Capillary Electrophoresis Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics of Plasma Samples from Healthy Subjects in a Cross-Sectional Japanese Population Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
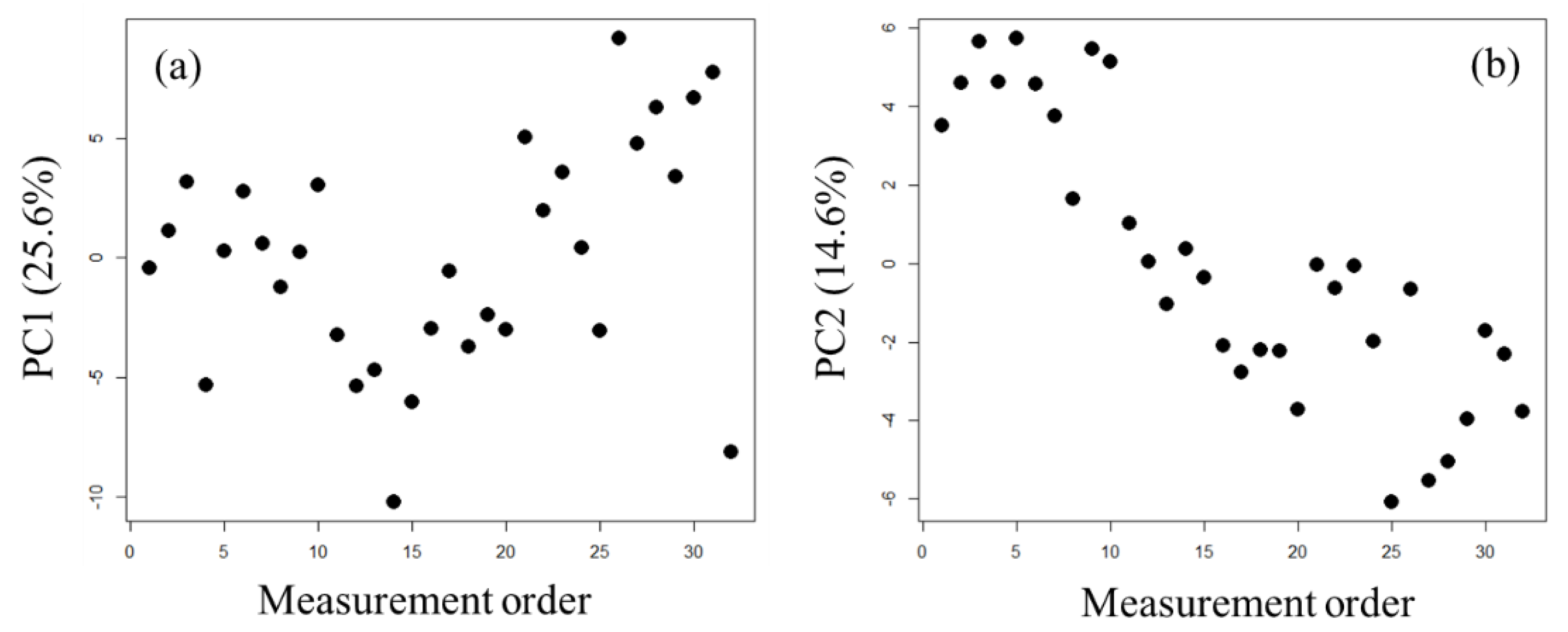
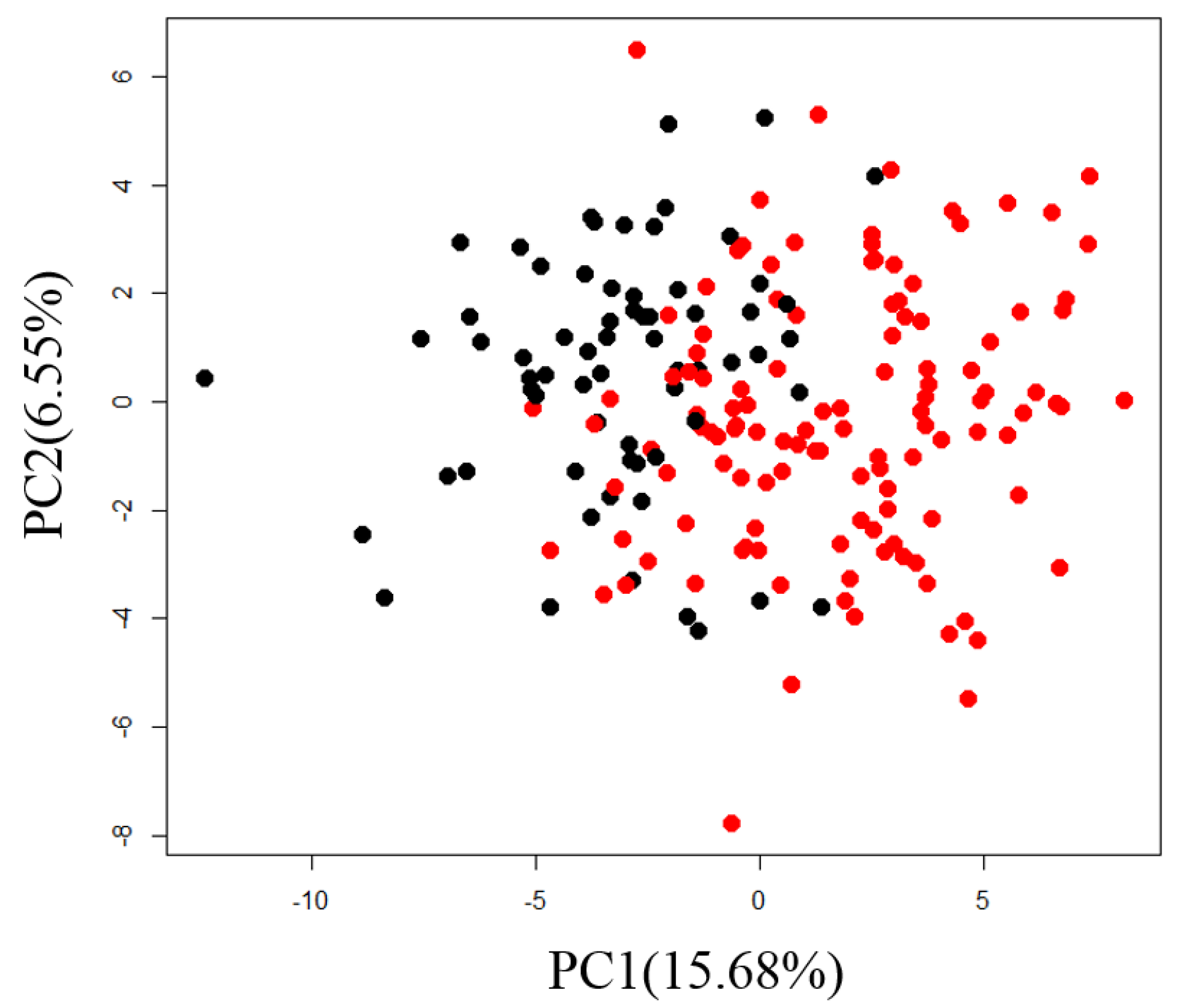
2.1. Exploration of Factors Causing Variation in Large-Scale Measurements
2.2. Evaluation of Normalization Using the QC Samples with Smoothing
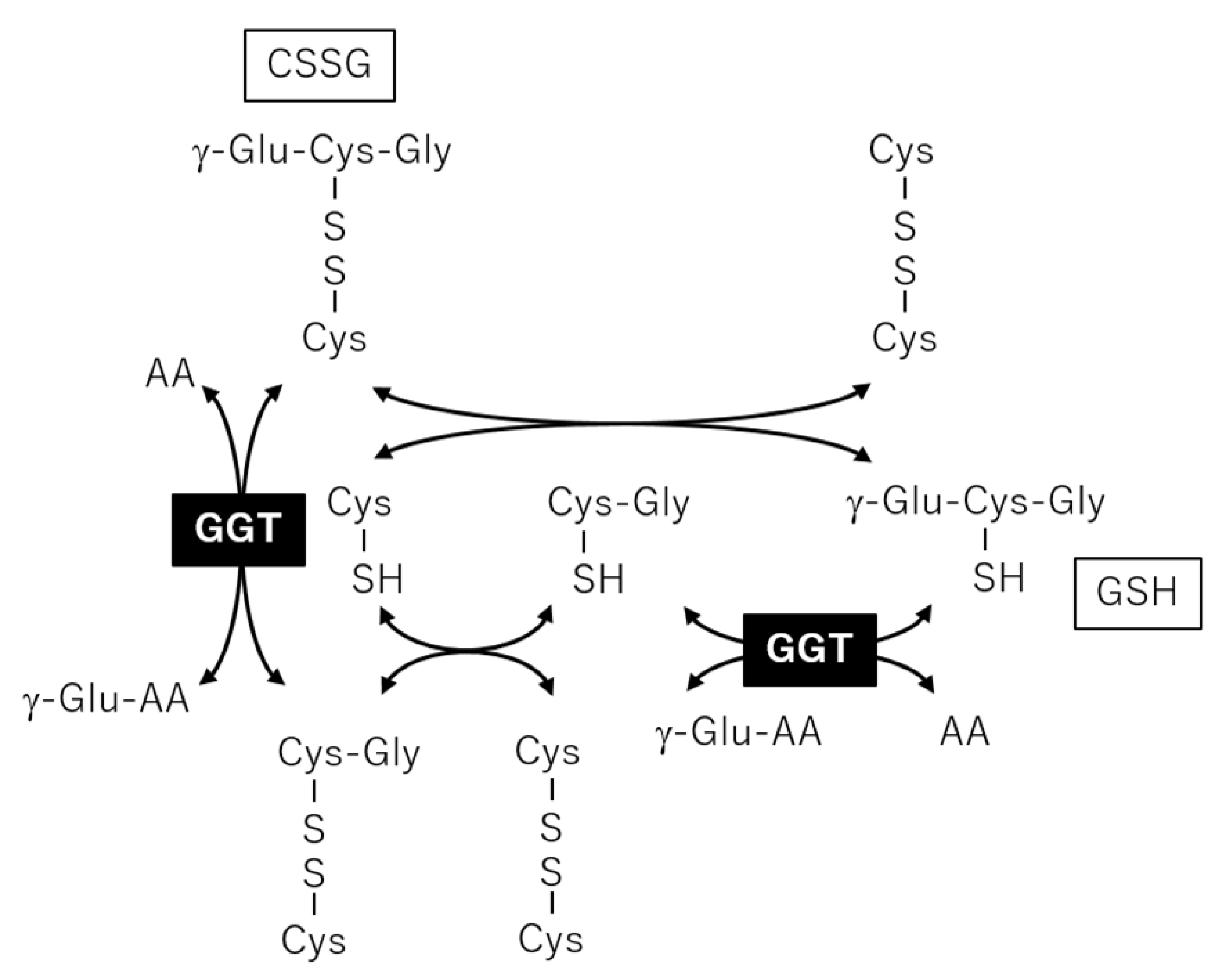
2.3. Correlation Analysis between Plasma Metabolites and Diagnostic Blood Tests
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Human Participants and Sample Collection
3.2. Exclusion Criteria for Medical Parameters and Diagnostic Blood Tests
3.3. Metabolome Analysis
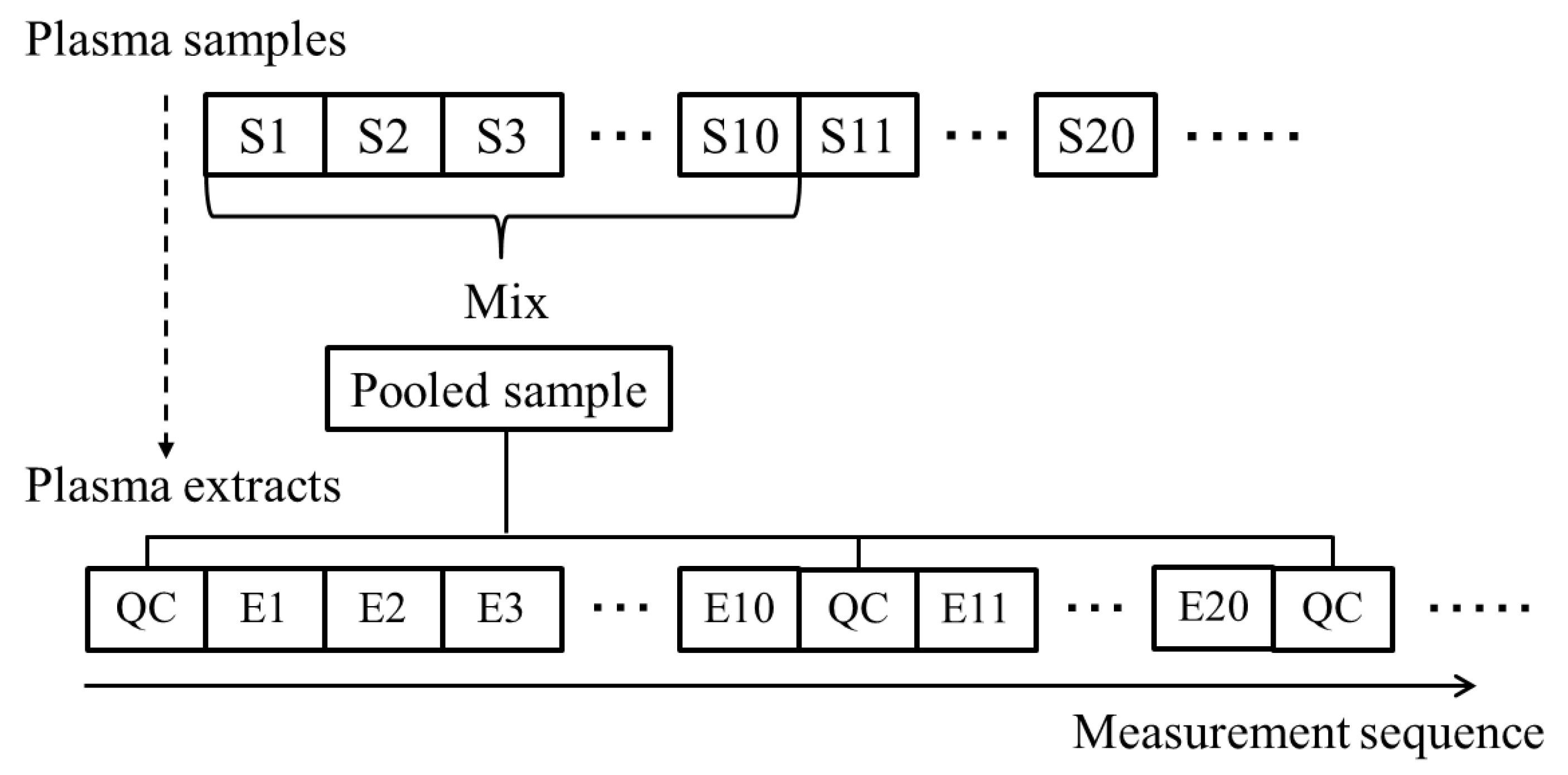
3.4. QC Samples and Normalization with Whittaker Smoothing
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; McCabe, E.; Lewis, G.D.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Fernandez, C.; et al. Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floegel, A.; Stefan, N.; Yu, Z.; Mühlenbruch, K.; Drogan, D.; Joost, H.-G.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.-U.; Hrabě de Angelis, M.; Peters, A.; et al. Identification of serum metabolites associated with risk of type 2 diabetes using a targeted metabolomic approach. Diabetes 2013, 62, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.H.W.; Wang, Z.; Levison, B.S.; Koeth, R.A.; Britt, E.B.; Fu, X.; Wu, Y.; Hazen, S.L. Intestinal microbial metabolism of phosphatidylcholine and cardiovascular risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zanetti, K.A.; Temprosa, M.; Albanes, D.; Appel, N.; Barrera, C.B.