In-Needle Pre-Column Derivatization for Amino Acid Quantification (iPDAQ) Using HPLC
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
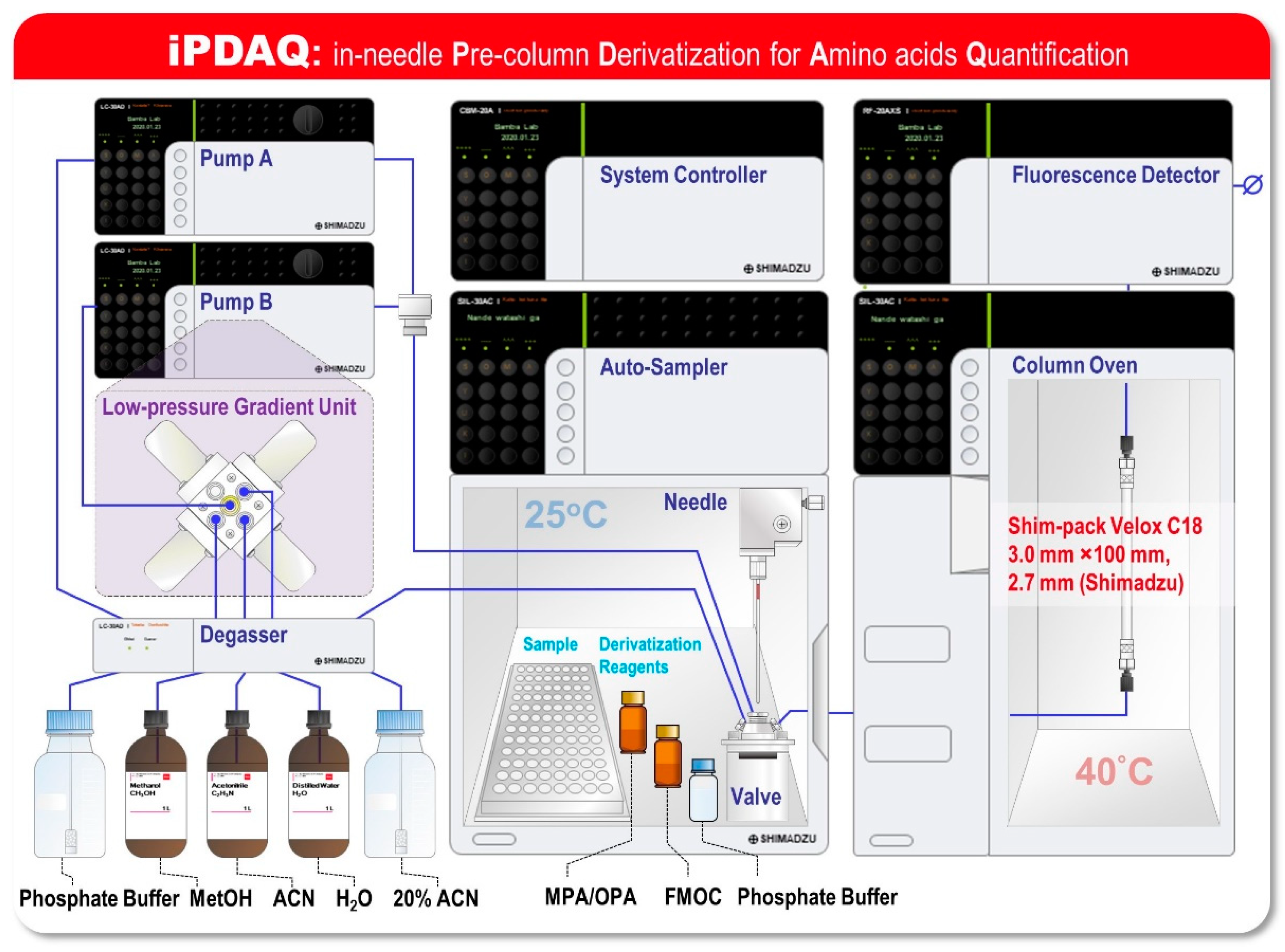
2.1. Development of the iPDAQ Method
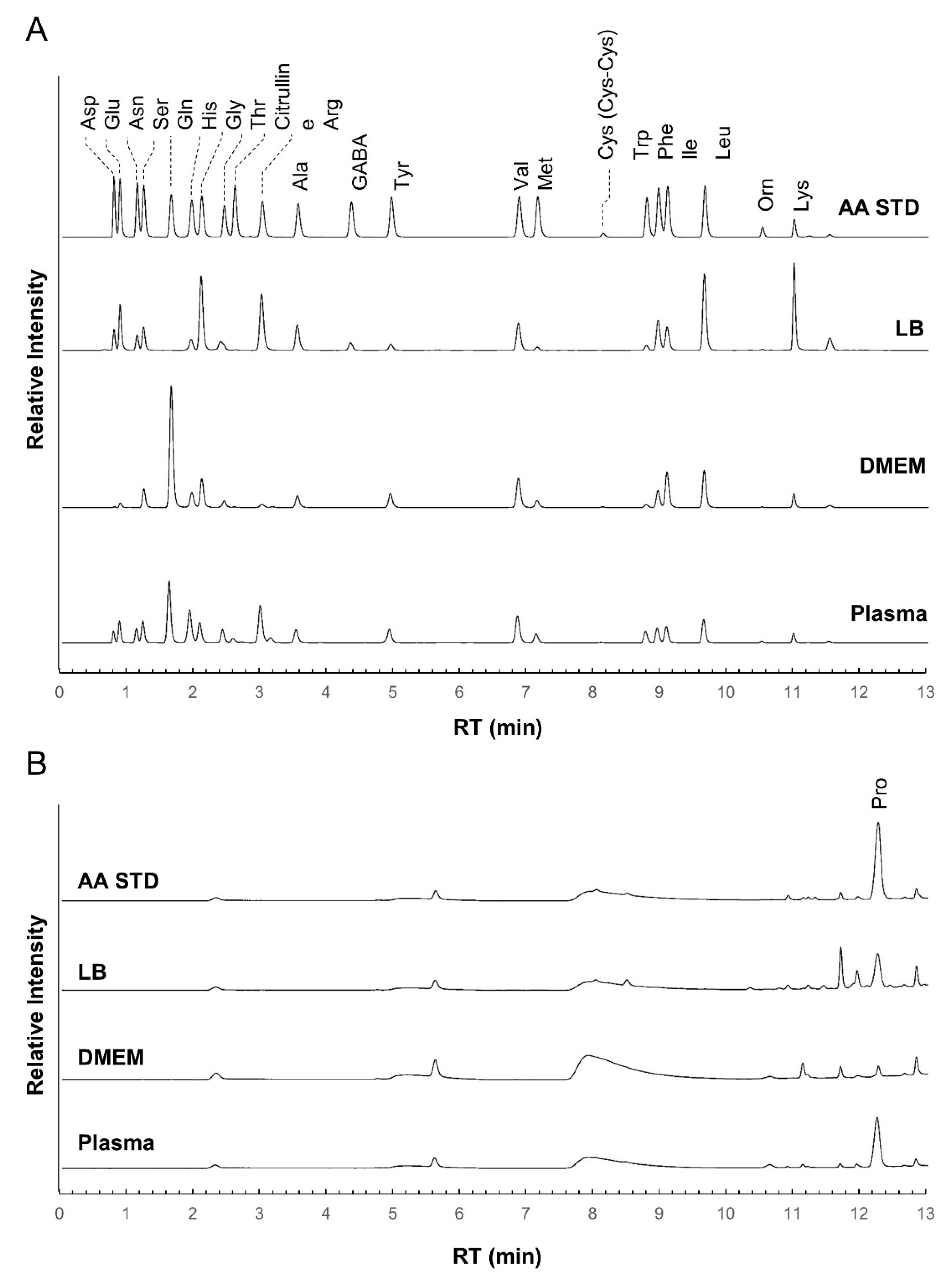
2.2. System Validation of the Optimized iPDAQ
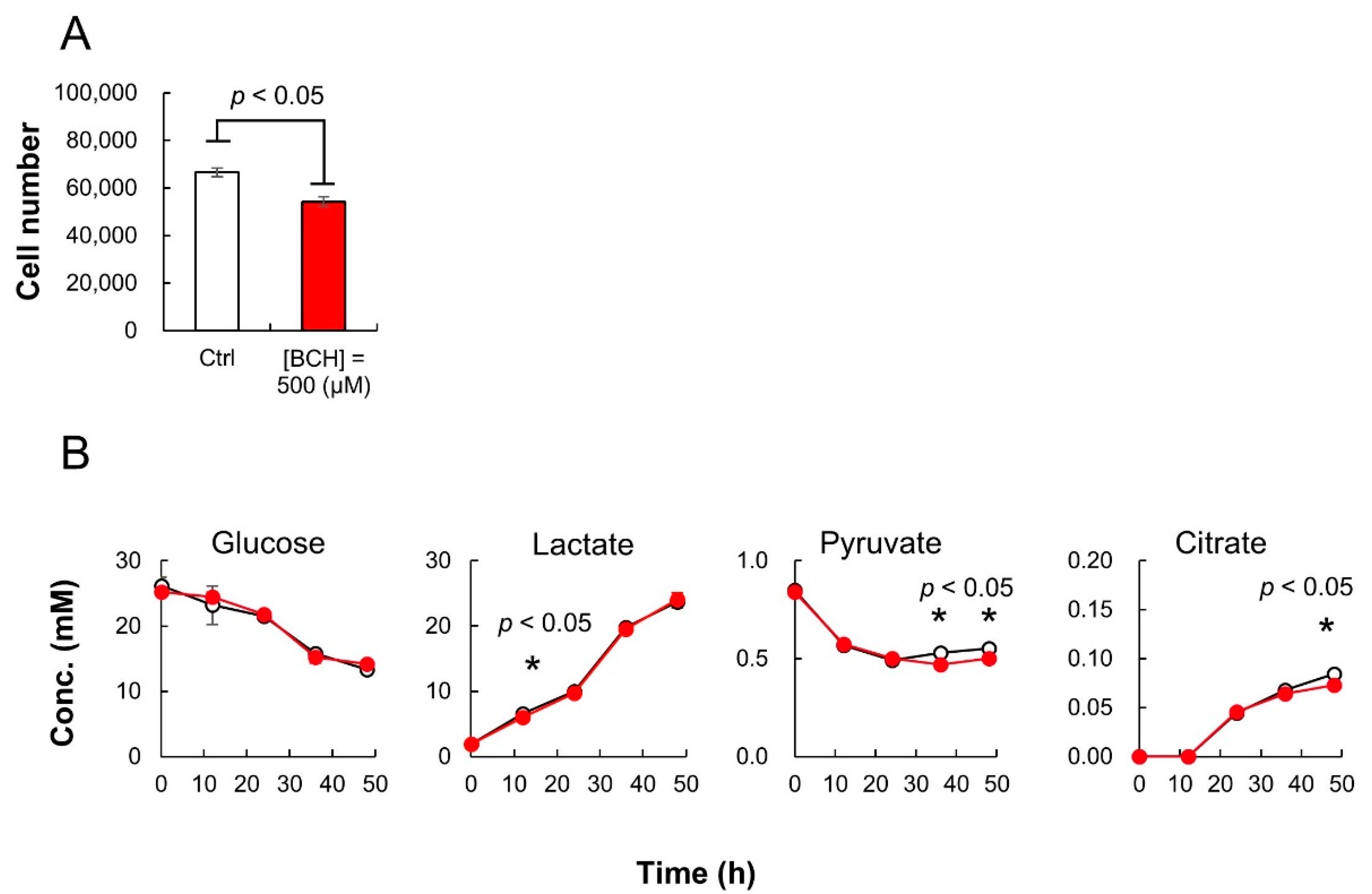
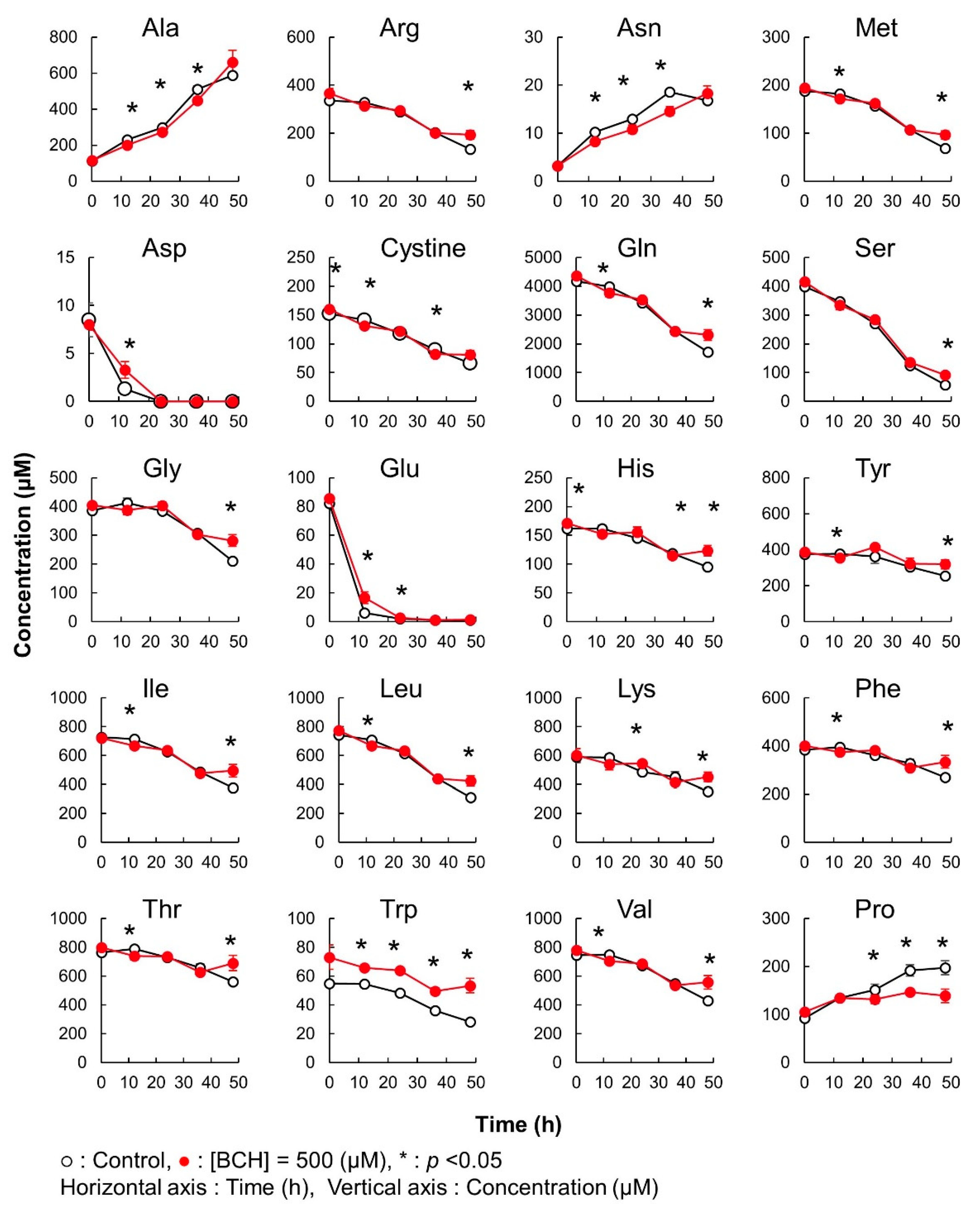
2.3. Time Course Monitoring of Amino Acids in Cell Culture Medium
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of LB Medium, DMEM, and Human Plasma Extract
3.3. Derivatization Reagents
3.4. In-Needle Derivatization of Amino Acids
3.5. Preparation of Calbration Curve and Quantification of Amino Acids
3.6. Cultivation of HeLa Cells
3.7. Amino Acid Transporter Inhibitor Assay
3.8. HPLC Analysis of Glucose and Organic Acids in HeLa Cell Culture Medium
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institution Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharer, J.D.; De Biase, I.; Matern, D.; Young, S.; Bennett, M.J.; Tolun, A.A. Laboratory analysis of amino acids, 2018 revision: A technical standard of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG). Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 1499–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Yin, Y.L.; Li, D.; Kim, W.S.; Wu, G. Amino acids and immune function. Br. J. Nutr. 2007, 98, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, Y.; Zhang, Q.W.; Sugimoto, T.; Furuhata, Y.; Sakai, R.; Mori, M.; Takahashi, M.; Kimura, T. Network analysis of plasma and tissue amino acids and the generation of an amino index for potential diagnostic use. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saurina, J.; Hernández-Cassou, S. Determination of amino acids by ion-pair liquid chromatography with post-column derivatization using 1,2-naphthoquinone-4-sulfonate. J. Chromatogr. A 1994, 676, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimura, N.; Kinoshita, T. o-phthalaldehyde-n-acetyl-l-cysteine as a chiral derivatization reagent for liquid chromatographic optical resolution of amino acid ernantiomers and its application to conventional amino acid analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 1986, 352, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidlingmeyer, B.A.; Cohen, S.A.; Tarvin, T.L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1984, 336, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürst, P.; Pollack, L.; Graser, T.A.; Godel, H.; Stehle, P. Appraisal of four pre-column derivatization methods for the high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of free amino acids in biological materials. J. Chromatogr. A 1990, 499, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, J.D.H.; Lewis, M.T.; Turnell, D.C. Pre-column o-phthalaldehyde derivatization of amino acids and their separation using reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. I. Detection of the imino acids hyroxyproline and proline. J. Chromatogr. A 1984, 285, 484–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heems, D.; Luck, G.; Fraudeau, C.; Vérette, E. Fully automated precolumn derivatization, on-line dialysis and high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of amino acids in food, beverages and feedstuff. J. Chromatogr. A 1998, 798, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrlink, T.; van Leeuwen, P.A.; Houdijk, A. Plasma amino acids determined by liquid chromatography within 17 minutes. Clin. Chem. 1994, 40, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godel, H.; Graser, T.; Földi, P.; Pfaender, P.; Fürst, P. Measurement of free amino acids in human biological fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 1984, 297, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasanits, A.; Kutlán, D.; Sass, P.; Molnár-Perl, I. Retention/quantitation properties of the o-phthaldialdehyde-3-mercaptopropionic acid and the o-phthaldialdehyde-n-acetyl-l-cysteine amino acid derivatives in reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 870, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, M.P.; Powers, R.W. Simple and rapid quantitative high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of plasma amino acids. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 852, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, P.; Barros, P.; Ratola, N.; Alves, A. HPLC determination of amino acids in musts and port wine using OPA/FMOC derivatives. J. Food Sci. 2000, 65, 1130–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbert, P.; Santos, L.; Alves, A. Simultaneous quantification of primary, secondary amino acids, and biogenic amines in musts and wines using OPA/3-MPA/FMOC-CI fluorescent derivatives. J. Food Sci. 2001, 66, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar]
- Azevedo, M.S.; Seraglio, S.K.T.; Rocha, G.; Balderas, C.B.; Piovezan, M.; Gonzaga, L.V.; Falkenberg, D.D.B.; Fett, R.; de Oliveira, M.A.L.; Costa, A.C.O. Free amino acid determination by GC-MS combined with a chemometric approach for geographical classification of bracatinga honeydew honey (Mimosa scabrella Bentham). Food Control 2017, 78, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, H.; Dettmer, K.; Chan, Q.; Daniels, S.; Nimkar, S.; Daviglus, M.L.; Stamler, J.; Elliott, P.; Oefner, P.J. Urinary amino acid analysis: A comparison of iTRAQ-LC-MS/MS, GC-MS, and amino acid analyzer. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 1838–1846. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, K.; Soma, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Takahashi, M.; Sugitate, K.; Serino, T.; Miyagawa, H.; Suzuki, K.; Yamada, K.; Kawamukai, T.; et al. Calibration-curve-locking database for semi-quantitative metabolomics by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Metabolites 2021, 11, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Bligh, E.G.; Dyer, W.J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 1959, 37, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soma, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Tomiyasu, N.; Goto, M.; Hanai, T.; Izumi, Y.; Bamba, T. Quantitative Metabolomics for Dynamic Metabolic Engineering Using Stable Isotope Labeled Internal Standards Mixture (SILIS). J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2021, 133, 46–55. [Google Scholar]
- Soma, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shinohara, T.; Izumi, Y.; Hanai, T.; Bamba, T. Design of Synthetic Quorum Sensing Achieving Induction Timing-Independent Signal Stabilization for Dynamic Metabolic Engineering of E. coli. ACS Synth. Biol. 2021, 10, 1384–1393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| # | Amino Acid | Abbreviation | KEGG ID | Retention Time (n = 3) | LOD * | Linear Range ** | R2 | Recovery Ratio *** | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± SD | RSD (%) | (μM) | (μM) | (%) | |||||
| 1 | L-Aspartic acid | Asp | C00049 | 0.710 ± 0.003 | 0.403 | 0.004 | 0.05–50 | 1.000 | 98.8 |
| 2 | L-Glutamic acid | Glu | C00025 | 0.997 ± 0.003 | 0.296 | 0.009 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 96.7 |
| 3 | L-Asparagine | Asn | C00152 | 1.419 ± 0.005 | 0.372 | 0.008 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 98.8 |
