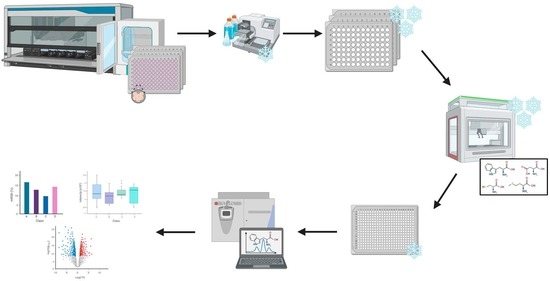
Automated Sample Preparation and Data Collection Workflow for High-Throughput In Vitro Metabolomics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
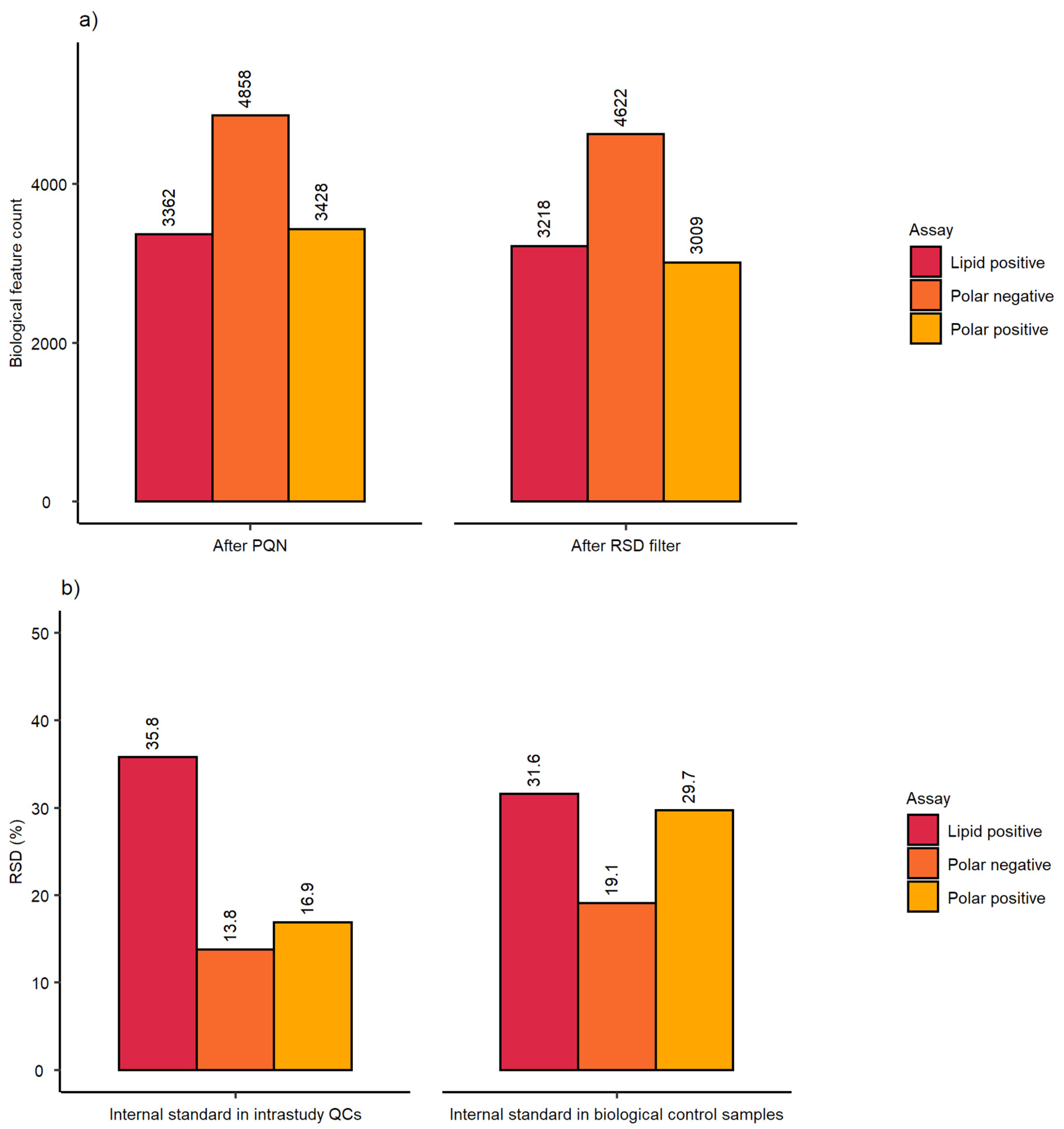
2.1. Evaluation of Sensitivity and Repeatability of the Automated Platform for Intracellular Metabolite Extraction and Analysis
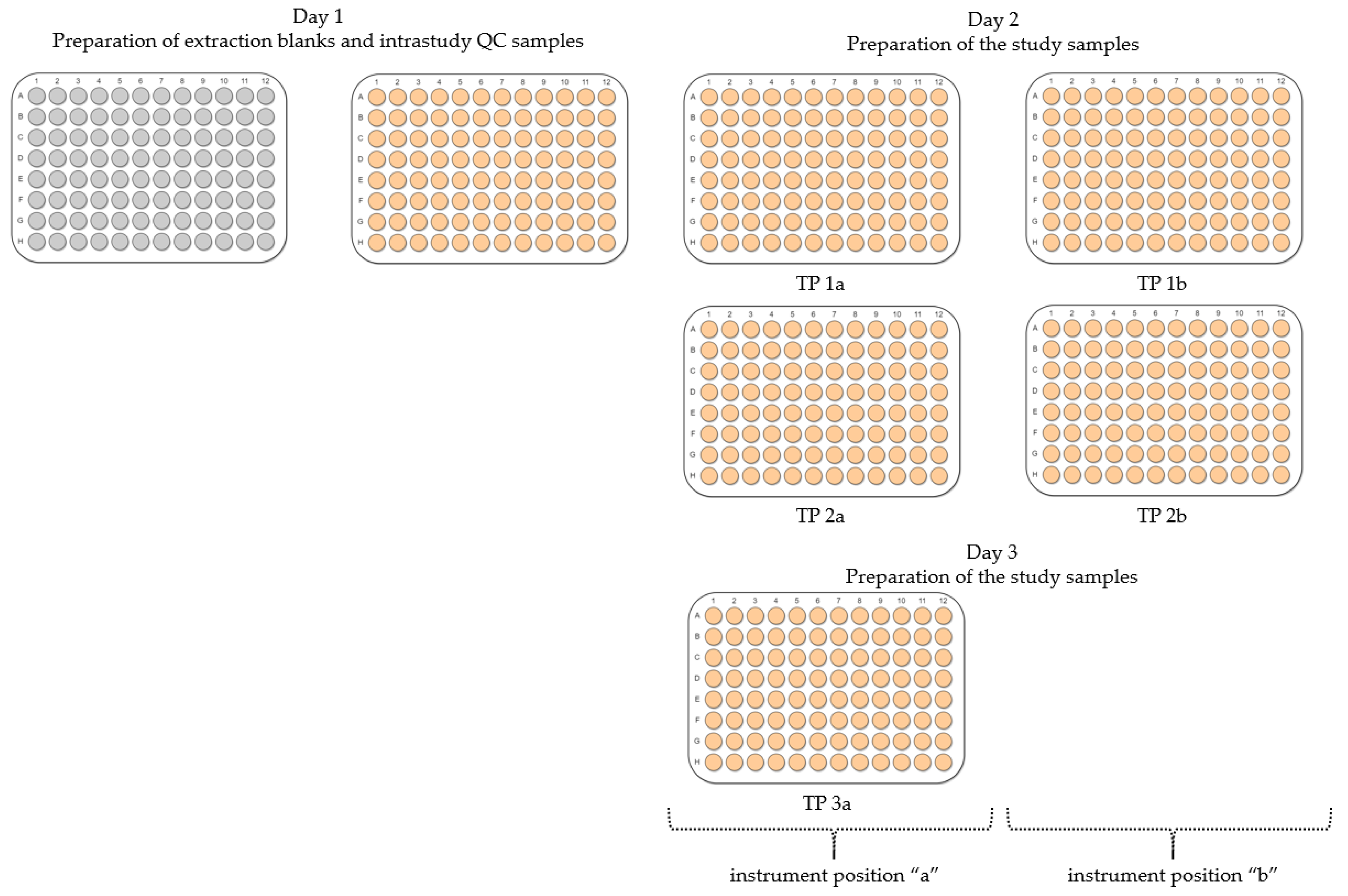
2.2. Evaluation of Experimental Conditions and Intra/Inter-Day Variation of the Automated In Vitro Metabolomics Workflow
- Inter-day repeatability of metabolite extractions from HepaRG samples in 96-well microplates (Test plate (TP) 1a vs. 3a)
- Order of metabolite extraction from 96-well microplates (TP 1a vs. 2a, TP 1b vs. 2b), evaluated within one day, and only relevant to polar metabolites
- Position of 96-well microplate on the sample preparation platform’s deck (TP 1a vs. 1b, TP 2a vs. 2b)
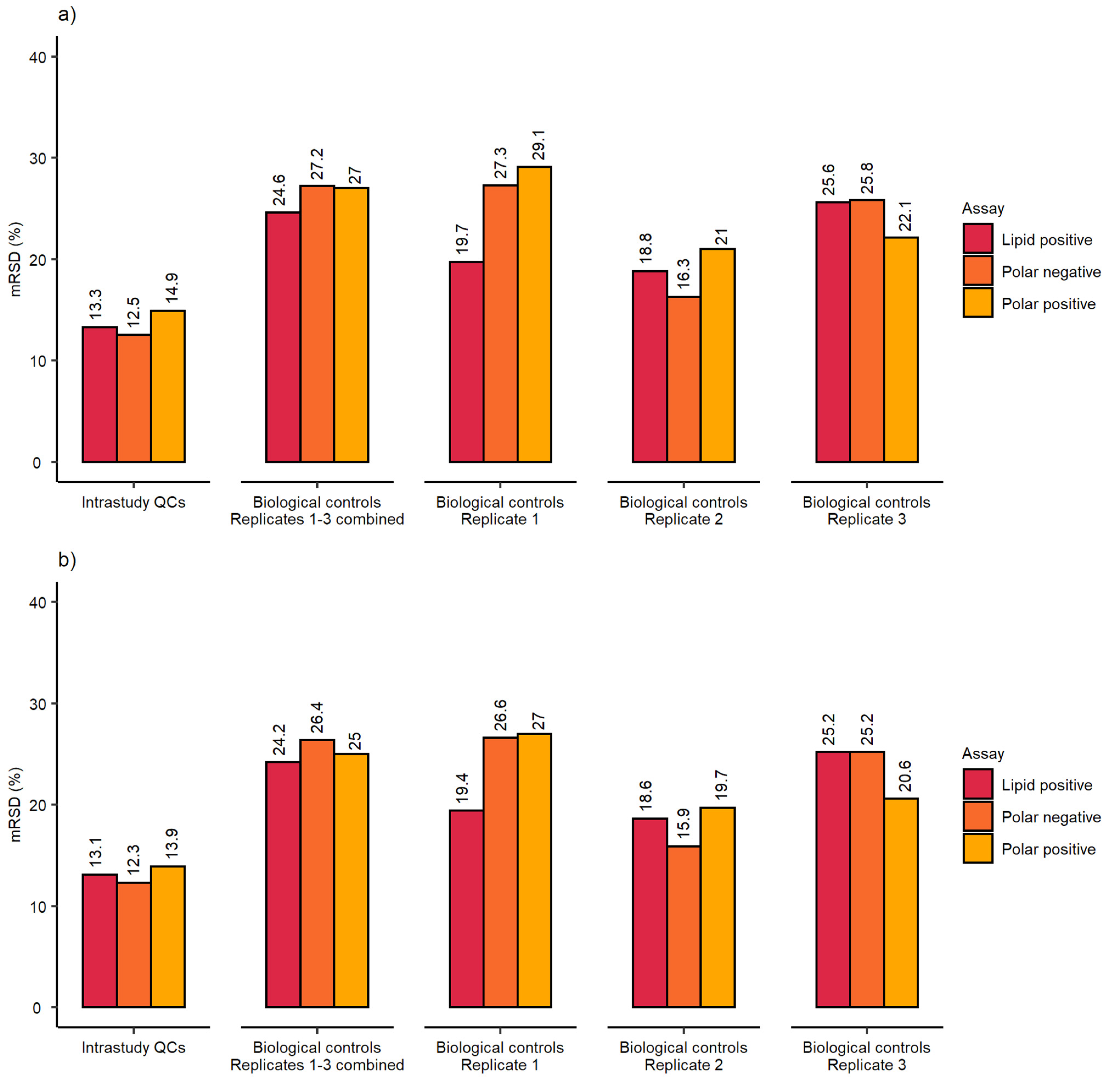
2.3. Demonstration of the Developed Workflow for High-Throughput Metabolomics Studies
3. Discussion
3.1. Assessment of Automated Sample Preparation Workflow for Metabolomics
3.2. Demonstration of the Developed Workflow for High-Throughput Metabolomics Studies
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Assessment of Automated Sample Preparation Workflow for Metabolomics
4.1.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.1.2. Automated Metabolite Extraction
4.1.3. Data Acquisition
4.1.4. Data Processing and Analysis
4.2. Demonstration of the Developed Workflow for High-Throughput Metabolomics Studies
4.2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.2.2. Automated Metabolite Extraction
4.2.3. Data Acquisition
