Metabolome-Wide Associations of Gestational Weight Gain in Pregnant Women with Overweight and Obesity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
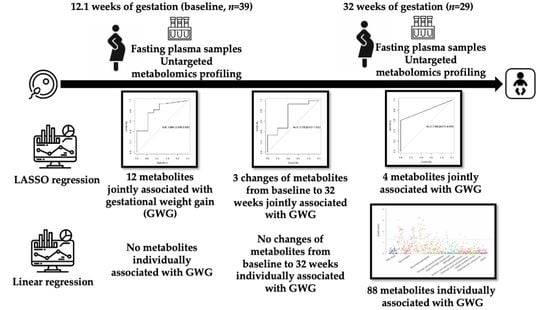
3.2. Associations of Metabolites with GWG
3.3. Correlations between Metabolites and Cardiometabolic Biomarkers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldstein, R.F.; Abell, S.K.; Ranasinha, S.; Misso, M.; Boyle, J.A.; Black, M.H.; Li, N.; Hu, G.; Corrado, F.; Rode, L.; et al. Association of Gestational Weight Gain With Maternal and Infant Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA 2017, 317, 2207–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine; National Research Council Committee to Reexamine IOM Pregnancy Weight Guidelines. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health. In Weight Gain During Pregnancy: Reexamining the Guidelines; Rasmussen, K.M., Yaktine, A.L., Eds.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Deputy, N.P.; Sharma, A.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Hinkle, S.N. Prevalence and characteristics associated with gestational weight gain adequacy. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 125, 773–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.L.; Farr, S.L.; Dietz, P.M.; Sharma, A.J.; Barfield, W.D.; Robbins, C.L. Trends in gestational weight gain: The Pregnancy Risk Assessment Monitoring System, 2000–2009. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 806.e1–806.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stuebe, A.M.; Oken, E.; Gillman, M.W. Associations of diet and physical activity during pregnancy with risk for excessive gestational weight gain. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2009, 201, 58.e1–58.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Francis, E.C.; Zhang, L.; Witrick, B.; Chen, L. Health behaviors of American pregnant women: A cross-sectional analysis of NHANES 2007–2014. J. Public Health 2021, 43, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma-Pillay, P.; Nelson-Piercy, C.; Tolppanen, H.; Mebazaa, A. Physiological changes in pregnancy. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2016, 27, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zampieri, M.; Sekar, K.; Zamboni, N.; Sauer, U. Frontiers of high-throughput metabolomics. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2017, 36, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadeau-Hyam, M.; Ebbels, T.M.; Brown, I.J.; Chan, Q.; Stamler, J.; Huang, C.C.; Daviglus, M.L.; Ueshima, H.; Zhao, L.; Holmes, E.; et al. Metabolic profiling and the metabolome-wide association study: Significance level for biomarker identification. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4620–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangel-Huerta, O.D.; Pastor-Villaescusa, B.; Gil, A. Are we close to defining a metabolomic signature of human obesity? A systematic review of metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shearer, J.; Klein, M.S.; Vogel, H.J.; Mohammad, S.; Bainbridge, S.; Adamo, K.B. Maternal and Cord Blood Metabolite Associations with Gestational Weight Gain and Pregnancy Health Outcomes. J. Proteome Res. 2021, 20, 1630–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelman, S.K.; Romero, R.; Tarca, A.L.; Pacora, P.; Ingram, B.; Maymon, E.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Hassan, S.S.; Erez, O. The plasma metabolome of women in early pregnancy differs from that of non-pregnant women. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delplancke, T.D.; De Seymour, J.V.; Tong, C.; Sulek, K.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Han, T.