A New Look at Novel Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers: The Role of Atherogenic Lipoproteins and Innovative Antidiabetic Therapies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
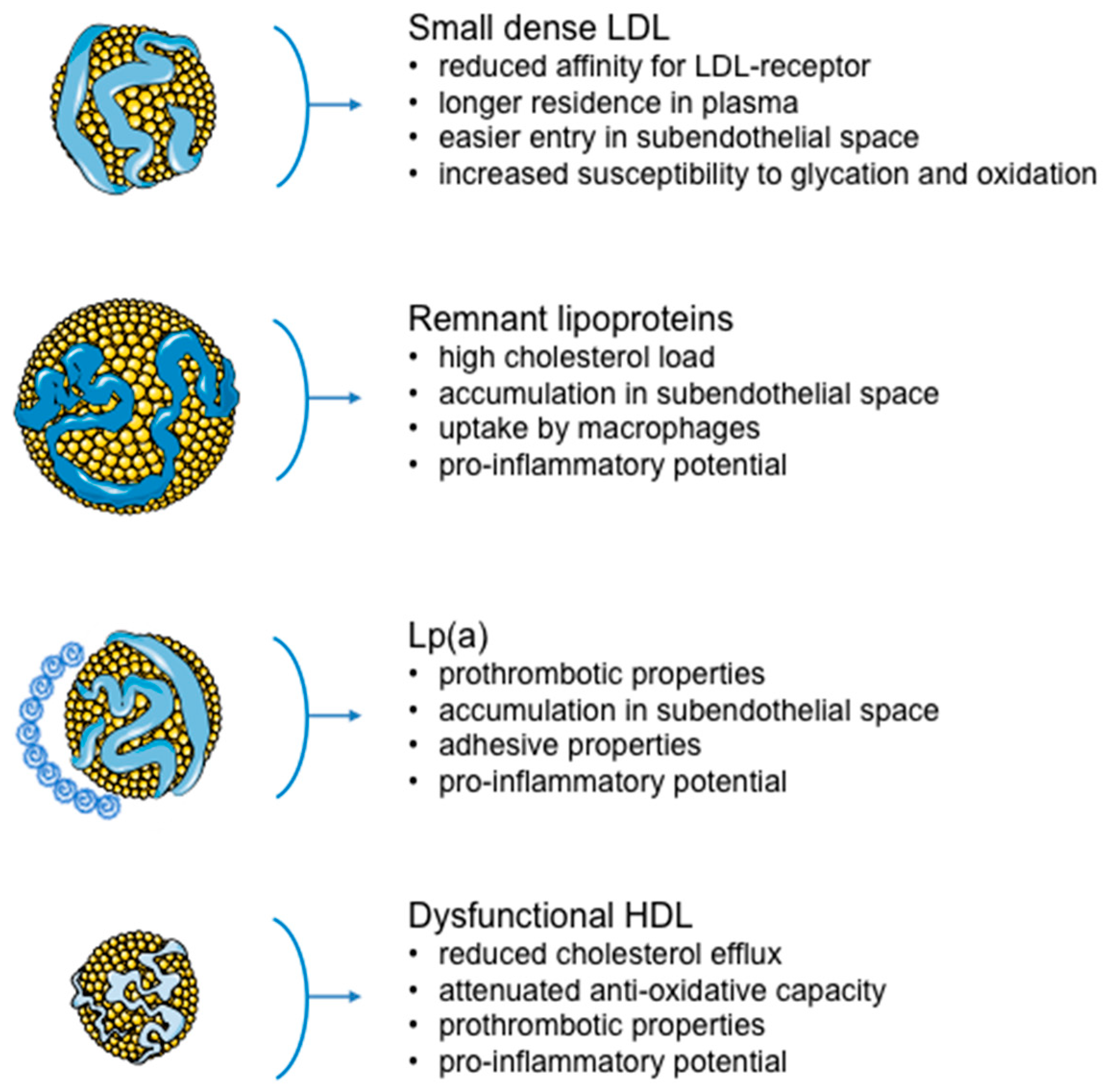
2. Small, Dense LDL
3. Lipoprotein(a)
4. Atherogenic Lipoproteins and Residual Cardiovascular Risk
5. Dysfunctional HDL
6. The Role of Innovative Antidiabetic Therapies on Atherogenic Lipoproteins
7. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Disclosures
References
- Ference, B.A.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Graham, I.; Ray, K.K.; Packard, C.J.; Bruckert, E.; Hegele, R.A.; Krauss, R.M.; Raal, F.J.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. 1. Evidence from genetic, epidemiologic, and clinical studies. A consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 2459–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabatine, M.S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Keech, A.C.; Honarpour, N.; Wiviott, S.D.; Murphy, S.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Wasserman, S.M.; et al. Evolocumab and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visseren, F.L.J.; Mach, F.; Smulders, Y.M.; Carballo, D.; Koskinas, K.C.; Back, M.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhindsa, D.S.; Sandesara, P.B.; Shapiro, M.D.; Wong, N.D. The Evolving Understanding and Approach to Residual Cardiovascular Risk Management. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2020, 7, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, D.; Banach, M.; Nikfar, S.; Salari, P.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Toth, P.P.; Abdollahi, M.; Ray, K.K.; Pencina, M.J.; Malyszko, J.; et al. Lipid and Blood Pressure Meta-Analysis Collaboration Group. A meta-analysis of the role of statins on renal outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease. Is the duration of therapy important? Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 5437–5447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, R.V.; Patti, A.M.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Lippi, G.; Rizzo, M.; Toth, P.P.; Banach, M. Polyphenols: Potential Use in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogacci, F.; Banach, M.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Bruckert, E.; Toth, P.P.; Watts, G.F.; Reiner, Ž.; Mancini, J.; Rizzo, M.; Mitchenko, O.; et al. Safety of red yeast rice supplementation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 143, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Berneis, K. Should we measure routinely the LDL peak particle size? Int. J. Cardiol. 2006, 107, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikezaki, H.; Lim, E.; Cupples, L.A.; Liu, C.T.; Asztalos, B.F.; Schaefer, E.J. Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Is the Most Atherogenic Lipoprotein Parameter in the Prospective Framingham Offspring Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2021, 10, e019140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, E.K.; Aday, A.W.; Cook, N.R.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M.; Pradhan, A.D. Triglyceride-Rich Lipoprotein Cholesterol, Small Dense LDL Cholesterol, and Incident Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 2122–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toth, P.P.; Barylski, M.; Nikolic, D.; Rizzo, M.; Montalto, G.; Banach, M. Should low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) be treated? Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, F.; Kocer, D.; Gundogan, K.; Kaya, A.; Demir, O.; Coskun, R.; Sabuncu, T.; Karaman, A.; Cesur, M.; Rizzo, M.; et al. Prevalence of dyslipidemia and associated risk factors in Turkish adults. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 8, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontush, A.; Lindahl, M.; Lhomme, M.; Calabresi, L.; Chapman, M.J.; Davidson, W.S. Structure of HDL: Particle subclasses and molecular components. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2015, 224, 3–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gugliucci, A.; Caccavello, R.; Kotani, K.; Sakane, N.; Kimura, S. Enzymatic assessment of paraoxonase 1 activity on HDL subclasses: A practical zymogram method to assess HDL function. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 415, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonmez, A.; Nikolic, D.; Dogru, T.; Ercin, C.N.; Genc, H.; Cesur, M.; Tapan, S.; Karslioğlu, Y.; Montalto, G.; Banach, M.; et al. Low- and high-density lipoprotein subclasses in subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2015, 9, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendler, W.; Rizzo, M.; Borowiec, M.; Malachowska, B.; Antosik, K.; Szadkowska, A.; Banach, M.; Urbanska-Kosinska, M.; Szopa, M.; Malecki, M.; et al. Less but better: Cardioprotective lipid profile of patients with GCK-MODY despite lower HDL cholesterol level. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berthold, H.K.; Rizzo, M.; Spenrath, N.; Montalto, G.; Krone, W.; Gouni-Berthold, I. Effects of lipid-lowering drugs on high-density lipoprotein subclasses in healthy men-a randomized trial. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McGarrah, R.W.; Craig, D.M.; Haynes, C.; Dowdy, Z.E.; Shah, S.H.; Kraus, W.E. High-density lipoprotein subclass measurements improve mortality risk prediction, discrimination and reclassification in a cardiac catheterization cohort. Atherosclerosis 2016, 246, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hafiane, A.; Genest, J. High density lipoproteins: Measurement techniques and potential biomarkers of cardiovascular risk. BBA Clin. 2015, 3, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Langlois, M.R.; Chapman, M.J.; Cobbaert, C.; Mora, S.; Remaley, A.T.; Ros, E.; Watts, G.F.; Boren, J.; Baum, H.; Bruckert, E.; et al. Quantifying Atherogenic Lipoproteins: Current and Future Challenges in the Era of Personalized Medicine and Very Low Concentrations of LDL Cholesterol. A Consensus Statement from EAS and EFLM. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1006–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prodan Zitnik, I.; Cerne, D.; Mancini, I.; Simi, L.; Pazzagli, M.; Di Resta, C.; Podgornik, H.; Repic Lampret, B.; Trebusak Podkrajsek, K.; Sipeky, C.; et al. Personalized laboratory medicine: A patient-centered future approach. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2018, 56, 1981–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rizzo, M.; Kotur-Stevuljevic, J.; Berneis, K.; Spinas, G.; Rini, G.B.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V.; Vekic, J. Atherogenic dyslipidemia and oxidative stress: A new look. Transl. Res. 2009, 153, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Berneis, K. Who needs to care about small, dense low-density lipoproteins? Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2007, 61, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vekic, J.; Topic, A.; Zeljkovic, A.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V. LDL and HDL subclasses and their relationship with Framingham risk score in middle-aged Serbian population. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeljkovic, A.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V.; Vekic, J.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Topic, A.; Bogavac-Stanojevic, N.; Spasic, S.; Vujovic, A.; Kalimanovska-Ostric, D. Does simultaneous determination of LDL and HDL particle size improve prediction of coronary artery disease risk? Clin. Exp. Med. 2008, 8, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeljkovic, A.; Vekic, J.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Bogavac-Stanojevic, N.; Gulan, B.; Spasic, S. LDL and HDL subclasses in acute ischemic stroke: Prediction of risk and short-term mortality. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekimoto, T.; Koba, S.; Mori, H.; Sakai, R.; Arai, T.; Yokota, Y.; Sato, S.; Tanaka, H.; Masaki, R.; Oishi, Y.; et al. Small Dense Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol: A Residual Risk for Rapid Progression of Non-Culprit Coronary Lesion in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2021, 11, 61052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Berneis, K. The clinical relevance of low-density-lipoproteins size modulation by statins. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2006, 20, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Minno, A.; Gentile, M.; Iannuzzo, G.; Calcaterra, I.; Tripaldella, M.; Porro, B.; Cavalca, V.; Di Taranto, M.D.; Tremoli, E.; Fortunato, G.; et al. Endothelial function improvement in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia receiving PCSK-9 inhibitors on top of maximally tolerated lipid lowering therapy. Thromb. Res. 2020, 194, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Berneis, K.; Zeljkovic, A.; Vekic, J. Should we routinely measure low-density and high-density lipoprotein subclasses? Clin. Lab. 2009, 55, 421–429. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Chang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Z. Triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and cardiovascular events in the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 32, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonmez, A.; Yilmaz, M.I.; Saglam, M.; Unal, H.U.; Gok, M.; Cetinkaya, H.; Karaman, M.; Haymana, C.; Eyileten, T.; Oguz, Y.; et al. The role of plasma triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio to predict cardiovascular outcomes in chronic kidney disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2015, 14, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikhailidis, D.P.; Elisaf, M.; Rizzo, M.; Berneis, K.; Griffin, B.; Zambon, A.; Athyros, V.; de Graaf, J.; März, W.; Parhofer, K.G.; et al. European panel on low density lipoprotein (LDL) subclasses: A statement on the pathophysiology, atherogenicity and clinical significance of LDL subclasses. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 9, 533–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Luo, F.; Ruan, G.; Peng, R.; Li, X. Hypertriglyceridemia and atherosclerosis. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginsberg, H.N.; Packard, C.J.; Chapman, M.J.; Boren, J.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; Averna, M.; Ference, B.A.; Gaudet, D.; Hegele, R.A.; Kersten, S.; et al. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and their remnants: Metabolic insights, role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and emerging therapeutic strategies-a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 11, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo-Vaz, A.J.; Fayyad, R.; Boekholdt, S.M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kastelein, J.J.; Melamed, S.; Barter, P.; Waters, D.D.; Ray, K.K. Triglyceride-Rich Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Risk of Cardiovascular Events among Patients Receiving Statin Therapy in the TNT Trial. Circulation 2018, 138, 770–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollstein, T.; Vogt, A.; Grenkowitz, T.; Stojakovic, T.; Marz, W.; Laufs, U.; Bolukbasi, B.; Steinhagen-Thiessen, E.; Scharnagl, H.; Kassner, U. Treatment with PCSK9 inhibitors reduces atherogenic VLDL remnants in a real-world study. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2019, 116, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kuang, J.; Tang, X.; Mao, L.; Guo, X.; Luo, Q.; Peng, D.; Yu, B. Comparison of calculated remnant lipoprotein cholesterol levels with levels directly measured by nuclear magnetic resonance. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskinas, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 111–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeljkovic, A.; Bogavac-Stanojevic, N.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V.; Vekic, J.; Spasic, S. Combined effects of small apolipoprotein (a) isoforms and small, dense LDL on coronary artery disease risk. Arch. Med. Res. 2009, 40, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhainds, D.; Brodeur, M.R.; Tardif, J.C. Lipoprotein (a): When to Measure and How to Treat? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestel, P.J.; Barnes, E.H.; Tonkin, A.M.; Simes, J.; Fournier, M.; White, H.D.; Colquhoun, D.M.; Blankenberg, S.; Sullivan, D.R. Plasma lipoprotein(a) concentration predicts future coronary and cardiovascular events in patients with stable coronary heart disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2902–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, G.G.; Szarek, M.; Bittner, V.A.; Diaz, R.; Goodman, S.G.; Jukema, J.W.; Landmesser, U.; Lopez-Jaramillo, P.; Manvelian, G.; Pordy, R.; et al. Lipoprotein(a) and Benefit of PCSK9 Inhibition in Patients With Nominally Controlled LDL Cholesterol. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 78, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donoghue, M.L.; Fazio, S.; Giugliano, R.P.; Stroes, E.S.G.; Kanevsky, E.; Gouni-Berthold, I.; Im, K.; Lira Pineda, A.; Wasserman, S.M.; Ceska, R.; et al. Lipoprotein(a), PCSK9 Inhibition, and Cardiovascular Risk. Circulation 2019, 139, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogavac-Stanojevic, N.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V.; Spasic, S.; Kalimanovska-Ostric, D. Lipid and inflammatory markers for the prediction of coronary artery disease: A multi-marker approach. Clin. Biochem. 