4.2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Becker, R.A. Transforming regulatory safety evaluations using New Approach Methodologies: A perspective of an industrial toxicologist. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loizou, G.D. Animal-free chemical safety assessment. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pistollato, F.; Madia, F.; Corvi, R.; Munn, S.; Grignard, E.; Paini, A.; Worth, A.; Bal-Price, A.; Prieto, P.; Casati, S.; et al. Current EU Regulatory Requirements for the Assessment of Chemicals and Cosmetic Products: Challenges and Opportunities for introducing New Approach Methodologies; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; ISBN 0123456789. [Google Scholar]
- Viant, M.R.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Beger, R.D.; Ekman, D.R.; Epps, D.J.T.; Kamp, H.; Leonards, P.E.G.; Loizou, G.D.; MacRae, J.I.; van Ravenzwaay, B.; et al. Use cases, best practice and reporting standards for metabolomics in regulatory toxicology. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campos, B.; Colbourne, J.K. How omics technologies can enhance chemical safety regulation: Perspectives from academia, government, and industry. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperber, S.; Wahl, M.; Berger, F.; Kamp, H.; Lemke, O.; Starck, V.; Walk, T.; Spitzer, M.; Ravenzwaay, B.V. Metabolomics as read-across tool: An example with 3-aminopropanol and 2-aminoethanol. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2019, 108, 104442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority); Aguilera, J.; Aguilera-Gomez, M.; Barrucci, F.; Cocconcelli, P.S.; Davies, H.; Denslow, N.; Dorne, J.L.; Grohmann, L.; Herman, L.; et al. EFSA Scientific Colloquium 24—’Omics in Risk Assessment: State of the Art and Next Steps. EFSA Support. Publ. 2018, 15, 1512E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- European Chemicals Agency. New Approach