Circulating Levels of Pro-Neurotensin and Its Relationship with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Subjects
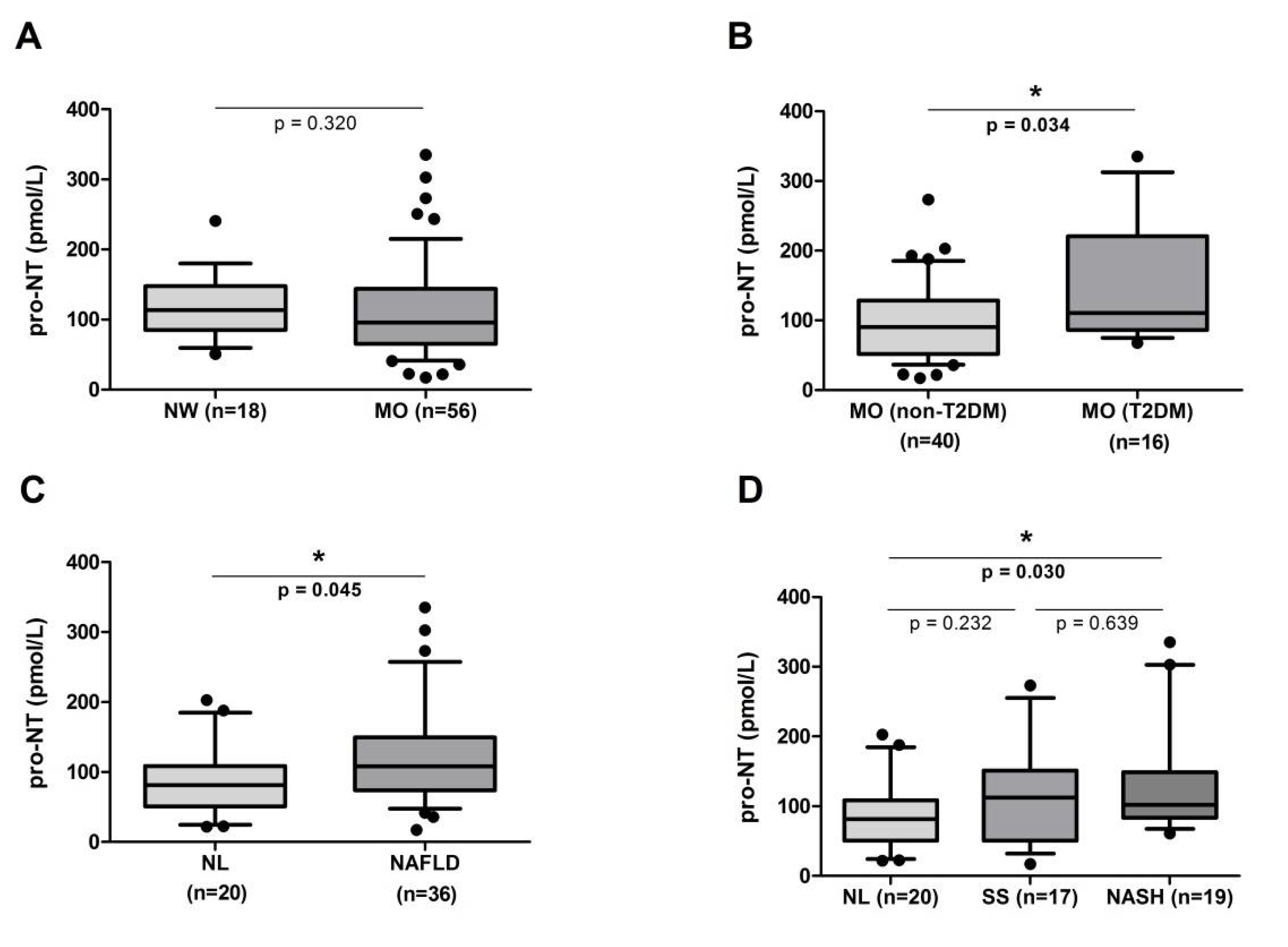
2.2. Circulating Levels of Pro-Neurotensin in the Cohort Studied
2.3. Hepatic Expression of the Main Genes Related to the Liver Lipid Metabolism
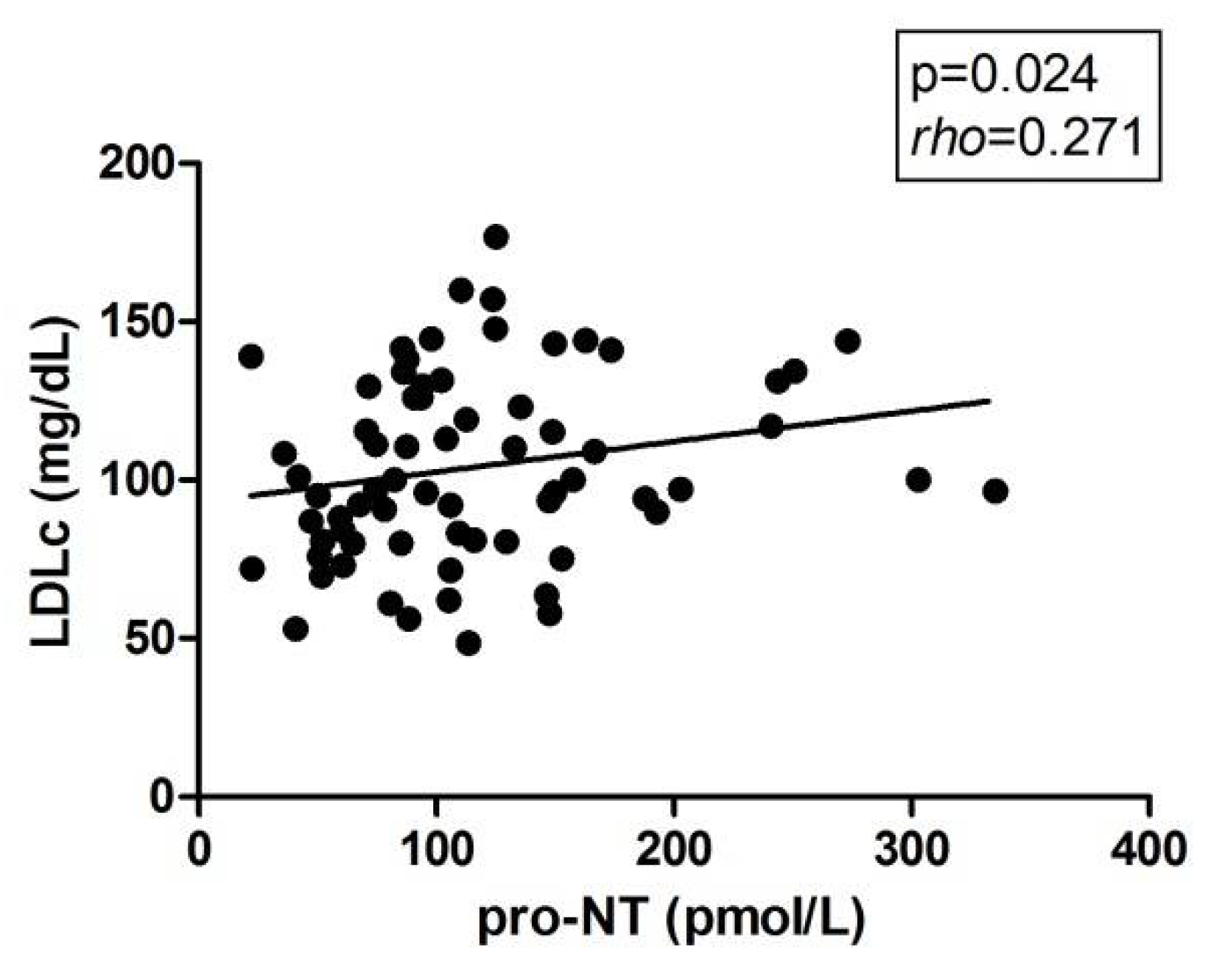
2.4. Correlations of Pro-NT Levels with Biochemical and Clinical Parameters and with the Hepatic Expression of the Main Lipid Metabolism-Related Genes to the Liver
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Subjects
4.2. Sample Size
4.3. Liver Pathology
4.4. Biochemical Analyses
4.5. Gene Expression in the Liver
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global Burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, Predictions, Risk Factors and Prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, G.; Day, C.P.; Dufour, J.F.; Canbay, A.; Nobili, V.; Ratziu, V.; Tilg, H.; Roden, M.; Gastaldelli, A.; Yki-Jarvinen, H.; et al. EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blüher, M. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction Contributes to Obesity Related Metabolic Diseases. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 27, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiyasit, N.; Sripetchwandee, J.; Chattipakorn, N.; Chattipakorn, S.C. Potential Roles of Neurotensin on Cognition in Conditions of Obese-Insulin Resistance. Neuropeptides 2018, 72, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Song, J.; Zaytseva, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.; Rychahou, P.; Jiang, K.; Starr, M.E.; Kim, J.T.; Harris, J.W.; Yiannikouris, F.B.; et al. An Obligatory Role for Neurotensin in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity. Nature 2016, 533, 411–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schroeder, L.E.; Leinninger, G.M. Role of Central Neurotensin in Regulating Feeding: Implications for the Development and Treatment of Body Weight Disorders. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 900–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melander, O.; Maisel, A.S.; Almgren, P.; Manjer, J.; Belting, M.; Hedblad, B.; Engström, G.; Kilger, U.; Nilsson, P.; Bergmann, A.; et al. Plasma Proneurotensin and Incidence of Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, Breast Cancer, and Mortality. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2012, 308, 1469–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auguet, T.; Aragonès, G.; Berlanga, A.; Martínez, S.; Sabench, F.; Aguilar, C.; Villar, B.; Sirvent, J.J.; Del Castillo, D.; Richart, C.; et al. Low Circulating Levels of Neurotensin in Women with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Associated with Severe Obesity. Obesity 2018, 26, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, H.; Labeck, B.; Klocker, J.; Nehoda, H.; Mittermair, R.; Aigner, F.; Gadenstätter, M.; Schwelberger, H.; Wetscher, G. Effects of Adjustable Gastric Banding on Altered Gut Neuropeptide Levels in Morbidly Obese Patients. Obes. Surg. 2001, 11, 735–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Näslund, E.; Melin, I.; Grybäck, P.; Hägg, A.; Hellström, P.M.; Jacobsson, H.; Theodorsson, E.; Rössner, S.; Backman, L. Reduced Food Intake after Jejunoileal Bypass: A Possible Association with Prolonged Gastric Emptying and Altered Gut Hormone Patterns. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 66, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christ-Crain, M.; Stoeckli, R.; Ernst, A.; Morgenthaler, N.G.; Bilz, S.; Korbonits, M.; Struck, J.; Bergmann, A.; Müller, B.; Keller, U. Effect of Gastric Bypass and Gastric Banding on Proneurotensin Levels in Morbidly Obese Patients. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 3544–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holdstock, C.; Zethelius, B.; Sundbom, M.; Karlsson, F.A.; Edén Engström, B. Postprandial Changes in Gut Regulatory Peptides in Gastric Bypass Patients. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 1640–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Capoccia, D.; Bertoccini, L.; Ceccarelli, V.; Chiappetta, C.; Leonetti, F.; Di Cristofano, C.; Silecchia, G.; Orho-Melander, M.; et al. Neurotensin Is a Lipid-Induced Gastrointestinal Peptide Associated with Visceral Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Leonetti, F.; Capoccia, D.; Di Cristofano, C.; Silecchia, G.; Orho-Melander, M.; Melander, O.; Cavallo, M.G. Increased Plasma Proneurotensin Levels Identify NAFLD in Adults with and Without Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 2253–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, H.; Kushiyama, A.; Nakatsu, Y.; Yamamotoya, T.; Matsunaga, Y.; Fujishiro, M.; Sakoda, H.; Ohno, H.; Yoneda, M.; Asano, T. Roles of Gut-Derived Secretory Factors in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Their Possible Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leeman, S.E.; Carraway, R.E. Neurotensin: Discovery, Isolation, Characterization, Synthesis and Possible Physiological Roles. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 1982, 400, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barelli, H.; Fox-Threlkeld, J.E.T.; Dive, V.; Daniel, E.E.; Vincent, J.P.; Checler, F. Role of Endopeptidase 3.4.24.16 in the Catabolism of Neurotensin, in Vivo, in the Vascularly Perfused Dog Ileum. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 112, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cavalcanti, D.M.L.P.; Castro, L.M.; Rosa Neto, J.C.; Seelaender, M.; Neves, R.X.; Oliveira, V.; Forti, F.L.; Iwai, L.K.; Gozzo, F.C.; Todiras, M.; et al. Neurolysin Knockout Mice Generation and Initial Phenotype Characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 15426–15440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gui, X.; Dobner, P.R.; Carraway, R.E. Endogenous Neurotensin Facilitates Enterohepatic Bile Acid Circulation by Enhancing Intestinal Uptake in Rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, 1413–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchetta, I.; Bertoccini, L.; Sentinelli, F.; Bailetti, D.; Marini, G.; Cimini, F.A.; Ceccarelli, V.; Struck, J.; Schulte, J.; Loche, S.; et al. Circulating Pro-Neurotensin Levels Predict Bodyweight Gain and Metabolic Alterations in Children. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Petta, S.; Longo, M.; Alisi, A.; Soardo, G.; Valenti, L.; Miele, L.; Grimaudo, S.; Pennisi, G.; et al. Neurotensin Up-Regulation Is Associated with Advanced Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with MAFLD. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatrath, H.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Chalasani, N. Dyslipidemia in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Semin Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 022–029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marquart, T.J.; Allen, R.M.; Ory, D.S.; Baldan, A. MiR-33 Links SREBP-2 Induction to Repression of Sterol Transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12228–12232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Auguet, T.; Aragonès, G.; Berlanga, A.; Guiu-Jurado, E.; Martí, A.; Martínez, S.; Sabench, F.; Hernández, M.; Aguilar, C.; Sirvent, J.; et al. MiR33a/MiR33b* and MiR122 as Possible Contributors to Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in Obese Women with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. IJMS 2016, 17, 1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azhar, S. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors, Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease. Future Cardiol. 2010, 6, 657–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Napolitano, A.; Miller, S.; Nicholls, A.W.; Baker, D.; Van Horn, S.; Thomas, E.; Rajpal, D.; Spivak, A.; Brown, J.R.; Nunez, D.J. Novel Gut-Based Pharmacology of Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.M.; Van Natta, M.; Behling, C.; Contos, M.J.; Cummings, O.W.; Ferrell, L.D.; Liu, Y.C.; Torbenson, M.S.; Unalp-Arida, A.; et al. Design and Validation of a Histological Scoring System for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1313–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Janney, C.G.; Di Bisceglie, M.A.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.; Bacon, B.R. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Proposal for Grading and Staging the Histological Lesions. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2467–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | NW (n = 18) | MO (n = 56) | NAFLD (n = 36) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NL (n = 20) | NAFLD (n = 36) | SS (n = 17) | NASH (n = 19) | ||
| Age (years) | 43.50 ± 6.73 | 44.54 ± 10.02 | 48 ± 9.79 | 46.19 ± 10.78 | 49.63 ± 8.78 |
| Weight (kg) | 54.2 (51–65.43) a | 115.5 (41.54–50.79) | 119.5 (109–129.75) | 120 (109.80–134) | 119 (107–123) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.97 (20.79–24.08) a | 46.41 (41.53–50.79) | 46.5 (44.03–51.69) | 46.87 (43.03–56.09) | 46.2 (44.26–48.59) |
| WC (cm) | 71.5 (68.5–82.5) a | 125.25 (115–144) | 130 (124–136.5) | 133 (124–137) | 129 (122.75–133) |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 90 (84.5–98.50) a | 83 (76–95) | 116 (103–152) b | 115.5 (101.50–139.25) c | 116 (103–152) d |
| Insulin (mUI/L) | 7.8 (4.90–10.06) a | 11 (7.31–14.03) | 16.31 (10.69–24.26) b | 17.6 (10.60–25.4) | 15.24 (10.78–22.50) d |
| HOMA2-IR | 1.05 (0.60–1.30) a | 1.15 (0.90–1.65) | 2.3 (1.45–3.4) b | 2.65 (1.30–3.45) | 2 (1.50–3.20) d |