| 4 | L-Serine | Ser | C00065 | 1.676 ± 0.005 | 0.322 | 0.005 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 98.6 |
| 5 | L-Glutamine | Gln | C00064 | 2.074 ± 0.005 | 0.228 | 0.010 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 88.0 |
| 6 | L-Histidine | His | C00135 | 2.455 ± 0.007 | 0.278 | 0.008 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 97.8 |
| 7 | Glycine | Gly | C00037 | 2.570 ± 0.007 | 0.283 | 0.009 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 97.3 |
| 8 | L-Threonine | Thr | C00188 | 2.794 ± 0.008 | 0.275 | 0.008 | 0.05–50 | 0.998 | 98.9 |
| 9 | L-Citrulline | Citrulline | C00327 | 3.108 ± 0.008 | 0.265 | 0.006 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 100.2 |
| 10 | L-Arginine | Arg | C00062 | 3.413 ± 0.008 | 0.231 | 0.008 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 99.2 |
| 11 | L-Alanine | Ala | C00041 | 4.071 ± 0.009 | 0.219 | 0.016 | 0.05–50 | 0.996 | 95.5 |
| 12 | γ-Aminobutyric acid | GABA | C00334 | 5.199 ± 0.010 | 0.190 | 0.009 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 97.1 |
| 13 | L-Tyrosine | Tyr | C00082 | 5.872 ± 0.011 | 0.188 | 0.008 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 97.4 |
| 14 | L-Valine | Val | C00183 | 8.154 ± 0.008 | 0.104 | 0.007 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 97.9 |
| 15 | L-Methionine | Met | C00073 | 8.291 ± 0.008 | 0.097 | 0.008 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 93.8 |
| 16 | L-Cystine | Cys-Cys | C00491 | 8.842 ± 0.037 | 0.419 | 0.124 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 98.4 |
| 17 | L-Tryptophan | Trp | C00078 | 9.301 ± 0.006 | 0.068 | 0.007 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 96.9 |
| 18 | L-Phenylalanine | Phe | C00079 | 9.501 ± 0.006 | 0.065 | 0.006 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 105.5 |