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Boerwinkle, E.; Casas, J.P.; Clish, C.; et al. The Consortium of Metabolomics Studies (COMETS): Metabolomics in 47 Prospective Cohort Studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 991–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S.-Y.; Fauman, E.B.; Petersen, A.-K.; Krumsiek, J.; Santos, R.; Huang, J.; Arnold, M.; Erte, I.; Forgetta, V.; Yang, T.-P.; et al. An atlas of genetic influences on human blood metabolites. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krumsiek, J.; Mittelstrass, K.; Do, K.T.; Stückler, F.; Ried, J.; Adamski, J.; Peters, A.; Illig, T.; Kronenberg, F.; Friedrich, N.; et al. Gender-specific pathway differences in the human serum metabolome. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1815–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menni, C.; Kastenmüller, G.; Petersen, A.K.; Bell, J.T.; Psatha, M.; Tsai, P.-C.; Gieger, C.; Schulz, H.; Erte, I.; John, S.; et al. Metabolomic markers reveal novel pathways of ageing and early development in human populations. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.C.; Matthews, C.E.; Sampson, J.N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Zheng, W.; Cai, Q.; Tan, Y.T.; Chow, W.-H.; Ji, B.-T.; Liu, D.K.; et al. Human metabolic correlates of body mass index. Metabolomics 2014, 10, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Li, L. Evaluating and minimizing batch effects in metabolomics. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2020, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, N.P.; Nghi, T.D.; Kang, Y.P.; Anh, N.H.; Kim, H.M.; Park, S.K.; Kwon, S.W. Toward a standardized strategy of clinical metabolomics for the advancement of precision medicine. Metabolites 2020, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Want, E.J.; Masson, P.; Michopoulos, F.; Wilson, I.D.; Theodoridis, G.; Plumb, R.S.; Shockcor, J.; Loftus, N.