Comparative Transcriptome and Phytochemical Analysis Provides Insight into Triterpene Saponin Biosynthesis in Seeds and Flowers of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
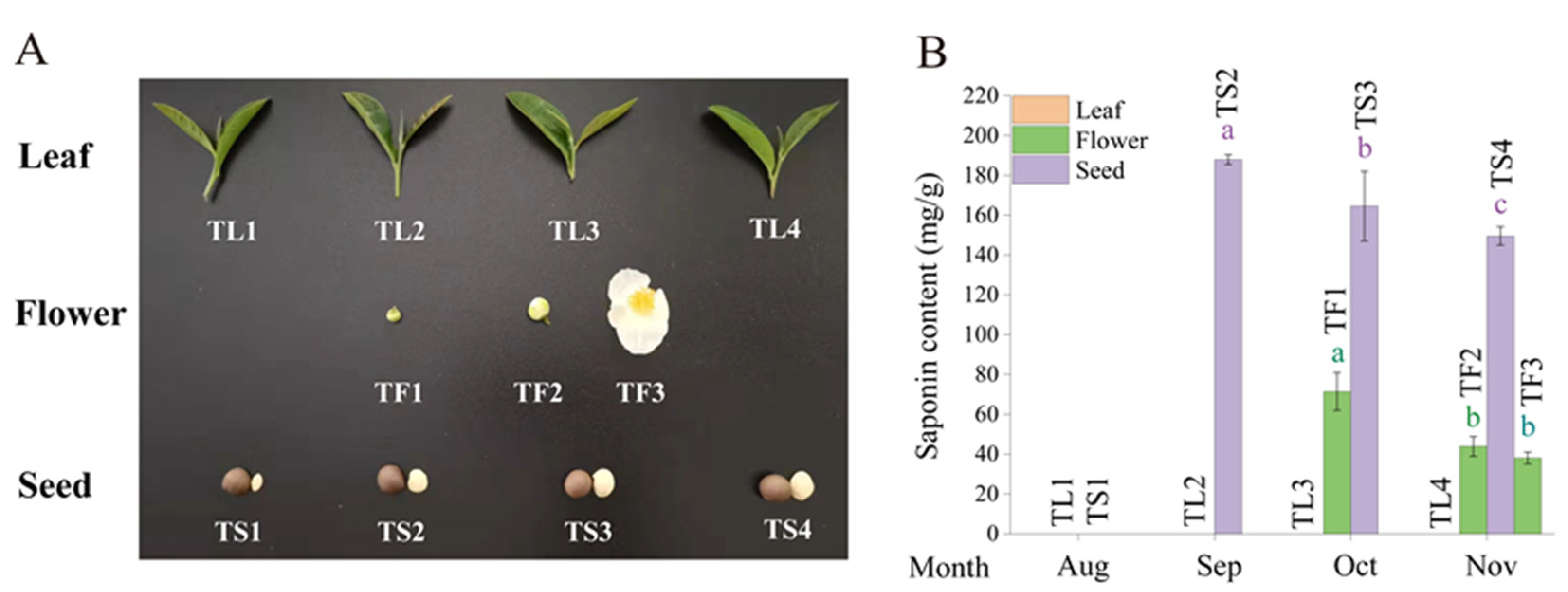
2.1. Determination of Saponin Content in Tea Leaves, Flowers and Seeds
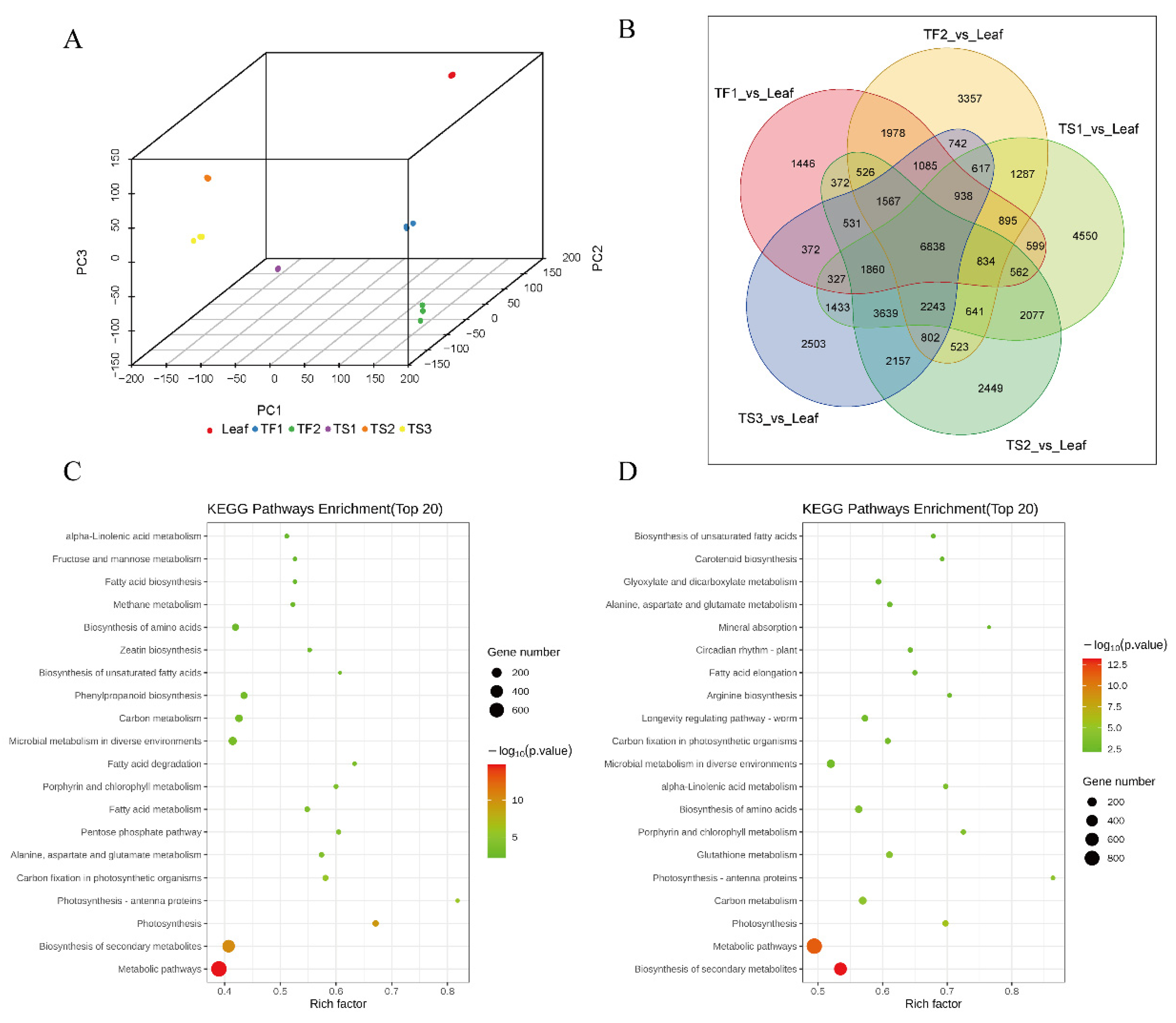
2.2. Characterization and Quality Assessment of Transcriptome Data
2.3. Differential Gene Expression Analysis
2.4. Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
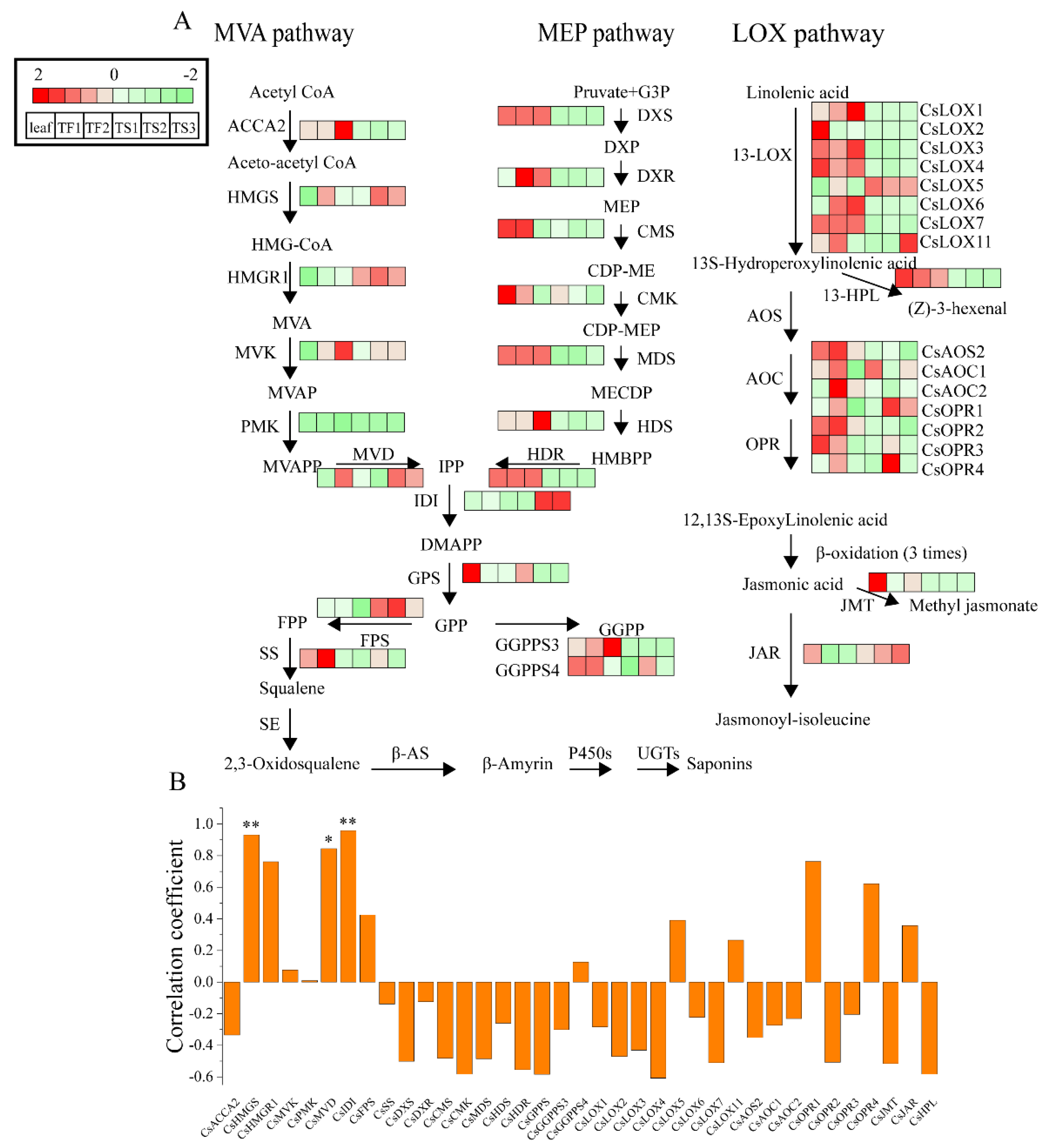
2.5. Characterization of Genes Involved in Saponin Biosynthesis
2.6. Characterization of Hub TFs Involved in Saponin Biosynthesis
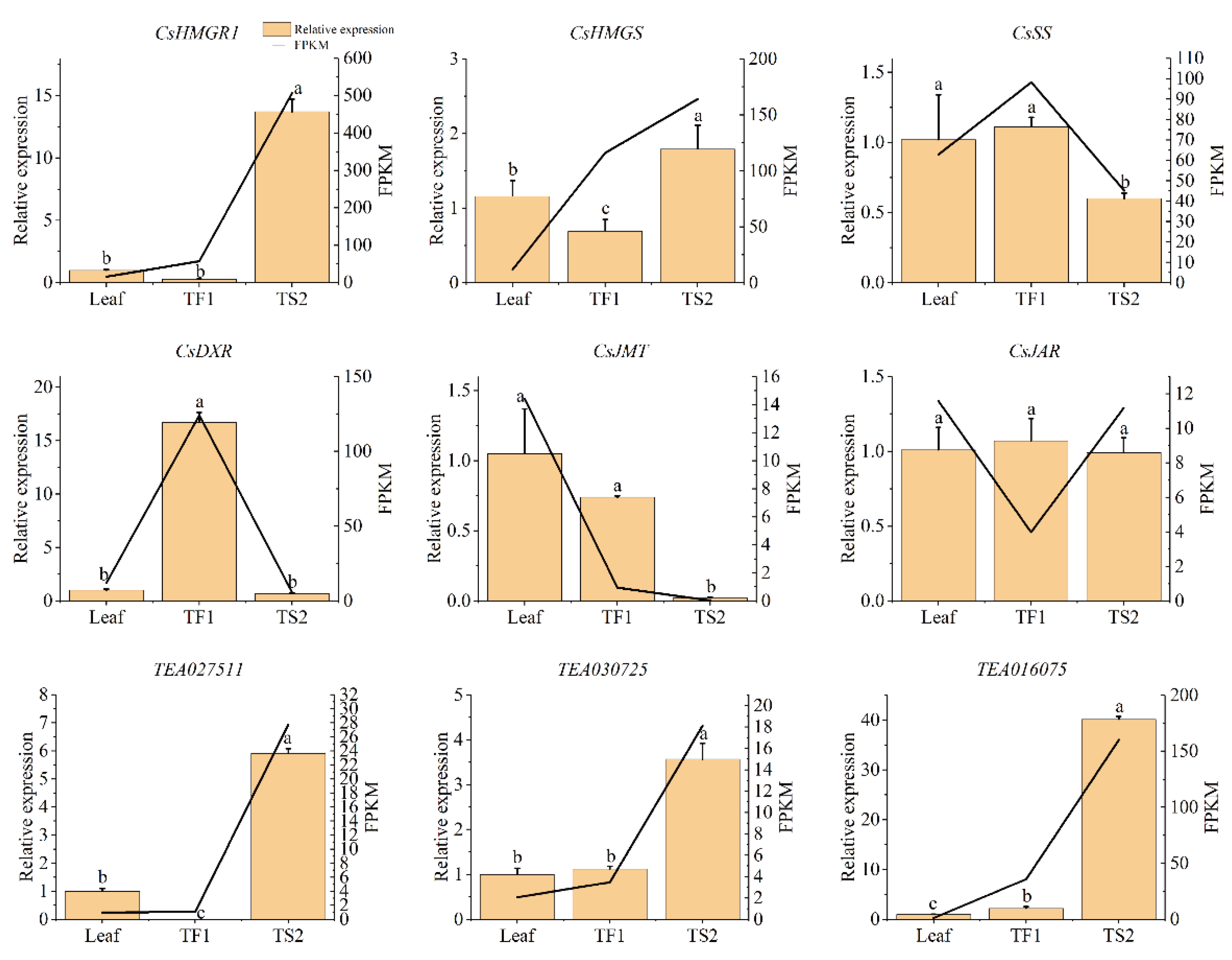
2.7. qRT-PCR Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Determination of Triterpene Saponins by UPLC-PDA-MS
4.3. RNA-Seq Analysis
4.4. Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Aanalysis (WGCNA)
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zeng, L.; Watanabe, N.; Yang, Z. Understanding the biosyntheses and stress response mechanisms of aroma compounds in tea (Camellia sinensis) to safely and effectively improve tea aroma. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2321–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Contreras, M.D.M.; Xu, D.; Jia, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, D. New insights into free and bound phenolic compounds as antioxidant cluster in tea seed oil: Distribution and contribution. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 136, 110315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, L.; Yao, Y.; Li, C.; Xu, F.; Ying, Y.; Shao, Z.; Bao, J. Pasting, gelatinization, and retrogradation characteristics related to structural properties of tea seed starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Jin, Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, J.; Tu, Y. Safety evaluation of tea (Camellia sinensis (L.) O. Kuntze) flower extract: Assessment of mutagenicity, and acute and subchronic toxicity in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Chen, G.; Ding, Y.; Wan, P.; Peng, Y.; Chen, C.; Ye, H.; Zeng, X.; Ran, L. Polysaccharides from the flowers of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) modulate gut health and ameliorate cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression. J. Funct. Food. 2019, 61, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ding, Y.