano, M.R.; Moreira, E.H.; Averbeck, M.A. The effects of Pilates method on pelvic floor muscle strength in patients with post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence: A randomized clinical trial. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Culligan, P.J.; Scherer, J.; Dyer, K.; Priestley, J.L.; Guingon-White, G.; Delvecchio, D.; Vangeli, M. A randomized clinical trial comparing pelvic floor muscle training to a Pilates exercise program for improving pelvic muscle strength. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2010, 21, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torelli, L.; de Jarmy Di Bella, Z.I.; Rodrigues, C.A.; Stüpp, L.; Girão, M.J.; Sartori, M.G. Effectiveness of adding voluntary pelvic floor muscle contraction to a Pilates exercise program: An assessor-masked randomized controlled trial. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2016, 27, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, K. Pelvic floor muscle strength and response to pelvic floor muscle training for stress urinary incontinence. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2003, 22, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.H.; Byun, J.; Pennathur, S. Analytical approaches to metabolomics and applications to systems biology. Semin. Nephrol. 2010, 30, 500–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weckwerth, W. Metabolomics: An integral technique in systems biology. Bioanalysis 2010, 2, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawler, N.G.; Abbiss, C.R.; Gummer, J.P.A.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Govus, A.D.; Fairchild, T.J.; Thompson, K.G.; Garvican-Lewis, L.A.; Gore, C.J.; Maker, G.L.; et al. Characterizing the plasma metabolome during 14 days of live-high, train-low simulated altitude: A metabolomic approach. Exp. Physiol. 2019, 104, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manaf, F.A.; Lawler, N.; Peiffer, J.J.; Maker, G.L.; Boyce, M.C.; Fairchild, T.J.; Broadhurst, D. Characterizing the plasma metabolome during and following a maximal exercise cycling test. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Gao, R.; Xing, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. Serum metabolomic response to exercise training in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. JASH 2017, 11, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugnara, L.; Vinaixa, M.; Murillo, S.; Samino, S.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Beltran, A.; Lerin, C.; Davison, G.; Correig, X.; Novials, A. Metabolomics approach for analyzing the effects of exercise in subjects with type 1 diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos de Oliveira, L.; Gonçalves de Oliveira, R.; Pires-Oliveira, D.A.d.A. Effects of Pilates on muscle strength, postural balance and quality of life of older adults: A randomized, controlled, clinical trial. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015, 27, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, M.L.; Fell, J. Positive long-term effects of Pilates exercise on the aged-related decline in balance and strength in older, community-dwelling men and women. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2014, 22, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, K.; Wu, P.J.; Whillier, S. Is Pilates an effective rehabilitation tool? A systematic review. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2018, 22, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savkin, R.; Aslan, U.B. The effect of Pilates exercise on body composition in sedentary overweight and obese women. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2017, 57, 1464–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, S.; Yoo, H.J. Understanding Metabolomics in Biomedical Research. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 31, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiovanni, T.; Pintus, R.; Dessì, A.; Noto, A.; Sardo, S.; Finco, G.; Corsello, G.; Fanos, V. Sportomics: Metabolomics applied to sports. The new revolution? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 11011–11019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Metabolomics. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, R.D.; Dunn, W.; Schmidt, M.A.; Gross, S.S.; Kirwan, J.A.; Cascante, M.; Brennan, L.; Wishart, D.S.; Oresic, M.; Hankemeier, T.; et al. Metabolomics enables precision medicine: “A White Paper, Community Perspective”. Metab. Off. J. Metab. Soc. 2016, 12, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triba, M.N.; Le Moyec, L.; Amathieu, R.; Goossens, C.; Bouchemal, N.; Nahon, P.; Rutledge, D.N.; Savarin, P. PLS/OPLS models in metabolomics: The impact of permutation of dataset rows on the K-fold cross-validation quality parameters. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uppal, K.; Ma, C.; Go, Y.-M.; Jones, D.P. xMWAS: A data-driven integration and differential network analysis tool. Bioinformatics 2017, 34, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bø, K.; Sherburn, M. Evaluation of Female Pelvic-Floor Muscle Function and Strength. Phys. Ther. 2005, 85, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raizada, V.; Mittal, R.K. Pelvic floor anatomy and applied physiology. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 37, 493–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curi, R.; Lagranha, C.J.; Doi, S.Q.; Sellitti, D.F.; Procopio, J.; Pithon-Curi, T.C.; Corless, M.; Newsholme, P. Molecular mechanisms of glutamine action. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 204, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M. Dosing and efficacy of glutamine supplementation in human exercise and sport training. J. Nutr. 2008, 138, 2045s–2049s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, M.J.; MacLennan, P.A.; Hundal, H.S.; Weryk, B.; Smith, K.; Taylor, P.M.; Egan, C.; Watt, P.W. Skeletal muscle glutamine transport, intramuscular glutamine concentration, and muscle-protein turnover. Metab. Clin. Exp. 1989, 38, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, P.A.; Brown, R.A.; Rennie, M.J. A positive relationship between protein synthetic rate and intracellular glutamine concentration in perfused rat skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1987, 215, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligthart-Melis, G.C.; van de Poll, M.C.G.; Boelens, P.G.; Dejong, C.H.C.; Deutz, N.E.P.; van Leeuwen, P.A.M. Glutamine is an important precursor for de novo synthesis of arginine in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1282–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, N.P.; Blannin, A.K.; Robson, P.J.; Gleeson, M. Glutamine, Exercise and Immune Function. Sports Med. 1998, 26, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewell, D.A.; Gleeson, M.; Blannin, A.K. Hyperammonaemia in relation to high-intensity exercise duration in man. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1994, 69, 350–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castell, L.M.; Newsholme, E.A.; Poortmans, J.R. Does glutamine have a role in reducing infections in athletes? Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1996, 73, 488–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castell, L.M.; Poortmans, J.R.; Leclercq, R.; Brasseur, M.; Duchateau, J.; Newsholme, E.A. Some aspects of the acute phase response after a marathon race, and the effects of glutamine supplementation. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1996, 75, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, P.J.; Blannin, A.K.; Walsh, N.P.; Castell, L.M.; Gleeson, M. Effects of exercise intensity, duration and recovery on in vitro neutrophil function in male athletes. Int. J. Sports Med. 1999, 20, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gildenhuys, G.; Fourie, M.; Shaw, I.; Shaw, B.; Toriola, A.; Witthuhn, J. Evaluation of Pilates training on agility, functional mobility and cardiorespiratory fitness in elderly women. AJPHERD 2013, 19, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Guimarães, G.V.; Carvalho, V.O.; Bocchi, E.A.; d’Avila, V.M. Pilates in Heart Failure Patients: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2012, 30, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Rodríguez, R.; Álvarez-Bueno, C.; Ferri-Morales, A.; Torres-Costoso, A.I.; Cavero-Redondo, I.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V. Pilates Method Improves Cardiorespiratory Fitness: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, C.R.; Hamilton-Reeves, J.; Martindale, R.G.; Sarav, M.; Ochoa Gautier, J.B. Acquired Amino Acid Deficiencies: A Focus on Arginine and Glutamine. Nutr. Clin. Pract. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2017, 32, 30S–47S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Morris, S.M., Jr. Arginine metabolism: Nitric oxide and beyond. Biochem. J. 1998, 336 Pt 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, S.M., Jr. Arginine: Beyond protein. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 508S–512S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jhee, K.H.; Hua, X.; DiBello, P.M.; Jacobsen, D.W.; Kruger, W.D. Modulation of cystathionine beta-synthase level regulates total serum homocysteine in mice. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sugahara, K.; Sagara, Y.; Fontana, M.; Duprè, S.; Kodama, H. Effect of cystathionine ketimine on the stimulus coupled responses of neutrophils and their modulation by various protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 218, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kodama, H.; Zhang, J.; Sugahara, K. Novel Priming Compounds of Cystathionine Metabolites on Superoxide Generation in Human Neutrophils. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 269, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghibelli, L.; Fanelli, C.; Rotilio, G.; Lafavia, E.; Coppola, S.; Colussi, C.; Civitareale, P.; Ciriolo, M.R. Rescue of cells from apoptosis by inhibition of active GSH extrusion. FASEB J. 1998, 12, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclean, K.N.; Greiner, L.S.; Evans, J.R.; Sood, S.K.; Lhotak, S.; Markham, N.E.; Stabler, S.P.; Allen, R.H.; Austin, R.C.; Balasubramaniam, V.; et al. Cystathionine protects against endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced lipid accumulation, tissue injury, and apoptotic cell death. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 31994–32005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Du, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, A.D.; Holmberg, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, C.; Jin, H. L-cystathionine inhibits the mitochondria-mediated macrophage apoptosis induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23059–23073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, D.; Bai, L.; Kong, W.; Huang, Y.; Tang, C.; Du, J.; Jin, H. L-Cystathionine Protects against Homocysteine-Induced Mitochondria-Dependent Apoptosis of Vascular Endothelial Cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1253289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HMDB. Showing Metabocard for (3R,5S)-1-pyrroline-3-hydroxy-5-carboxylic Acid (HMDB0062585). Available online: https://hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0062585 (accessed on 6 January 2021).