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. Global metabolic profiling of animal and human tissues via UPLC-MS. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, N.; van Mever, M.; Zhang, W.; Tobolkina, E.; Ferre, S.; Servais, A.-C.; Gou, M.-J.; Nyssen, L.; Fillet, M.; Lageveen-Kammeijer, G.S.M.; et al. Capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry at trial by metabo-ring: Effective electrophoretic mobility for reproducible and robust compound annotation. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 14103–14112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, S.; Hirayama, A.; Chan, Q.; Kurihara, A.; Fukai, K.; Iida, M.; Kato, S.; Sugiyama, D.; Kuwabara, K.; Takeuchi, A.; et al. Reliability of plasma polar metabolite concentrations in a large-scale cohort study using capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilers, P.H.C. A perfect smoother. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3631–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thonusin, C.; IglayReger, H.B.; Soni, T.; Rothberg, A.E.; Burant, C.F.; Evans, C.R. Evaluation of intensity drift correction strategies using MetaboDrift, a normalization tool for multi-batch metabolomics data. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1523, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Albert, F.; Llorach, R.; Garcia-Aloy, M.; Ziyatdinov, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Perera, A. Intensity drift removal in LC/MS metabolomics by common variance compensation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2899–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Fujimori, T.; Sato, H.; Ishikawa, G.; Kami, K.; Ohashi, Y. Statistical