A Checklist for Reproducible Computational Analysis in Clinical Metabolomics Research
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Clinical Metabolomics
1.2. Reproducibility Issue
1.3. The Checklist
1.4. Objective
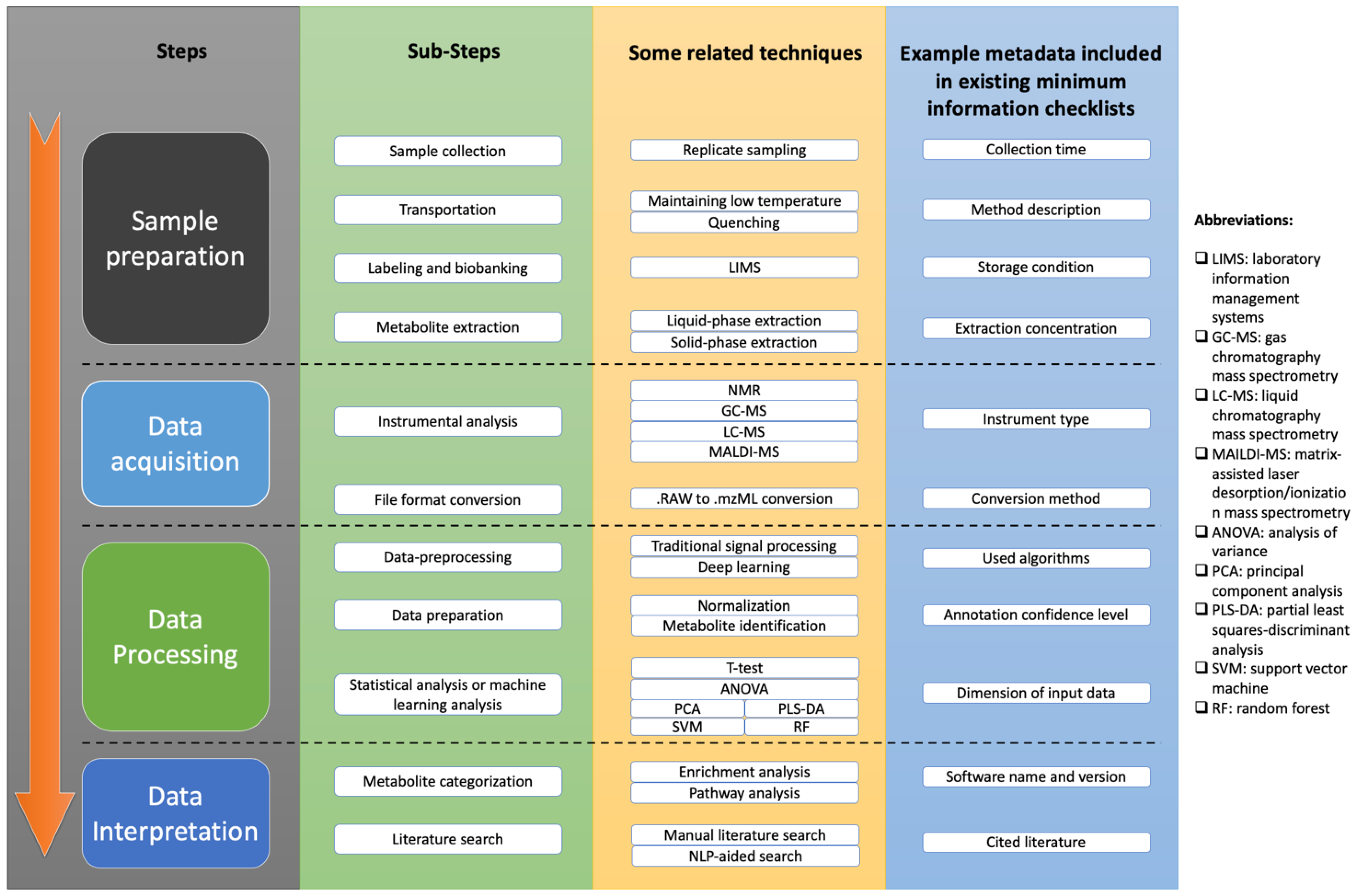
2. Workflow
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.1.1. Overview
2.1.2. Sample Collection
2.1.3. Transportation
2.1.4. Biobanking and Labeling
2.1.5. Metabolite Extraction
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.2.1. Overview
2.2.2. Instrumental Analysis
2.2.3. File Format Conversion
2.3. Data Processing
2.3.1. Overview
2.3.2. Data Preprocessing
2.3.3. Data Preparation
2.3.4. Statistical Analysis or Machine Learning Analysis
2.4. Data Interpretation
2.4.1. Overview
2.4.2. Metabolite Categorization
3. Reusable Data Sharing
3.1. Deposit Data to a Public Metabolomics Data Repository
3.2. Present Metadata Clearly
4. Reproducible Computational Workflow Development
4.1. Share Workflow Information with a Version Control System
4.2. Use Open-Source and Downloadable Software
4.3. Use Virtual Machine or Software Container
4.4. Document Runtime Hardware Information
4.5. Semantic Annotation for Workflow Components
4.6. Use Workflow Automation or Literate Programming
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, D.R.; Patel, R.; Kirsch, D.G.; Lewis, C.A.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Locasale, J.W. Metabolomics in cancer research and emerging applications in clinical oncology. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balashova, E.E.; Maslov, D.L.; Lokhov, P.G. A Metabolomics Approach to Pharmacotherapy Personalization. J. Pers. Med. 2018, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trivedi, D.K.; Hollywood, K.A.; Goodacre, R. Metabolomics for the masses: The future of metabolomics in a personalized world. Eur. J. Mol. Clin. Med. 2017, 3, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Helland, T.; Hagen, K.B.; Haugstøyl, M.E.; Kvaløy, J.T.; Lunde, S.; Lode, K.; Lind, R.A.; Gripsrud, B.H.; Jonsdottir, K.; Gjerde, J.; et al. Drug monitoring of tamoxifen metabolites predicts vaginal dryness and verifies a low discontinuation rate from the Norwegian Prescription Database. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 177, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pevsner, P.H.; Melamed, J.; Remsen, T.; Kogos, A.; Francois, F.; Kessler, P.; Stern, A.; Anand, S. Mass spectrometry MALDI imaging of colon cancer biomarkers: A new diagnostic paradigm. Biomark. Med. 2009, 3, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebholz, C.M.; Yu, B.; Zheng, Z.; Chang, P.; Tin, A.; Köttgen, A.; Wagenknecht, L.E.; Coresh, J.; Boerwinkle, E.; Selvin, E. Serum metabolomic profile of incident diabetes. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, P.; Yin, P.; Hua, R.; Tan, Y.; Li, Z.; Qiu, G.; Yin, Z.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, W.; et al. A Large-scale, multicenter serum metabolite biomarker identification study for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 662–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-W.; Li, Q.