-L.; Baker, P.N. Analysis of sequential hair segments reflects changes in the metabolome across the trimesters of pregnancy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilcox, S.; Liu, J.; Addy, C.L.; Turner-McGrievy, G.; Burgis, J.T.; Wingard, E.; Dahl, A.A.; Whitaker, K.M.; Schneider, L.; Boutté, A.K. A randomized controlled trial to prevent excessive gestational weight gain and promote postpartum weight loss in overweight and obese women: Health In Pregnancy and Postpartum (HIPP). Contemp. Clin. Trials 2018, 66, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wilcox, S.; Wingard, E.; Turner-McGrievy, G.; Hutto, B.; Burgis, J. A Behavioral Lifestyle Intervention to Limit Gestational Weight Gain in Pregnant Women with Overweight and Obesity. Obesity 2021, 29, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djoumbou Feunang, Y.; Eisner, R.; Knox, C.; Chepelev, L.; Hastings, J.; Owen, G.; Fahy, E.; Steinbeck, C.; Subramanian, S.; Bolton, E.; et al. ClassyFire: Automated chemical classification with a comprehensive, computable taxonomy. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonelli, J.; Claggett, B.L.; Henglin, M.; Kim, A.; Ovsak, G.; Kim, N.; Deng, K.; Rao, K.; Tyagi, O.; Watrous, J.D.; et al. Statistical Workflow for Feature Selection in Human Metabolomics Data. Metabolites 2019, 9, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Subar, A.F.; Douglass, D.; Zimmerman, T.P.; Thompson, F.E.; Kahle, L.L.; George, S.M.; Dodd, K.W.; Potischman, N. Performance of the Automated Self-Administered 24-hour Recall relative to a measure of true intakes and to an interviewer-administered 24-h recall. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Pannucci, T.E.; Subar, A.F.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Lerman, J.L.; Tooze, J.A.; Wilson, M.M.; Reedy, J. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, K.M.; Lanningham-Foster, L.M.; Welk, G.J.; Campbell, C.G. Validity of the SenseWear® Armband to predict energy expenditure in pregnant women. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 2001–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmuth, C.; Lindsay, K.L.; Uhl, O.; Buss, C.; Wadhwa, P.D.; Koletzko, B.; Entringer, S. Association of maternal prepregnancy BMI with metabolomic profile across gestation. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, C.E.; Taylor-Bateman, V.; Vorkas, P.A.; Graça, G.; Vu, T.T.; Hou, L.; Chekmeneva, E.; Ebbels, T.M.D.; Chan, Q.; Van Horn, L.; et al. Metabolic Signatures of Gestational Weight Gain and Postpartum Weight Loss in a Lifestyle Intervention Study of Overweight and Obese Women. Metabolites 2020, 10, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Zanetti, K.A.; Temprosa, M.; Albanes, D.; Appel, N.; Barrera, C.B.; Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Boerwinkle, E.; Casas, J.P.; Clish, C.; et al. The Consortium of Metabolomics Studies (COMETS): Metabolomics in 47 Prospective Cohort Studies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 991–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Decsi, T.; Molnár, D.; Koletzko, B. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in plasma lipids of obese children. Lipids 1996, 31, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco-Ramell, A.; Tulipani, S.; Palau-Rodriguez, M.; Gonzalez-Dominguez, R.; Miñarro, A.; Jauregui, O.; Sanchez-Pla, A.; Macias-Gonzalez, M.; Cardona, F.; Tinahones, F.J.; et al. Untargeted Profiling of Concordant/Discordant Phenotypes of High Insulin Resistance and Obesity To Predict the Risk of Developing Diabetes. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2307–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietiläinen, K.H.; Sysi-Aho, M.; Rissanen, A.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Kaprio, J.; Oresic, M. Acquired obesity is associated with changes in the serum lipidomic profile independent of genetic effects—A monozygotic twin study. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papandreou, C.; García-Gavilán, J.; Camacho-Barcia, L.; Toft Hansen, T.; Harrold, J.A.; Sjödin, A.; Halford, J.C.; Bulló, M. Changes in Circulating Metabolites During Weight Loss are Associated with Adiposity Improvement, and Body Weight and Adiposity Regain during Weight Loss Maintenance: The SATIN Study. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2021, 65, 2001154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Aitken, D.; Nevitt, M.C.; Rockel, J.S.; Pelletier, J.