2007, 40, 1000–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzatti, A.J.; Monsalvo, M.L.; Lopez, J.A.G.; Wang, H.; Rosenson, R.S. Effects of evolocumab in individuals with type 2 diabetes with and without atherogenic dyslipidemia: An analysis from BANTING and BERSON. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, D.J.; Probstfield, J.L.; Garrison, R.J.; Neaton, J.D.; Castelli, W.P.; Knoke, J.D.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Bangdiwala, S.; Tyroler, H.A. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation 1989, 79, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ko, D.T.; Alter, D.A.; Guo, H.; Koh, M.; Lau, G.; Austin, P.C.; Booth, G.L.; Hogg, W.; Jackevicius, C.A.; Lee, D.S.; et al. High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Cause-Specific Mortality in Individuals Without Previous Cardiovascular Conditions: The CANHEART Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 68, 2073–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Ansell, B.J.; Barter, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jozefczuk, E.; Guzik, T.J.; Siedlinski, M. Significance of sphingosine-1-phosphate in cardiovascular physiology and pathology. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 156, 104793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vekic, J.; Zeljkovic, A.; Stefanovic, A.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V. Obesity and dyslipidemia. Metabolism 2019, 92, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soria-Florido, M.T.; Castaner, O.; Lassale, C.; Estruch, R.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Corella, D.; Ros, E.; Aros, F.; Elosua, R.; et al. Dysfunctional High-Density Lipoproteins Are Associated With a Greater Incidence of Acute Coronary Syndrome in a Population at High Cardiovascular Risk: A Nested Case-Control Study. Circulation 2020, 141, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denimal, D.; Monier, S.; Brindisi, M.C.; Petit, J.M.; Bouillet, B.; Nguyen, A.; Demizieux, L.; Simoneau, I.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Verges, B.; et al. Impairment of the Ability of HDL From Patients With Metabolic Syndrome but Without Diabetes Mellitus to Activate eNOS: Correction by S1P Enrichment. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karavia, E.A.; Zvintzou, E.; Petropoulou, P.I.; Xepapadaki, E.; Constantinou, C.; Kypreos, K.E. HDL quality and functionality: What can proteins and genes predict? Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2014, 12, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben-Aicha, S.; Escate, R.; Casani, L.; Padro, T.; Pena, E.; Arderiu, G.; Mendieta, G.; Badimon, L.; Vilahur, G. High-density lipoprotein remodelled in hypercholesterolaemic blood induce epigenetically driven down-regulation of endothelial HIF-1alpha expression in a preclinical animal model. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 1288–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beazer, J.D.; Patanapirunhakit, P.; Gill, J.M.R.; Graham, D.; Karlsson, H.; Ljunggren, S.; Mulder, M.T.; Freeman, D.J. High-density lipoprotein’s vascular protective functions in metabolic and cardiovascular disease—Could extracellular vesicles be at play? Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerin, M.; Silvain, J.; Gall, J.; Darabi, M.; Berthet, M.; Frisdal, E.; Hauguel-Moreau, M.; Zeitouni, M.; Kerneis, M.; Lattuca, B.; et al. Association of Serum Cholesterol Efflux Capacity With Mortality in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 3259–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajala, O.N.; Demler, O.V.; Liu, Y.; Farukhi, Z.; Adelman, S.J.; Collins, H.L.; Ridker, P.M.; Rader, D.J.; Glynn, R.J.; Mora, S. Anti-Inflammatory HDL Function, Incident Cardiovascular Events, and Mortality: A Secondary Analysis of the JUPITER Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e016507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, E.W.; Nordestgaard, L.T.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. HDL Cholesterol and Non-Cardiovascular Disease: A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kon, V.; Yang, H.C.; Smith, L.E.; Vickers, K.C.; Linton, M.F. High-Density Lipoproteins in Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganjali, S.; Banach, M.; Pirro, M.; Fras, Z.; Sahebkar, A. HDL and cancer—Causality still needs to be confirmed? Update 2020. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2021, 73, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladimirov, S.; Gojkovic, T.; Zeljkovic, A.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Zeljkovic, D.; Antonic, T.; Trifunovic, B.