-H.; Xu, Z.-D.; Dou, J.-J. Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in health and medical science: A systematic review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 3092–3104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Gorman, A.; Brennan, L. The role of metabolomics in determination of new dietary biomarkers. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2017, 76, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, G.; Haick, H.; Garoli, D. Detecting COVID-19 from Breath: A Game Changer for a Big Challenge. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1408–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, D.D.; Slessarev, M.; Martin, C.M.; Daley, M.; Patel, M.A.; Miller, M.R.; Patterson, E.K.; O’Gorman, D.B.; Gill, S.E.; Wishart, D.S.; et al. Metabolomics Profiling of Critically Ill Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients: Identification of Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarkers. Crit. Care Explor. 2020, 2, e0272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberis, E.; Timo, S.; Amede, E.; Vanella, V.V.; Puricelli, C.; Cappellano, G.; Raineri, D.; Cittone, M.G.; Rizzi, E.; Pedrinelli, A.R.; et al. Large-Scale Plasma Analysis Revealed New Mechanisms and Molecules Associated with the Host Response to SARS-CoV-2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.R.; Suleiman, M.; Pérez-López, A. Metabolomics in the Diagnosis and Prognosis of COVID. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 721556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, P.; Mylonas, R.; Shahaf, N.; Scholz, M.; Arapitsas, P.; Masuero, D.; Weingart, G.; Carlin, S.; Vrhovsek, U.; Mattivi, F.; et al. MetaDB a Data Processing Workflow in Untargeted MS-Based Metabolomics Experiments. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2014, 2, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, M.; Dolios, G.; Petrick, L. Reproducible Untargeted Metabolomics Data Analysis Workflow for Exhaustive MS/MS Annotation. Anal. Chem. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siskos, A.P.; Jain, P.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Bennett, M.; Achaintre, D.; Asad, Y.; Marney, L.; Richardson, L.; Koulman, A.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Interlaboratory Reproducibility of a Targeted Metabolomics Platform for Analysis of Human Serum and Plasma. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tebani, A.; Abily-Donval, L.; Afonso, C.; Marret, S.; Bekri, S. Clinical Metabolomics: The New Metabolic Window for Inborn Errors of Metabolism Investigations in the Post-Genomic Era. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Caldwell, G.W.; Li, Y.; Lang, W.; Masucci, J. Inter-laboratory reproducibility of an untargeted metabolomics GC–MS assay for analysis of human plasma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States; Food and Drug Administration; Office of Combination Products. Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Office of the Commissioner, Office of Combination Products: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; p. 53.
