Modulation of Deiodinase Types 2 and 3 during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
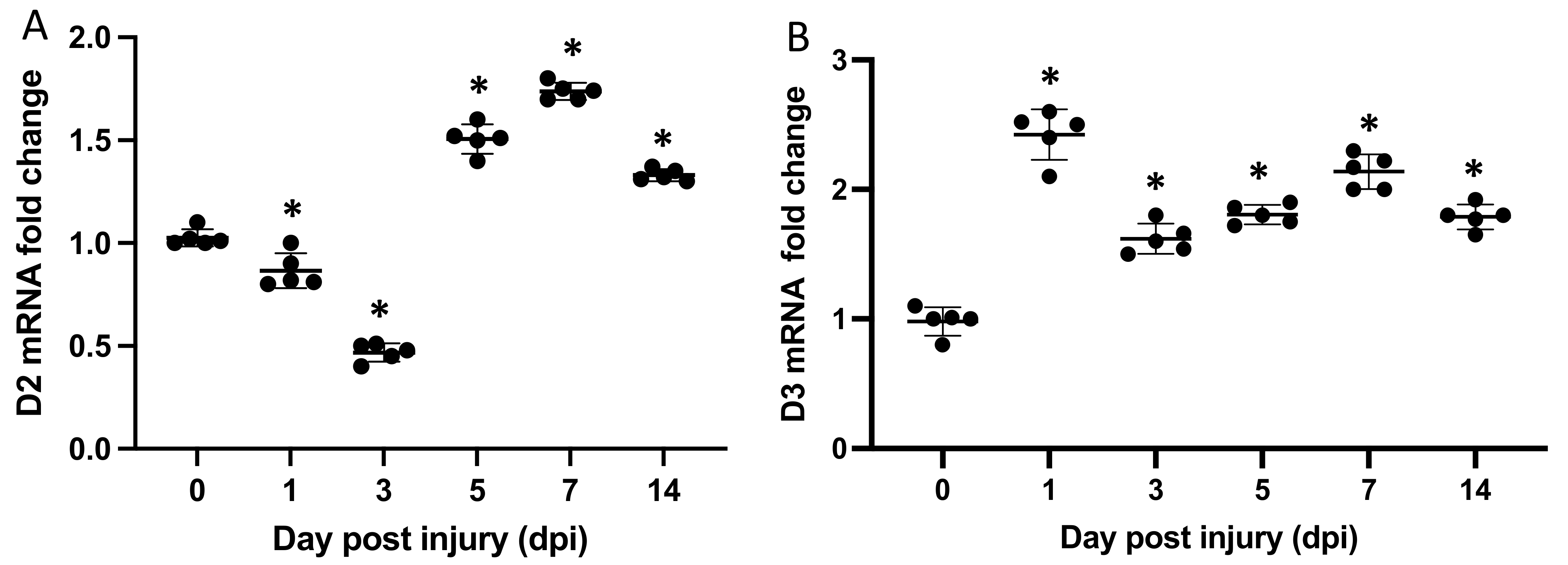
2.1. Dio2 and Dio3 Are Expressed throughout the Regeneration Process
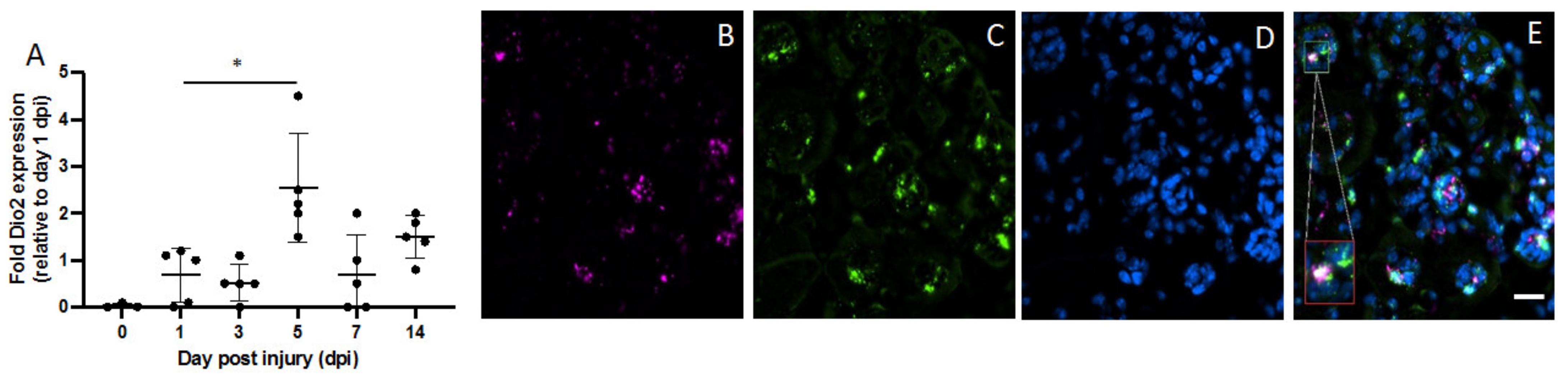
2.2. Dio2 Is Located in Muscle Satellite Pax7+ Cells
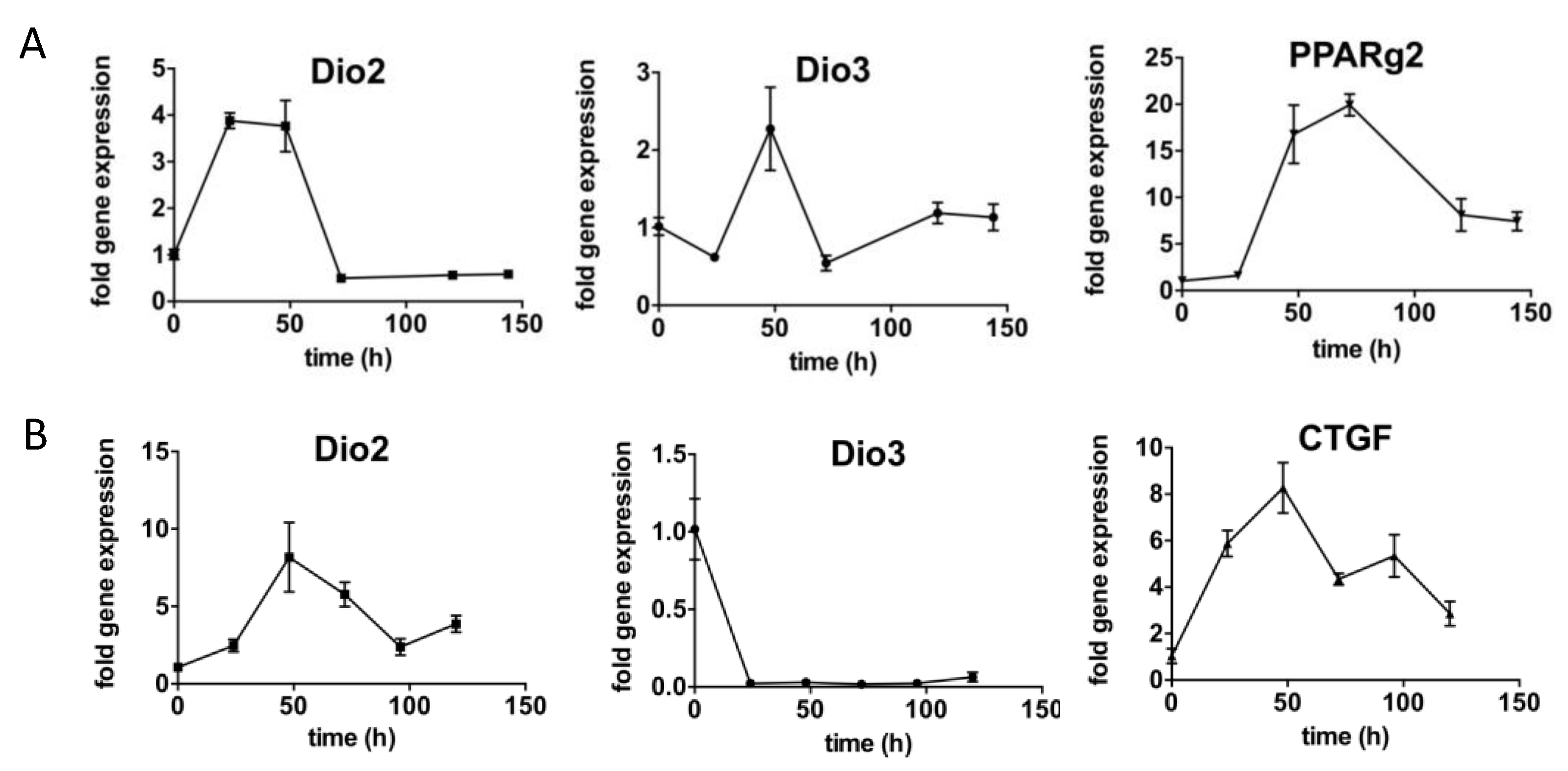
2.3. Fibroadipogenic Progenitors (FAPs) Express Dio2 and Dio3 in a Temporal Fashion
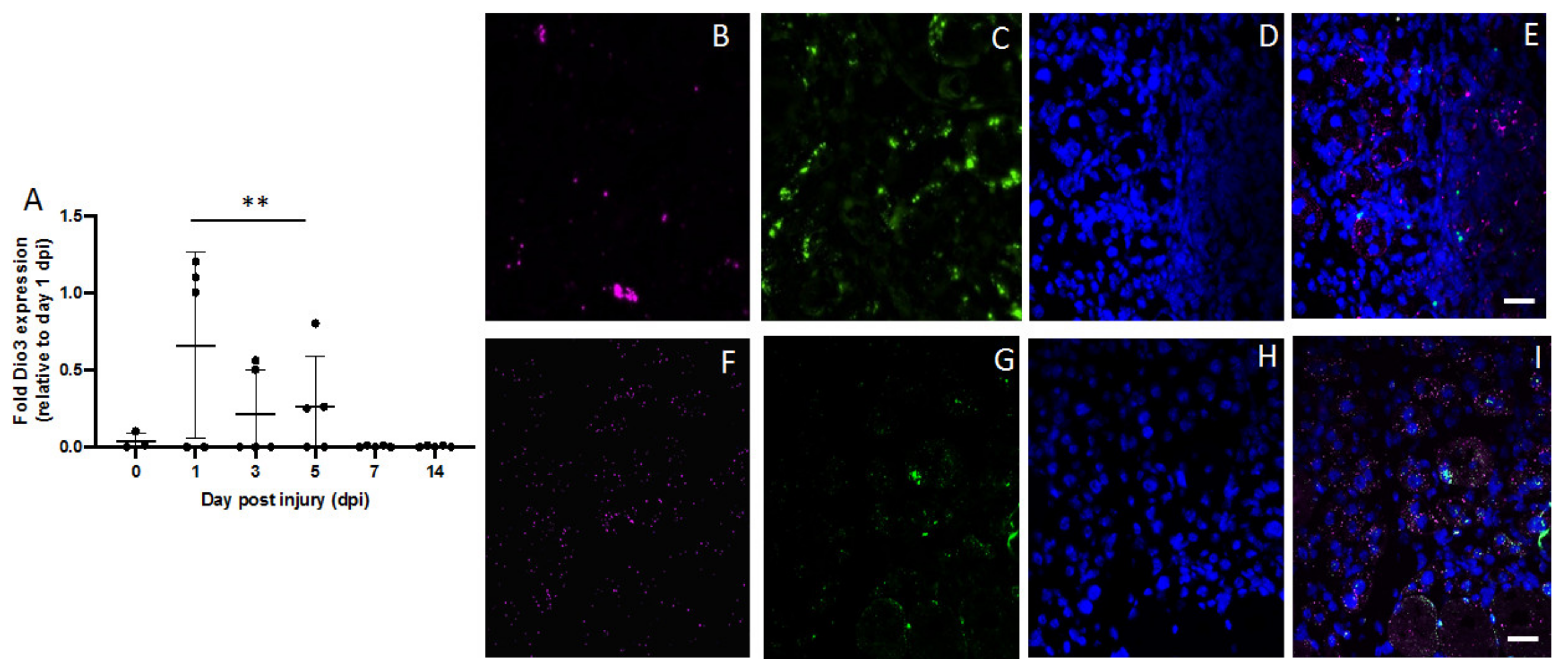
2.4. Type 3 Deiodinase Is Mainly Expressed in Macrophages during the Muscle Recovery Process
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting
4.3. Cell Culture
4.4. RNAscope In Situ Hybridization
4.5. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giordani, L.; He, G.J.; Negroni, E.; Sakai, H.; Law, J.Y.; Siu, M.M.; Wan, R.; Corneau, A.; Tajbakhsh, S.; Cheung, T.H.; et al. High-Dimensional Single-Cell Cartography Reveals Novel Skeletal Muscle-Resident Cell Populations. Mol. Cell 2019, 74, 609–621.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia, J.E.; Mukundan, L.; Chen, F.M.; Mueller, A.A.; Deo, R.C.; Locksley, R.M.; Rando, T.A.; Chawla, A. Type 2 innate signals stimulate fibro/adipogenic progenitors to facilitate muscle regeneration. Cell 2013, 153, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oprescu, S.N.; Yue, F.; Qiu, J.; Brito, L.F.; Kuang, S. Temporal Dynamics and Heterogeneity of Cell Populations during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. iScience 2020, 23, 100993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chargé, S.B.P.; Rudnicki, M. Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 209–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, E.; McCormick, K.M. Skeletal muscle satellite cells. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1994, 123, 213–257. [Google Scholar]