-P.; Lewis, C.E.; Torner, J.; Rampersaud, Y.R.; et al. Restricting Branched-Chain Amino Acids within a High-Fat Diet Prevents Obesity. Metabolites 2022, 12, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, V.S.; Hafez, E.A.A. Synopsis of arachidonic acid metabolism: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 11, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickens, C.A.; Sordillo, L.M.; Zhang, C.; Fenton, J.I. Obesity is positively associated with arachidonic acid-derived 5- and 11-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (HETE). Metabolism 2017, 70, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gault, C.R.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A. An overview of sphingolipid metabolism: From synthesis to breakdown. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2010, 688, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cavus, E.; Karakas, M.; Ojeda, F.M.; Kontto, J.; Veronesi, G.; Ferrario, M.M.; Linneberg, A.; Jørgensen, T.; Meisinger, C.; Thorand, B.; et al. Association of Circulating Metabolites With Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in a European Population: Results from the Biomarkers for Cardiovascular Risk Assessment in Europe (BiomarCaRE) Consortium. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klop, B.; Elte, J.W.; Cabezas, M.C. Dyslipidemia in obesity: Mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1218–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, M.T.; Yudell, B.E.; Loor, J.J. Regulation of energy metabolism by long-chain fatty acids. Prog. Lipid Res. 2014, 53, 124–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Semiz, S.; van der Lee, S.J.; van der Spek, A.; Verhoeven, A.; van Klinken, J.B.; Sijbrands, E.; Harms, A.C.; Hankemeier, T.; van Dijk, K.W.; et al. Metabolomics based markers predict type 2 diabetes in a 14-year follow-up study. Metabolomics 2017, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vorkas, P.A.; Isaac, G.; Holmgren, A.; Want, E.J.; Shockcor, J.P.; Holmes, E.; Henein, M.Y. Perturbations in fatty acid metabolism and apoptosis are manifested in calcific coronary artery disease: An exploratory lipidomic study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 197, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.N.; Boca, S.M.; Shu, X.O.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Matthews, C.E.; Hsing, A.W.; Tan, Y.T.; Ji, B.T.; Chow, W.H.; Cai, Q.; et al. Metabolomics in epidemiology: Sources of variability in metabolite measurements and implications. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masood, S.N.; Lakho, N.; Saeed, S.; Masood, Y. Non-fasting OGTT versus Fasting OGTT for screening of Hyperglycaemia in Pregnancy (HIP). Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 1008–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creanga, A.A.; Catalano, P.M.; Bateman, B.T. Obesity in Pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristics 1 | n = 39 |
|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | |
| Gestational age at baseline (week, mean (SD)) | 12.09 (2.26) |
| Age (year, mean (SD)) | 30.41 (5.41) |
| Prepregnancy BMI (kg/m2, mean (SD)) | 33.25 (7.04) |
| Obese (%) | 22 (56.4) |
| Nulliparous (%) | 14 (35.9) |
| Black (%) | 15 (38.5) |
| Married (%) | 26 (66.7) |
| Full time employed (%) | 23 (59.0) |
| Medicaid use (%) | 12 (30.8) |
| Physical activity at baseline (mean (SD)) 2 | |
| Moderate physical activity (min/day) | 40.35 (21.99) |
| Vigorous physical activity (min/day) | 0.33 (0.87) |
| Moderate to vigorous physical activity (min/day) | 40.88 (23.00) |
| Steps per day | 5727.62 (2427.90) |
| Dietary intake at baseline (mean (SD)) | |
| Total energy (kcal/day) | 1869.05 (560.79) |
| Total protein (g/day) | 73.04 (22.46) |
| Total fatty acids (g/day) | 75.31 (26.25) |
| Saturated fatty acids (g/day) | 24.53 (10.60) |
| Monounsaturated fatty acids (g/day) | 26.33 (8.98) |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids (g/day) | 18.41 (7.95) |