- Shao, J.; Chow, S.-C. Reproducibility probability in clinical trials. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1727–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Advancing Regulatory Science at FDA: Focus Areas of Regulatory Science (FARS); FDA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2021; p. 60. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Olonisakin, T.F.; Pribis, J.P.; Zupetic, J.; Yoon, J.H.; Holleran, K.; Jeong, K.; Shaikh, N.; Rubio, D.M.; Lee, J. A checklist is associated with increased quality of reporting preclinical biomedical research: A systematic review. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hales, B.; Terblanche, M.; Fowler, R.; Sibbald, W. Development of medical checklists for improved quality of patient care. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2007, 20, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaparro, A.; Keebler, J.; Lazzara, E.H.; Diamond, A. Checklists: A Review of Their Origins, Benefits, and Current Uses as a Cognitive Aid in Medicine. Ergon. Des. Q. Hum. Factors Appl. 2019, 27, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendicke, F.; Singh, T.; Lee, J.-H.; Gaudin, R.; Chaurasia, A.; Wiegand, T.; Uribe, S.; Krois, J. Artificial intelligence in dental research: Checklist for authors, reviewers, readers. J. Dent. 2021, 107, 103610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Park, D.S.; Walker, C.; Peterson, A.T.; Merow, C.; Papeş, M. A checklist for maximizing reproducibility of ecological niche models. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 3, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fiehn, O.; Robertson, D.; Griffin, J.; Van Der Werf, M.; Nikolau, B.; Morrison, N.; Sumner, L.W.; Goodacre, R.; Hardy, N.W.; Taylor, C.; et al. The metabolomics standards initiative (MSI). Metabolomics 2007, 3, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salek, R.M.; Steinbeck, C.; Viant, M.R.; Goodacre, R.; Dunn, W.B. The role of reporting standards for metabolite annotation and identification in metabolomic studies. GigaScience 2013, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, L.W.; Amberg, A.; Barrett, D.; Beale, M.H.; Beger, R.; Daykin, C.A.; Fan, T.W.-M.; Fiehn, O.; Goodacre, R.; Griffin, J.L.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goodacre, R.; Broadhurst, D.; Smilde, A.K.; Kristal, B.S.; Baker, J.D.; Beger, R.; Bessant, C.; Connor, S.; Capuani, G.; Craig, A.; et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for data analysis in metabolomics. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, N.; Bearden, D.; Bundy, J.G.; Collette, T.; Currie, F.; Davey, M.P.; Watson-Haigh, N.; Hancock, D.; Jones, O.; Rochfort, S.; et al. Standard reporting requirements for biological samples in metabolomics experiments: Environmental context. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.L.; Nicholls, A.W.; Daykin, C.A.; Heald, S.; Keun, H.C.; Schuppe-Koistinen, I.; Griffiths, J.R.; Cheng, L.L.; Rocca-Serra, P.; Rubtsov, D.V.; et al. Standard reporting requirements for biological samples in metabolomics experiments: Mammalian/in vivo experiments. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Werf, M.J.; Takors, R.; Smedsgaard, J.; Nielsen, J.; Ferenci, T.; Portais, J.C.; Wittmann, C.; Hooks, M.; Tomassini, A.; Oldiges, M.; et al. Standard reporting requirements for biological samples in metabolomics experiments: Microbial and in vitro biology experiments. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiehn, O.; Sumner, L.W.; Rhee, S.Y.; Ward, J.; Dickerson, J.; Lange, B.M.; Lane, G.; Roessner, U.; Last, R.; Nikolau, B. Minimum reporting standards for plant biology context information in metabolomic studies. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rubtsov, D.V.; Jenkins, H.; Ludwig, C.; Easton, J.; Viant, M.R.; Günther, U.; Griffin, J.L.; Hardy, N. Proposed reporting requirements for the description of NMR-based metabolomics experiments. Metabolomics 2007, 3, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, M.; Mias, G.; Stanberry, L.; Kolker, E. Metadata Checklist for the Integrated Personal Omics Study: Proteomics and Metabolomics Experiments. Big Data 2013, 1, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Long, N.P.; Nghi, T.D.; Kang, Y.P.; Anh, N.H.; Kim, H.M.; Park, S.K.; Kwon, S.W. Toward a Standardized Strategy of Clinical Metabolomics for the Advancement of Precision Medicine. Metabolites 2020, 10, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Considine, E.C.; Salek, R.M. A Tool to Encourage Minimum Reporting Guideline Uptake for Data Analysis in Metabolomics. Metabolites 2019, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viant, M.R.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Beger, R.D.; Ekman, D.R.; Epps, D.J.T.; Kamp, H.; Leonards, P.E.G.; Loizou, G.D.; Macrae, J.I.; Van Ravenzwaay, B.; et al. Use cases, best practice and reporting standards for metabolomics in regulatory toxicology. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Considine, E.C.; Thomas, G.; Boulesteix, A.L.; Khashan, A.S.; Kenny, L.C. Critical review of reporting of the data analysis step in metabolomics. Metabolomics 2017, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicer, R.A.; Salek, R.; Steinbeck, C. A decade after the metabolomics standards initiative it’s time for a revision. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, L. The Checklist Manifesto: How to Get Things Right. Lond. J. Prim. Care 2010, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spicer, R.A.; Salek, R.; Steinbeck, C. Compliance with minimum information guidelines in public metabolomics repositories. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heil, B.J.; Hoffman, M.M.; Markowetz, F.; Lee, S.-I.; Greene, C.S.; Hicks, S.C. Reproducibility standards for machine learning in the life sciences. Nat. Methods 2021, 18, 1132–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambiaghi, A.; Ferrario, M.; Masseroli, M. Analysis of metabolomic data: Tools, current strategies and future challenges for omics data integration. Briefings Bioinform. 2016, 18, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nalbantoglu, S. Metabolomics: Basic Principles and Strategies. Mol. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-E.; Kim, Y.-Y. Impact of Preanalytical Variations in Blood-Derived Biospecimens on Omics Studies: Toward Precision Biobanking? OMICS 2017, 21, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirwan, J.A.; Brennan, L.; Broadhurst, D.; Fiehn, O.; Cascante, M.; Dunn, W.B.; Schmidt, M.A.; Velagapudi, V. Preanalytical Processing and Biobanking Procedures of Biological Samples for Metabolomics Research: A White Paper, Community Perspective (for “Precision Medicine and Pharmacometabolomics Task Group”—The Metabolomics Society Initiative). Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1158–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, H.; Guo, Z.; Jia, X.; Liu, H.; Ma, L.; Xue, L. The key points in the pre-analytical procedures of blood and urine samples in metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 2020, 16, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biais, B.; Bernillon, S.; Deborde, C.; Cabasson, C.; Rolin, M.; Tadmor, Y.; Burger, J.; Schaffer, A.A.; Moing, A. Precautions for Harvest, Sampling, Storage, and Transport of Crop Plant Metabolomics Samples. In Advanced Structural Safety Studies; Springer: Singapore, 2011; Volume 860, pp. 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.; Villaret-Cazadamont, J.; Claus, S.P.; Canlet, C.; Guillou, H.; Cabaton, N.J.; Ellero-Simatos, S. Important Considerations for Sample Collection in Metabolomics Studies with a Special Focus on Applications to Liver Functions. Metabolites 2020, 10, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nussbeck, S.Y.; Skrowny, D.; O’Donoghue, S.; Schulze, T.G.; Helbing, K. How to Design Biospecimen Identifiers and Integrate Relevant Functionalities into Your Biospecimen Management System. Biopreservation Biobanking 2014, 12, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cooper, D.R.; Grabowski, M.; Zimmerman, M.D.; Porebski, P.J.; Shabalin, I.G.; Woinska, M.; Domagalski, M.J.; Zheng, H.; Sroka, P.; Cymborowski, M.; et al. State-of-the-Art Data Management: Improving the Reproducibility, Consistency, and Traceability of Structural Biology and in Vitro Biochemical Experiments. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2199, 209–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macneil, R. The benefits of integrated systems for managing both samples and experimental data: An opportunity for labs in universities and government research institutions to lead the way. Autom. Exp. 2011, 3, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rasmussen, L.; Wilhelmsen, M.; Christensen, I.J.; Andersen, J.; Jørgensen, L.N.; Rasmussen, M.; Hendel, J.W.; Madsen, M.R.; Vilandt, J.; Hillig, T.; et al. Protocol Outlines for Parts 1 and 2 of the Prospective Endoscopy III Study for the Early Detection of Colorectal Cancer: Validation of a Concept Based on Blood Biomarkers. JMIR Res. Protoc. 2016, 5, e182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Faraji, M.; Yamini, Y.; Gholami, M. Recent Advances and Trends in Applications of Solid-Phase Extraction Techniques in Food and Environmental Analysis. Chromatographia 2019, 82, 1207–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sana, T.; Fischer, S.; Clara, S. Maximizing Metabolite Extraction for Comprehensive Metabolomics Studies of Erythrocytes. Agil. Technol. 2007, 5989–7407EN. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.-G.; Hu, J.; Wu, X.; Xu, Y.-J. The Recent Developments in Sample Preparation for Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 47, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade-Eiroa, A.; Canle, M.; Leroy-Cancellieri, V.; Cerdà, V. Solid-phase extraction of organic compounds: A critical review (Part I). TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 80, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Lu, D.; Wang, P.; Ying, K.; Chen, E.; Zhang, W. A study of the volatile organic compounds exhaled by lung cancer cells in vitro for breath diagnosis. Cancer 2007, 110, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaceau, J.; Haynes, K.; Chambers, E. A Comprehensive Comparison of Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) vs. Solid Liquid Extraction (SLE) vs. Liquid Liquid Extraction (LLE) Sample Prep Techniques in Bioanalysis and Forensic Toxicology Analyses. Available online: https://www.waters.com/nextgen/xg/en/library/application-notes/2017/solid-phase-extraction-vs-solid-liquid-extraction-vs-liquid-liquid-extraction.html (accessed on 29 November 2021).