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Zeng, X.; Ye, H. Components identification and nutritional value exploration of tea (Camellia sinensis L.) flower extract: Evidence for functional food. Food Res. Int. 2020, 132, 109100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheok, C.Y.; Salman, H.A.K.; Sulaiman, R. Extraction and quantification of saponins: A review. Food Res. Int. 2014, 59, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Tong, T.; Ren, N.; Tu, Y.; Li, B. Saponins from seeds of genus Camellia: Phytochemistry and bioactivity. Phytochemistry 2018, 149, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Zong, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ho, C.T.; Wan, X.; Hou, R. Triterpenoid saponins from the genus Camellia: Structures, biological activities, and molecular simulation for structure-activity relationship. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 3069–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, J.M.; Kuzina, V.; Andersen, S.B.; Bak, S. Molecular activities, biosynthesis and evolution of triterpenoid saponins. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 435–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Fazio, G.C.; Matsuda, S.P. On the origins of triterpenoid skeletal diversity. Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 261–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, H.; Tamura, K.; Muranaka, T. P450s and UGTs: Key players in the structural diversity of triterpenoid saponins. Plant Cell Physiol. 2015, 56, 1463–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavya, N.M.; Adil, L.; Senthilkumar, P. A review on saponin biosynthesis and its transcriptomic resources in medicinal plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 39, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmappa, R.; Geisler, K.; Louveau, T.; O’Maille, P.; Osbourn, A. Triterpene