| Cholesterol (mg/day) | 269.94 (150.32) |
| Total HEI—2015 score 3 | 52.98 (14.31) |
| Maternal pregnancy complications | |
| Gestational diabetes (%) | 3 (7.7) |
| Gestational hypertension (%) | 8 (20.5) |
| Offspring conditions | |
| Girl (%) | 19 (48) |
| Low birth weight (%) 4 | 2 (5.1) |
| Preterm birth (%)4 | 1 (2.6) |
| Small for gestational age (%) 4 | 4 (10.3) |
| Large for gestational age (%) 4 | 4 (10.3) |
| 12 Weeks of Gestation | 32 Weeks of Gestation | Changes from 12 to 32 Weeks of Gestation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolite | Class | Direction | Metabolite | Class | Direction | Metabolite | Class | Direction |
| PC (40:6) A | Glycerophospholipids | Positive | PC (34:4) | Glycerophospholipids | Positive | PC (40:7) A | Phosphatidylcholine | Negative |
| TAG (43:0) or TAG (13:0-14:0-16:0) | Glycerolipids | Positive | TAG (52:6) | Glycerolipids | Positive | TAG (60:4) | Glycerolipids | Negative |
| SM (d30:1) | Sphingolipids | Positive | Arachidonic acid | Omega-6 PUFA | Positive | Adenosine | Purine nucleosides | Positive |
| SM (d32:0) | Sphingolipids | Positive | Isoleucine | Amino acid | Positive | |||
| PE (p-38:2) or PE (o-38:3) | Glycerophospholipids | Positive | ||||||
| 3-Hydroxybutyrylcarnitine | Fatty Acyls | Negative | ||||||
| Methyltestosterone | Steroids and steroid derivatives | Positive | ||||||
| Aconitic acid | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | Negative | ||||||
| 1-methylgalactose | Organooxygen compounds | Positive | ||||||
| Trans-3’-Hydroxycotinine | Pyridines and derivatives | Positive | ||||||
| Trigonelline | Alkaloids | Negative | ||||||
| Adipic acid | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | Positive | ||||||
| Insulin | C-Peptide | Hs-CRP | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolite 1 | Superclass | Class | β | P | FDR | β | P | FDR | β | P | FDR |
| Arachidonic acid | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Fatty Acyls | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.70 | −0.08 | 0.68 | 0.84 | −0.12 | 0.52 | 0.88 |
| TAG 45:0 or TAG 14:0-15:0-16:0 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.15 | 0.44 | 0.68 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.50 | −0.12 | 0.54 | 0.88 |
| TAG 45:1 or TAG 12:0-16:0-17:1 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.15 | 0.43 | 0.68 | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.50 | −0.11 | 0.57 | 0.88 |
| TAG 46:2 or TAG 12:0-16:1-18:1 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.68 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.50 | −0.30 | 0.11 | 0.88 |
| TAG 47:1 or TAG 15:0-16:0-16:1 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.10 | 0.59 | 0.78 | 0.23 | 0.24 | 0.49 | 0.00 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| TAG 47:2 or TAG 14:0-15:0-18:2 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.71 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.47 | −0.13 | 0.50 | 0.88 |
| TAG 48:3 or TAG 14:0-16:1-18:2 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.17 | 0.39 | 0.68 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.47 | −0.29 | 0.13 | 0.88 |
| TAG 49:3 or TAG 15:0-16:1-18:2 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.09 | 0.65 | 0.82 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.45 | −0.02 | 0.91 | 0.94 |
| TAG 50:5 or TAG 14:1-18:2-18:2 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.68 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.31 | −0.35 | 0.06 | 0.88 |
| TAG 52:4 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.41 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.31 | −0.07 | 0.70 | 0.88 |
| TAG 52:6 or TAG 14:0-18:2-20:4 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.38 | 0.04 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 0.31 | −0.23 | 0.23 | 0.88 |
| TAG 58:7 or TAG 18:0-18:2-22:5 | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.38 | 0.04 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.31 | −0.21 | 0.28 | 0.88 |