- Liu, R.; Chou, J.; Hou, S.; Liu, X.; Yu, J.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Sun, C. Evaluation of two-step liquid-liquid extraction protocol for untargeted metabolic profiling of serum samples to achieve broader metabolome coverage by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1035, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adusumilli, R.; Mallick, P. Data Conversion with ProteoWizard msConvert. In Proteomics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 339–368. [Google Scholar]
- Emwas, A.-H.; Roy, R.; McKay, R.T.; Tenori, L.; Saccenti, E.; Gowda, G.A.N.; Raftery, D.; AlAhmari, F.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M.; et al. NMR Spectroscopy for Metabolomics Research. Metabolites 2019, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urban, P.L. Quantitative mass spectrometry: An overview. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2016, 374, 20150382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cajka, T.; Fiehn, O. Toward Merging Untargeted and Targeted Methods in Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics and Lipidomics. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 524–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S. Computational strategies for metabolite identification in metabolomics. Bioanalysis 2009, 1, 1579–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, D.J.; Pinu, F.R.; Kouremenos, K.A.; Poojary, M.M.; Narayana, V.K.; Boughton, B.A.; Kanojia, K.; Dayalan, S.; Jones, O.A.H.; Dias, D.A. Review of recent developments in GC–MS approaches to metabolomics-based research. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, B.B.; Olivier, M. High Resolution GC-Orbitrap-MS Metabolomics Using Both Electron Ionization and Chemical Ionization for Analysis of Human Plasma. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 2717–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, S.E. An integrated method for spectrum extraction and compound identification from gas chromatography/mass spectrometry data. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1999, 10, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pitt, J.J. Principles and Applications of Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Biochemistry. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2009, 30, 19–34. [Google Scholar]
- Malviya, R.; Bansal, V.; Pal, O.P.; Sharma, P.K. High performance liquid chromatography: A short review. J. Glob. Pharma Technol. 2010, 2, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.F.; Zhou, B.; Ressom, H.W. Metabolite identification and quantitation in LC-MS/MS-based metabolomics. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varghese, R.S.; Zhou, B.; Ranjbar, M.R.N.; Zhao, Y.; Ressom, H.W. Ion annotation-assisted analysis of LC-MS based metabolomic experiment. Proteome Sci. 2012, 10, S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hillenkamp, F.; Karas, M.; Beavis, R.C.; Chait, B.T. Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization Mass Spectrometry of Biopolymers. Anal. Chem. 1991, 63, 1193A–1203A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoegen, B.; Zammit, A.; Gerritsen, A.; Engelke, U.F.H.; Castelein, S.; van de Vorst, M.; Kluijtmans, L.A.J.; Huigen, M.C.D.G.; Wevers, R.A.; van Gool, A.J.; et al. Metabolomics-Based Screening of Inborn Errors of Metabolism: Enhancing Clinical Application with a Robust Computational Pipeline. Metabolites 2021, 11, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Orešič, M. MZmine 2: Modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC Bioinform. 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing Mass Spectrometry Data for Metabolite Profiling Using Nonlinear Peak Alignment, Matching, and Identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Z.Q.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.Y.; de Lima Morais, D.A.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.-É.; Li, S.Z.; Xia, J.G. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röst, H.; Sachsenberg, T.; Aiche, S.; Bielow, C.; Weisser, H.; Aicheler, F.; Andreotti, S.; Ehrlich, H.-C.; Gutenbrunner, P.; Kenar, E.; et al. OpenMS: A flexible open-source software platform for mass spectrometry data analysis. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsugawa, H.; Cajka, T.; Kind, T.; Ma, Y.; Higgins, B.; Ikeda, K.; Kanazawa, M.; VanderGheynst, J.; Fiehn, O.; Arita, M. MS-DIAL: Data-independent MS/MS deconvolution for comprehensive metabolome analysis. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teruya, T.; Chen, Y.-J.; Kondoh, H.; Fukuji, Y.; Yanagida, M. Whole-blood metabolomics of dementia patients reveal classes of disease-linked metabolites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2022857118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altadill, T.; Campoy, I.; Lanau, L.; Gill, K.; Rigau, M.; Gil-Moreno, A.; Reventos, J.; Byers, S.; Colas, E.; Cheema, A.K. Enabling Metabolomics Based Biomarker Discovery Studies Using Molecular Phenotyping of Exosome-Like Vesicles. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Jin, F.; Wang, C.; Zhao, S.; Han, S.; Jiang, P.; Cui, C. Targeted metabolomics analysis of serum amino acid profiles in patients with Moyamoya disease. Amino Acids 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCall, L.-I.; Tripathi, A.; Vargas, F.; Knight, R.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Siqueira-Neto, J.L. Experimental Chagas disease-induced perturbations of the fecal microbiome and metabolome. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klont, F.; Kremer, D.; Neto, A.W.G.; Berger, S.P.; Touw, D.J.; Hak, E.; Bonner, R.; Bakker, S.J.; Hopfgartner, G. Metabolomics data complemented drug use information in epidemiological databases: Pilot study of potential kidney donors. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2021, 135, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzubaidi, L.; Zhang, J.; Humaidi, A.J.; Al-Dujaili, A.; Duan, Y.; Al-Shamma, O.; Santamaría, J.; Fadhel, M.A.; Al-Amidie, M.; Farhan, L. Review of deep learning: Concepts, CNN architectures, challenges, applications, future directions. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantz, E.D.; Tiwari, S.; Watrous, J.D.; Cheng, S.; Jain, M. Deep Neural Networks for Classification of LC-MS Spectral Peaks. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 12407–12413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnikov, A.D.; Tsentalovich, Y.P.; Yanshole, V.V. Deep Learning for the Precise Peak Detection in High-Resolution LC–MS Data. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zohora, F.T.; Rahman, M.Z.; Tran, N.H.; Xin, L.; Shan, B.; Li, M. DeepIso: A Deep Learning Model for Peptide Feature Detection from LC-MS map. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloaguen, Y.; Kirwan, J.; Beule, D. Deep Learning assisted Peak Curation for large scale LC-MS Metabolomic. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, W.B.; Broadhurst, D.; Begley, P.; Zelena, E.; Francis-McIntyre, S.; Anderson, N.; Brown, M.; Knowles, J.D.; Halsall, A.; Haselden, J.N.; et al. Procedures for large-scale metabolic profiling of serum and plasma using gas chromatography and liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1060–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, B.B. Data normalization strategies in metabolomics: Current challenges, approaches, and tools. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 26, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhold, D.; Pielke-Lombardo, H.; Jacobson, S.; Ghosh, D.; Kechris, K. Pre-analytic Considerations for Mass Spectrometry-Based Untargeted Metabolomics Data. High-Throughput Metab. 2019, 1978, 323–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrimpe-Rutledge, A.C.; Codreanu, S.G.; Sherrod, S.D.; McLean, J.A. Untargeted Metabolomics Strategies—Challenges and Emerging Directions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 27, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Walker, D.; Uppal, K.; Liu, Z.; Ma, C.; Tran, V.; Li, S.; Jones, D.P.; Yu, T. Addressing the batch effect issue for LC/MS metabolomics data in data preprocessing. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, J.; Krumsiek, J.; Theis, F.J. Statistical methods for the analysis of high-throughput metabolomics data. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2013, 4, e201301009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Livera, A.M.; Olshansky, M.; Speed, T.P. Statistical Analysis of Metabolomics Data. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2013, 1055, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebal, U.W.; Phan, A.N.T.; Sudhakar, M.; Raman, K.; Blank, L.M. Machine Learning Applications for Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics. Metabolites 2020, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, E.L.-W.; Billings, E.M.; Benton, H.P.; Martin, R.L.; Palermo, A.; Guijas, C.; Rinschen, M.M.; Domingo-Almenara, X.; Montenegro-Burke, J.R.; Tagtow, B.A.; et al. Cognitive analysis of metabolomics data for systems biology. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 1376–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocca-Serra, P.; Salek, R.M.; Arita, M.; Correa, E.; Dayalan, S.; Gonzalez-Beltran, A.; Ebbels, T.; Goodacre, R.; Hastings, J.; Haug, K.; et al. Data standards can boost metabolomics research, and if there is a will, there is a way. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haug, K.; Cochrane, K.; Nainala, V.C.; Williams, M.; Chang, J.; Jayaseelan, K.V.; O’Donovan, C. MetaboLights: A resource evolving in response to the needs of its scientific community. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 48, D440–D444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sud, M.; Fahy, E.; Cotter, D.; Azam, K.; Vadivelu, I.; Burant, C.; Edison, A.; Fiehn, O.; Higashi, R.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Metabolomics Workbench: An international repository for metabolomics data and metadata, metabolite standards, protocols, tutorials and training, and analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D463–D470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neef, S.K.; Janssen, N.; Winter, S.; Wallisch, S.K.; Hofmann, U.; Dahlke, M.H.; Schwab, M.; Mürdter, T.E.; Haag, M. Metabolic Drug Response Phenotyping in Colorectal Cancer Organoids by LC-QTOF-MS. Metabolites 2020, 10, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Chen, W.; Miao, M.; Jin, Q.; Zhang, S.; Bai, M.; Fan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Jia, Z.; et al. Anti-anemia drug FG4592 retards the AKI-to-CKD transition by improving vascular regeneration and antioxidative capability. Clin. Sci. 2021, 135, 1707–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getting the Facts Right|UNECE. Available online: https://unece.org/getting-facts-right (accessed on 8 November 2021).
- STAR Methods: Cell Press. Available online: https://www.cell.com/star-methods (accessed on 9 November 2021).