| HbA1c (%) | 5 (4.6–5.3) a | 5 (4.6–5.3) | 5.5 (5–6.5) b | 5.8 (5–6.2) c | 5.1 (4.9–6.6) |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 197.59 ± 30.21 a | 166.60 ± 29.64 | 181.14 ± 34.12 | 177.25 ± 36.29 | 184.42 ± 32.81 |
| HDLc (mg/dL) | 64 (49.75–73) a | 48 (40–57) | 38.10 (35.75–43.25) b | 36.5(29–41.05) c | 41 (36.75–44) d |
| LDLc (mg/dL) | 114.46 ± 28.85 | 89.61 ± 25.27 | 107.01 ± 29.12 b | 105.49 ± 30.69 | 108.53 ± 28.38 d |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 85 (52.5–169.25) a | 124 (75–167) | 162 (122.50–239) b | 168 (109.37- 243.75) | 160 (124–239) |
| AST (UI/L) | 19.5 (15.25–22.50) a | 21 (18.25–26.25) | 32 (24.75–54) b | 31.5 (25.25–54) c | 36.5 (20.50–52.50) d |
| ALT (UI/L) | 15 (11.50–20.50) a | 18.5 (16–27.25) | 35 (27–53) b | 33 (27.50–51.25) c | 37 (24–62) d |
| GGT (UI/L) | 11 (9–21) a | 17 (10.50–26) | 27.5 (15.75–43) b | 30 (16–41) | 25 (15–66) |
| ALP (Ul/L) | 55.71 ± 14.67 a | 60.33 ± 11.49 | 70.80 ± 15.71 b | 68.87± 15.58 c | 72.51 ± 16.07 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villar, B.; Bertran, L.; Aguilar, C.; Binetti, J.; Martínez, S.; Sabench, F.; Real, M.; Riesco, D.; París, M.; Del Castillo, D.; et al. Circulating Levels of Pro-Neurotensin and Its Relationship with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. Metabolites 2021, 11, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060373
Villar B, Bertran L, Aguilar C, Binetti J, Martínez S, Sabench F, Real M, Riesco D, París M, Del Castillo D, et al. Circulating Levels of Pro-Neurotensin and Its Relationship with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. Metabolites. 2021; 11(6):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060373
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillar, Beatriz, Laia Bertran, Carmen Aguilar, Jessica Binetti, Salomé Martínez, Fàtima Sabench, Monica Real, David Riesco, Marta París, Daniel Del Castillo, and et al. 2021. "Circulating Levels of Pro-Neurotensin and Its Relationship with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism" Metabolites 11, no. 6: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060373
APA StyleVillar, B., Bertran, L., Aguilar, C., Binetti, J., Martínez, S., Sabench, F., Real, M., Riesco, D., París, M., Del Castillo, D., Richart, C., & Auguet, T. (2021). Circulating Levels of Pro-Neurotensin and Its Relationship with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. Metabolites, 11(6), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060373