- Bray, R.; Cacciatore, S.; Jimenez, B.; Cartwright, R.; Digesu, A.; Fernando, R.; Holmes, E. Urinary Metabolic Phenotyping of Women with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 4208–4216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.; Yin, A.; Chen, M.; Tan, N.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, W. Serum metabolomics reveals the effect of electroacupuncture on urinary leakage in women with stress urinary incontinence. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 190, 113513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani Ahmadi, A.; Rayyani, E.; Bahreini, M.; Mansoori, A. The effect of glutamine supplementation on athletic performance, body composition, and immune function: A systematic review and a meta-analysis of clinical trials. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1076–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viribay, A.; Burgos, J.; Fernandez-Landa, J.; Seco-Calvo, J.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J. Effects of Arginine Supplementation on Athletic Performance Based on Energy Metabolism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TMOov. About the OOV. Available online: https://www.theoov.com/about-the-oov/ (accessed on 11 November 2020).
- Karvonen, J.; Vuorimaa, T. Heart rate and exercise intensity during sports activities. Practical application. Sports Med. 1988, 5, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arab, A.M.; Behbahani, R.B.; Lorestani, L.; Azari, A. Correlation of digital palpation and transabdominal ultrasound for assessment of pelvic floor muscle contraction. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2009, 17, e75–e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.A.; O’Sullivan, P.B.; Briffa, N.K.; Neumann, P. Comparison of transperineal and transabdominal ultrasound in the assessment of voluntary pelvic floor muscle contractions and functional manoeuvres in continent and incontinent women. Int. Urogynecol. J. Pelvic Floor Dysfunct. 2007, 18, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.W.; Wang, S.; Egger, M.J.; Masters, M.; Nygaard, I. Can women correctly contract their pelvic floor muscles without formal instruction? Female Pelvic. Med. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 19, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teyhen, D.S.; Miltenberger, C.E.; Deiters, H.M.; Del Toro, Y.M.; Pulliam, J.N.; Childs, J.D.; Boyles, R.E.; Flynn, T.W. The use of ultrasound imaging of the abdominal drawing-in maneuver in subjects with low back pain. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2005, 35, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlgrim, C.; Pottgiesser, T.; Robinson, N.; Sottas, P.E.; Ruecker, G.; Schumacher, Y.O. Are 10 min of seating enough to guarantee stable haemoglobin and haematocrit readings for the athlete’s biological passport? Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2010, 32, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, G.J.; Yanes, O.; Siuzdak, G. Innovation: Metabolomics: The apogee of the omics trilogy. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uppal, K.; Soltow, Q.A.; Strobel, F.H.; Pittard, W.S.; Gernert, K.M.; Yu, T.; Jones, D.P. xMSanalyzer: Automated pipeline for improved feature detection and downstream analysis of large-scale, non-targeted metabolomics data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardinassi, L.G.; Cordy, R.J.; Lacerda, M.V.G.; Salinas, J.L.; Monteiro, W.M.; Melo, G.C.; Siqueira, A.M.; Val, F.F.; Tran, V.; Jones, D.P.; et al. Metabolome-wide association study of peripheral parasitemia in Plasmodium vivax malaria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2017, 307, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Park, Y.; Johnson, J.M.; Jones, D.P. apLCMS--adaptive processing of high-resolution LC/MS data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1930–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Marcu, A.; Guo, A.C.; Liang, K.; Vazquez-Fresno, R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Karu, N.; et al. HMDB 4.0: The human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D608–D617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Soufan, O.; Li, C.; Caraus, I.; Li, S.; Bourque, G.; Wishart, D.S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 4.0: Towards more transparent and integrative metabolomics analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W486–W494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group | Control | UIP (UI + Pilates) | UINP (UI + No Pilates) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participant (n) | 8 | 13 | 8 | |||
| Age (yr) | 42.5 ± 6.2 | 42.4 ± 5.1 | 46.4 ± 8.5 | |||
| Height (cm) | 161.9 ± 8.3 | 160.7 ± 5.1 | 156.6 ± 10.5 | |||
| Pre | Post | Pre | Post | Pre | Post | |
| Body mass (kg) | 63.2 ± 12.2 | 62.2 ± 11.3 | 64.1 ± 10.2 | 63.8 ± 9.5 | 62.0 ± 12.6 | 62.2 ± 12.3 |
| BMI | 23.9 ± 3.3 | 23.3 ± 3.0 | 24.7 ± 3.0 | 24.6 ± 2.8 | 24.3 ± 3.1 | 24.6 ± 2.9 |
| Body fat (%) | 32.3 ± 7.2 | 30.1 ± 6.3 | 32.4 ± 4.6 | 31.8 ± 4.6 | 32.9 ± 6.5 | 34.2 ± 5.6 |
| FMP ratio | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.9 ± 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0.2 | 0.4 ± 0.2 * | 0.9 ± 0.1 | 0.8 ± 0.4 |
| Group | Pathway Name (Metabolism) | Match Status | p-Value | −Log(p) | Pathway Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | D-Glutamine and D-glutamate | 2/6 | 0.2845 | 1.2571 | 0 |
| Glycine, serine and threonine | 4/33 | 0.8577 | 0.1535 | 0.0029 | |
| Arginine and proline | 3/38 | 0.9745 | 0.0258 | 0.1106 | |
| UIP | D-Glutamine and D-glutamate | 4/6 | 0.0004 | 7.7956 | 1.0 |
| Glycine, serine and threonine | 8/33 | 0.0023 | 6.0662 | 0.3381 | |
| Arginine and proline | 8/38 | 0.0059 | 5.1278 | 0.2205 | |
| UINP | D-Glutamine and D-glutamate | N.I | N.I | N.I | N.I |
| Glycine, serine and threonine | 6/33 | 0.6212 | 0.4762 | 0.0503 | |
| Arginine and proline | 7/38 | 0.6053 | 0.5020 | 0.3554 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, G.; Lee, H.; Shin, M.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Park, Y. The Efficacy of Pilates on Urinary Incontinence in Korean Women: A Metabolomics Approach. Metabolites 2021, 11, 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020118
Kang G, Lee H, Shin M, Kim J, Lee S, Park Y. The Efficacy of Pilates on Urinary Incontinence in Korean Women: A Metabolomics Approach. Metabolites. 2021; 11(2):118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020118
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Gyumin, Haelim Lee, Malsoon Shin, Jaekwan Kim, Sungki Lee, and Youngja Park. 2021. "The Efficacy of Pilates on Urinary Incontinence in Korean Women: A Metabolomics Approach" Metabolites 11, no. 2: 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020118
APA StyleKang, G., Lee, H., Shin, M., Kim, J., Lee, S., & Park, Y. (2021). The Efficacy of Pilates on Urinary Incontinence in Korean Women: A Metabolomics Approach. Metabolites, 11(2), 118. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11020118