- Pavlovich, M.J.; Buttery, S. How peer review and publication can make a good protocol even better. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Sullivan, N.L.; Rouphael, N.; Yu, T.; Banton, S.; Maddur, M.S.; McCausland, M.; Chiu, C.; Canniff, J.; Dubey, S.; et al. Metabolic Phenotypes of Response to Vaccination in Humans. Cell 2017, 169, 862–877.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, F.; Song, C.; Liu, W.; Chen, G. Protocol for intracellular and extracellular metabolite detection in human embryonic stem cells. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.; Ren, Z.; Xu, F.; Zhou, X.; Song, C.; Wang, V.Y.-F.; Liu, W.; Lu, L.; Thomson, J.A.; Chen, G. Nicotinamide Promotes Cell Survival and Differentiation as Kinase Inhibitor in Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, C.; Xu, F.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lingadahalli, S.; Cheung, E.; Li, G.; Liu, W.; et al. Elevated Exogenous Pyruvate Potentiates Mesodermal Differentiation through Metabolic Modulation and AMPK/mTOR Pathway in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2019, 13, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Ren, Z.; Xu, F.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ai, N.; Long, Y.; Fok, H.I.; Deng, C.; Zhao, X.; et al. Endogenous IGF Signaling Directs Heterogeneous Mesoderm Differentiation in Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 3374–3384.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blischak, J.D.; Davenport, E.R.; Wilson, G. A Quick Introduction to Version Control with Git and GitHub. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alvarez-Mulett, S.; Buyukozkan, M.; Racanelli, A.C.; Schmidt, F.; Batra, R.; Hoffman, K.L.; Sarwath, H.; Engelke, R.; Gomez-Escobar, L.; Simmons, W. Integrative Metabolomic and Proteomic Signatures Define Clinical Outcomes in Severe COVID-19. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nederbragt, A.J. On the middle ground between open source and commercial software—The case of the Newbler program. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ince, D.C.; Hatton, L.; Graham-Cumming, J. The case for open computer programs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 482, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schloss, P.D. Identifying and Overcoming Threats to Reproducibility, Replicability, Robustness, and Generalizability in Microbiome Research. mBio 2018, 9, 00525-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Tommaso, P.; Chatzou, M.; Floden, E.W.; Barja, P.P.; Palumbo, E.; Notredame, C. Nextflow enables reproducible computational workflows. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiebels, K.; Moreau, D. Leveraging Containers for Reproducible Psychological Research. Adv. Methods Pract. Psychol. Sci. 2021, 4, 25152459211017852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viereck, M. x11docker: Run GUI applications in Docker containers. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, L.-H.; Kristiyanto, D.; Lee, S.B.; Yeung, K.Y. GUIdock: Using Docker Containers with a Common Graphics User Interface to Address the Reproducibility of Research. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senington, R.; Pataki, B.; Wang, X.V. Using docker for factory system software management: Experience report. Procedia CIRP 2018, 72, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, D. Docker: Lightweight Linux containers for consistent development and deployment. Linux J. 2014, 239, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzer, G.M.; Sochat, V.; Bauer, M.W. Singularity: Scientific containers for mobility of compute. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango, C.; Dernat, R.; Sanabria, J. Performance evaluation of container-based virtualization for high performance computing environments. Revista UIS Ingenierías 2019, 18, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Documentation—Oracle VM VirtualBox. Available online: https://www.virtualbox.org/wiki/Documentation (accessed on 21 October 2021).
- Lamprecht, A.-L.; Palmblad, M.; Ison, J.; Schwämmle, V.; Al Manir, M.S.; Altintas, I.; Baker, C.J.O.; Amor, A.B.H.; Capella-Gutierrez, S.; Charonyktakis, P.; et al. Perspectives on automated composition of workflows in the life sciences. F1000Research 2021, 10, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belhajjame, K.; Zhao, J.; Garijo, D.; Gamble, M.; Hettne, K.; Palma, R.; Mina, E.; Corcho, O.; Gómez-Pérez, J.M.; Bechhofer, S.; et al. Using a suite of ontologies for preserving workflow-centric research objects. J. Web Semant. 2015, 32, 16–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmblad, M.; Lamprecht, A.-L.; Ison, J.; Schwämmle, V. Automated workflow composition in mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Bioinform. 2019, 35, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil, Y.; Ratnakar, V.; Garijo, D. OntoSoft. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Knowledge Capture, Palisades, NY, USA, 7–10 October 2015; p. 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.A.M.C.; Garijo, D.; Medeiros, C.B.; Gil, Y. Semantic Software Metadata for Workflow Exploration and Evolution. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 14th International Conference on e-Science (e-Science), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 October–1 November 2018; pp. 431–441. [Google Scholar]
- Garijo, D.; Osorio, M.; Khider, D.; Ratnakar, V.; Gil, Y. OKG-Soft: An Open Knowledge Graph with Machine Readable Scientific Software Metadata. In Proceedings of the 2019 15th International Conference on eScience (eScience), San Diego, CA, USA, 24–27 September 2019; pp. 349–358. [Google Scholar]
- Ison, J.; Kalaš, M.; Jonassen, I.; Bolser, D.; Uludag, M.; McWilliam, H.; Malone, J.R.; López, R.; Pettifer, S.; Rice, P. EDAM: An ontology of bioinformatics operations, types of data and identifiers, topics and formats. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 1325–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malone, J.; Brown, A.; Lister, A.L.; Ison, J.; Hull, D.; Parkinson, H.; Stevens, R. The Software Ontology (SWO): A resource for reproducibility in biomedical data analysis, curation and digital preservation. J. Biomed. Semant. 2014, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Santana-Perez, I.; Hernandez, M.D.L.S.P. Towards Reproducibility in Scientific Workflows: An Infrastructure-Based Approach. Sci. Program. 2015, 2015, 243180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, J.; Martín-Requena, V.; Ríos, J.; Trelles, O. Workflow Composition and Enactment Using jORCA. In Leveraging Applications of Formal Methods, Verification, and Validation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 328–339. [Google Scholar]
