What Is the Metabolic Amplification of Insulin Secretion and Is It (Still) Relevant?
Abstract
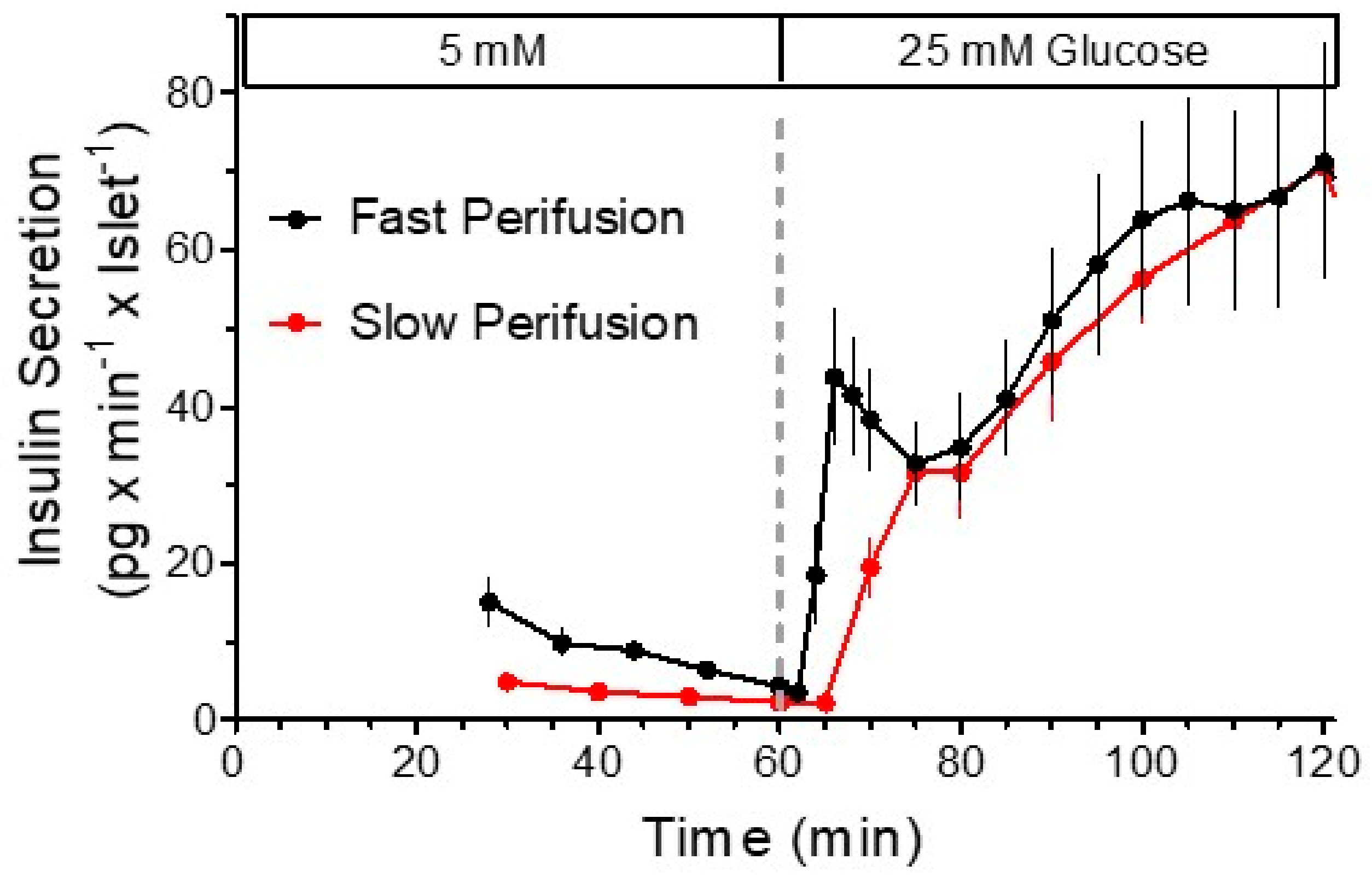
:1. The Biphasic Pattern of Insulin Secretion Can Be Produced in Different Experimental Settings