Methodologies in Regulatory Science, Proceedings of the Scientific Workshop: Helsinki, Finland, 19–20 April 2016; European Chemicals Agency: Helsinki, Finland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wishart, D.S. Metabolomics for investigating physiological and pathophysiological processes. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 1819–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ravenzwaay, B.; Sperber, S.; Lemke, O.; Fabian, E.; Faulhammer, F.; Kamp, H.; Mellert, W.; Strauss, V.; Strigun, A.; Peter, E.; et al. Metabolomics as read-across tool: A case study with phenoxy herbicides. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 288–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harrill, J.; Shah, I.; Setzer, R.W.; Haggard, D.; Auerbach, S.; Judson, R.; Thomas, R.S. Considerations for strategic use of high-throughput transcriptomics chemical screening data in regulatory decisions. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 15, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miggiels, P.; Wouters, B.; van Westen, G.J.P.; Dubbelman, A.C.; Hankemeier, T. Novel technologies for metabolomics: More for less. Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, I.; Zhang, P.; Sinha, A.; Skld, C.M.; Wheelock, M.; Izumi, T.; Chaleckis, R.; Wheelock, C.E. High-Precision Automated Workflow for Urinary Untargeted Metabolomic Epidemiology. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 5248–5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.J.; Ivanov, D.P.; Weber, R.J.M.; Wingfield, J.; Viant, M.R. Acoustic Mist Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Ultrahigh-Throughput Metabolomics Screening. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 9258–9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, N.S.; Gavin, A.; Viant, M.R. Metabolomics discovers early-response metabolic biomarkers that can predict chronic reproductive fitness in individual daphnia magna. Metabolites 2018, 8, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Southam, A.D.; Weber, R.J.M.; Engel, J.; Jones, M.R.; Viant, M.R. A complete workflow for high-resolution spectral-stitching nanoelectrospray direct-infusion mass-spectrometry-based metabolomics and lipidomics. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 310–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southam, A.D.; Payne, T.G.; Cooper, H.J.; Arvanitis, T.N.; Viant, M.R. Dynamic range and mass accuracy of wide-scan direct infusion nanoelectrospray fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry-based metabolomics increased by the spectral stitching method. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4595–4602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fuhrer, T.; Heer, D.; Begemann, B.; Zamboni, N. High-throughput, accurate mass metabolome profiling of cellular extracts by flow injection-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7074–7080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, M.; Szappanos, B.; Buchieri, M.V.; Trauner, A.; Piazza, I.; Picotti, P.; Gagneux, S.; Borrell, S.; Gicquel, B.; Lelievre, J.; et al. High-throughput metabolomic analysis predicts mode of action of uncharacterized antimicrobial compounds. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarvin, B.; Lagziel, S.; Sarvin, N.; Mukha, D.; Kumar, P.; Aizenshtein, E.; Shlomi, T. Fast and sensitive flow-injection mass spectrometry metabolomics by analyzing sample-specific ion distributions. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chetwynd, A.J.; David, A. A review of nanoscale LC-ESI for metabolomics and its potential to enhance the metabolome coverage. Talanta 2018, 182, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kempa, E.E.; Hollywood, K.A.; Smith, C.A.; Barran, P.E. High throughput screening of complex biological samples with mass spectrometry-from bulk measurements to single cell analysis. Analyst 2019, 144, 872–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, G.A.; Corso, T.N.; Prosser, S.J.; Zhang, S. A fully integrated monolithic microchip electrospray device for mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 4058–4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Li, H.; Feng, D.; Dou, P.; Shi, X.; Hu, C.; Xu, G. Lipid Profiling of 20 Mammalian Cells by Capillary Microsampling Combined with High-Resolution Spectral Stitching Nanoelectrospray Ionization Direct-Infusion Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 10031–10038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowska, J.M.; Palosaari, T.; Sund, J.; CARPI, D.; Bouhifd, M.; Weber, R.J.M.; Whelan, M.; Viant, M.R. Integrating in vitro metabolomics with a 96-well high-throughput screening platform. Metabolomics 2022, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, H.M.; Ekman, D.R.; Collette, T.W.; Viant, M.R. Spectral relative standard deviation: A practical benchmark in metabolomics. Analyst 2009, 134, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, J.A.; Broadhurst, D.I.; Davidson, R.L.; Viant, M.R. Characterising and correcting batch variation in an automated direct infusion mass spectrometry (DIMS) metabolomics workflow. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5147–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joossens, E.; Macko, P.; Palosaari, T.; Gerloff, K.; Ojea-Jiménez, I.; Gilliland, D.; Novak, J.; Fortaner Torrent, S.; Gineste, J.M.; Römer, I.; et al. A high throughput imaging database of toxicological effects of nanomaterials tested on HepaRG cells. Sci. Data 2019, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, G.; Neubert, T.A. Metabolomic Analysis of Glioma Cells Using Nanoflow Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1741, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, R.J.; Zhou, J. DIMSpy: Python package for processing direct-infusion mass spectrometry-based metabolomics and lipidomics data (Version v2.0.0). Zenodo 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, G.R.; Jankevics, A.; Weber, R.J.M. Struct: An R/Bioconductor-based framework for standardized metabolomics data analysis and beyond. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 5551–5552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sostare, E.; Lawson, T.N.; Saunders, L.R.; Colbourne, J.K.; Weber, R.J.M.; Sobanski, T.; Viant, M.R.V. Knowledge-driven approaches to create the MTox700+ metabolite panel for predicting toxicity. Toxicol. Sci. submitted.
- Dieterle, F.; Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Senn, H. Probabilistic quotient normalization as robust method to account for dilution of complex biological mixtures. Application in1H NMR metabonomics. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
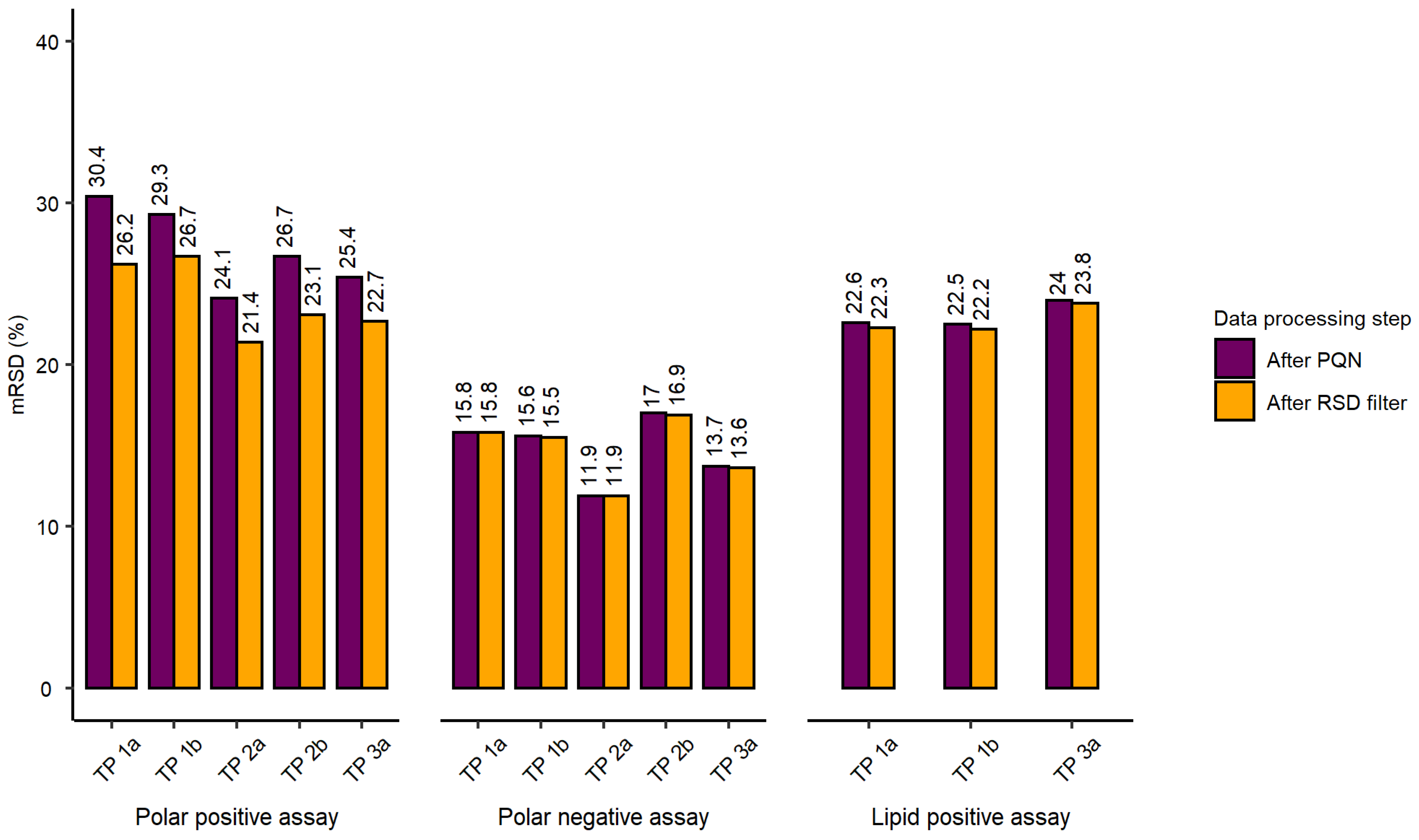

| Dataset after PQN | Dataset after RSD Filter | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assessment | Parameter | P(+) | P(−) | L(+) | P(+) | P(−) | L(+) |
| Analytical sensitivity | Spectral feature count | 3120 | 4862 | 3937 | 2329 | 4782 | 3788 |
| Analytical repeatability | mRSD (%) intrastudy QCs | 20.9 (n = 14) | 7.8 (n = 14) | 13.1 (n = 9) | 17.3 (n = 14) | 7.8 (n = 14) | 12.8 (n = 9) |