hypothesis testing of factor loading in principal component analysis and its application to metabolite set enrichment analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopple, J.D.; Gordon, S.I.; Wang, M.; Swendseid, M.E. Factors affecting serum and urinary guanidinosuccinic acid levels in normal and uremic subjects. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1977, 90, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Natelson, S.; Sherwin, J.E. Proposed mechanism for urea nitrogen re-utilization: Relationship between urea and proposed guanidine cycles. Clin. Chem. 1979, 25, 1343–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, K.; Nagase, S.; Tomida, C.; Takemura, K.; Akiyama, K.; Koyama, A. Synthesis of guanidinosuccinate from argininosuccinate and reactive oxygen in vitro. Enzym. Protein 1996, 49, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, K.; Akiyama, K.; Shahrzad, S.; Tomida, C.; Hirayama, A.; Nagase, S.; Takemura, K.; Koyama, A.; Ohba, S.; Narita, M. Formation of guanidinosuccinic acid, a stable nitric oxide mimic, from argininosuccinic acid and nitric oxide-derived free radicals. Free Radic. Res. 1999, 31, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menyhárt, J.; Gróf, J. Urea as a selective inhibitor of argininosuccinate lyase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1977, 75, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, K.; Ohba, S.; Narita, M.; Tojo, S. Regulation of biosynthesis of guanidinosuccinic acid in isolated rat hepatocytes and in vivo. Kidney Int. Suppl. 1983, 16, S224–S228. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, D.P.; Carlson, J.L.; Mody, V.C.; Cai, J.; Lynn, M.J.; Sternberg, P. Redox state of glutathione in human plasma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleinman, W.A.; Richie, J.P.J. Status of glutathione and other thiols and disulfides in human plasma. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachhawat, A.K.; Yadav, S. The glutathione cycle: Glutathione metabolism beyond the γ-glutamyl cycle. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, H.; Kondo, K.; Tanaka, T.; Muramatsu, T.; Yoshida, H.; Imaizumi, A.; Nagao, K.; Noguchi, Y.; Miyano, H. Reference intervals for plasma-free amino acid in a Japanese population. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 53, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soga, T.; Ohashi, Y.; Ueno, Y.; Naraoka, H.; Tomita, M.; Nishioka, T. Quantitative metabolome analysis using capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. J. Proteome Res. 2003, 2, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, M.; Wong, D.T.; Hirayama, A.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M. Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Male | Female | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample size | 66 | 122 | 188 |
| Age (year) | |||
| Mean | 42.9 | 45.1 | 44.3 |
| Median | 39.5 | 43.5 | 43 |
| Range | 20–74 | 20–73 | 20–74 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | |||
| Mean | 23.1 | 21.2 | 21.9 |
| Median | 22.85 | 21.1 | 21.5 |
| Range | 18.2–29 | 15.5–28.1 | 15.5–29 |
| Blood Tests | Lower Limit | Upper Limit |
|---|---|---|
| ALB (g/L) | <41 | >51 |
| TG (mmol/L) | <0.47 (M), <0.34 (F) | >2.51 (M), >1.4 (F) |
| UA (mmol/L) | <224 (M), <154 (F) | >474 (M), >334 (F) |
| GLU (mmol/L) | <4.2 | >5.9 |
| γ-GT (U/L) | <9 | >55 |