2. The Early Years: Substrate Site Hypothesis versus Receptor Site Hypothesis
3. What Are Nutrient Secretagogues?
4. Which Features of the Mitochondrial Metabolism Are Typical for Beta Cells?
5. Which Observations Have Led to the Hypothesis of a Bifurcating Pathway Emanating from the Mitochondria?
6. Models of the Biphasic Kinetics of Secretion
7. Relation of the Triggering and Amplifying Pathways to the Biphasic Secretion Kinetics
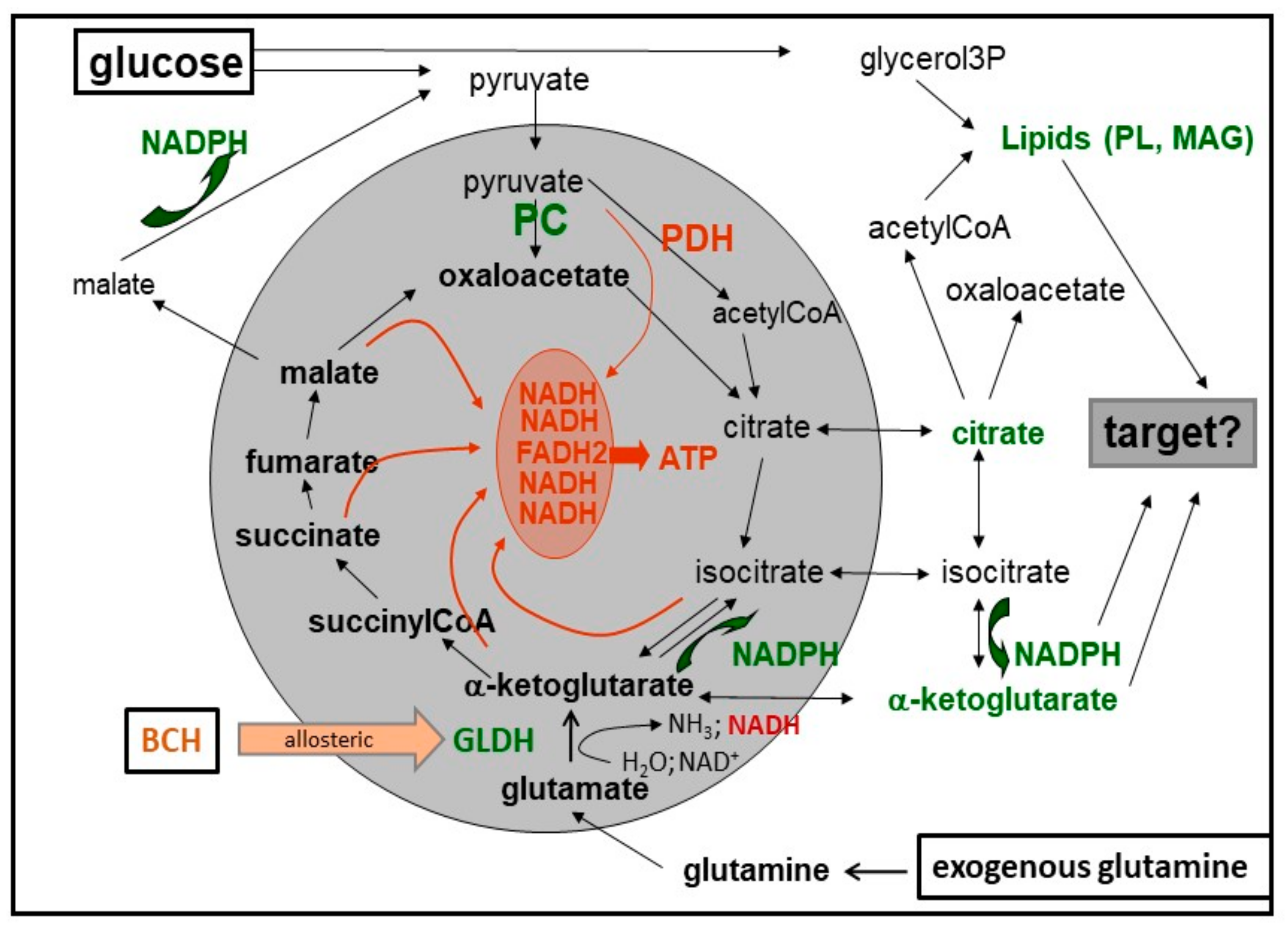
8. Cataplerosis and Putative Amplification Signals
9. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cerasi, E.; Luft, R. Plasma-insulin response to sustained hyperglycemia induced by glucose infusion in human subjects. Lancet 1963, 2, 1359–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerich, J.E. Is Reduced First-Phase Insulin Release the Earliest Detectable Abnormality in Individuals Destined to Develop Type 2 Diabetes? Diabetes 2002, 51, S117–S121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Prato, S. Loss of early insulin secretion leads to postprandial hyperglycaemia. Diabetologia 2003, 46 (Suppl. 1), M2–M8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pimenta, W.; Korytkowski, M.; Mitrakou, A.; Jenssen, T.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; Evron, W.; Dailey, G.; Gerich, J. Pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction as the primary genetic lesion in NIDDM. Evidence from studies in normal glucose-tolerant individuals with a first-degree NIDDM relative. JAMA 1995, 273, 1855–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, M.; Pacini, G.; Petrie, J.; Luger, A.; Anderwald, C. Beta cell (dys)function in non-diabetic offspring of diabetic patients. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 2435–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, A.R.; Jonsson, A.; Jackson, A.U.; Wang, N.; van Leewen, N.; Palmer, N.D.; Kobes, S.; Deelen, J. A Genome-Wide Associa-tion Study of IVGTT-Based Measures of First-Phase Insulin Secretion Refines the Underlying Physiology of Type 2 Diabetes Variants. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2296–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curry, D.L.; Bennett, L.L.; Grodsky, G.M. Dynamics of Insulin Secretion by the Perfused Rat Pancreas. Endocrinology 1968, 83, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesher, R.; Waldman, L.; Cerasi, E. Time-dependent inhibition of insulin release: Glucose-arginine interactions in the perfused rat pancreas. Diabetologia 1984, 26, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lenzen, S. Insulin secretion by isolated perfused rat and mouse pancreas. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1979, 236, E391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panten, U.; Kriegstein, E.; Poser, W.; Schönborn, J.; Hasselblatt, A. Effects of L-leucine and α-ketoisocaproic acid upon insulin secretion and metabolism of isolated pancreatic islets. FEBS Lett. 1972, 20, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henquin, J.-C. Relative Importance of Extracellular and Intracellular Calcium for the Two Phases of Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Release: Studies with Theophylline*. Endocrinology 1978, 102, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minami, K.; Yano, H.; Miki, T.; Nagashima, K.; Wang, C.-Z.; Tanaka, H.; Miyazaki, J.-I.; Seino, S. Insulin secretion and differential gene expression in glucose-responsive and -unresponsive MIN6 sublines. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2000, 279, E773–E781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClenaghan, N.H.; Barnett, C.R.; O’Harte, F.P.; Flatt, P.R. Mechanisms of amino acid-induced insulin secretion from the glu-cose-responsive BRIN-BD11 pancreatic B-cell line. J. Endocrinol. 1996, 151, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halban, P.A.; Praz, G.A.; Wollheim, C. Abnormal glucose metabolism accompanies failure of glucose to stimulate insulin release from a rat pancreatic cell line (RINm5F). Biochem. J. 1983, 212, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merglen, A.; Theander, S.; Rubi, B.; Chaffard, G.; Wollheim, C.B.; Maechler, P. Glucose Sensitivity and Metabolism-Secretion Coupling Studied during Two-Year Continuous Culture in INS-1E Insulinoma Cells. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luther, M.J.; Hauge-Evans, A.; Souza, K.L.; Jörns, A.; Lenzen, S.; Persaud, S.J.; Jones, P.M. MIN6 beta-cell-beta-cell interactions influ-ence insulin secretory responses to nutrients and non-nutrients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 343, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grodsky, G.M.; Batts, A.A.; Bennett, L.L.; Vcella, C.; McWilliams, N.B.; Smith, D.F. Effects of carbohydrates on secretion of insulin from isolated rat pancreas. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1963, 205, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coore, H.; Randle, P. Regulation of insulin secretion studied with pieces of rabbit pancreas incubated in vitro. Biochem. J. 1964, 93, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matschinsky, F.M.; Landgraf, R.; Ellerman, J.; Kotler-Brajtburg, J. Glucoreceptor mechanisms in islets of Langerhans. Diabetes 1972, 21, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panten, U.; Christians, J.; von Kriegstein, E.; Poser, W.; Hasselblatt, A. Effect of carbo-hydrates upon fluorescence of reduced pyridine nucleotides from perifused isolated pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 1973, 9, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanchez-Andres, J.V.; Malaisse, W.J.; Kojima, I. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic islet β-cell sweet taste receptor TIR3. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2018, 471, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randle, P.J. Glucokinase and candidate genes for Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matschinsky, F.M. Evolution of the glucokinase glucose sensor paradigm for pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 1993, 36, 1215–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisse, W.J. Is glucokinase the beta-cell glucoreceptor? Diabetologia 1994, 37, 442. [Google Scholar]
- Baltrusch, S.; Langer, S.; Massa, L.; Tiedge, M.; Lenzen, S. Improved Metabolic Stimulus for Glucose-Induced Insulin Secretion through GK and PFK-2/FBPase-2 Coexpression in Insulin-Producing RINm5F Cells. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 5768–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doliba, N.M.; Fenner, D.; Zelent, B.; Bass, J.; Sarabu, R.; Matschinsky, F.M. Repair of diverse diabetic defects of β-cells in man and mouse by pharmacological glucokinase activation. Diabetes, Obes. Metab. 2012, 14, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, M.J. Elusive proximal signals of beta-cells for insulin secretion. Diabetes 1990, 39, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisse, W.J.; Sener, A.; Malaisse-Lagae, F.; Welsh, M.; Matthews, D.E.; Bier, D.M.; Hellerström, C. The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insulin release. Metabolic response of pancreatic islets of L-glutamine and L-leucine. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 8731–8737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisse, W.J. Branched-chain amino and keto acid metabolism in pancreatic islets. Adv. Enzym. Regul. 1986, 25, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenzen, S.; Schmidt, W.; Rustenbeck, I.; Panten, U. Transamination of neutral amino acids and 2-keto acids in pancreatic B-cell mitochondria. Biosci. Rep. 1986, 6, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchizono, Y.; Alarcón, C.; Wicksteed, B.L.; Marsh, B.J.; Rhodes, C.J. The balance between proinsulin biosynthesis and insulin secre-tion: Where can imbalance lead? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2007, 9 (Suppl. 2), 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gylfe, E. Comparison of the effects of leucines, non-metabolizable leucine analogues and other insulin secretagogues on the activity of glutamate dehydrogenase. Acta Diabetol. 1976, 13, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenzen, S.; Rustenbeck, I.; Panten, U. Transamination of 3-phenylpyruvate in pancreatic B-cell mitochondria. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 2043–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazit, V.; Ben-Abraham, R.; Rudin, M.; Katz, Y. Glucose-lowering effect of beta-phenylpyruvate in neonatal mice: A possible mechanism for phenylketonuria-related neurodegenerative changes. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 2003, 141, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, M.; Sener, A.; Malaisse-Lagae, F.; Malaisse, W.J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insulin release. Inhibition of islet respiration and insulin release by aminooxyacetate. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1984, 63, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bränström, R.; Efendić, S.; Berggren, P.O.; Larsson, O. Direct inhibition of the pancreatic beta-cell ATP-regulated potassium channel by alpha-ketoisocaproate. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14113–14118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heissig, H.; Urban, K.A.; Hastedt, K.; Zünkler, B.J.; Panten, U. Mechanism of the Insulin-Releasing Action of α-Ketoisocaproate and Related α-Keto Acid Anions. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 68, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, F.M.; Ashcroft, S.J.; Harrison, D.E. Effects of 2-ketoisocaproate on insulin release and single potassium channel activity in dispersed rat pancreatic beta-cells. J. Physiol. 1987, 385, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duchen, M.R.; Smith, P.A.; Ashcroft, F.M. Substrate-dependent changes in mitochondrial function, intracellular free calcium con-centration and membrane channels in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem. J. 1993, 294, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.A.; Sakura, H.; Coles, B.; Gummerson, N.; Proks, P.; Ashcroft, F.M. Electrogenic arginine transport mediates stimu-lus-secretion coupling in mouse pancreatic beta-cells. J. Physiol. 1997, 499, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panten, U.; Ishida, H. Fluorescence of oxidized flavoproteins from perifused isolated pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 1975, 11, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panten, U. Effects of alpha-ketomonocarboxylic acids upon insulin secretion and metabolism of isolated pancreatic islets. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1975, 291, 405–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocheleau, J.V.; Head, W.S.; Piston, D.W. Quantitative NAD(P)H/Flavoprotein Autofluorescence Imaging Reveals Metabolic Mechanisms of Pancreatic Islet Pyruvate Response. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31780–31787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellerström, C. Effects of Carbohydrates on the Oxygen Consumption of Isolated Pancreatic Islets of Mice. Endocrinology 1967, 81, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panten, U.; Klein, H. O2Consumption by Isolated Pancreatic Islets, as Measured in a Microincubation System with a Clark-Type Electrode*. Endocrinology 1982, 111, 1595–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doliba, N.M.; Wehrli, S.L.; Vatamaniuk, M.Z.; Qin, W.; Buettger, C.W.; Collins, H.W.; Matschinsky, F.M. Metabolic and ionic coupling factors in amino acid-stimulated insulin release in pancreatic beta-HC9 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 292, E1507–E1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, T.; Morsi, M.; Reckers, K.; Brüning, D.; Seemann, N.; Panten, U.; Rustenbeck, I. Metabolic amplification of insulin secretion is differentially desensitized by depolarization in the absence of exogenous fuels. Metabolism 2017, 67, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergsten, P.; Westerlund, J.; Liss, P.; Carlsson, P.-O. Primary in vivo oscillations of metabolism in the pancreas. Diabetes 2002, 51, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, P.M. Ultrastructural morphometry of the pancreatic beta-cell. Diabetologia 1973, 9, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonner-Weir, S.; Orci, L. New perspectives on the microvasculature of the islets of Langerhans in the rat. Diabetes 1982, 31, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, L.R.; Ford, E.; Powers, A.C.; Piston, D.W. Glucose-dependent blood flow dynamics in murine pancreatic islets in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2010, 298, E807–E814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denton, R.M. Regulation of mitochondrial dehydrogenases by calcium ions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2009, 1787, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, M.; Jung, S.R.; Reed, B.J.; Sweet, I.R. Islet oxygen consumption and insulin secretion tightly coupled to calcium derived from L-type calcium channels but not from the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 24334–24342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuit, F.; De Vos, A.; Farfari, S.; Moens, K.; Pipeleers, D.; Brun, T.; Prentki, M. Metabolic Fate of Glucose in Purified Islet Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 18572–18579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamarit-Rodriguez, J.; Idahl, L.A.; Giné, E.; Alcazar, O.; Sehlin, J. Lactate production in pancreatic islets. Diabetes 1998, 47, 1219–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, N.; Cirulli, V.; Regazzi, R.; Brown, L.J.; Gine, E.; Tamarit-Rodriguez, J.; Girotti, M.; Marie, S.; MacDonald, M.J.; Wollheim, C.B.; et al. Low lactate dehydrogenase and high mitochondrial glycerol phosphate dehydrogenase in pancreatic beta-cells. Potential role in nutrient sensing. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 4895–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jitrapakdee, S.; Wutthisathapornchai, A.; Wallace, J.C.; Macdonald, M.J. Regulation of insulin secretion: Role of mitochondrial signalling. Diabetologia 2010, 53, 1019–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fex, M.; Nicholas, L.M.; Vishnu, N.; Medina, A.; Sharoyko, V.V.; Nicholls, D.G.; Spégel, P.; Mulder, H. The pathogenetic role of β-cell mitochondria in type 2 diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 236, R145–R159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dean, P.M.; Matthews, E.K. Electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. Nature 1968, 219, 389–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meissner, H.P. Electrical characteristics of the beta-cells in pancreatic islets. J. Physiol. 1976, 72, 757–767. [Google Scholar]
- Henquin, J.C. D-Glucose inhibits potassium efflux from pancreatic islet cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 1978, 271, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, S.J.H.; Weerasinghe, L.C.C.; Randle, P.J. Interrelationship of islet metabolism, adenosine triphosphate content and insulin release. Biochem. J. 1973, 132, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erecińska, M.; Bryła, J.; Michalik, M.; Meglasson, M.D.; Nelson, D. Energy metabolism in islets of Langerhans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1101, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Detimary, P.; Jonas, J.C.; Henquin, J.C. Possible links between glucose-induced changes in the energy state of pancreatic B cells and insulin release. Unmasking by decreasing a stable pool of adenine nucleotides in mouse islets. J. Clin. Investig. 1995, 96, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, D.L.; Hales, C.N. Intracellular ATP directly blocks K+ channels in pancreatic B-cells. Nature 1984, 311, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, F.M.; Rorsman, P. Electrophysiology of the pancreatic beta-cell. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 1989, 54, 87–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagaki, N.; Gonoi, T.; Clement, J.P.; Namba, N.; Inazawa, J.; Gonzalez, G.; Aguilar-Bryan, L.; Seino, S.; Bryan, J. Reconstitution of IKATP: An inward rectifier subunit plus the sulfonylurea receptor. Science 1995, 270, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zünkler, B.; Lins, S.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Trube, G.; Panten, U. Cytosolic ADP enhances the sensitivity to tolbutamide of ATP-dependent K+channels from pancreatic B-cells. FEBS Lett. 1988, 239, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichols, C.G. KATP channels as molecular sensors of cellular metabolism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 440, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plecitá-Hlavatá, L.; Jaburek, M.; Holendova, B.; Tauber, J.; Pavluch, V.; Berková, Z.; Cahová, M.; Schröder, K.; Brandes, R.P.; Siemen, D.; et al. Glucose-Stimulated Insulin Secretion Fundamentally Requires H2O2 Signaling by NADPH Oxidase 4. Diabetes 2020, 69, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bränström, R.; Aspinwall, C.A.; Välimäki, S.; Ostensson, C.G.; Tibell, A.; Eckhard, M.; Brandhorst, H.; Corkey, B.E.; Berggren, P.O.; Lars-son, O. Long-chain CoA esters activate human pancreatic beta-cell KATP channels: Potential role in Type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rorsman, P.; Ashcroft, F.M. Pancreatic β-Cell Electrical Activity and Insulin Secretion: Of Mice and Men. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 117–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panten, U.; Schwanstecher, M.; Wallasch, A.; Lenzen, S. Glucose both inhibits and stimulates insulin secretion from isolated pan-creatic islets exposed to maximally effective concentrations of sulfonylureas. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1988, 338, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gembal, M.; Gilon, P.; Henquin, J.C. Evidence that glucose can control insulin release independently from its action on ATP-sensitive K+ channels in mouse B cells. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 89, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eliasson, L.; Renström, E.; Ammälä, C.; Berggren, P.O.; Bertorello, A.M.; Bokvist, K.; Chibalin, A.; Deeney, J.T.; Flatt, P.R.; Gäbel, J.; et al. PKC-dependent stimulation of exocytosis by sulfonylureas in pancreatic beta cells. Science 1996, 271, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Li, L.; Bottino, R.; Balamurugan, A.N.; Bertera, S.; Densmore, E.; Su, A.; Chang, Y.; Trucco, M.; Drain, P. Antidiabetic sulfonyl-urea stimulates insulin secretion independently of plasma membrane KATP channels. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E293–E301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grimmsmann, T.; Rustenbeck, I. Direct effects of diazoxide on mitochondria in pancreatic B-cells and on isolated liver mito-chondria. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1998, 123, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Willenborg, M.; Hatlapatka, K.; Ghaly, H.; Belz, M.; Panten, U.; Rustenbeck, I. Studies of first phase insulin secretion using imposed plasma membrane depolarization. Front. Biosci. 2011, 3, 662–679. [Google Scholar]
- Willenborg, M.; Belz, M.; Schumacher, K.; Paufler, A.; Hatlapatka, K.; Rustenbeck, I. Ca2+-dependent desensitization of insulin secretion by strong potassium depolarization. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2012, 303, E223–E233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Komatsu, M.; Sato, Y.; Aizawa, T.; Hashizume, K. KATP channel-independent glucose action: An elusive pathway in stimu-lus-secretion coupling of pancreatic beta-cell. Endocr. J. 2001, 48, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henquin, J.-C. Triggering and amplifying pathways of regulation of insulin secretion by glucose. Diabetes 2000, 49, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholls, D.G. The Pancreatic β-Cell: A Bioenergetic Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1385–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grodsky, G.M. A threshold distribution hypothesis for packet storage of insulin and its mathematical modeling. J. Clin. Investig. 1972, 51, 2047–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, L.; Renström, E.; Ding, W.-G.; Proks, P.; Rorsman, P. Rapid ATP-Dependent Priming of Secretory Granules Precedes Ca2+-Induced Exocytosis in Mouse Pancreatic B-Cells. J. Physiol. 1997, 503, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barg, S.; Eliasson, L.; Renström, E.; Rorsman, P. A subset of 50 secretory granules in close contact with L-type Ca2+ channels ac-counts for first-phase insulin secretion in mouse beta-cells. Diabetes 2002, 51 (Suppl. 1), S74–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rorsman, P.; Renström, E. Insulin granule dynamics in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.; Noda, M.; Straub, S.G.; Sharp, G.W. Identification of the docked granule pool responsible for the first phase of glu-cose-stimulated insulin secretion. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1686–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, S.G.; Shanmugam, G.; Sharp, G.W. Stimulation of insulin release by glucose is associated with an increase in the number of docked granules in the beta-cells of rat pancreatic islets. Diabetes 2004, 53, 3179–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grodsky, G.M. A new phase of insulin secretion. How will it contribute to our understanding of beta-cell function? Diabetes 1989, 38, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesher, R.; Cerasi, E. Modeling Phasic Insulin Release: Immediate and Time-Dependent Effects of Glucose. Diabetes 2002, 51, S53–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nesher, R.; Cerasi, E. Biphasic Insulin Release as the Expression of Combined Inhibitory and Potentiating Effects of Glucose*. Endocrinology 1987, 121, 1017–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grill, V.; Adamson, U.; Cerasi, E. Immediate and Time-Dependent Effects of Glucose on Insulin Release from Rat Pancreatic Tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 1978, 61, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connor, M.D.; Landahl, H.; Grodsky, G.M. Comparison of storage- and signal-limited models of pancreatic insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. 1980, 238, R378–R389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, M.D.L.; Landahl, H.D.; Grodsky, G.M. Role of Rate of Change of Glucose Concentration as a Signal for Insulin Release. Endocrinology 1977, 101, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morsi, M.; Schulze, T.; Früh, E.; Brüning, D.; Panten, U.; Rustenbeck, I. Fresh and cultured mouse islets differ in their response to nutrient stimulation. Endocr. Connect. 2020, 9, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, S.G.; Sharp, G.W.G. Hypothesis: One rate-limiting step controls the magnitude of both phases of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2004, 287, C565–C571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, E.D.; Maechler, P.; Wollheim, C.B. Effects of depletion of mitochondrial DNA in metabolism secretion coupling in INS-1 cells. Diabetes 1998, 47, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustenbeck, I.; Herrmann, C.; Grimmsmann, T. Energetic requirement of insulin secretion distal to calcium influx. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1305–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuruzoe, K.; Araki, E.; Furukawa, N.; Shirotani, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Kaneko, K.; Motoshima, H.; Yoshizato, K.; Shirakami, A.; Kishikawa, H.; et al. Creation and characterization of a mitochondrial DNA-depleted pancreatic beta-cell line: Impaired insulin secretion induced by glucose, leucine, and sulfonylureas. Diabetes 1998, 47, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolenšek, J.; Stožer, A.; Skelin Klemen, M.; Miller, E.W.; Slak Rupnik, M. The relationship between membrane potential and calci-um dynamics in glucose-stimulated beta cell syncytium in acute mouse pancreas tissue slices. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schulze, T.; Mattern, K.; Erfle, P.; Brüning, D.; Scherneck, S.; Dietzel, A.; Rustenbeck, I. A Parallel Perifusion Slide from Glass for the Functional and Morphological Analysis of Pancreatic Islets. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 615639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatlapatka, K.; Willenborg, M.; Rustenbeck, I. Plasma membrane depolarization as a determinant of the first phase of insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2009, 297, E315–E322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belz, M.; Willenborg, M.; Görgler, N.; Hamada, A.; Schumacher, K.; Rustenbeck, I. Insulinotropic effect of high potassium concen-tration beyond plasma membrane depolarization. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E697–E706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henquin, J.C.; Nenquin, M.; Stiernet, P.; Ahren, B. In vivo and in vitro glucose-induced biphasic insulin secretion in the mouse: Pattern and role of cytoplasmic Ca2+ and amplification signals in beta-cells. Diabetes 2006, 55, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Müller, A.; Mziaut, H.; Neukam, M.; Knoch, K.-P.; Solimena, M. A 4D view on insulin secretory granule turnover in the β-cell. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brüning, D.; Reckers, K.; Drain, P.; Rustenbeck, I. Glucose but not KCl diminishes submembrane granule turnover in mouse be-ta-cells. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2017, 59, 311–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gandasi, N.; Yin, P.; Omar-Hmeadi, M.; Laakso, E.O.; Vikman, P.; Barg, S. Glucose-Dependent Granule Docking Limits Insulin Secretion and Is Decreased in Human Type 2 Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 470–478.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farfari, S.; Schulz, V.; Corkey, B.; Prentki, M. Glucose-regulated anaplerosis and cataplerosis in pancreatic beta-cells: Possible im-plication of a pyruvate/citrate shuttle in insulin secretion. Diabetes 2000, 49, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.; Ling, Z.C.; Landau, B.R. Quantifying the Carboxylation of Pyruvate in Pancreatic Islets. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 2539–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maechler, P.; Wollheim, C.B. Mitochondrial glutamate acts as a messenger in glucose-induced insulin exocytosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 402, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabaglia, M.E.; Gray-Keller, M.P.; Frey, B.L.; Shortreed, M.R.; Smith, L.M.; Attie, A.D. Alpha-Ketoisocaproate-induced hypersecretion of insulin by islets from diabetes-susceptible mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 289, E218–E224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.J.; Smith, A.D.; Hasan, N.M.; Sabat, G.; Fahien, L.A. Feasibility of pathways for transfer of acyl groups from mi-tochondria to the cytosol to form short chain acyl-CoAs in the pancreatic beta cell. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 30596–30606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macdonald, M.J. Feasibility of a mitochondrial pyruvate malate shuttle in pancreatic islets. Further implication of cytosolic NADPH in insulin secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 20051–20058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.V.; Joseph, J.W.; Ronnebaum, S.M.; Burgess, S.C.; Sherry, A.D.; Newgard, C.B. Metabolic cycling in control of glu-cose-stimulated insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E1287–E1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vergari, E.; Plummer, G.; Dai, X.; Macdonald, P.E. DeSUMOylation Controls Insulin Exocytosis in Response to Metabolic Signals. Biomolecules 2012, 2, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferdaoussi, M.; Dai, X.; Jensen, M.V.; Wang, R.; Peterson, B.S.; Huang, C.; Ilkayeva, O.; Smith, N.; Miller, N.; Hajmrle, C.; et al. Iso-citrate-to-SENP1 signaling amplifies insulin secretion and rescues dysfunctional β cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3847–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panten, U.; Rustenbeck, I. Fuel-induced amplification of insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic islets exposed to a high sulfonylurea concentration: Role of the NADPH/NADP+ ratio. Diabetologia 2007, 51, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prentki, M.; Corkey, B.E.; Madiraju, S.R.M. Lipid-associated metabolic signalling networks in pancreatic beta cell function. Diabetologia 2019, 63, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urban, K.A.; Panten, U. Selective loss of glucose-induced amplification of insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic islets pretreated with sulfonylurea in the absence of fuels. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 2563–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Panten, U.; Früh, E.; Reckers, K.; Rustenbeck, I. Acute metabolic amplification of insulin secretion in mouse islets: Role of cytosolic acetyl-CoA. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1225–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panten, U.; Willenborg, M.; Schumacher, K.; Hamada, A.; Ghaly, H.; Rustenbeck, I. Acute metabolic amplification of insulin secretion in mouse islets is mediated by mitochondrial export of metabolites, but not by mitochondrial energy generation. Metabolism 2013, 62, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, M.J.; Hasan, N.M.; Longacre, M.J. Studies with leucine, β-hydroxybutyrate and ATP citrate lyase-deficient beta cells support the acetoacetate pathway of insulin secretion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2008, 1780, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tengholm, A.; Gylfe, E. cAMP signalling in insulin and glucagon secretion. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabinovitch, A.; Grill, V.; Renold, A.E.; Cerasi, E. Insulin release and cyclic AMP accumulation in response to glucose in pancre-atic islets of fed and starved rats. J. Clin. Investig. 1976, 58, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dyachok, O.; Isakov, Y.; Sågetorp, J.; Tengholm, A. Oscillations of cyclic AMP in hormone-stimulated insulin-secreting beta-cells. Nature 2006, 439, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henquin, J.C.; Nenquin, M.; Ravier, M.A.; Szollosi, A. Shortcomings of current models of glucose-induced insulin secretion. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2009, 11, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalwat, M.A.; Cobb, M.H. Mechanisms of the amplifying pathway of insulin secretion in the β cell. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 179, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, C.; Weinert, B.T.; Nishida, Y.; Verdin, E.; Mann, M. The growing landscape of lysine acetylation links metabolism and cell signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grespan, E.; Giorgino, T.; Arslanian, S.; Natali, A.; Ferrannini, E.; Mari, A. Defective Amplifying Pathway of β-Cell Secretory Re-sponse to Glucose in Type 2 Diabetes: Integrated Modeling of In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence. Diabetes 2018, 67, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rustenbeck, I.; Schulze, T.; Morsi, M.; Alshafei, M.; Panten, U. What Is the Metabolic Amplification of Insulin Secretion and Is It (Still) Relevant? Metabolites 2021, 11, 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060355
Rustenbeck I, Schulze T, Morsi M, Alshafei M, Panten U. What Is the Metabolic Amplification of Insulin Secretion and Is It (Still) Relevant? Metabolites. 2021; 11(6):355. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060355
Chicago/Turabian StyleRustenbeck, Ingo, Torben Schulze, Mai Morsi, Mohammed Alshafei, and Uwe Panten. 2021. "What Is the Metabolic Amplification of Insulin Secretion and Is It (Still) Relevant?" Metabolites 11, no. 6: 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060355
APA StyleRustenbeck, I., Schulze, T., Morsi, M., Alshafei, M., & Panten, U. (2021). What Is the Metabolic Amplification of Insulin Secretion and Is It (Still) Relevant? Metabolites, 11(6), 355. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060355