| TAG (40:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.68 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.39 | −0.08 | 0.69 | 0.88 |
| TAG (44:0) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.50 | −0.21 | 0.27 | 0.88 |
| TAG (44:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.71 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.57 | −0.18 | 0.34 | 0.88 |
| TAG (44:2) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.38 | 0.61 | −0.33 | 0.08 | 0.88 |
| TAG (46:0) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.17 | 0.39 | 0.68 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.50 | −0.19 | 0.33 | 0.88 |
| TAG (46:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.68 | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.50 | −0.17 | 0.38 | 0.88 |
| TAG (46:3) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.68 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.45 | −0.30 | 0.11 | 0.88 |
| TAG (48:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.68 | 0.31 | 0.11 | 0.39 | −0.09 | 0.65 | 0.88 |
| TAG (48:2) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.68 | 0.31 | 0.10 | 0.39 | −0.17 | 0.38 | 0.88 |
| TAG (48:3) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.42 | 0.02 | 0.37 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.31 | −0.18 | 0.34 | 0.88 |
| TAG (48:4) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.31 | −0.26 | 0.18 | 0.88 |
| TAG (48:5) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.41 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.41 | 0.03 | 0.31 | −0.18 | 0.34 | 0.88 |
| TAG (49:2) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.08 | 0.67 | 0.83 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.45 | 0.08 | 0.68 | 0.88 |
| TAG (49:3) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.11 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 0.03 | 0.89 | 0.94 |
| TAG (50:2) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.68 | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.31 | −0.02 | 0.90 | 0.94 |
| TAG (50:3) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.22 | 0.25 | 0.68 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.31 | −0.10 | 0.59 | 0.88 |
| TAG (50:5) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.39 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.31 | −0.19 | 0.31 | 0.88 |
| TAG (52:5) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.16 | 0.42 | 0.68 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.46 | −0.05 | 0.80 | 0.89 |
| TAG (52:6) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.39 | −0.17 | 0.37 | 0.88 |
| TAG (53:5) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.68 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.39 | 0.07 | 0.72 | 0.88 |
| TAG (54:5) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.47 | 0.01 | 0.31 | −0.07 | 0.74 | 0.88 |
| TAG (54:6) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.47 | 0.01 | 0.37 | 0.45 | 0.01 | 0.31 | −0.21 | 0.28 | 0.88 |
| TAG (54:7) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.40 | 0.03 | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.05 | 0.31 | −0.32 | 0.09 | 0.88 |
| TAG (54:7) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.05 | 0.31 | −0.18 | 0.34 | 0.88 |
| TAG (54:8) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.68 | 0.30 | 0.11 | 0.39 | −0.28 | 0.15 | 0.88 |
| TAG (56:9) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.21 | 0.27 | 0.68 | 0.34 | 0.07 | 0.35 | −0.19 | 0.32 | 0.88 |
| TAG (58:9) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerolipids | 0.22 | 0.26 | 0.68 | 0.20 | 0.30 | 0.53 | −0.08 | 0.67 | 0.88 |
| LPC (14:0) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.02 | 0.90 | 0.94 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.62 | −0.15 | 0.45 | 0.88 |
| LPC (16:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.09 | 0.65 | 0.82 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 0.88 |