| CRE (mmol/L) | <0.64 (M), <0.46 (F) | >1.06 (M), >0.78 (F), |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | - | >1.4 |
| Hb (g/L) | <135 (M), <110 (F) | >169 (M), >148 (F) |
| MCV (fl) | <82 | >98 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yamamoto, H.; Suzuki, M.; Matsuta, R.; Sasaki, K.; Kang, M.-I.; Kami, K.; Tatara, Y.; Itoh, K.; Nakaji, S. Capillary Electrophoresis Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics of Plasma Samples from Healthy Subjects in a Cross-Sectional Japanese Population Study. Metabolites 2021, 11, 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050314
Yamamoto H, Suzuki M, Matsuta R, Sasaki K, Kang M-I, Kami K, Tatara Y, Itoh K, Nakaji S. Capillary Electrophoresis Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics of Plasma Samples from Healthy Subjects in a Cross-Sectional Japanese Population Study. Metabolites. 2021; 11(5):314. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050314
Chicago/Turabian StyleYamamoto, Hiroyuki, Makoto Suzuki, Rira Matsuta, Kazunori Sasaki, Moon-Il Kang, Kenjiro Kami, Yota Tatara, Ken Itoh, and Shigeyuki Nakaji. 2021. "Capillary Electrophoresis Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics of Plasma Samples from Healthy Subjects in a Cross-Sectional Japanese Population Study" Metabolites 11, no. 5: 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050314
APA StyleYamamoto, H., Suzuki, M., Matsuta, R., Sasaki, K., Kang, M.-I., Kami, K., Tatara, Y., Itoh, K., & Nakaji, S. (2021). Capillary Electrophoresis Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics of Plasma Samples from Healthy Subjects in a Cross-Sectional Japanese Population Study. Metabolites, 11(5), 314. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11050314