- Lamprecht, A.-L.; Naujokat, S.; Margaria, T.; Steffen, B. Synthesis-Based Loose Programming. In Proceedings of the 2010 Seventh International Conference on the Quality of Information and Communications Technology, Faro, Portugal, 29 September–2 October 2010; pp. 262–267. [Google Scholar]
- Naujokat, S.; Lamprecht, A.-L.; Steffen, B. Loose Programming with PROPHETS. In Fundamental Approaches to Software Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 94–98. [Google Scholar]
- Gil, Y.; Ratnakar, V.; Kim, J.; Gonzalez-Calero, P.A.; Groth, P.; Moody, J.; Deelman, E. Wings: Intelligent Workflow-Based Design of Computational Experiments. IEEE Intell. Syst. 2010, 26, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasalica, V.; Lamprecht, A.-L. APE: A Command-Line Tool and API for Automated Workflow Composition. In Security and Trust Management; Springer Science and Business Media LLC: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 464–476. [Google Scholar]
- Goble, C.A.; Bhagat, J.; Aleksejevs, S.; Cruickshank, D.; Michaelides, D.; Newman, D.; Borkum, M.; Bechhofer, S.; Roos, M.; Li, P.; et al. myExperiment: A repository and social network for the sharing of bioinformatics workflows. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W677–W682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, J.; Gomez-Perez, J.M.; Belhajjame, K.; Klyne, G.; Garcia-Cuesta, E.; Garrido, A.; Hettne, K.; Roos, M.; De Roure, D.; Goble, C. Why workflows break Understanding and combating decay in Taverna workflows. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 8th International Conference on E-Science, Chicago, IL, USA, 8–12 October 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kasalica, V.; Schwämmle, V.; Palmblad, M.; Ison, J.; Lamprecht, A.-L. APE in the Wild: Automated Exploration of Proteomics Workflows in the bio.tools Registry. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 2157–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasalica, V.; Lamprecht, A.-L. Automated composition of scientific workflows: A case study on geographic data manipulation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 14th International Conference on e-Science (e-Science), Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 29 October–1 November 2018; pp. 362–363. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.L.; Ratnakar, V.; Gil, Y.; McWeeney, S.K. Use of semantic workflows to enhance transparency and reproducibility in clinical omics. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piccolo, S.R.; Frampton, M.B. Tools and techniques for computational reproducibility. GigaScience 2016, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kluyver, T.; Ragan-Kelley, B.; Pérez, F.; Granger, B.; Bussonnier, M.; Frederic, J.; Kelley, K.; Hamrick, J.; Grout, J.; Corlay, S.; et al. Jupyter Notebooks—A Publishing Format for Reproducible Computational Workflows; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 87–90. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y. knitr: A Comprehensive Tool for Reproducible Research in R. In Implementing Reproducible Research; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 3–31. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y. knitr. Available online: https://yihui.org/knitr/ (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L. Python 3 Reference Manual; CreateSpace: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Bash–GNU Project–Free Software Foundation. Available online: https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/ (accessed on 20 October 2021).
- Afgan, E.; Baker, D.; Batut, B.; van den Beek, M.; Bouvier, D.; Čech, M.; Chilton, J.; Clements, D.; Coraor, N.; Grüning, B.A.; et al. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2018 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W537–W544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulmer, C.Z.; Maus, A.; Hines, J.; Singh, R. Challenges in Translating Clinical Metabolomics Data Sets from the Bench to the Bedside. Clin. Chem. 2021, 67, 1581–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ontology Name | Owl File |
|---|---|
| Research Object Ontology | http://purl.org/wf4ever/ro#, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
| Workflow Description Ontology | http://purl.org/wf4ever/wfdesc#, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
| Workflow Provenance Ontology | http://purl.org/wf4ever/wfprov#, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
| Research Object Evolution Ontology | http://purl.org/wf4ever/roevo#, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
| OntoSoft Ontology | http://ontosoft-earthcube.github.io/ontosoft/ontosoft%20ontology/v1.0.1/doc/ontosoft-v1.0.1.owl, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
| Software Description Ontology | https://w3id.org/okn/o/sd, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
| DOAP Ontology | http://usefulinc.com/ns/doap, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
| EDAM Ontology | http://edamontology.org/EDAM.owl, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
| Software Ontology | http://www.ebi.ac.uk/swo/swo.owl, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
| WICUS Ontology | http://vocab.linkeddata.es/wicus/hwspecs/hwspecs.owl, accessed on 29 November 2021 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, X.; Aristizabal-Henao, J.J.; Garrett, T.J.; Brochhausen, M.; Hogan, W.R.; Lemas, D.J. A Checklist for Reproducible Computational Analysis in Clinical Metabolomics Research. Metabolites 2022, 12, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010087
Du X, Aristizabal-Henao JJ, Garrett TJ, Brochhausen M, Hogan WR, Lemas DJ. A Checklist for Reproducible Computational Analysis in Clinical Metabolomics Research. Metabolites. 2022; 12(1):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010087
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Xinsong, Juan J. Aristizabal-Henao, Timothy J. Garrett, Mathias Brochhausen, William R. Hogan, and Dominick J. Lemas. 2022. "A Checklist for Reproducible Computational Analysis in Clinical Metabolomics Research" Metabolites 12, no. 1: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010087
APA StyleDu, X., Aristizabal-Henao, J. J., Garrett, T. J., Brochhausen, M., Hogan, W. R., & Lemas, D. J. (2022). A Checklist for Reproducible Computational Analysis in Clinical Metabolomics Research. Metabolites, 12(1), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12010087