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V. Can non-cholesterol sterols indicate the presence of specific dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism in patients with colorectal cancer? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 11, 114595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.; Nauck, M.A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Incretin-based therapies in 2021—Current status and perspectives for the future. Metabolism 2021, 122, 154843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgino, F.; Caruso, I.; Moellmann, J.; Lehrke, M. Differential indication for SGLT-2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with established atherosclerotic heart disease or at risk for congestive heart failure. Metabolism 2020, 104, 154045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Nikolic, D.; Patti, A.M.; Mannina, C.; Montalto, G.; McAdams, B.S.; Rizvi, A.A.; Cosentino, F. GLP-1 receptor agonists and reduction of cardiometabolic risk: Potential underlying mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 2814–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R.; Wefers, J.; Meier, J.J. GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes—State-of-the-art. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Fukui, T.; Nakanishi, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Tomoyasu, M.; Osamura, A.; Ohara, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Ito, Y.; Hirano, T. Dapagliflozin decreases small dense low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol and increases high-density lipoprotein 2-cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes: Comparison with sitagliptin. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiquette, E.; Toth, P.P.; Ramirez, G.; Cobble, M.; Chilton, R. Treatment with exenatide once weekly or twice daily for 30 weeks is associated with changes in several cardiovascular risk markers. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2012, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar]
- Nikolic, D.; Giglio, R.V.; Rizvi, A.A.; Patti, A.M.; Montalto, G.; Maranta, F.; Cianflone, D.; Stoian, A.P.; Rizzo, M. Liraglutide reduces carotid intima-media thickness by reducing small dense low-density lipoproteins in a real-world setting of patients with type 2 diabetes: A novel anti-atherogenic effect. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anholm, C.; Kumarathurai, P.; Pedersen, L.R.; Samkani, A.; Walzem, R.L.; Nielsen, O.W.; Kristiansen, O.P.; Fenger, M.; Madsbad, S.; Sajadieh, A.; et al. Liraglutide in combination with metformin may improve the atherogenic lipid profile and decrease C-reactive protein level in statin treated obese patients with coronary artery disease and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Atherosclerosis 2019, 288, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sánchez-García, A.; Simental-Mendía, M.; Millán-Alanís, J.M.; Simental-Mendía, L.E. Effect of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors on lipid profile: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 48 randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monami, M.; Dicembrini, I.; Nardini, C.; Fiordelli, I.; Mannucci, E. Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on cardiovascular risk: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2014, 16, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krauss, R.M. Lipids and lipoproteins in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1496–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Berneis, K.; Rizzo, M.; Stettler, C.; Chappuis, B.; Braun, M.; Diem, P.; Christ, E.R. Comparative effects of rosiglitazone and pioglitazone on fasting and postprandial low-density lipoprotein size and subclasses in patients with Type 2 diabetes. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2008, 9, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K. Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2457–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Derosa, G.; Franzetti, I.G.; Querci, F.; Carbone, A.; Ciccarelli, L.; Piccinni, M.N.; Fogari, E.; Maffioli, P. Variation in inflammatory markers and glycemic parameters after 12 months of exenatide plus metformin treatment compared with metformin alone: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Pharmacotherapy 2013, 33, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Ye, L.; Lee, K.O.; Ma, J. Liraglutide treatment causes upregulation of adiponectin and downregulation of resistin in Chinese type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 110, 224–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, N.; Sallam, H.S.; Rizzo, M.; Nikolic, D.; Obradovic, M.; Bjelogrlic, P.; Isenovic, E.R. Resistin: An inflammatory cytokine. Role in cardiovascular diseases, diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 4961–4969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, M.; Thiele, K.; Korbinian Hartmann, N.U.; Möllmann, J.; Wied, S.; Böhm, M.; Scharnagl, H.; März, W.; Marx, N.; Lehrke, M. Effects of empagliflozin on lipoprotein subfractions in patients with type 2 diabetes: Data from a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Atherosclerosis 2021, 330, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariel, D.; Kim, S.H.; Abbasi, F.; Lamendola, C.A.; Liu, A.; Reaven, G.M. Effect of liraglutide administration and a calorie-restricted diet on lipoprotein profile in overweight/obese persons with prediabetes. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2014, 24, 1317–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, S.A.; Park, Y.M.; Yun, J.S.; Lim, T.S.; Song, K.H.; Yoo, K.D.; Ahn, Y.B.; Ko, S.H. A comparison of effects of DPP-4 inhibitor and SGLT2 inhibitor on lipid profile in patients with type 2 diabetes. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, N.P.; Wang, Q.; Wolski, K.E.; Cho, L.; McErlean, E.; Ruotolo, G.; Weerakkody, G.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Nicholls, S.J.; Lincoff, A.M.; et al. The Role of Lipoprotein (a) as a Marker of Residual Risk in Patients With Diabetes and Established Cardiovascular Disease on Optimal Medical Therapy: Post Hoc Analysis of ACCELERATE. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, e22–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hjerpsted, J.B.; Flint, A.; Brooks, A.; Axelsen, M.B.; Kvist, T.; Blundell, J. Semaglutide improves postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism, and delays first-hour gastric emptying in subjects with obesity. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dahl, K.; Brooks, A.; Almazedi, F.; Hoff, S.T.; Boschini, C.; Baekdal, T.A. Oral semaglutide improves postprandial glucose and lipid metabolism, and delays gastric emptying, in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 1594–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mahmeed, W.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Banerjee, Y.; Ceriello, A.; Cosentino, F.; Galia, M.; Goh, S.-Y.; Kempler, P.; Lessan, N.; Papanas, N.; et al. The Cardiometabolic Panel of International experts on Syndemic COVID-19 (CAPISCO). Promoting a Syndemic Approach for Cardiometabolic Disease Management during COVID-19: The CAPISCO International Expert Panel. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 787761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoian, A.P.; Banerjee, Y.; Rizvi, A.A.; Rizzo, M. Diabetes and the COVID-19 Pandemic: How Insights from Recent Experience Might Guide Future Management. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2020, 18, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vekic, J.; Zeljkovic, A.; Al Rasadi, K.; Cesur, M.; Silva-Nunes, J.; Stoian, A.P.; Rizzo, M. A New Look at Novel Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers: The Role of Atherogenic Lipoproteins and Innovative Antidiabetic Therapies. Metabolites 2022, 12, 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020108
Vekic J, Zeljkovic A, Al Rasadi K, Cesur M, Silva-Nunes J, Stoian AP, Rizzo M. A New Look at Novel Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers: The Role of Atherogenic Lipoproteins and Innovative Antidiabetic Therapies. Metabolites. 2022; 12(2):108. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020108
Chicago/Turabian StyleVekic, Jelena, Aleksandra Zeljkovic, Khalid Al Rasadi, Mustafa Cesur, José Silva-Nunes, Anca Pantea Stoian, and Manfredi Rizzo. 2022. "A New Look at Novel Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers: The Role of Atherogenic Lipoproteins and Innovative Antidiabetic Therapies" Metabolites 12, no. 2: 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020108
APA StyleVekic, J., Zeljkovic, A., Al Rasadi, K., Cesur, M., Silva-Nunes, J., Stoian, A. P., & Rizzo, M. (2022). A New Look at Novel Cardiovascular Risk Biomarkers: The Role of Atherogenic Lipoproteins and Innovative Antidiabetic Therapies. Metabolites, 12(2), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12020108