- Yablonka-Reuveni, Z. Development and postnatal regulation of adult myoblasts. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1995, 30, 366–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salvatore, D.; Simonides, W.S.; Dentice, M.; Zavacki, A.M.; Larsen, P.R. Thyroid hormones and skeletal muscle—New insights and potential implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simonides, W.S.; van Hardeveld, C. Thyroid hormone as a determinant of metabolic and contractile phenotype of skeletal muscle. Thyroid 2008, 18, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanesi, A.; Lee, J.-W.; Yang, A.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Sedrakyan, S.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Perin, L.; Brent, G.A. Thyroid Hormone Receptor Alpha is Essential to Maintain the Satellite Cell Niche during Skeletal Muscle Injury and Sarcopenia of Aging. Thyroid 2017, 27, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wosczyna, M.N.; Rando, T.A. A Muscle Stem Cell Support Group: Coordinated Cellular Responses in Muscle Regeneration. Dev. Cell 2018, 46, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez, M.N.; De Mello, W.; Butler-Browne, G.S.; Silva-Barbosa, S.D.; Mouly, V.; Savino, W.; Riederer, I. HGF potentiates extracellular matrix-driven migration of human myoblasts: Involvement of matrix metalloproteinases and MAPK/ERK pathway. Skelet Muscle 2017, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mueller, A.A.; Van Velthoven, C.T.; Fukumoto, K.D.; Cheung, T.H.; Rando, T.A. Intronic polyadenylation of PDGFRalpha in resident stem cells attenuates muscle fibrosis. Nature 2016, 540, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- An, X.; Ogawa-Wong, A.; Carmody, C.; Ambrosio, R.; Cicatiello, A.G.; Luongo, C.; Salvatore, D.; Handy, D.E.; Larsen, P.R.; Wajner, S.M.; et al. A Type 2 Deiodinase-Dependent Increase in Vegfa Mediates Myoblast-Endothelial Cell Crosstalk During Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Thyroid 2021, 31, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dentice, M.; Marsili, A.; Ambrosio, R.; Guardiola, O.; Sibilio, A.; Paik, J.H.; Minchiotti, G.; DePinho, R.A.; Fenzi, G.; Larsen, P.R.; et al. The FoxO3/type 2 deiodinase pathway is required for normal mouse myogenesis and muscle regeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4021–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heemstra, K.A.; Soeters, M.R.; Fliers, E.; Serlie, M.J.; Burggraaf, J.; Van Doorn, M.B.; Van Der Klaauw, A.A.; Romijn, J.A.; Smit, J.W.; Corssmit, E.P.; et al. Type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in skeletal muscle: Effects of hypothyroidism and fasting. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2144–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marsili, A.; Ramadan, W.; Harney, J.W.; Mulcahey, M.; Castroneves, L.A.; Goemann, I.; Wajner, S.; Huang, S.A.; Zavacki, A.M.; Maia, A.L.; et al. Type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase levels are higher in slow-twitch than fast-twitch mouse skeletal muscle and are increased in hypothyroidism. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5952–5960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebis, L.; Langouche, L.; Visser, T.J.; Berghe, G.V.D. The type II iodothyronine deiodinase is up-regulated in skeletal muscle during prolonged critical illness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 3330–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dentice, M.; Ambrosio, R.; Damiano, V.; Sibilio, A.; Luongo, C.; Guardiola, O.; Yennek, S.; Zordan, P.; Minchiotti, G.; Colao, A.; et al. Intracellular inactivation of thyroid hormone is a survival mechanism for muscle stem cell proliferation and lineage progression. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lehnen, T.E.; Marschner, R.; Dias, F.; Maia, A.L.; Wajner, S.M. Oxidative remote induction of type 3 deiodinase impacts nonthyroidal illness syndrome. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 246, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, R.P.; Wouters, P.J.; Van Toor, H.; Kaptein, E.; Visser, T.J.; Van den Berghe, G. Serum 3,3′,5′-triiodothyronine (rT3) and 3,5,3′-triiodothyronine/rT3 are prognostic markers in critically ill patients and are associated with postmortem tissue deiodinase activities. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4559–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seale, P.; Sabourin, L.A.; Girgis-Gabardo, A.; Mansouri, A.; Gruss, P.; Rudnicki, M.A. Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell 2000, 102, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Maltzahn, J.; Jones, A.E.; Parks, R.J.; Rudnicki, M.A. Pax7 is critical for the normal function of satellite cells in adult skeletal muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16474–16479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joe, A.W.; Yi, L.; Natarajan, A.; Le Grand, F.; So, L.; Wang, J.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Rossi, F. Muscle injury activates resident fibro/adipogenic progenitors that facilitate myogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wosczyna, M.N.; Konishi, C.T.; Carbajal, E.E.P.; Wang, T.T.; Walsh, R.A.; Gan, Q.; Wagner, M.W.; Rando, T.A. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Are Required for Regeneration and Homeostatic Maintenance of Skeletal Muscle. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2029–2035.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gereben, B.; Kollár, A.; Harney, J.W.; Larsen, P.R. The mRNA structure has potent regulatory effects on type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 1667–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinsapir, J.; Harney, J.; Larsen, P.R. Type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in rat pituitary tumor cells is inactivated in proteasomes. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1895–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwakkel, J.; Van Beeren, H.C.; Ackermans, M.T.; Schiphorst, M.C.P.-T.; Fliers, E.; Wiersinga, W.M.; Boelen, A. Skeletal muscle deiodinase type 2 regulation during illness in mice. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 203, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaro, L.; Passafaro, M.; Sala, D.; Etxaniz, U.; Lugarini, F.; Proietti, D.; Alfonsi, M.V.; Nicoletti, C.; Gatto, S.; De Bardi, M.; et al. Denervation-activated STAT3-IL-6 signalling in fibro-adipogenic progenitors promotes myofibres atrophy and fibrosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 917–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavasani, M.; Lu, A.; Thompson, S.D.; Robbins, P.D.; Huard, J.; Niedernhofer, L.J. Isolation of muscle-derived stem/progenitor cells based on adhesion characteristics to collagen-coated surfaces. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 976, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Uezumi, A.; Ito, T.; Morikawa, D.; Shimizu, N.; Yoneda, T.; Segawa, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Ogawa, R.; Matev, M.M.; Miyagoe-Suzuki, Y.; et al. Fibrosis and adipogenesis originate from a common mesenchymal progenitor in skeletal muscle. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124 Pt 21, 3654–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogawa-Wong, A.; Carmody, C.; Le, K.; Marschner, R.A.; Larsen, P.R.; Zavacki, A.M.; Wajner, S.M. Modulation of Deiodinase Types 2 and 3 during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Metabolites 2022, 12, 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070612
Ogawa-Wong A, Carmody C, Le K, Marschner RA, Larsen PR, Zavacki AM, Wajner SM. Modulation of Deiodinase Types 2 and 3 during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Metabolites. 2022; 12(7):612. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070612
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgawa-Wong, Ashley, Colleen Carmody, Katherine Le, Rafael Aguiar Marschner, P. Reed Larsen, Ann Marie Zavacki, and Simone Magagnin Wajner. 2022. "Modulation of Deiodinase Types 2 and 3 during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration" Metabolites 12, no. 7: 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070612
APA StyleOgawa-Wong, A., Carmody, C., Le, K., Marschner, R. A., Larsen, P. R., Zavacki, A. M., & Wajner, S. M. (2022). Modulation of Deiodinase Types 2 and 3 during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Metabolites, 12(7), 612. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12070612