biosynthesis in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2014, 65, 225–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Jia, L.; Weng, X. Advances in understanding of the biosynthetic pathway and regulatory mechanism of triterpenoid saponins in plants. Sci. Sin. (Vitae) 2021, 51, 525–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Chen, W.; Luo, M.; Xu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Z. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals regulatory network and regulators associated with proanthocyanidin accumulation in persimmon. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhao, S.; Xu, M.; Niu, Y.; Nasier, M.; Fan, G.; Quan, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liao, K. Identification of key genes controlling carotenoid metabolism during apricot fruit development by integrating metabolic phenotypes and gene expression profiles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 9472–9483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, E.; Li, F.; Tong, W.; Li, P.; Wu, Q.; Zhao, H.; Ge, R.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Tea Plant Information Archive: A comprehensive genomics and bioinformatics platform for tea plant. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 1938–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, J.; Fernandez-Calvo, P.; Schweizer, F.; Goossens, A. Jasmonates: Signal transduction components and their roles in environmental stress responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 91, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, P.Y.; Jahidin, A.H.; Lehmann, R.; Penman, K.; Kitching, W.; De Voss, J.J. Steroidal saponins from the roots of Asparagus racemosus. Phytochemistry 2008, 69, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinig, U.; Aharoni, A. Analysis of steroidal alkaloids and saponins in Solanaceae plant extracts using UPLC-qTOF mass spectrometry. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1153, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Wang, P.; Wu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Idehen, E.; Sang, S. Steroidal saponins in Oat Bran. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, Y.; Zhang, W.; Christopher, M.M.F. Distribution of saponins in the sea Cucumber Holothuria lessoni; the Body Wall Versus the Viscera, and their Biological Activities. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, L.; He, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J. Triterpenoid saponins in tea (Camellia sinensis) plants: Biosynthetic gene expression, content variations, chemical identification and cytotoxicity. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Shi, L.; Pan, H.; Li, B.; Wu, Y.; Tu, Y. Identification of triterpenoid saponins in flowers of four Camellia Sinensis cultivars from Zhejiang province: Differences between cultivars, developmental stages, and tissues. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 95, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Jia, L.; Wu, J.; Liu, Y.; Kang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, P.; He, P.; Tu, Y.; Li, B. Simultaneous determination and quantification of triterpene saponins from Camellia sinensis seeds using UPLC-PDA-QTOF-MS/MS. Molecules 2019, 24, 3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Li, J.; Yang, W.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Liu, C. Transcriptome analysis of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis illuminates the biosynthesis and accumulation of steroidal saponins in rhizomes and leaves. Phytochemistry 2020, 178, 112460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzina, V.; Ekstrom, C.T.; Andersen, S.B.; Nielsen, J.K.; Olsen, C.E.; Bak, S. Identification of defense compounds in Barbarea vulgaris against the herbivore Phyllotreta nemorum by an ecometabolomic approach. Plant Physiol. 2009, 151, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Augustin, J.M.; Drok, S.; Shinoda, T.; Sanmiya, K.; Nielsen, J.K.; Khakimov, B.; Olsen, C.E.; Hansen, E.H.; Kuzina, V.; Ekstrom, C.T.; et al. UDP-glycosyltransferases from the UGT73C subfamily in Barbarea vulgaris catalyze sapogenin 3-O-glucosylation in saponin-mediated insect resistance. Plant Physiol. 2012, 160, 1881–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Li, W.; Xia, E.