| 19 | L-Isoleucine | Ile | C00407 | 9.653 ± 0.007 | 0.069 | 0.006 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 100.4 |
| 20 | L-Leucine | Leu | C00123 | 9.945 ± 0.005 | 0.054 | 0.006 | 0.05–50 | 0.999 | 100.1 |
| 21 | L-Ornithine | Orn | C00077 | 10.185 ± 0.007 | 0.066 | 0.043 | 0.05–50 | 0.994 | 92.0 |
| 22 | L-Lysine | Lys | C00047 | 10.496 ± 0.008 | 0.075 | 0.029 | 0.05–50 | 0.996 | 100.1 |
| 23 | L-Proline | Pro | C00148 | 11.446 ± 0.005 | 0.046 | 0.010 | 0.05–50 | 0.997 | 105.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soma, Y.; Izumi, Y.; Shimohira, T.; Takahashi, M.; Imado, Y.; Tominaga, S.; Tokito, K.; Hata, K.; Shinadama, S.; Oshiro, M.; et al. In-Needle Pre-Column Derivatization for Amino Acid Quantification (iPDAQ) Using HPLC. Metabolites 2022, 12, 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090807
Soma Y, Izumi Y, Shimohira T, Takahashi M, Imado Y, Tominaga S, Tokito K, Hata K, Shinadama S, Oshiro M, et al. In-Needle Pre-Column Derivatization for Amino Acid Quantification (iPDAQ) Using HPLC. Metabolites. 2022; 12(9):807. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090807
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoma, Yuki, Yoshihiro Izumi, Takehiko Shimohira, Masatomo Takahashi, Yuri Imado, Saki Tominaga, Kanako Tokito, Kosuke Hata, Shoji Shinadama, Mana Oshiro, and et al. 2022. "In-Needle Pre-Column Derivatization for Amino Acid Quantification (iPDAQ) Using HPLC" Metabolites 12, no. 9: 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090807
APA StyleSoma, Y., Izumi, Y., Shimohira, T., Takahashi, M., Imado, Y., Tominaga, S., Tokito, K., Hata, K., Shinadama, S., Oshiro, M., Hayakawa, Y., & Bamba, T. (2022). In-Needle Pre-Column Derivatization for Amino Acid Quantification (iPDAQ) Using HPLC. Metabolites, 12(9), 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12090807