| LPC (20:3) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.68 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.44 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 0.88 |
| LPC (14:0) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.15 | 0.43 | 0.68 | 0.27 | 0.16 | 0.45 | −0.25 | 0.19 | 0.88 |
| LPC (16:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.19 | 0.32 | 0.68 | 0.36 | 0.06 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 0.76 | 0.88 |
| LPC (20:3) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.68 | 0.35 | 0.06 | 0.31 | 0.06 | 0.76 | 0.88 |
| LPC (22:5) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.01 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.07 | 0.72 | 0.84 | 0.28 | 0.14 | 0.88 |
| PC (32:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.03 | 0.86 | 0.91 | 0.14 | 0.48 | 0.72 | 0.07 | 0.71 | 0.88 |
| PC (32:2) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.04 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 0.95 | −0.27 | 0.15 | 0.88 |
| PC (33:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.28 | 0.15 | 0.68 | −0.07 | 0.71 | 0.84 | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.88 |
| PC (34:3) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.15 | 0.43 | 0.68 | 0.23 | 0.22 | 0.47 | −0.04 | 0.82 | 0.89 |
| PC (34:4) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.01 | 0.97 | 0.97 | 0.07 | 0.70 | 0.84 | −0.17 | 0.37 | 0.88 |
| PC (36:3) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.10 | 0.61 | 0.79 | 0.26 | 0.17 | 0.45 | 0.05 | 0.82 | 0.89 |
| PC (36:5) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.20 | 0.30 | 0.68 | −0.04 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 0.53 | 0.88 |
| PC (40:6) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.01 | 0.96 | 0.97 | −0.02 | 0.91 | 0.95 | −0.04 | 0.83 | 0.89 |
| PC (28:0) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.05 | 0.79 | 0.91 | 0.02 | 0.93 | 0.95 | −0.19 | 0.33 | 0.88 |
| PC (30:0) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.04 | 0.84 | 0.91 | 0.11 | 0.59 | 0.77 | −0.10 | 0.61 | 0.88 |
| PC (31:0) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.22 | 0.26 | 0.68 | −0.04 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 0.15 | 0.44 | 0.88 |
| PC (31:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.11 | 0.58 | 0.78 | 0.06 | 0.77 | 0.88 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.88 |
| PC (32:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.05 | 0.78 | 0.91 | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 0.64 | 0.88 |
| PC (32:2) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.04 | 0.82 | 0.91 | 0.04 | 0.84 | 0.91 | −0.25 | 0.19 | 0.88 |
| PC (33:0) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.19 | 0.31 | 0.68 | −0.01 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.88 |
| PC (33:1) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.14 | 0.47 | 0.70 | 0.06 | 0.75 | 0.87 | 0.19 | 0.33 | 0.88 |
| PC (34:3) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.11 | 0.57 | 0.78 | 0.09 | 0.65 | 0.82 | 0.10 | 0.59 | 0.88 |
| PC (34:3) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.20 | 0.29 | 0.68 | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.45 | −0.11 | 0.56 | 0.88 |
| PC (34:3) C | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.68 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.39 | −0.01 | 0.95 | 0.97 |
| PC (34:4) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.04 | 0.85 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 0.53 | 0.74 | −0.17 | 0.38 | 0.88 |
| PC (35:4) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.34 | 0.08 | 0.53 | −0.10 | 0.59 | 0.77 | 0.11 | 0.58 | 0.88 |
| PC (36:3) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.16 | 0.40 | 0.68 | 0.34 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 0.08 | 0.69 | 0.88 |
| PC (36:4) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.16 | 0.41 | 0.68 | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.46 | −0.05 | 0.78 | 0.88 |