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, Y.; Xu, J.; et al. The medicinal herb Panax notoginseng genome provides insights into ginsenoside biosynthesis and genome evolution. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 903–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, M.; Debnath, B.; Qasim, M.; Bamisile, B.S.; Islam, W.; Hameed, M.S.; Wang, L.; Qiu, D. Role of saponins in plant defense against specialist herbivores. Molecules 2019, 24, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Khakimov, B.; Cardenas, P.D.; Cozzi, F.; Olsen, C.E.; Jensen, K.R.; Hauser, T.P.; Bak, S. The cytochrome P450 CYP72A552 is key to production of hederagenin-based saponins that mediate plant defense against herbivores. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 1599–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Szakiel, A.; Pączkowski, C.; Henry, M. Influence of environmental abiotic factors on the content of saponins in plants. Phytochem. Rev. 2010, 10, 471–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawai, S.; Saito, K. Triterpenoid biosynthesis and engineering in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2011, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Shamala, L.F.; Yi, X.K.; Yan, Z.; Wei, S. Analysis of terpene synthase family genes in Camellia sinensis with an emphasis on abiotic stress conditions. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Liu, D.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Liu, S.; Gao, W. Jasmonic acid and methyl dihydrojasmonate enhance saponin biosynthesis as well as expression of functional genes in adventitious roots of Panax notoginseng F.H. Chen. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2017, 64, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Sukweenadhi, J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.C. PgLOX6 encoding a lipoxygenase contributes to jasmonic acid biosynthesis and ginsenoside production in Panax ginseng. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strader, L.; Weijers, D.; Wagner, D. Plant transcription factors—Being in the right place with the right company. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 65, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, J.; Pollier, J.; Vanden Bossche, R.; Lopez-Vidriero, I.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Goossens, A. The bHLH transcription factors TSAR1 and TSAR2 regulate triterpene saponin biosynthesis in Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Cui, X.; Ge, F. The transcription factor PjERF1 enhances the biosynthesis of triterpenoid saponins in Panax japonicus. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2021, 15, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, S.; Xu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Sui, C.; Wei, J. Overexpression of BcbZIP134 negatively regulates the biosynthesis of saikosaponins. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2019, 137, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Langfelder, P.; Zhang, B.; Horvath, S. Defining clusters from a hierarchical cluster tree: The Dynamic Tree Cut package for R. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 719–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoot, M.E.; Ono, K.; Ruscheinski, J.; Wang, P.L.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Family | Gene ID in CSS | R with Flower Saponin Content | R with Seed Saponin Content | Connected Genes Involving Saponin Synthesis |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP2 | TEA000303 | 0.168 | 0.984 ** | |
| TEA004791 | 0.860 * | 0.742 * | CsHMGR1 | |
| TEA010368 | 0.717 | 0.762 * | CsHMGS, CsIDI | |
| TEA012848 | 0.885 * | 0.882 ** | CsHMGR1 | |
| TEA014088 | −0.878 * | −0.991 ** | CsHMGR1 | |
| TEA017527 | 0.381 | 0.275 | ||
| TEA017531 | 0.904 * | 0.844 ** | CsHMGS | |
| bHLH | TEA016075 | 0.889 * | 0.935 ** | |
| TEA027511 | 0.953 ** | 0.513 | CsHMGR1 | |
| TEA030725 | −0.890 * | 0.818 ** | CsHMGR1 | |
| TEA033198 | −0.914 * | −0.975 ** | CsHMGS, CsMVD, CsIDI | |
| bZIP | TEA011482 | 0.896 * | 0.831 ** | CsHMGR1 |
| TEA015989 | 0.884 * | 0.907 ** | CsHMGR1, CsOPR4 | |
| TEA027854 | 0.860 * | 0.892 ** | ||
| GARP | TEA011475 | −0.333 | 0.783 * | CsHMGS, CsIDI |
| GATA | TEA016123 | 0.938 ** | 0.542 | |