| Biological and analytical repeatability | mRSD (%) biological control samples | 31.3 (n = 75) | 19.5 (n = 75) | 24 (n = 47) | 27.6 (n = 75) | 19.3 (n = 75) | 23.6 (n = 47) |
| Assessment | Parameter | Class | P(+) | P(−) | L(+) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Workflow repeatability (excluding cell culture) | RSD (%) of internal standard | Intrastudy QCs | 12.6 (n = 14) | 5.4 (n = 14) | 7.1 (n = 9) |
| Workflow repeatability (excluding cell culture) | RSD (%) of internal standard | Control samples | 19.4 (n = 75) | 16.0 (n = 75) | 14.6 (n = 47) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malinowska, J.M.; Palosaari, T.; Sund, J.; Carpi, D.; Lloyd, G.R.; Weber, R.J.M.; Whelan, M.; Viant, M.R. Automated Sample Preparation and Data Collection Workflow for High-Throughput In Vitro Metabolomics. Metabolites 2022, 12, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010052
Malinowska JM, Palosaari T, Sund J, Carpi D, Lloyd GR, Weber RJM, Whelan M, Viant MR. Automated Sample Preparation and Data Collection Workflow for High-Throughput In Vitro Metabolomics. Metabolites. 2022; 12(1):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010052
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalinowska, Julia M., Taina Palosaari, Jukka Sund, Donatella Carpi, Gavin R. Lloyd, Ralf J. M. Weber, Maurice Whelan, and Mark R. Viant. 2022. "Automated Sample Preparation and Data Collection Workflow for High-Throughput In Vitro Metabolomics" Metabolites 12, no. 1: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010052
APA StyleMalinowska, J. M., Palosaari, T., Sund, J., Carpi, D., Lloyd, G. R., Weber, R. J. M., Whelan, M., & Viant, M. R. (2022). Automated Sample Preparation and Data Collection Workflow for High-Throughput In Vitro Metabolomics. Metabolites, 12(1), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010052