| PC (36:5) C | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.05 | 0.81 | 0.91 | 0.13 | 0.51 | 0.73 | 0.14 | 0.46 | 0.88 |
| PC (36:5) D | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.16 | 0.40 | 0.68 | 0.00 | 0.98 | 0.98 | 0.10 | 0.62 | 0.88 |
| PC (36:6) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.08 | 0.68 | 0.83 | 0.09 | 0.64 | 0.81 | −0.14 | 0.46 | 0.88 |
| PC (37:5) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.38 | 0.04 | 0.37 | −0.14 | 0.46 | 0.70 | 0.08 | 0.70 | 0.88 |
| PC (38:3) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.68 | 0.30 | 0.12 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 0.53 | 0.88 |
| PC (38:4) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.26 | 0.18 | 0.68 | 0.25 | 0.20 | 0.46 | 0.05 | 0.78 | 0.88 |
| PC (38:6) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.05 | 0.80 | 0.91 | −0.07 | 0.71 | 0.84 | −0.08 | 0.67 | 0.88 |
| PC (38:6) C | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.18 | 0.34 | 0.68 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 0.31 | 0.09 | 0.63 | 0.88 |
| PC (38:7) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.13 | 0.49 | 0.71 | 0.11 | 0.57 | 0.77 | 0.15 | 0.44 | 0.88 |
| PC (40:7) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.06 | 0.76 | 0.91 | 0.14 | 0.47 | 0.72 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.88 |
| PC (40:8) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | −0.01 | 0.95 | 0.97 | −0.02 | 0.93 | 0.95 | 0.07 | 0.73 | 0.88 |
| PC (42:6) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Glycerophospholipids | 0.17 | 0.37 | 0.68 | 0.21 | 0.28 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 0.69 | 0.88 |
| SM (d30:1) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Sphingolipids | −0.19 | 0.32 | 0.68 | −0.13 | 0.50 | 0.73 | 0.08 | 0.68 | 0.88 |
| SM (d32:2) A | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Sphingolipids | −0.13 | 0.50 | 0.71 | 0.04 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.08 | 0.69 | 0.88 |
| SM (d30:1) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Sphingolipids | −0.18 | 0.36 | 0.68 | −0.10 | 0.60 | 0.77 | 0.07 | 0.72 | 0.88 |
| SM (d32:0) | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Sphingolipids | −0.24 | 0.20 | 0.68 | −0.11 | 0.59 | 0.77 | 0.13 | 0.50 | 0.88 |
| SM (d32:2) B | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | Sphingolipids | −0.04 | 0.83 | 0.91 | 0.12 | 0.53 | 0.74 | 0.07 | 0.73 | 0.88 |
| Isoleucine | Organic acids and derivatives | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | 0.25 | 0.19 | 0.68 | 0.05 | 0.79 | 0.89 | 0.01 | 0.97 | 0.98 |
| Phe-Trp | Organic acids and derivatives | Carboxylic acids and derivatives | 0.24 | 0.20 | 0.68 | 0.18 | 0.36 | 0.60 | 0.09 | 0.64 | 0.88 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, J.; Boghossian, N.S.; Sarzynski, M.A.; Luo, F.; Sun, X.; Li, J.; Fiehn, O.; Liu, J.; Chen, L. Metabolome-Wide Associations of Gestational Weight Gain in Pregnant Women with Overweight and Obesity. Metabolites 2022, 12, 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100960
Dai J, Boghossian NS, Sarzynski MA, Luo F, Sun X, Li J, Fiehn O, Liu J, Chen L. Metabolome-Wide Associations of Gestational Weight Gain in Pregnant Women with Overweight and Obesity. Metabolites. 2022; 12(10):960. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100960
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Jin, Nansi S. Boghossian, Mark A. Sarzynski, Feng Luo, Xiaoqian Sun, Jian Li, Oliver Fiehn, Jihong Liu, and Liwei Chen. 2022. "Metabolome-Wide Associations of Gestational Weight Gain in Pregnant Women with Overweight and Obesity" Metabolites 12, no. 10: 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100960
APA StyleDai, J., Boghossian, N. S., Sarzynski, M. A., Luo, F., Sun, X., Li, J., Fiehn, O., Liu, J., & Chen, L. (2022). Metabolome-Wide Associations of Gestational Weight Gain in Pregnant Women with Overweight and Obesity. Metabolites, 12(10), 960. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12100960