| MYB | TEA009081 | 0.845 * | 0.815 ** | CsHMGS |
| TEA025060 | −0.577 | 0.894 ** | CsHMGS, CsIDI | |
| TEA025405 | 0.891 * | 0.644 | CsHMGS | |
| TEA028258 | 0.845 * | 0.555 | ||
| TEA028875 | 0.897 * | 0.549 | ||
| TEA031988 | 0.600 | 0.780 * | CsHMGS | |
| TCP | TEA033591 | 0.694 | 0.971 ** | |
| TEA024520 | 0.309 | 0.149 | ||
| Trihelix | TEA004951 | 0.832 * | −0.184 | CsOPR4 |
| TEA021268 | 0.952 ** | 0.649 | CsOPR4, CsHMGR1 | |
| WRKY | TEA017544 | 0.521 | 0.842 ** | CsOPR4, CsHMGR1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, C.; Zhu, H.; Kang, J.; Warusawitharana, H.K.; Chen, S.; Wang, K.; Yu, F.; Wu, Y.; He, P.; Tu, Y.; et al. Comparative Transcriptome and Phytochemical Analysis Provides Insight into Triterpene Saponin Biosynthesis in Seeds and Flowers of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Metabolites 2022, 12, 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030204
Chen C, Zhu H, Kang J, Warusawitharana HK, Chen S, Wang K, Yu F, Wu Y, He P, Tu Y, et al. Comparative Transcriptome and Phytochemical Analysis Provides Insight into Triterpene Saponin Biosynthesis in Seeds and Flowers of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Metabolites. 2022; 12(3):204. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030204
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Cong, Huanqing Zhu, Jiaxin Kang, Hasitha Kalhari Warusawitharana, Shuna Chen, Kaixi Wang, Fei Yu, Yuanyuan Wu, Puming He, Youying Tu, and et al. 2022. "Comparative Transcriptome and Phytochemical Analysis Provides Insight into Triterpene Saponin Biosynthesis in Seeds and Flowers of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis)" Metabolites 12, no. 3: 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030204
APA StyleChen, C., Zhu, H., Kang, J., Warusawitharana, H. K., Chen, S., Wang, K., Yu, F., Wu, Y., He, P., Tu, Y., & Li, B. (2022). Comparative Transcriptome and Phytochemical Analysis Provides Insight into Triterpene Saponin Biosynthesis in Seeds and Flowers of the Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis). Metabolites, 12(3), 204. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030204