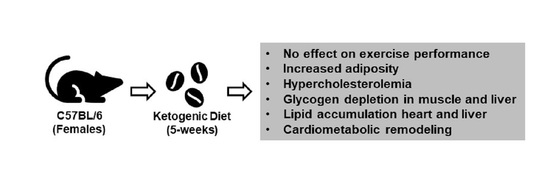
The Effects of Fasting or Ketogenic Diet on Endurance Exercise Performance and Metabolism in Female Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fasting Induces Physiological Ketosis but Does Not Improve Endurance Exercise Capacity
2.2. Fasting Does Not Alter Endogenous Triacylglycerol or Glycogen Content in the Heart, Gastrocnemius, or Liver
2.3. Short-Term Ketogenic Diet Increases Weight Gain and Adiposity
2.4. Short-Term Ketogenic Diet Elevates Serum Ketone Bodies and Total Cholesterol
2.5. Short-Term Ketogenic Diet Depletes Glycogen and Increases Tissue Triglycerides
2.6. Short-Term Ketogenic Diet Alters Gene Expression in the Heart, Skeletal Muscle, and Liver
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Composition of Diet
4.3. Serum Analyses
4.4. Endurance Exercise Capacity Tests
4.5. Gravimetric Analysis
4.6. Biochemical Analysis in Tissues
4.7. Analysis of Gene Expression
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wentz, A.; D’Avignon, D.A.; Weber, M.L.; Cotter, D.G.; Doherty, J.M.; Kerns, R.; Nagarajan, R.; Reddy, N.; Sambandam, N.; Crawford, P.A. Adaptation of Myocardial Substrate Metabolism to a Ketogenic Nutrient Environment. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 24447–24456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, P.; O’Neill, C.; DeWitt, E.; Kolwicz, S.C., Jr. Endurance Exercise Capacity and Substrate Metabolism in Male and Female Mice. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 698.1. [Google Scholar]
- Avogaro, A.; Crepaldi, C.; Miola, M.; Maran, A.; Pengo, V.; Tiengo, A.; Del Prato, S. High blood ketone body concentration in Type 2 non-insulin dependent diabetic patients. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1996, 19, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerci, B.; Benichou, M.; Floriot, M.; Bohme, P.; Fougnot, S.; Franck, P.; Drouin, P. Accuracy of an electrochemical sensor for measuring capillary blood ketones by fingerstick samples during metabolic deterioration after continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion interruption in type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1137–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, K.L.; Holcomb, L.E.; Kolwicz, S.C., Jr. Ketogenic Diets and Exercise Performance. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, G.; Martin, O.J.; Horton, J.L.; Lai, L.; Vega, R.B.; Leone, T.C.; Koves, T.; Gardell, S.J.; Krüger, M.; Hoppel, C.L.; et al. The Failing Heart Relies on Ketone Bodies as a Fuel. Circulation 2016, 133, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedi, K.C., Jr.; Snyder, N.W.; Brandimarto, J.; Aziz, M.; Mesaros, C.; Worth, A.J.; Wang, L.L.; Javaheri, A.; Blair, I.A.; Margulies, K.B.; et al. Evidence for Intramyocardial Disruption of Lipid Metabolism and Increased Myocardial Ketone Utilization in Advanced Human Heart Failure. Circulation 2016, 133, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, J.L.; Davidson, M.T.; Kurishima, C.; Vega, R.B.; Powers, J.C.; Matsuura, T.R.; Petucci, C.; Lewandowski, E.D.; Crawford, P.A.; Muoio, D.M.; et al. The failing heart utilizes 3-hydroxybutyrate as a metabolic stress defense. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e124079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, D.G.; Schugar, R.C.; Crawford, P.A. Ketone body metabolism and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2013, 304, H1060–H1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veech, R.L. The therapeutic implications of ketone bodies: The effects of ketone bodies in pathological conditions: Ketosis, ketogenic diet, redox states, insulin resistance, and mitochondrial metabolism. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2004, 70, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouhal, H.; Saeidi, A.; Salhi, A.; Li, H.; Essop, M.F.; Laher, I.; Rhibi, F.; Amani-Shalamzari, S.; Ben Abderrahman, A. Exercise Training and Fasting: Current Insights. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2020, 11, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Cogan, K.E.; Egan, B. Metabolism of ketone bodies during exercise and training: Physiological basis for exogenous supplementation. J. Physiol. 2017, 595, 2857–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A. Ketogenic Diet for Obesity: Friend or Foe? Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 2092–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheless, J.W. History of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia 2008, 49, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, M.N.; Wallace, M.A.; Tomilov, A.A.; Zhou, Z.; Marcotte, G.R.; Tran, D.; Perez, G.; Gutierrez-Casado, E.; Koike, S.; Knotts, T.A.; et al. A Ketogenic Diet Extends Longevity and Healthspan in Adult Mice. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 539–546.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badman, M.K.; Kennedy, A.R.; Adams, A.C.; Pissios, P.; Maratos-Flier, E. A very low carbohydrate ketogenic diet improves glucose tolerance in ob/ob mice independently of weight loss. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E1197–E1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partsalaki, I.; Karvela, A.; Spiliotis, B.E. Metabolic impact of a ketogenic diet compared to a hypocaloric diet in obese children and adolescents. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 25, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samaha, F.F.; Iqbal, N.; Seshadri, P.; Chicano, K.L.; Daily, D.A.; McGrory, J.; Williams, T.; Williams, M.; Gracely, E.J.; Stern, L. A Low-Carbohydrate as Compared with a Low-Fat Diet in Severe Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2074–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, J.D.; Baker, J.A.; Rogers, T.; Davis, J.; Satapati, S.; Burgess, S.C. Short-term weight loss and hepatic triglyceride reduction: Evidence of a metabolic advantage with dietary carbohydrate restriction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbow, J.R.; Doherty, J.M.; Schugar, R.C.; Travers, S.; Weber, M.L.; Wentz, A.; Ezenwajiaku, N.; Cotter, D.G.; Brunt, E.M.; Crawford, P.A. Hepatic steatosis, inflammation, and ER stress in mice maintained long term on a very low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 300, G956–G967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Koning, L.; Fung, T.T.; Liao, X.; Chiuve, S.E.; Rimm, E.B.; Willett, W.C.; Spiegelman, D.; Hu, F.B. Low-carbohydrate diet scores and risk of type 2 diabetes in men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 844–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashti, H.M.; Al-Zaid, N.S.; Mathew, T.C.; Al-Mousawi, M.; Talib, H.; Asfar, S.K.; Behbahani, A.I. Long Term Effects of Ketogenic Diet in Obese Subjects with High Cholesterol Level. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 286, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellenbroek, J.H.; Van Dijck, L.; Töns, H.A.; Rabelink, T.J.; Carlotti, F.; Ballieux, B.E.P.B.; De Koning, E.J.P. Long-term ketogenic diet causes glucose intolerance and reduced β- and α-cell mass but no weight loss in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E552–E558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.J.; Kirk, T.; Ashmore, T.; Willerton, K.; Evans, R.; Smith, A.; Murray, A.; Stubbs, B.; West, J.; McLure, S.W.; et al. Nutritional Ketosis Alters Fuel Preference and Thereby Endurance Performance in Athletes. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.J.; Knight, N.S.; Cole, M.A.; Cochlin, L.E.; Carter, E.; Tchabanenko, K.; Pichulik, T.; Gulston, M.K.; Atherton, H.J.; Schroeder, M.A.; et al. Novel ketone diet enhances physical and cognitive performance. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 4021–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Ericsson, M.; Joibari, M.M.; Anderson, F.; Carlsson, L.; Nilsson, S.K.; Sjödin, A.; Burén, J. A low-carbohydrate high-fat diet decreases lean mass and impairs cardiac function in pair-fed female C57BL/6J mice. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, A.; Hellström, F.; Sehlstedt, E.; Svensson, M.; Burén, J. Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Muscle Fatigue in Healthy, Young, Normal-Weight Women: A Randomized Controlled Feeding Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkalec-Michalski, K.; Nowaczyk, P.; Główka, N.; Ziobrowska, A.; Podgórski, T. Is a Four-Week Ketogenic Diet an Effective Nutritional Strategy in Crossfit-Trained Female and Male Athletes? Nutrients 2021, 13, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durkalec-Michalski, K.; Nowaczyk, P.M.; Siedzik, K. Effect of a four-week ketogenic diet on exercise metabolism in Crossfit-trained athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2019, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.J.; Sharma, A.P.; Ross, M.L.; Welvaert, M.; Slater, G.J.; Burke, L.M. Chronic Ketogenic Low Carbohydrate High Fat Diet Has Minimal Effects on Acid-Base Status in Elite Athletes. Nutrients 2018, 10, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McSwiney, F.T.; Wardrop, B.; Hyde, P.N.; Lafountain, R.A.; Volek, J.S.; Doyle, L. Keto-adaptation enhances exercise performance and body composition responses to training in endurance athletes. Metabolism 2018, 81, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.M.; Merien, F.; Braakhuis, A.; Maunder, E.; Dulson, D.K. Effect of a Ketogenic Diet on Submaximal Exercise Capacity and Efficiency in Runners. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 2135–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinn, C.; Wood, M.; Williden, M.; Chatterton, S.; Maunder, E. Ketogenic diet benefits body composition and well-being but not performance in a pilot case study of New Zealand endurance athletes. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greene, D.A.; Varley, B.J.; Hartwig, T.; Chapman, P.; Rigney, M. A Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet Reduces Body Mass without Compromising Performance in Powerlifting and Olympic Weightlifting Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 3373–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kephart, W.C.; Pledge, C.D.; Roberson, P.A.; Mumford, P.W.; Romero, M.A.; Mobley, C.B.; Martin, J.S.; Young, K.C.; Lowery, R.P.; Wilson, J.M.; et al. The Three-Month Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Blood Parameters, and Performance Metrics in Crossfit Trainees: A Pilot Study. Sports 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, A.; Grimaldi, K.; D’Agostino, D.; Cenci, L.; Moro, T.; Bianco, A.; Palma, A. Ketogenic diet does not affect strength performance in elite artistic gymnasts. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2012, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.M.; Lowery, R.P.; Roberts, M.D.; Sharp, M.H.; Joy, J.M.; Shields, K.A.; Partl, J.; Volek, J.S.; D’Agostino, D. The Effects of Ketogenic Dieting on Body Composition, Strength, Power, and Hormonal Profiles in Resistance Training Males. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2020, 34, 3463–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Ma, S.; Tominaga, T.; Suzuki, K.; Liu, C. An 8-Week, Low Carbohydrate, High Fat, Ketogenic Diet Enhanced Exhaustive Exercise Capacity in Mice Part 2: Effect on Fatigue Recovery, Post-Exercise Biomarkers and Anti-Oxidation Capacity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Huang, Q.; Yada, K.; Liu, C.; Suzuki, K. An 8-Week Ketogenic Low Carbohydrate, High Fat Diet Enhanced Exhaustive Exercise Capacity in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.C.; Bryce, G.R.; Conlee, R.K. Adaptations to a high-fat diet that increase exercise endurance in male rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 1984, 56, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.M.; Kephart, W.C.; Mumford, P.W.; Mobley, C.B.; Lowery, R.P.; Shake, J.J.; Patel, R.K.; Healy, J.C.; McCullough, D.J.; Kluess, H.A.; et al. Effects of a ketogenic diet on adipose tissue, liver, and serum biomarkers in sedentary rats and rats that exercised via resisted voluntary wheel running. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 311, R337–R351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rang, Y.; Ma, S.; Yang, J.; Liu, H.; Suzuki, K.; Liu, C. A Low-Protein High-Fat Diet Leads to Loss of Body Weight and White Adipose Tissue Weight via Enhancing Energy Expenditure in Mice. Metabolites 2021, 11, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Yang, J.; Tominaga, T.; Liu, C.; Suzuki, K. A Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet and Treadmill Training Enhanced Fatty Acid Oxidation Capacity but Did Not Enhance Maximal Exercise Capacity in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearris, M.A.; Hammond, K.M.; Fell, J.M.; Morton, J.P. Regulation of Muscle Glycogen Metabolism during Exercise: Implications for Endurance Performance and Training Adaptations. Nutrients 2018, 10, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzig, K.P.; Honors, M.A.; Hargrave, S.L. Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Tolerance Are Altered by Maintenance on a Ketogenic Diet. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 3105–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearlove, D.J.; Faull, O.K.; Rolls, E.; Clarke, K.; Cox, P.J. Nutritional Ketoacidosis during Incremental Exercise in Healthy Athletes. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.; Egan, B. Intermittent Running and Cognitive Performance after Ketone Ester Ingestion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 2330–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leckey, J.J.; Ross, M.L.; Quod, M.; Hawley, J.A.; Burke, L.M. Ketone Diester Ingestion Impairs Time-Trial Performance in Professional Cyclists. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohm, G.L.; Beeker, R.T.; Israel, R.G.; Tapscott, E.B. Metabolic responses to exercise after fasting. J. Appl. Physiol. 1986, 61, 1363–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohm, G.L.; Tapscott, E.B.; Barakat, H.A.; Kasperek, G.J. Influence of fasting on glycogen depletion in rats during exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 1983, 55, 830–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón-Vargas, L.F. Effects of Fasting on Endurance Exercise. Sports Med. 1993, 16, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, B.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise Metabolism and the Molecular Regulation of Skeletal Muscle Adaptation. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 162–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno, N.B.; De Melo, I.S.V.; De Oliveira, S.L.; da Rocha Ataide, T. Very-Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet V. Low-Fat Diet for Long-Term Weight Loss: A Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 1178–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, D.; Kolwicz, S.C., Jr.; Wang, P.; Roe, N.D.; Villet, O.; Nishi, K.; Hsu, Y.-W.A.; Flint, G.V.; Caudal, A.; Wang, W.; et al. Increasing Fatty Acid Oxidation Prevents High Fat Diet Induced Cardiomyopathy through Regulating Parkin Mediated Mitophagy. Circulation 2020, 142, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosatos, K.; Schulze, P.C. Cardiac Lipotoxicity: Molecular Pathways and Therapeutic Implications. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2013, 10, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassir, F.; Rector, R.S.; Hammoud, G.M.; Ibdah, J.A. Pathogenesis and Prevention of Hepatic Steatosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 11, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, M.; Tozzi, R.; Risi, R.; Tuccinardi, D.; Mariani, S.; Basciani, S.; Spera, G.; Lubrano, C.; Gnessi, L. Beneficial effects of the ketogenic diet on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A comprehensive review of the literature. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e13024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, K.L.; Zhang, L.; Wagg, C.; Al Batran, R.; Gopal, K.; Levasseur, J.; Leone, T.; Dyck, J.R.B.; Ussher, J.R.; Muoio, D.M.; et al. Increased ketone body oxidation provides additional energy for the failing heart without improving cardiac efficiency. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolwicz, S.C., Jr.; Purohit, S.; Tian, R. Cardiac Metabolism and Its Interactions with Contraction, Growth, and Survival of Cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolwicz, S.C., Jr.; Tian, R. Glucose metabolism and cardiac hypertrophy. Cardiovasc. Res. 2011, 90, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopaschuk, G.D.; Karwi, Q.G.; Ho, K.L.; Pherwani, S.; Ketema, E.B. Ketone metabolism in the failing heart. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2020, 1865, 158813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beery, A.K. Inclusion of females does not increase variability in rodent research studies. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 2018, 23, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNulty, K.L.; Elliott-Sale, K.J.; Dolan, E.; Swinton, P.A.; Ansdell, P.; Goodall, S.; Thomas, K.; Hicks, K.M. The Effects of Menstrual Cycle Phase on Exercise Performance in Eumenorrheic Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rael, B.; Alfaro-Magallanes, V.M.; Romero-Parra, N.; Castro, E.A.; Cupeiro, R.; de Jonge, X.A.K.J.; Wehrwein, E.A.; Peinado, A.B.; IronFEMME Study Group. Menstrual Cycle Phases Influence on Cardiorespiratory Response to Exercise in Endurance-Trained Females. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, A.S., Jr.; Speck, A.E.; Amaral, I.M.; Canas, P.; Cunha, R.A. The exercise sex gap and the impact of the estrous cycle on exercise performance in mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, S.; Shao, D.; Tomasi, L.C.; Braun, A.; de Mattos, A.B.M.; Choi, Y.S.; Villet, O.; Roe, N.; Halterman, C.R.; Tian, R.; et al. The effects of fatty acid composition on cardiac hypertrophy and function in mouse models of diet-induced obesity. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 46, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beylot, M.; Neggazi, S.; Hamlat, N.; Langlois, D.; Forcheron, F. Perilipin 1 ablation in mice enhances lipid oxidation during exercise and does not impair exercise performance. Metabolism 2012, 61, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kregel, K.C.; Allen, D.L.; Booth, F.W.; Fleshner, M.R.; Henrikson, E.J.; Musch, T.I.; O’Leary, D.S.; Parks, C.M.; Poole, D.C.; Ra’anan, A.W.; et al. Exercise Protocols Using Rats and Mice. In Resource Book for the Design of Animal Exercise Protocols; American Physiological Society: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Passonneau, J.; Lauderdale, V. A comparison of three methods of glycogen measurement in tissues. Anal. Biochem. 1974, 60, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolwicz, S.C., Jr.; Olson, D.P.; Marney, L.C.; Garcia-Menendez, L.; Synovec, R.E.; Tian, R. Cardiac-Specific Deletion of Acetyl CoA Carboxylase 2 Prevents Metabolic Remodeling during Pressure-Overload Hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 2012, 111, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Holcomb, L.E.; O’Neill, C.C.; DeWitt, E.A.; Kolwicz, S.C., Jr. The Effects of Fasting or Ketogenic Diet on Endurance Exercise Performance and Metabolism in Female Mice. Metabolites 2021, 11, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060397
Holcomb LE, O’Neill CC, DeWitt EA, Kolwicz SC Jr. The Effects of Fasting or Ketogenic Diet on Endurance Exercise Performance and Metabolism in Female Mice. Metabolites. 2021; 11(6):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060397
Chicago/Turabian StyleHolcomb, Lola E., Caitlin C. O’Neill, Elizabeth A. DeWitt, and Stephen C. Kolwicz, Jr. 2021. "The Effects of Fasting or Ketogenic Diet on Endurance Exercise Performance and Metabolism in Female Mice" Metabolites 11, no. 6: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060397
APA StyleHolcomb, L. E., O’Neill, C. C., DeWitt, E. A., & Kolwicz, S. C., Jr. (2021). The Effects of Fasting or Ketogenic Diet on Endurance Exercise Performance and Metabolism in Female Mice. Metabolites, 11(6), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11060397